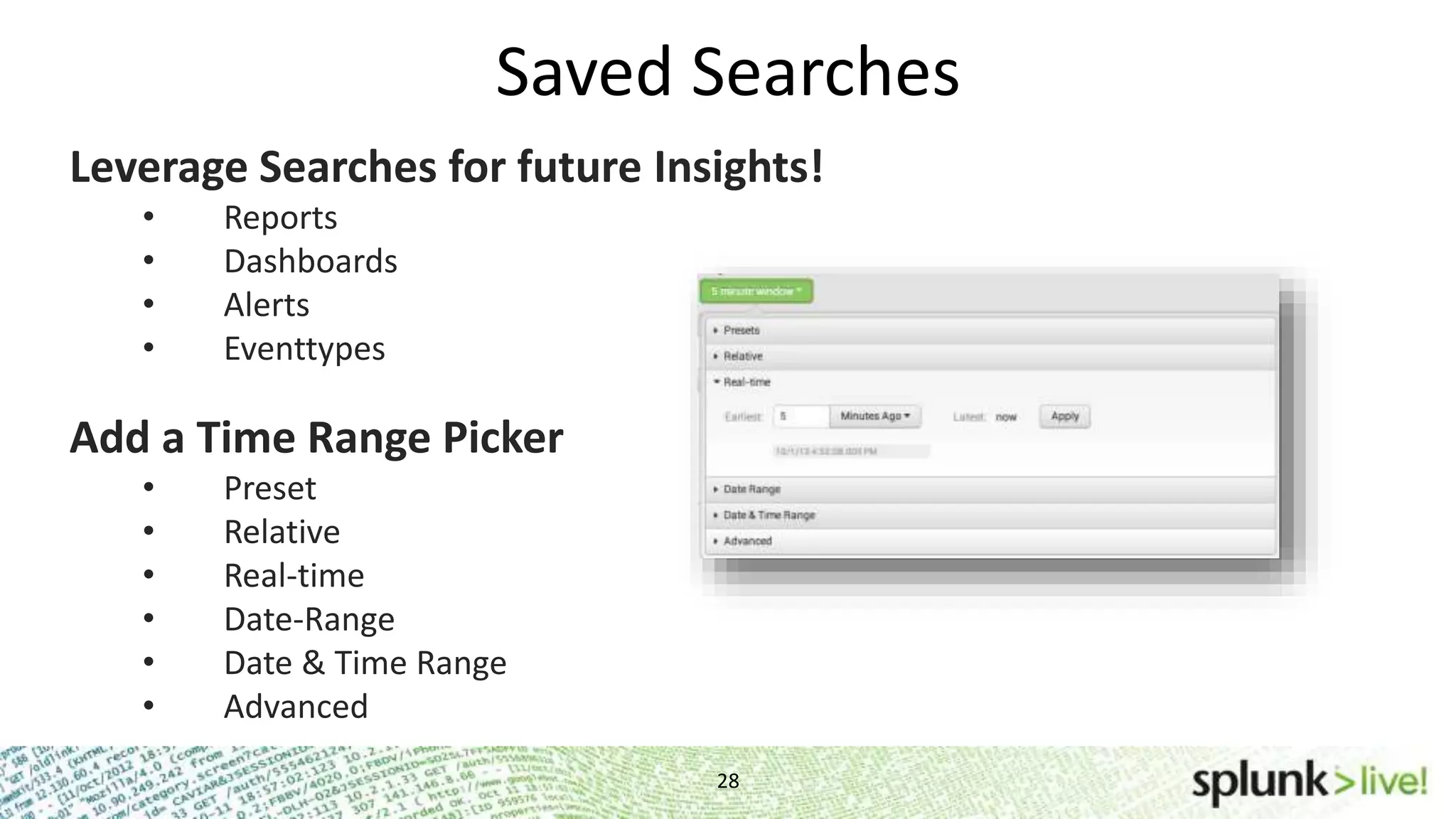
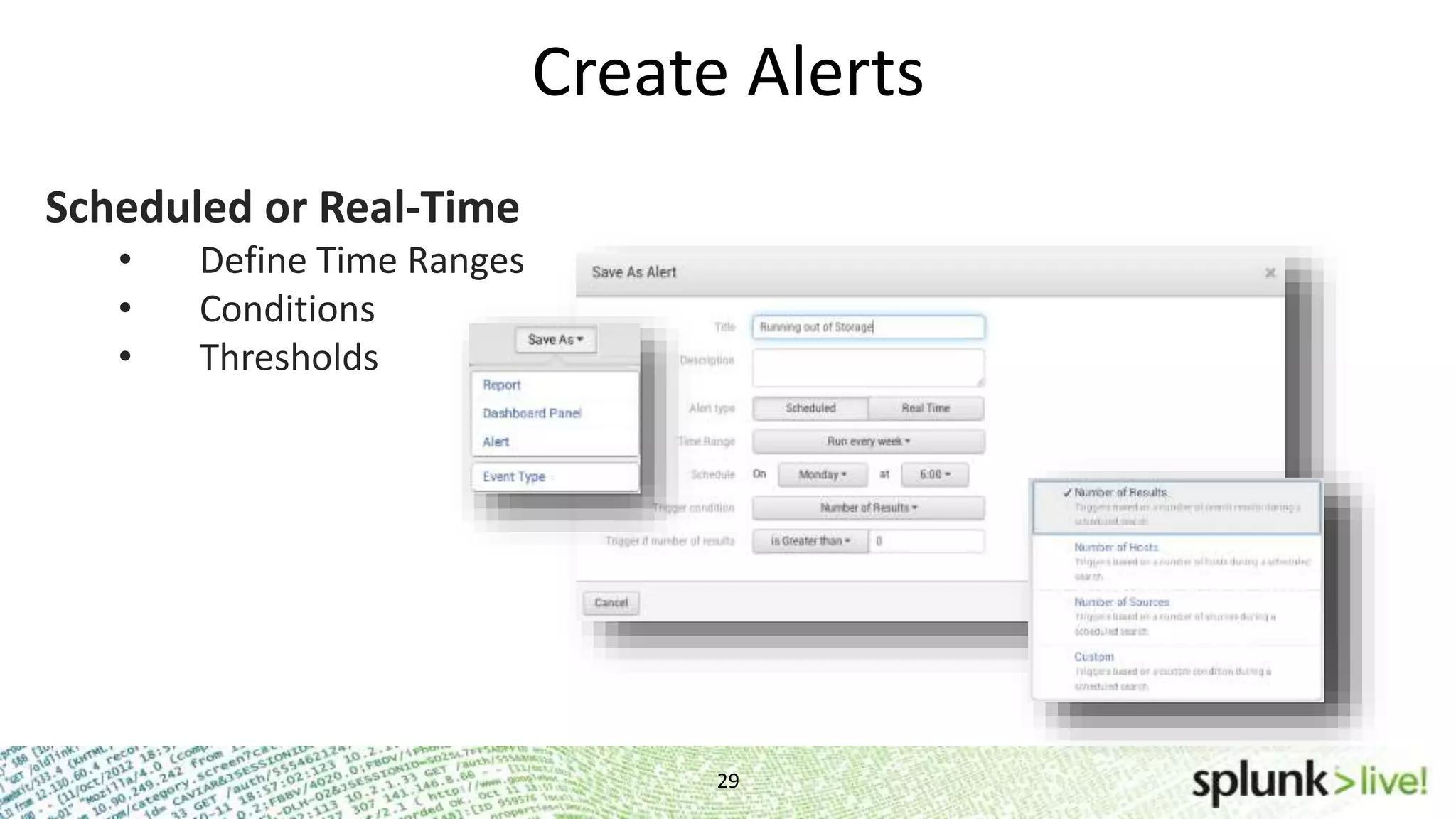
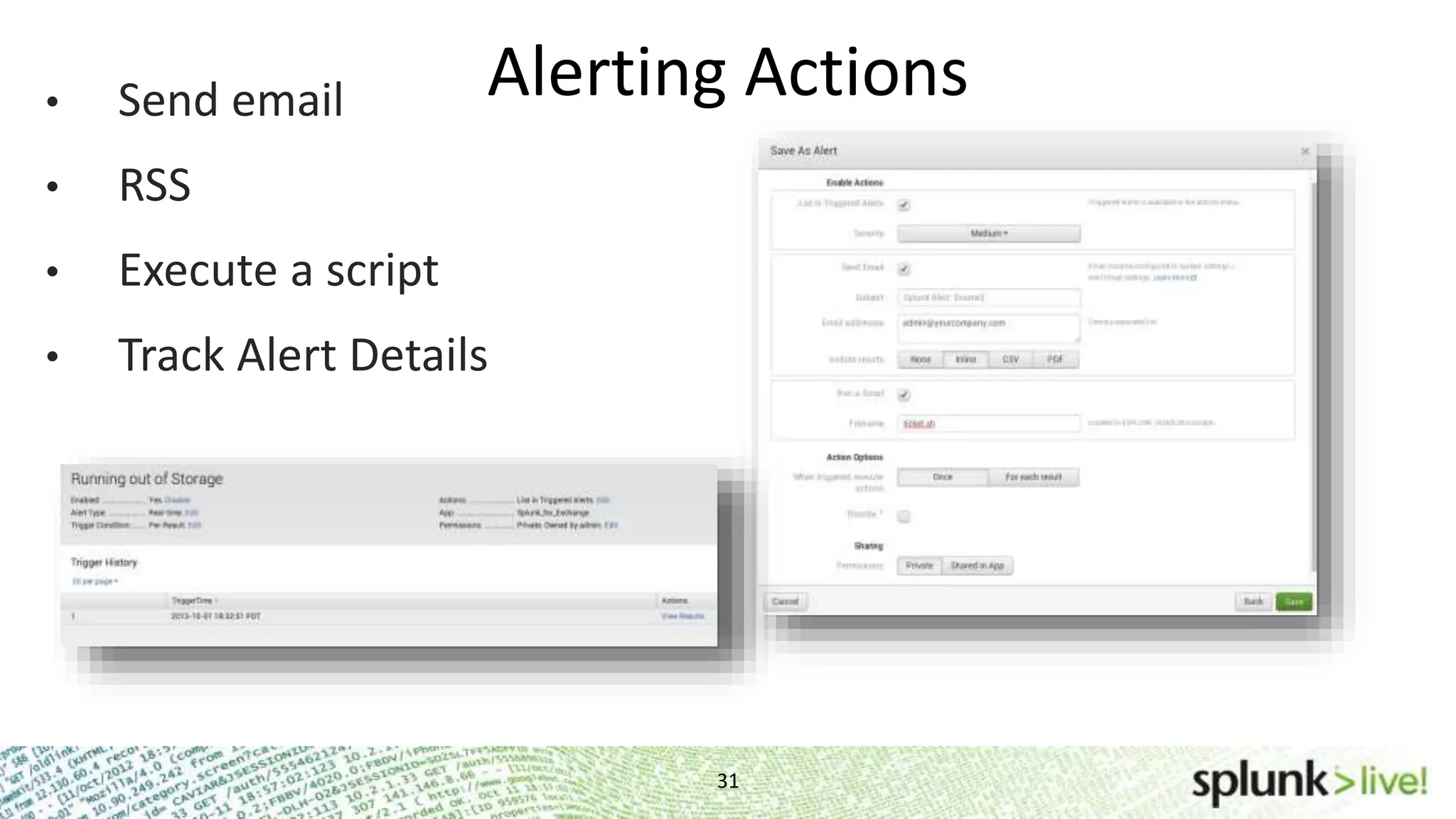
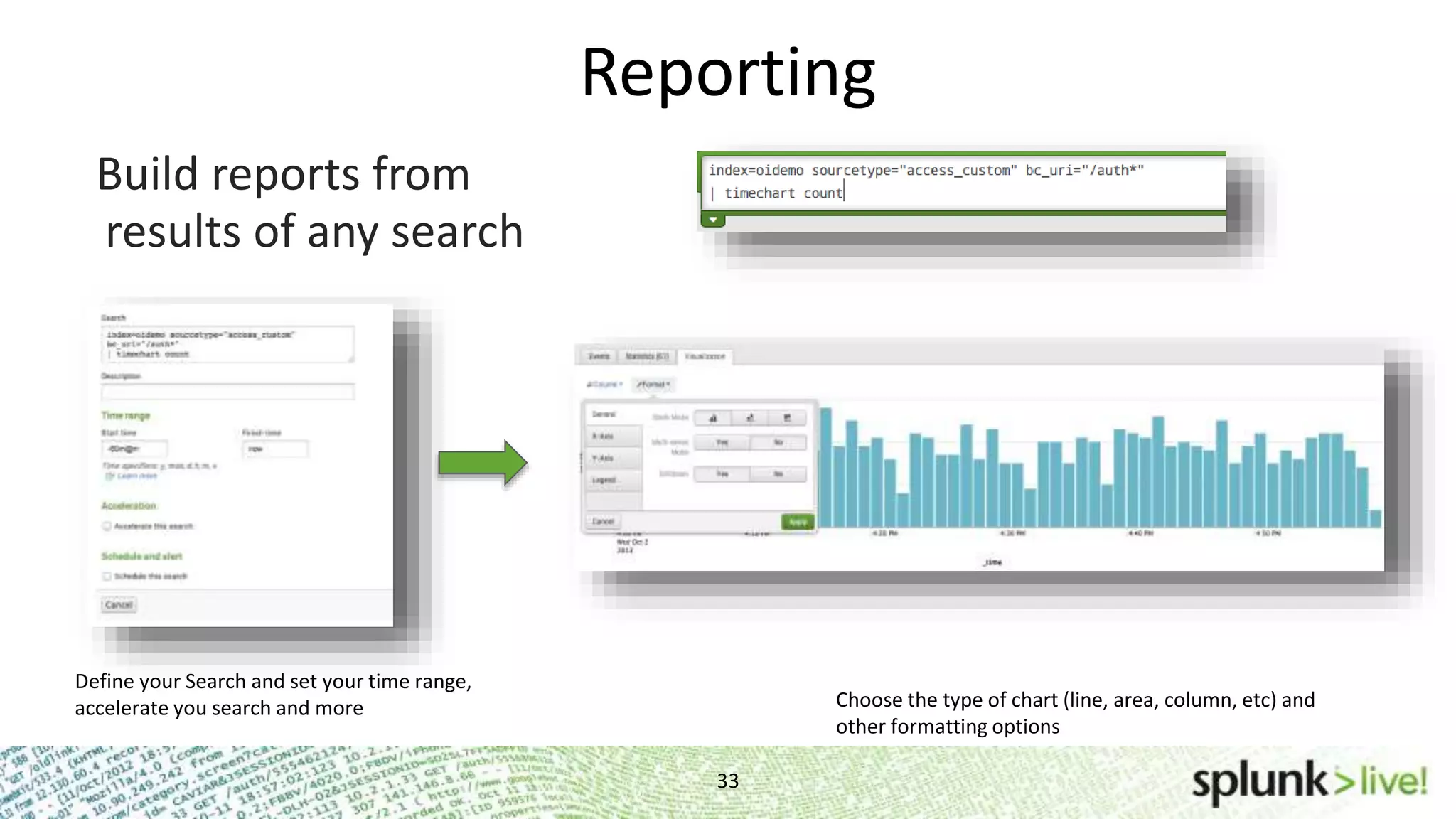
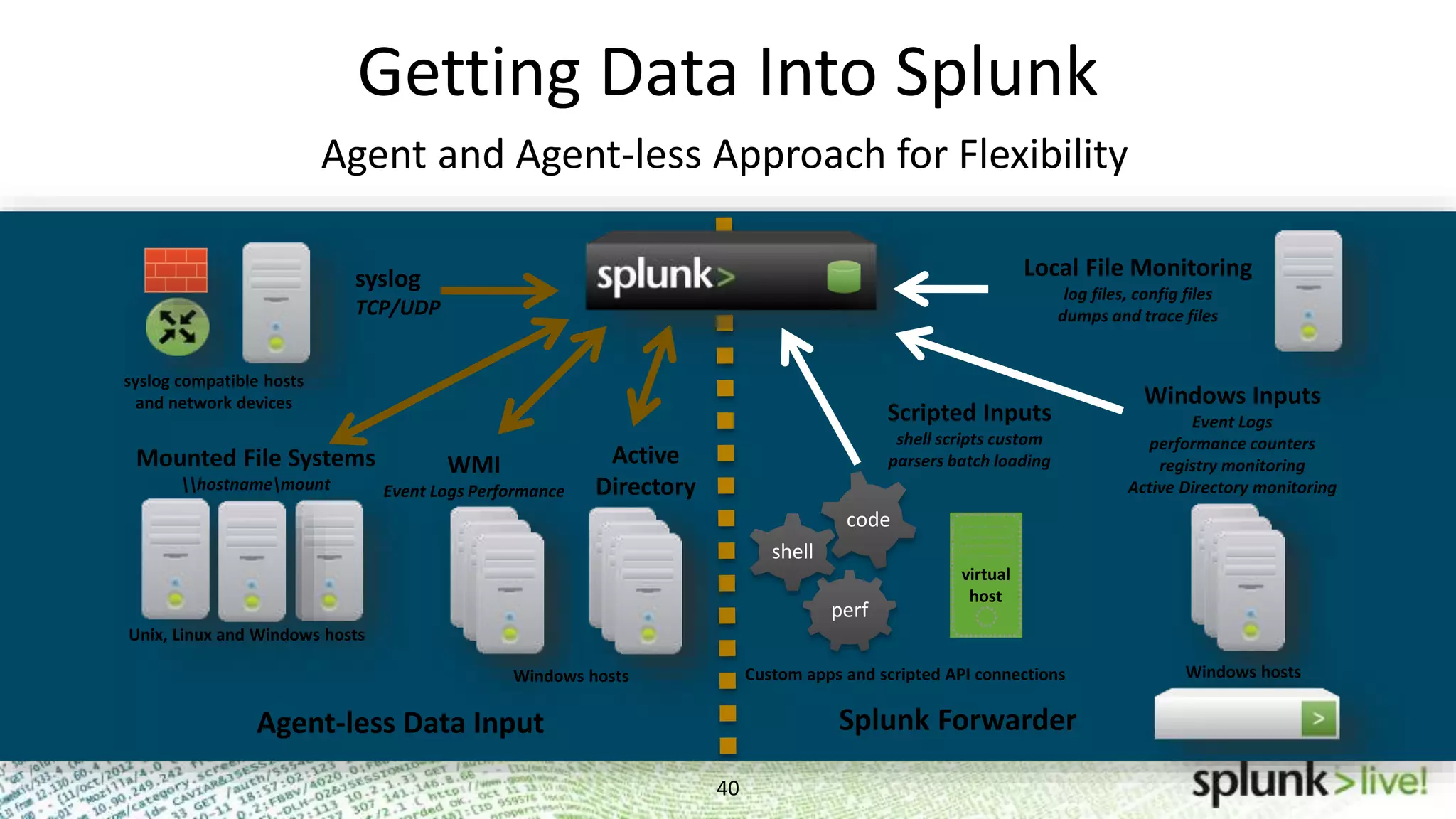
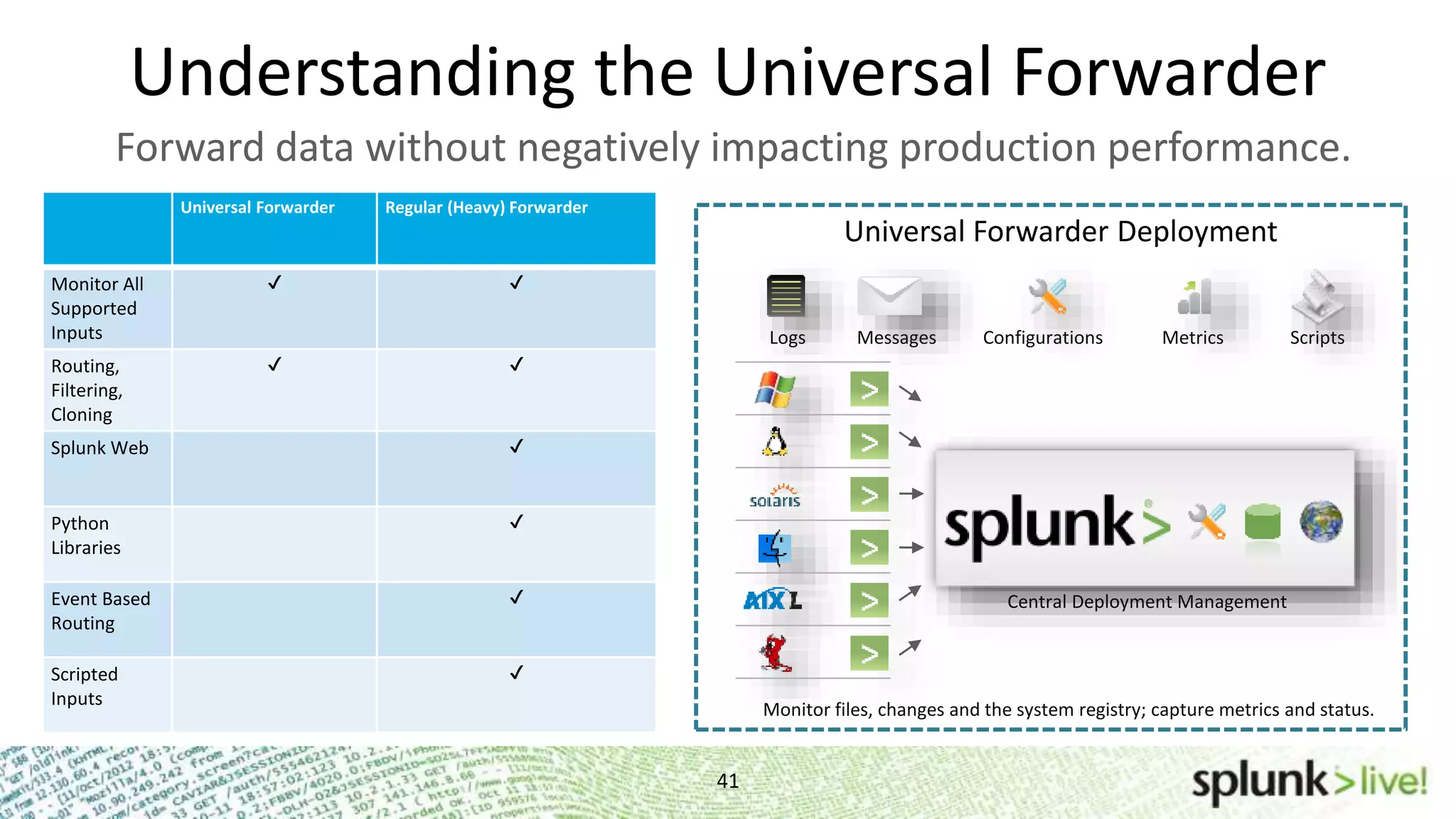
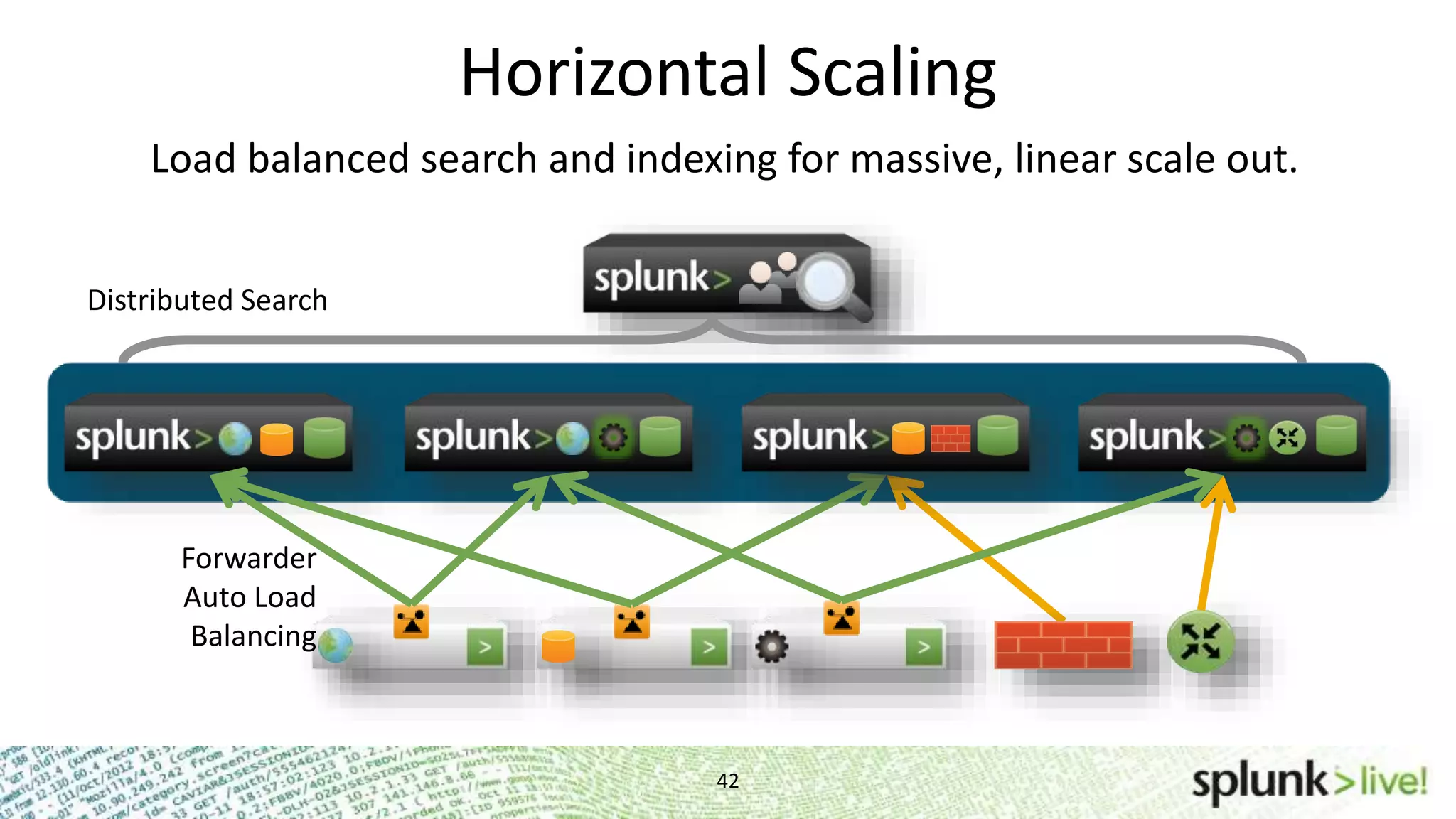
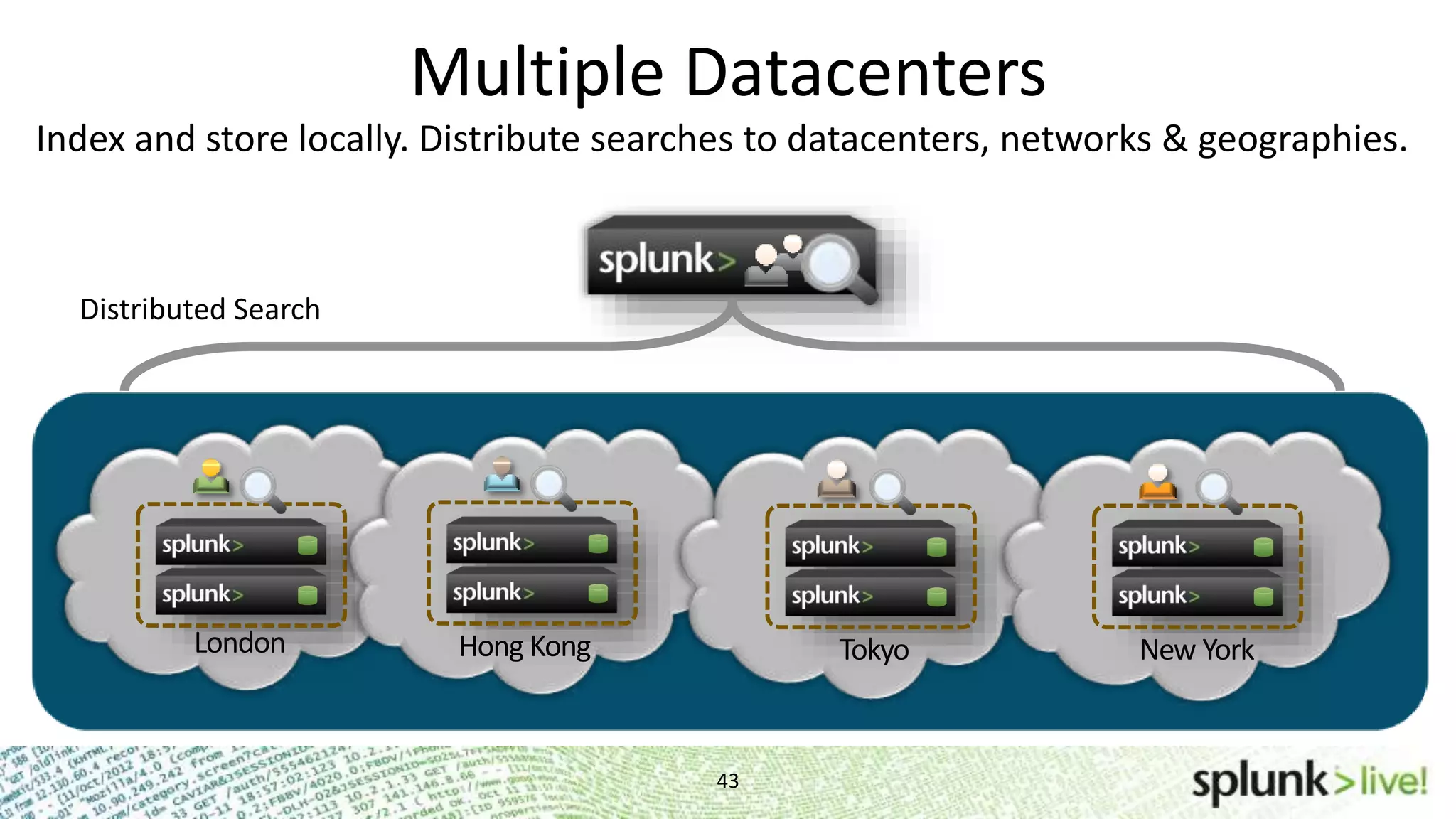
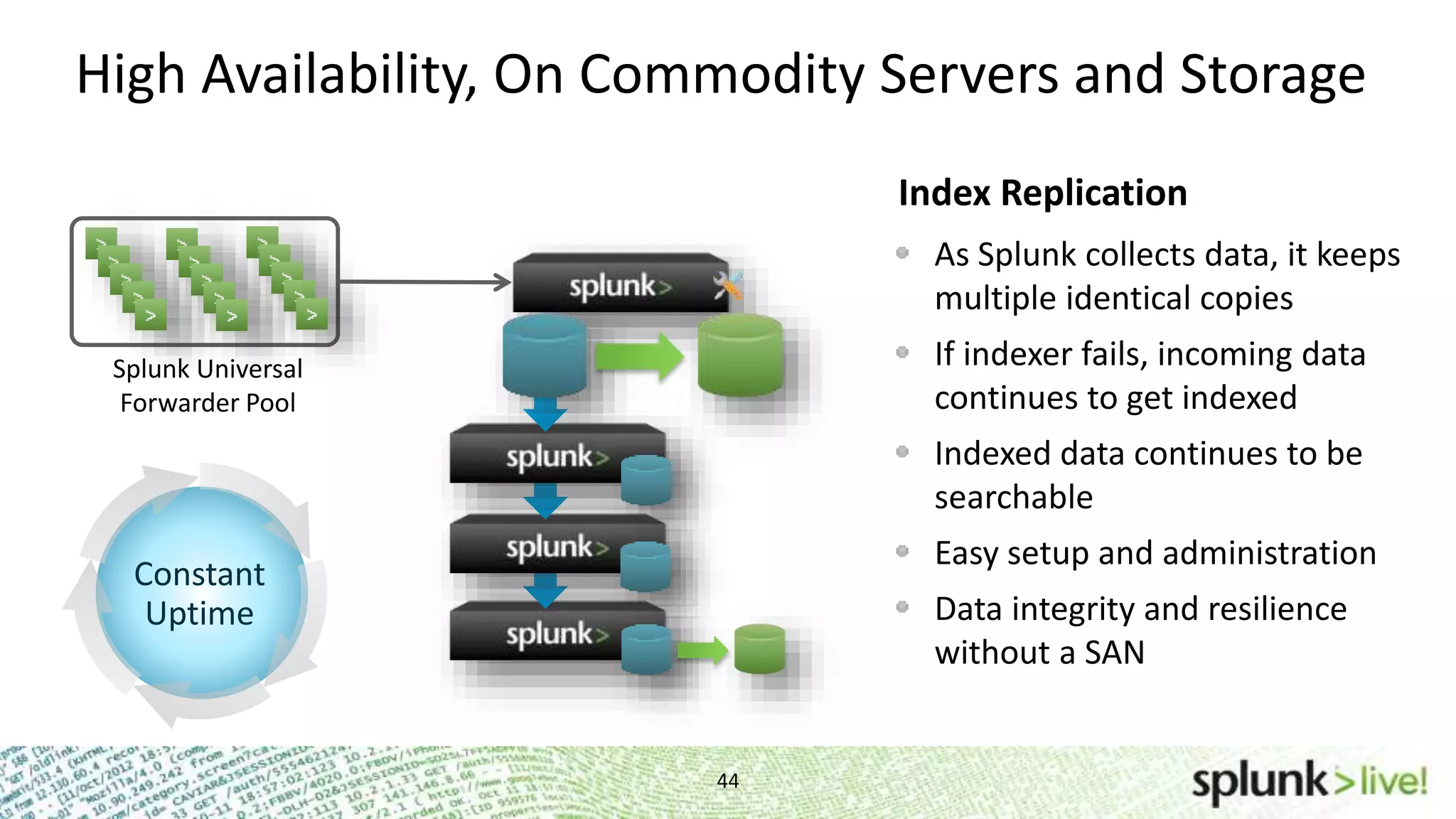
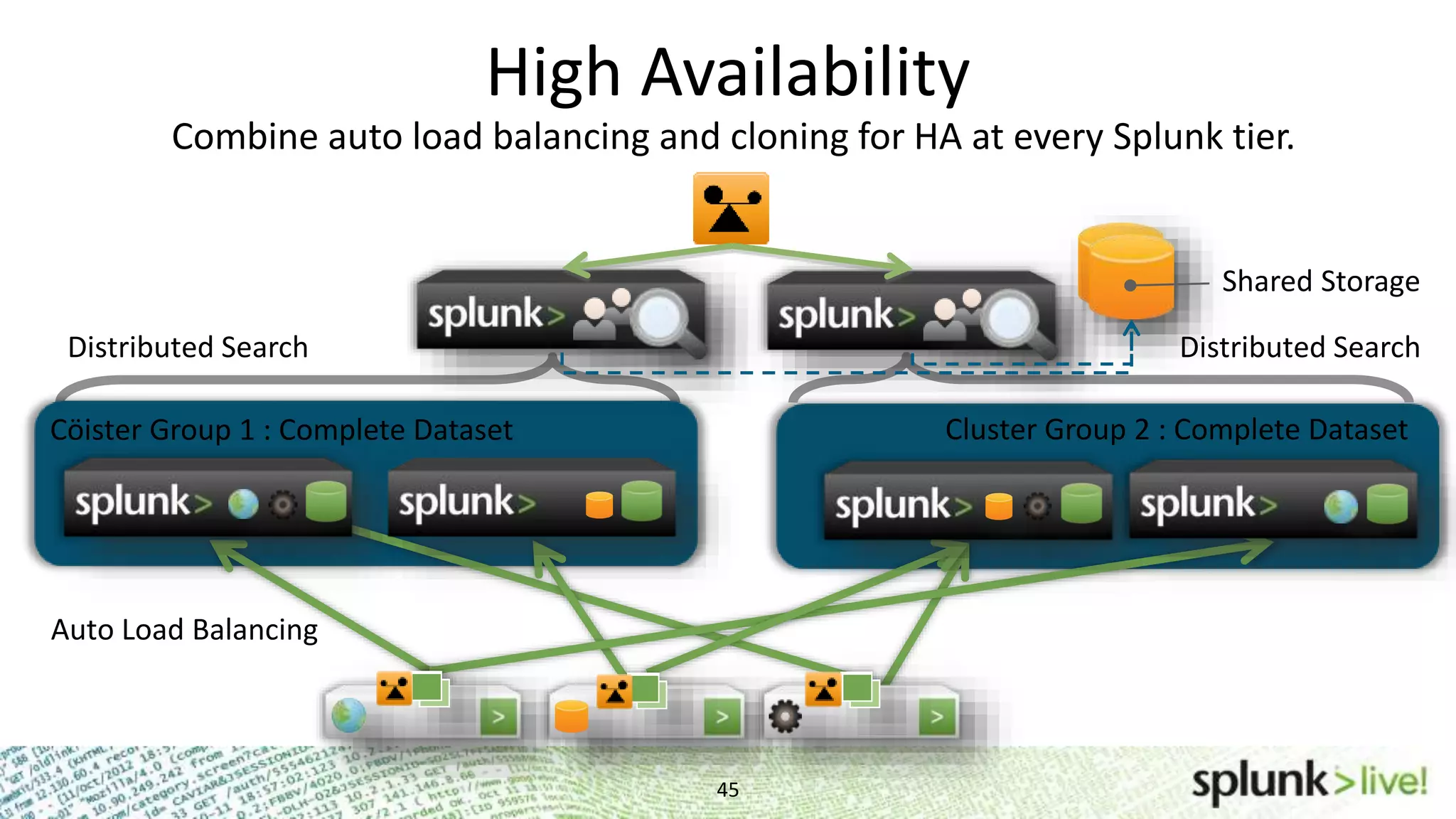
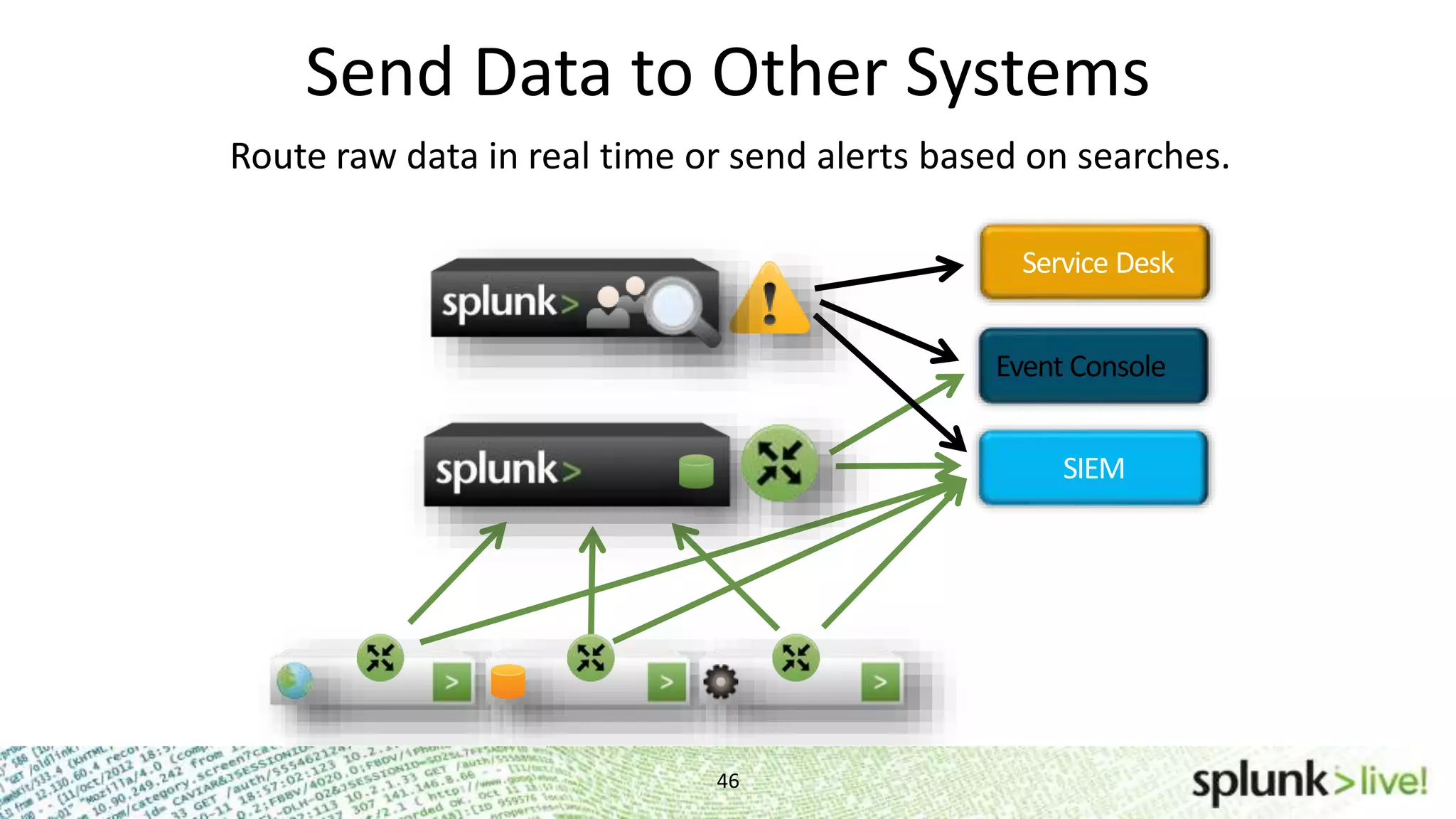
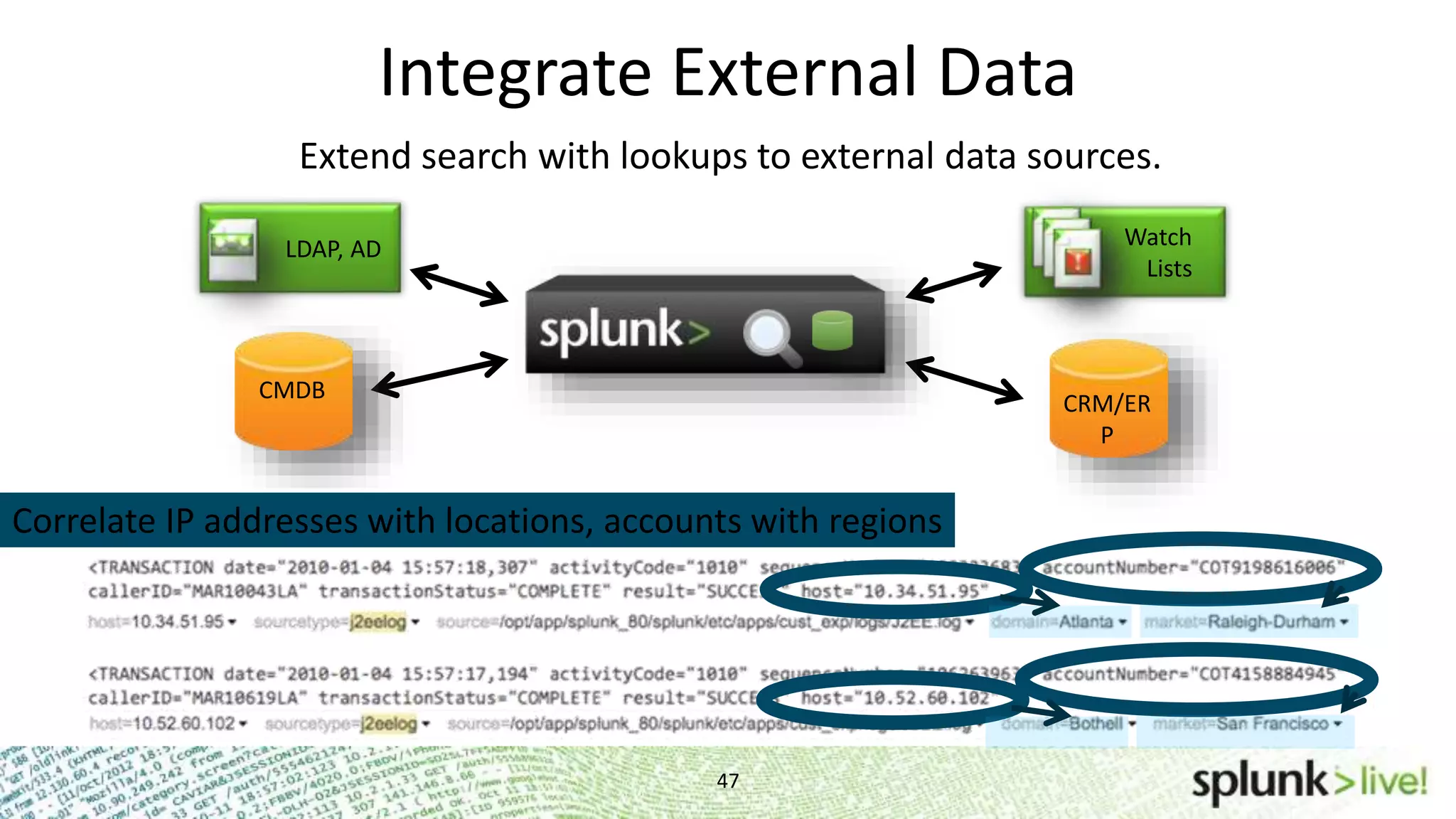
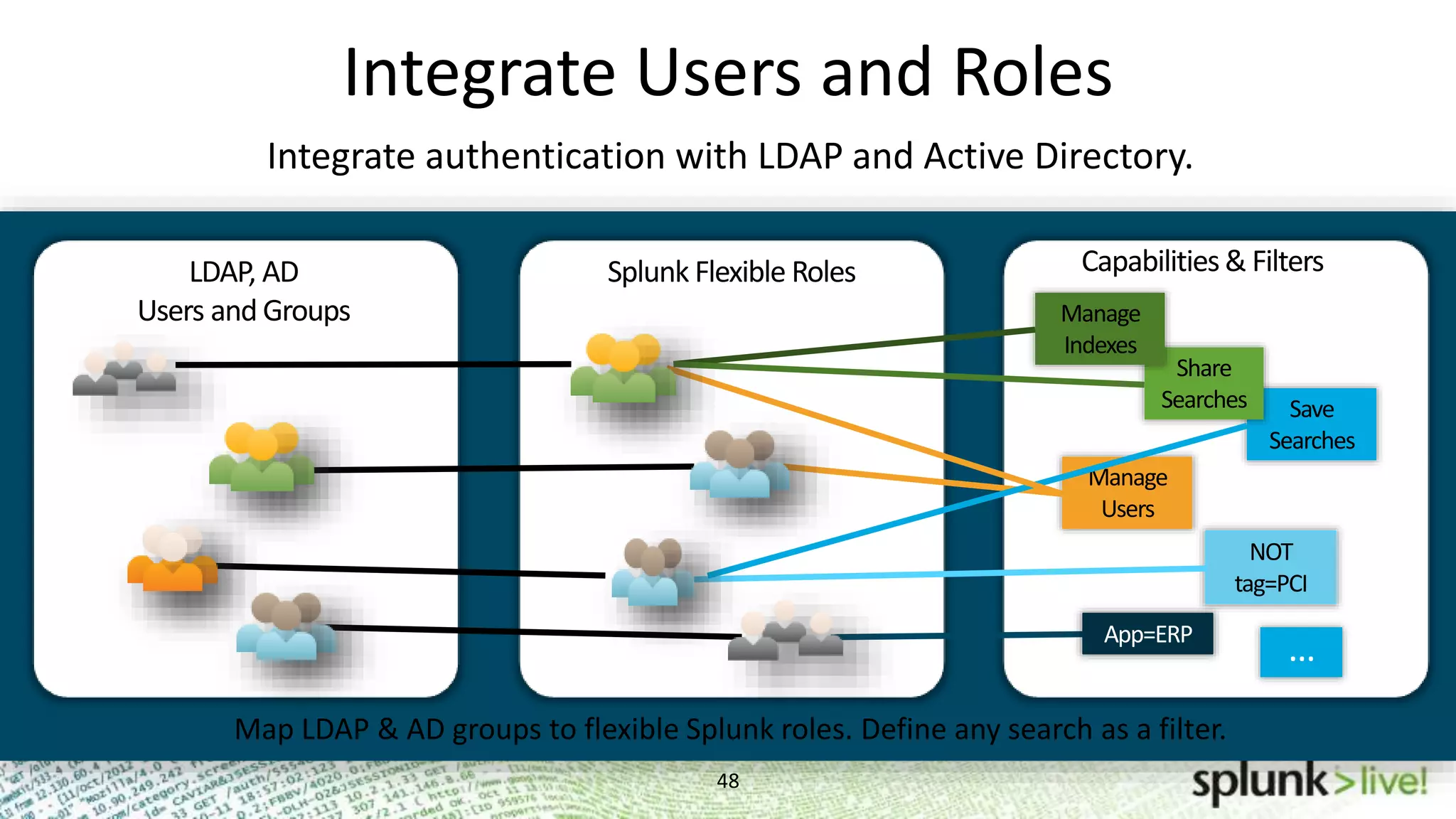
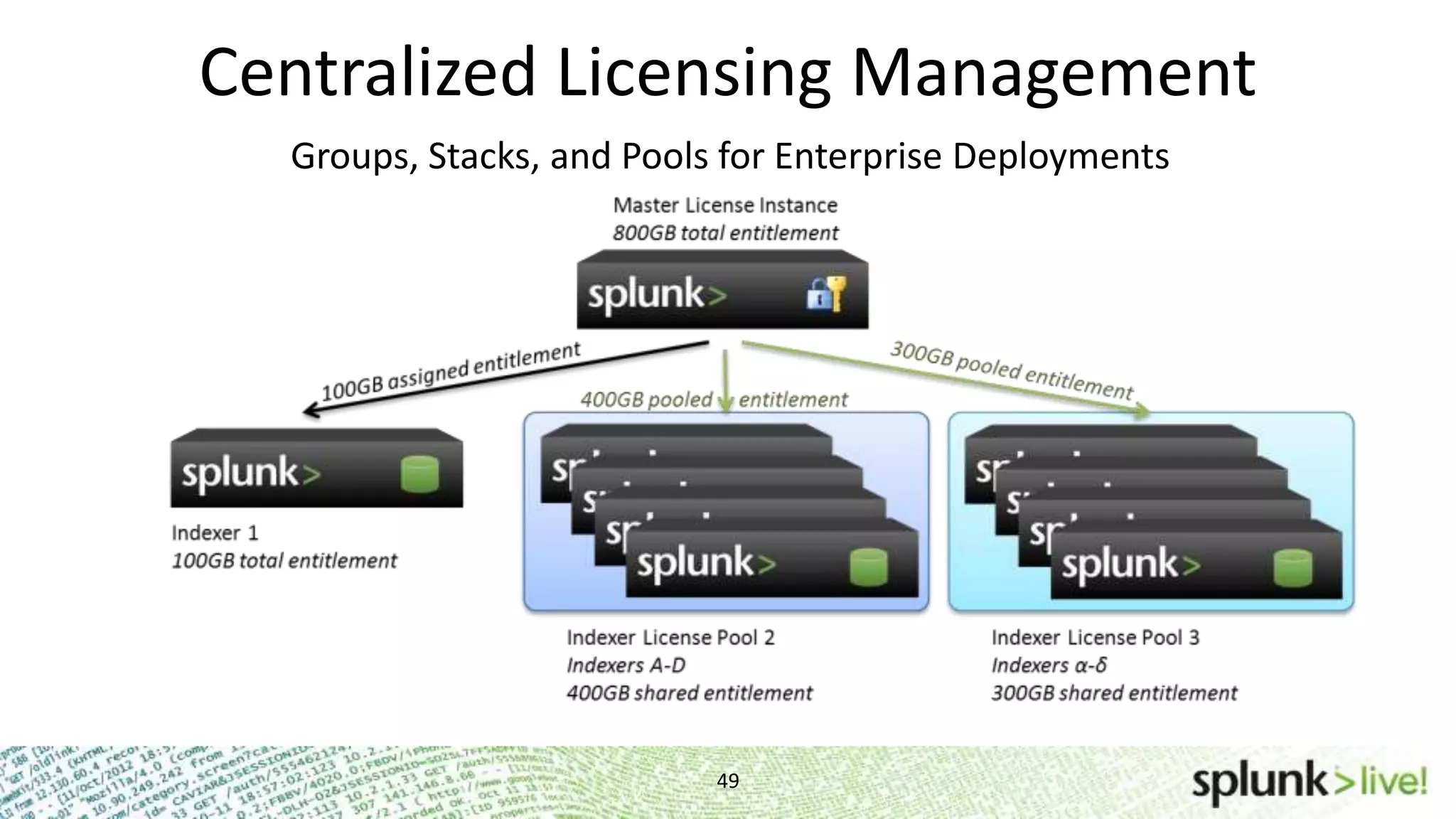
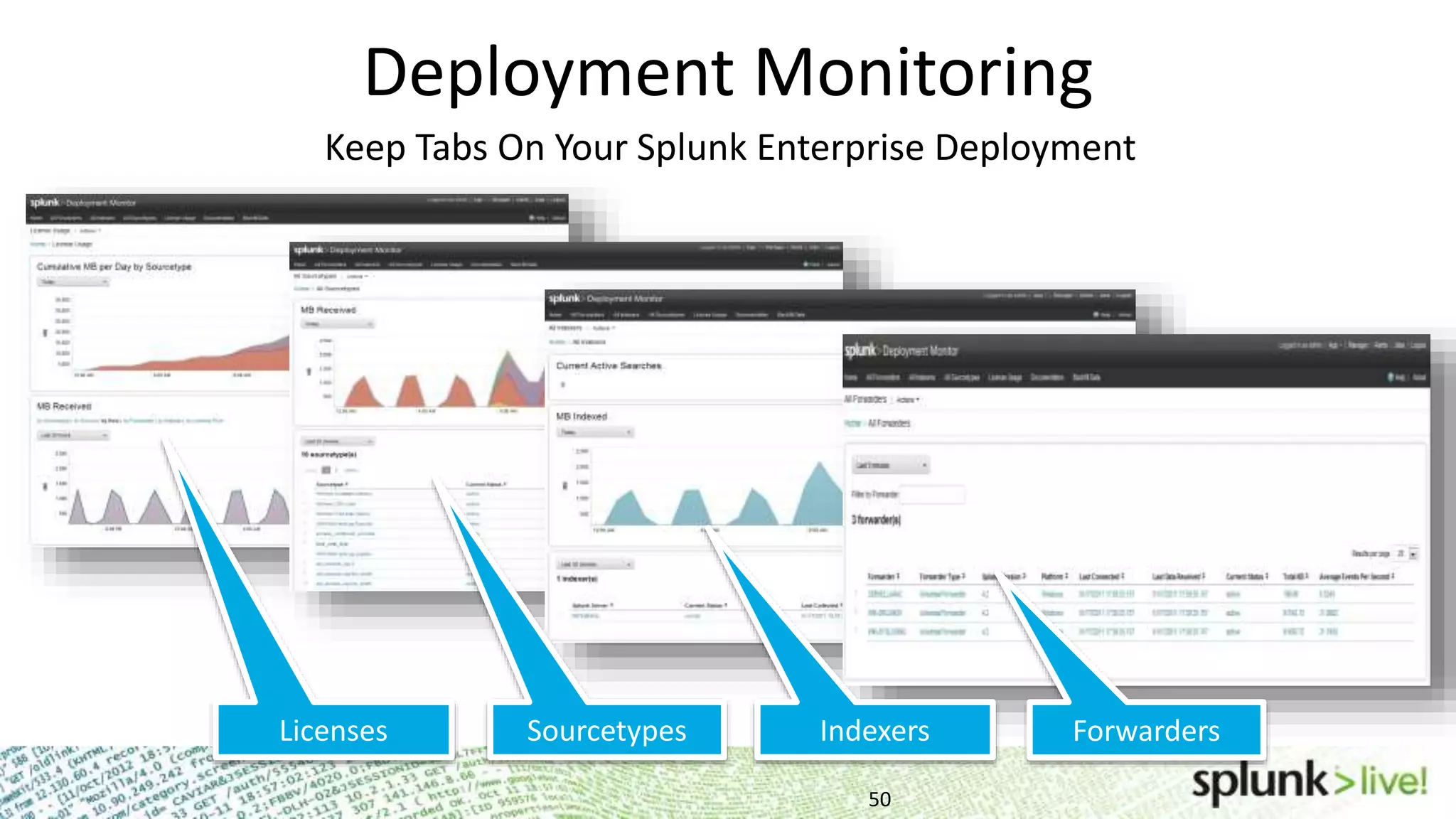
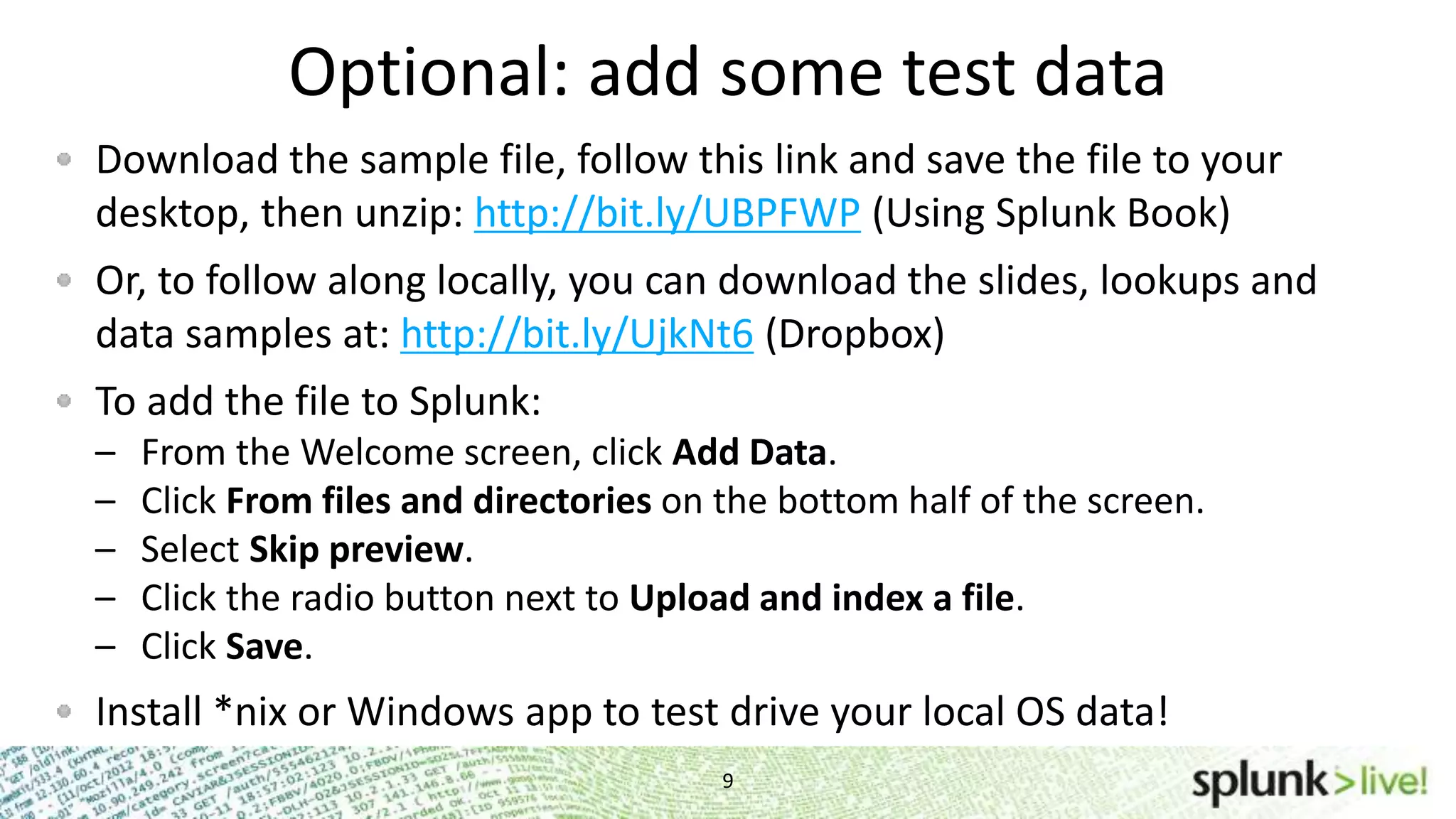
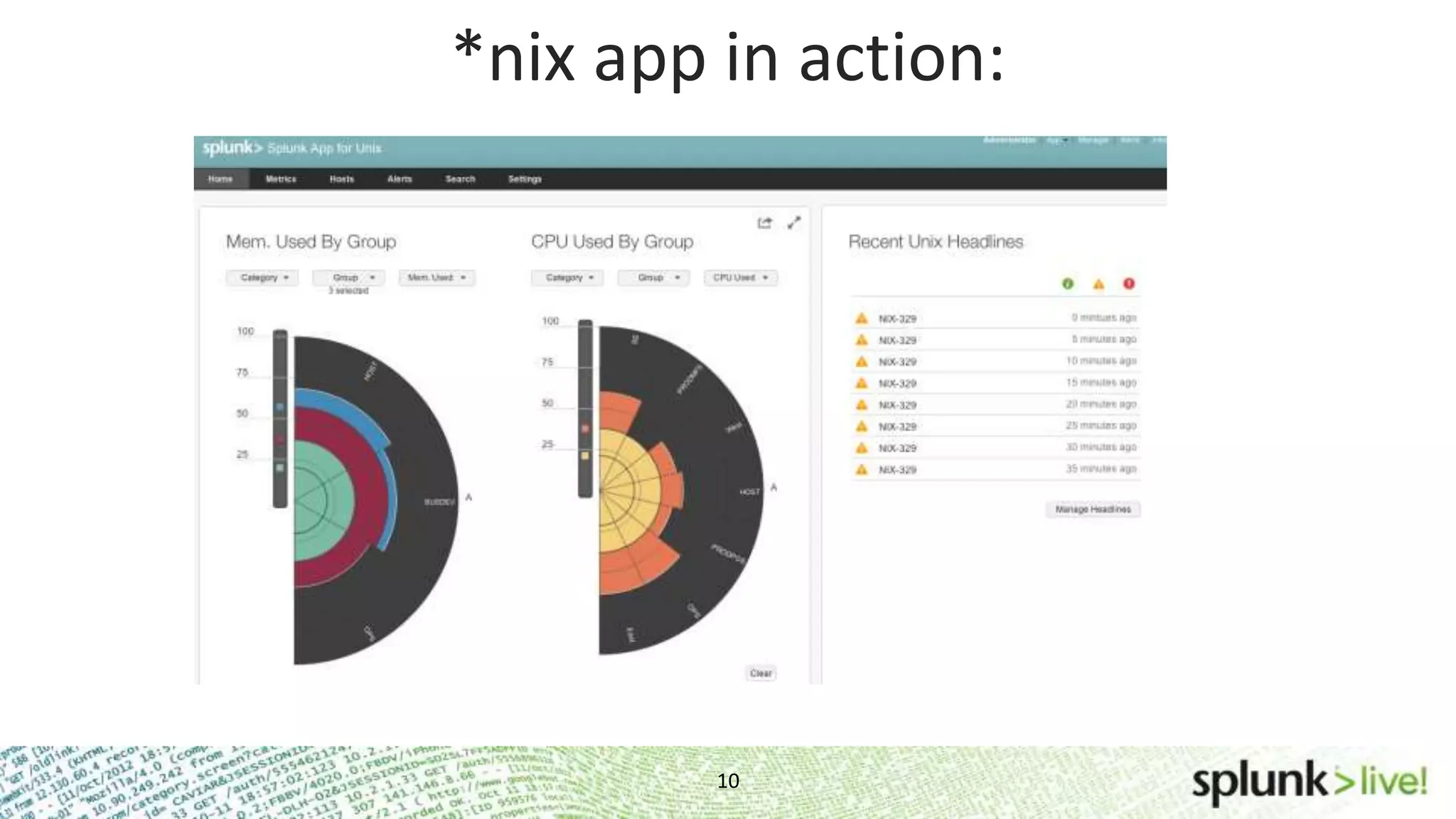
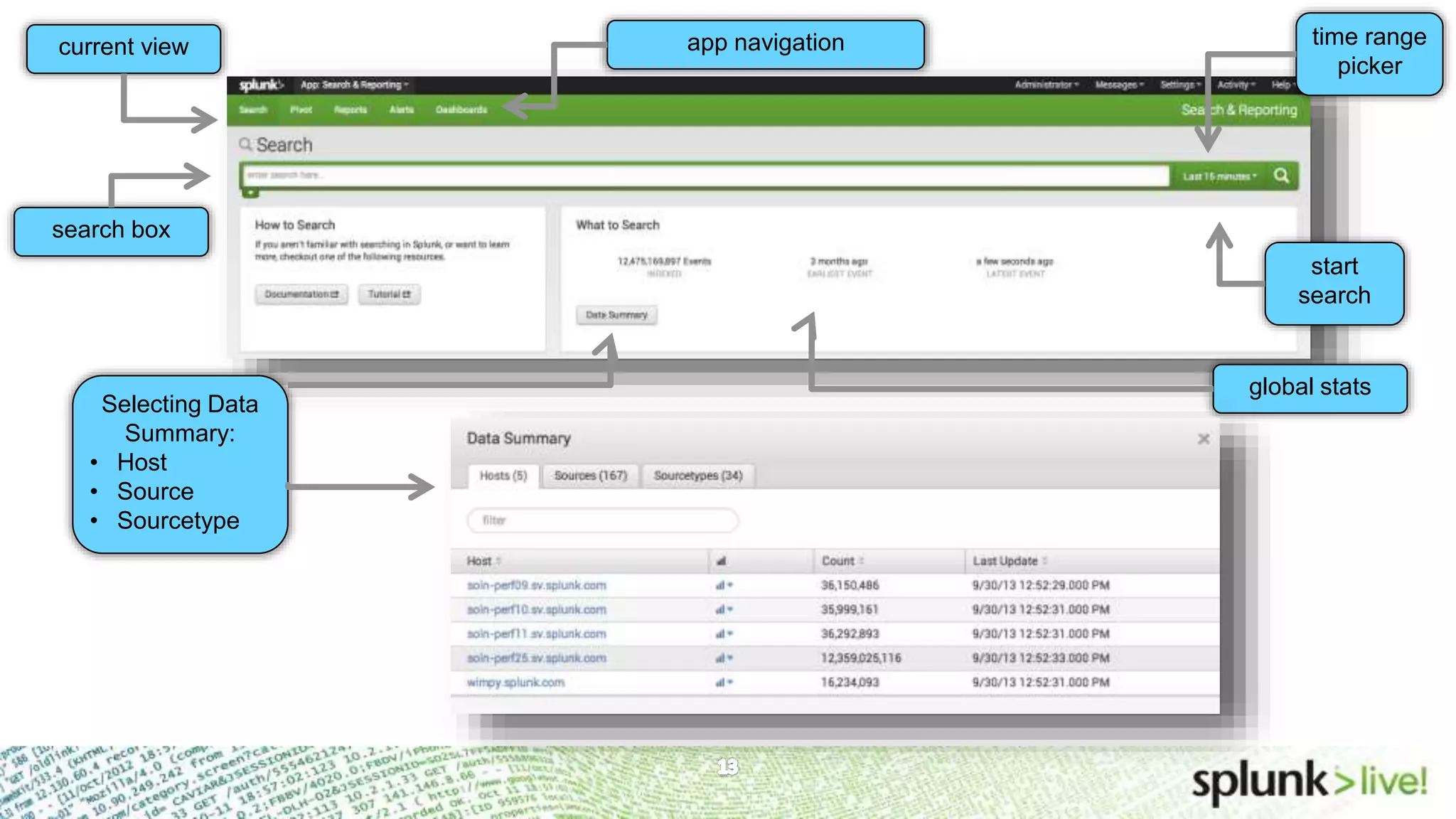
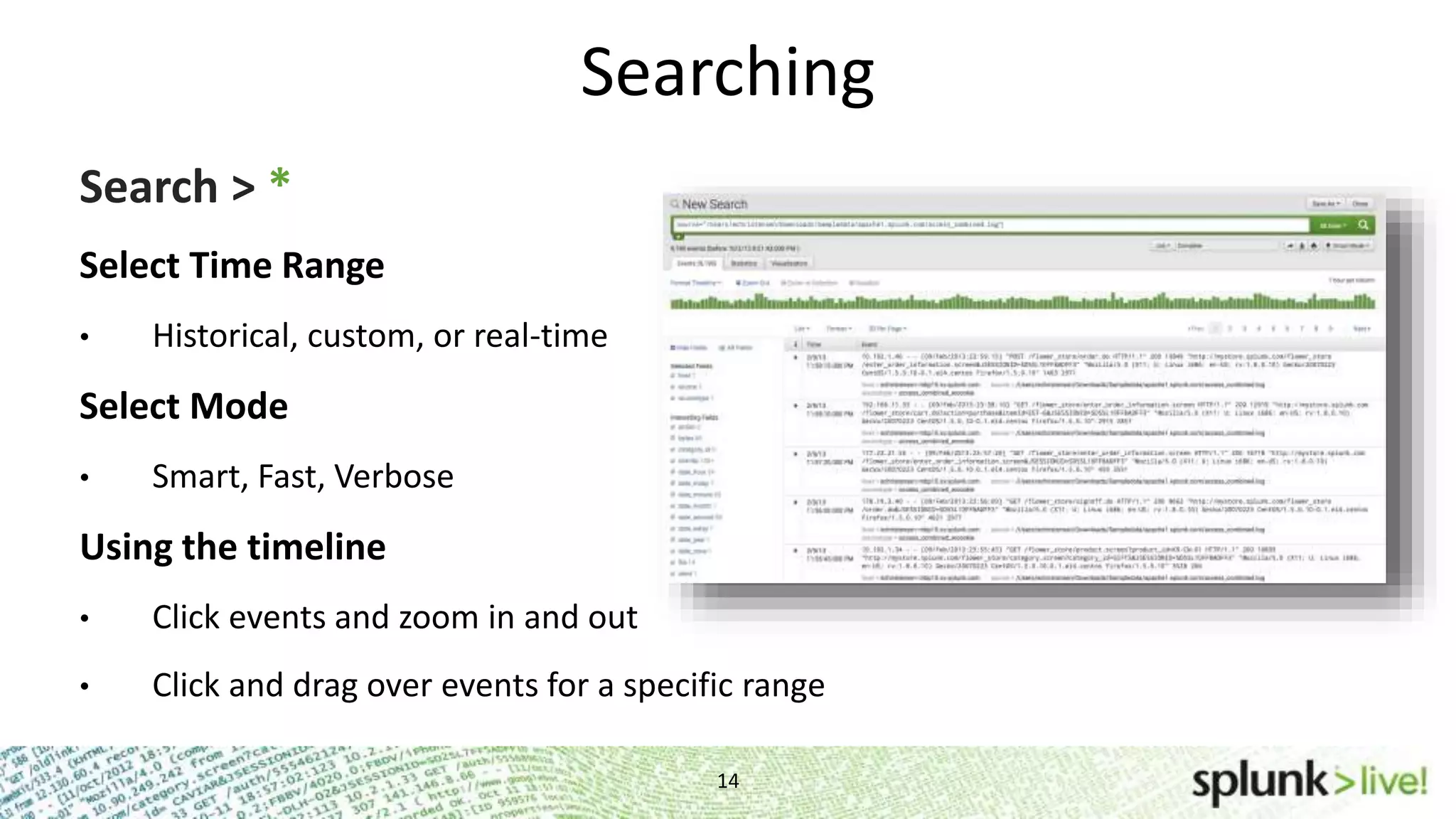
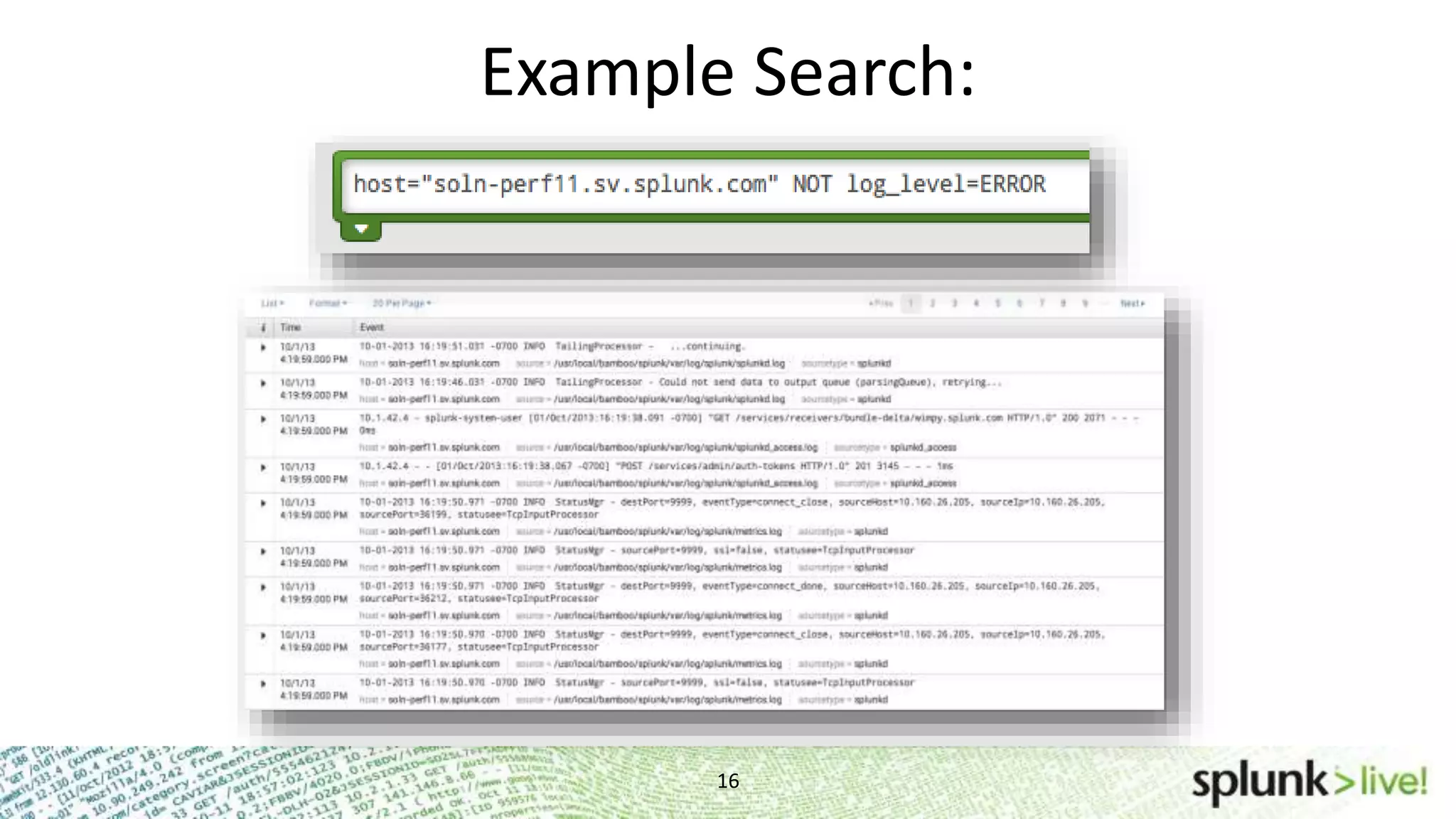
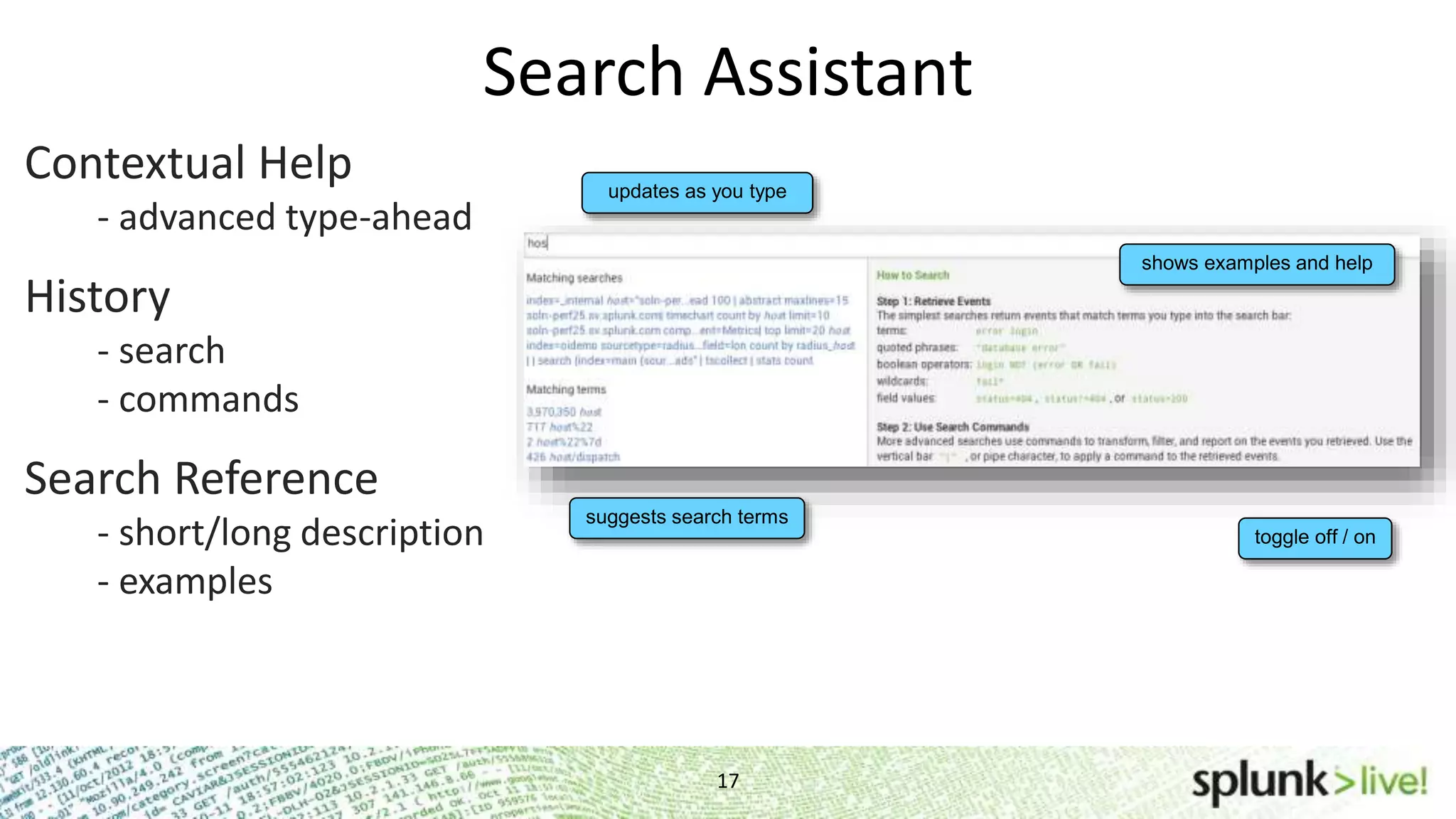
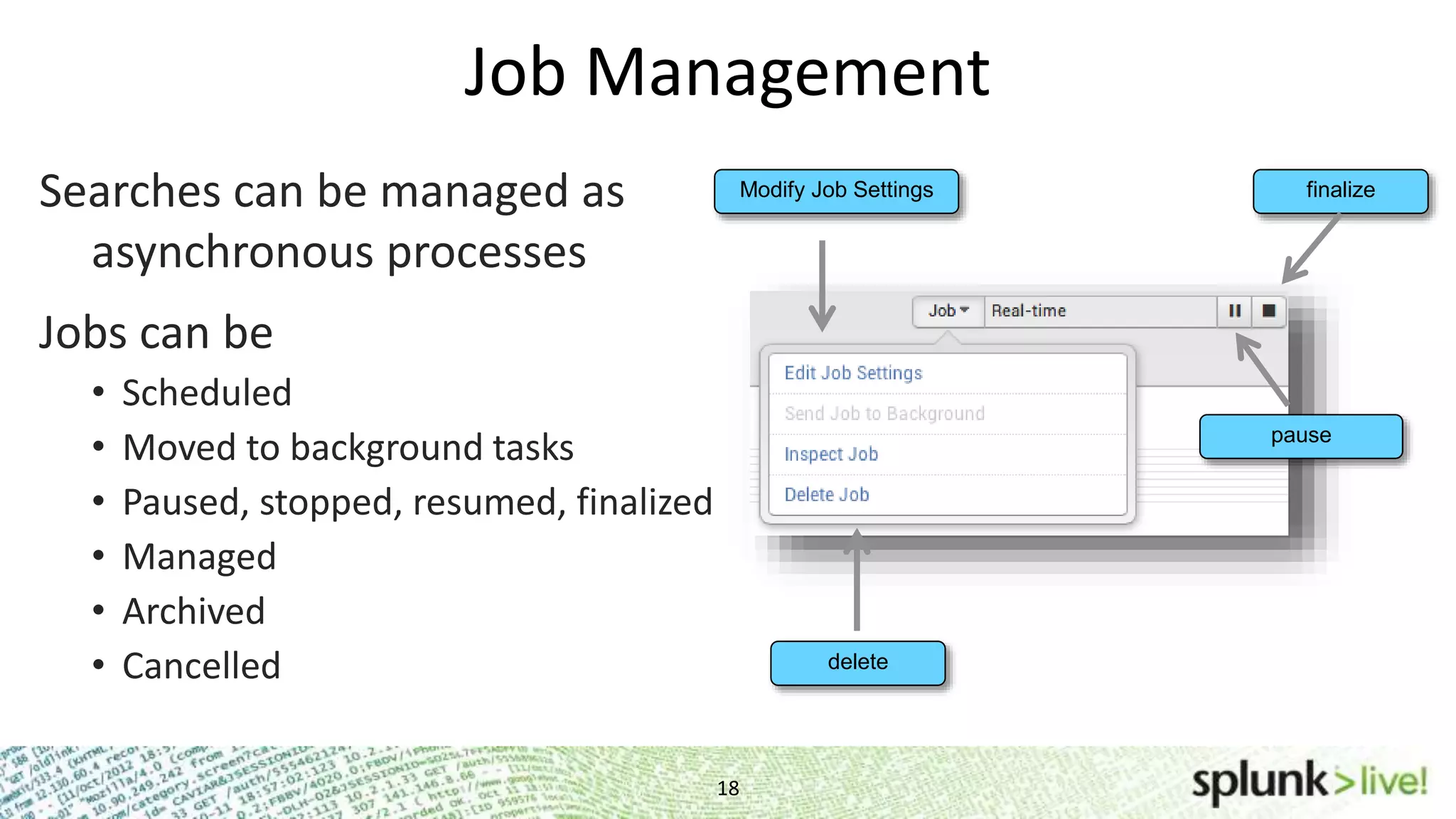
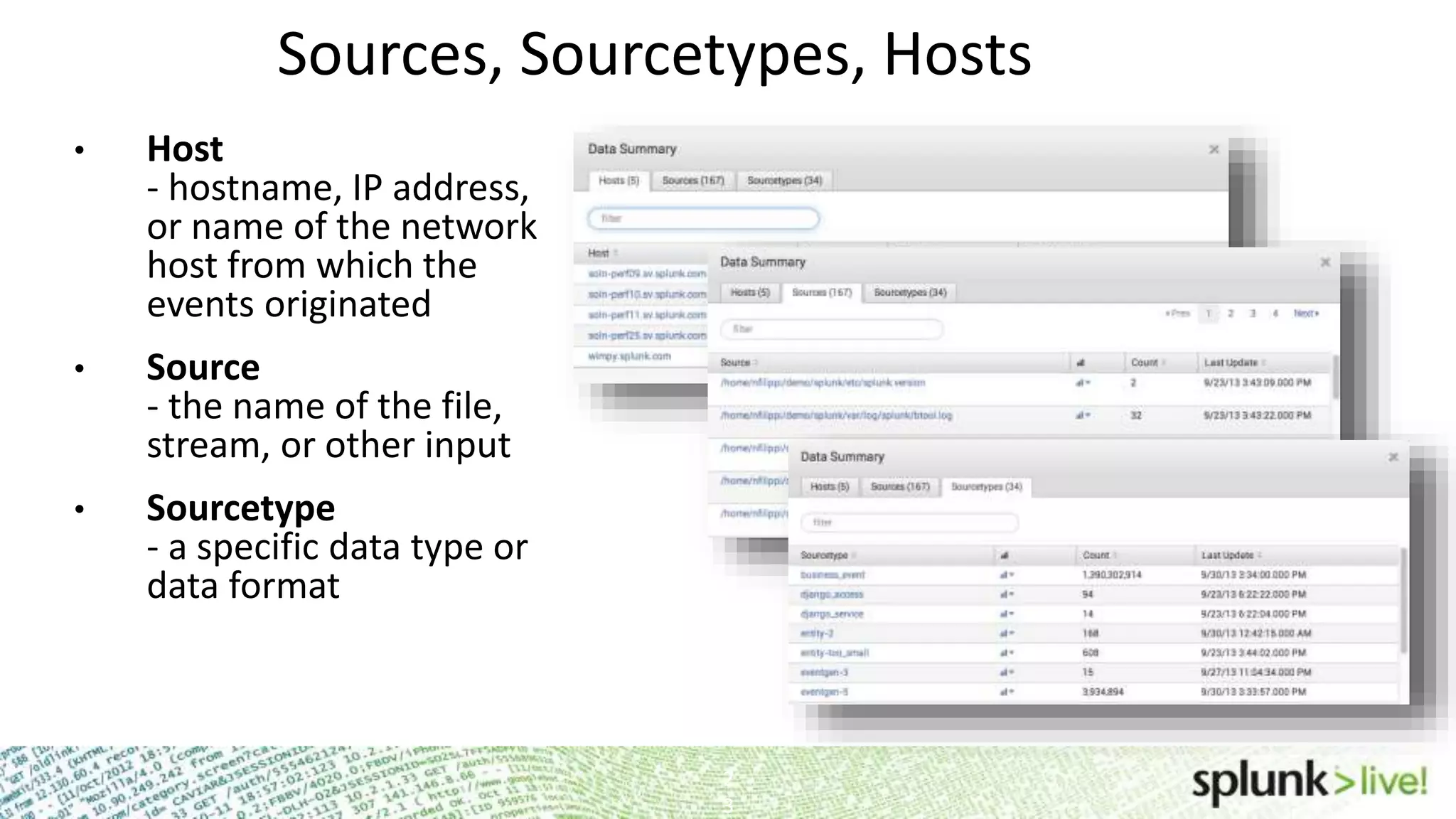
This document provides an agenda and overview for a Splunk getting started user training workshop. The agenda includes introductions to getting started with Splunk, searching, alerts, dashboards, deployment and integration, the Splunk community, and a question and answer session. It also provides information on installing Splunk, Splunk licenses, the Splunk web interface, search basics, saved searches and alerts, deployment and integration options like forwarding data to Splunk, and where to find support resources.















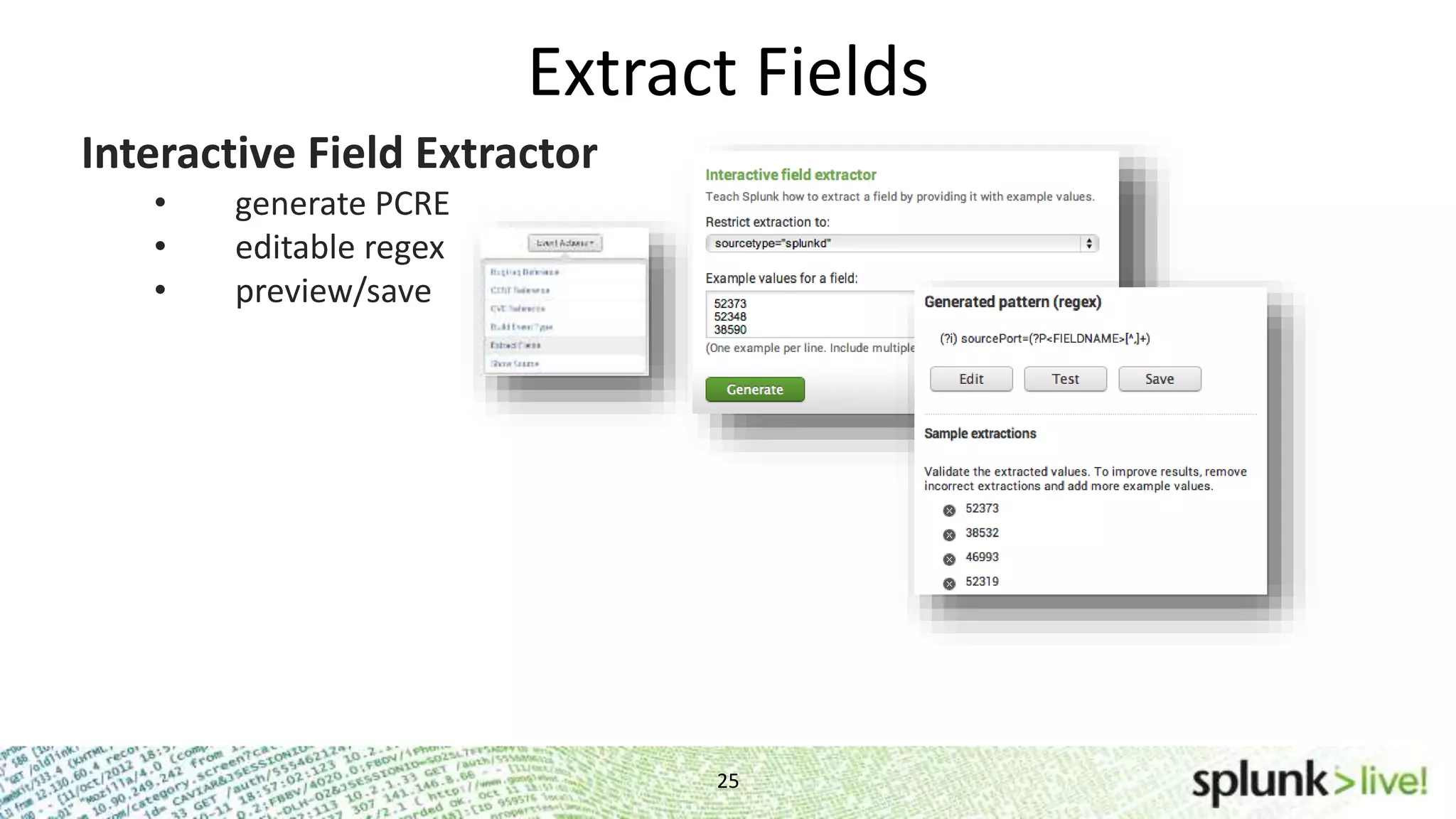
![Extract Fields 26 Interactive Field Extractor • generate PCRE • editable regex • preview/save props.conf [mysourcetype] REPORT-myclass = myFields transforms.conf [myFields] REGEX = ^(w+)s FORMAT = myFieldLabel::$1 Configuration File • manual field extraction • delim-based extractions Rex Search Command ... | rex field=_raw "From: (?<from>.*) To: (?<to>.*)"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-05-08gettingstartedwithsplunkbreakoutsession-140509035604-phpapp01/75/Getting-Started-with-Splunk-Break-out-Session-26-2048.jpg)