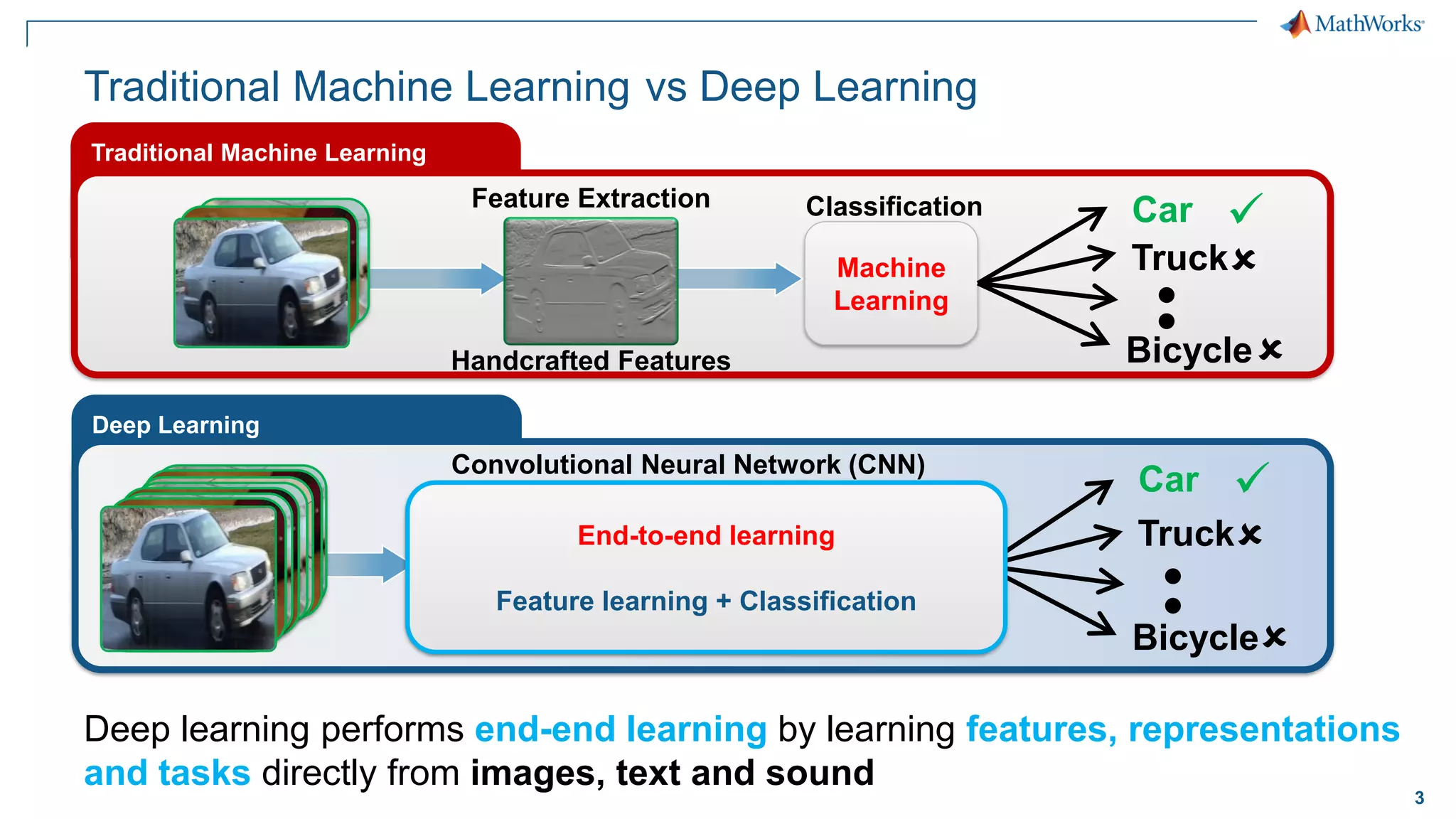
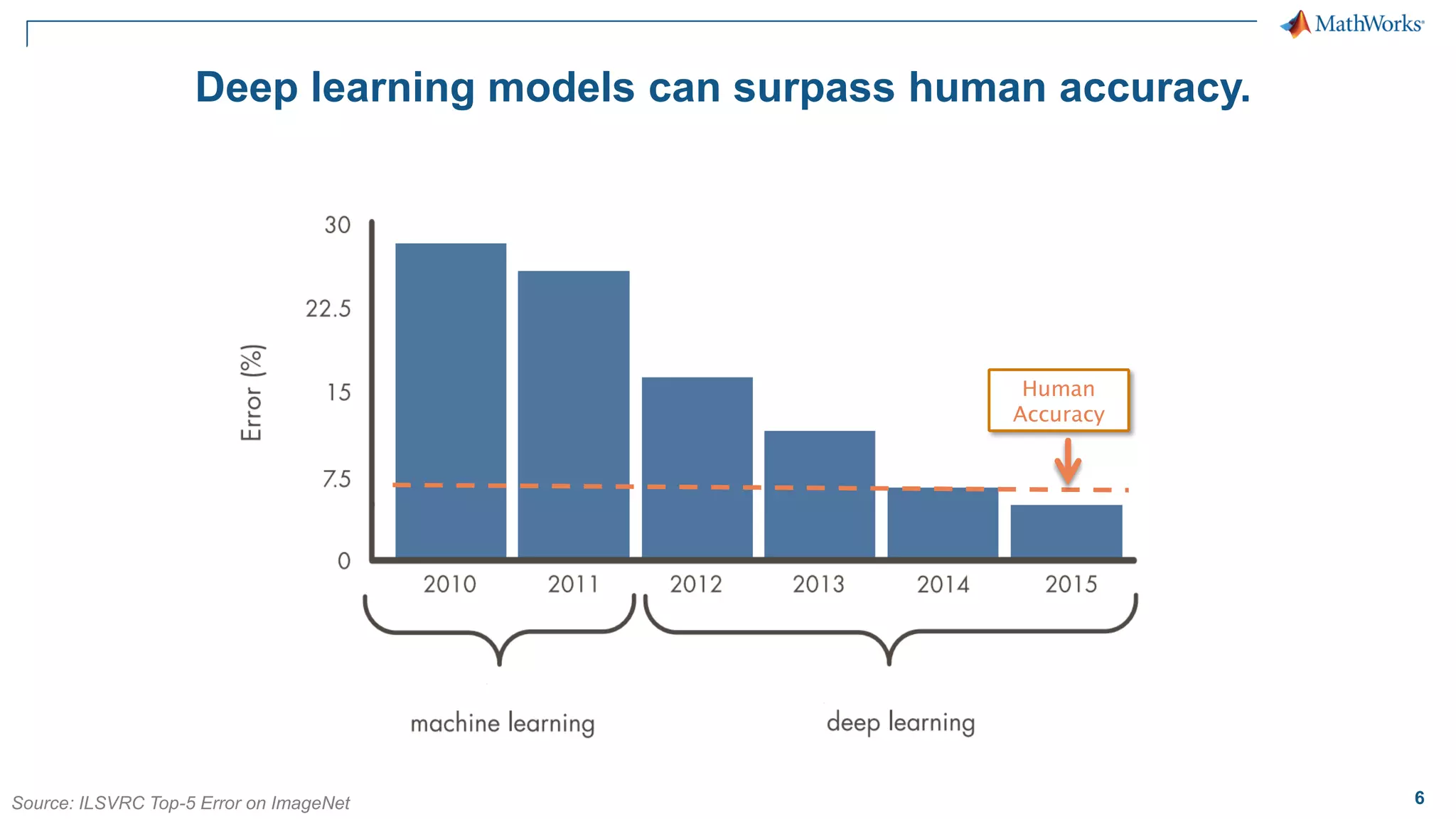
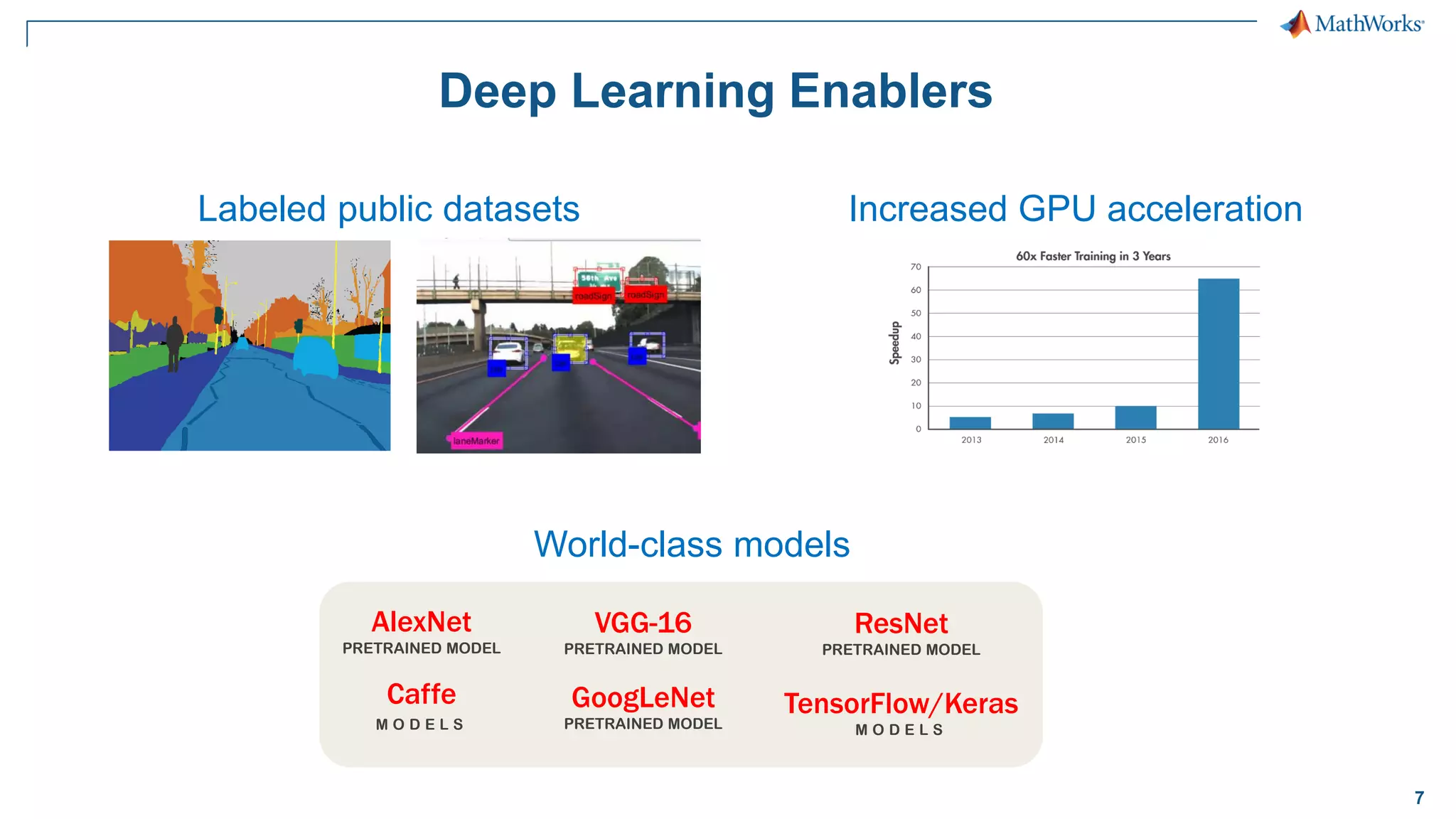
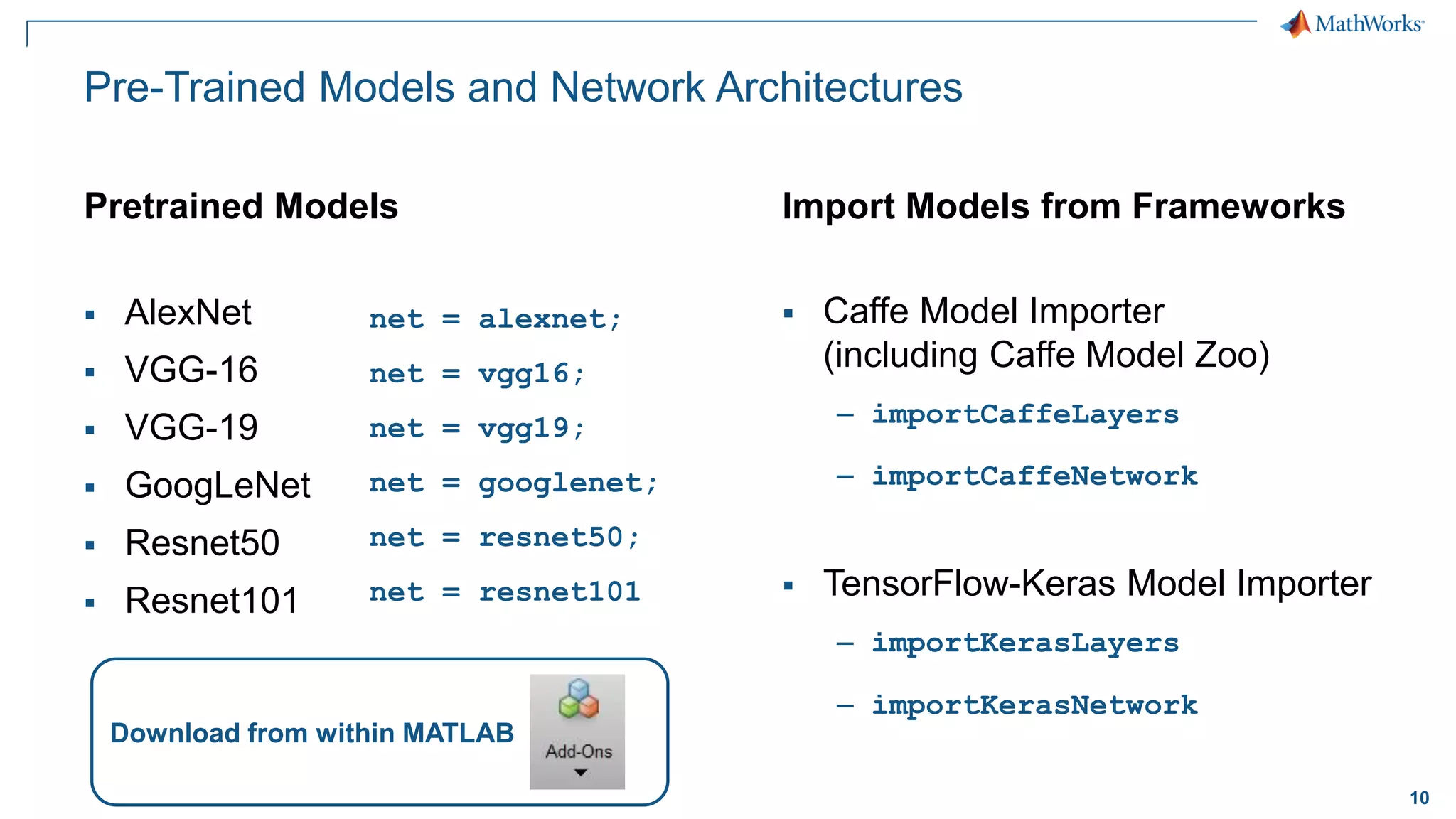
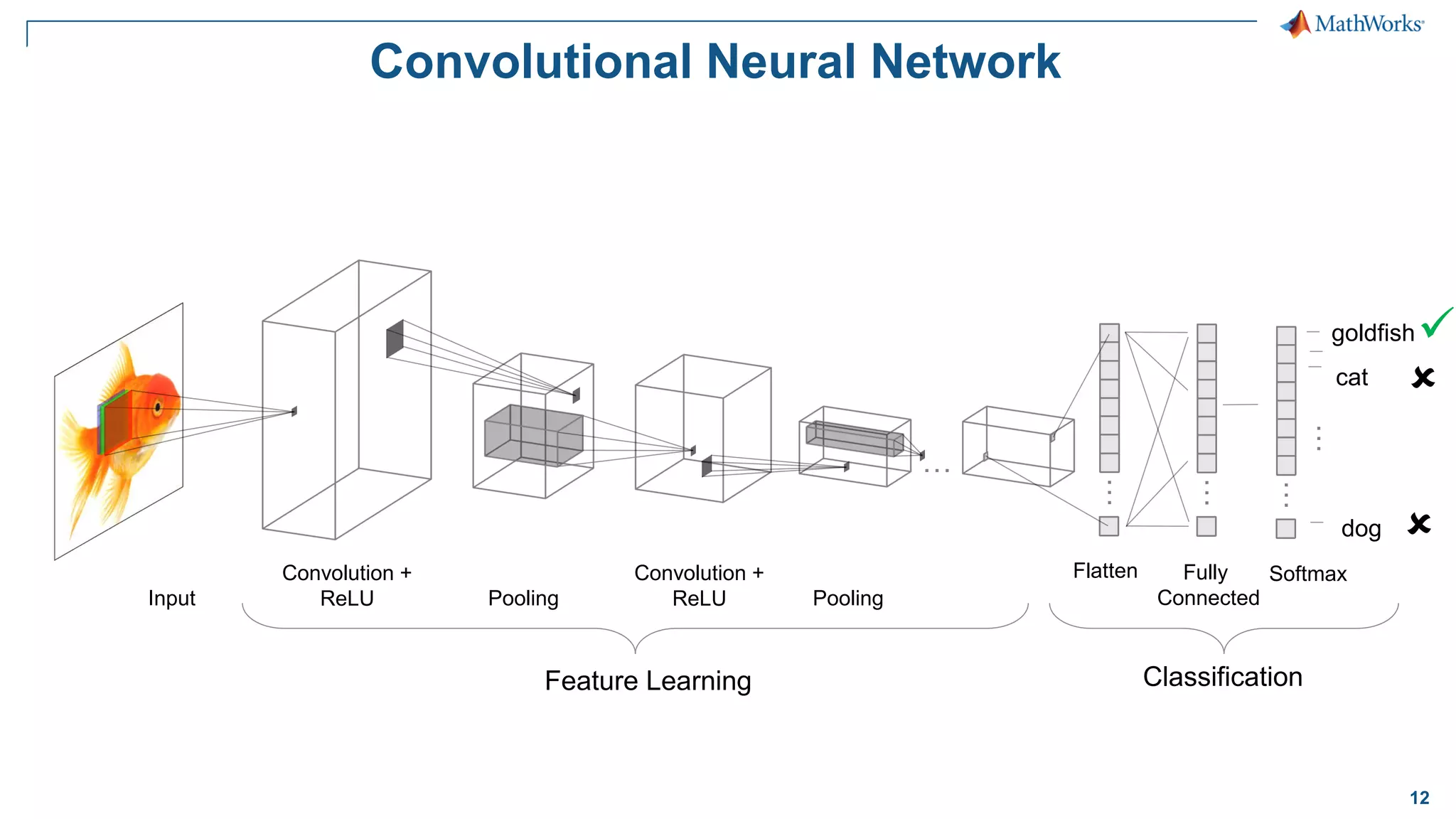
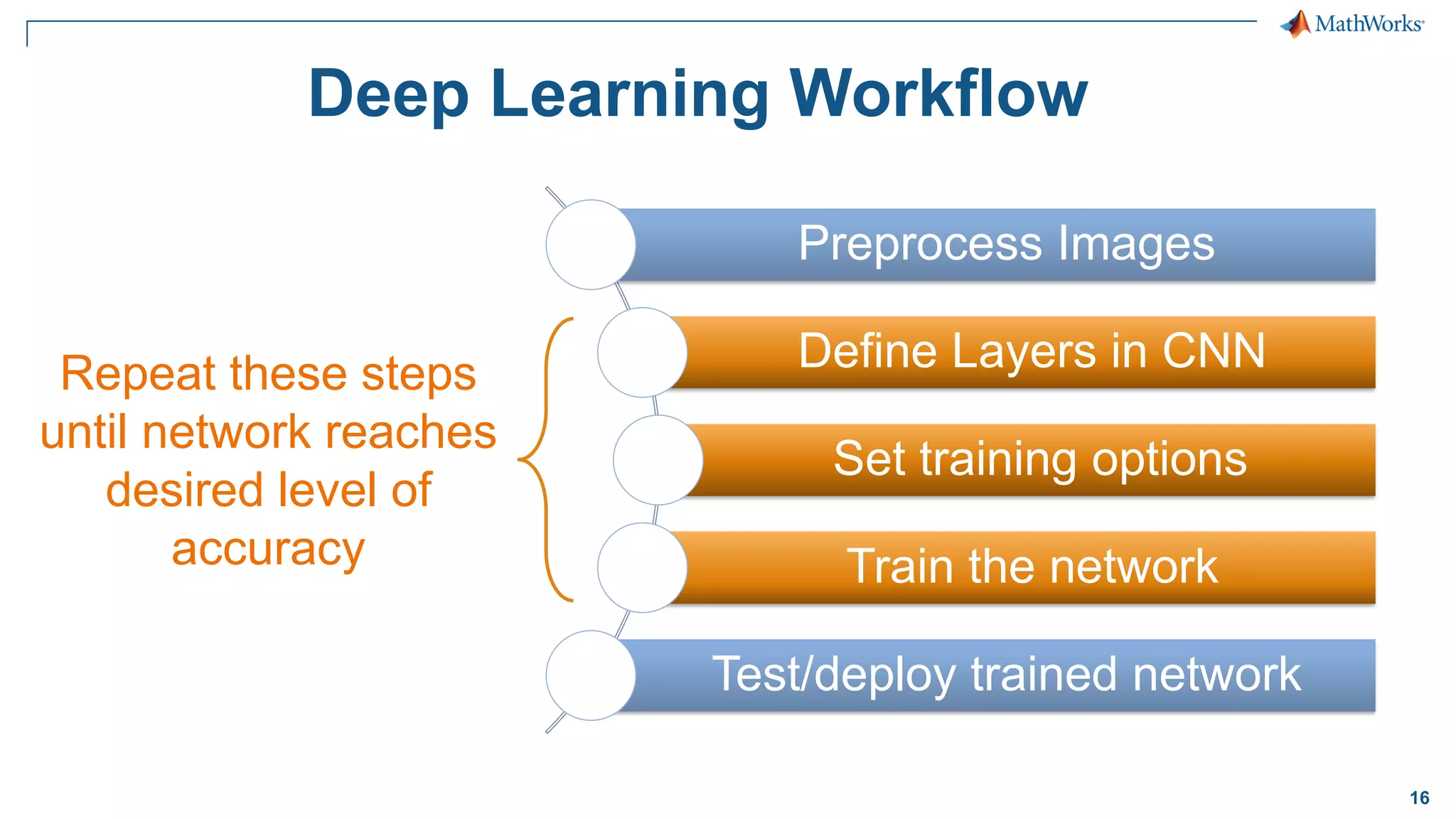
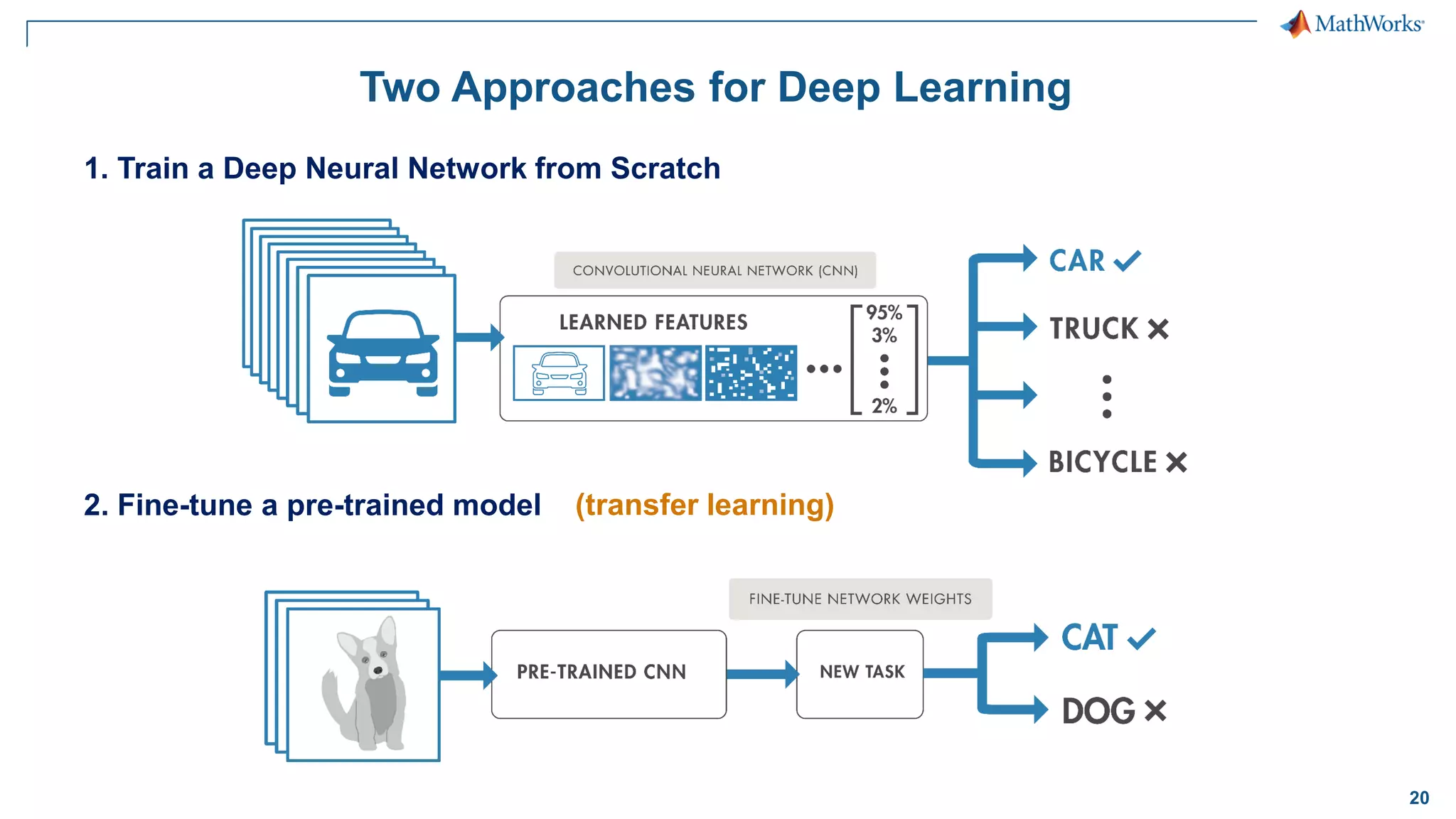
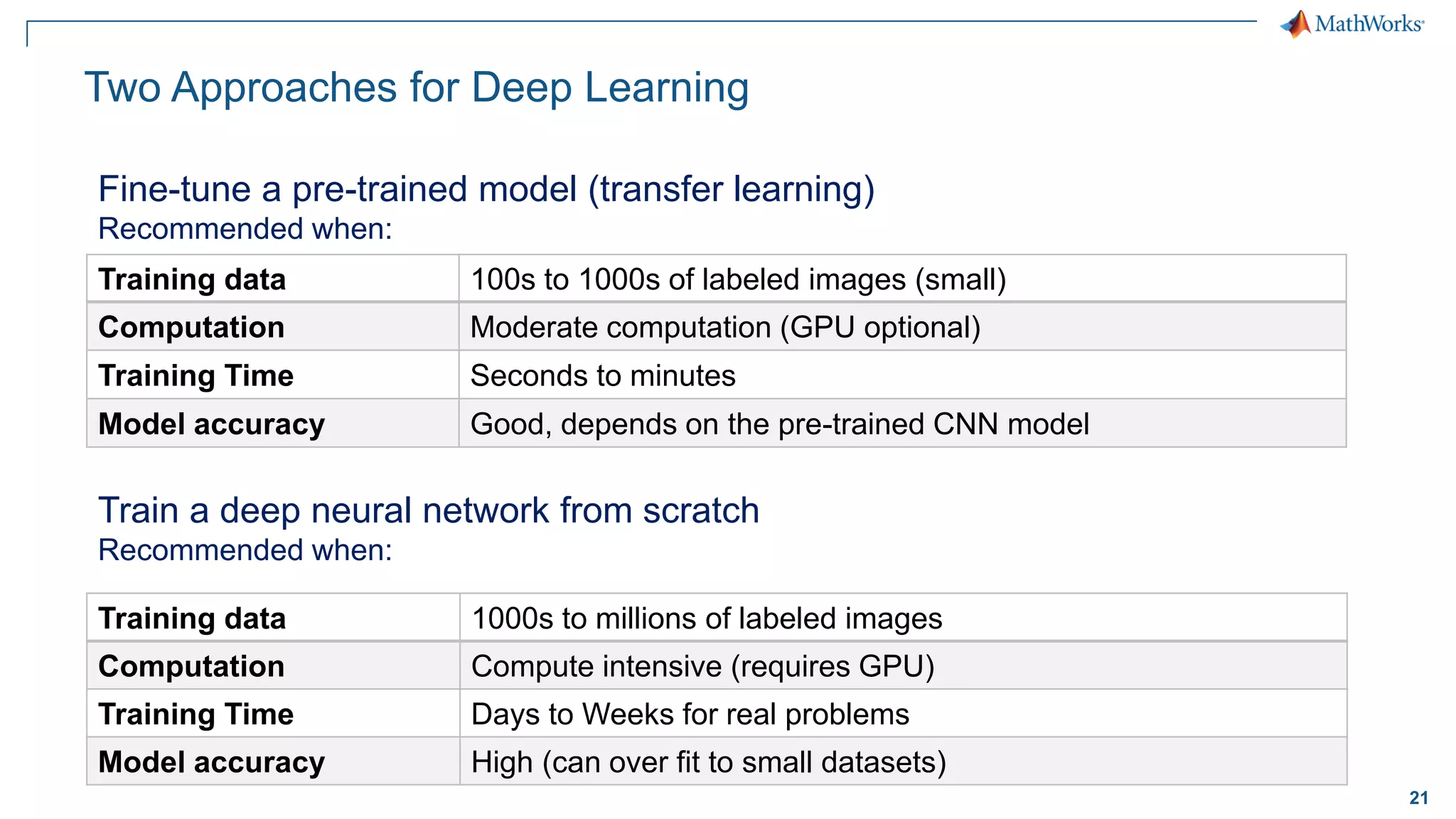
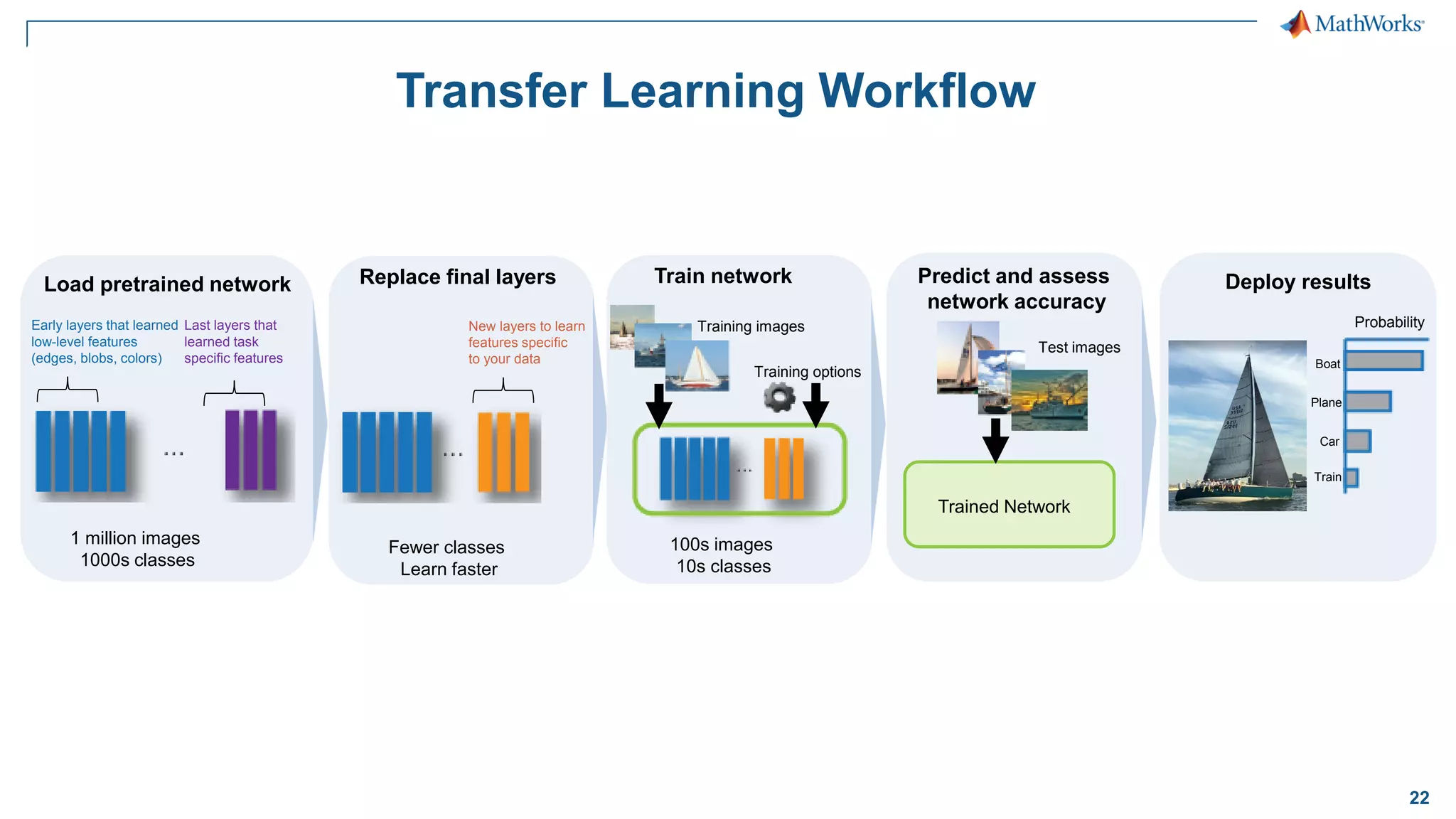
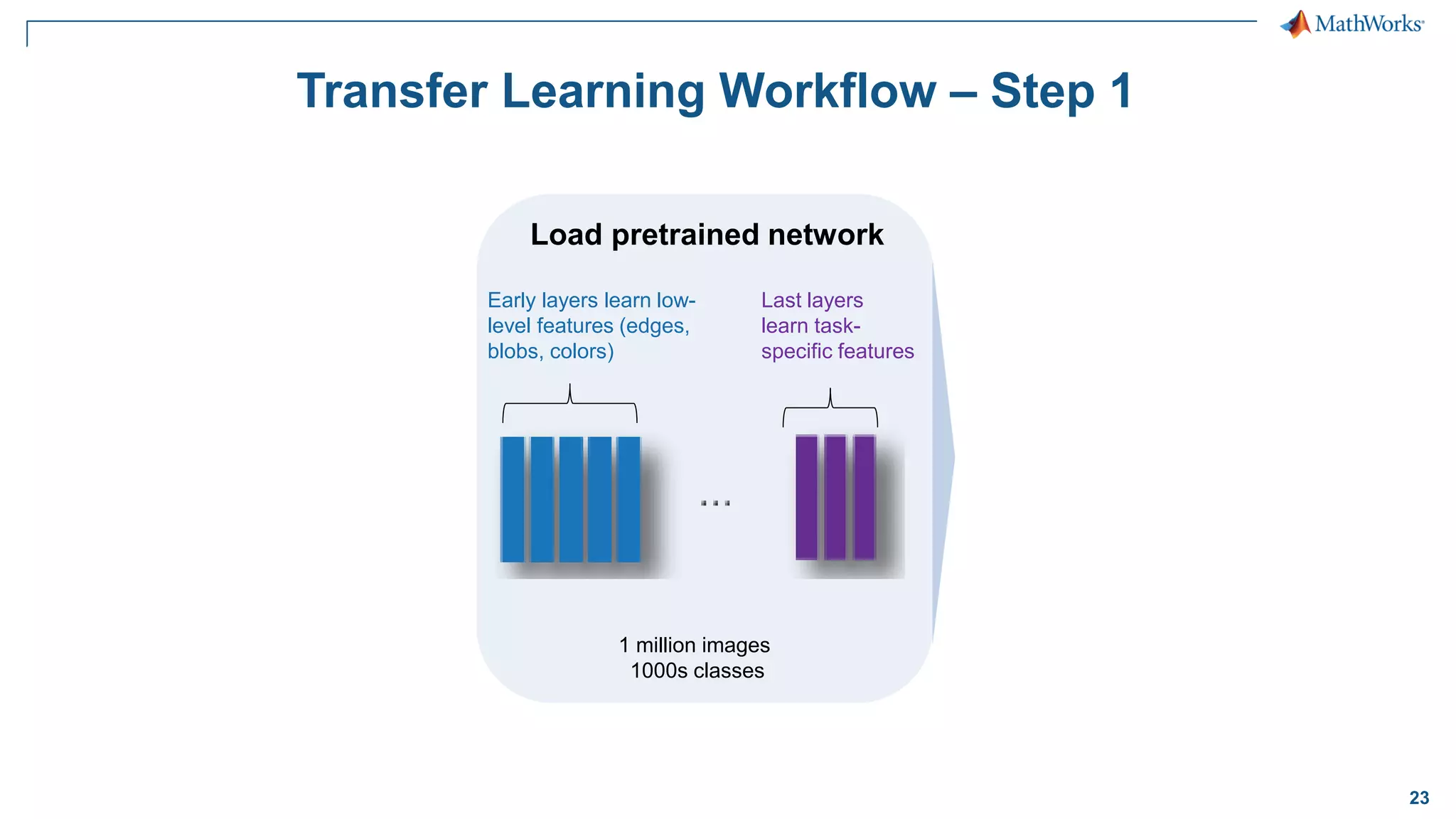
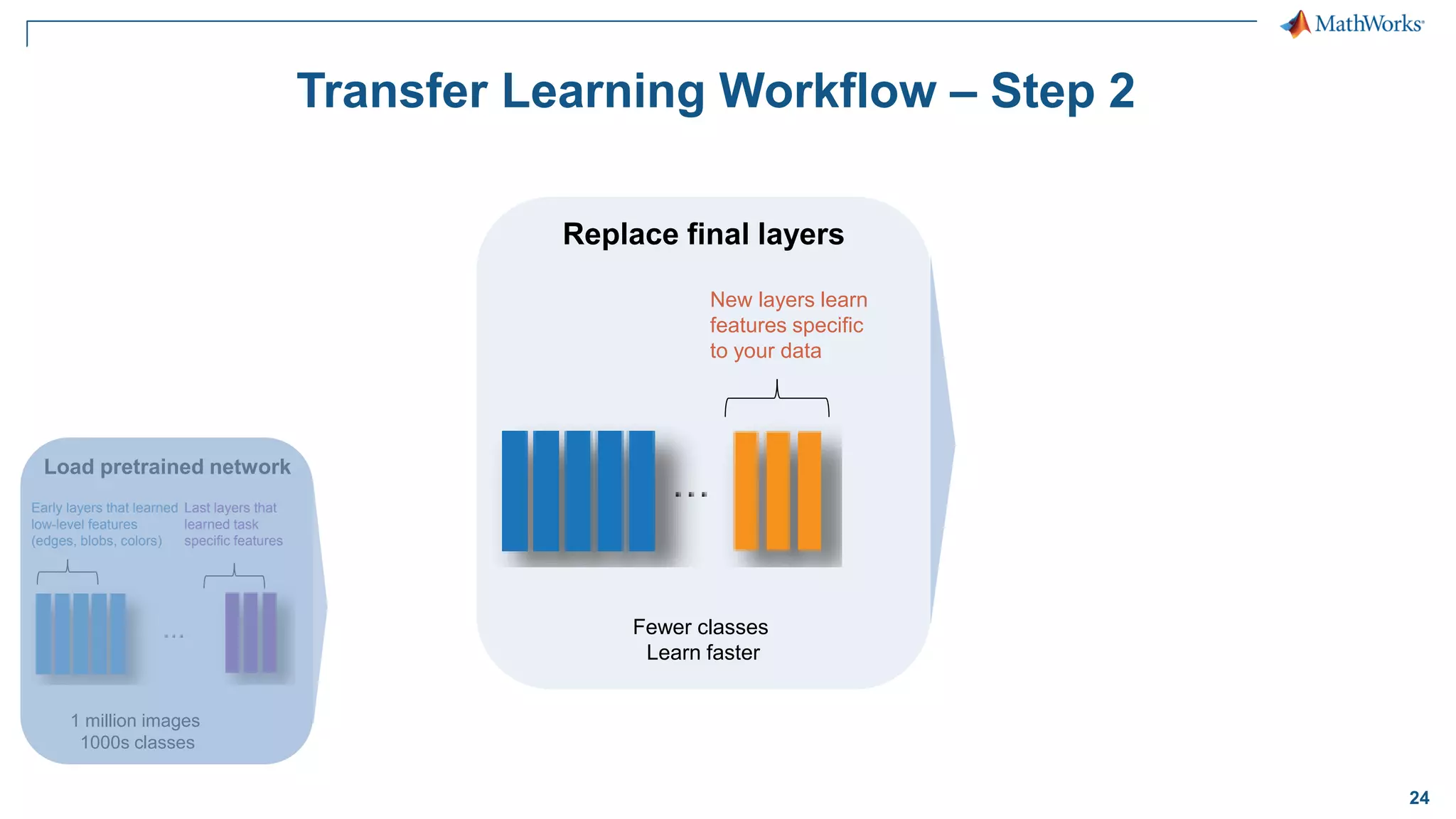
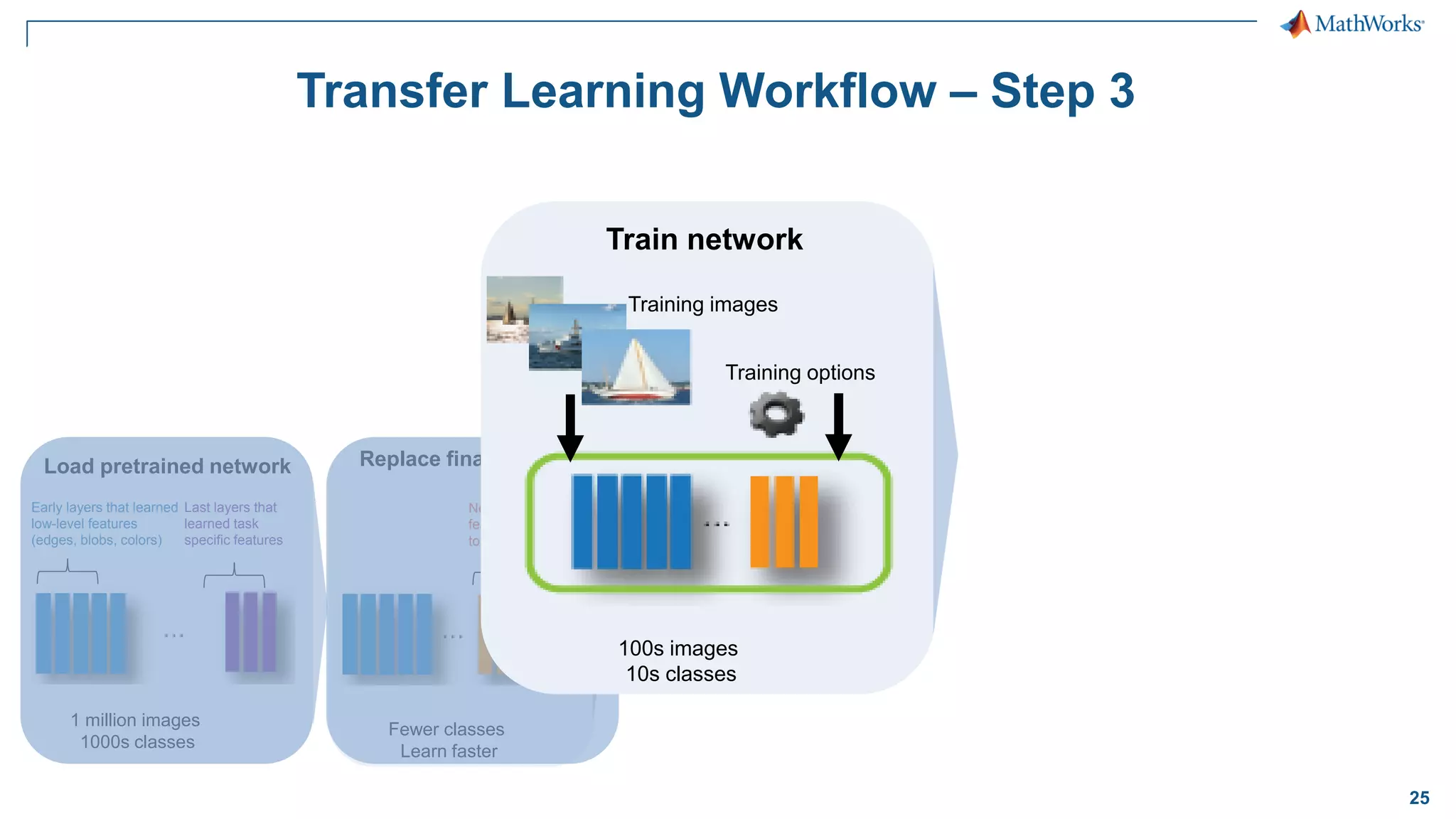
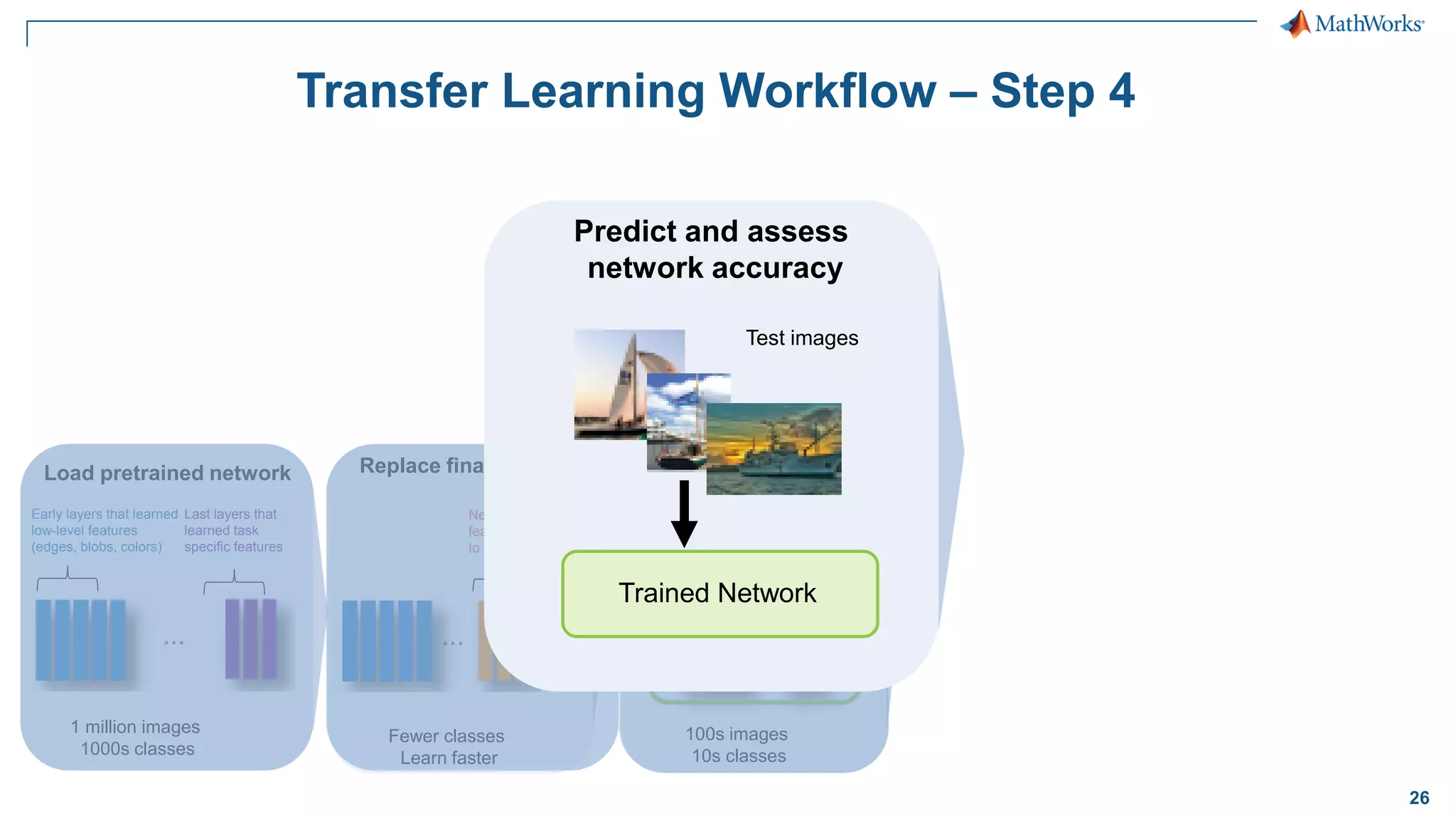
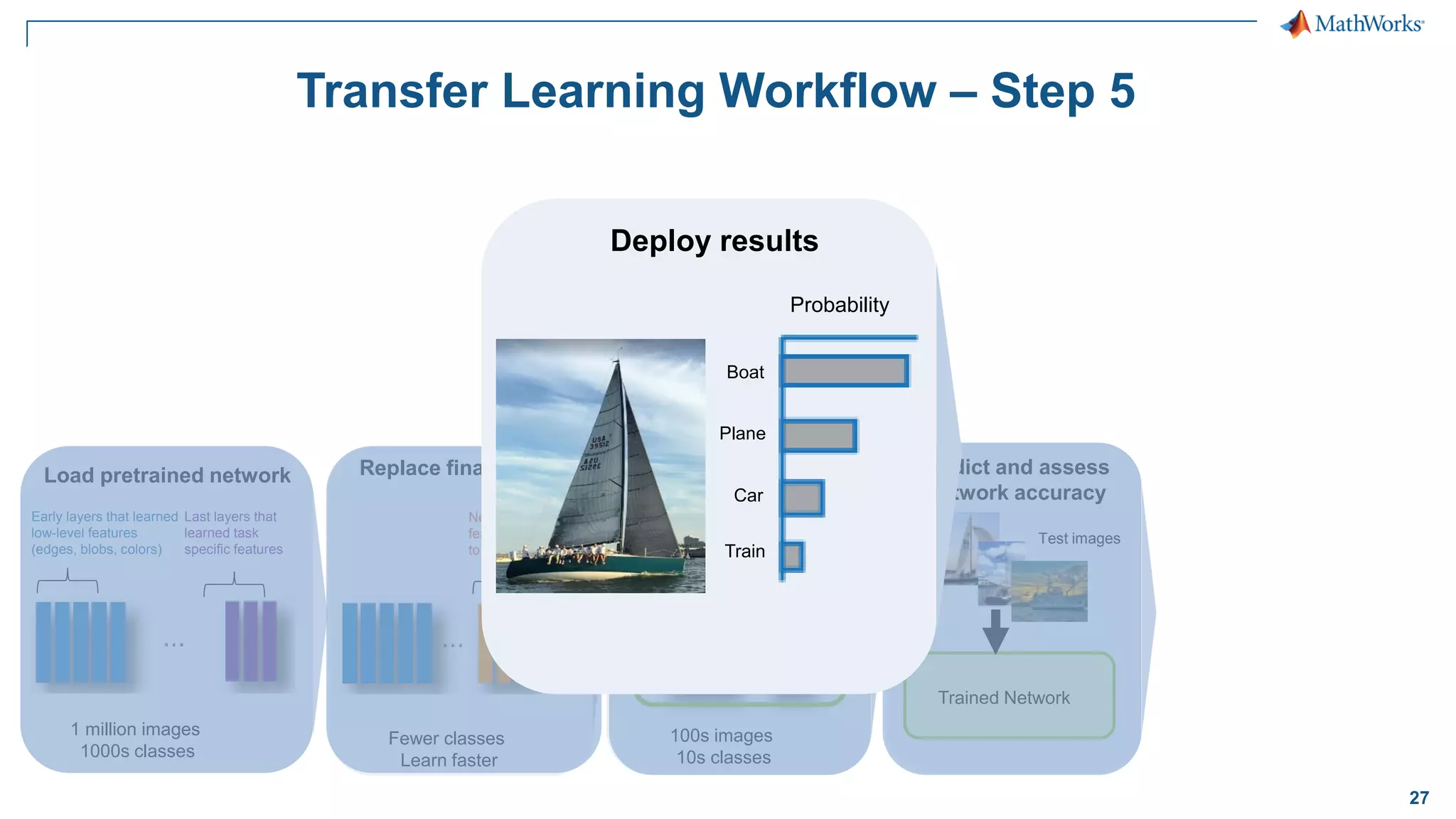
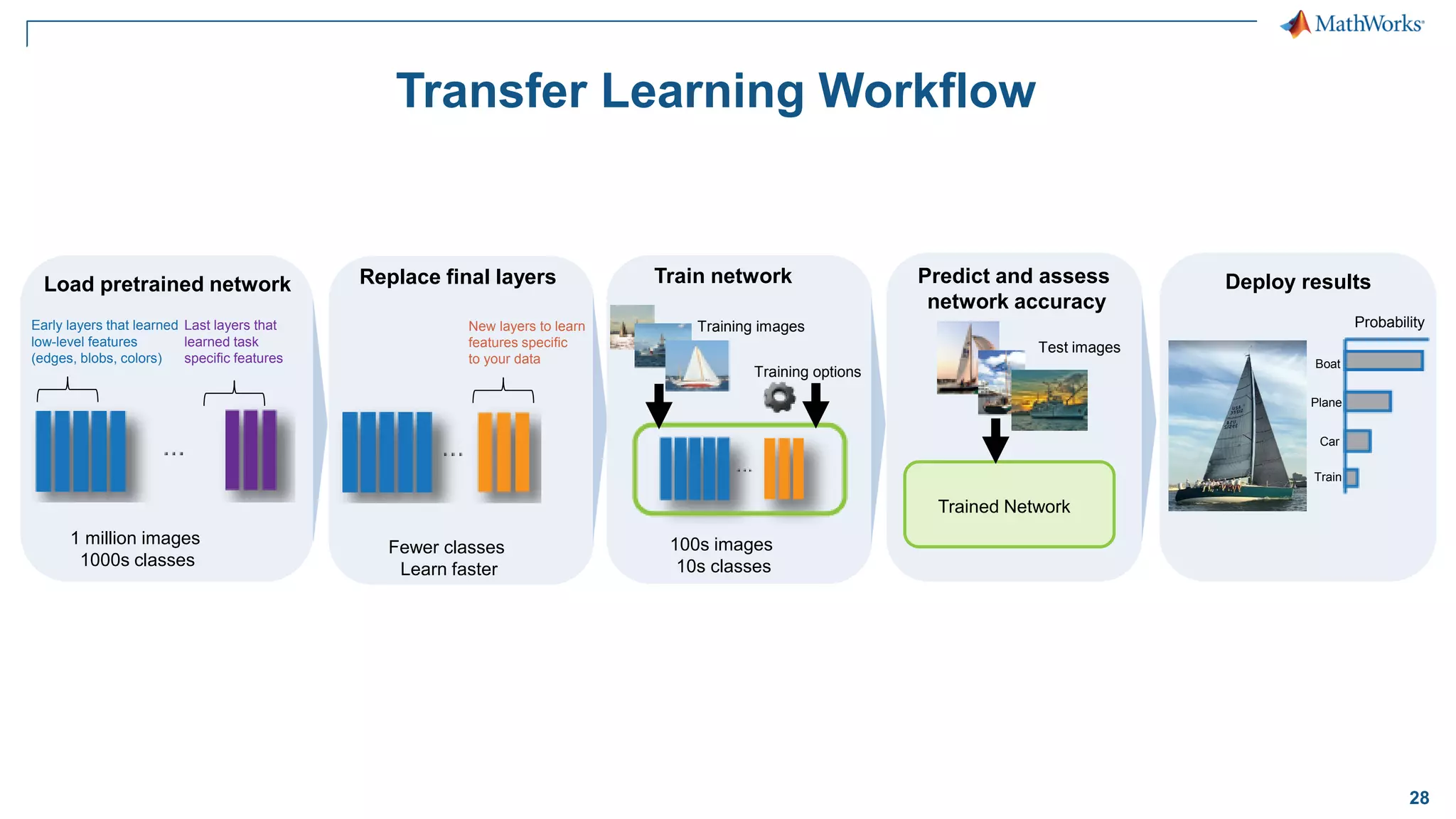
This document provides an overview of deep learning concepts and techniques for computer vision applications using MATLAB. It discusses traditional machine learning versus deep learning, popular pretrained deep learning models, building and training convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and using transfer learning to fine-tune pretrained models on new datasets with fewer samples. The key techniques covered are loading pretrained networks, replacing the final layers for a new task, training the modified network on a smaller labeled dataset, and evaluating the trained model on test data. The document aims to explain deep learning workflows and enable readers to implement techniques like transfer learning using MATLAB.