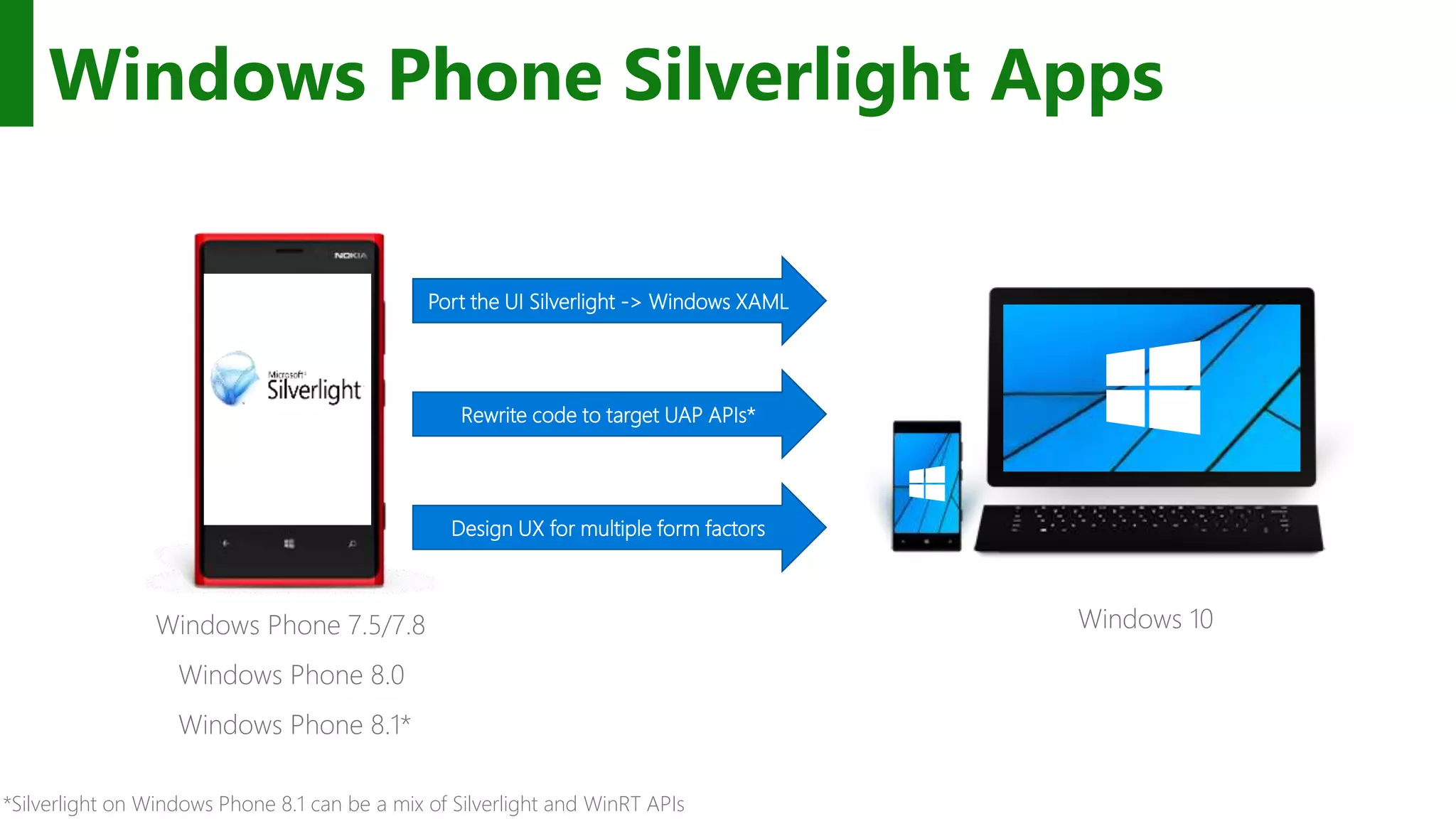
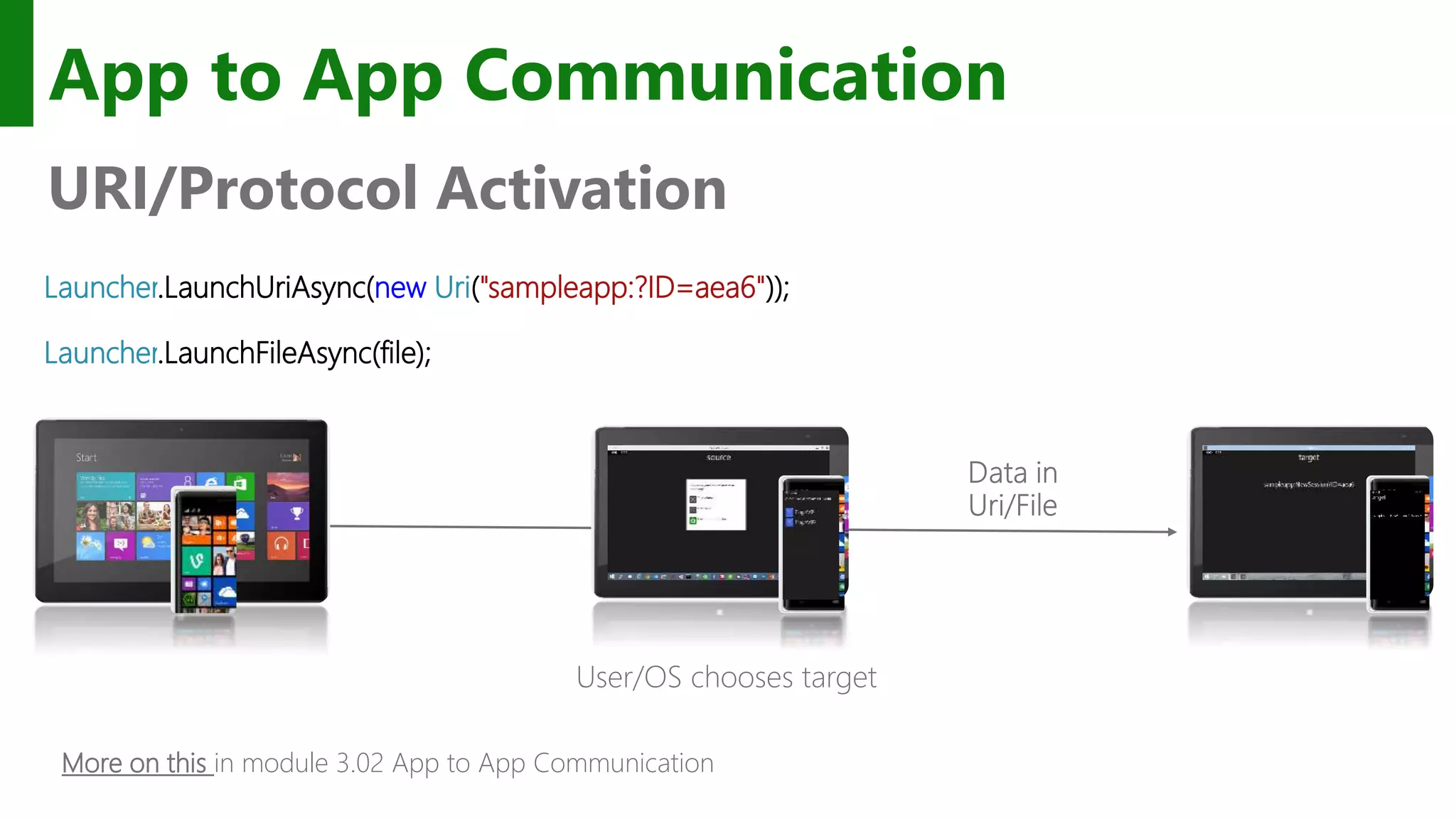
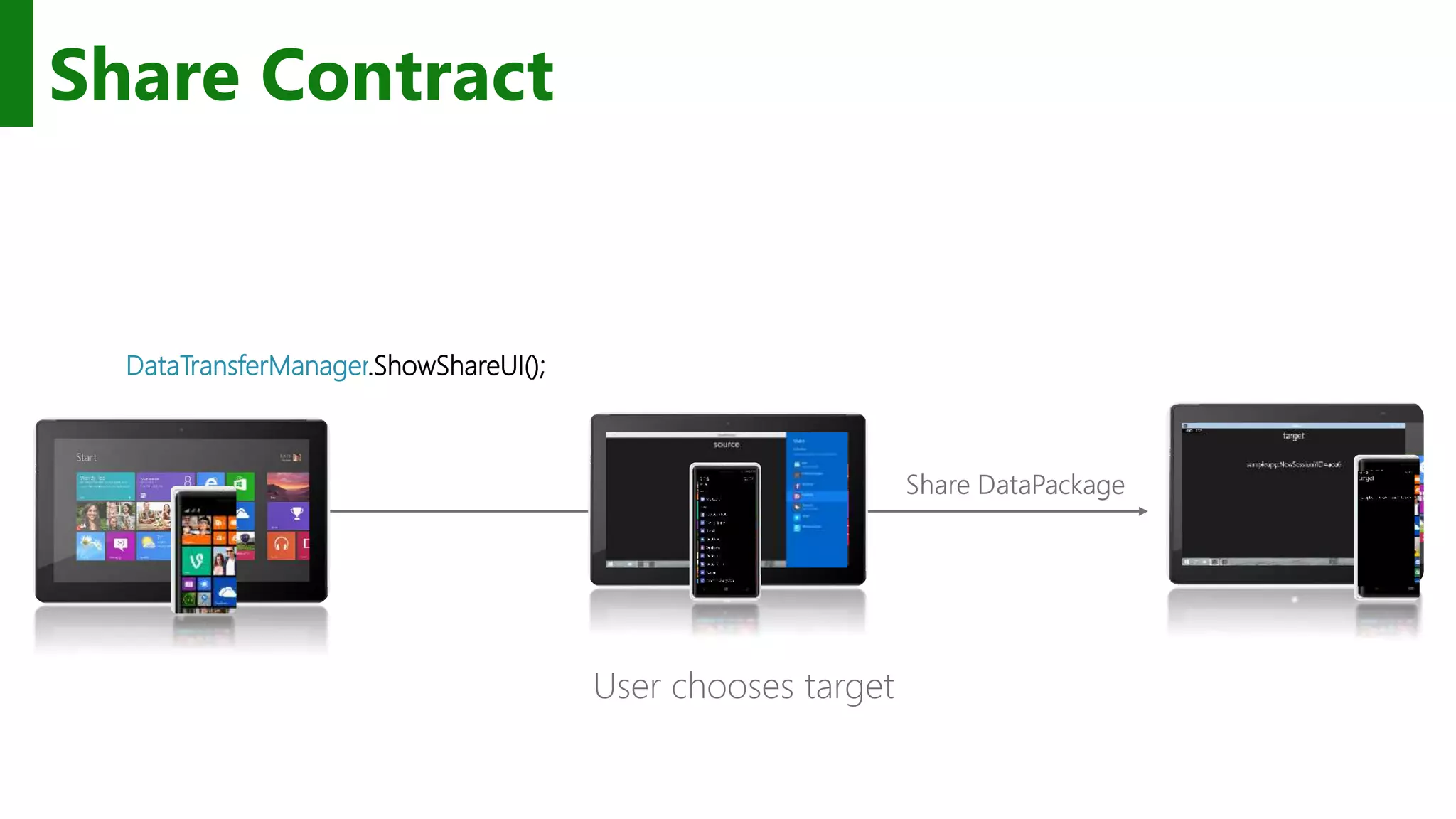
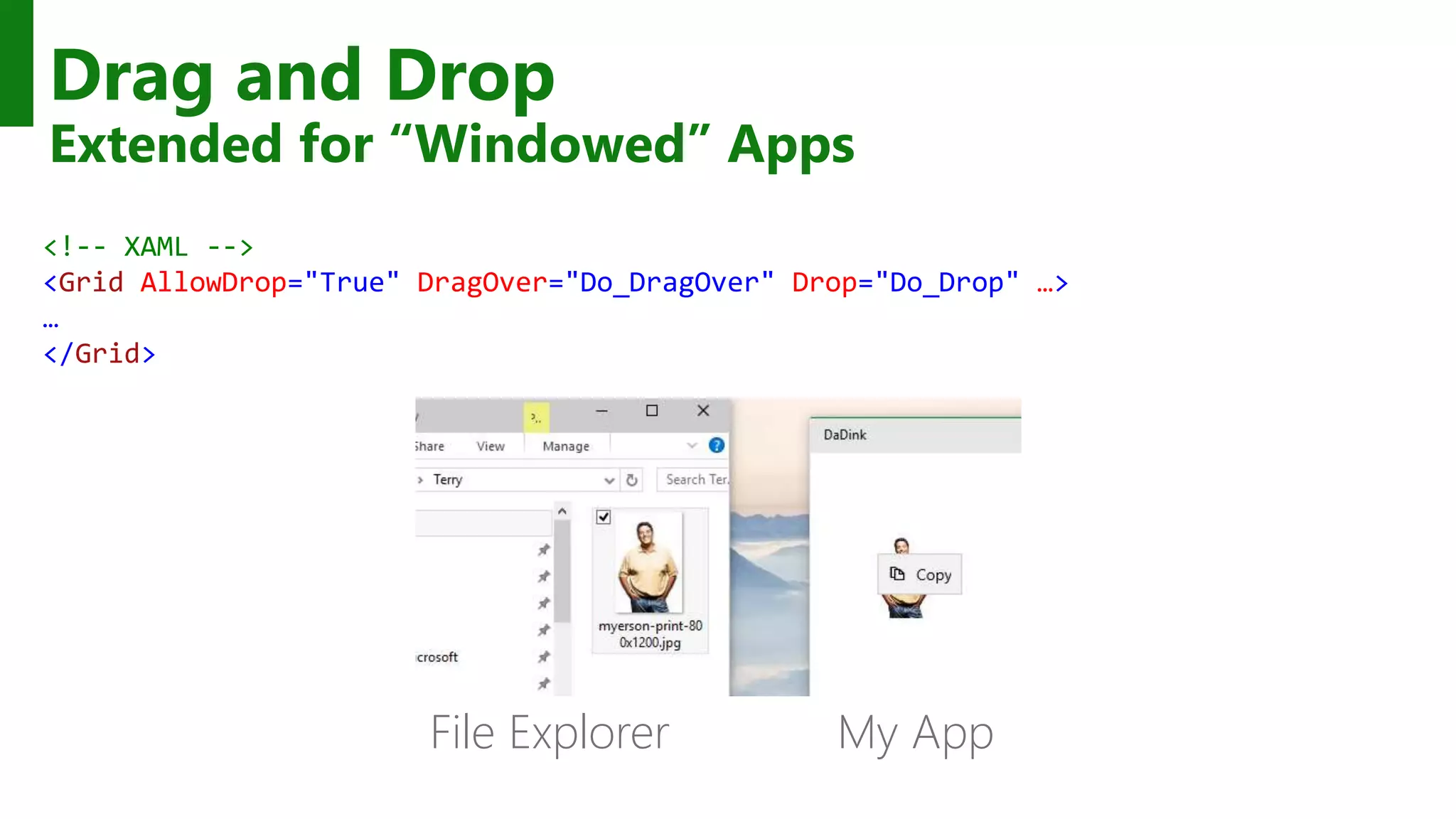
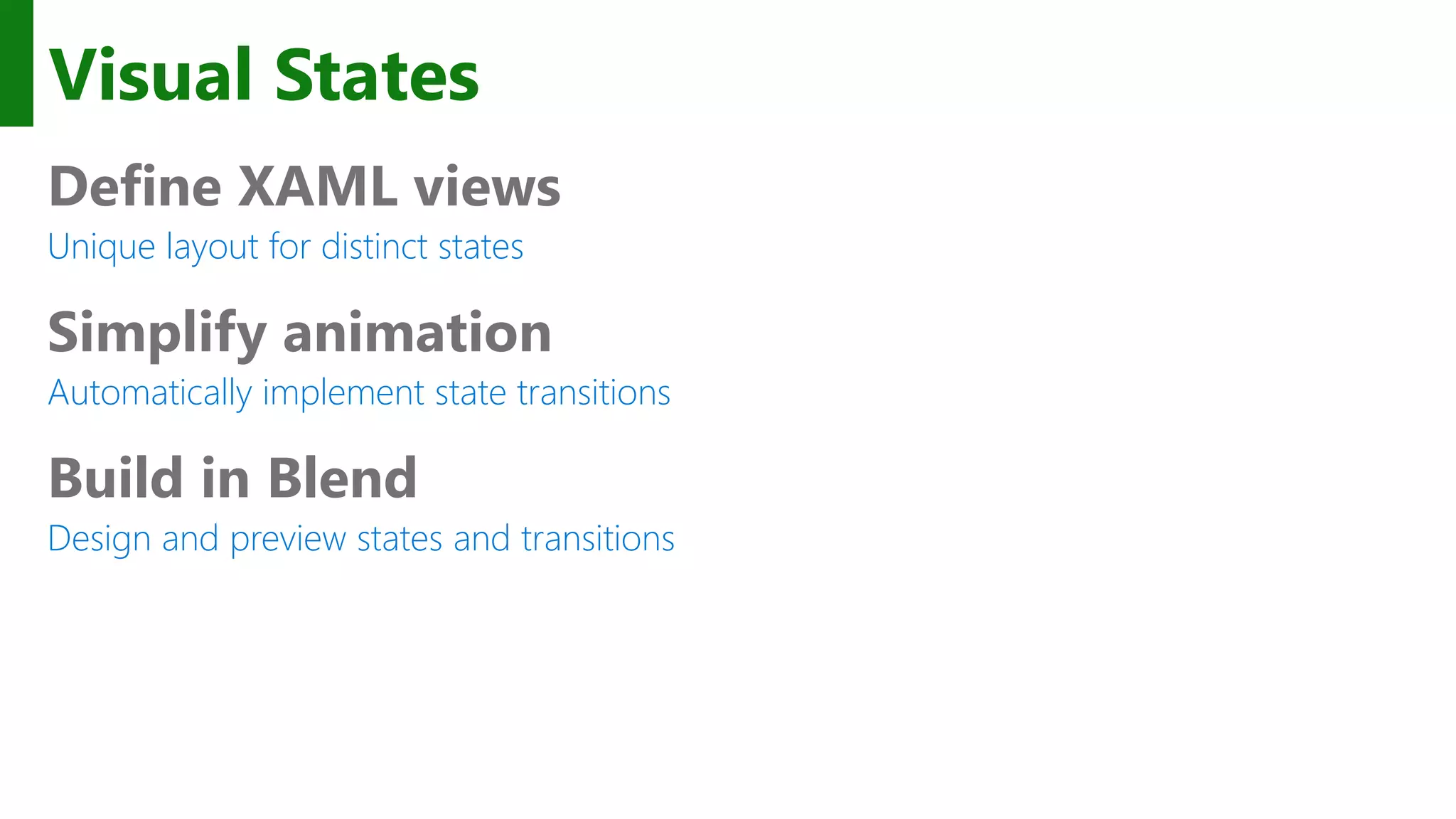
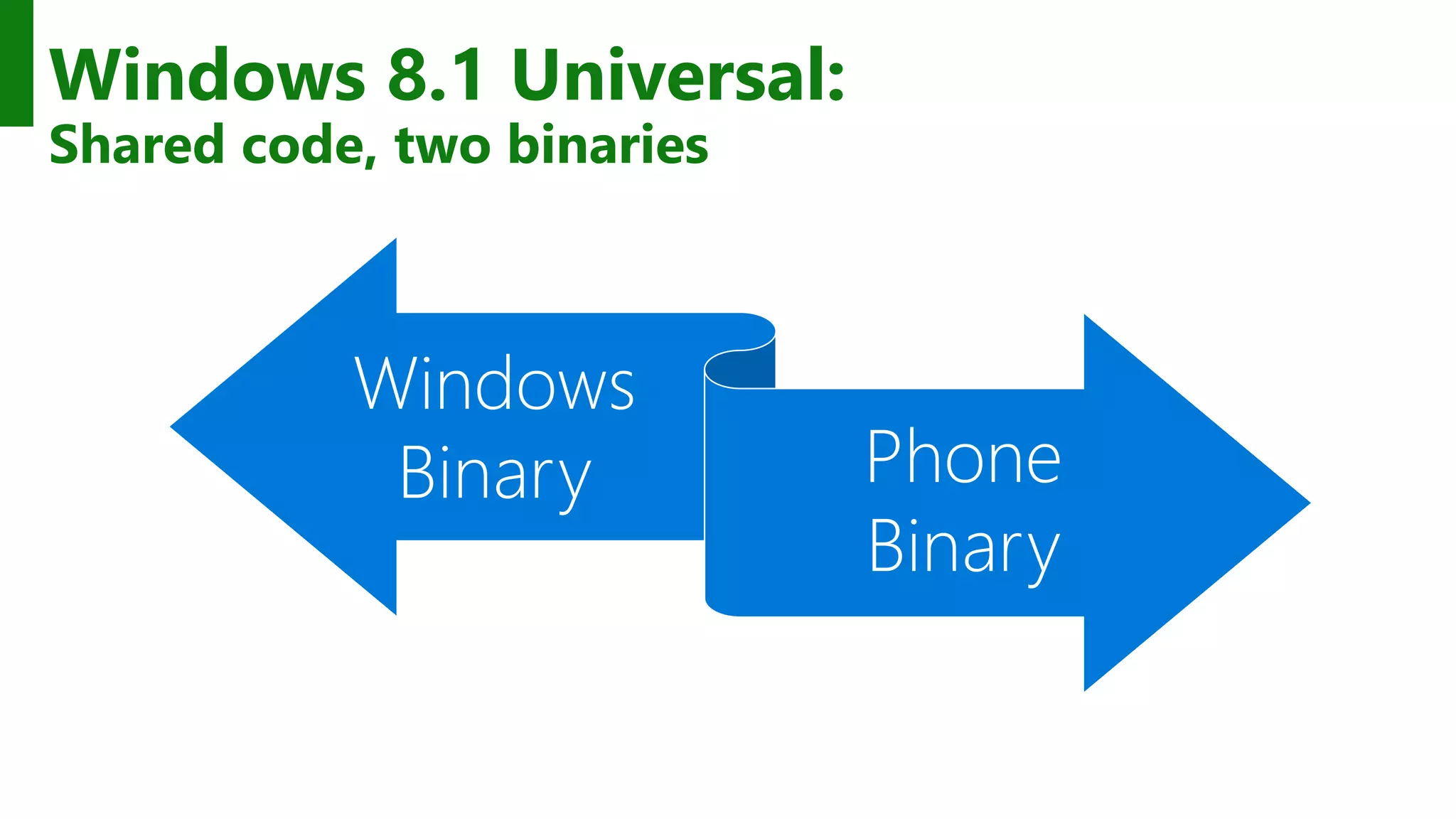
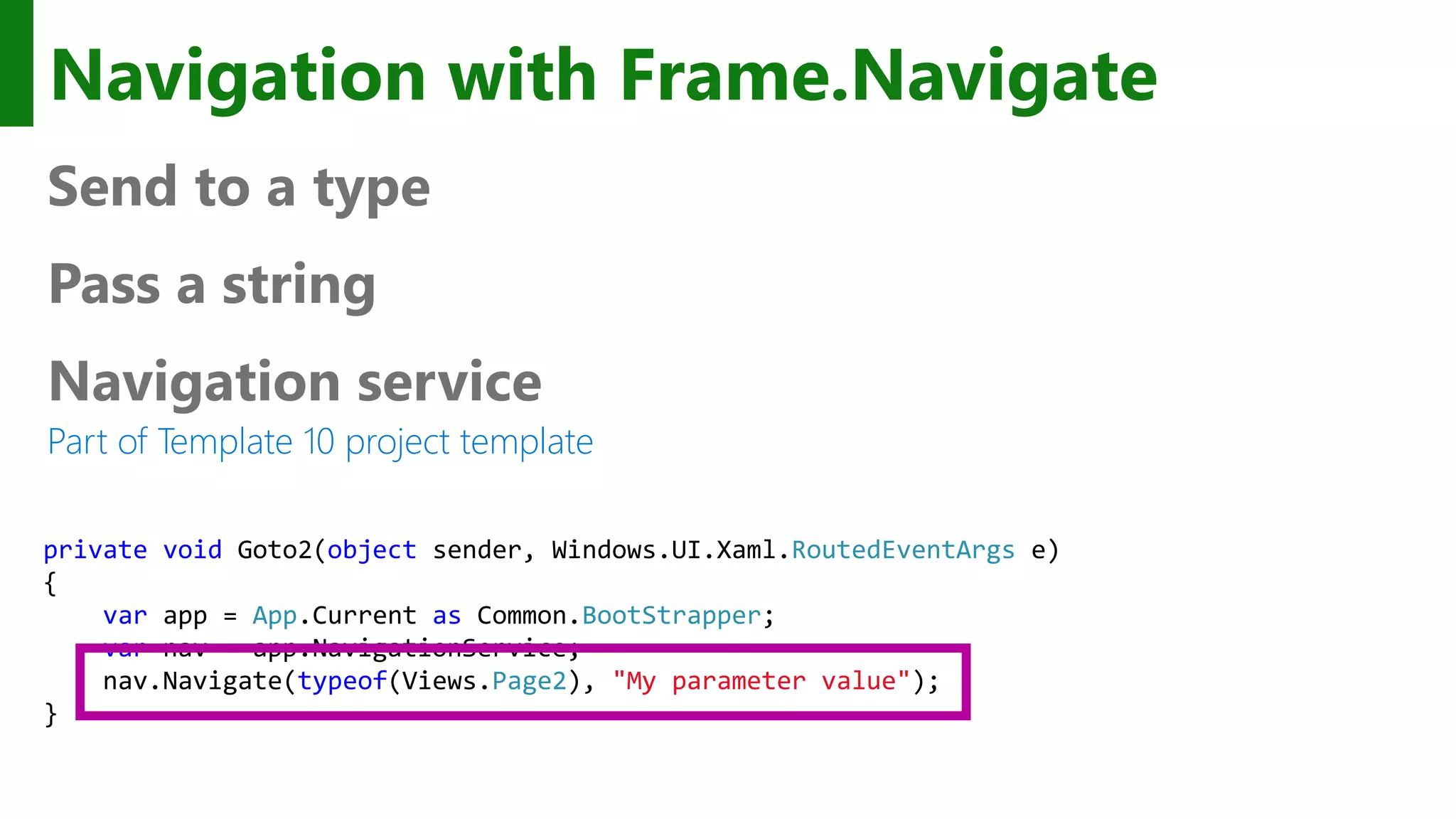
The document outlines the development of Universal Windows Apps on the Windows 10 platform, covering its architecture, coding standards, and adaptive UI capabilities. It discusses the integration of various device types and the importance of utilizing XAML for user interface design while providing guidance on app lifecycle, background tasks, and handling storage solutions. Additionally, it emphasizes the compatibility and monetization strategies available through the Windows Store.





![In-app purchases #if DEBUG var license = CurrentAppSimulator.LicenseInformation; if (license.ProductLicenses["AdFree"].IsActive) { // already owns this.ShowAds = false; } else { var result = await CurrentAppSimulator.RequestProductPurchaseAsync("AdFree"); switch (result.Status) { case ProductPurchaseStatus.Succeeded: case ProductPurchaseStatus.AlreadyPurchased: this.ShowAds = false; break; default: this.ShowAds = true; break; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/win10-appdev-shahedchowdhuri-150724024414-lva1-app6892/75/Deeper-into-Windows-10-Development-12-2048.jpg)














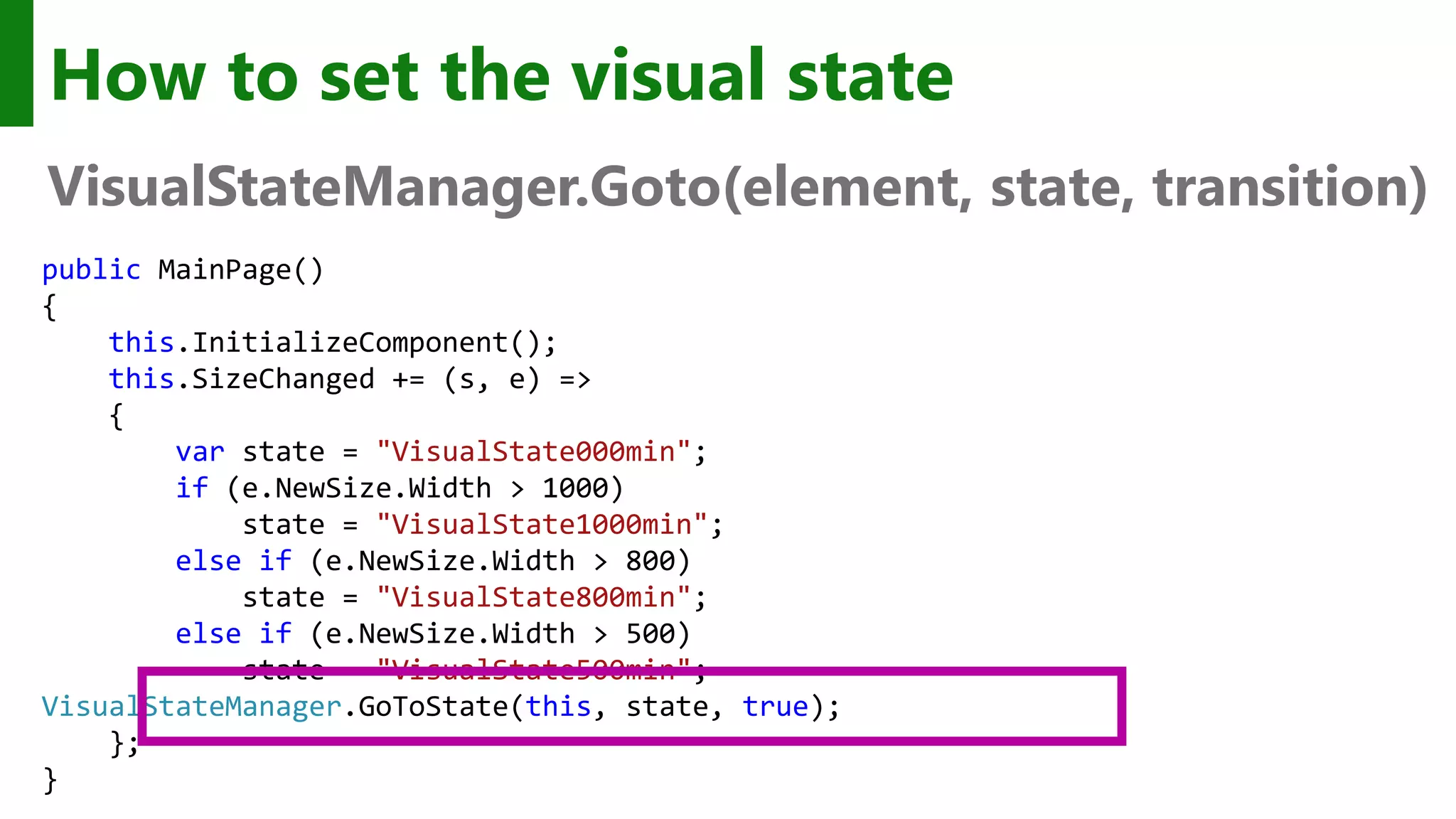
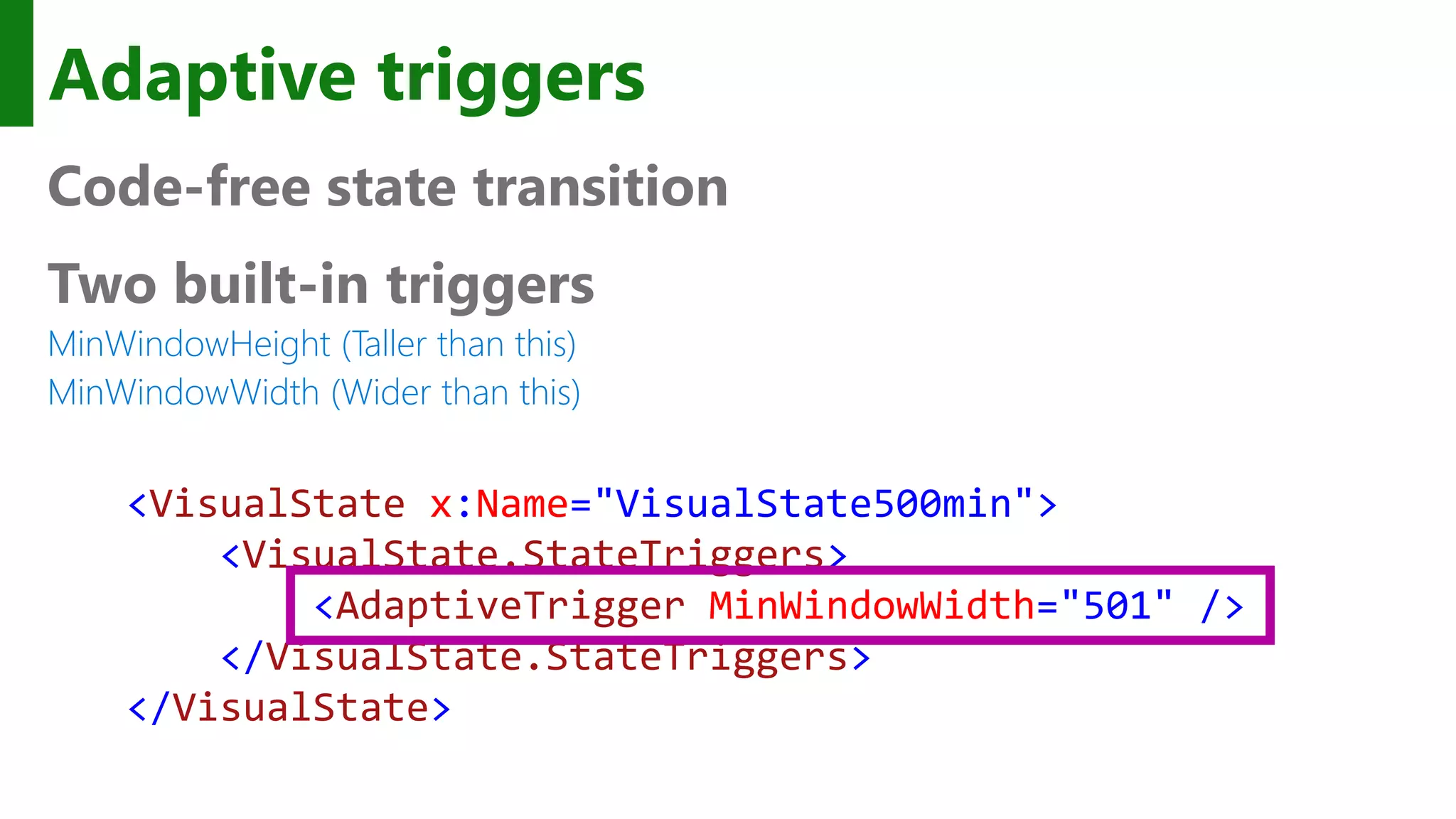
![Custom adaptive triggers Build to handle special cases. public class DeviceFamilyTrigger : StateTriggerBase { private string _deviceFamily; public string DeviceFamily { get { return _deviceFamily; } set { var qualifiers = Windows.ApplicationModel.Resources.Core .ResourceContext.GetForCurrentView().QualifierValues; if (qualifiers.ContainsKey("DeviceFamily")) SetActive(qualifiers["DeviceFamily"] == (_deviceFamily = value)); else SetActive(false); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/win10-appdev-shahedchowdhuri-150724024414-lva1-app6892/75/Deeper-into-Windows-10-Development-37-2048.jpg)





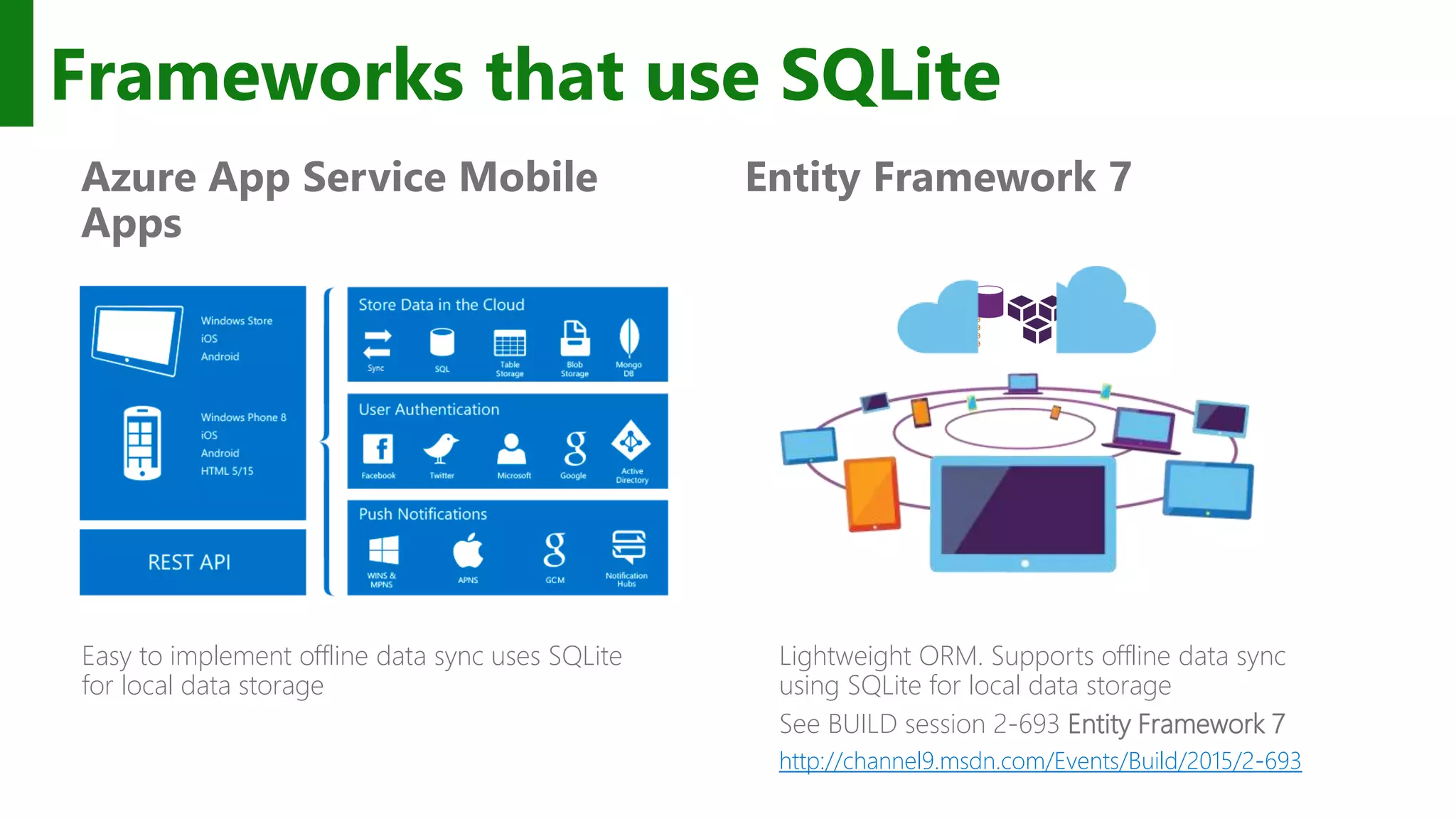
![Choice of .NET APIs SQLite-NET LINQ syntax Lightweight ORM SQLitePCL SQL statements Thin wrapper around the SQLite C API using (var conn = new SQLiteConnection("demo.db")) { Customer customer = null; using (var statement = conn.Prepare( "SELECT Id, Name FROM Customer WHERE Id = ?")) { statement.Bind(1, customerId); if (SQLiteResult.DONE == statement.Step()) { customer = new Customer() { Id = (long)statement[0], Name = (string)statement[1] }; } } } var db = new SQLite.SQLiteAsyncConnection(App.DBPath); var _customer = await (from c in db.Table<Customer>() where c.Id == customerId select c).FirstOrDefaultAsync(); if (customer != null) { var Id = _customer.Id; var Name = _customer.Name; } …and others!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/win10-appdev-shahedchowdhuri-150724024414-lva1-app6892/75/Deeper-into-Windows-10-Development-50-2048.jpg)














![System condition(s) [ if? ] User Present If the user is present User Not Present If the user is not present Internet Available If the internet is available Internet Not Available If the internet is not available Session Connected If the user is logged in Session Disconnected If the user is not logged in Free Network Available If a non-metered network is available Work Cost Not High If background resources are plentiful](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/win10-appdev-shahedchowdhuri-150724024414-lva1-app6892/75/Deeper-into-Windows-10-Development-73-2048.jpg)










![Back button Essentially same as Phone 8.1 Back navigates back within app, then to previous app UAP apps request the optional, shell-drawn back button With one improvement Backing out does not close the app And, a new scenario for tablet In split screen, there is a [back stack] for each side of the screen Windows.UI.ViewManagement.ApplicationView.GetForCurrentView().IsShellChromeBackEnabled = true; Windows.UI.Core.SystemNavigationManager.GetForCurrentView().BackRequested += HandleBack;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/win10-appdev-shahedchowdhuri-150724024414-lva1-app6892/75/Deeper-into-Windows-10-Development-95-2048.jpg)