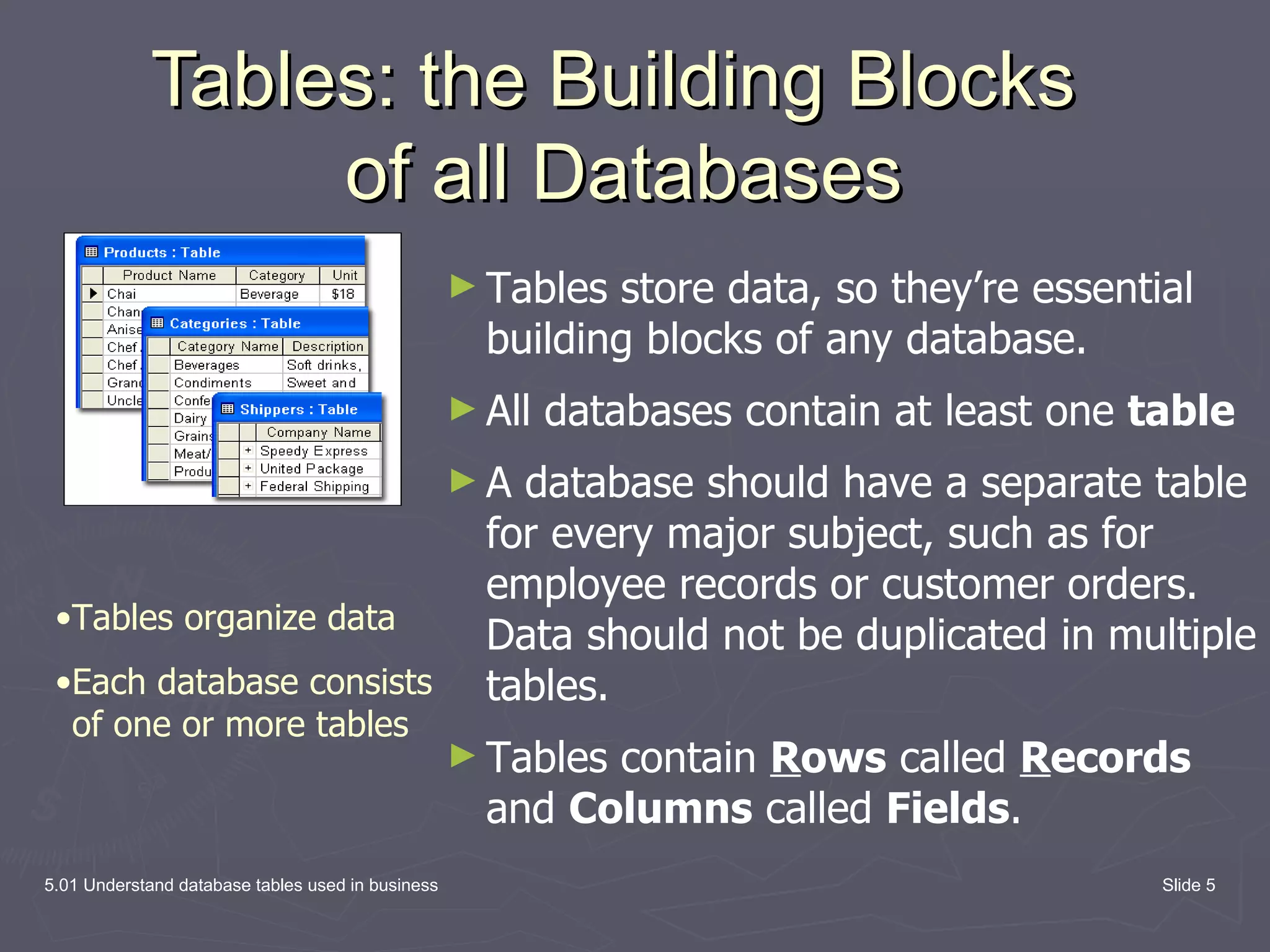
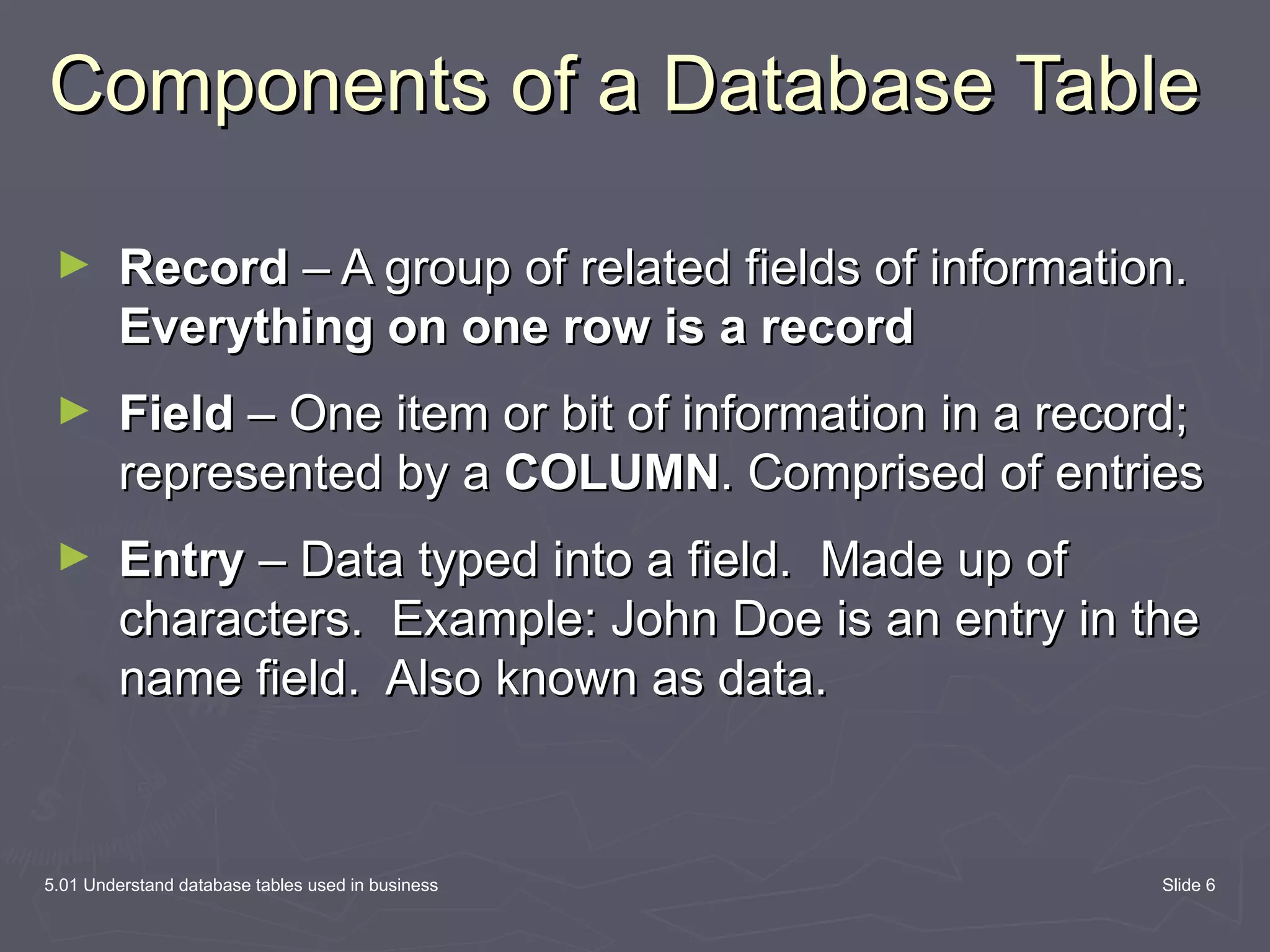
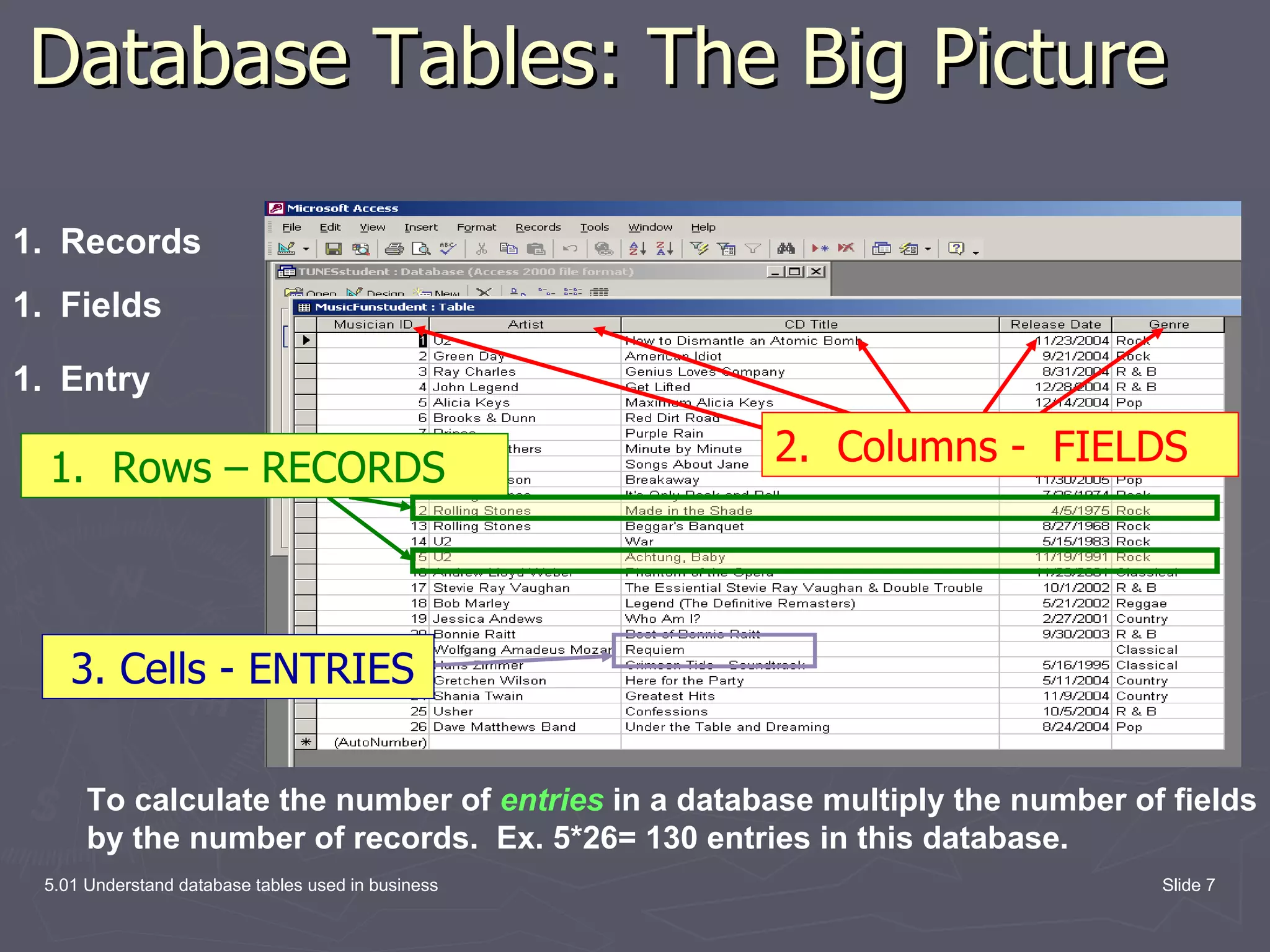
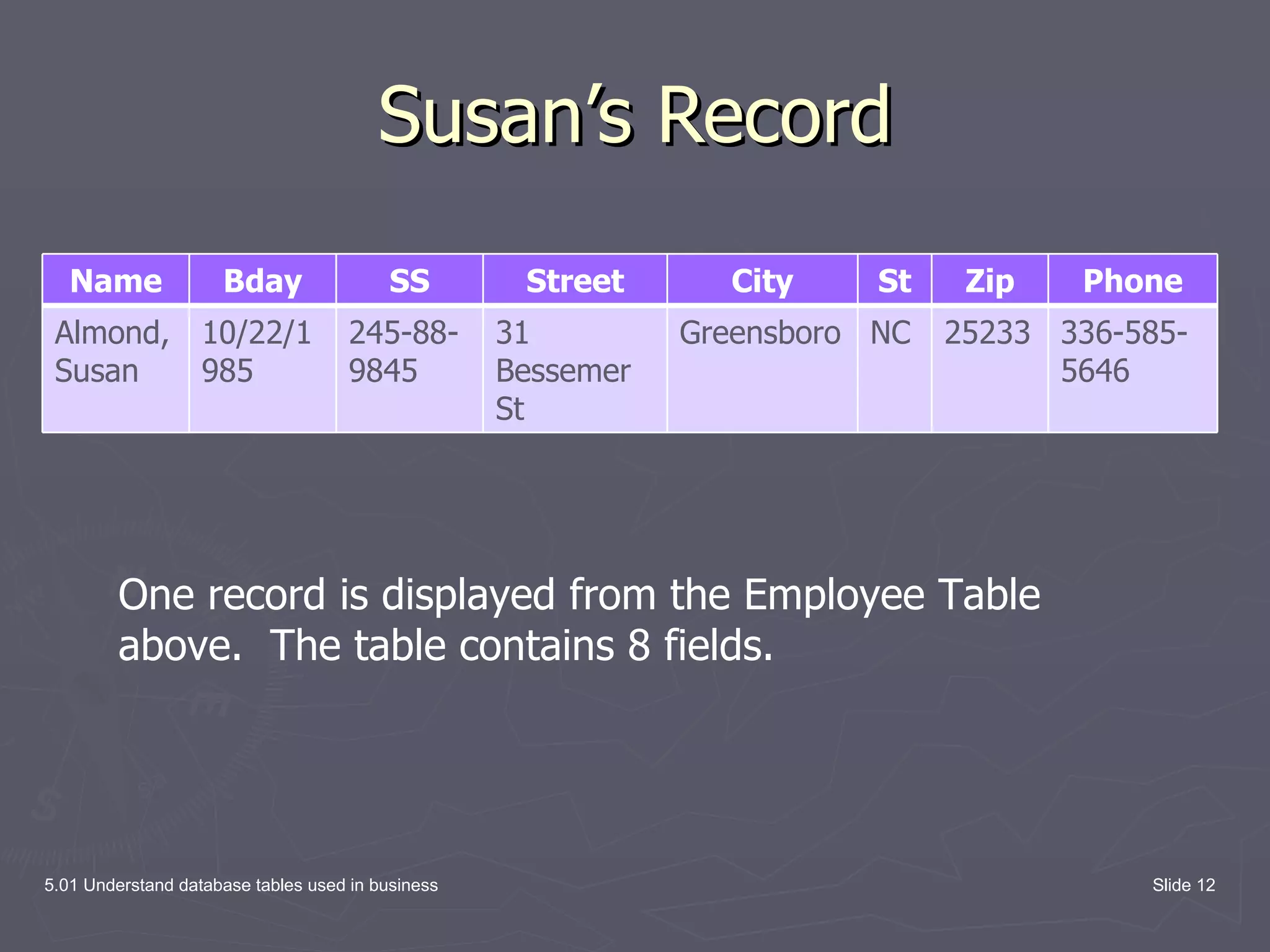
The document discusses database tables, which are the fundamental building blocks of databases. It defines key concepts like records, fields, and entries. A record contains all the data fields for one item, like a customer. A field is a single piece of data like a name. An entry is the actual data in a field, like "John Doe". The document provides examples of database tables and their structure, with rows representing records and columns representing fields.