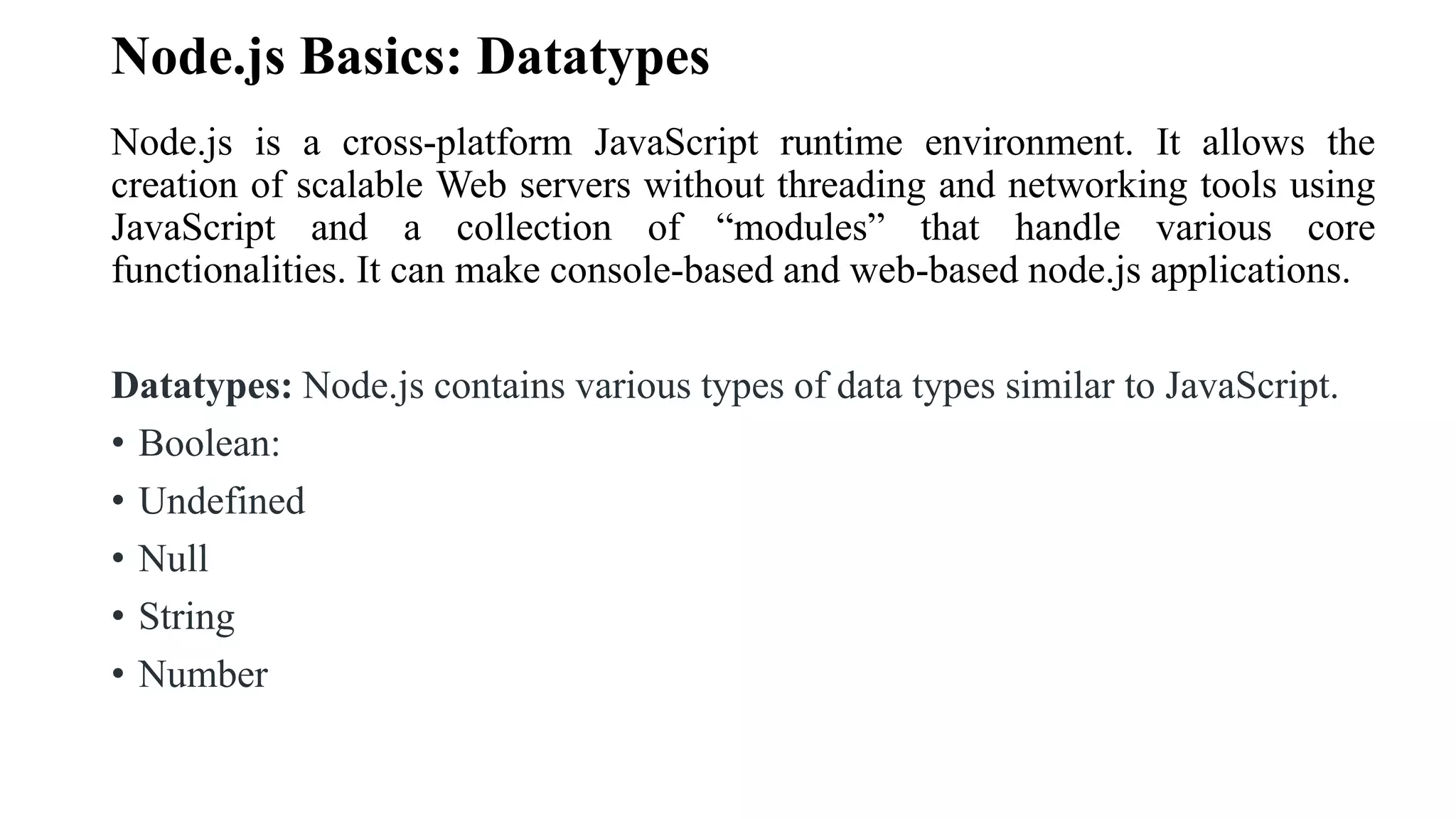
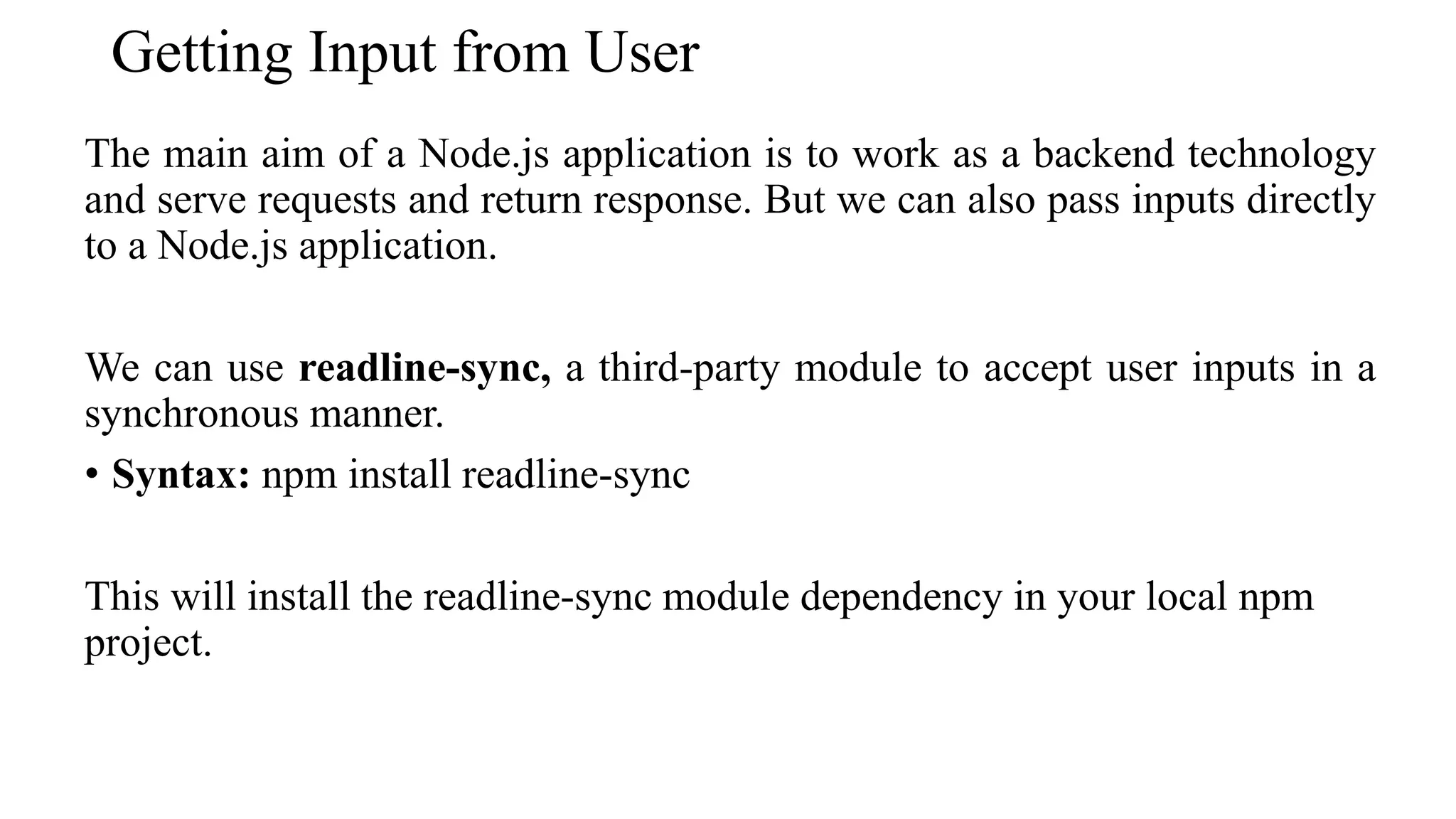
The document provides an overview of Node.js, covering its capabilities as a JavaScript runtime environment for building scalable web servers, data types, and functions similar to JavaScript. It highlights the use of loose typing, buffer for binary data, and the ability to read command-line arguments and user inputs using modules like readline-sync. Additionally, it includes examples of handling data types, creating objects, string manipulation, and executing programs based on user input.








![var x = "Welcome to Lovely Professional University"; var y = 'Node.js Tutorials'; var z = ['Lovely', 'Professional', 'University']; console.log(x); console.log(y); console.log("Concat Using (+) :", (x + y)); console.log("Concat Using Function :", (x.concat(y))); console.log("Split string: ", x.split(' ')); console.log("Join string: ", z.join(' ')); console.log("Char At Index 5: ", x.charAt(10));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-10-2048.jpg)


![Exp 1: Step 1: Save a file as index.js and paste the below code inside the file. var arguments = process.argv ; console.log(arguments); arguments: 0 1 2 3 4 5 ----- Arguments[0] = Path1, Arguments[1] = Path2 Step 2: Run index.js file using below command: node index.js The process.argv contains an array where the 0th index contains the node executable path, 1st index contains the path to your current file and then the rest index contains the passed arguments. Path1 Path2 “20” “10” “5”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-13-2048.jpg)
![Exp 2: Program to add two numbers passed as arguments Step 1: Save the file as index1.js and paste the below code inside the file. var arguments = process.argv function add(a, b) { // To extract number from string return parseInt(a)+parseInt(b) } var sum = add(arguments[2], arguments[3]) console.log("Addition of a and b is equal to ", sum)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-14-2048.jpg)
![var arg = process.argv var i console.log("Even numbers are:") for (i=1;i<process.argv.length;i++) { if (arg[i]%2 == 0) { console.log(arg[i]) } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-15-2048.jpg)
![Counting Table var arguments = process.argv let i; var mul=arguments[2] for (let i=1; i<=10; i++) { console.log(mul + " * " + i + " = " + mul*i); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-16-2048.jpg)


![How do you iterate over the given array in node.js? Node.js provides forEach()function that is used to iterate over items in a given array. const arr = ['fish', 'crab', 'dolphin', 'whale', 'starfish']; arr.forEach(element => { console.log(element); }); Const is the variables declared with the keyword const that stores constant values. const declarations are block-scoped i.e. we can access const only within the block where it was declared. const cannot be updated or re-declared i.e. const will be the same within its block and cannot be re- declare or update.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-19-2048.jpg)
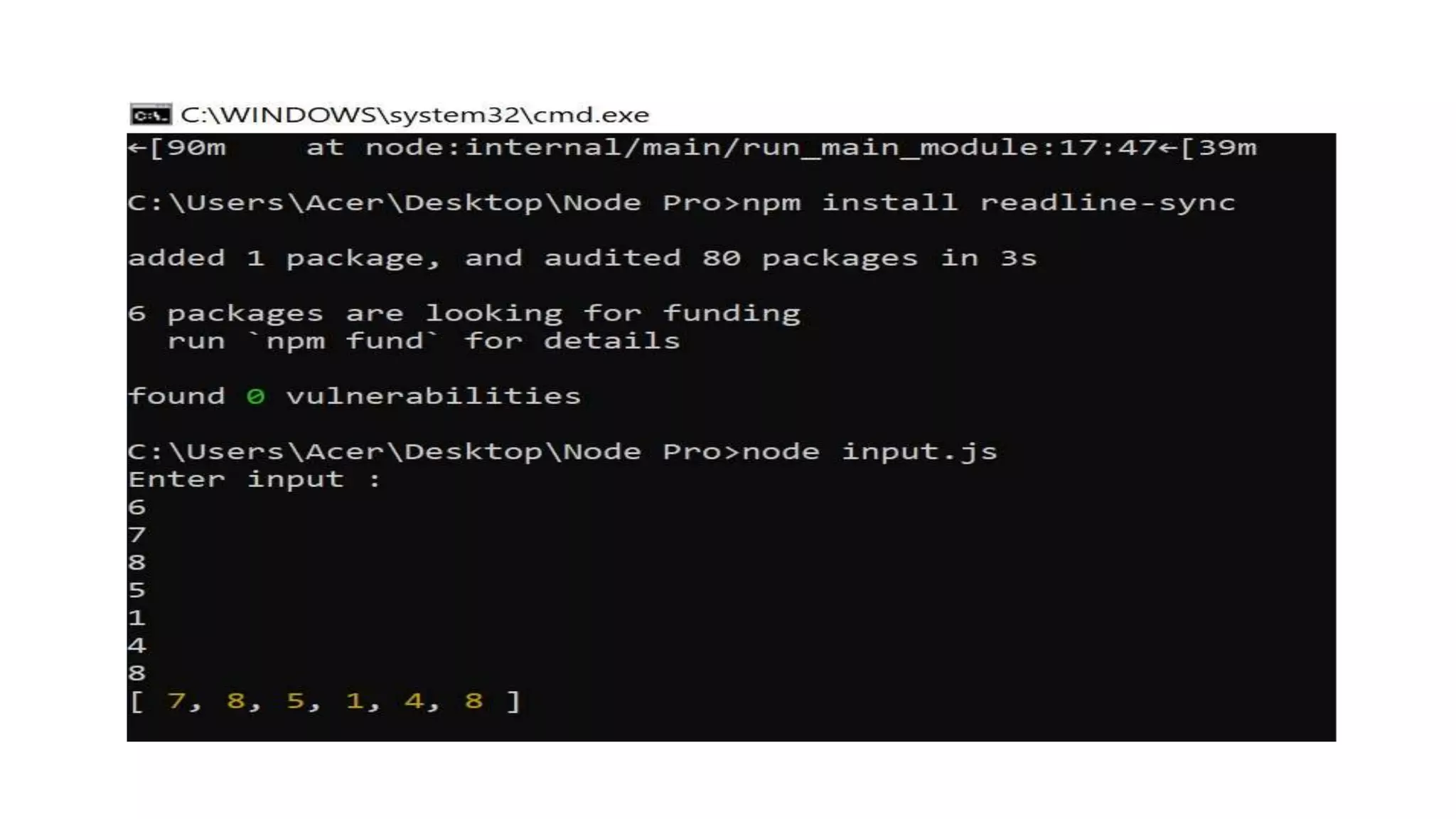
![Example 1: Create a file with the name "input.js". After creating the file, use the command "node input.js" to run this code. const readline = require("readline-sync"); console.log("Enter input : ") // Taking a number input let num = Number(readline.question()); let number = []; for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) { number.push(Number(readline.question())); } console.log(number);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-21-2048.jpg)

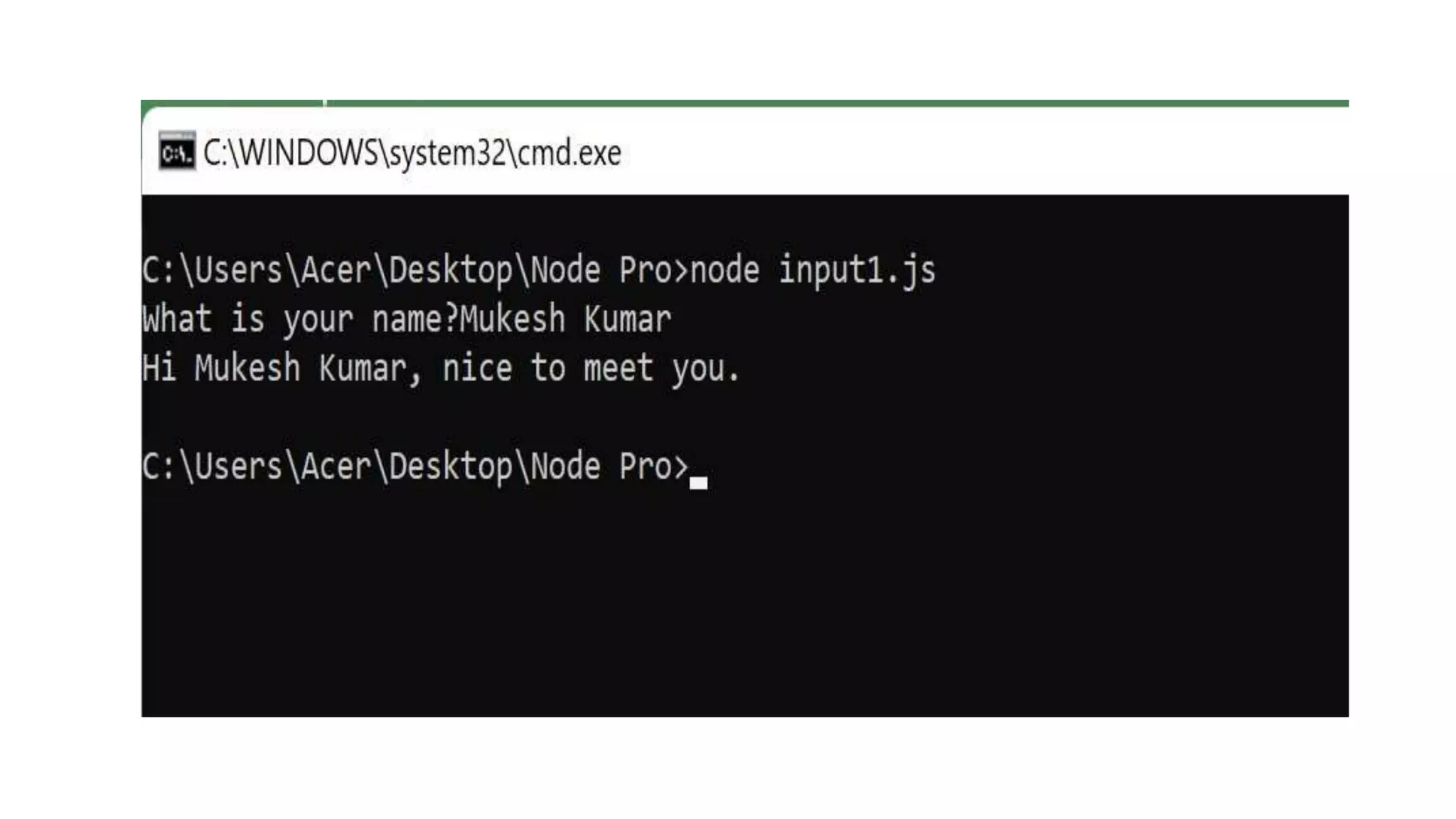

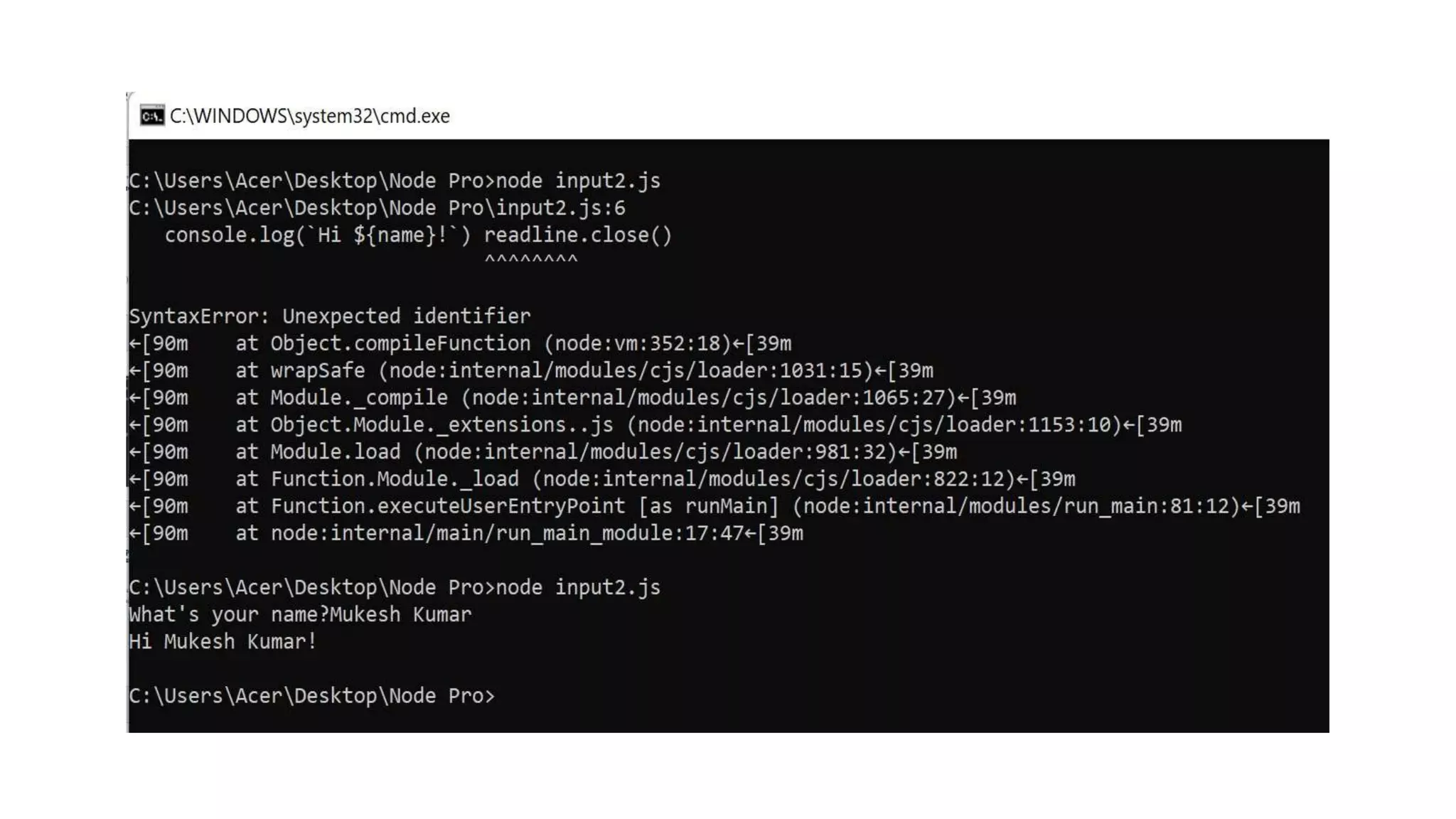
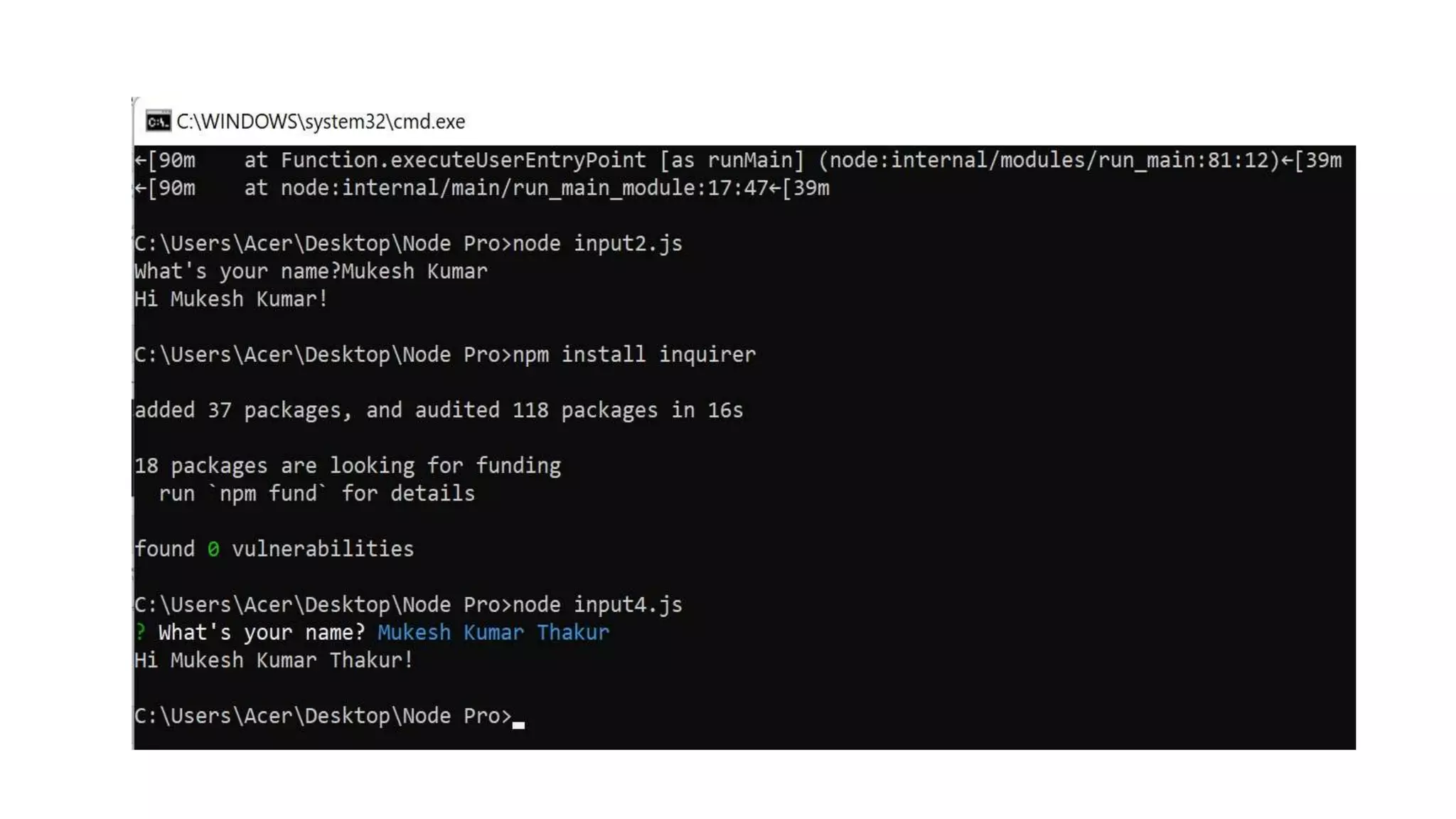
![You can install it using npm install inquirer, and then you can replicate the above code like this: input.js const inquirer = require('inquirer') var questions = [{ type: 'input', name: 'name', message: "What's your name?" }] inquirer.prompt(questions).then(answers => { console.log(`Hi ${answers['name']}!`) })](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettinginputfromuser-230507165608-b119ab01/75/Getting-Input-from-User-27-2048.jpg)