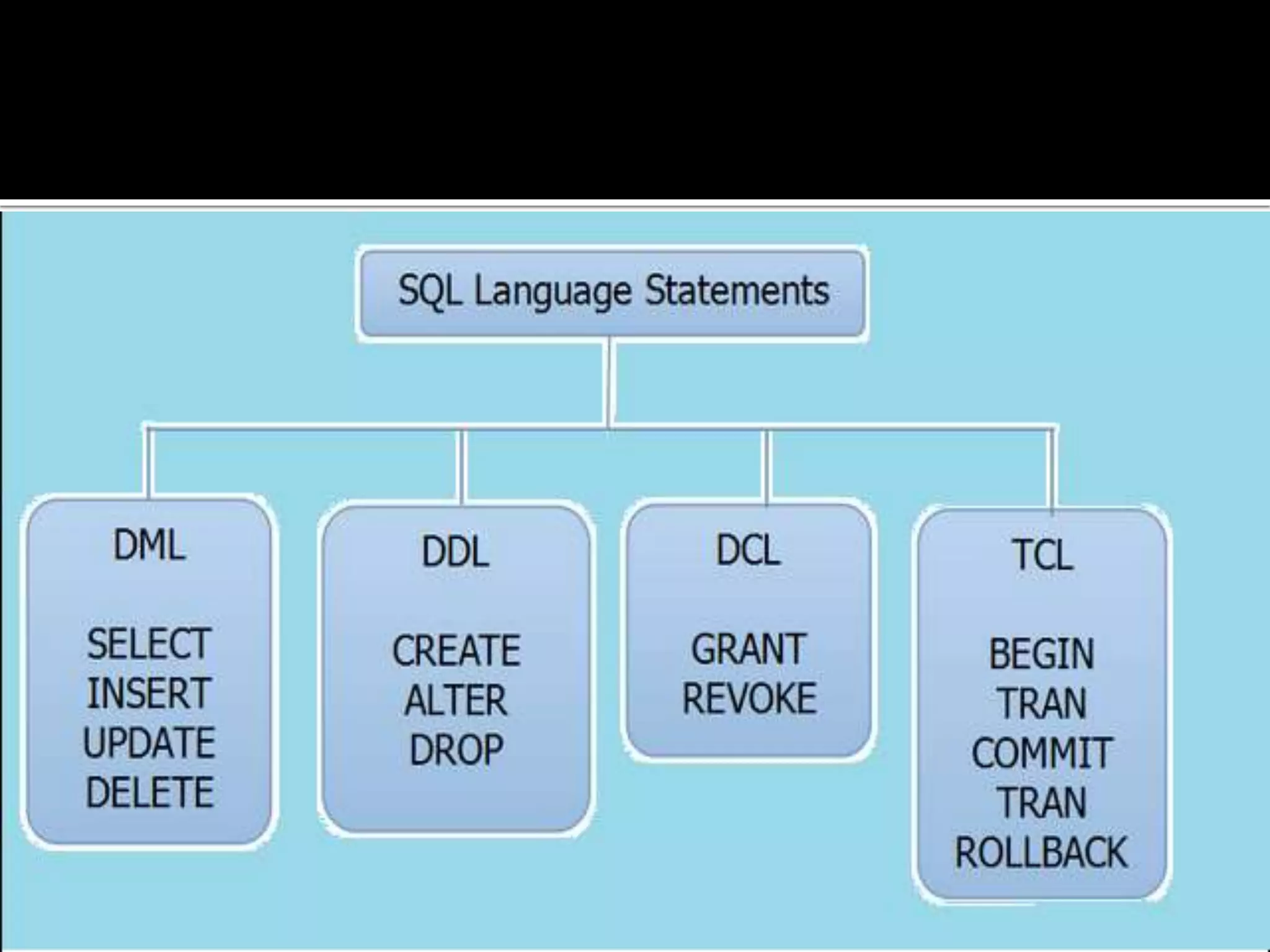
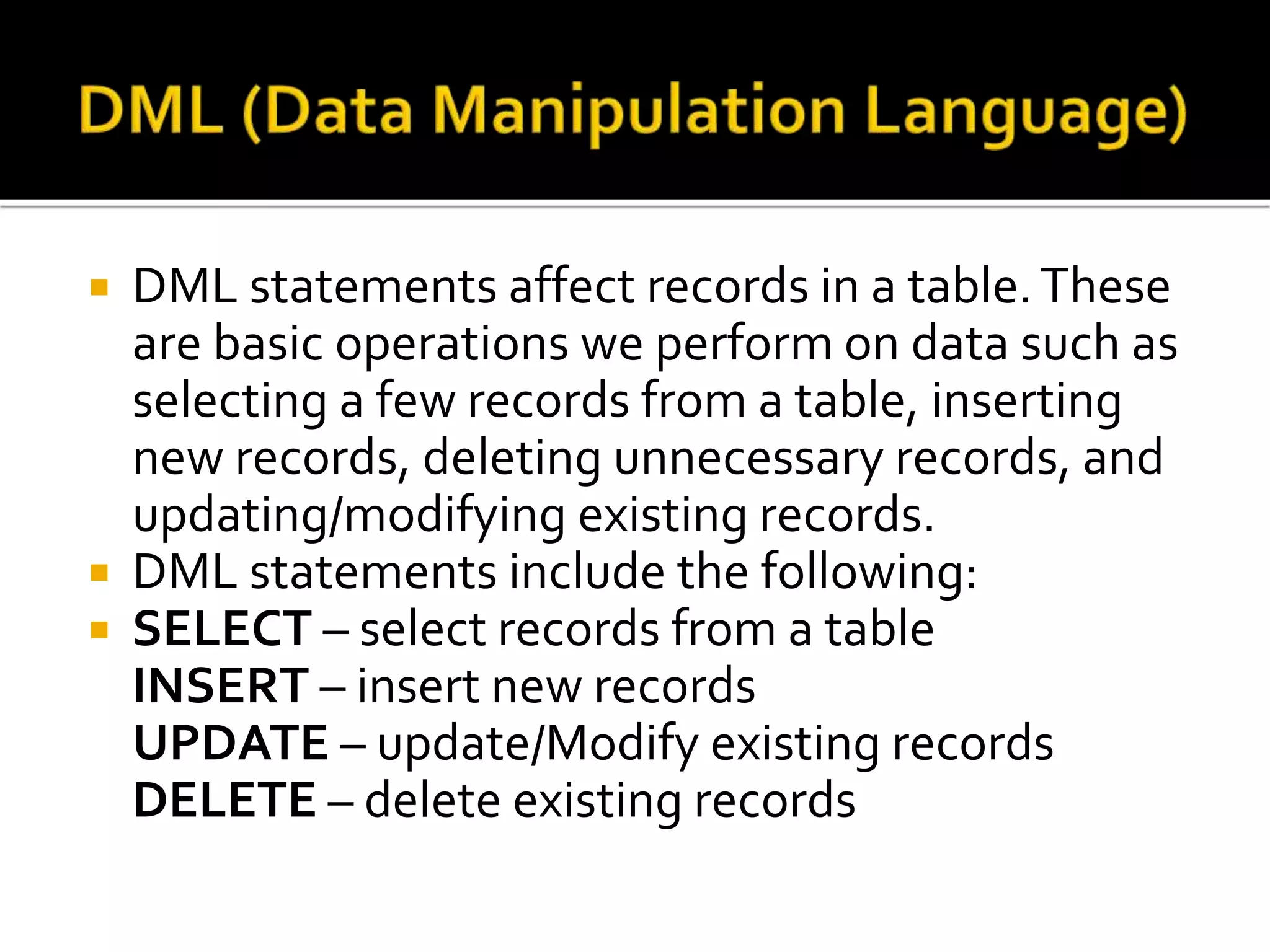
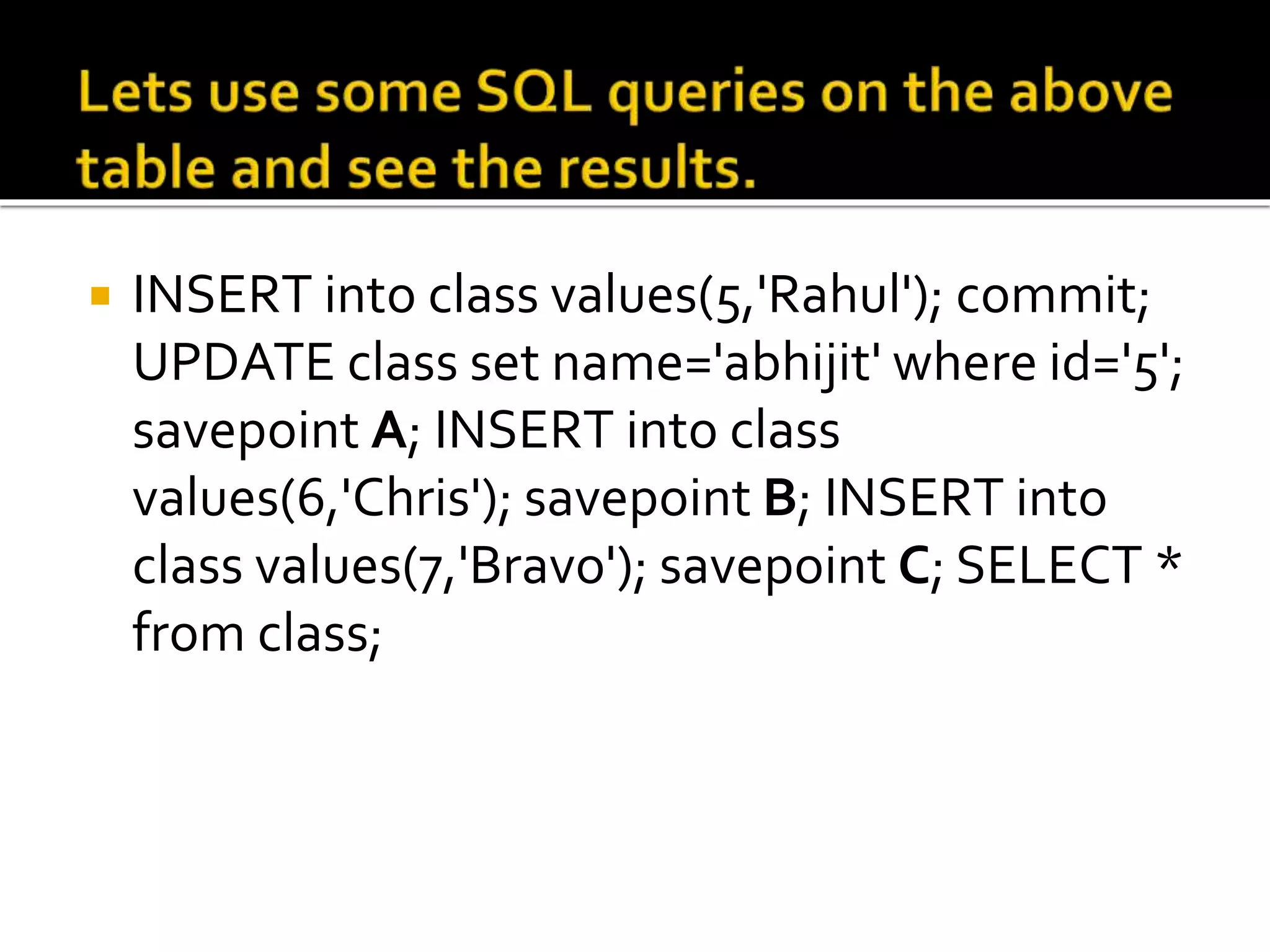
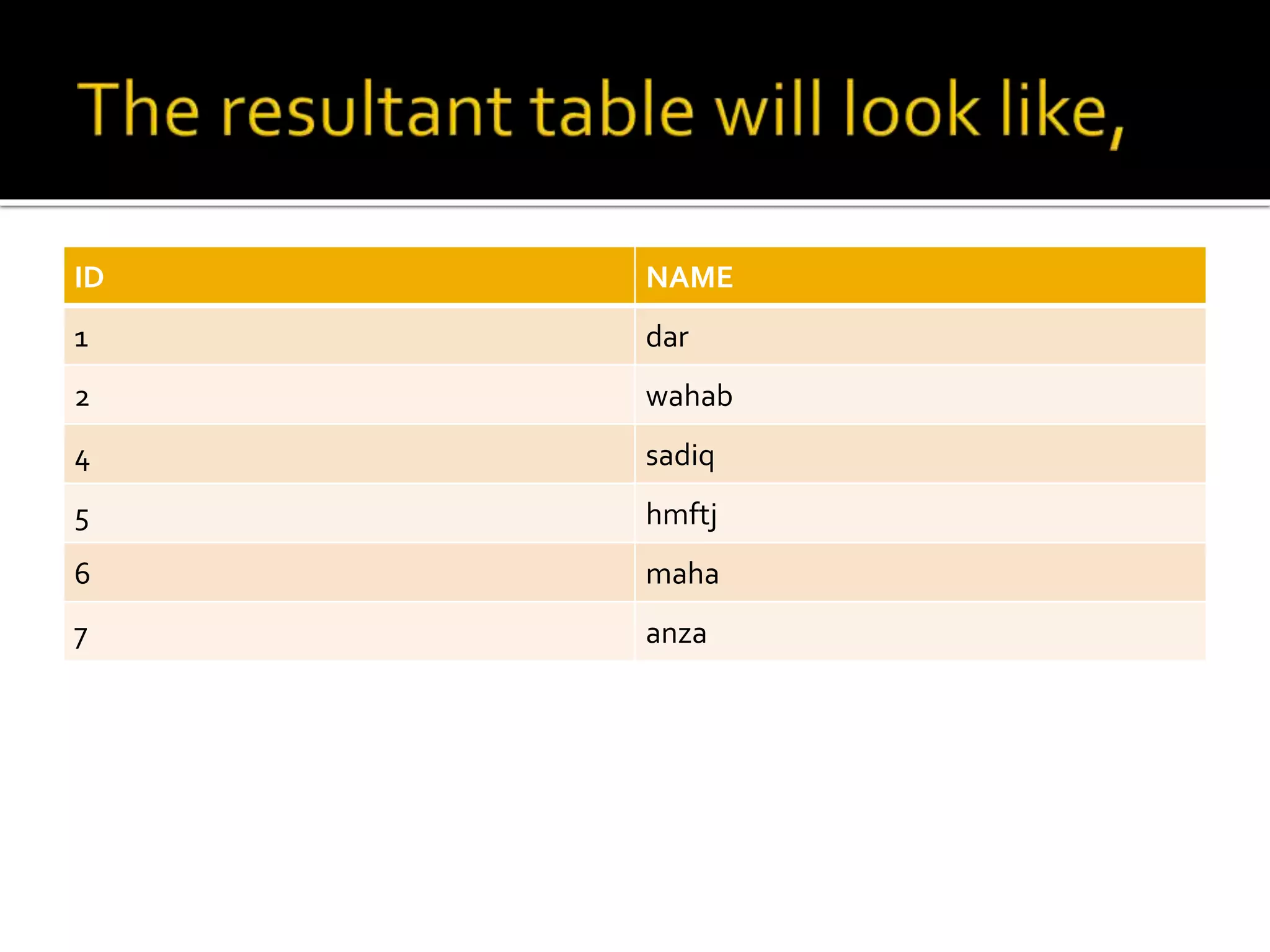
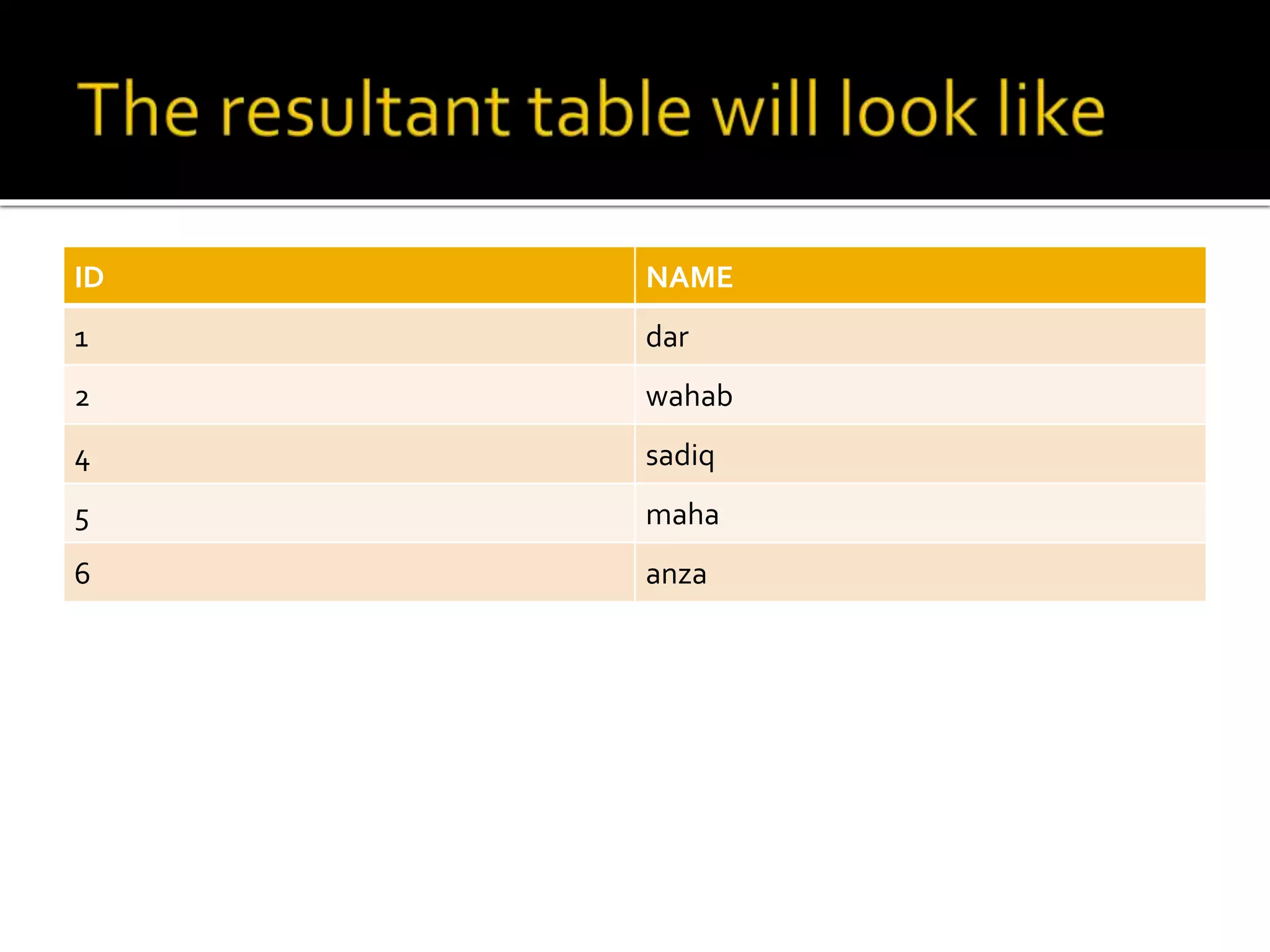
SQL language includes four primary statement types: DML, DDL, DCL, and TCL. DML statements manipulate data within tables using operations like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. DDL statements define and modify database schema using commands like CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. DCL statements control user access privileges with GRANT and REVOKE. TCL statements manage transactions with COMMIT, ROLLBACK, and SAVEPOINT to maintain data integrity.