Embed presentation
Download to read offline










This document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines what exceptions are, why they occur, and what exception handling is. It describes the advantages of exception handling and differences between exceptions and errors. It covers the exception class hierarchy and exception handling keywords like try, catch, finally, throw, and throws. It provides examples of common exception types and an example Java code demonstrating exception handling.
An overview of exception handling in Java presented by Ankit Rai.
An exception is an unwanted event disrupting program flow. Causes include user errors, hardware issues, and network problems.
Exception handling in Java prevents program termination by handling runtime errors using try-catch blocks.
Exception handling allows normal program execution and provides user-friendly error messages, enhancing user experience.
Differences between exceptions (recoverable issues by programming) and errors (non-recoverable issues caused by system resources).
Introduction to exception class hierarchy in Java, outlining the structure of exceptions.
Key Java keywords for exception handling: try, catch, and finally, each serving a unique purpose in managing exceptions.
Usage of 'throw' to explicitly raise exceptions and 'throws' for declaring checked exceptions in methods.
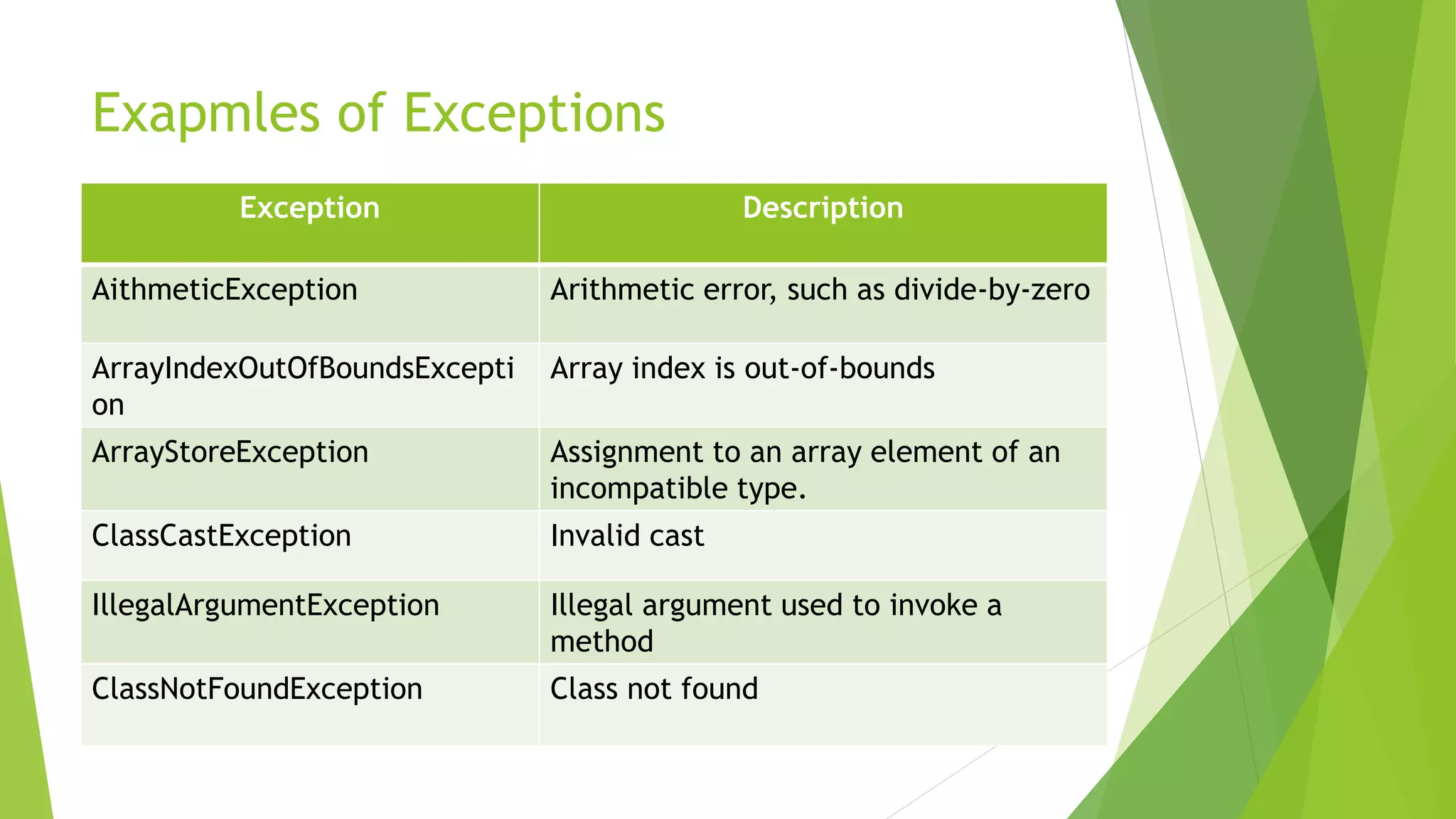
Examples of exceptions in Java, including ArithmeticException and ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, with descriptions.
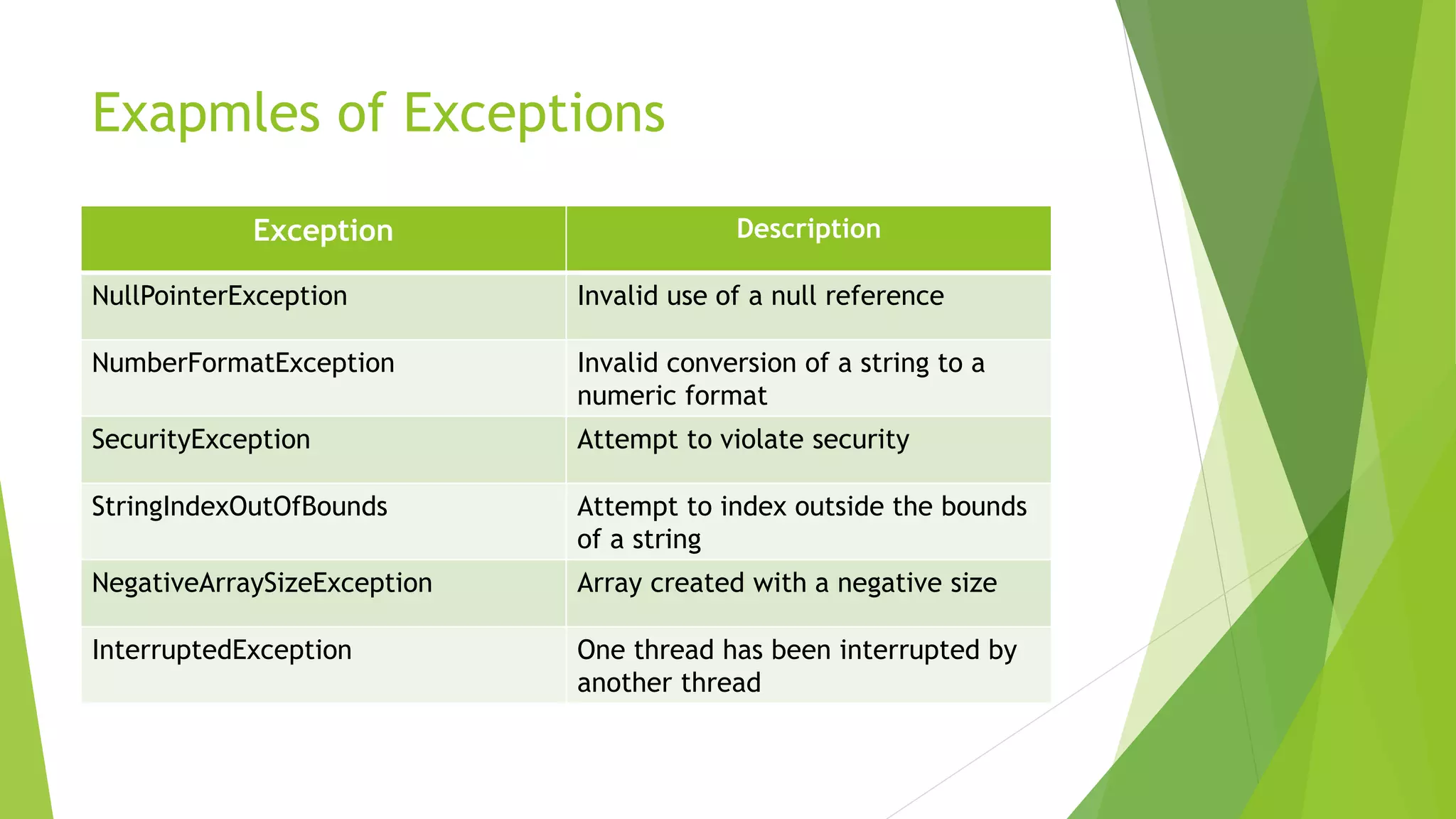
Further examples of Java exceptions such as NullPointerException and NegativeArraySizeException.
A sample Java code illustrating exception handling using try-catch to manage ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Continuation of the sample code, demonstrating successful completion of handling exceptions.











