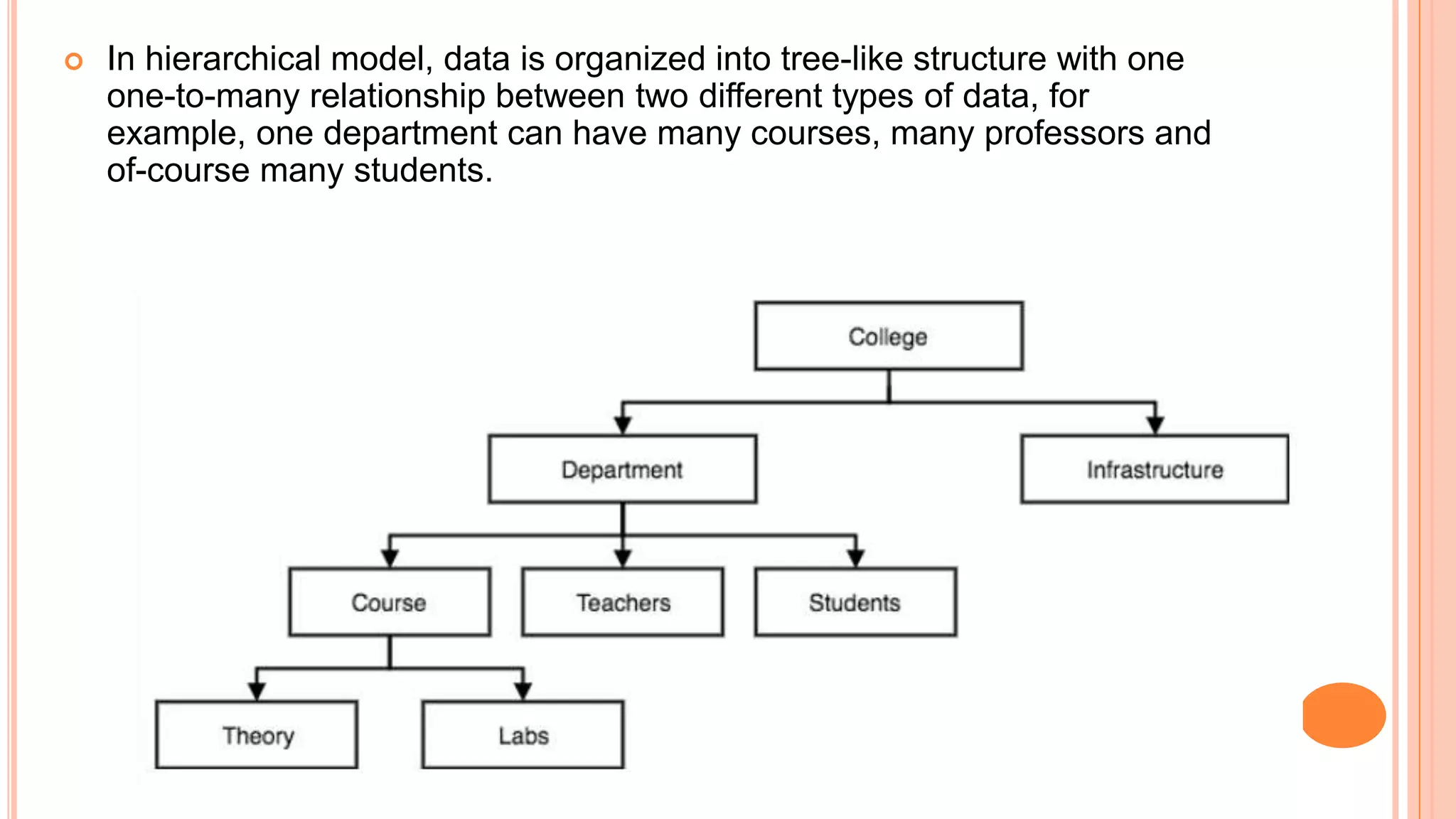
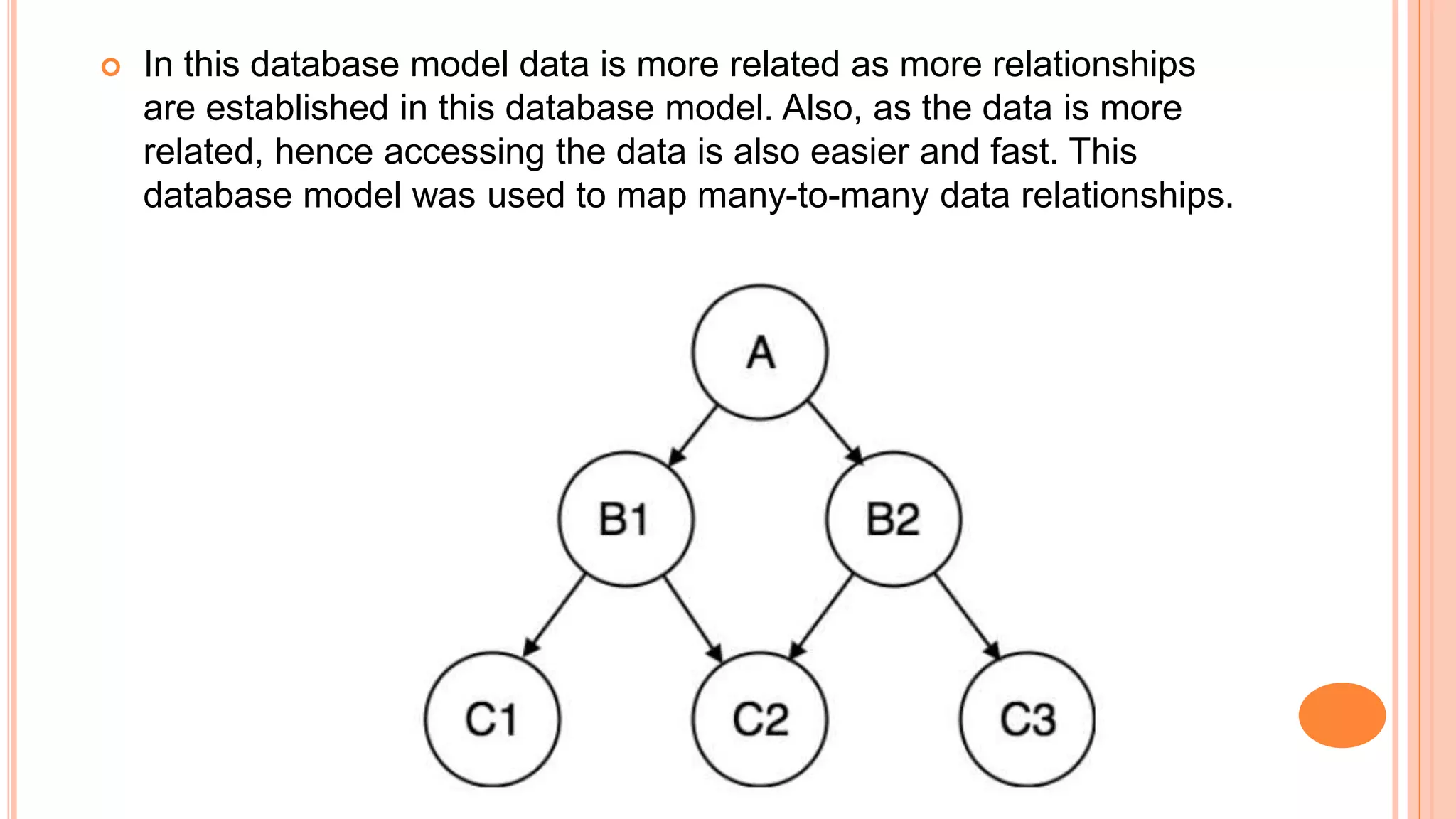
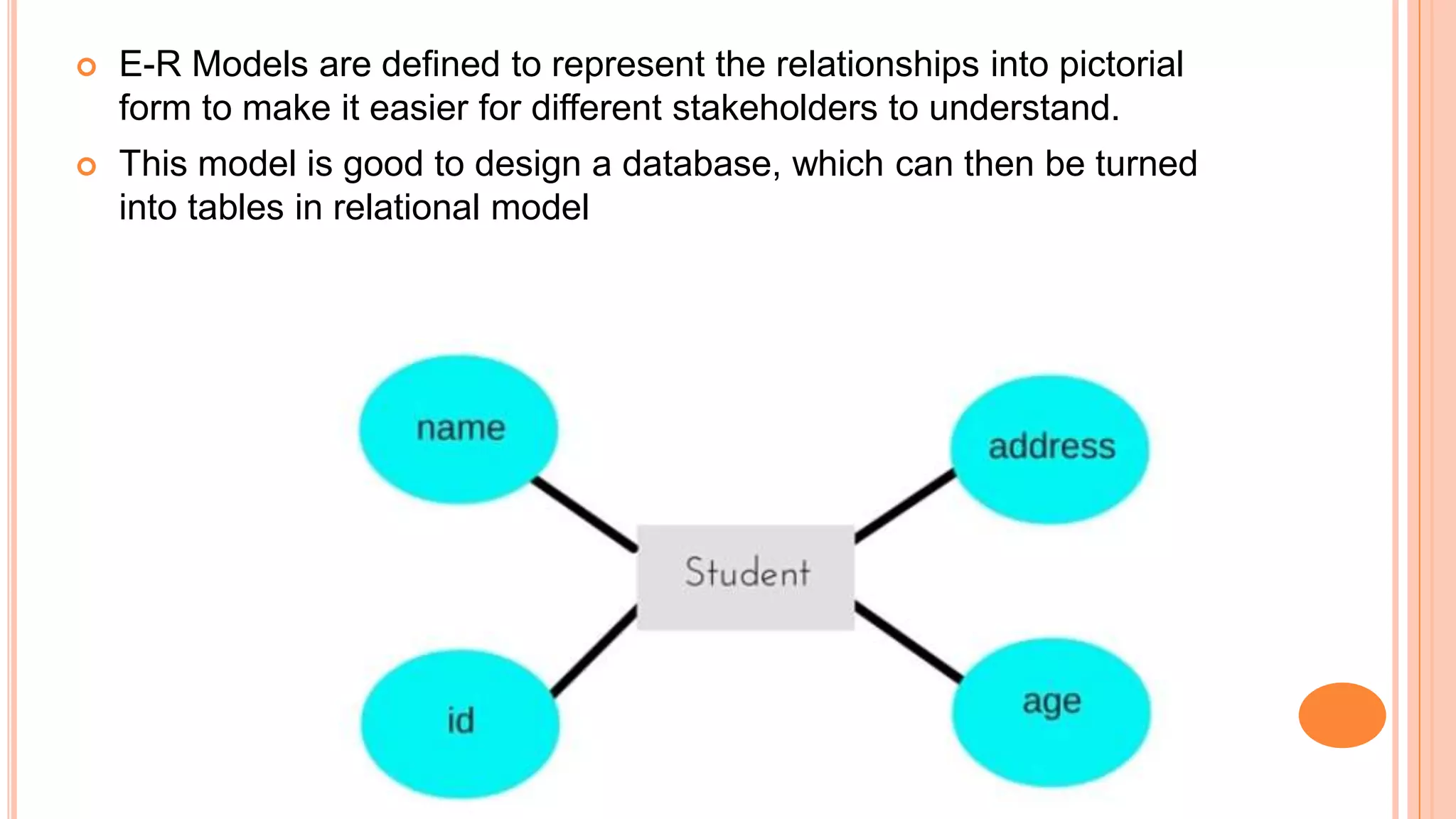
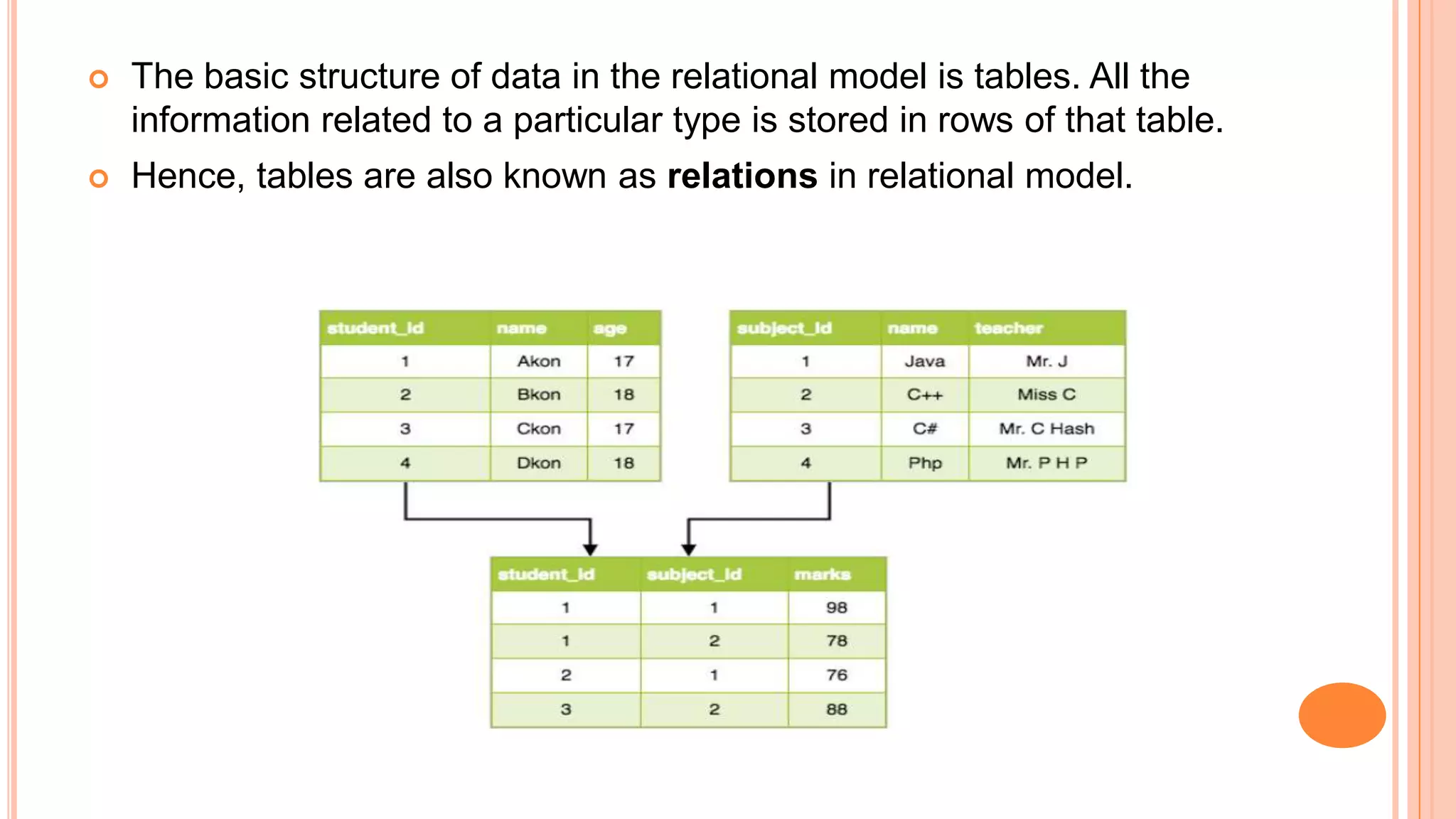
This document discusses different database models including hierarchical, network, entity-relationship, and relational models. The hierarchical model organizes data in a tree-like structure with parent-child relationships. The network model extends the hierarchical model by allowing nodes to have more than one parent. The entity-relationship model divides data into entities and attributes and represents relationships visually. The relational model, introduced by E.F. Codd in 1970, organizes data into two-dimensional tables related through common fields and is the most widely used database model today.