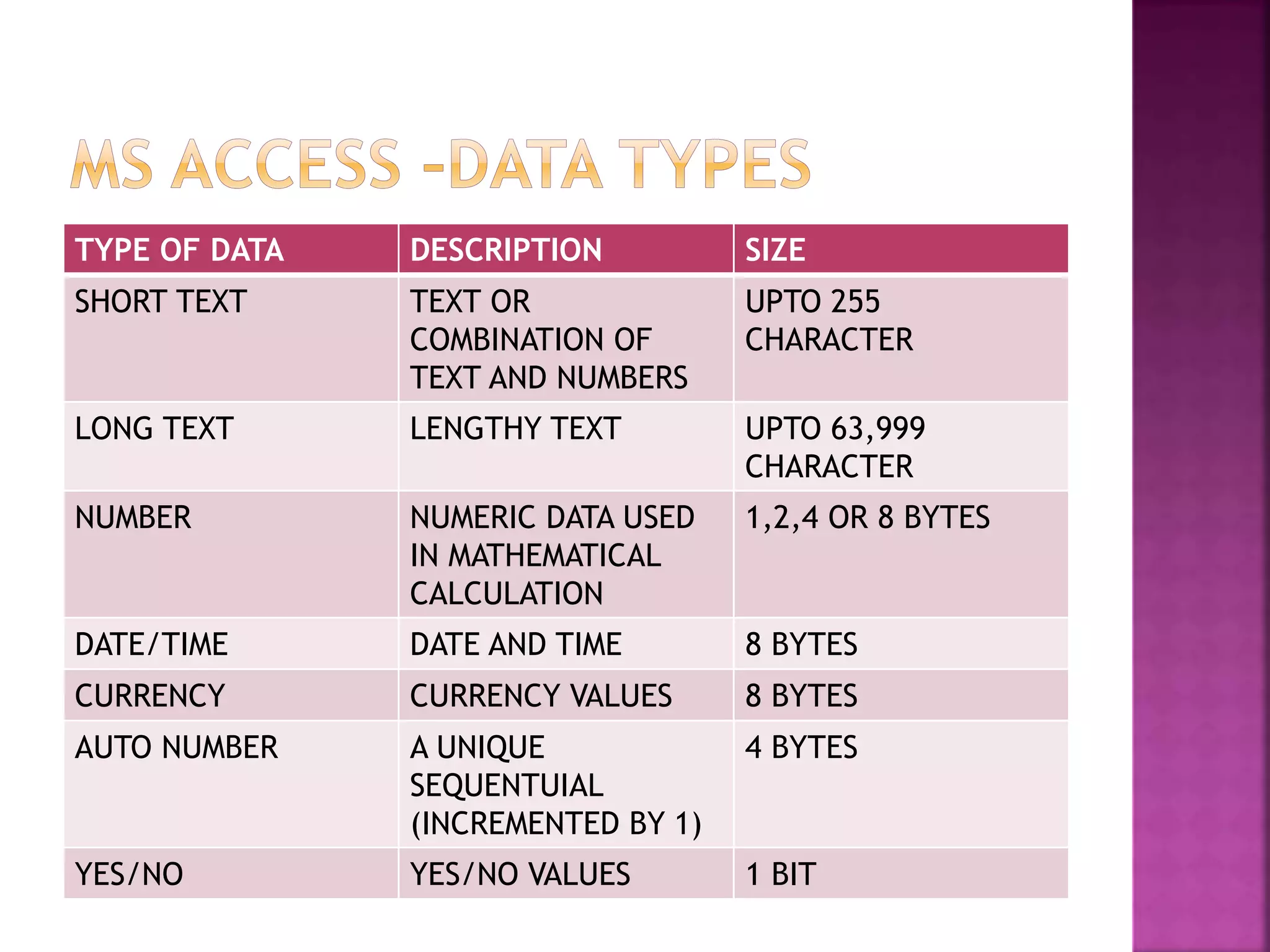
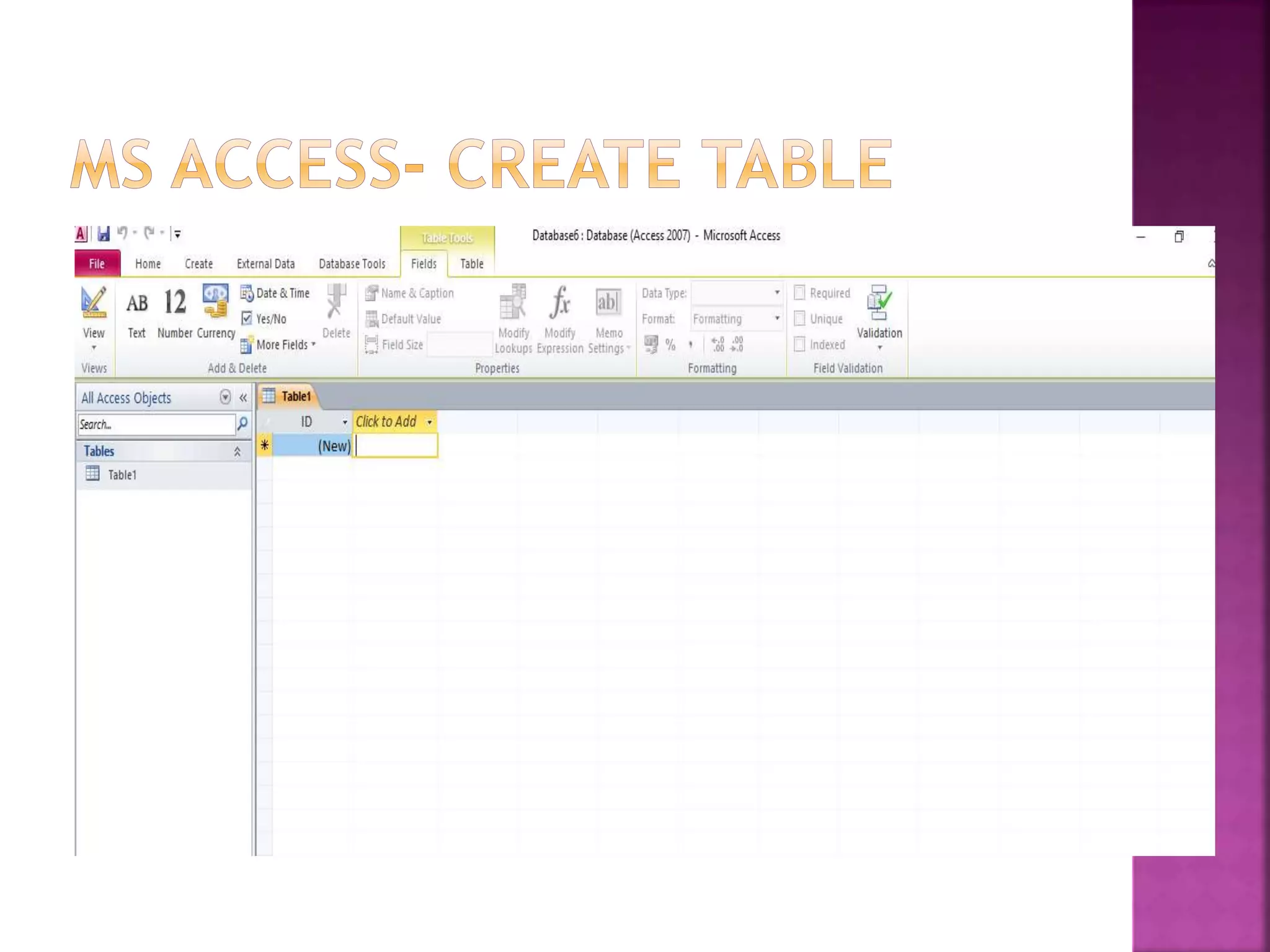
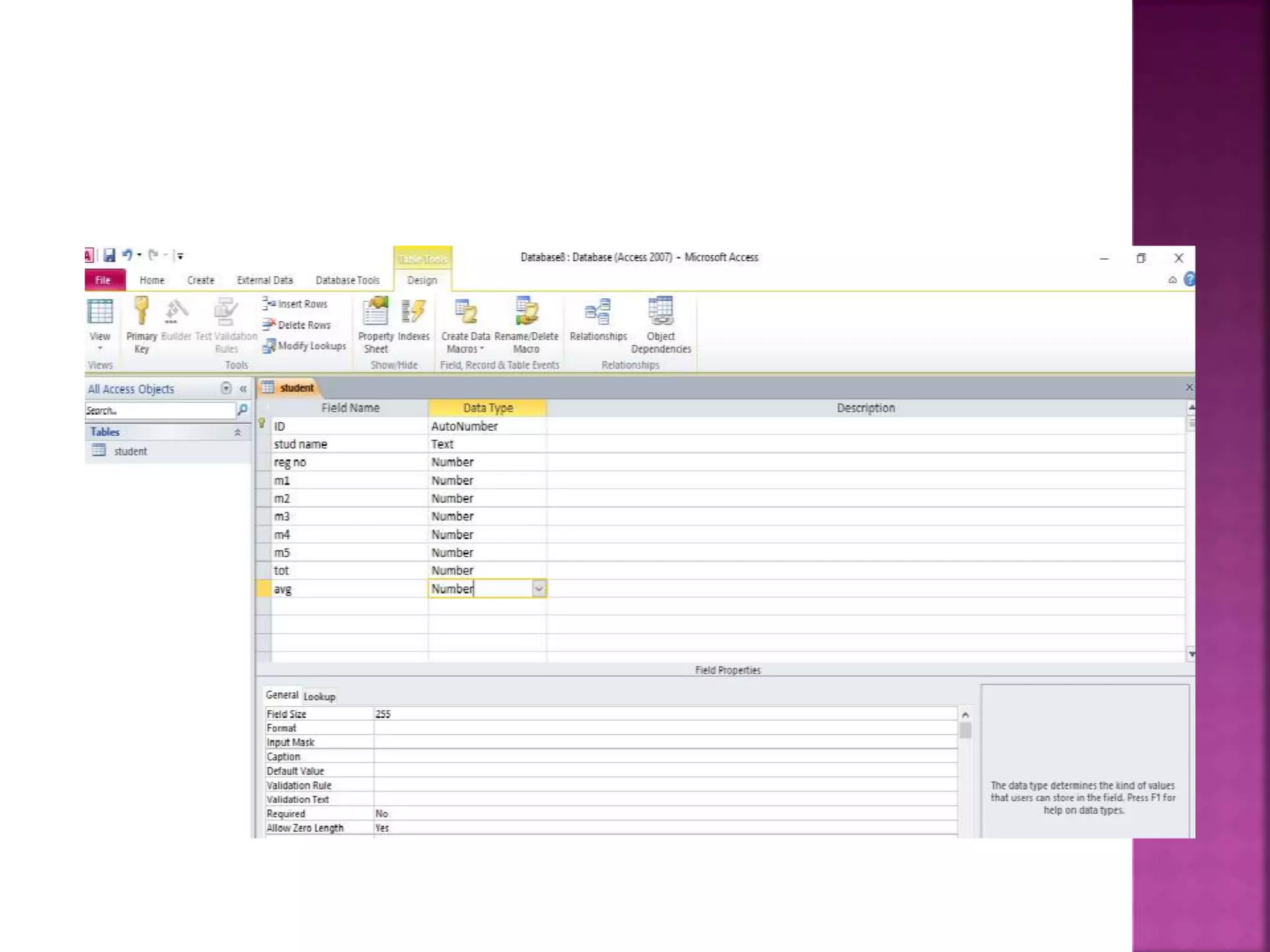
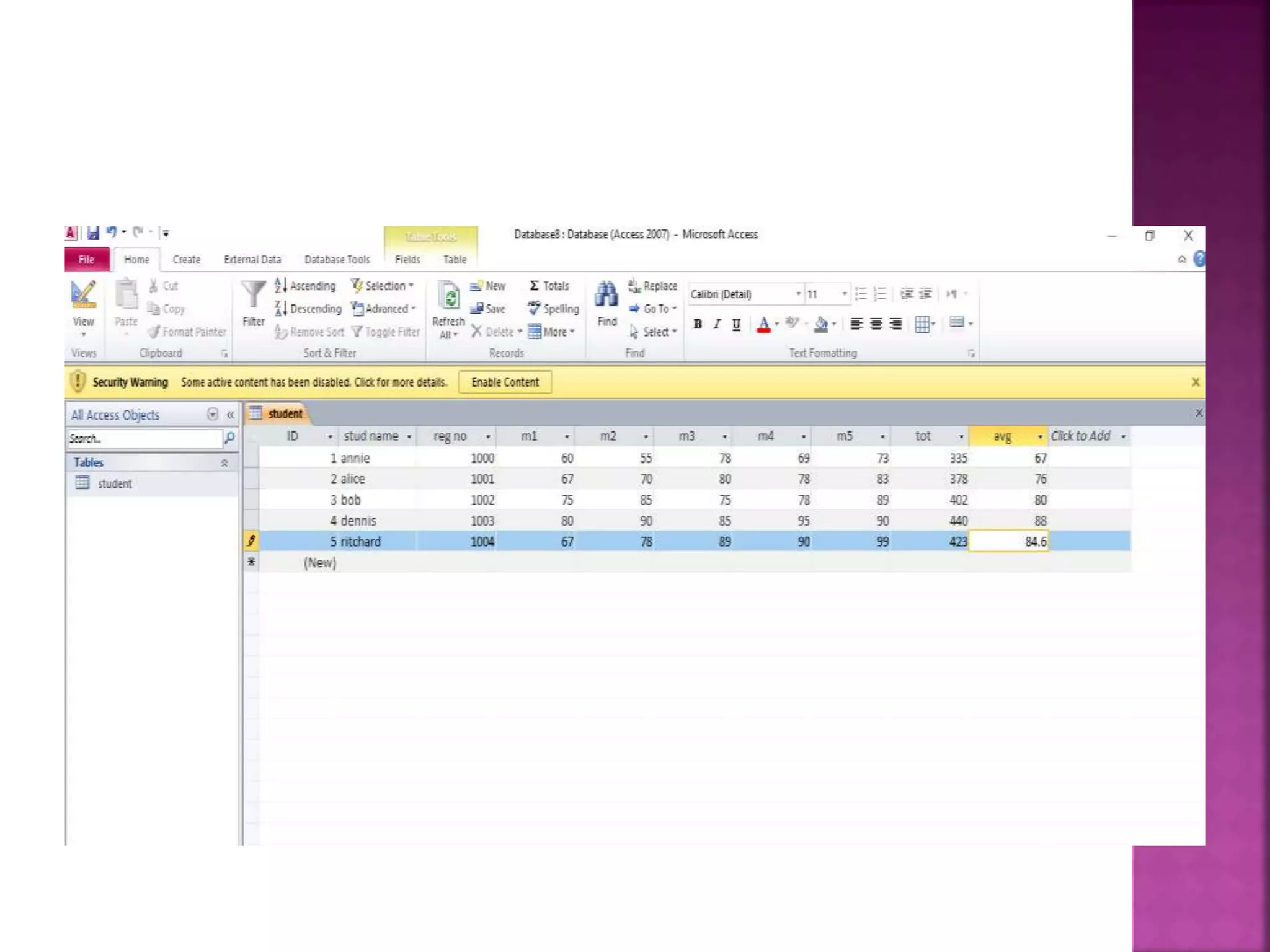
This document provides an overview of Microsoft Access, including that it is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores data in its own format. It can import or link to data from other sources. Access allows users to create databases and define data types for tables. Key objects in Access include tables, queries, forms and reports. Tables contain the data fields, queries retrieve specific data, forms provide interfaces for data entry and extraction, and reports organize data for presentation.