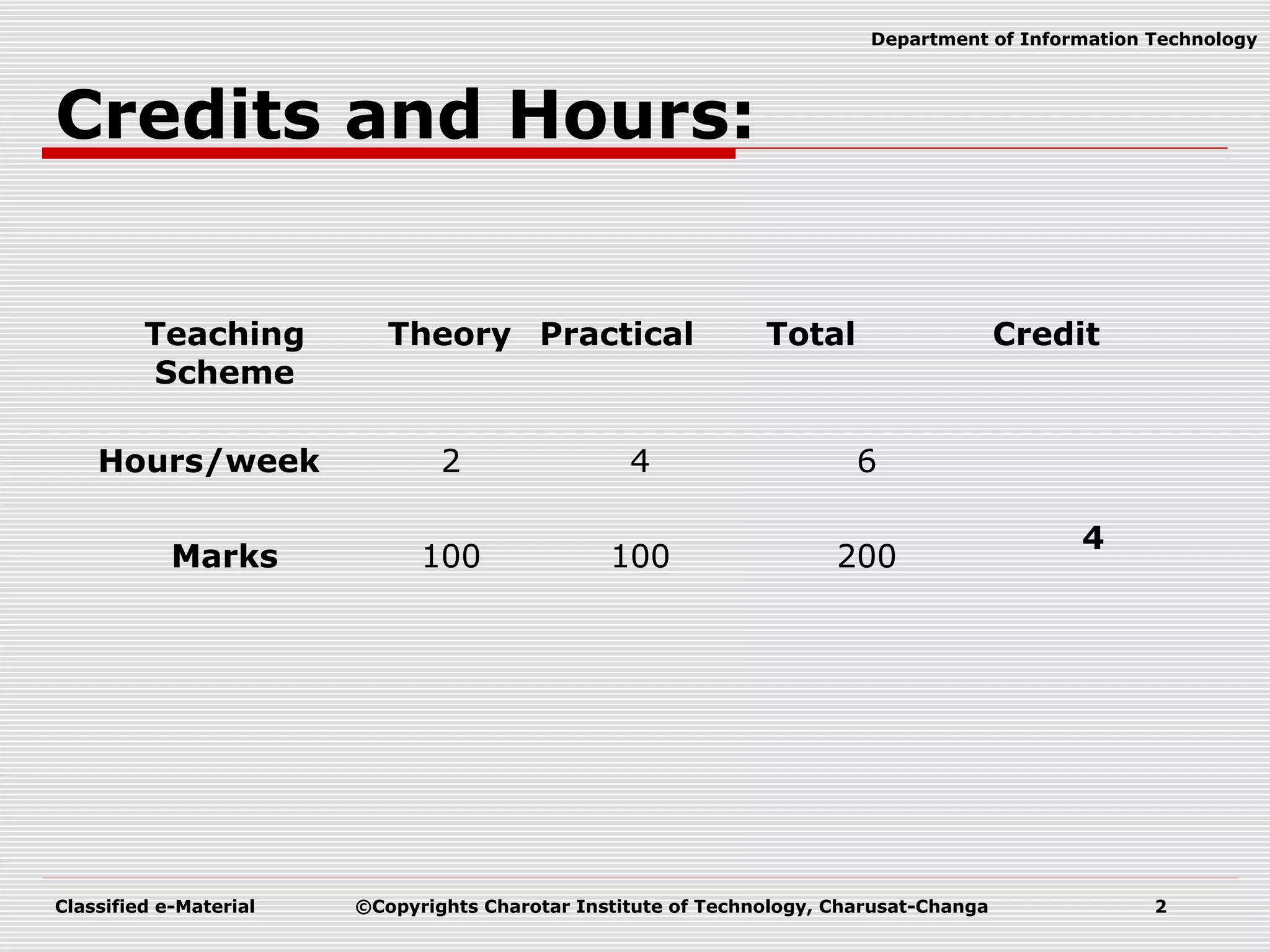
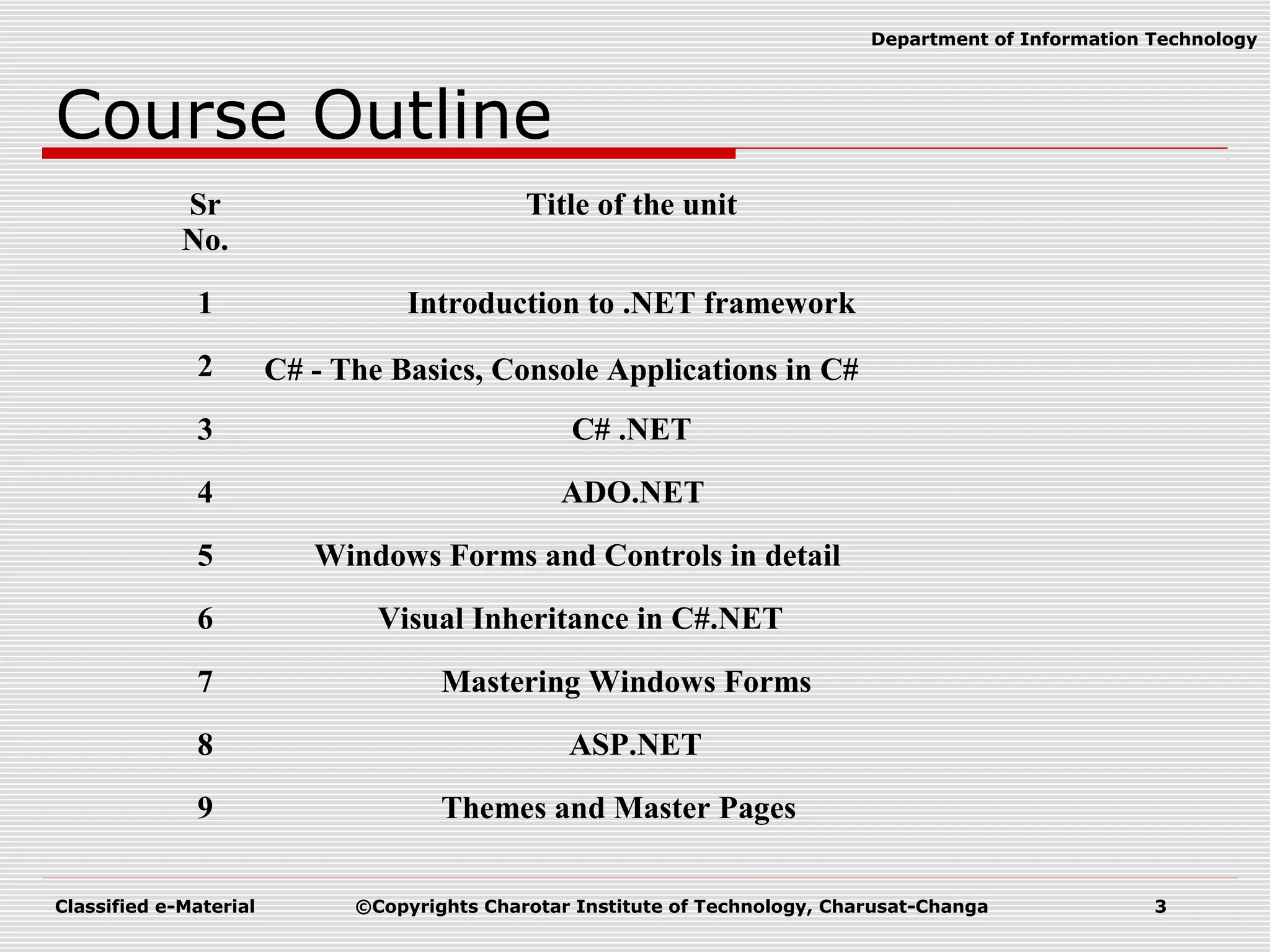
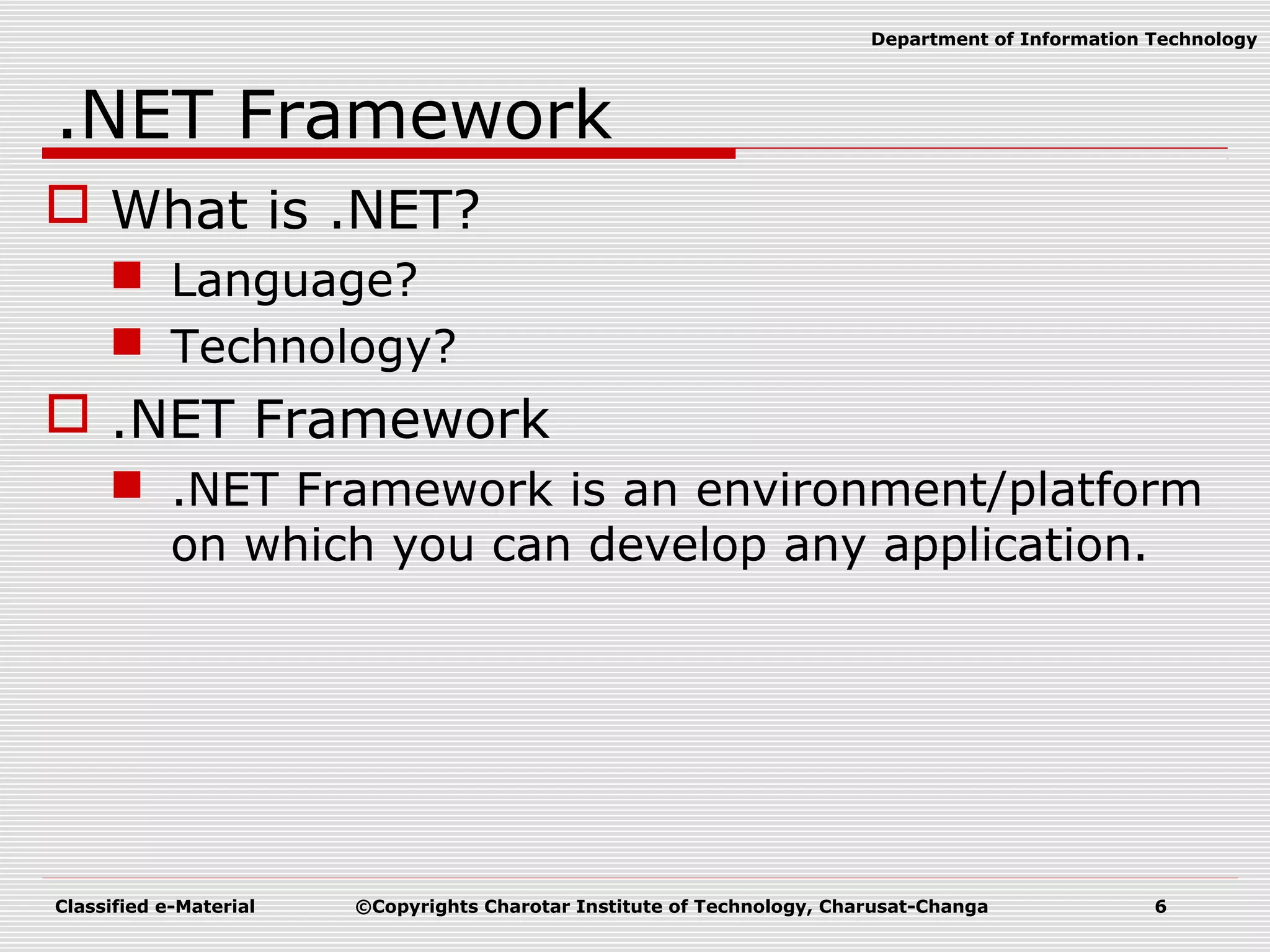
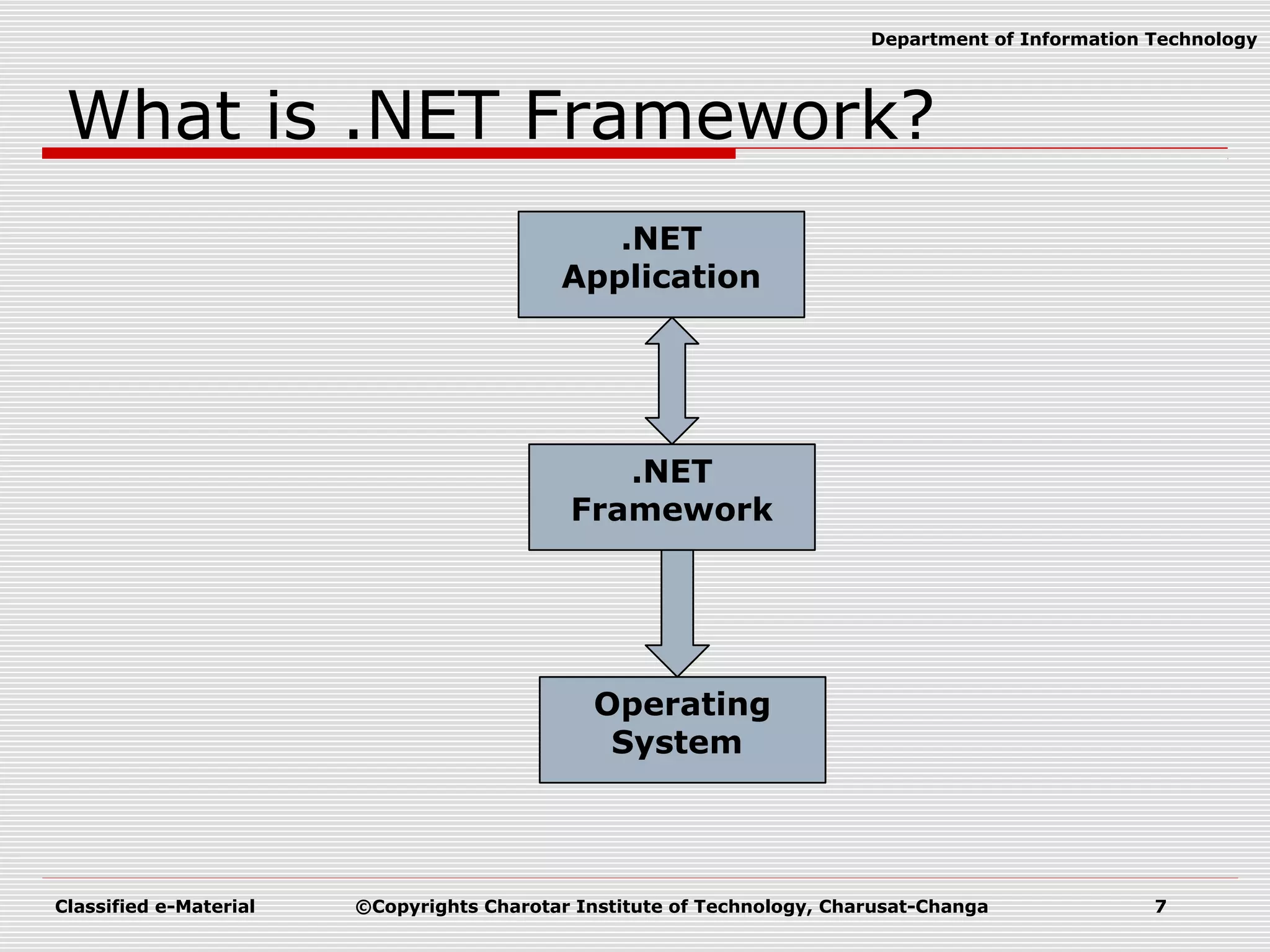
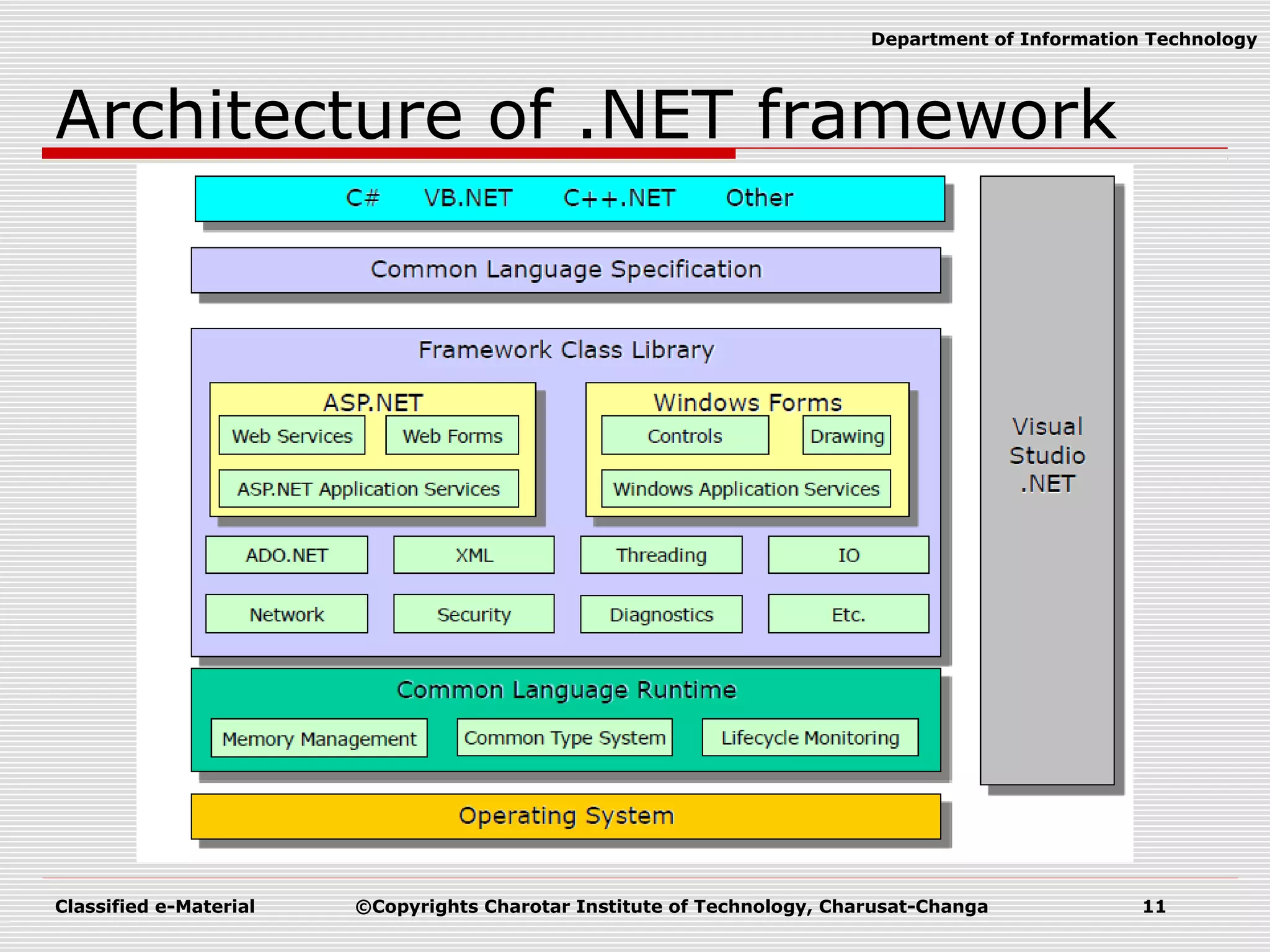
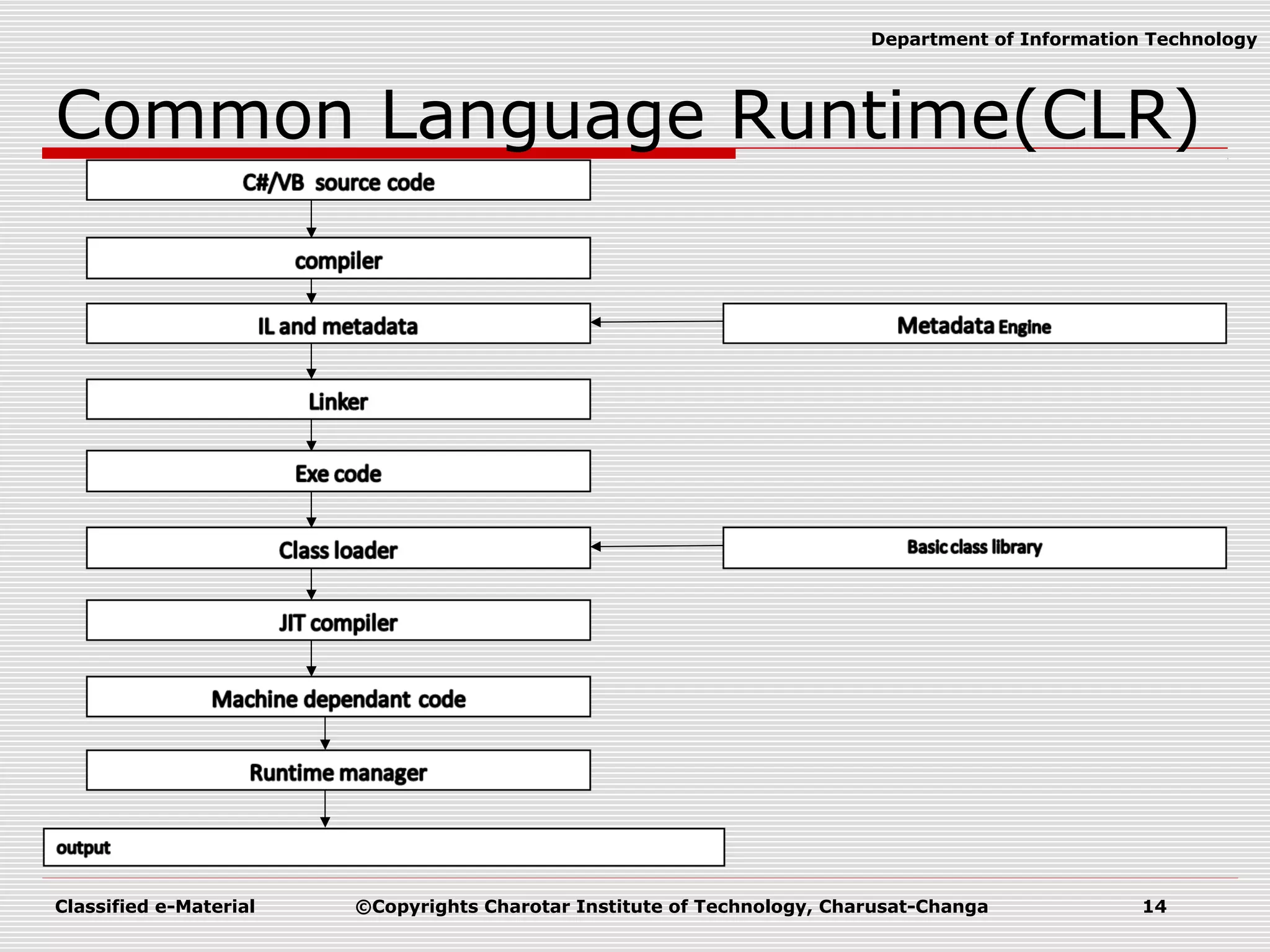
This document outlines a course on Advanced Programming Using .NET Framework. It includes details like the course credits, teaching scheme, course outline listing the titles of 12 units, recommended materials including textbooks and a reference book, and concepts related to .NET Framework like its architecture, features, Common Language Runtime, garbage collection, namespaces and assemblies.