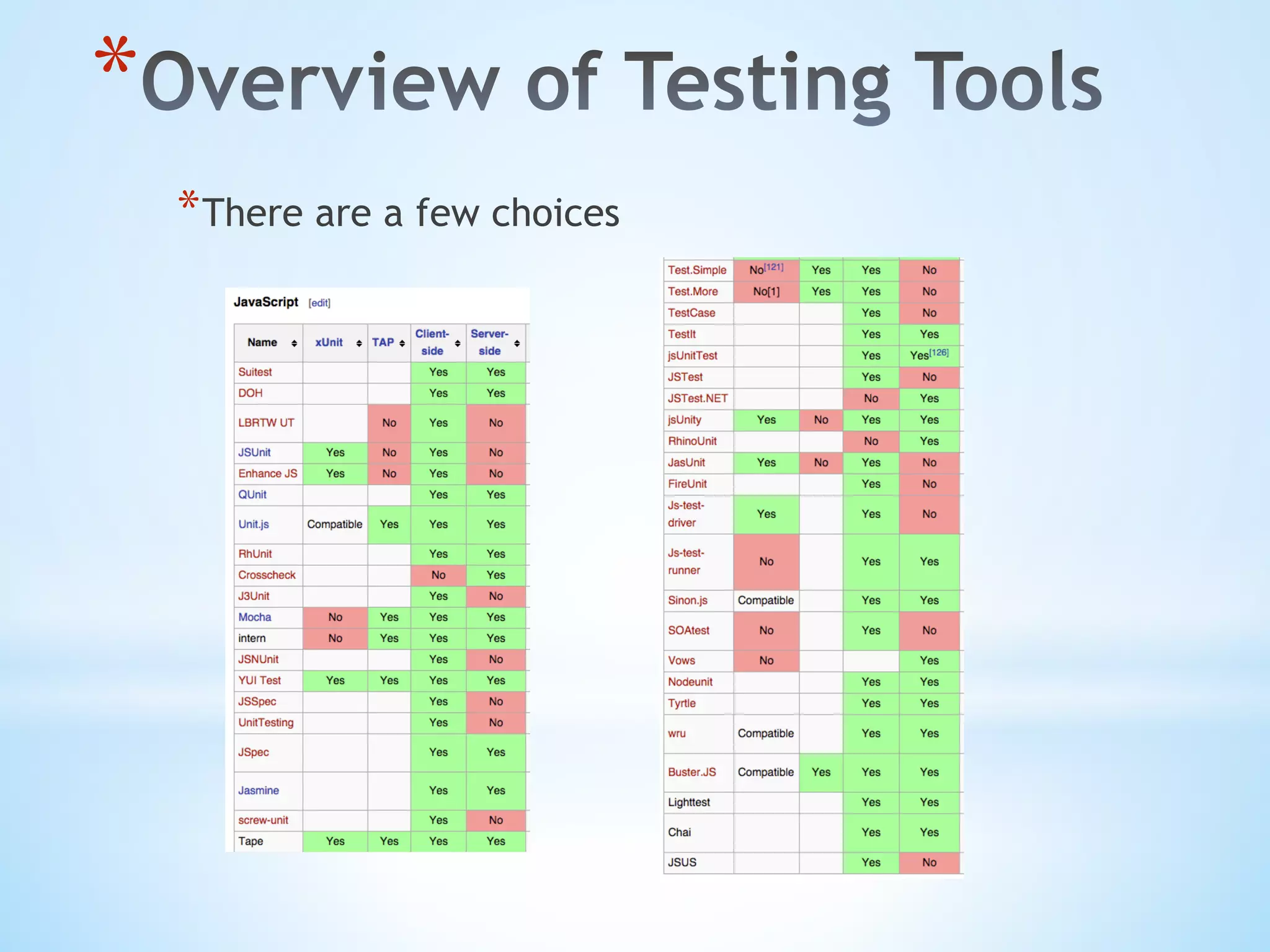
The document provides an overview of JavaScript testing, including testing environments, tools like Jasmine, Mocha, and QUnit, and methodologies such as Test Driven Development (TDD) and Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It emphasizes the importance of writing testable code and organizing tests effectively, alongside practical installations and setups for testing frameworks. Additionally, it highlights common types of tests and best practices to enhance code quality and maintainability.




































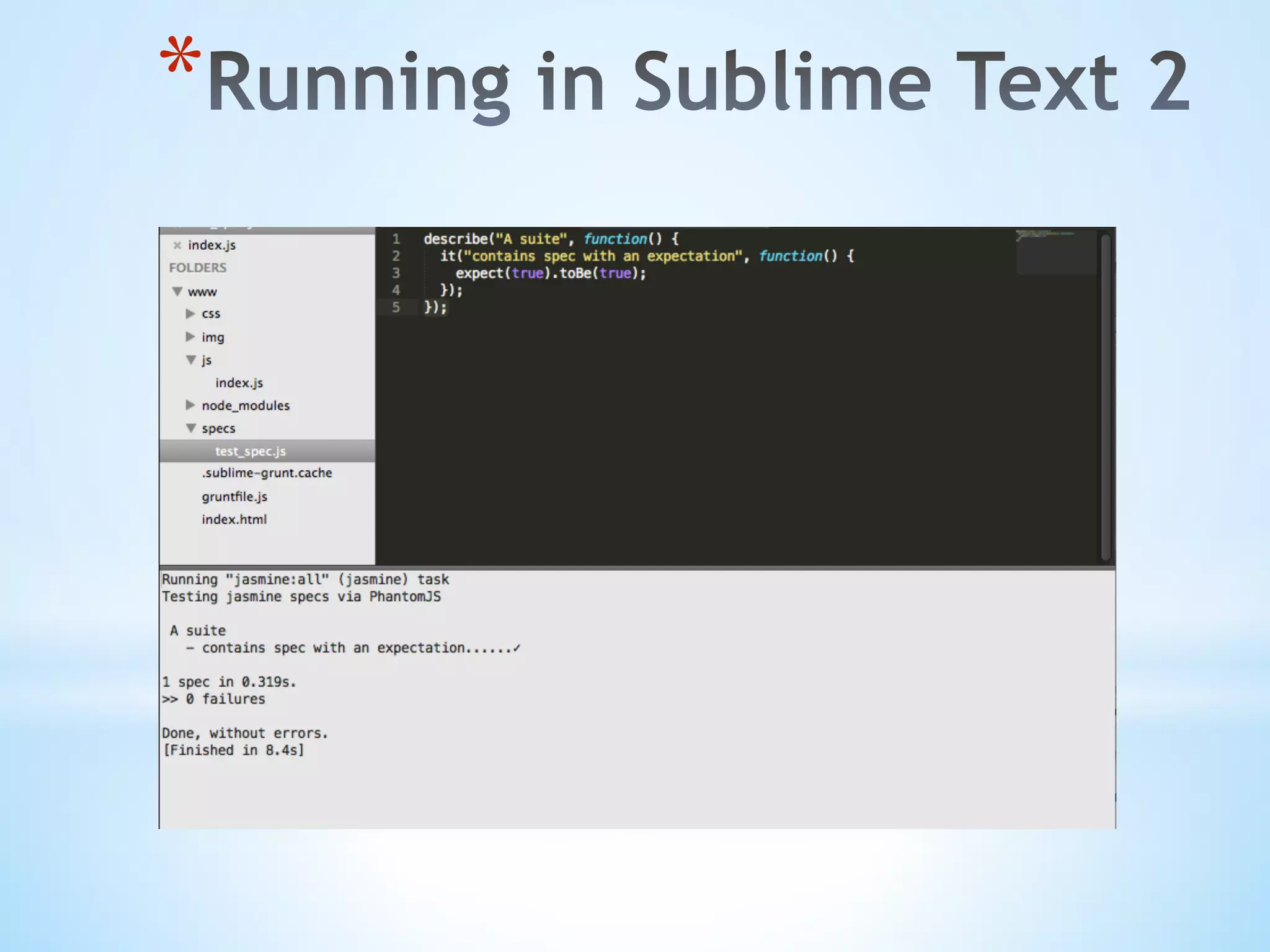
![* Edit Jasmine.json to update Locations for Spec Files and Helper Files { "spec_dir": "spec", "spec_files": [ "**/*[sS]pec.js" ], "helpers": [ "helpers/**/*.js" ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testable-jsv2-150516145852-lva1-app6891/75/How-do-I-write-Testable-Javascript-46-2048.jpg)



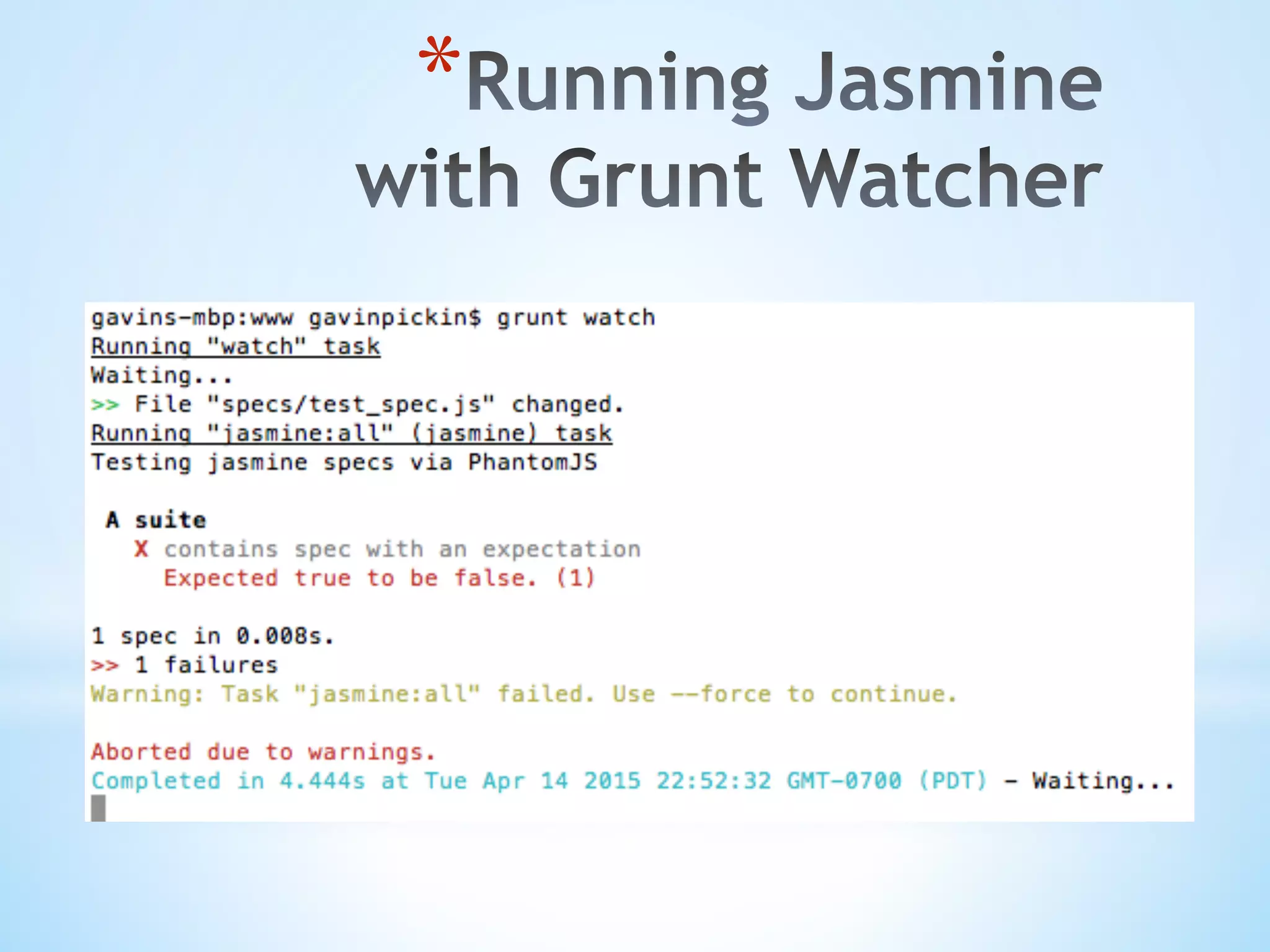
![* // gruntfile.js - https://gist.github.com/gpickin/1e1e7902d1d3676d23c5 module.exports = function (grunt) { grunt.initConfig({ pkg: grunt.file.readJSON('node_modules/grunt/package.json'), jasmine: { all: { src: ['js/*.js' ], options: { //'vendor': ['path/to/vendor/libs/*.js'], 'specs': ['specs/*.js' ] } } },](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testable-jsv2-150516145852-lva1-app6891/75/How-do-I-write-Testable-Javascript-50-2048.jpg)
![* // gruntfile.js part 2 watch: { js: { files: [ 'js/*.js', 'specs/*.js', ], tasks: ['jasmine:all'] } } });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testable-jsv2-150516145852-lva1-app6891/75/How-do-I-write-Testable-Javascript-51-2048.jpg)