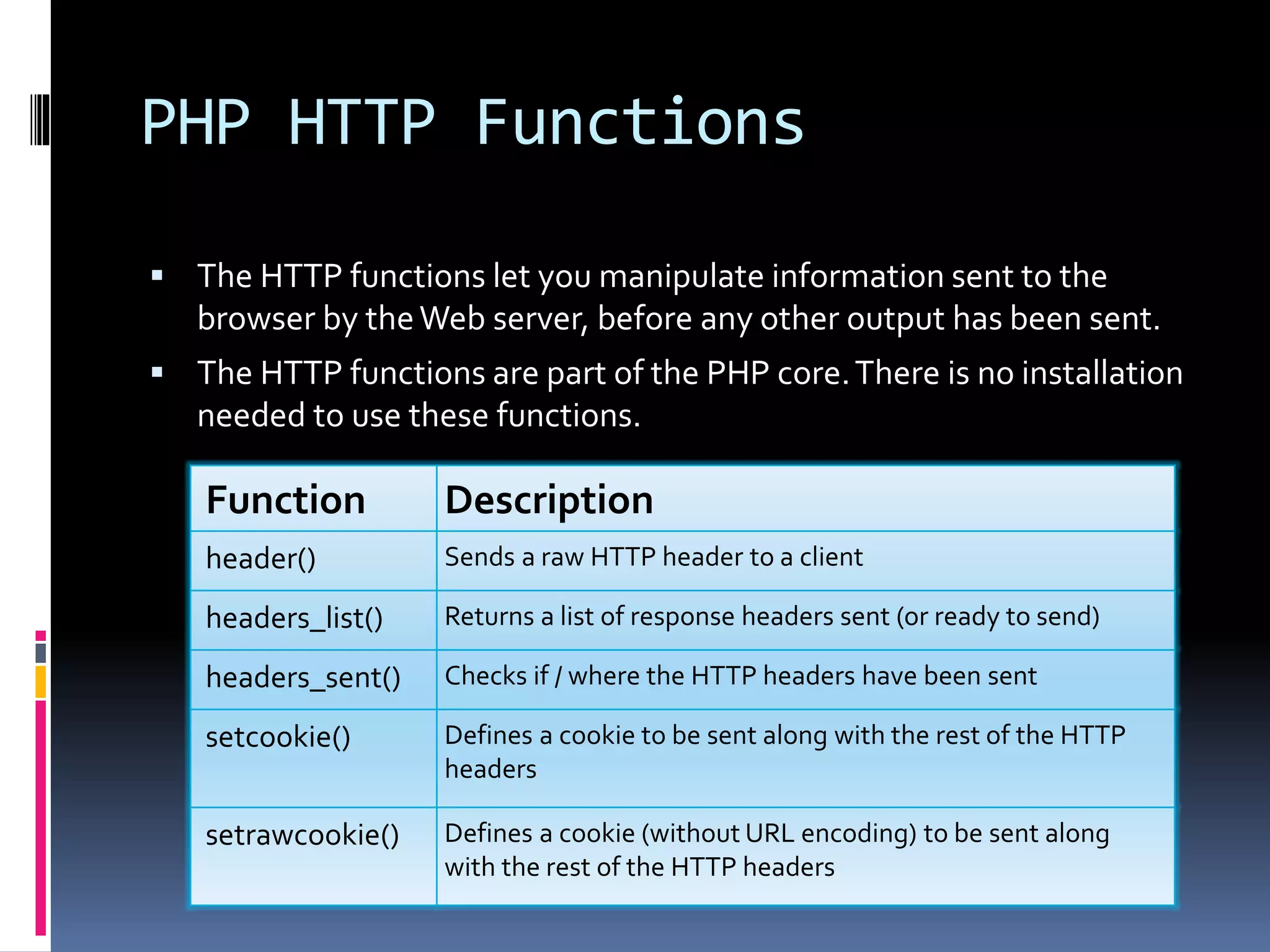
This document provides a comprehensive overview of using PHP and MySQL, detailing how to connect to and manipulate databases, create tables, insert and select data. It covers essential SQL commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, along with corresponding PHP code examples. Additionally, it explains cookies and sessions in PHP, outlining their creation and usage.





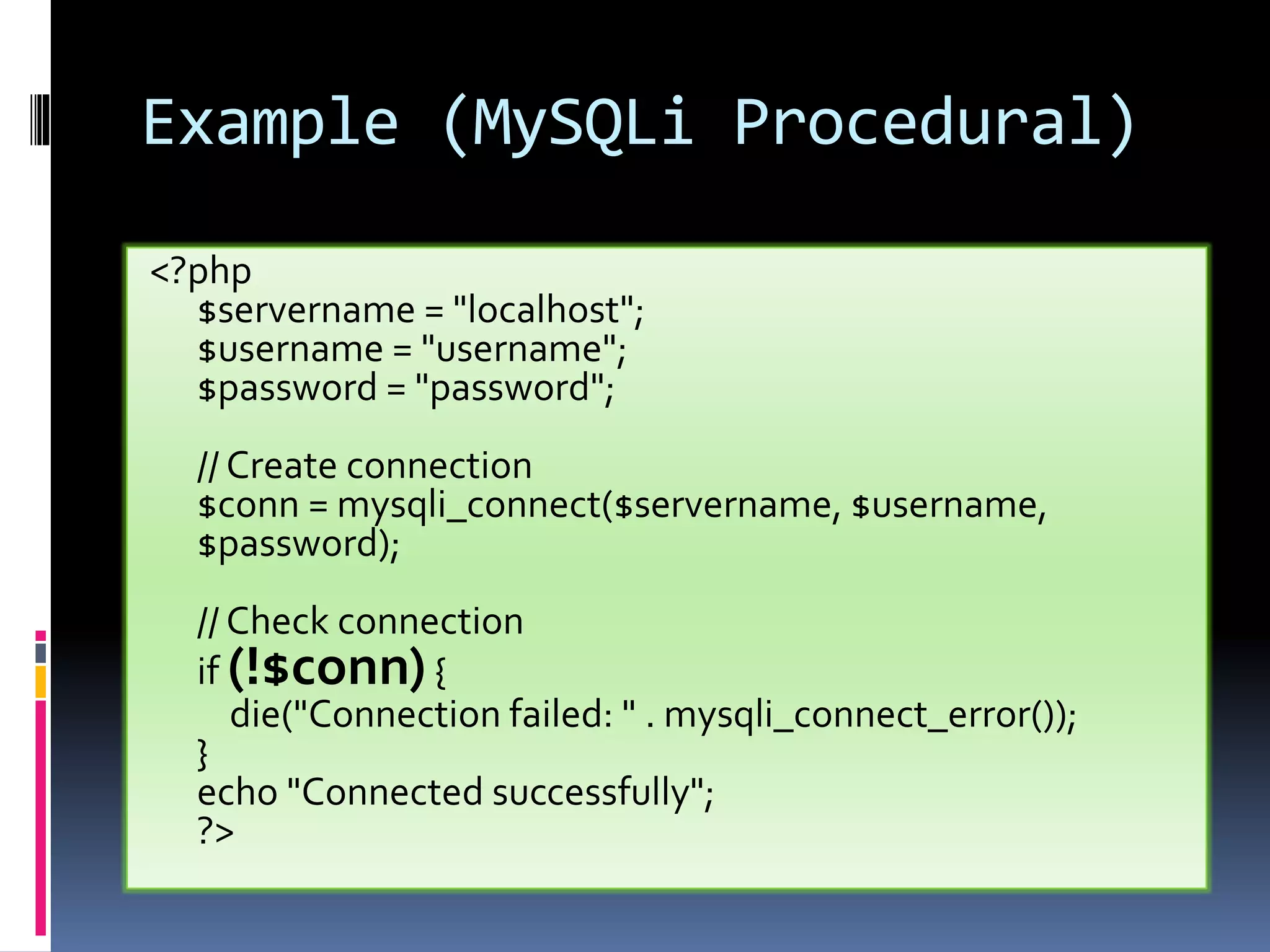



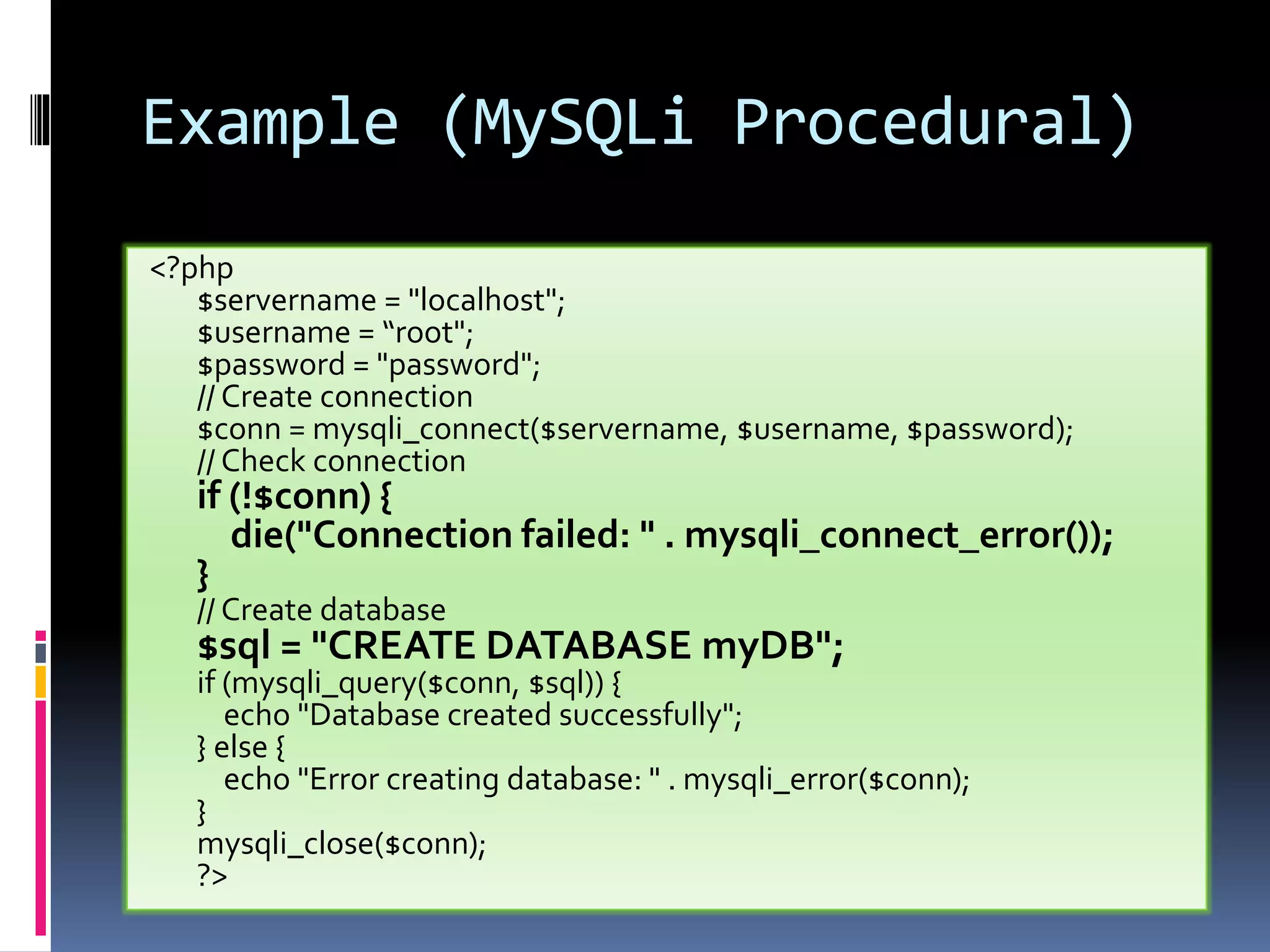



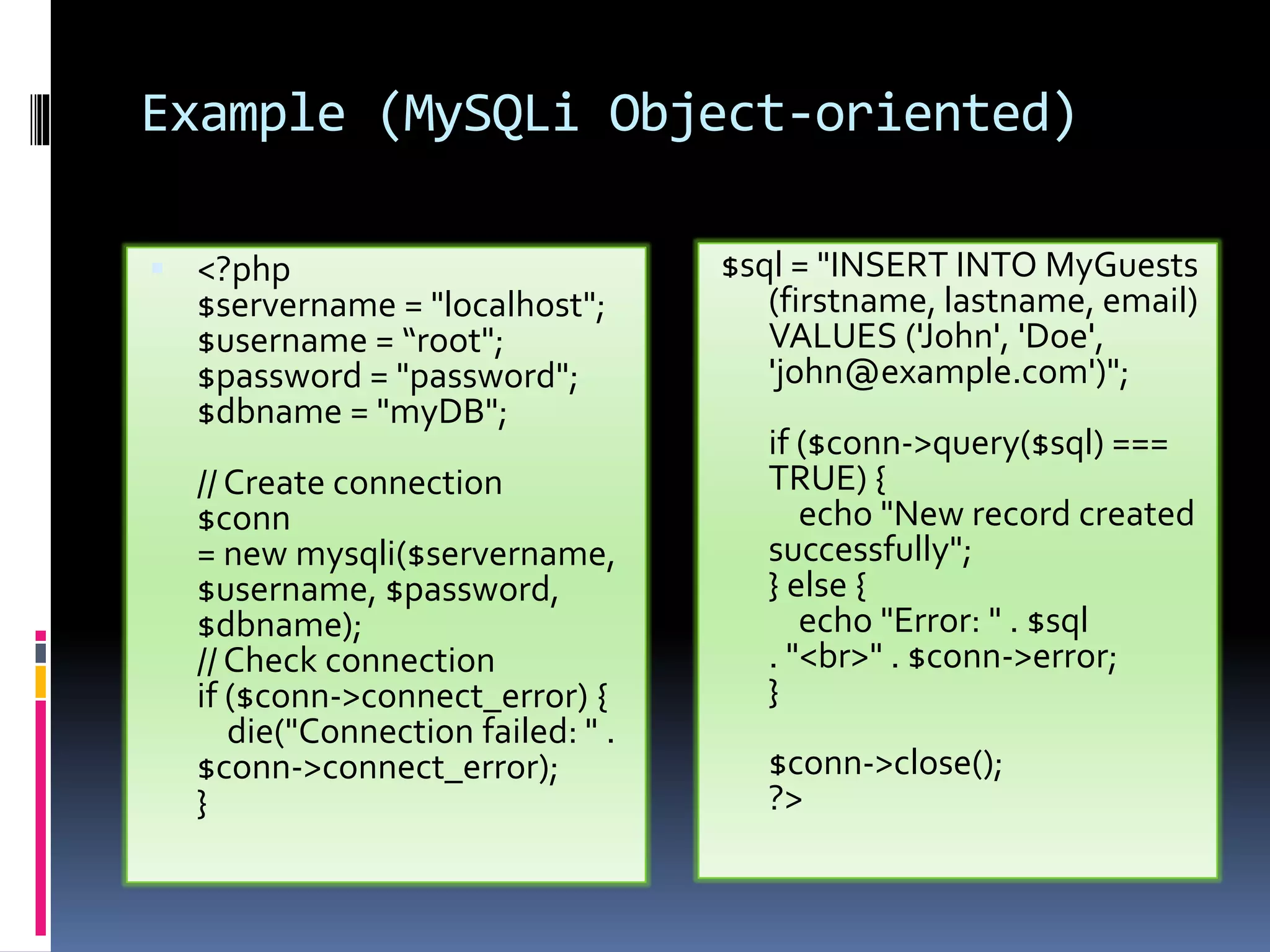


![Example (MySQLi Object- oriented) <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>PHP Demo</title> </head> <body> <?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "root"; $password = "password"; $dbname = "myDB"; // Create connection $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname); // Check connection if ($conn->connect_error) { die("Connection failed: " . $conn- >connect_error); } $sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests"; $result = $conn->query($sql); if ($result->num_rows > 0) { // output data of each row while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) { echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>"; } } else { echo "0 results"; } $conn->close(); ?> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitv-phpmysqldatabase-200424134752/75/FYBSC-IT-Web-Programming-Unit-V-Advanced-PHP-and-MySQL-19-2048.jpg)




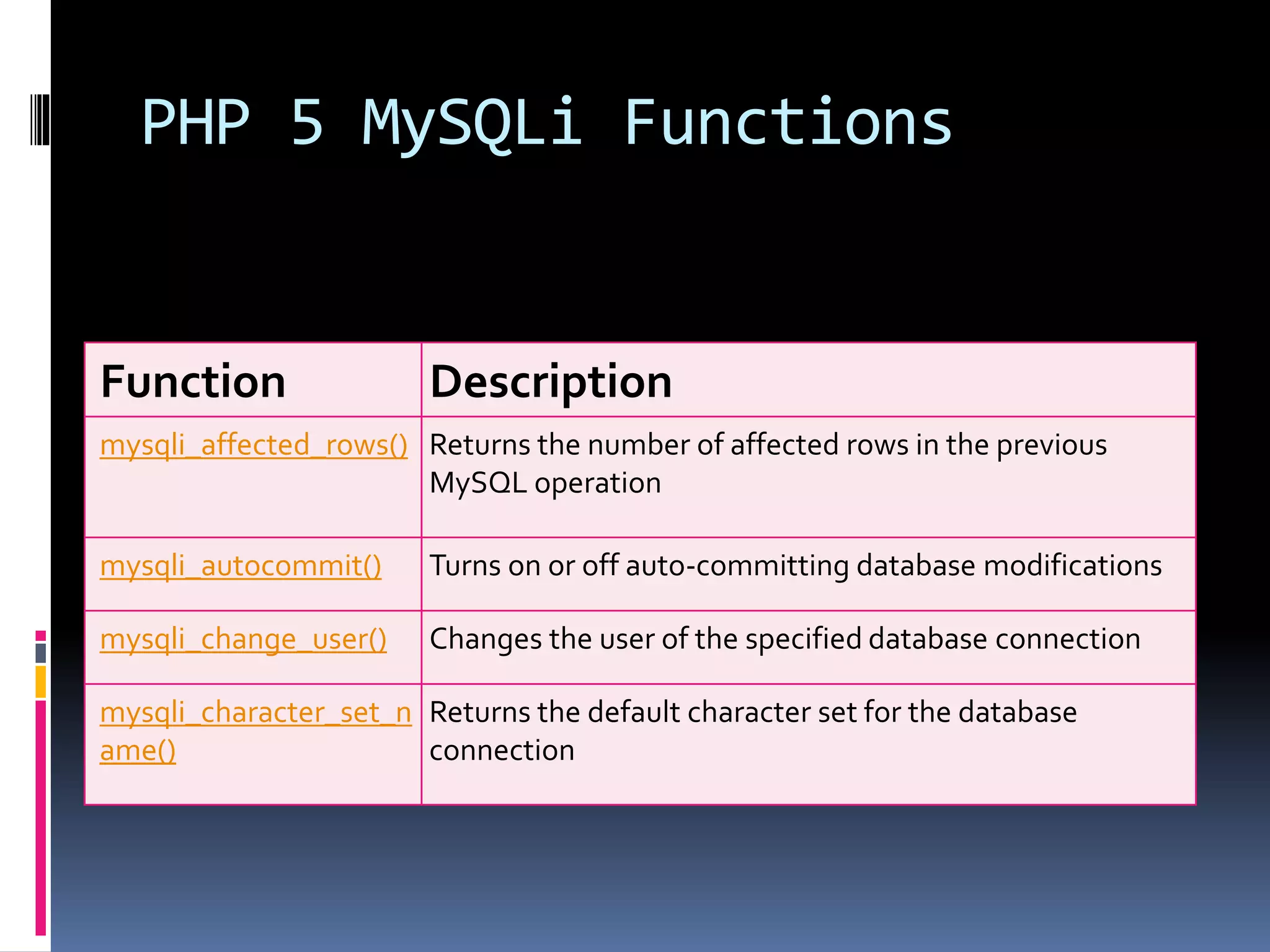
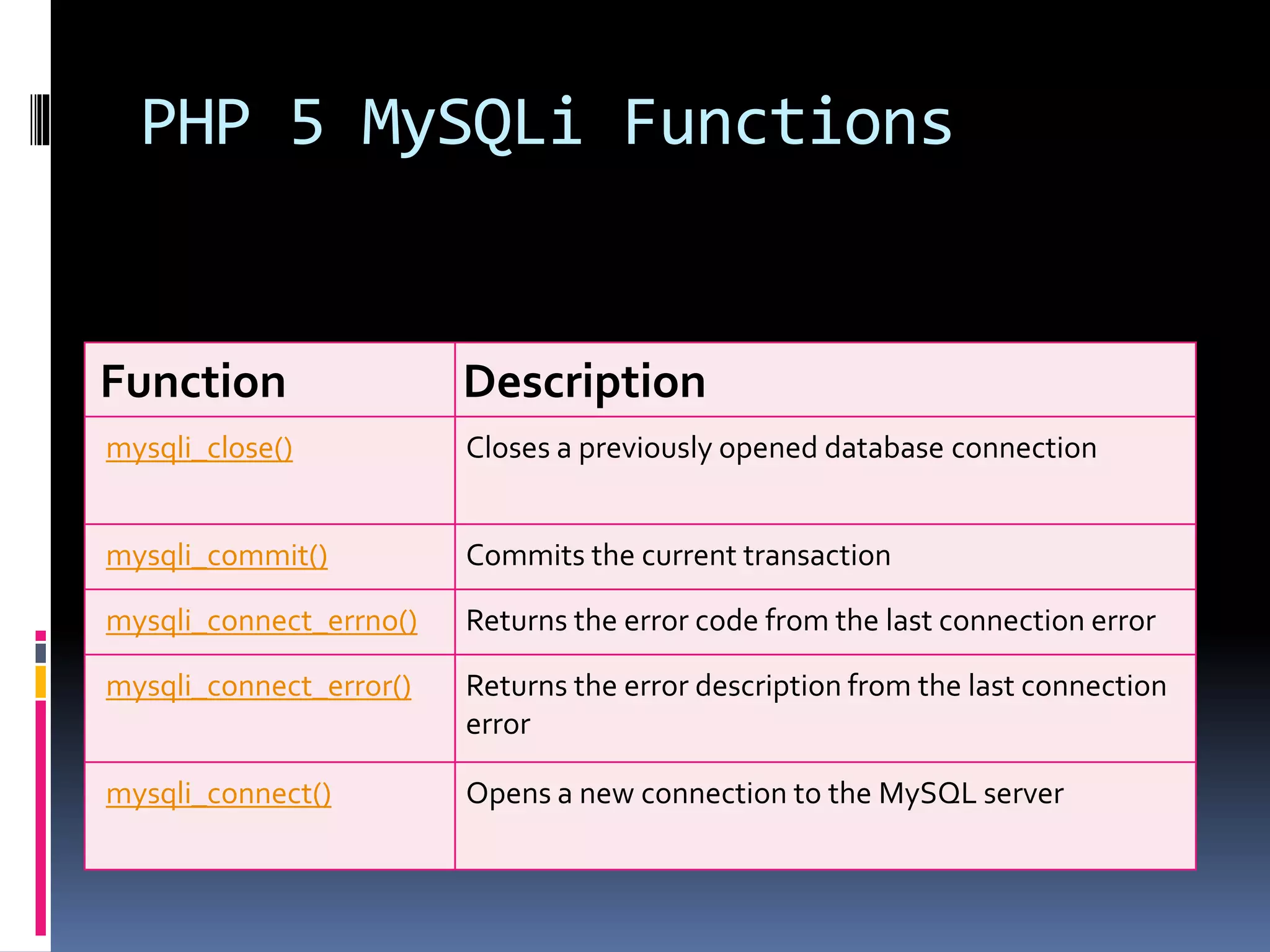
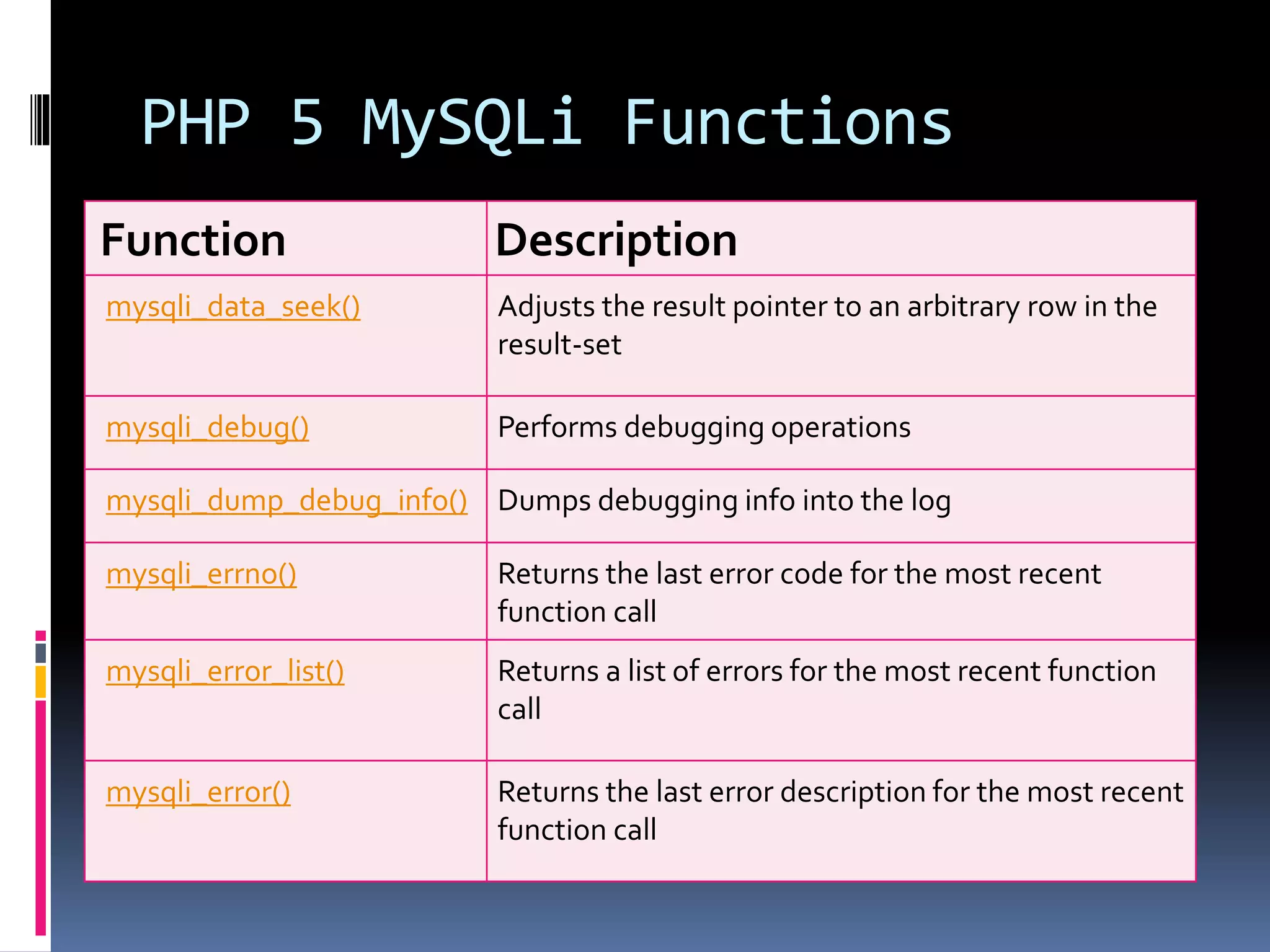
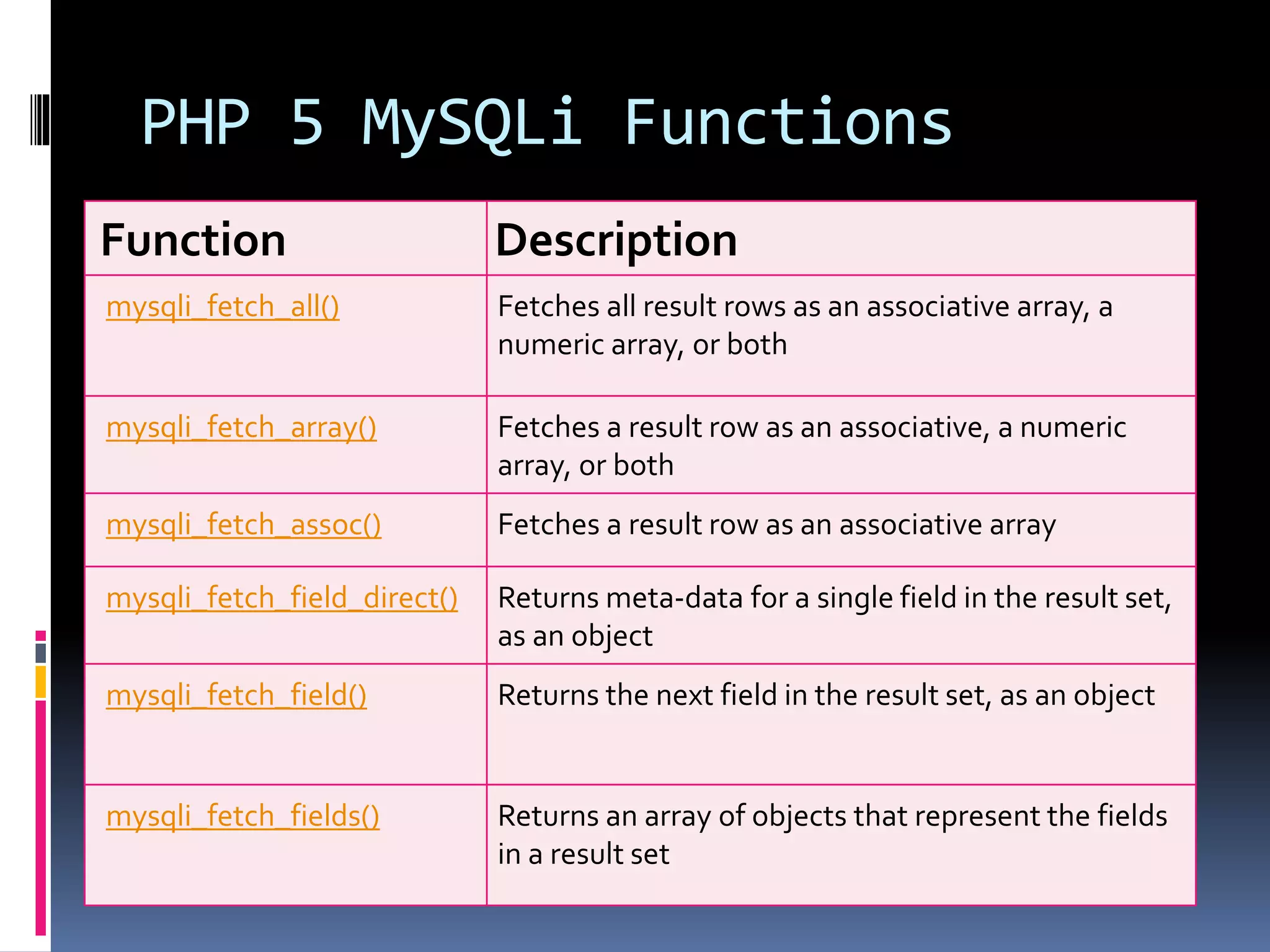
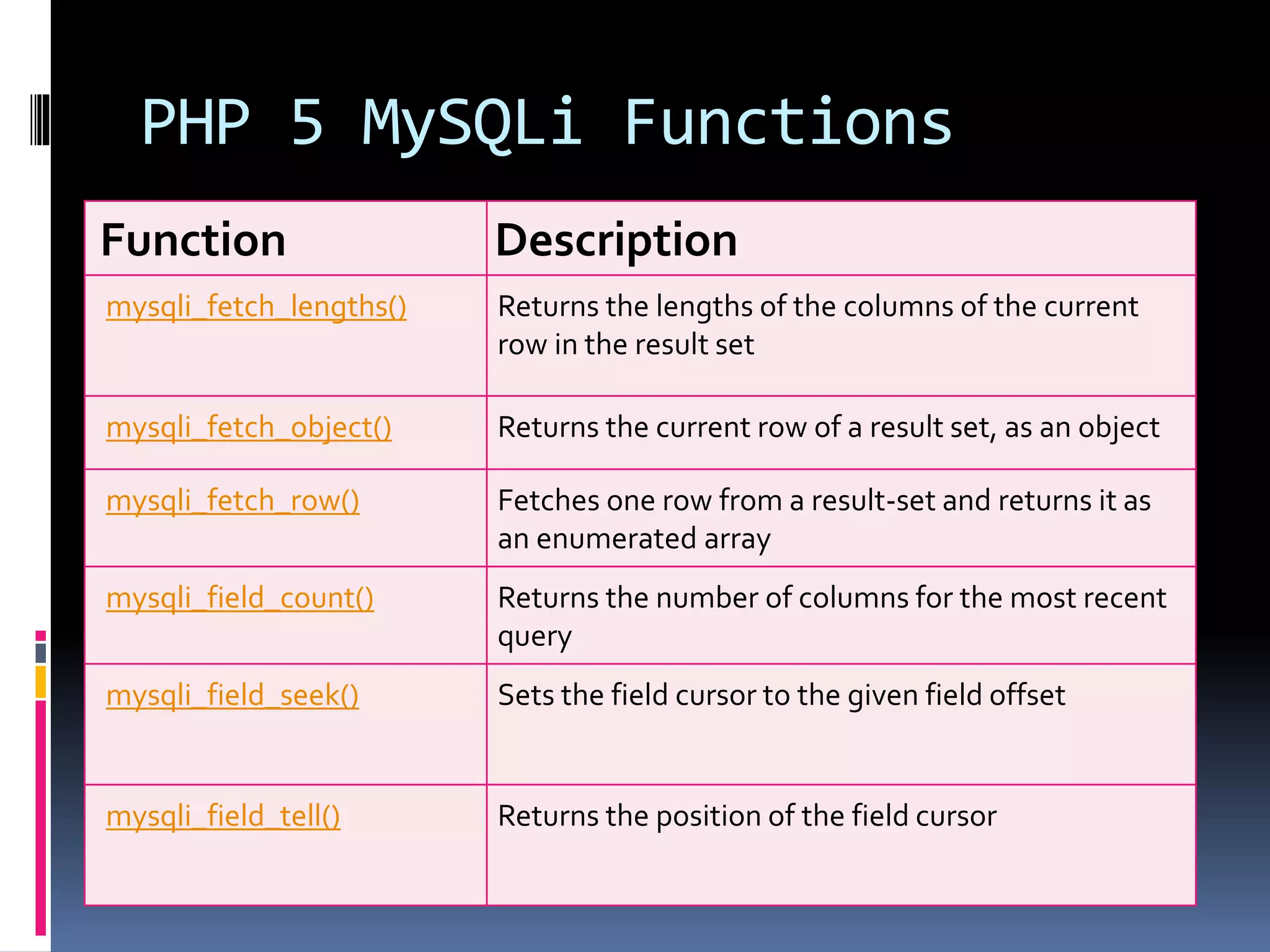
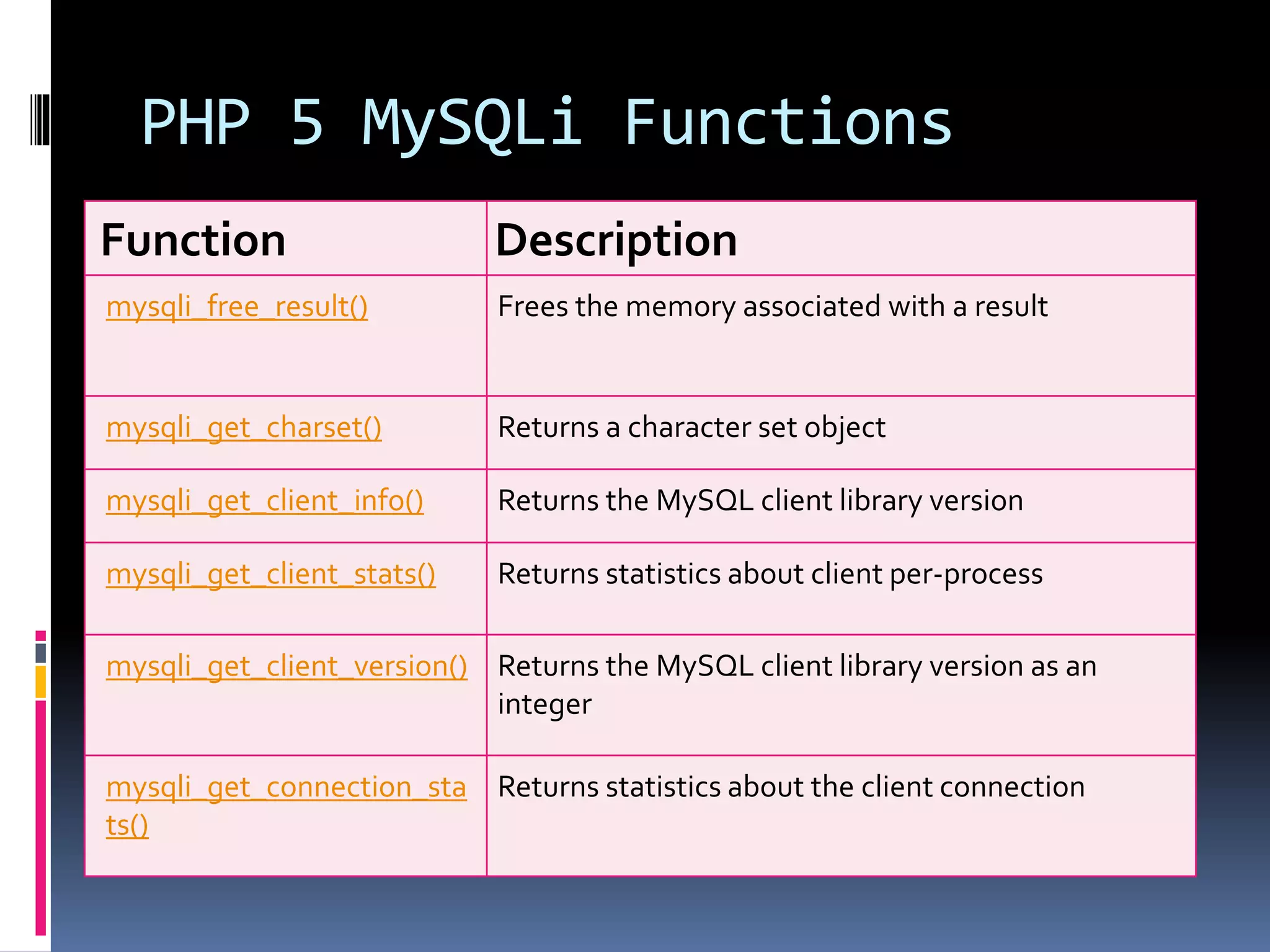
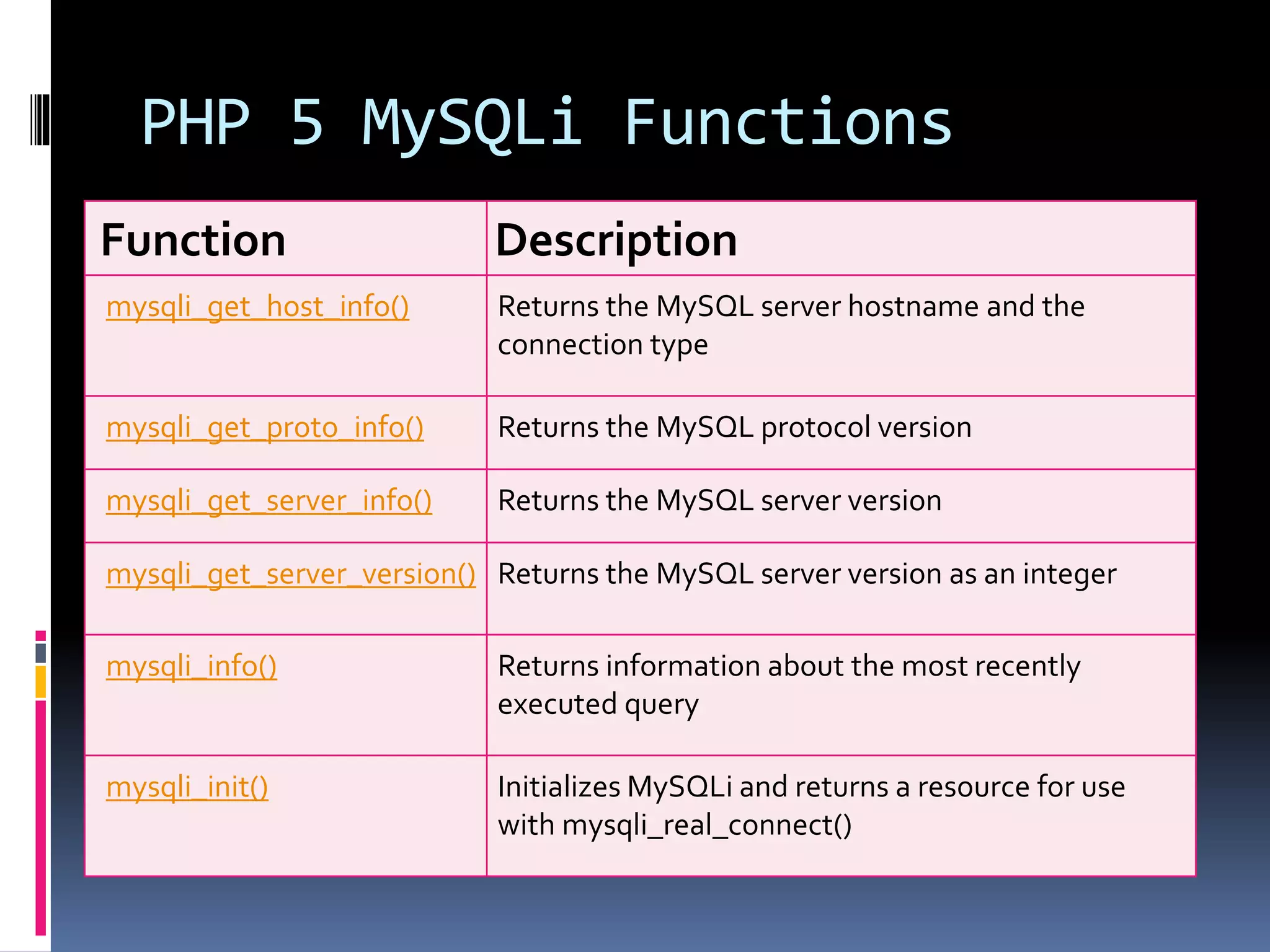
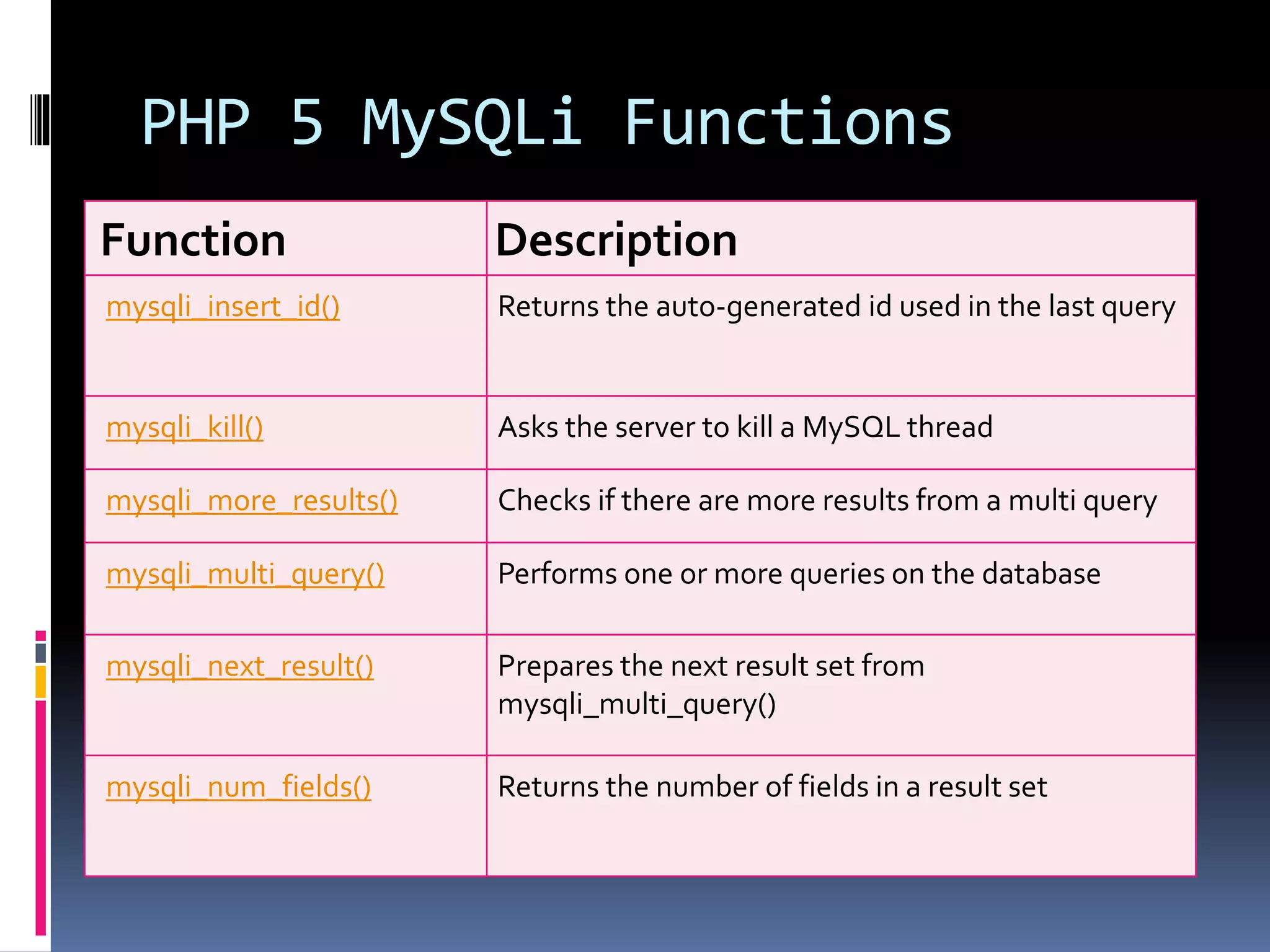

![Create Cookies With PHP <!DOCTYPE html> <?php $cookie_name = "user"; $cookie_value = "John Doe"; setcookie($cookie_name, $cookie_value, time() + (86400 * 30), "/"); // 86400 = 1 day ?> <html> <body> <?php if(!isset($_COOKIE[$cookie_name])) { echo "Cookie named '" . $cookie_name . "' is not set!"; } else { echo "Cookie '" . $cookie_name . "' is set!<br>"; echo "Value is: " . $_COOKIE[$cookie_name];} ?> <p><strong>Note:</strong>You might have to reload the page to see the value of the cookie.</p> </body></html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitv-phpmysqldatabase-200424134752/75/FYBSC-IT-Web-Programming-Unit-V-Advanced-PHP-and-MySQL-39-2048.jpg)

![Start a PHP Session <?php // Start the session session_start(); ?> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <?php // Set session variables $_SESSION["favcolor"] = "green"; $_SESSION["favanimal"] = "cat"; echo "Session variables are set."; ?> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitv-phpmysqldatabase-200424134752/75/FYBSC-IT-Web-Programming-Unit-V-Advanced-PHP-and-MySQL-41-2048.jpg)