The document discusses text detection and recognition using deep learning techniques. It begins with an introduction to deep learning and its use in optical character recognition (OCR). There are two main components of OCR - text detection, which locates text in an image, and text recognition, which identifies the text. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are effective for both tasks. The document then outlines the steps for text detection and recognition using deep learning, including data collection, preprocessing, feature extraction using CNNs, training and validating models on datasets, and testing the trained models on new data.
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 9 Deep Learning in Text Recognition and Text Detection : A Review Brindha Muthusamy1, Kousalya K2 1Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Erode 3Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Erode ---------------------------------------------------------------------***--------------------------------------------------------------------- Abstract - Detecting text in natural situations is a difficult task that is more difficult than extracting the text from those natural images in which the background and foreground are clearly separated and every character isisolatedfromtheimages. Textin the landscapes which is nature may occur in a range of states like a text in dark with the backgroundlightandviceversa, withabroad diversity of fonts, even for letters of the same word, sections of words can be overlapped by environment objects, makingdetection of these parts impossible. Deep learning which is a subset of Machine learning employs a neural network, a technique that replicates how the brain analyses data. An Optical Character Recognition engine has two parts: i)Text recognition and ii)Text detection. The process of locating the sections of text in a document is known as text detection. Since the different documents (invoices, newspapers, etc.) have varied structures, this work has historically proved difficult. A text recognition system, on the other hand, takes a portion of a document containing text (a word or a line of text) and outputs the associated text. Both text detection and text recognition have shown considerable promise with deep learning algorithms. Keywords: Deep learning, Convolutional Neural Network, text detection, text classification, Optical Character Recognition, optimization I. INTRODUCTION Deep learning algorithms learn about the image by passing through each neural network layer. For applications like machine translation and image searches, OCR mechanism is being used to recognise text within photographs. The method for recognising the text/characters from a photo, sends the features extracted text from an image/photo to the classifier which is trained to distinguish individual characters that is similar to object recognition. Recognition oftext,ontheotherhand,looksat the text as a group of meaningful characters rather than single characters. A text string can be recognized by clustering the similar characters, which means that every character in the text must separate for recognition [21]. Alternatively, in the instance of classification, train the network on a labelled datasets in order to categorize the samples in the datasets. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) was applied to extractthefeaturesforcharacter recognitionperformance.Abrief review on text detection and text recognition are shown in Table 2. The CNN model is trained in three steps : (i) Train the CNN model from the scratch, (ii) Using a transfer learning method for exploiting the features from a pretrained model on larger datasets and, (iii) Transfer learning and fine-tuning the weights of an CNN architecture. CNN architecture consists mostly of four layers. (i) Convolutional layer [Conv]; (ii) Pooling layer; (iii) Fully connected layer; and (iv) Rectified Linear units [4]. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is being trained to extractinformationthroughthedeep-learning-basedtechnologies from an image. VGG, ResNet, MobileNet, GoogleNet, Xception, and DenseNet are examples of CNN architecture where several convolution layers are utilized to extract the features from the images [21]. Handwritten texts are difficult while reading text from photographs or recognising that has attained a lot of attention. Most systems have two important components, (i) Text detection; and (ii) Text recognition. Text detection is a technique where the text instances from the images can be predicted and localized. The text recognition is done by autoencoder which is the process of decoding the textintothemachine-readable format.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-1-2048.jpg)
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 10 Figure 1 CNN architecture for text classification II. TEXT DETECTION AND RECOGNITION USING DEEP LEARNING 2.1 Text detection The local features can be extracted from CNN through the training of character pictures and sub-regionsbasedonthe characteristics of an individual’s handwriting. To train CNN, randomly selected instances of an image in the training sets are used, and the local features extracted from the image from these instances are aggregated in order to generate the global features. The process of randomly sampling instances is repeated for every training epoch. This results in the increase of training the patterns for training the CNN for text independent writer identification [1]. Deep learning can constantly learn by examining data and finding patterns and classifying images. For picture categorization, language transaction and character recognition, deep learning is applied. Deep Neural Networksarenetworks with multiple layers that can perform complex operations onimages,sound,andtext,suchasrepresentationandabstraction. It can be used for any type of recognition problem. The basic goal is only for computers to learn withouthumaninterventionand modify their activities accordingly. 2.2 Text recognition The recognition can be done by many techniques. It involves Convolutional Neural Network(CNN), Semi Incremental Method, Incremental Method, Line and Word Segmentation method etc. One of the most effective and prominent ways of handwriting recognition is Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The most prevalent application of CNN is in image analysis. Artificial neurons are used in CNN [11]. CNN canrecogniseimagesandvideos,classifyimages,analysemedical images,perform computer vision, and process natural language. CNN or ConvNets architecture has made significant contributions to the analysis of images. CNN is defined as , 1)A convolution tool that separates and identifies the distinct characteristics of the image for analysis in a process called Feature Extraction, which is part of the CNN architecture. 2) A fully connected layer makes use of the outputoftheconvolutionprocess in order to forecast the image's class using the information acquired in earlier stages. CNN extracts the features from handwritten text images of numerous characters by the end-to-end method based on deep learning and combines these extractedfeaturestorecognizethewriter’sspecific data duringloweringofcharacter’sclass- specific features. To create n-tuple images, a single writer’shandwrittensquaredimagesaresampledrandomly.Second,every image from n-tuple is sent into a local feature extractor (CNN). CNN can extract text-independent writer specificpropertiesby employing new techniques to structure the training samples as n tuple pictures. Finally,a global featureaggregator aggregates the retrieved local features in various ways, such as using the average or maximum. Finally, the combined characteristics are sent into a softmax classifier (fully connected with an Nfc unit which is equal to the number of writers) for predicting [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-2-2048.jpg)
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 11 III. PRELIMINARY STEPS FOR TEXT DETECTION AND RECOGNITION 3.1 Datasets The datasets are collected from various ImageNet dataset like, MNIST, NIST, IAM dataset, IFN/ENIT, and so on. The different dataset on different languages like, English, Arabic, Bangla handwritten character datasets are taken into consideration. The detailed view of these datasets are shown in table 2. 3.2 Image Pre-processing Pre-processing is a technology which transforms the raw data to useful and efficient data/information. This process consists of different operations which are used to perform on input images and in this process, the images are reshaped. The rearrangement of the form of the data is done without changing the contents of the data. Different kinds of arrangements are done in this process according to the parameters which are needed to carry on till further process [1].Imagepre-processingis nothing but to remove irrelevant data and delete the duplicate data fromthedatabases.Thetextintheimagecanbeindifferent styles, fonts and so on. In data pre-processing, the data are processed in different ways, they are: Data cleaning : Remove noise and data inconsistency from raw data. That is, the datasetwhichdoesnot belongto the dataset comes, this data cleaning process removes these datasets. It is done by filtering the dataset and handling the missing data. It ensures the quality of data. In other words, itonlyremovestheunwanteddata butmaintainstheoriginality of the data. Data integration : Data integration collects data from various multiple resources and combines it to form coherent data and also supports the consolidated perspective of the information. That is, it merges data from varioussourcesintoa coherent datastore (data warehouse). These data are stored and maintained for future use. It may be in the form of documents where the relevant data are stored in the different documents. Data reduction : Data reduction is the process of reducing the data size by instances, aggregation, eliminating irrelevant data/features or by clustering. Data reduction can increase the storage capacity and the cost is reduced. It does not lose any data, instead it maintains the originality of the data. Data reduction process is done with the help of data compression. Data compression is a technique to compressthedata ina reducedformofdata whichcanreducethestorage space. Data transformation : Data transformation is used to convert one form of format to another format. It is also known as data munging or data wrangling. Otherwise called Normalization. The data points in the scatter plot should be linear.If the points are in the form of a curve, it is difficult to calculate the accuracywhichaffects theperformanceofthemodel. This curve can be converted into a linear line by scaling the model in the range of 0 and 1. Activation functions are used when the model shows non-linearity in their respective model. 3.3 Normalization Normalization is the process of organizing data in the database. This process involves table creation and establishing relationships between these tables. It protects the data as well as makes the database moreflexible byeliminatingredundancy and inconsistent dependency. Redundant data takes more space and is complicated to maintain. The inconsistent dependent data can make it difficult to access the data since the path to find the data is either missing or broken. Hence, Normalization is more important since it can reduce these irrelevant data and data inconsistency and it can handle the missing data as well to make the database more flexible. Normalization includes three stages of normalization steps where each stage generates the table. Each table stores the relevant data which does not include duplicate data or miss any data. The three steps involved in the normalization process are as follows, 3.3.1 First Normal form The First Normal Form (1NF) sets the fundamental rulesfordatabasenormalizationwhichrelatestothesingletablein the relational database model. The steps involved in the First Normal Form are : Every column in the table are unique Separate tables are created for every relevant set of data Each table must be identified with a unique column or the concatenated columns are called with the primary key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-3-2048.jpg)
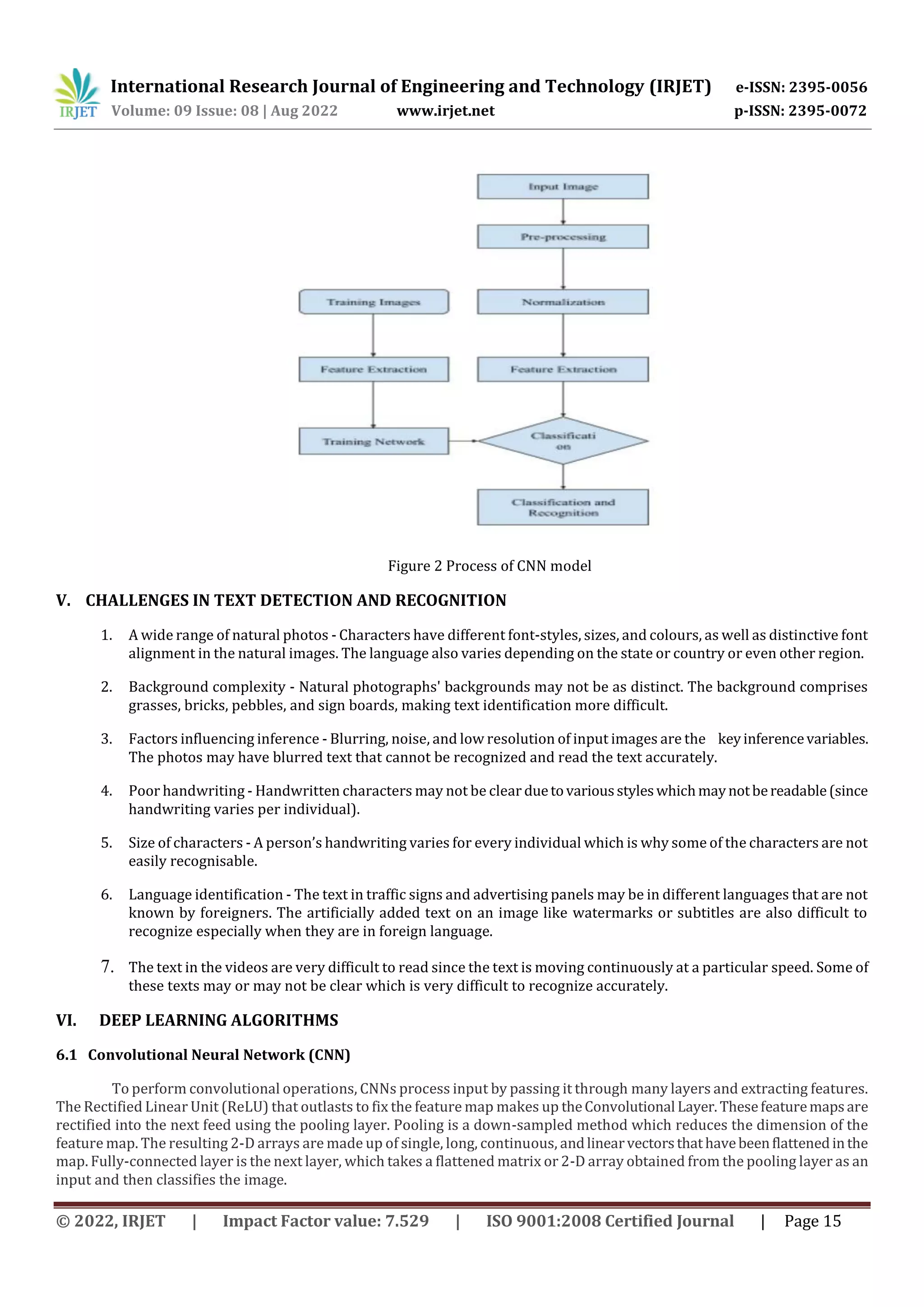
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 12 Neither row or column of the table are duplicated No row or column that intersects in the table contain a NULL value No row or column that intersects in the table can have multi-valued fields 3.3.2 Second Normal Form The Second Normal Form (2NF) follows the First Normal Form . The basic requirements of Second Normal Form for organizing the data include: No redundancy of data. All the data is stored in only one place. Data dependencies in Second Normal Form are logical. That is, all the related data items are stored together which is useful for easy access. 3.3.3 Third Normal Form The Third Normal Form (3NF)isthecombinationof both FirstNormal FormandSecondNormal Form(1NF+2NF).The main benefits of this Third normal form are: Reduces duplication of the data and achieves data integrity in a database. Useful to design a normal relational database 3NF are independent of anomalies of deletion, updation, and insertion It ensures losslessness and prevention of the functional dependencies 3.4 Feature extraction Text extraction or Feature extraction from an image is a method of extracting text from a photograph using machine learning techniques. Text extraction is also known as text localization. It is used for text detection and localizationwhich helps for text recognition. Text localization is the process which isusedtodevelopa computersystem(AI)toautomaticallyrecognize and read the text from the images. In deep learning models, the feature extraction process is done automatically since the models are pre-trained. It is done by text classification. 3.4.1 Text Classification Text classification is also known as text tagging or text categorization. Texts are always unstructured in handwritten words or characters. Hence, these texts are categorized into an organized group. This process is difficult since it takes more time and is a little expensive. By using Natural Language Processing (NLP) which can be used as a text classifier, the texts can be categorized and can be converted into structural textual data which is easy to understand, cost effective and is more scalable. Natural Language Processing can automatically analyse and understandthetypeofcharacteranditwill assigna set of pre-defined tags (Pre-trained image datasets) and can be categorized based on its characteristics. 3.5 Text detection In the testing stage, text detection is accomplishedbysegmentingphotos.Aseriesoftext/sub-imagesofindividual text is divided from a full image. Edge detection and the space between the different characters are used to segment the image. Following segmentation, the sub-divided portions are labelled and processed one at a time. This labellingisusedto determine the total number of characters in an image. After that, each sub picture is scaled (70x50) and normalized in relation to itself. This aids in the extraction of image quality attributes [9]. Text detection is a method in which the model is given an image and the text region is detected by building a bounding box around it. Text recognition is carried out by further processing the discovered textual sections in order to recognise the text. 3.5.1 Training the dataset Deep learning model is built while feeding data to a deep neural network (DNN) to "train" in order to do a specific AI task (such as image classification or speech to text conversion). The hidden layer in the neural network is used for backpropagation which helps to improve the performance of the training model. Hence, during the training process, known data is fed into the DNN, and this DNN generates a prediction on what the data represents.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-4-2048.jpg)

![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 14 Easy to extract relevant data Low cost for usage like copying, editing and so on High accuracy to detect and recognize Increase the storage capacity IV. DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS FOR TEXT DETECTION AND RECOGNITION Deep learning is a domain of study that aims to copy the functioning of human brains in order to process data and make decisions. Deep learning is also knownasDeepNeural Network (DNN)orDeepNeural Learning.Thedeeplearningmodel for Optical Character Recognition uses two types of neural network architecture. They are i)Convolutional Neural Network (CNN); ii)Artificial Neural Network (ANN). 4.1 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a neural network which has three layers. They are: (i) Input layer, (ii)Hidden layer ;and (iii) Output layer. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) considers the optical image of a character as an input and provides the corresponding recognisable character as an output. ThetrainedCNN isusedtoextractthefeaturesoftheimage.CNN classifiers along with other classifiers can be combined and give the best result for classification.Thatis,theaccuracyandefficiencyofthe classification can be improved. The hidden layer uses the input to perform feed-forward and backpropagation in order to improve the accuracy and reduce the error rate. Convolutional Neural Network and Error Correcting Output Code (CNN +ECOC) where CNN for feature extraction and ECOC for classification are combined to obtain Optical Character Recognition. This method gives high accuracy for handwritten characters. It is trained and validated with NIST dataset [46]. 4.2 Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Artificial Neural Network can be used to recognise the image with a single character and further include many characters for classification. The classification process can be done in two phases: i) Feature preprocessing - read each character and convert it into binary image and scan by all four sides (left, tp, right, bottom) and ii) a) Training the neural network and b) Testing the neural network with the datasets. Here, the training sets are used to learn how to remove noise from the data [50]. 4.3 Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Recurrent Neural Network is based on the sequential form of data. Recurrent neural network is most suitable for the text classification which can recognize the whole sentence or sequential set of words. When the words or characters are in sequence, this recurrent neural network can predict the next word of the sequence. Hence handwritten characters can be predicted more accurately while using recurrent neural networks. To achieve the prediction accuracy,RNN doesnotrequire a dataset in the form of labelled data (need not be supervised learning). Recurrent neural networks are capable of working the temporal information. The disadvantage of RNN is that it will raise the vanishing gradient problem. The trainingof datasetsis more complex and hence more difficult. It is also difficult to process the long sequential characters. LEARNING RATE IN DEEP LEARNING ALGORITHM The learning rate refers to the number of times the images are trained. In deep learning neural networks, the Stochastic Gradient Descent is used. The learning rate refers to the parameters or hyperparameter which controls how many times the dataset is trained in order to reduce error rate and improve accuracy which improves the performanceof themodel. While training this dataset, backpropagation technique is used where the weights are updated each time in order to getbetter performance of the neural network model. This learning rate affects the performance of the model when it reaches the local minima. Hence, it is important to adjust the learning rate from high to low to slow down once the model reaches the optimal solution during training.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-6-2048.jpg)
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 16 6.2 Long-Short Term Memory Networks(LSTMs) LSTMs are proven which outperforms the conventional recurrent neural networks and it suffers from the fading gradient problem, when modelling long-term dependencies. The CTC layer, whichcomesaftertheLSTMlayers[figure3],gives the feature sequences with the ground truth transcription during the training and decoding the LSTM layer’s outputs during evaluation to create the predicted transcription. From the start to finish, the system is taught through feeding the text lines, pictures and ground truth transcription (in UTF-8) [5]. Figure 3 CNN-BiLSTM architecture 6.3 Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) Recurrent Neural Networks is mainly used for feed-forward techniques. RNN can work both parallelly and sequentially. During computation. A number of sequence learning challenges have been successfully solved using Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and RNN variations (Bi-directional LSTMs and MDLSTM). According to several studies, LSTM outperforms HMMs on such tasks. 6.4 Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) GANs are the form of neural network architecture which enables the deep learning models to learn and capture the training data distribution, which provides the generation of new data instancesbased onthesedistributions.GANsareusedfor unsupervised machine learning to train the two models parallely. It gives the training data whichissimilartotheoriginal data. A discriminator and a generator are often included in GANs [51]. 6.5 Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLPs) The MLPs is a supervised learning convolutional artificial neural network that reduces error by continuously computing and updating all the weights in the network. In the first phase, which is a feed-forwarding phase, thetraineddata is delivered to the output layer, after that the output and the desired targets (errors) are back-propagated to update the network’s weight in the next phase. The Adam optimiser was employed to improve the performanceofMultiLayer Perceptron [22]. Adam optimizer : Adam optimizer is an extension of stochastic gradient descent that usesdeeplearningapplications for computer vision and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Adam optimizer is used to remove vanishing gradient problems. The computation time is faster and it requires only a few parameters for tuning.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-8-2048.jpg)
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 17 6.6 Deep Belief Networks (DBNs) A Deep Belief Network (DBN) is a type of deep neural network (DNN) or a generative graphical model. The DBN is constructed with multiple layers of “hidden units” which are latent variables with the connections across the levels and not in between the units in each layer. DBN can be learned to probabilisticallyrecreatetheinputswithoutsupervisionwhentheseare trained on the set of example datasets. Next, the DBN’s layers act as a feature for detection. Additionally, a DBN can be trained under supervision to categorize the text or object after completing the learning stage. To develop a Novel Q-ADBN for handwritten digit/character recognition, ADAE and Q-learning algorithms are introduced in Deep Belief Network [4]. 6.7 Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) The Adaptive Deep Auto-encoder(ADAE)hasbeenmadeupofnumeroussuccessivelystackedRBMs,wheretheoutput of one RBM acts as the input of the next. Each RBN is treated as an encoder. The encoder uses unique code torecognisethetext .ADAE’s hierarchical feature extraction technique is comparable to that of a human’s brain [4]. 6.8 Autoencoders Autoencoders are the combination of Encoders and Decoders. It is mainly used to learn the compressed representations of the datasets. The Autoencoders should be trained in order to learn the fixed dimensional latent space representation of the given image, making them ideal for the feature extraction [6]. The output of the autoencoder network is the reconstruction of the input data which is more efficient. Related Works Referen ce Proposed Algorithm Purpose Dataset Accuracy 1 Convolutional Neural Network extract feature from raw images JEITA-HP database Firemaker and IAM database 99.97% 91.81% 2 Codebook model, Clustering,Bayesianclassifier, Moore’s algorithm Feature generation and Feature selection, Classifiers using feature vectors IAM dataset AUT-FH dataset 93.7% 96.9% 3 Convolutional Neural Network + XGradientBoost CNN - feature extraction XGBoost - Recognition and classification HECR (CNN+XGBoost) 99.84% 4 Q-ADBN ADAE extract features from original images using ADAE MNIST dataset 99.18% 5 Convolutional Neural Network, Long Short Term Memory network feature extraction Increase the memory of RNN IFN/ENIT dataset 83% 6 Convolutional Neural Network autoencoder + Support Vector Machine Feature extractor Classify the images 4600 MODI characters 99.3% 7 Convolutional Neural Network, Algebraic fusion of multiple classifier Feature extractor Multi-level fusion classifier MNIST dataset 98% 8 Artificial Neural Network Classify and Recognize the text from USTB-Vid TEXT 85%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i802-221028095122-4a316d5c/75/Deep-Learning-in-Text-Recognition-and-Text-Detection-A-Review-9-2048.jpg)