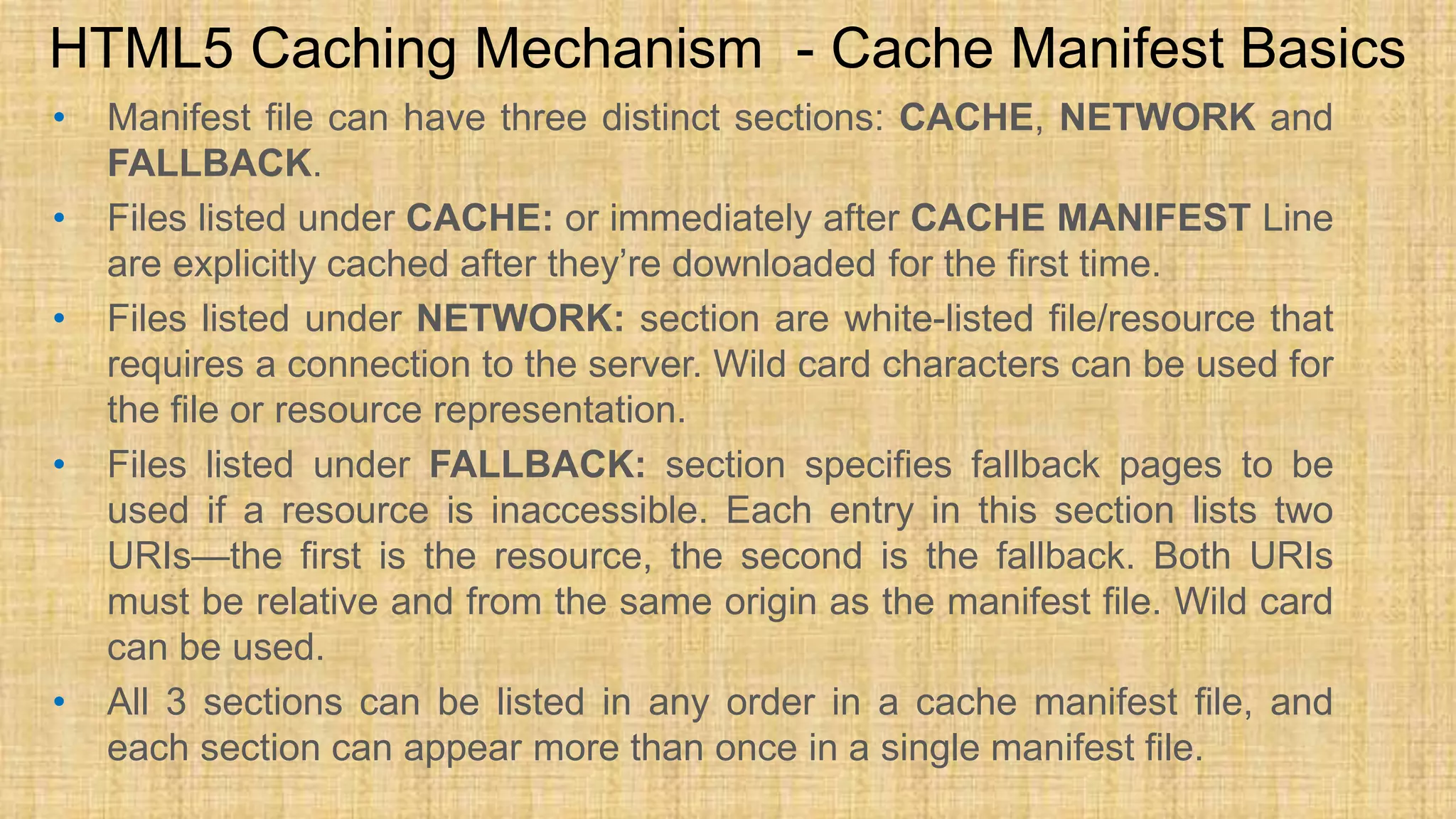
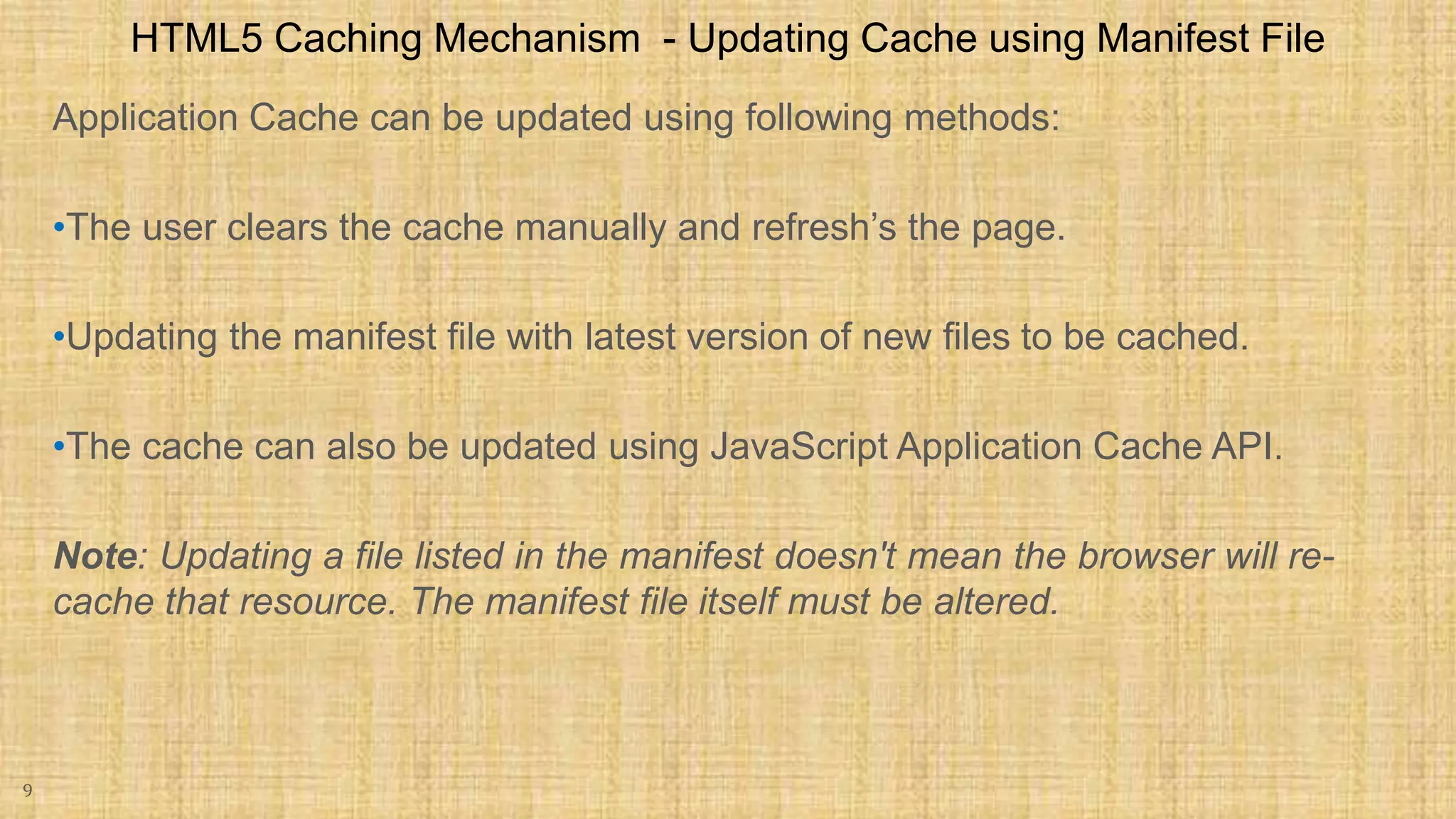
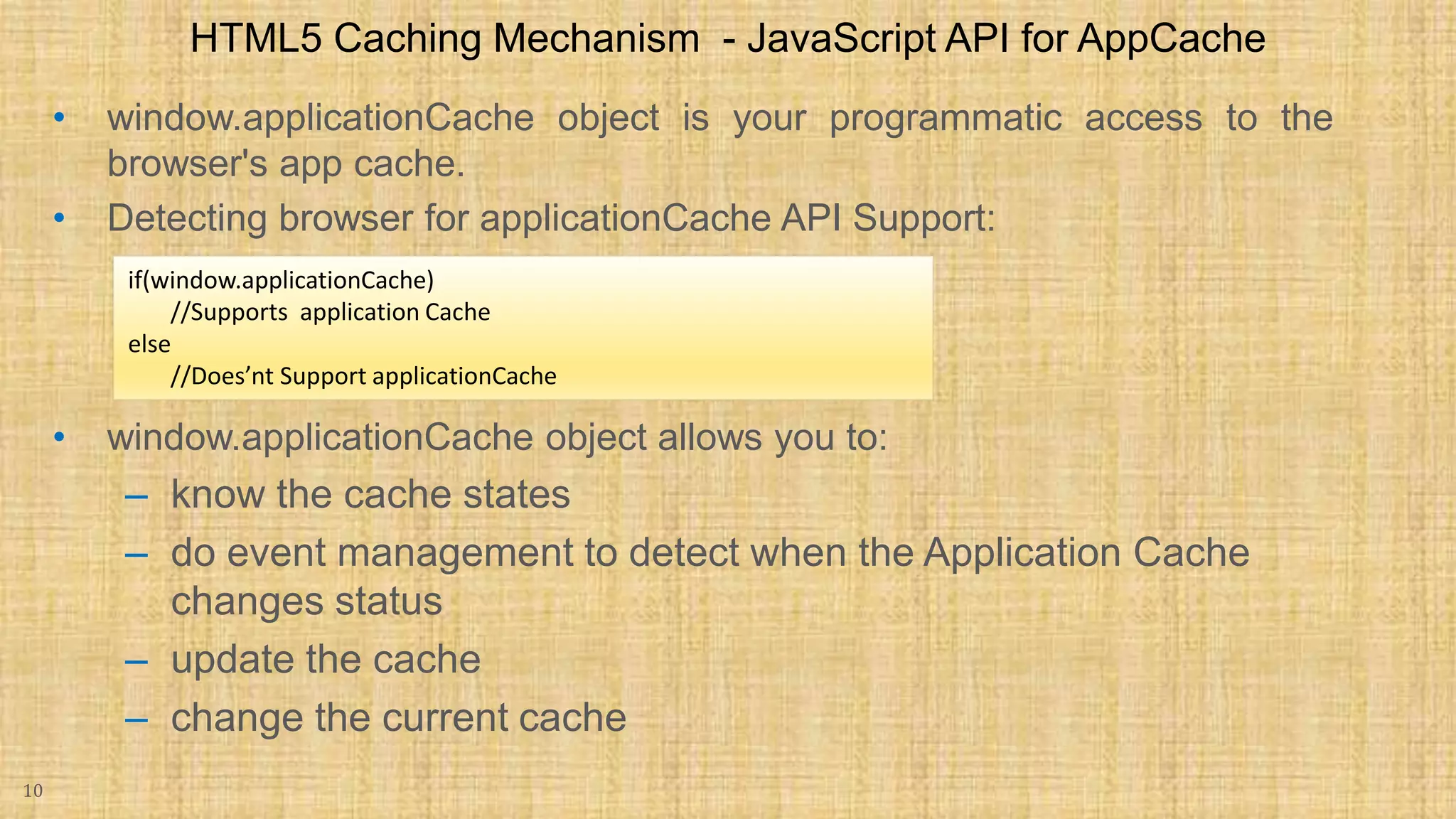
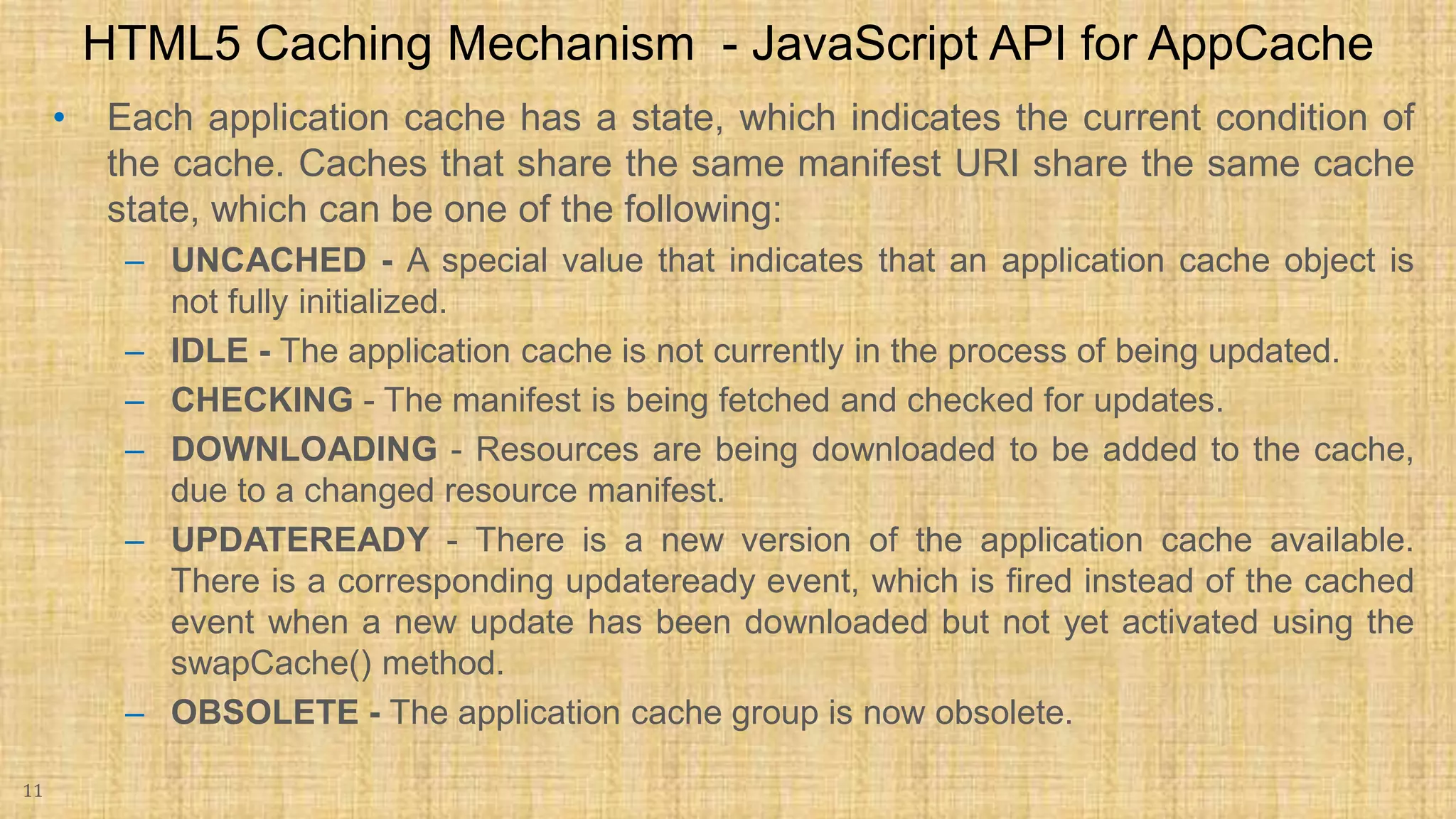
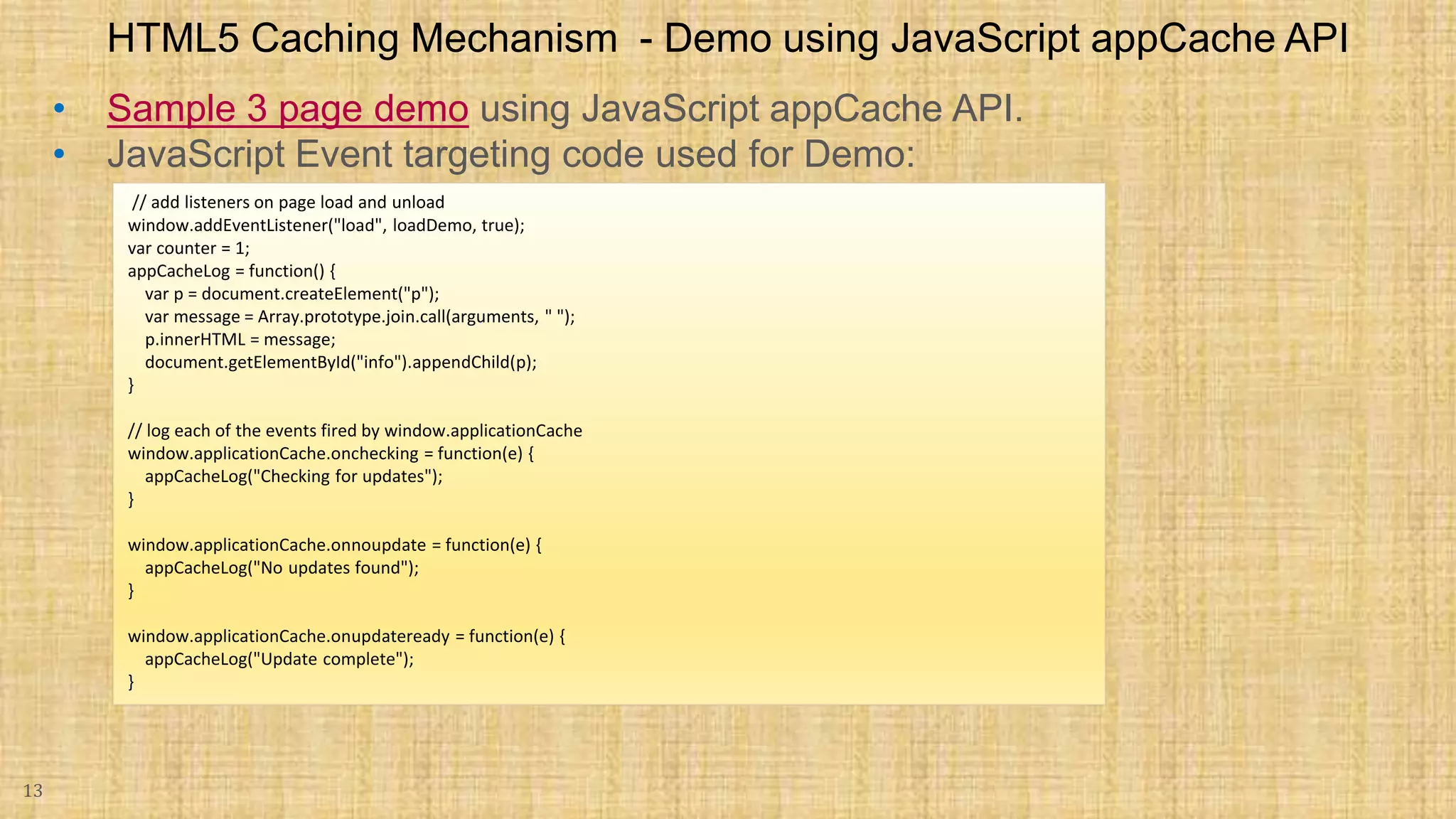
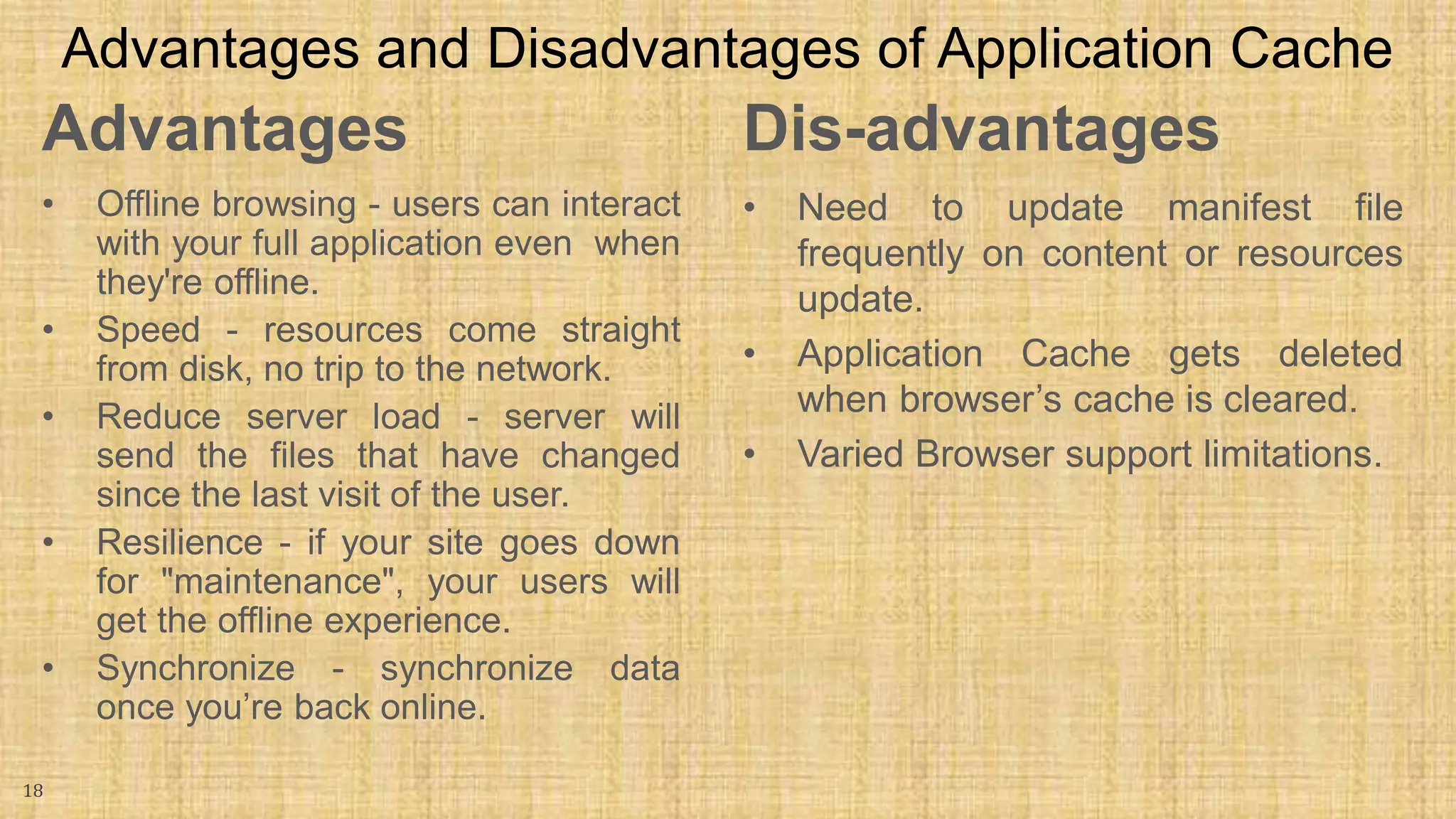
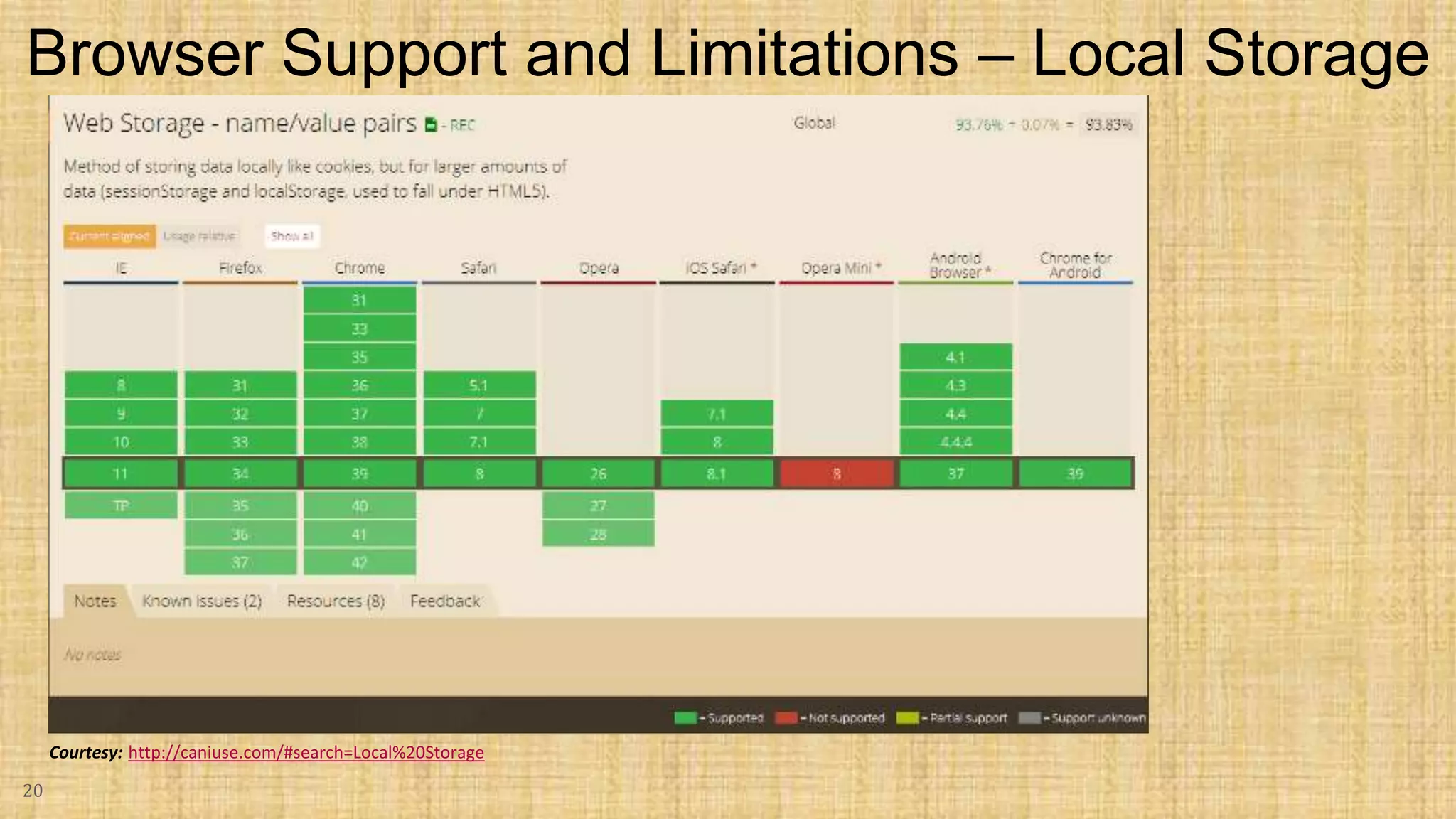
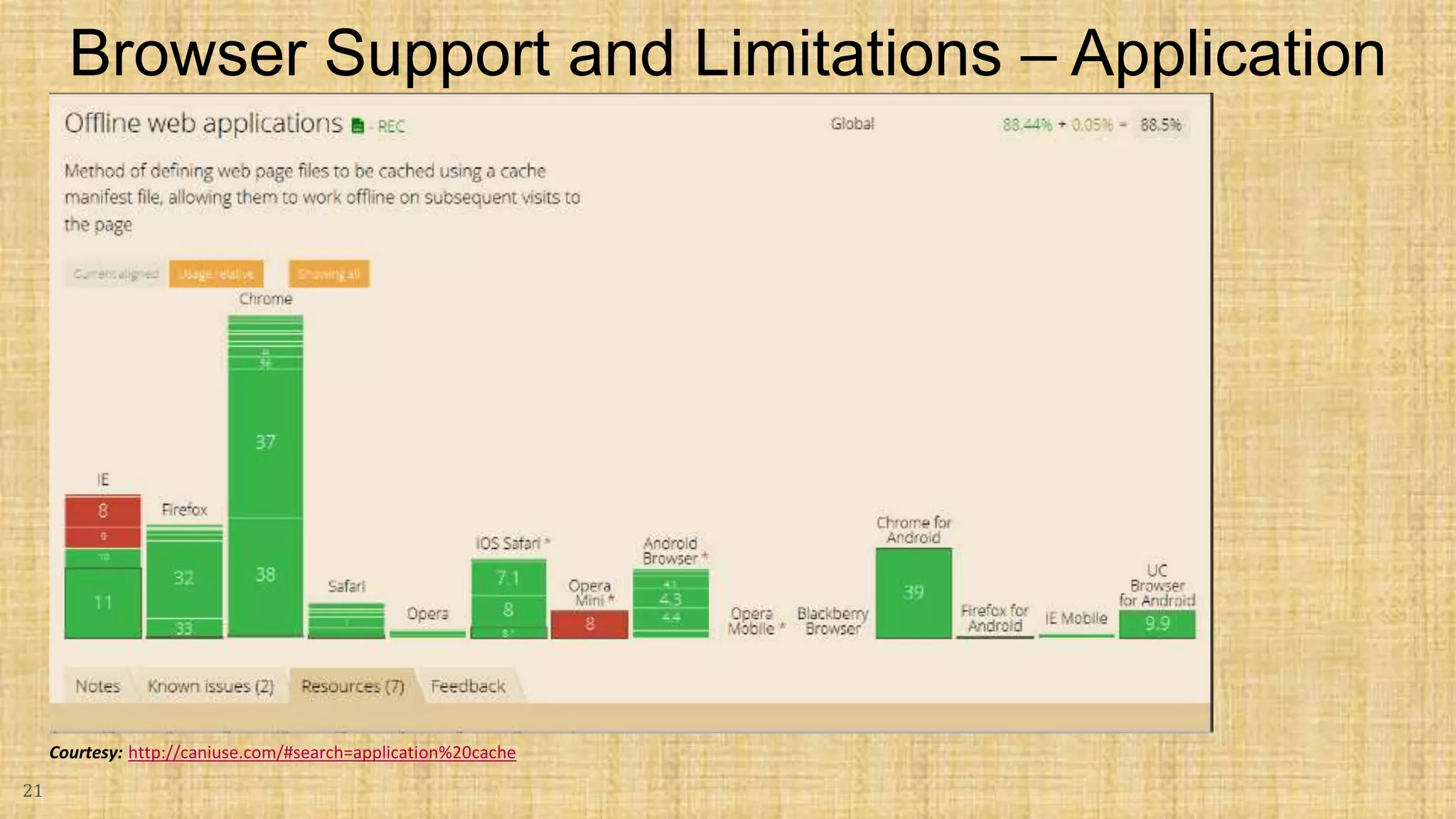
The document discusses HTML5 caching mechanisms and local storage. It provides information on application cache, which allows websites and web apps to be cached and accessed offline. Application cache uses a cache manifest file to specify files for caching. It also covers the JavaScript API for application cache and demonstrates how to detect cache updates and swap caches. The document also discusses HTML5 local storage objects (localStorage and sessionStorage) which can be used to store data on the client side in a web browser.