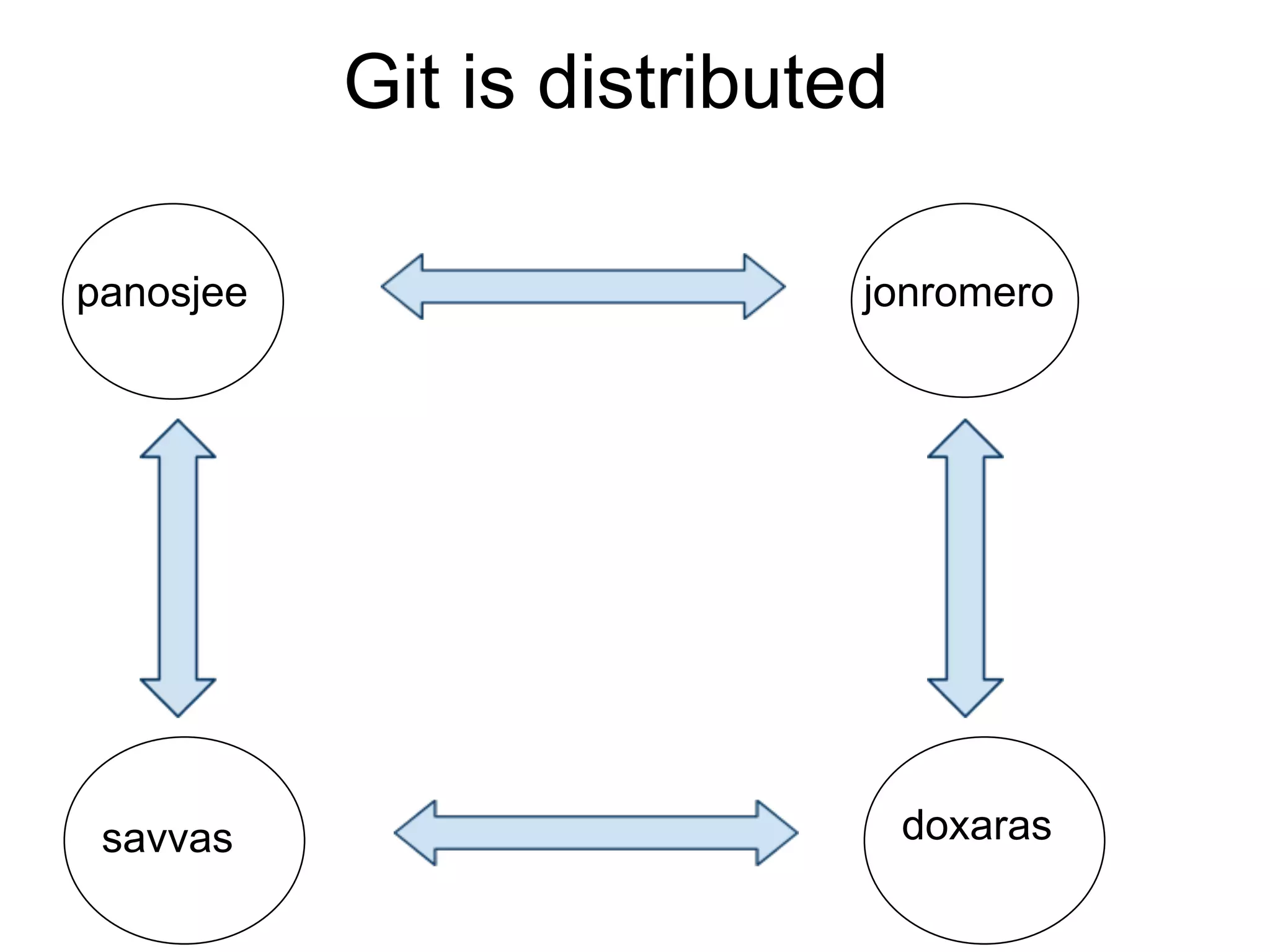
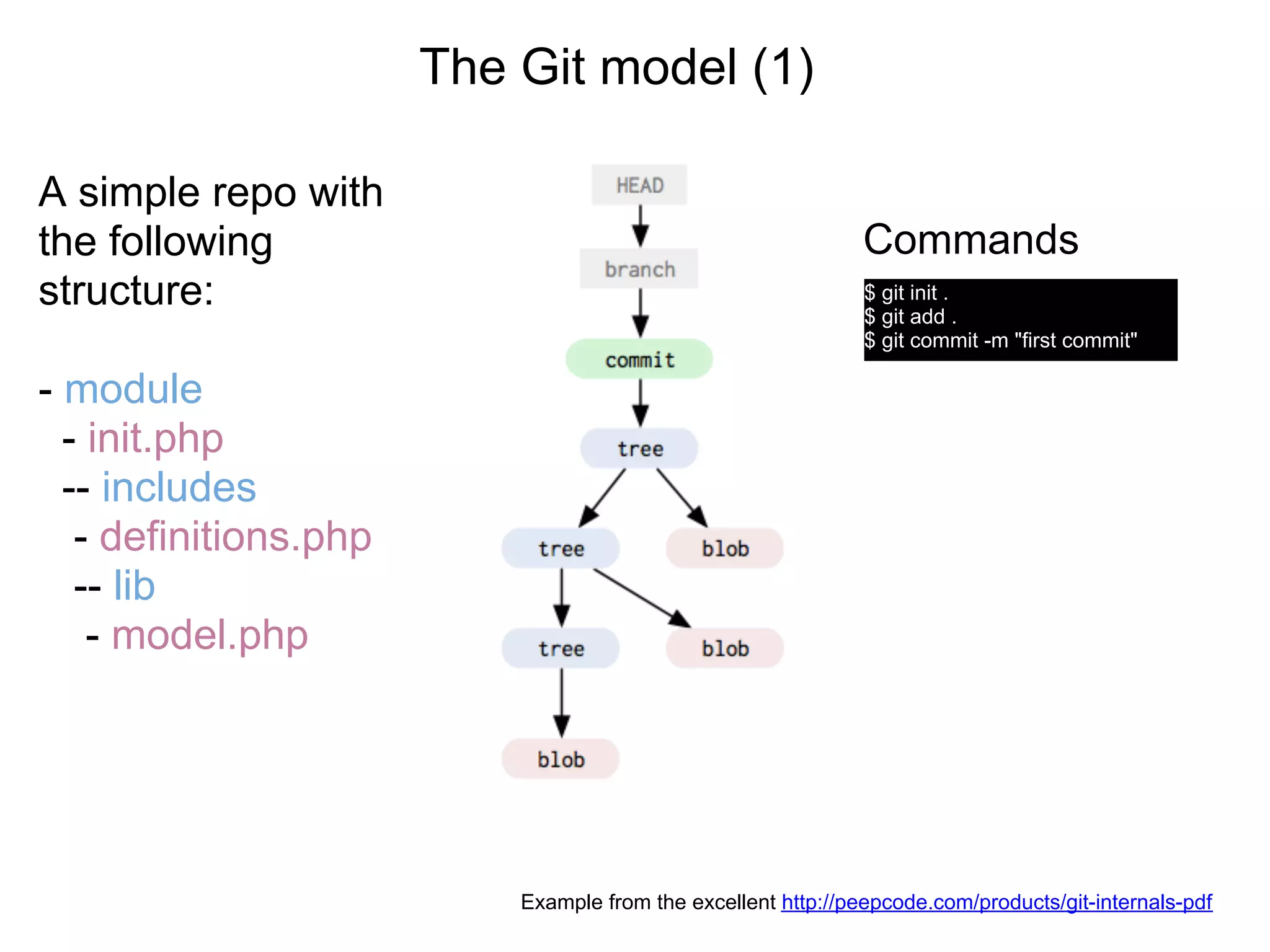
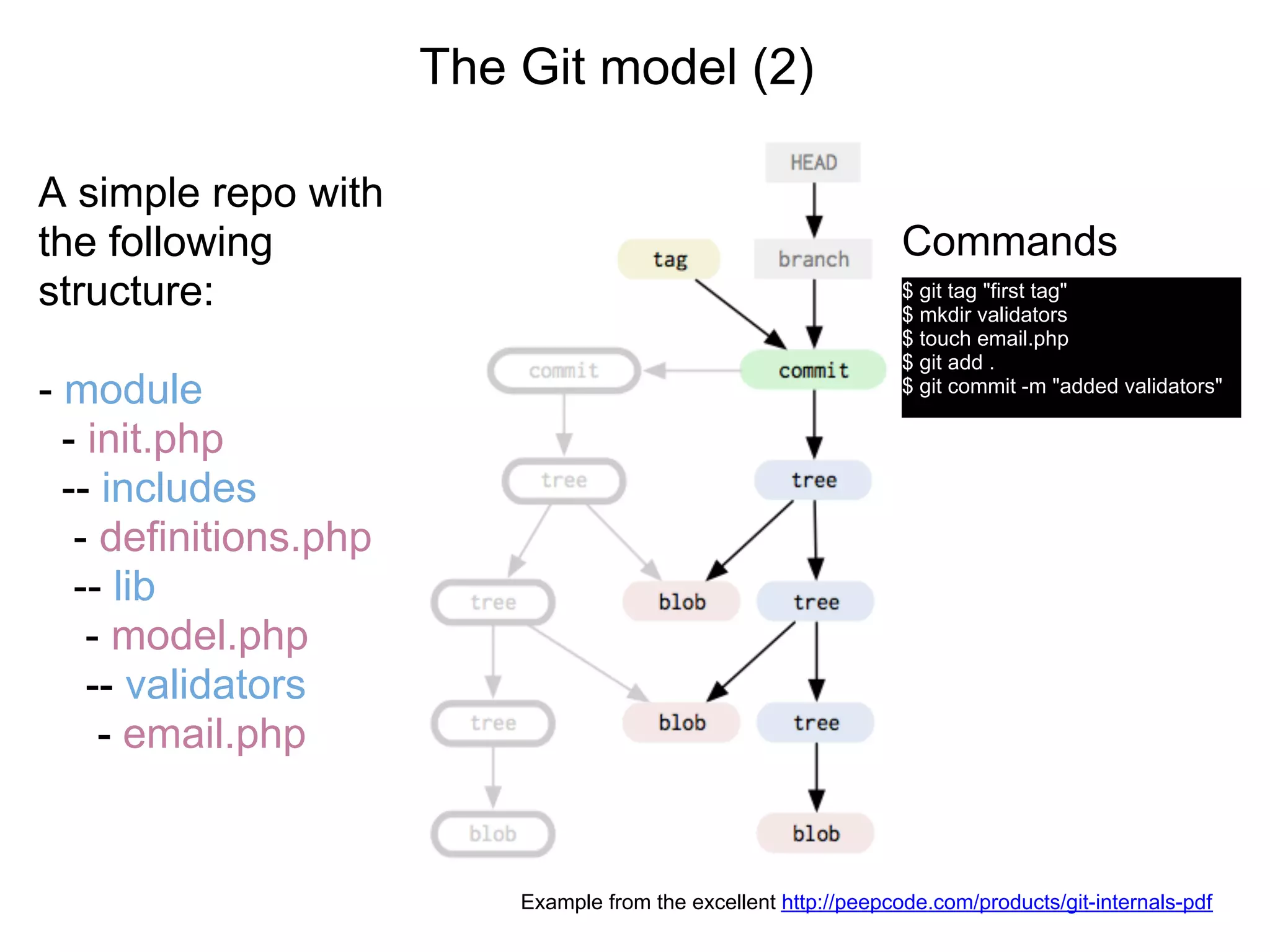
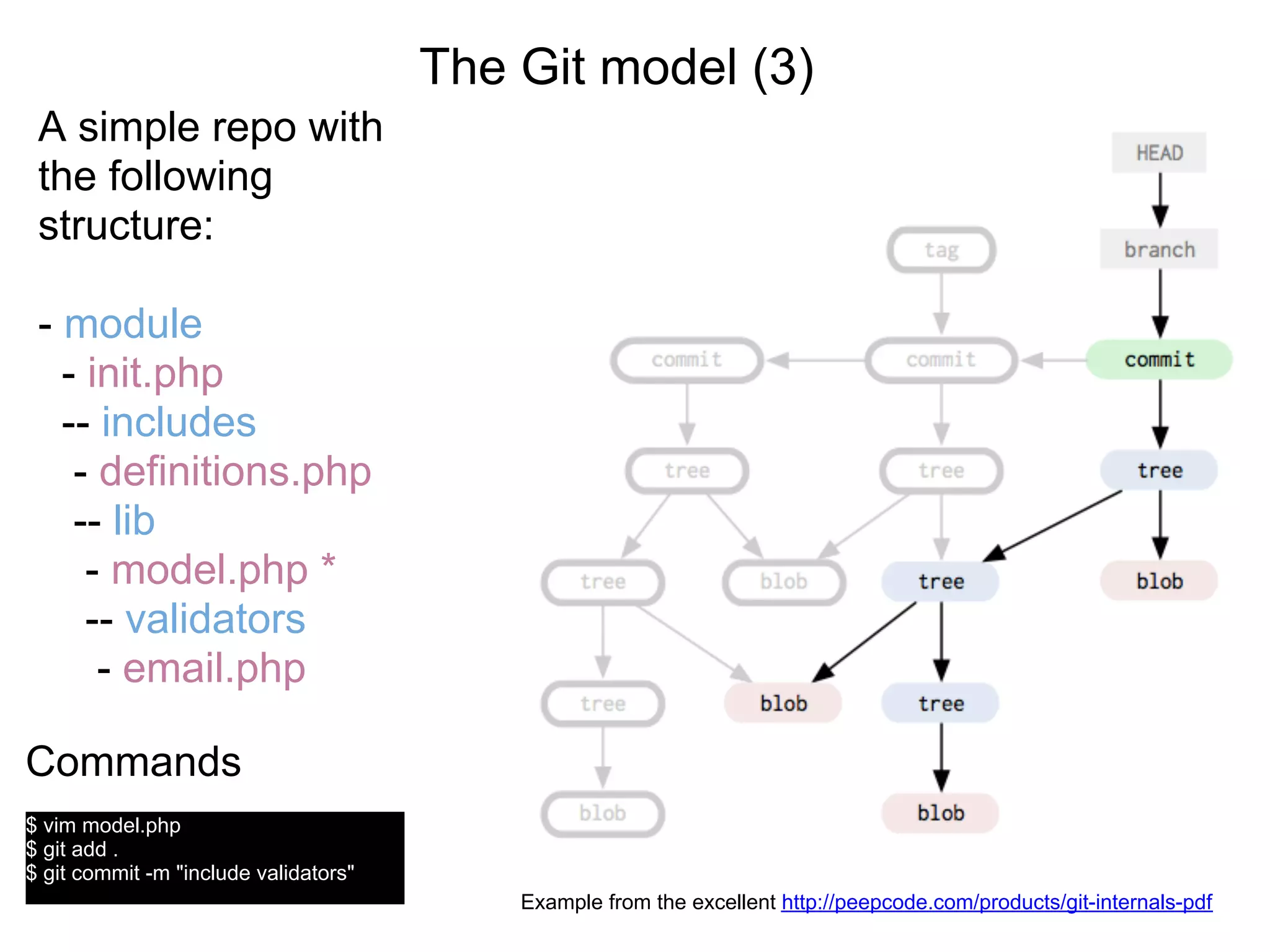
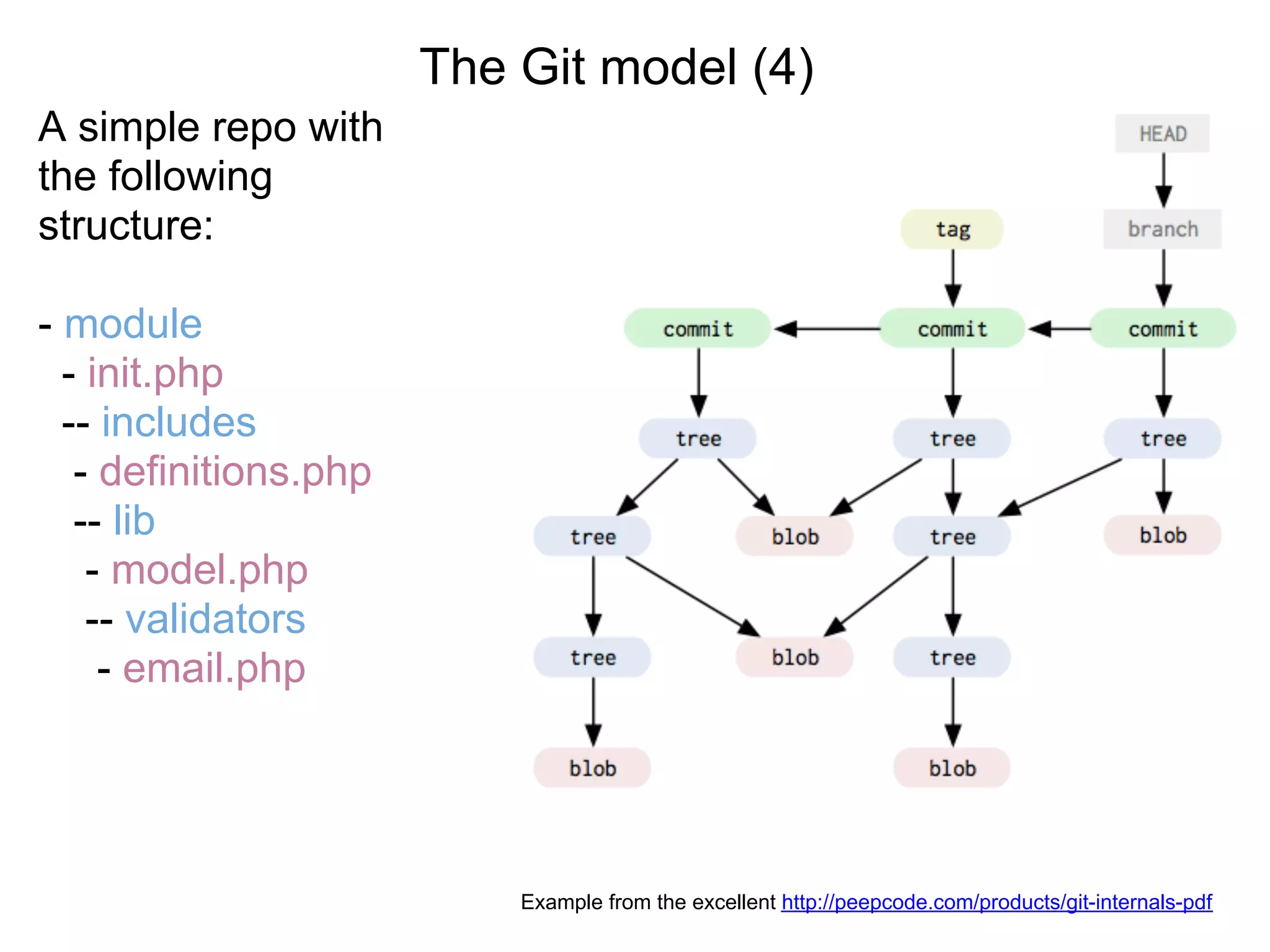
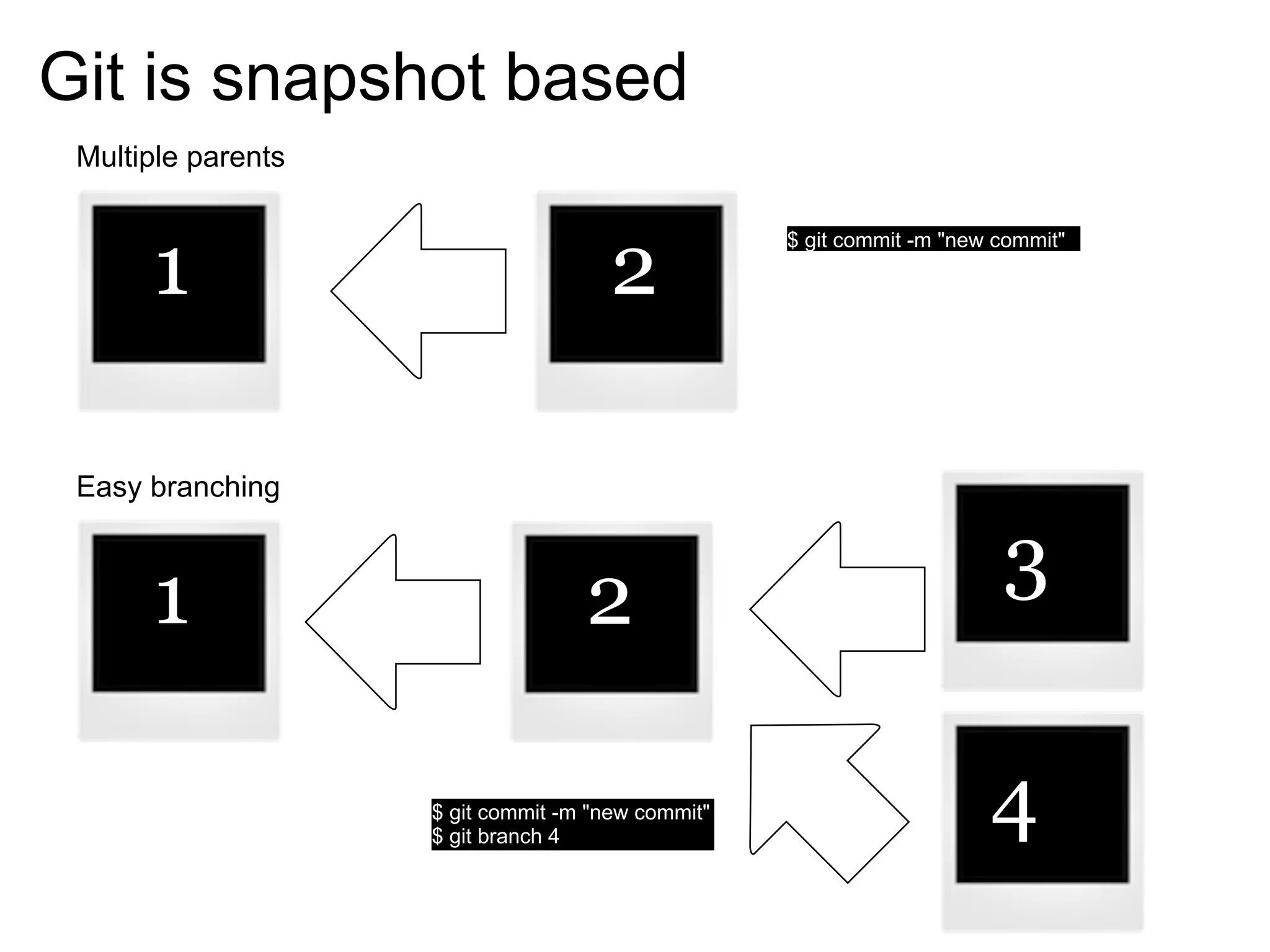
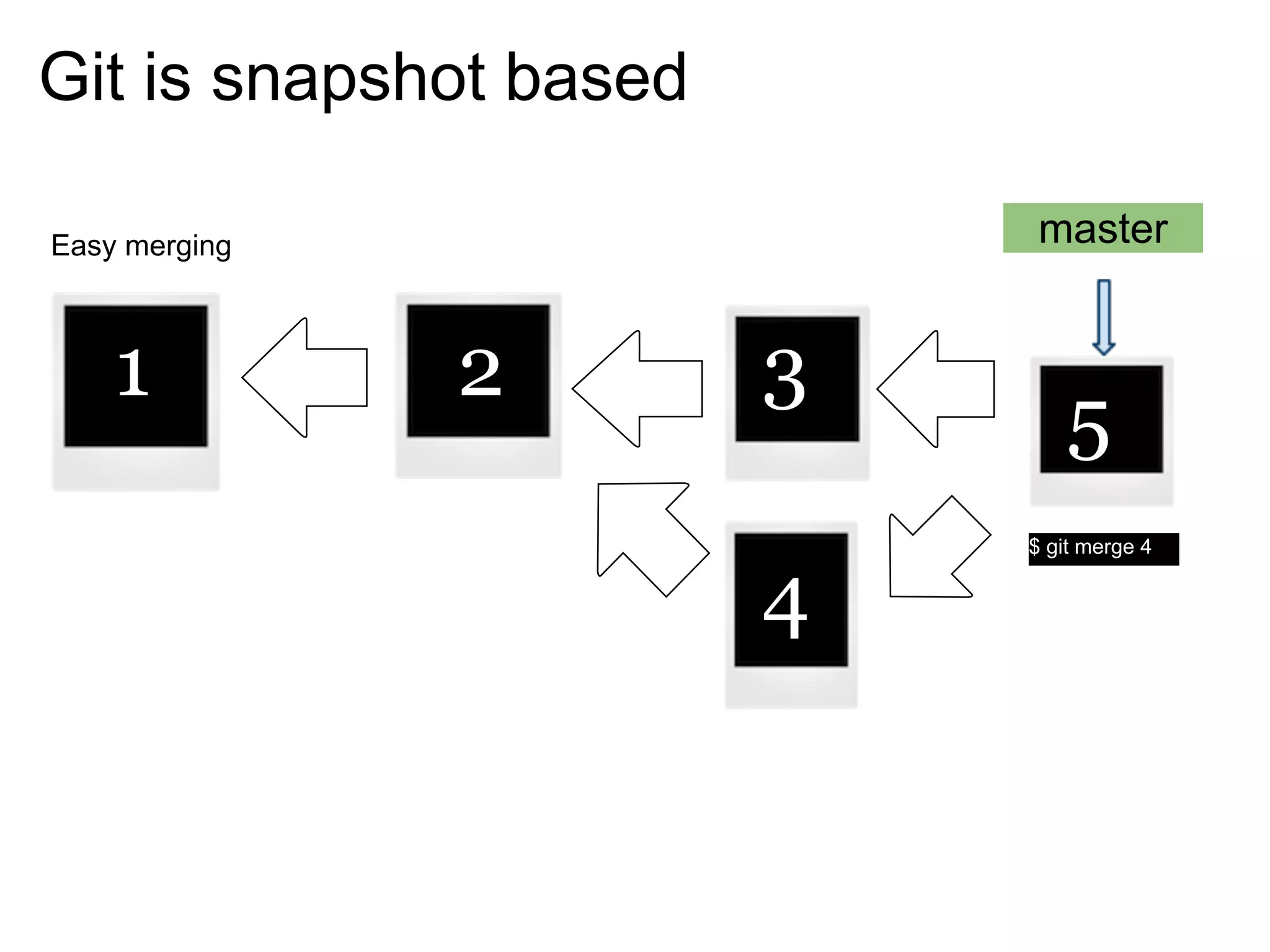
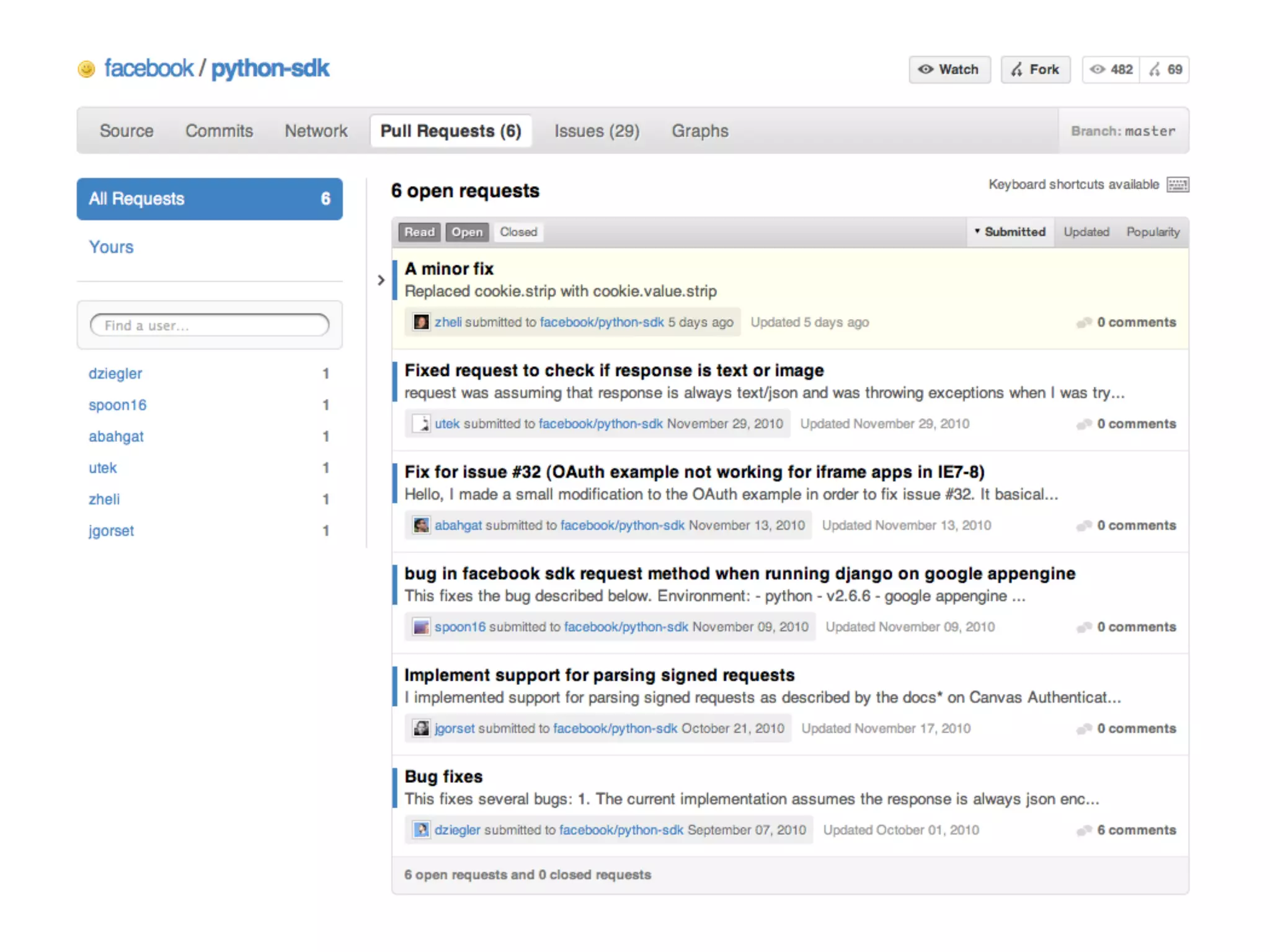
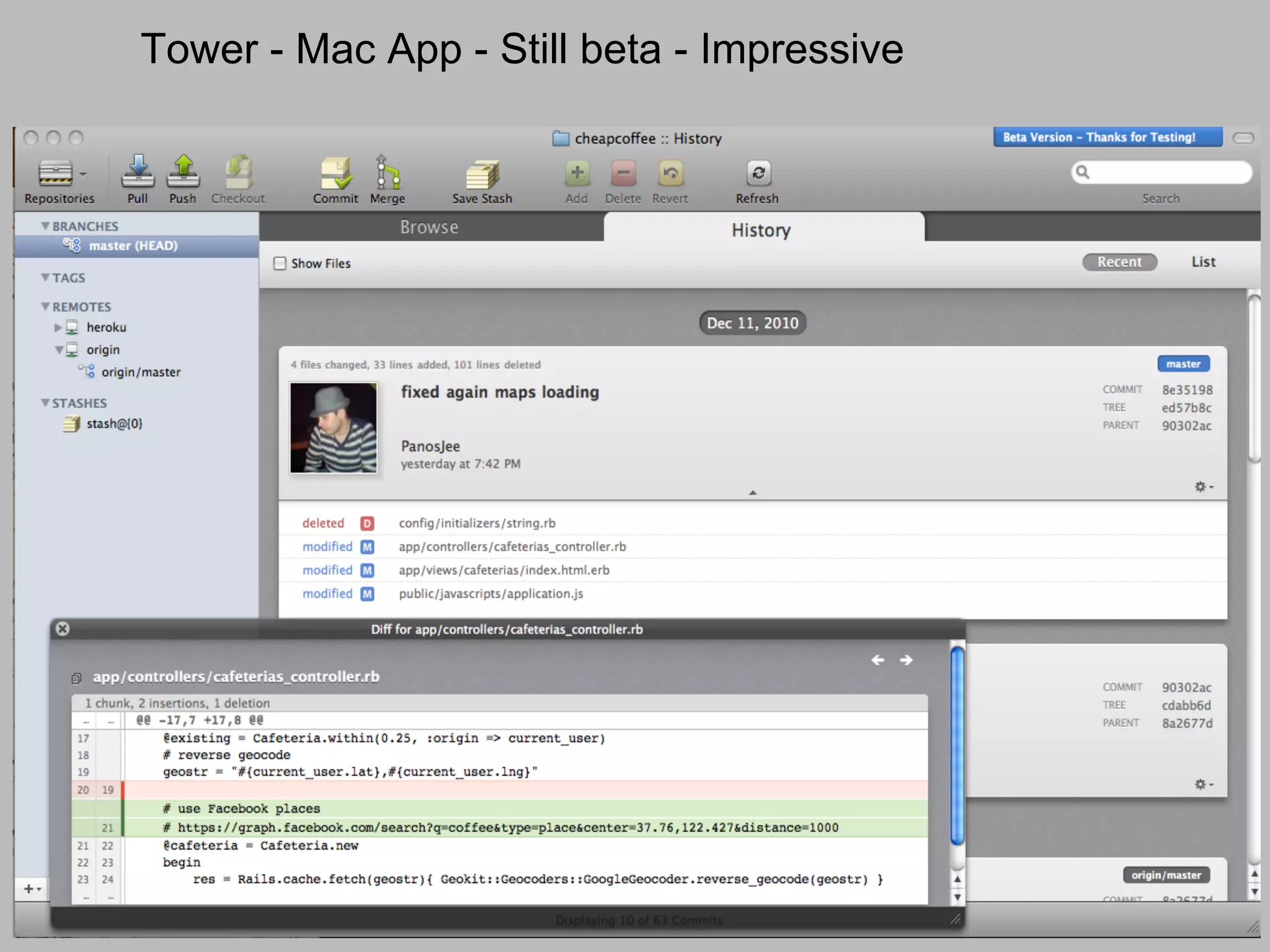
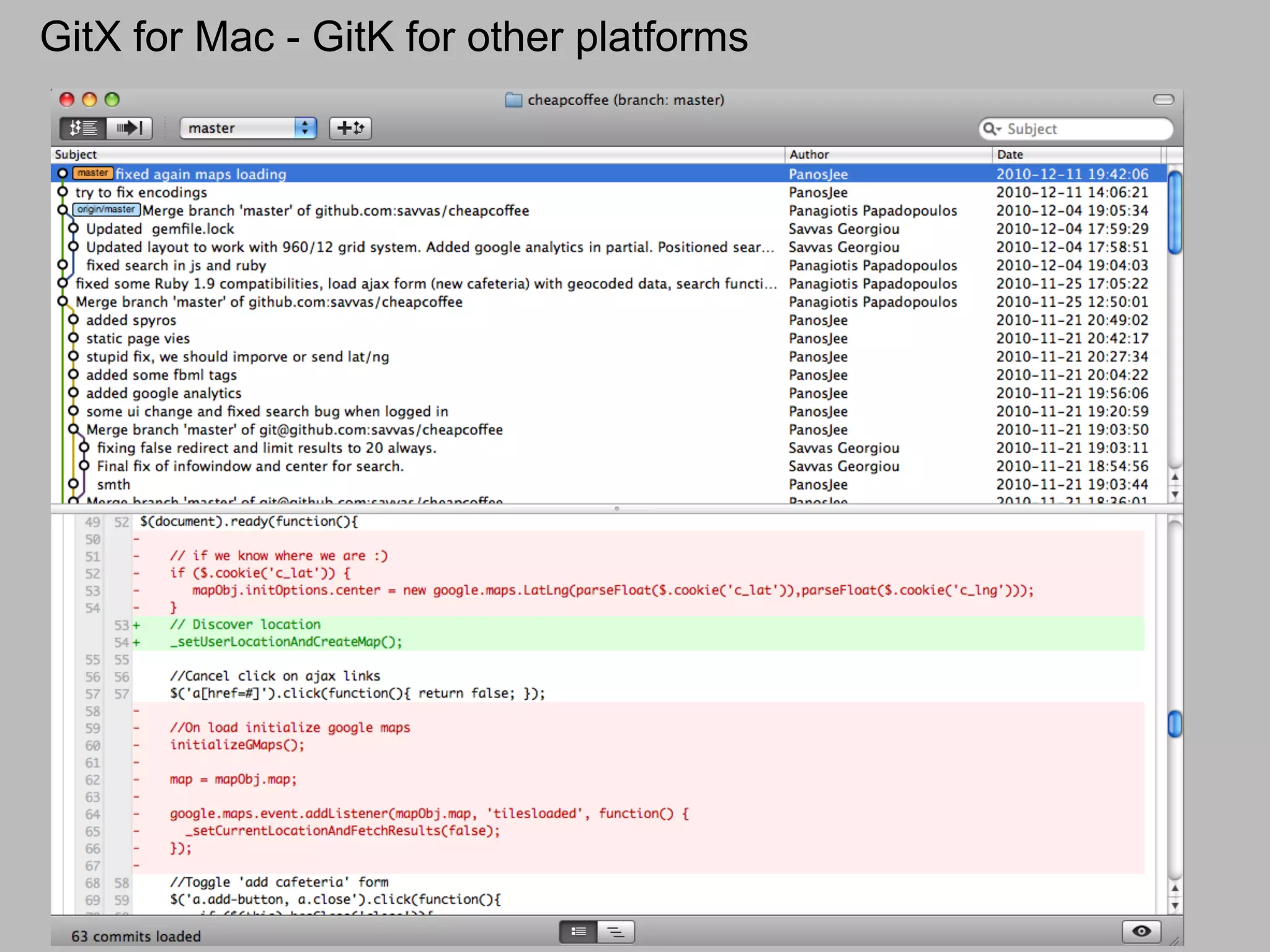
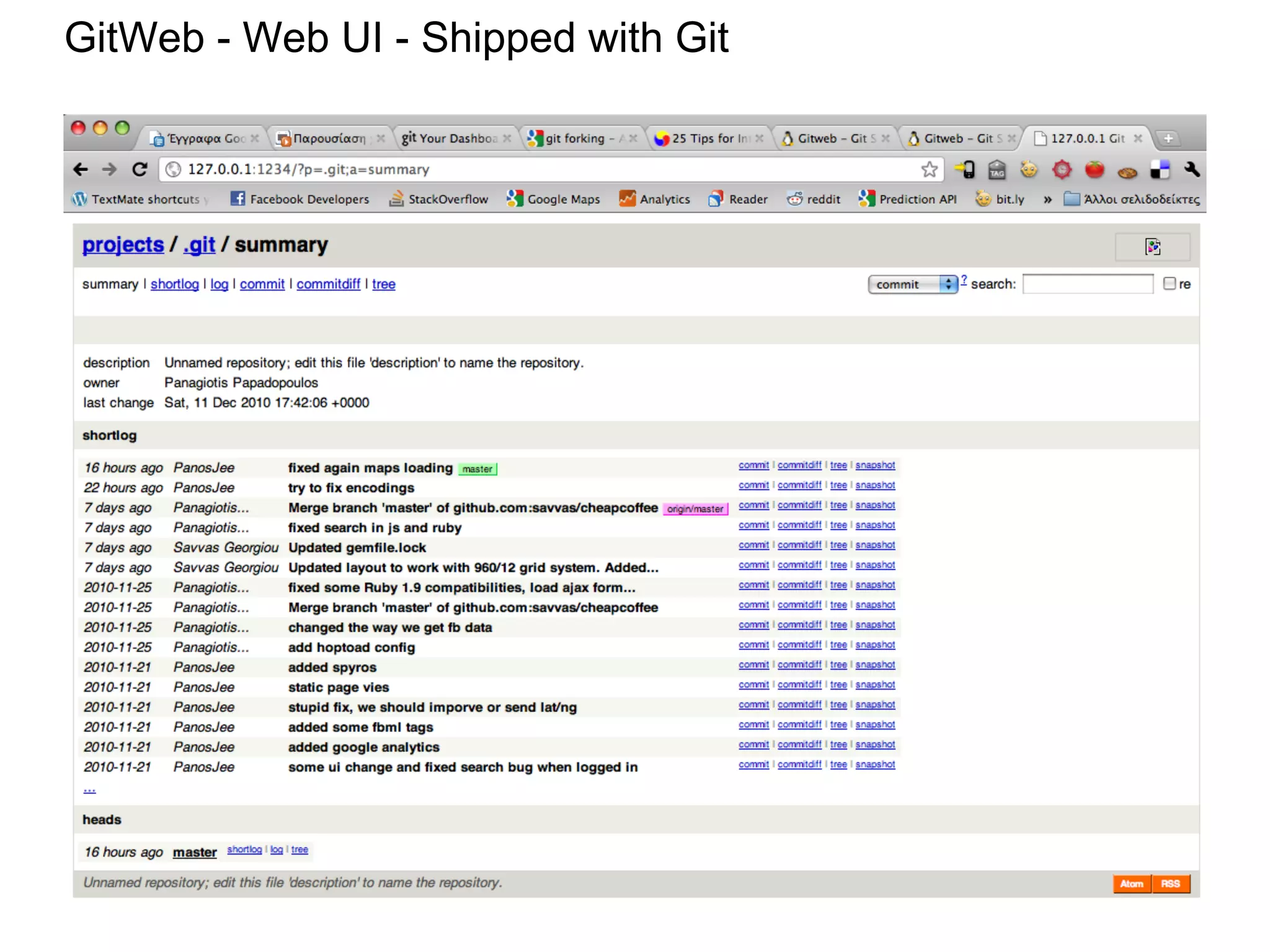
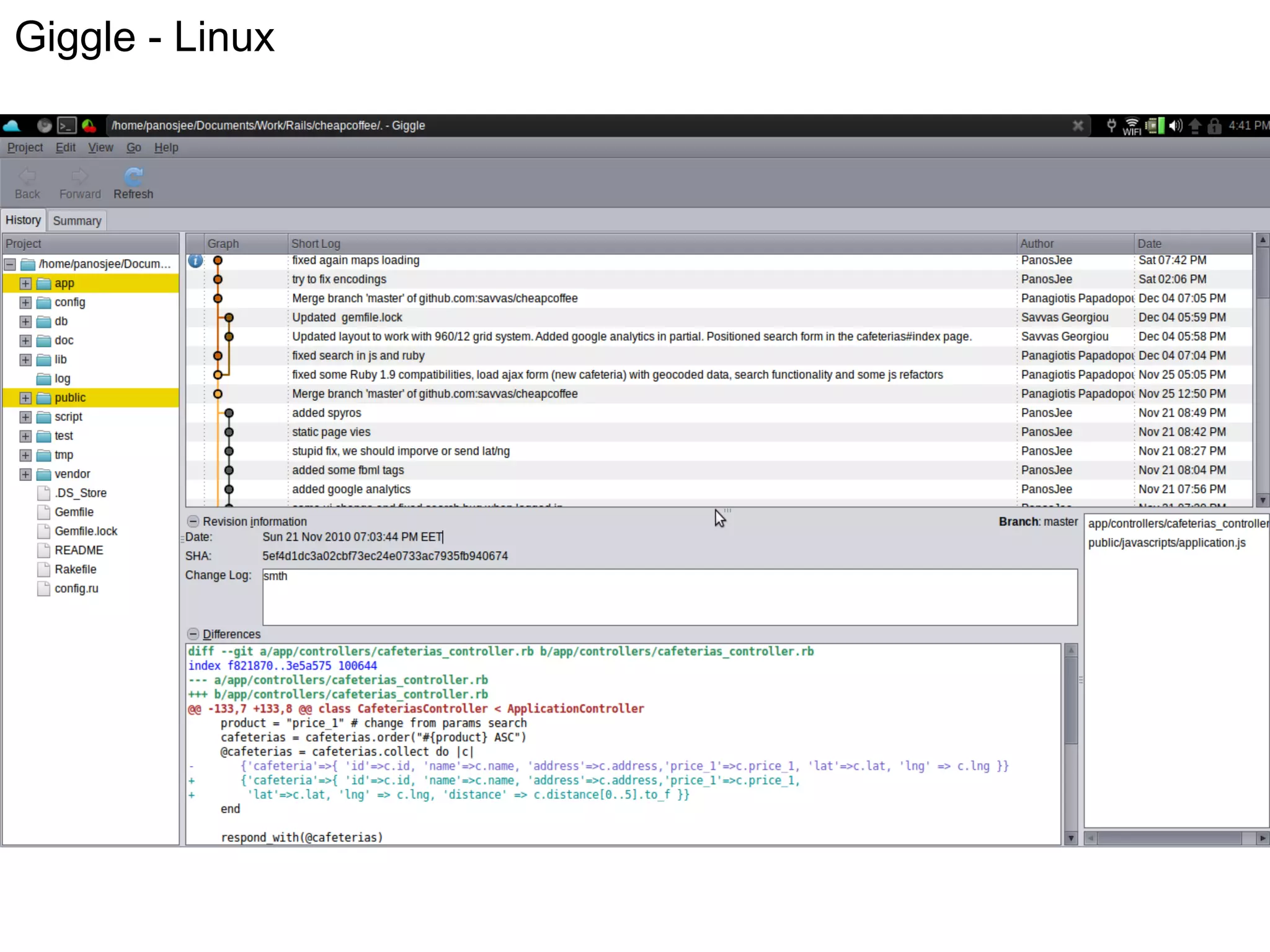
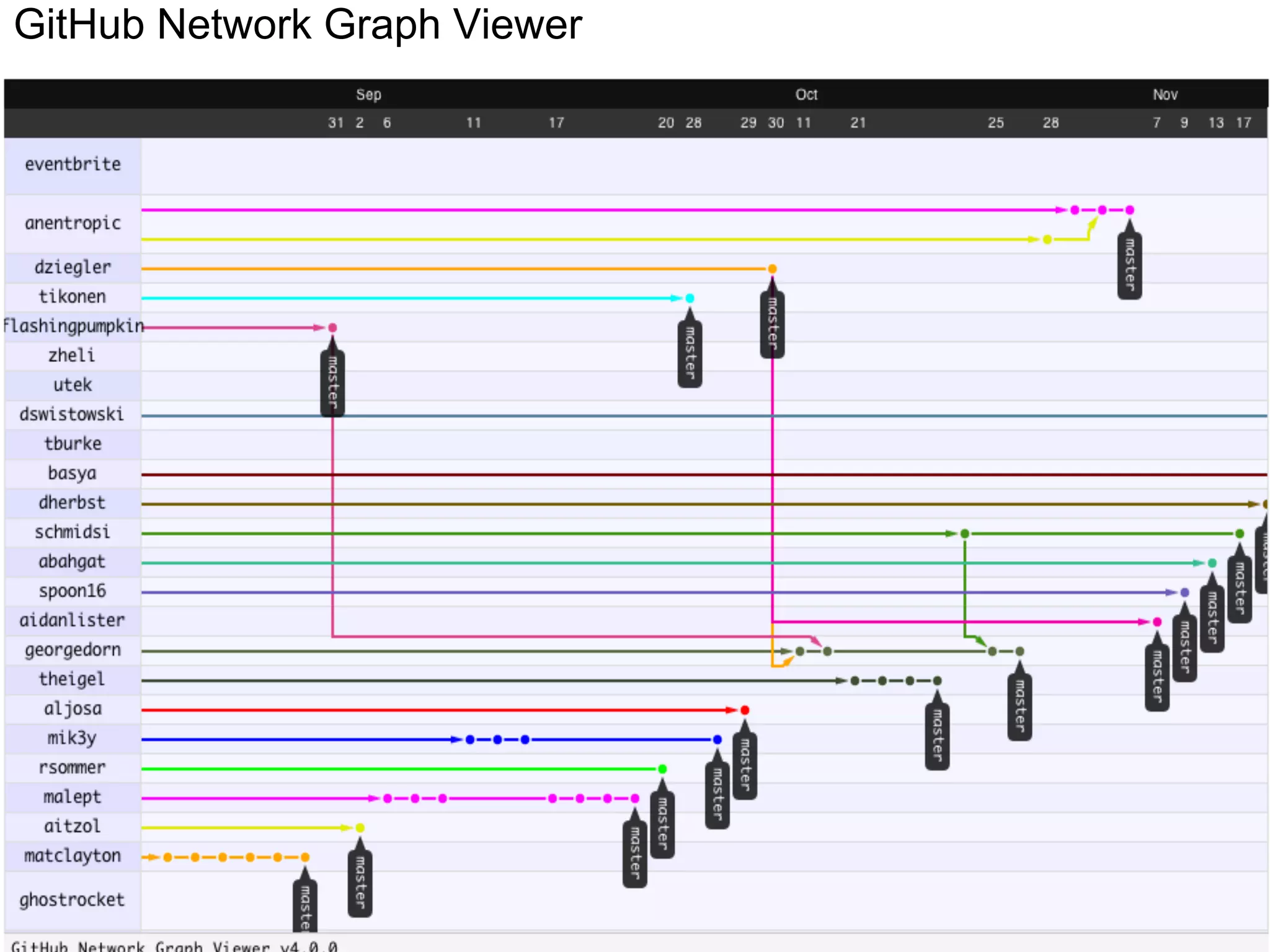
This document summarizes a presentation given at DrupalCamp in Athens on December 12, 2010 about Git and GitHub. The presentation introduced Git as a distributed version control system designed for speed and efficiency. It explained some of Git's core concepts like snapshots, branches, merging, and its distributed nature. It also promoted GitHub as a social coding platform that improves collaboration and code hosting for both open source and private projects. The presentation aimed to help attendees learn Git for their own benefit and prepare for Drupal moving to GitHub.