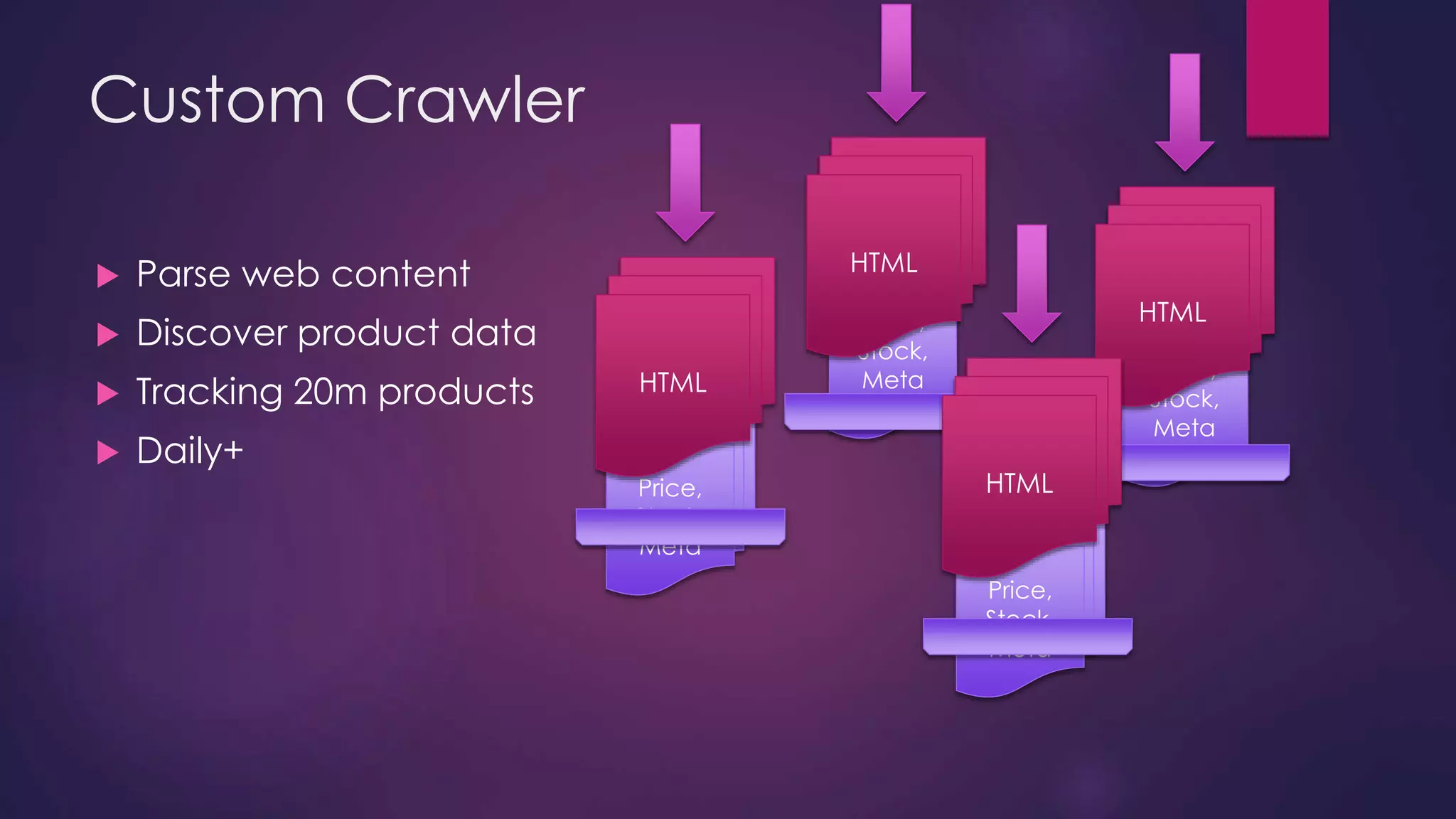
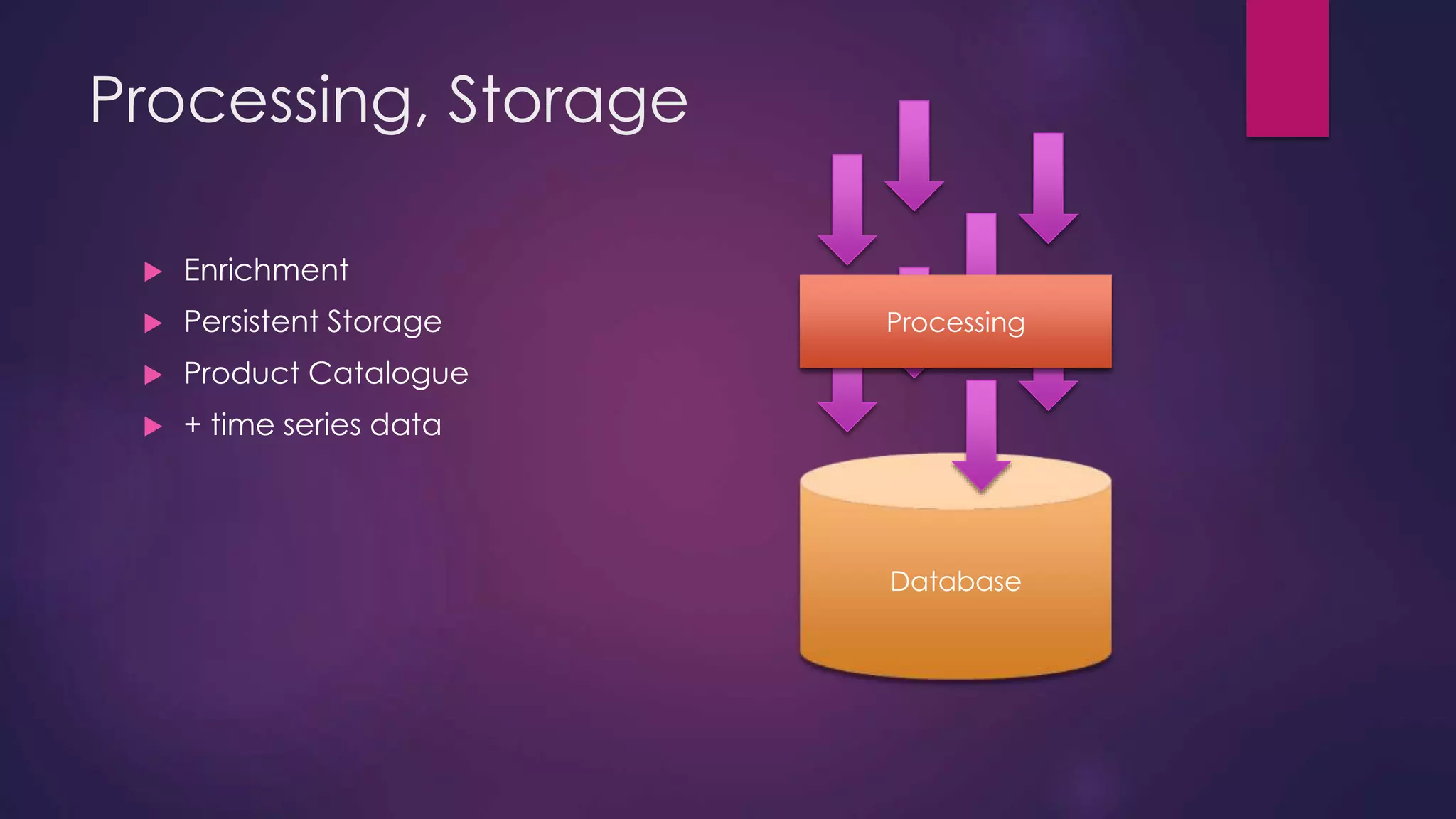
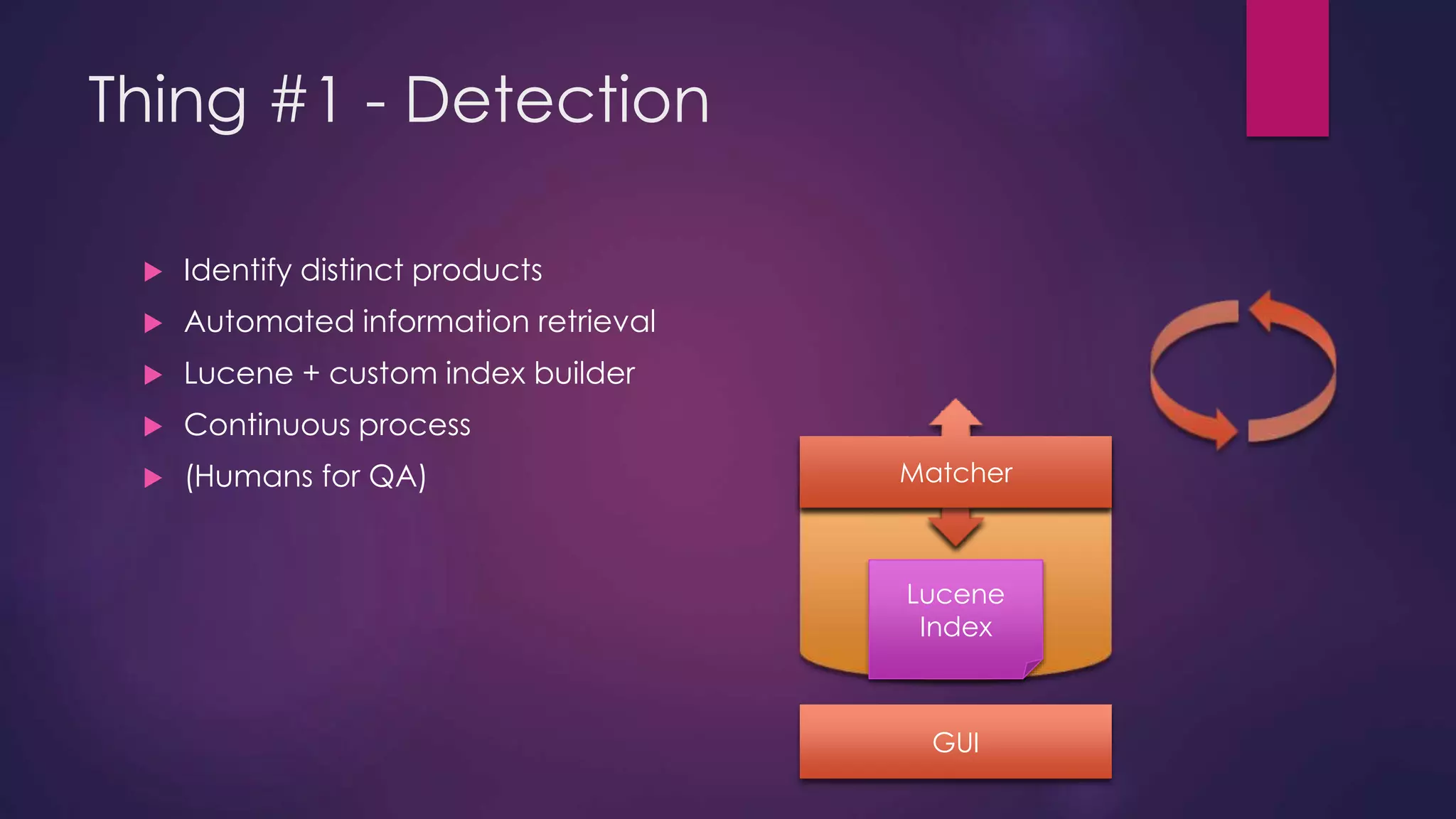
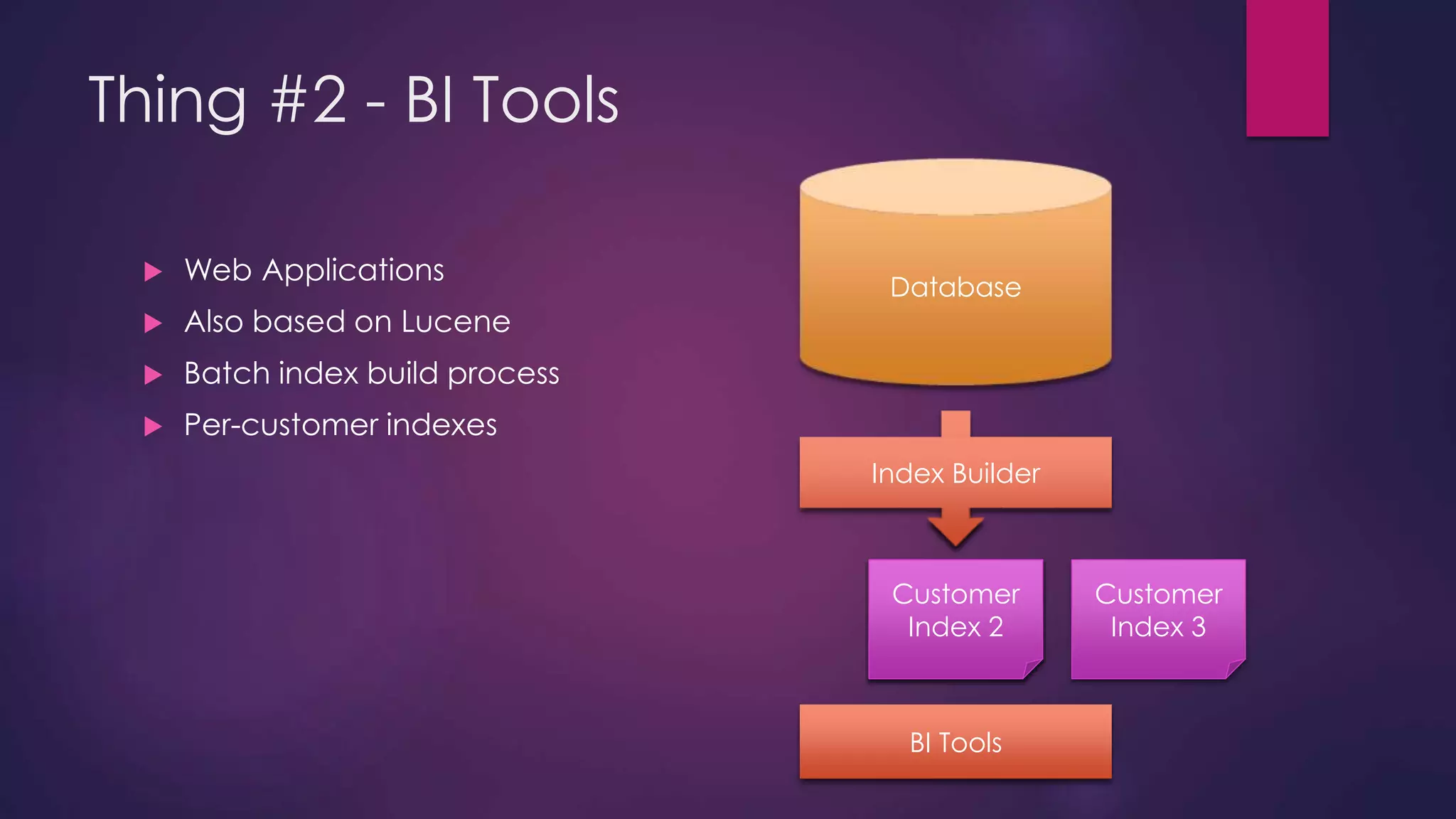
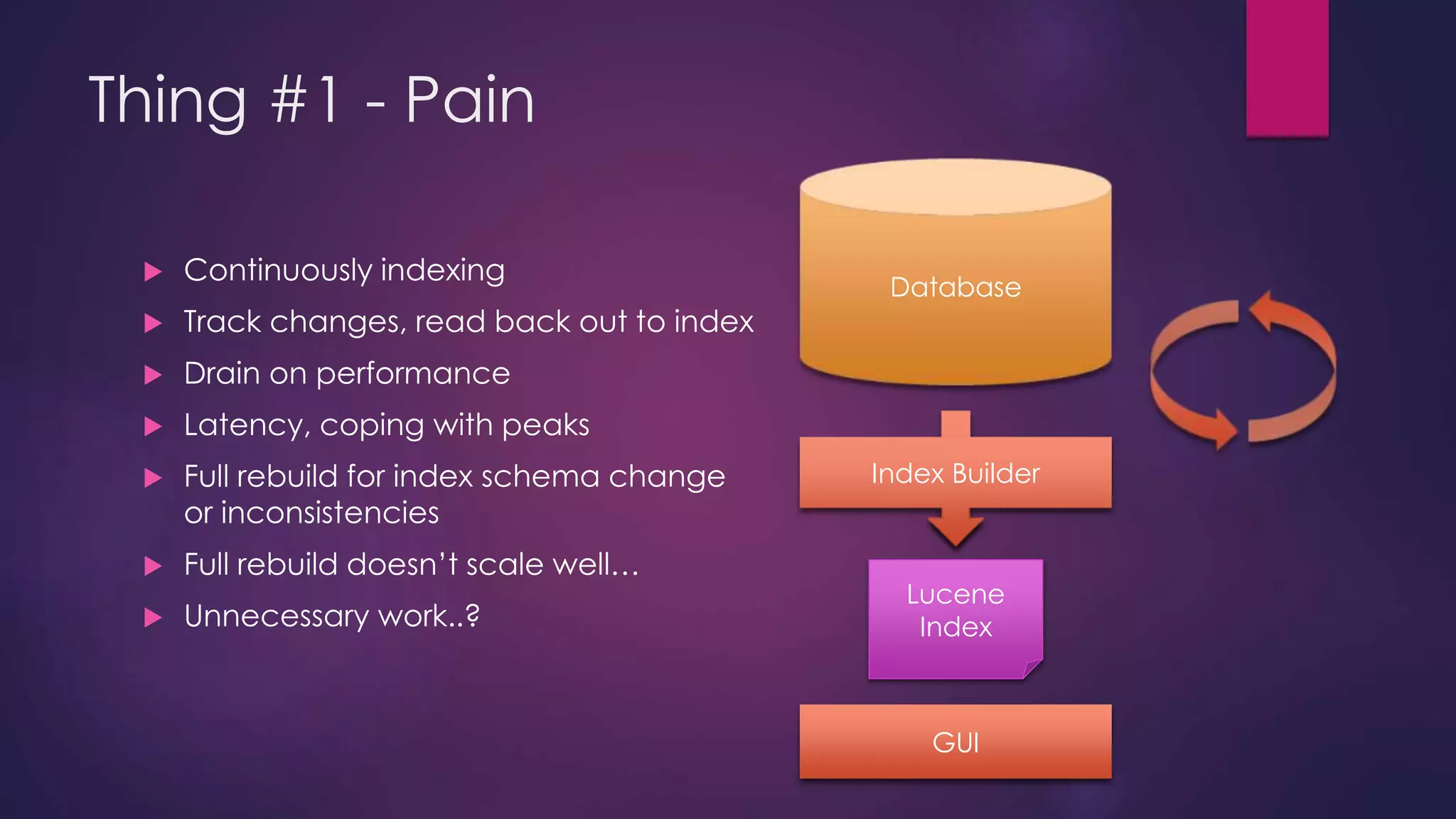
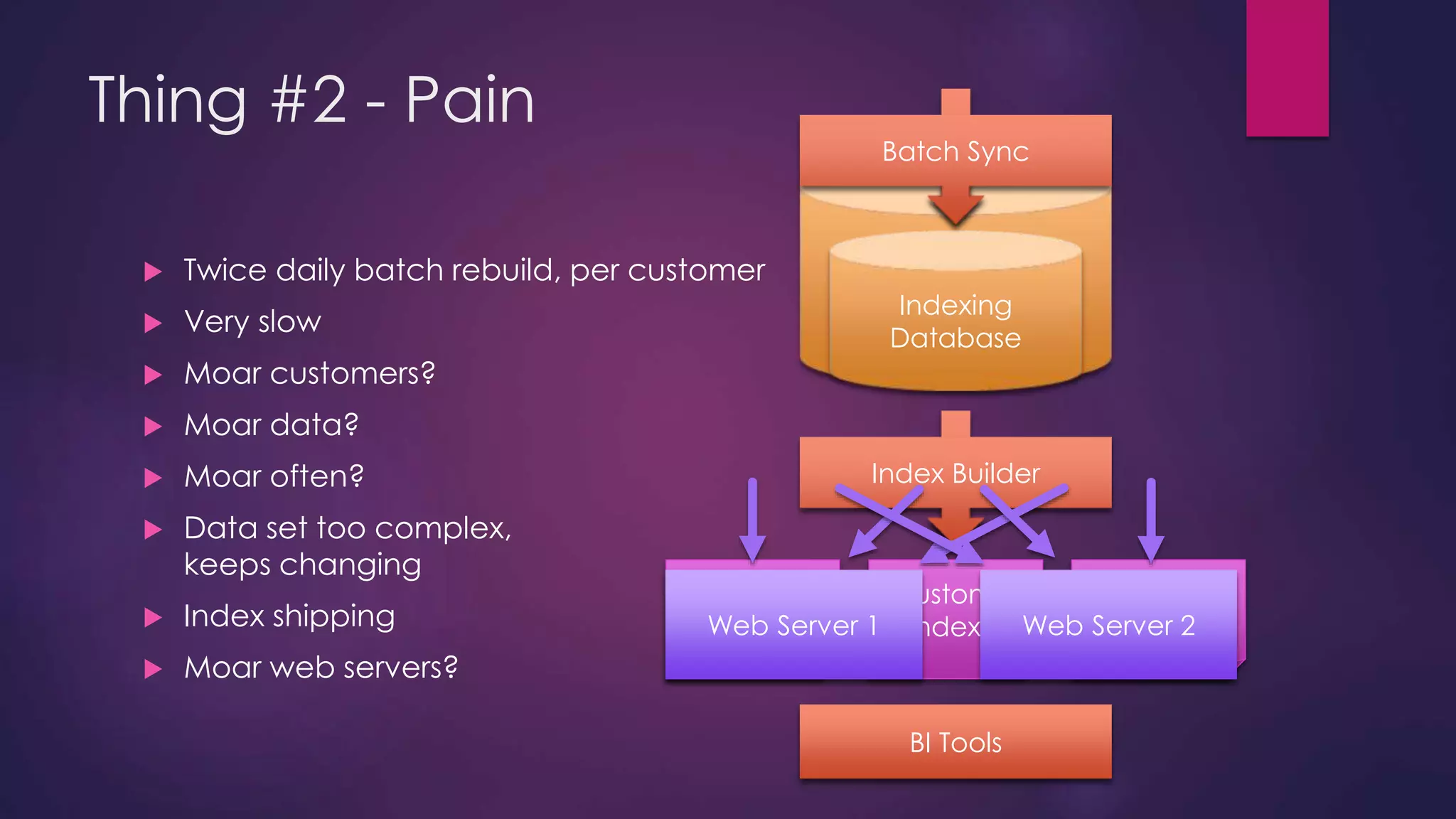
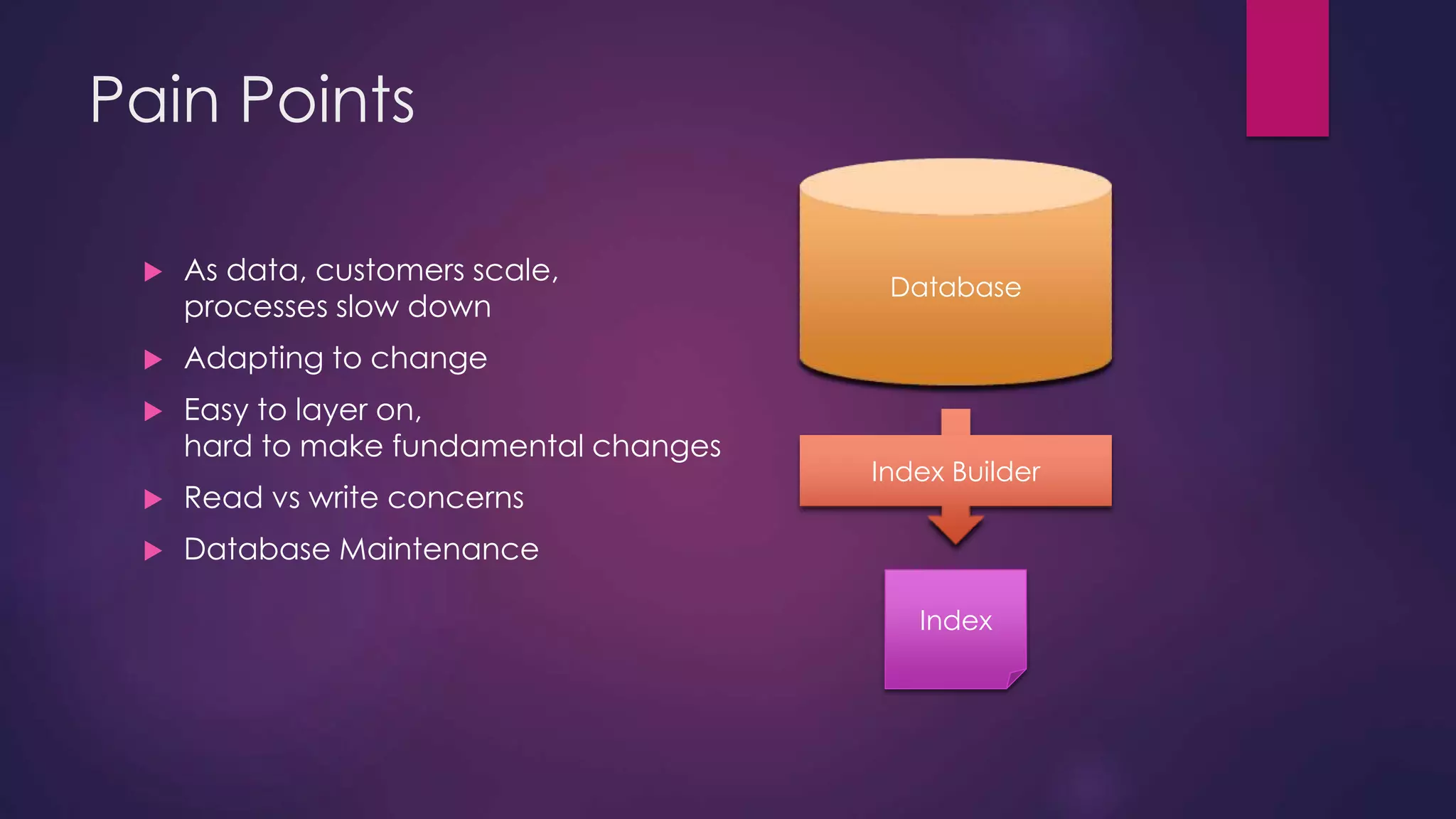
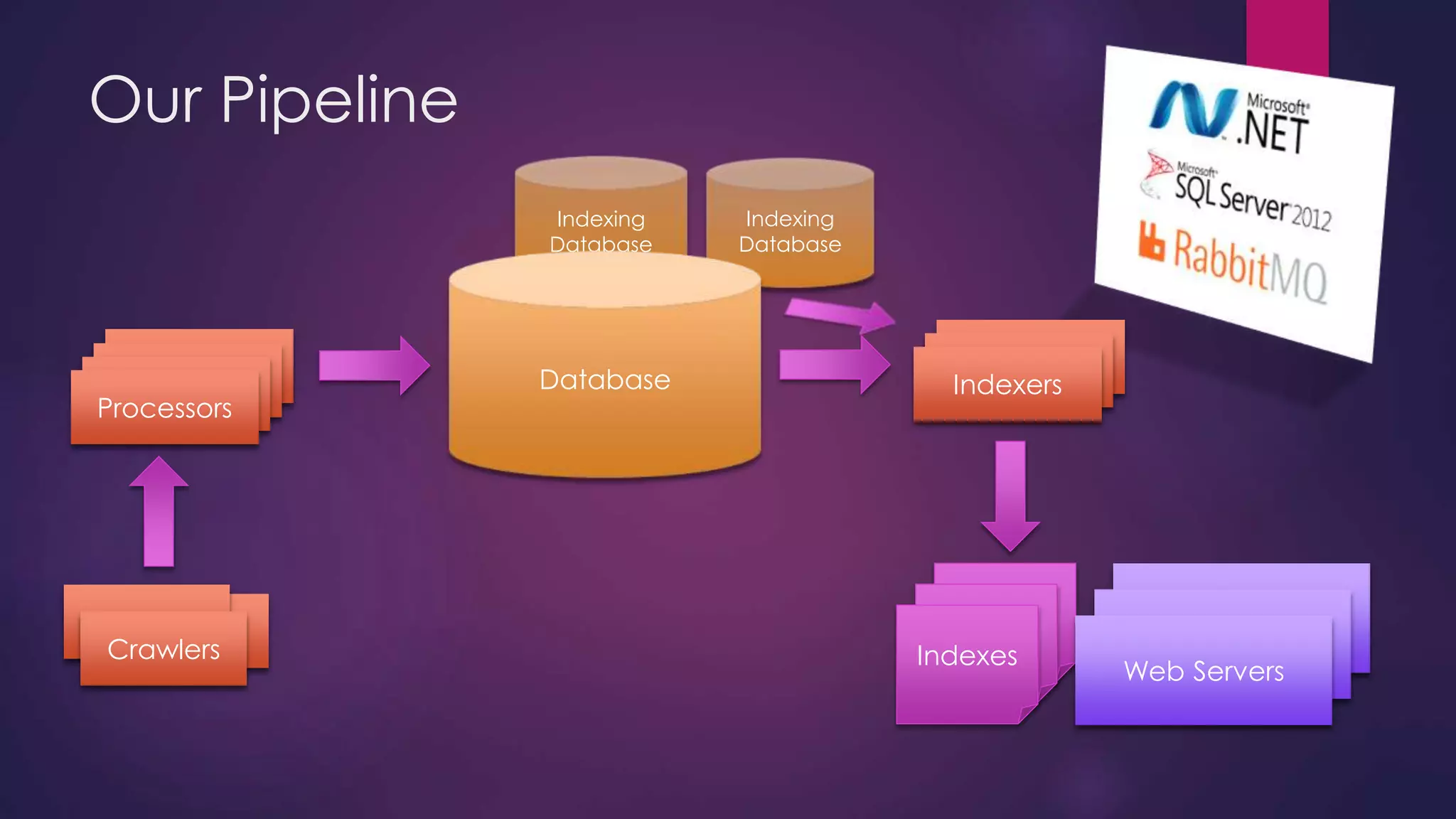
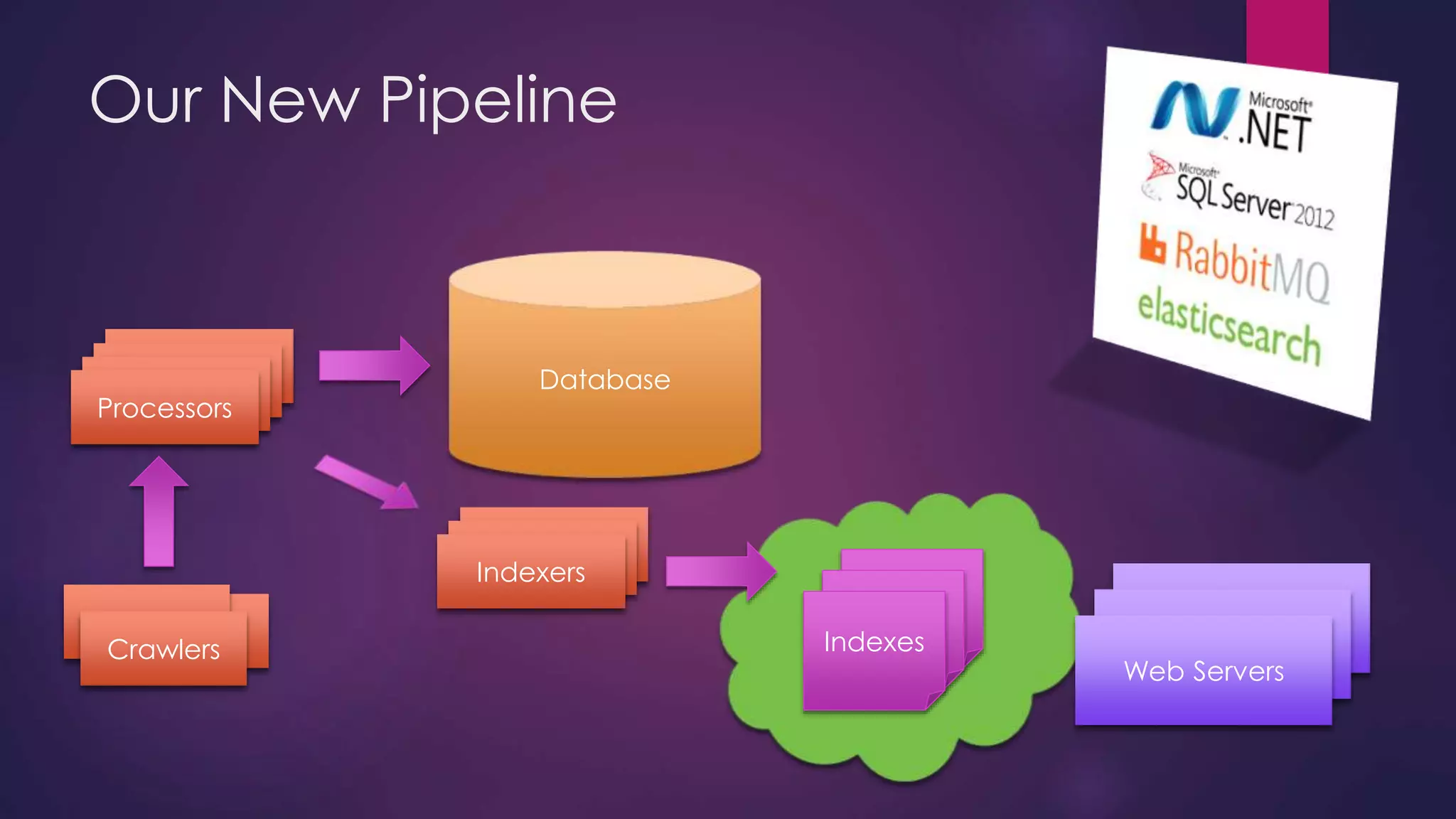
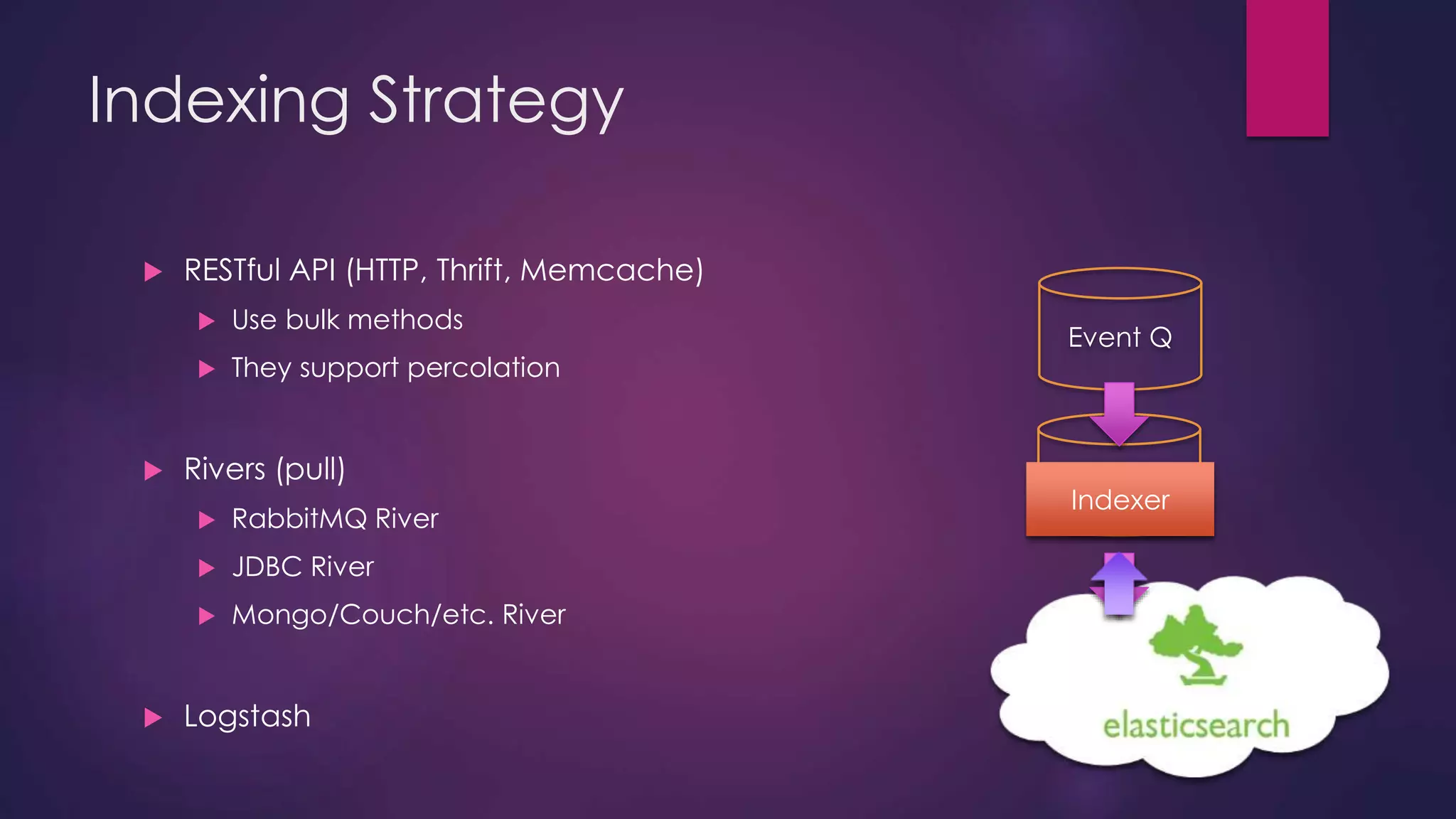
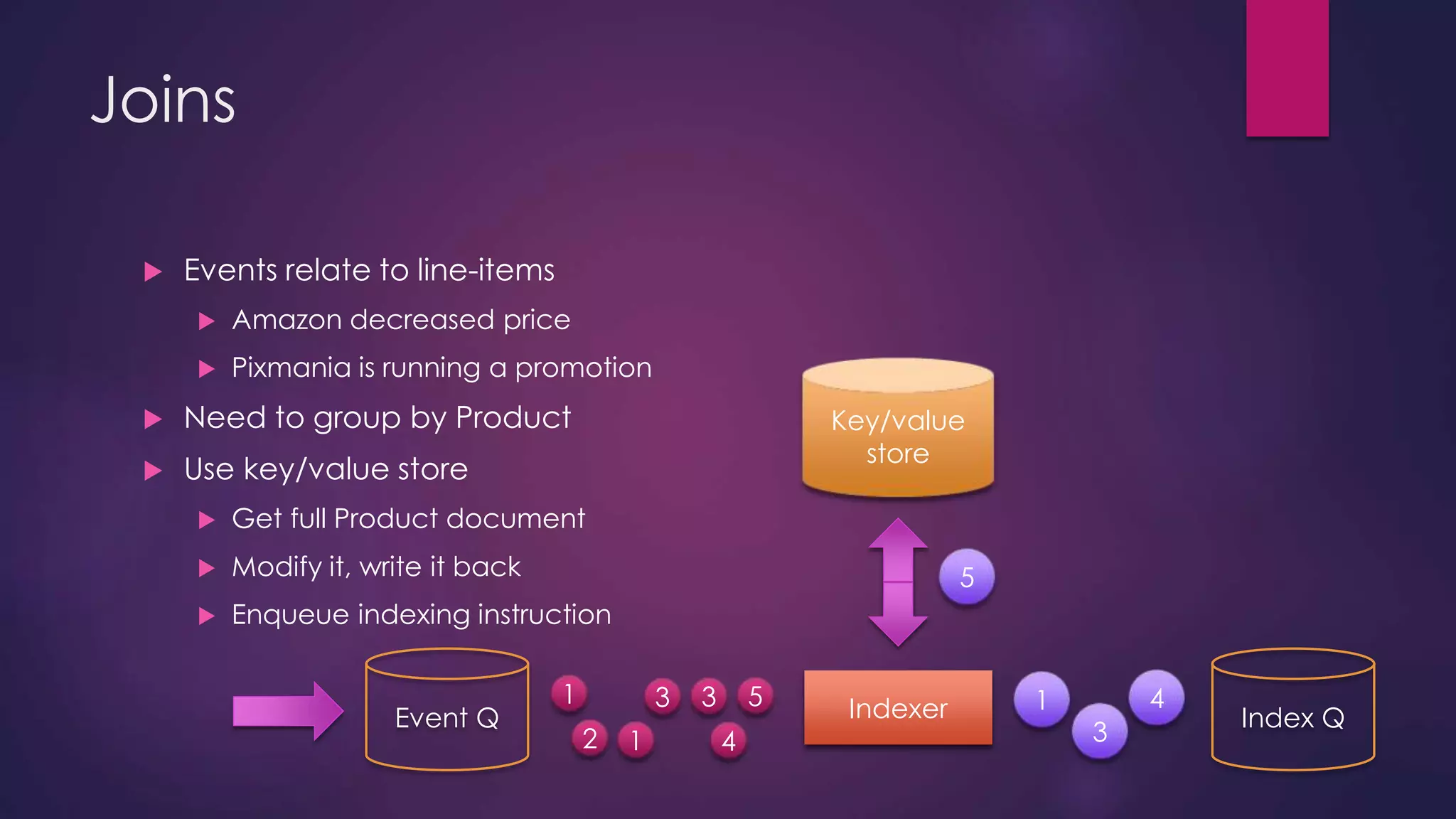
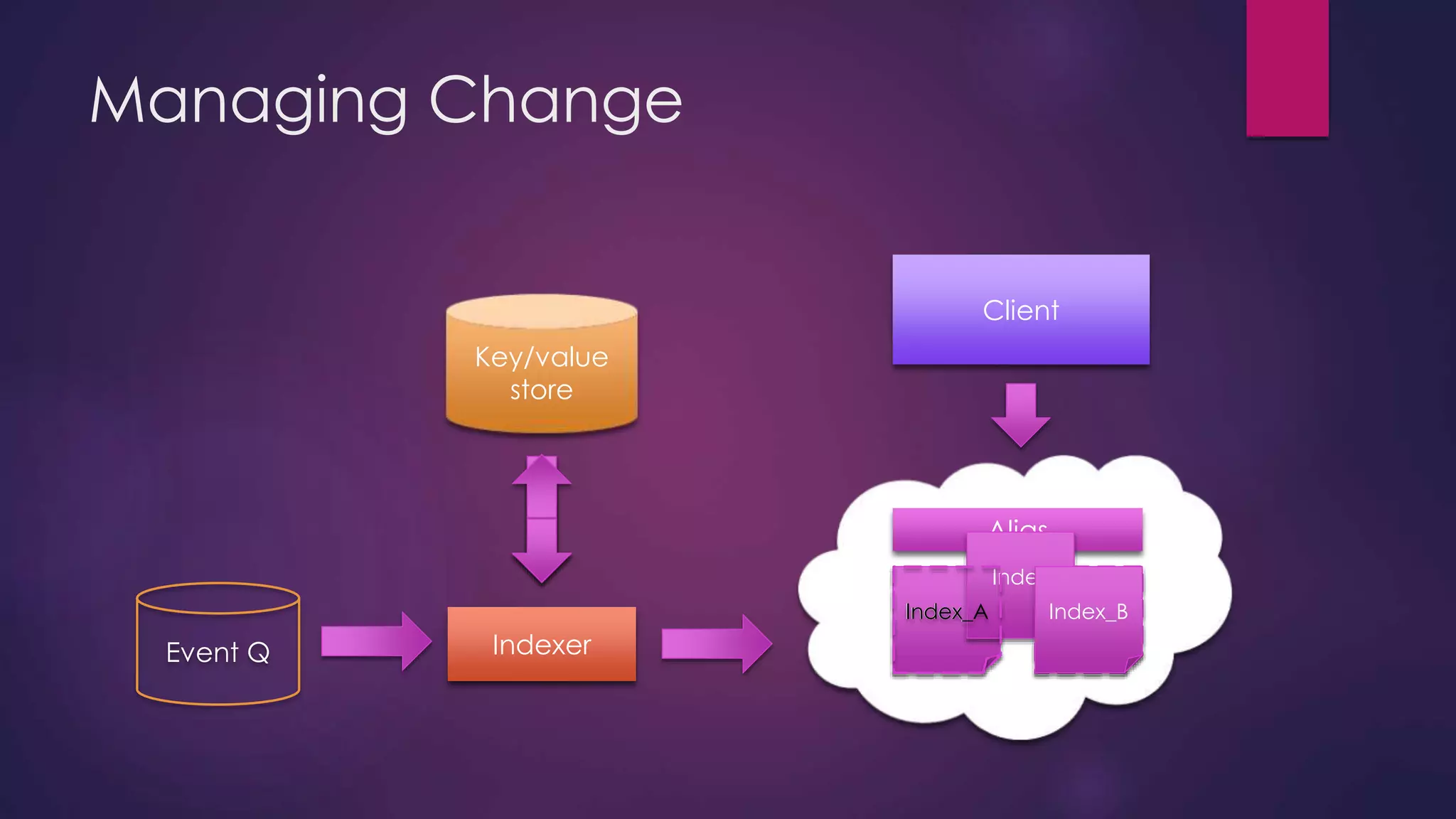
The document discusses leveraging Elasticsearch to provide real-time access to enterprise data, particularly for online pricing intelligence by aggregating and analyzing data from over 500 e-commerce sites. It outlines challenges with indexing performance and scalability, particularly when dealing with frequent changes in data and the volume of information processed. Additionally, it presents a new pipeline strategy using event-driven indexing and RabbitMQ to optimize the data processing workflow.