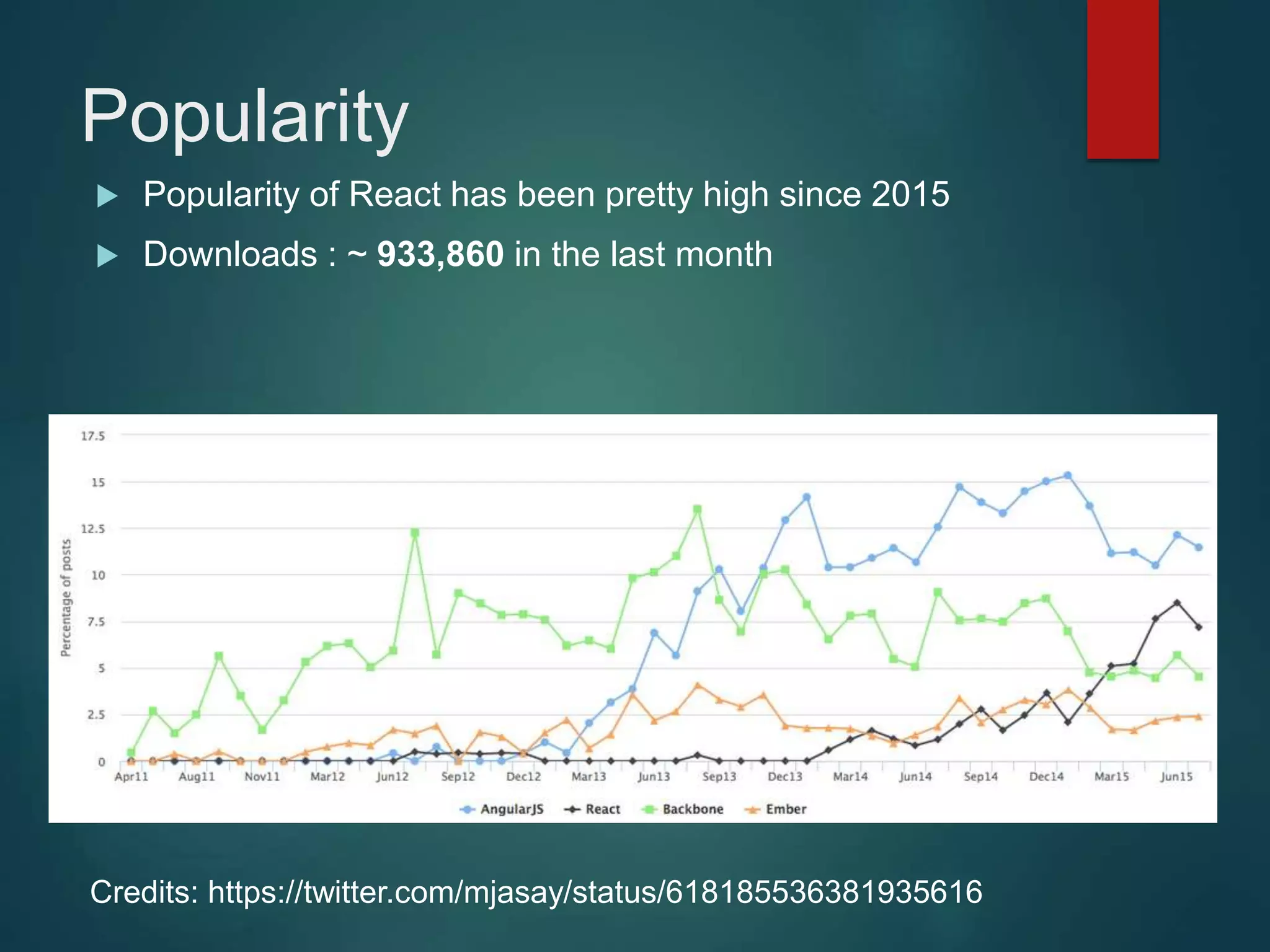
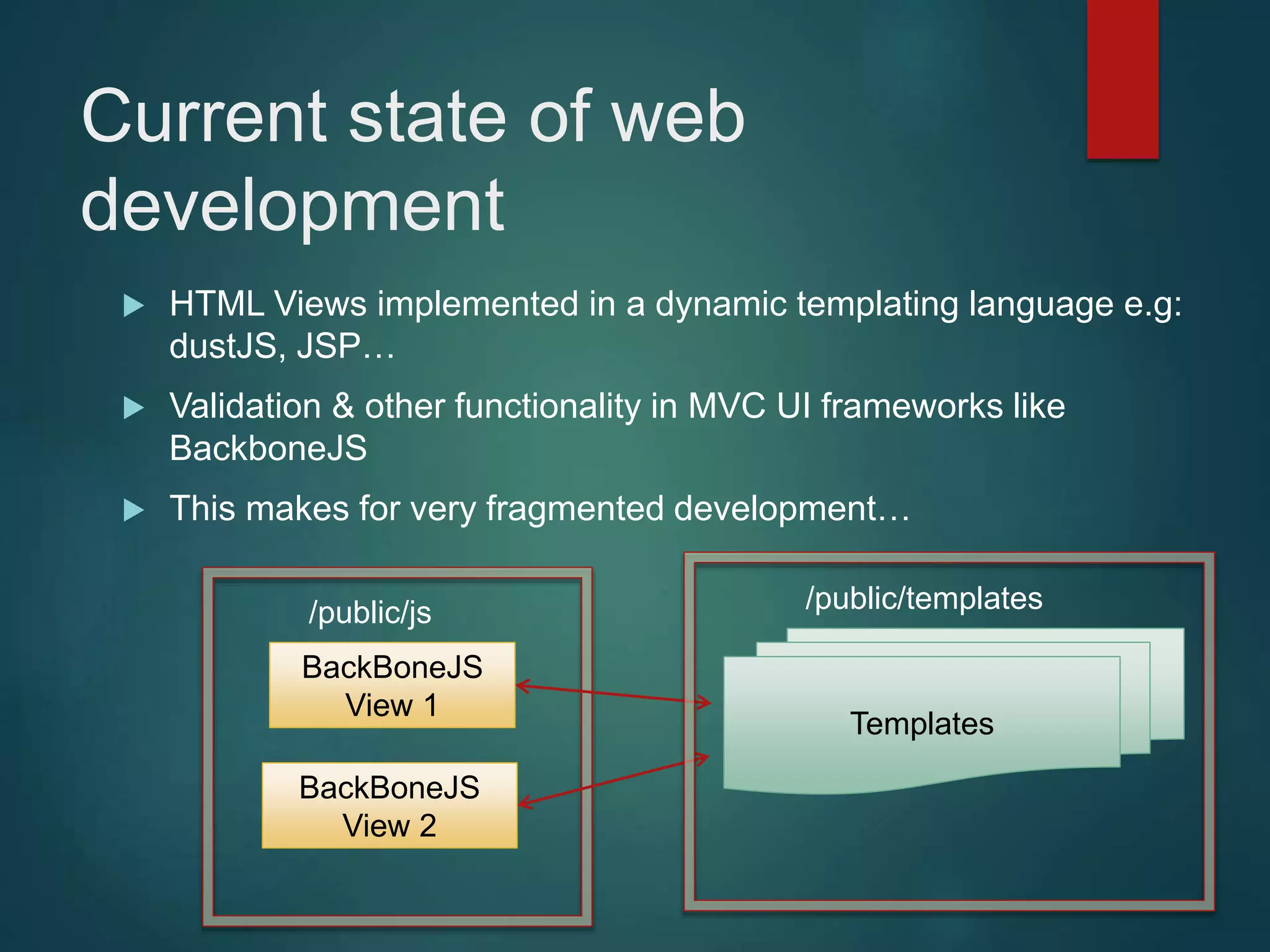
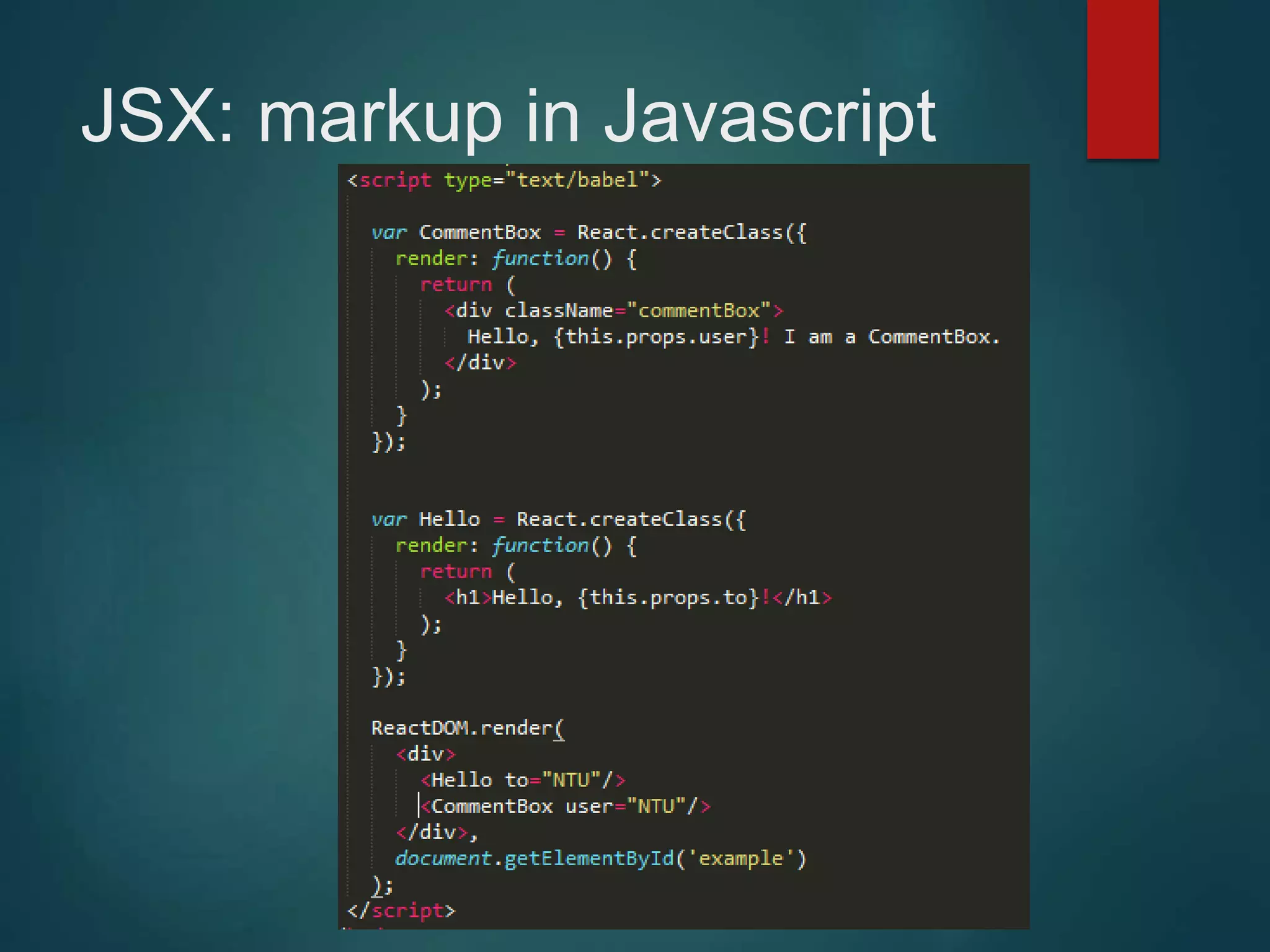
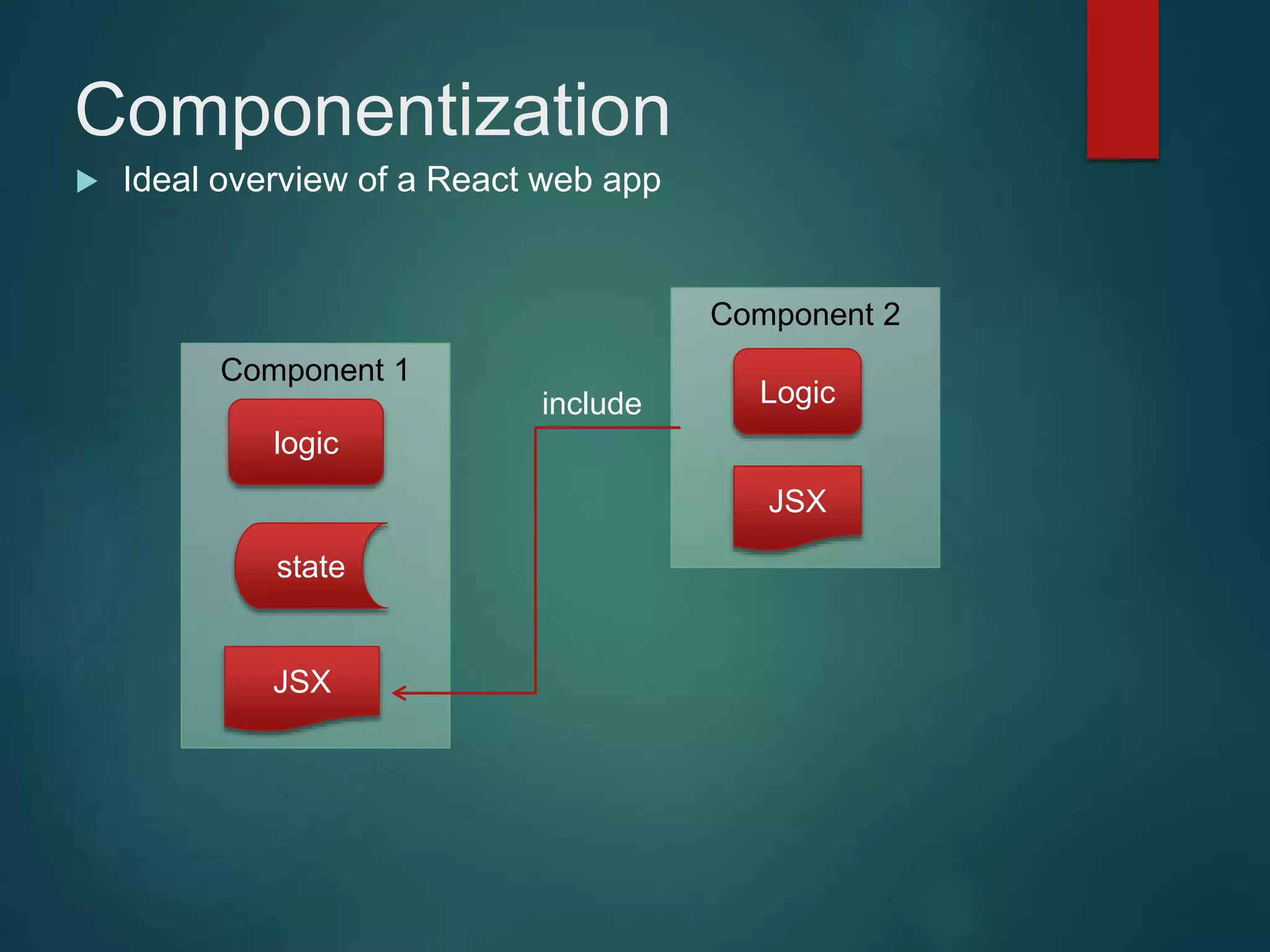
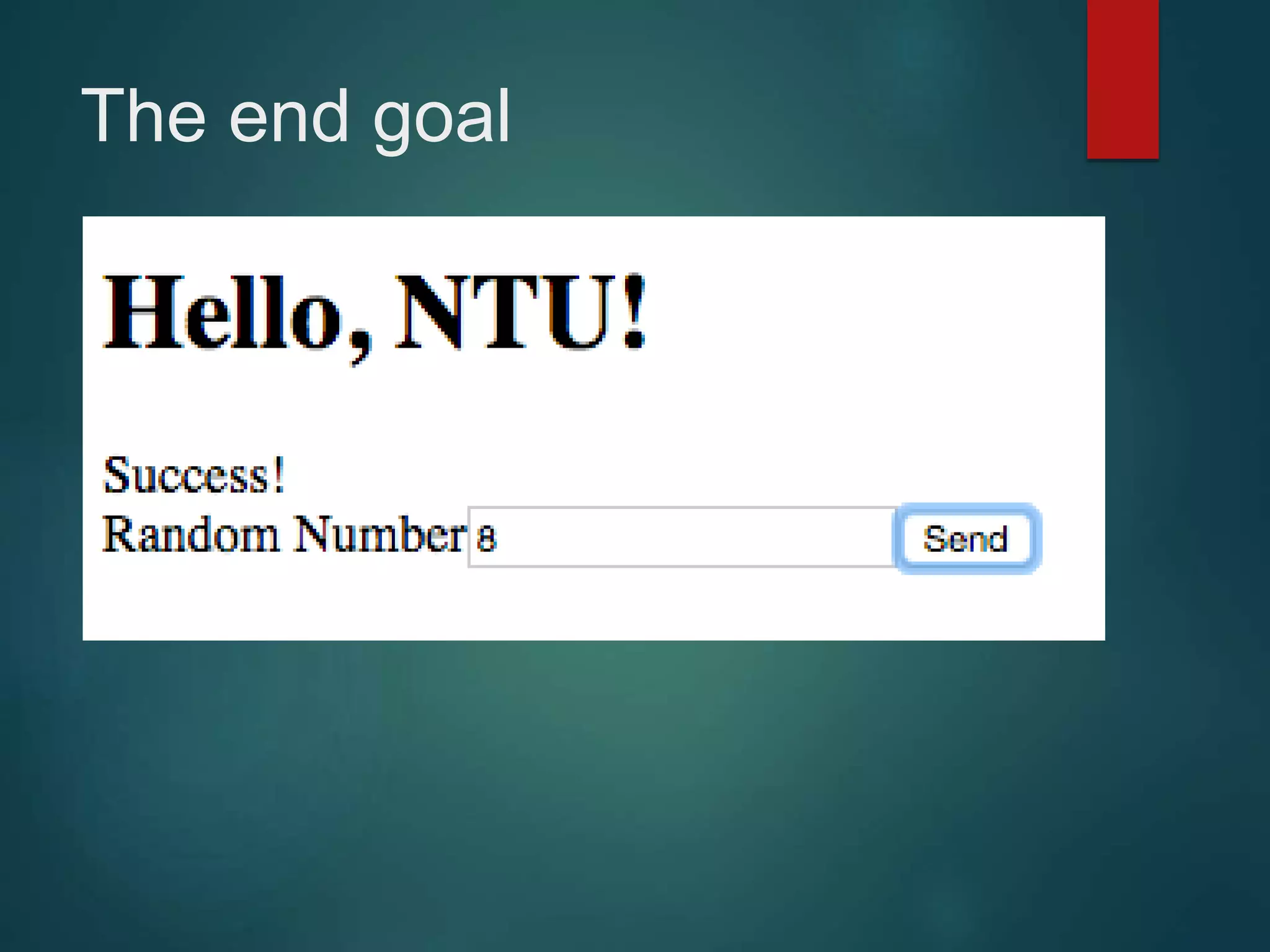
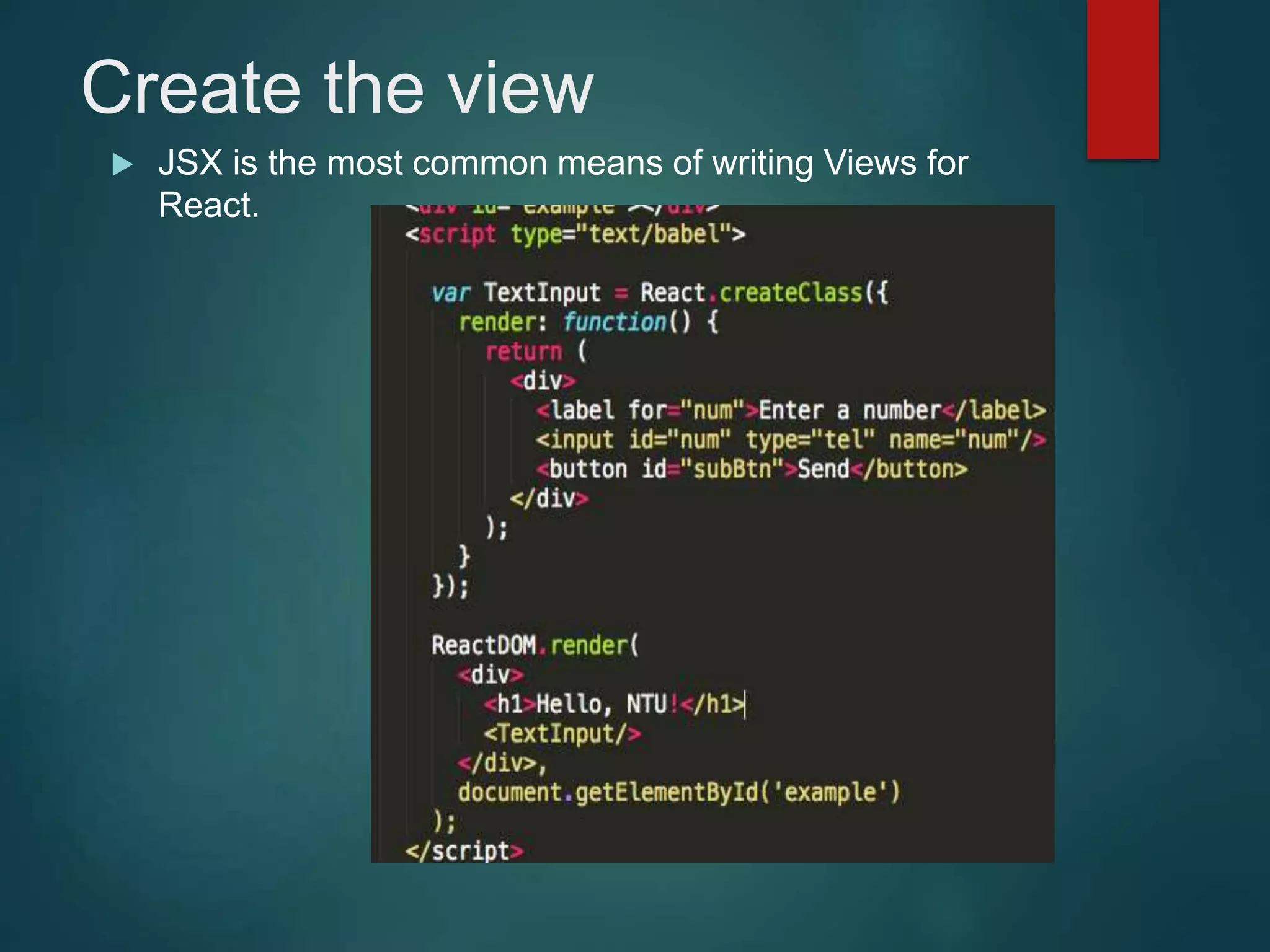
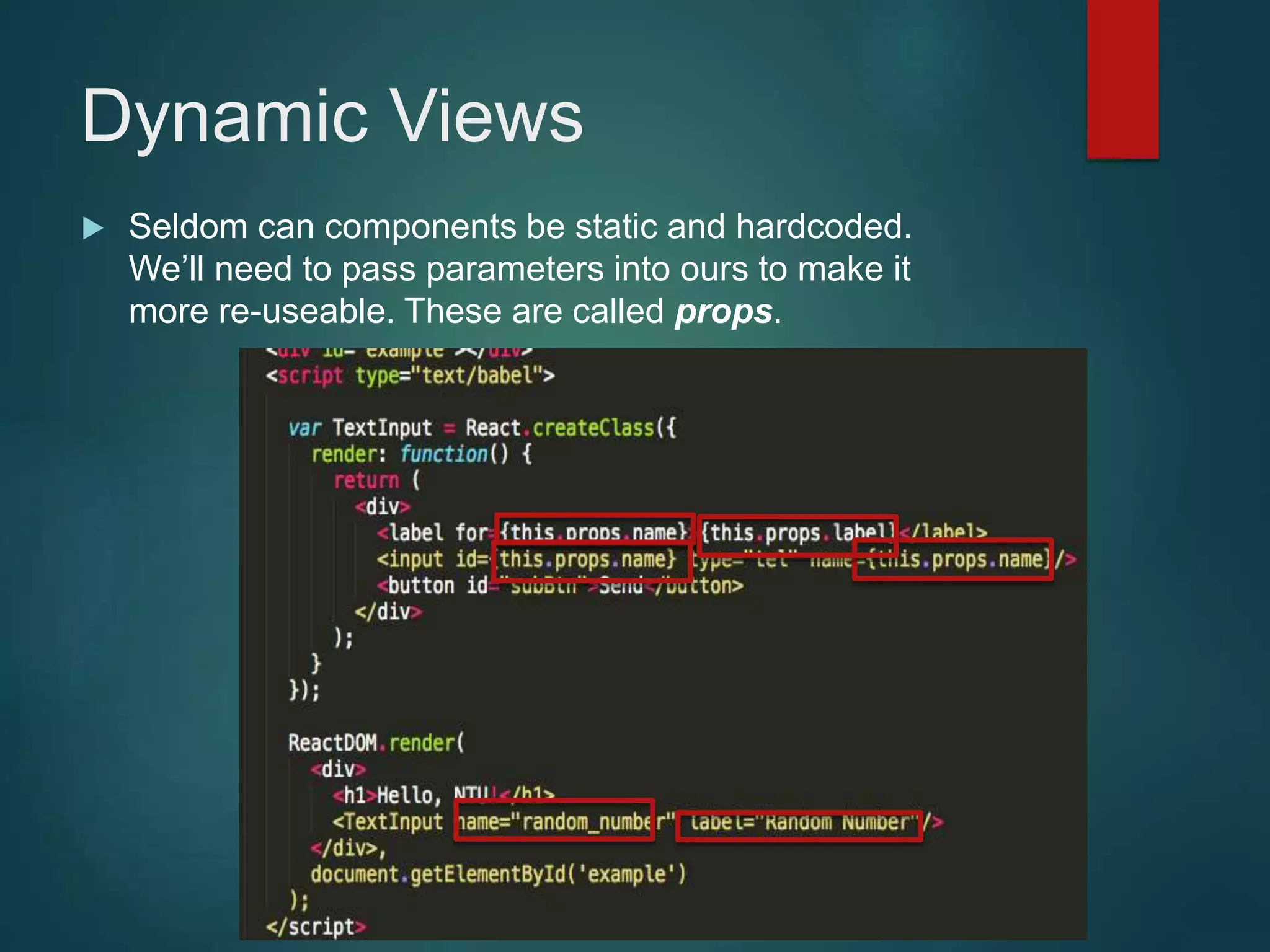
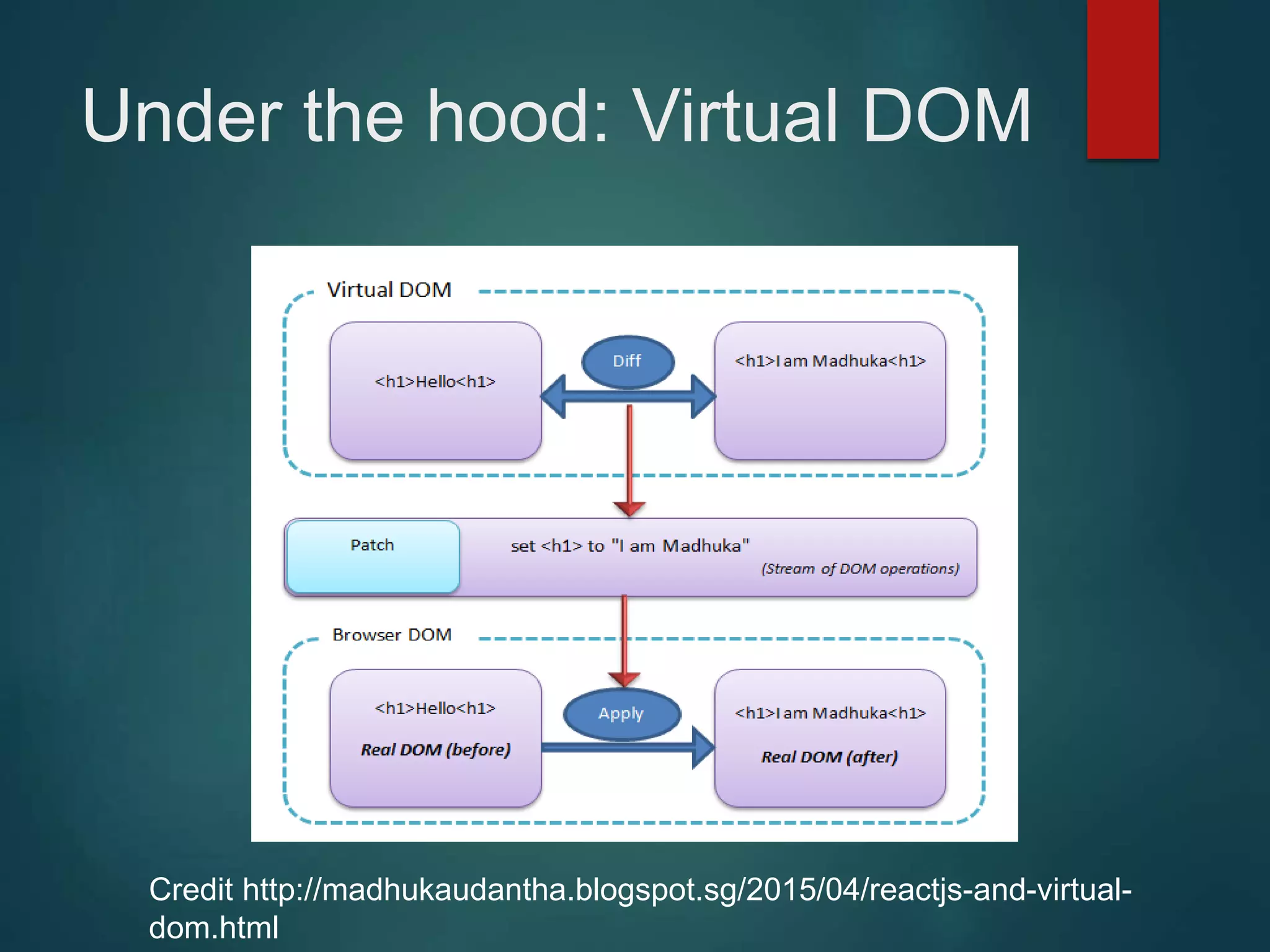
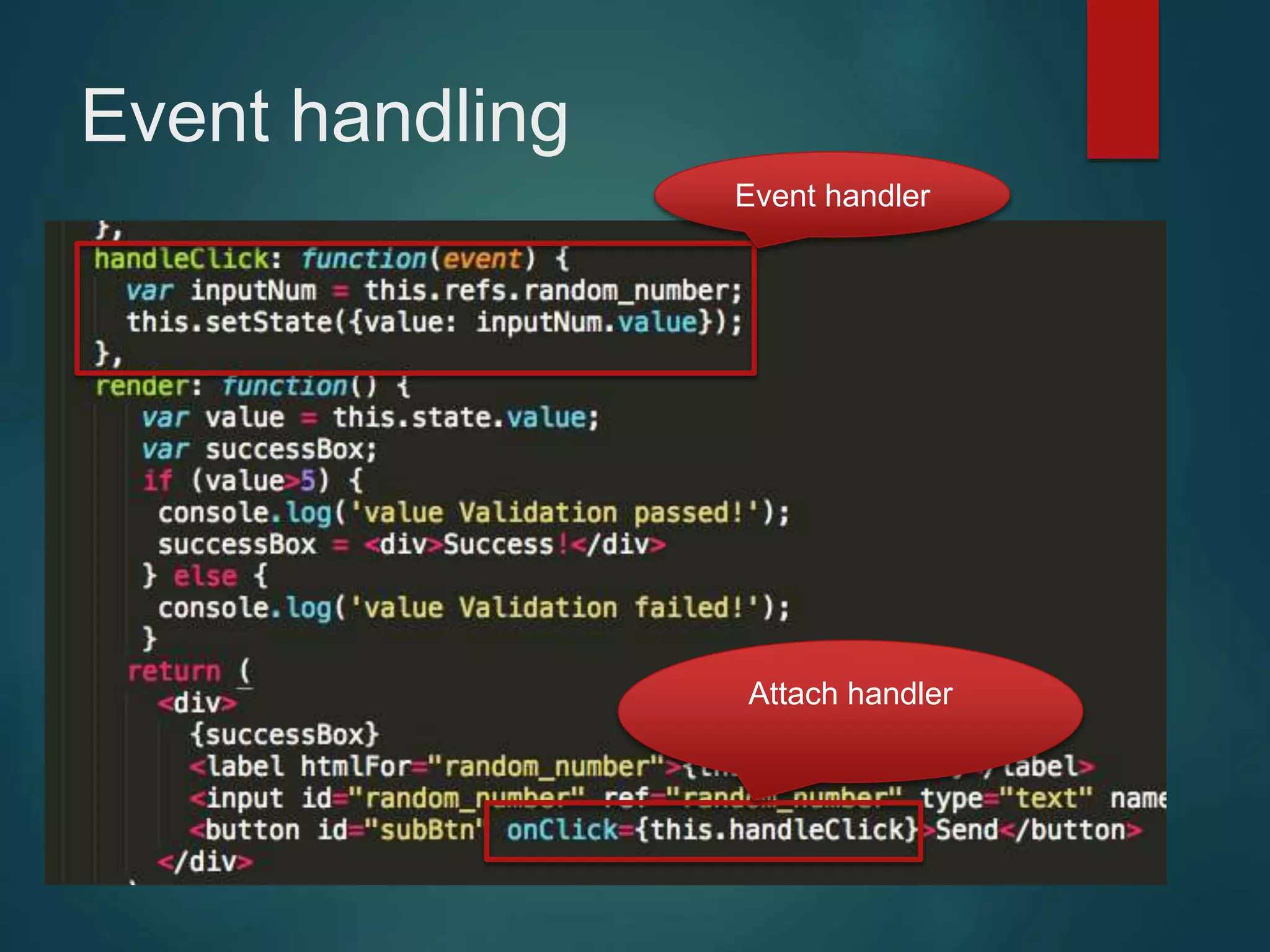
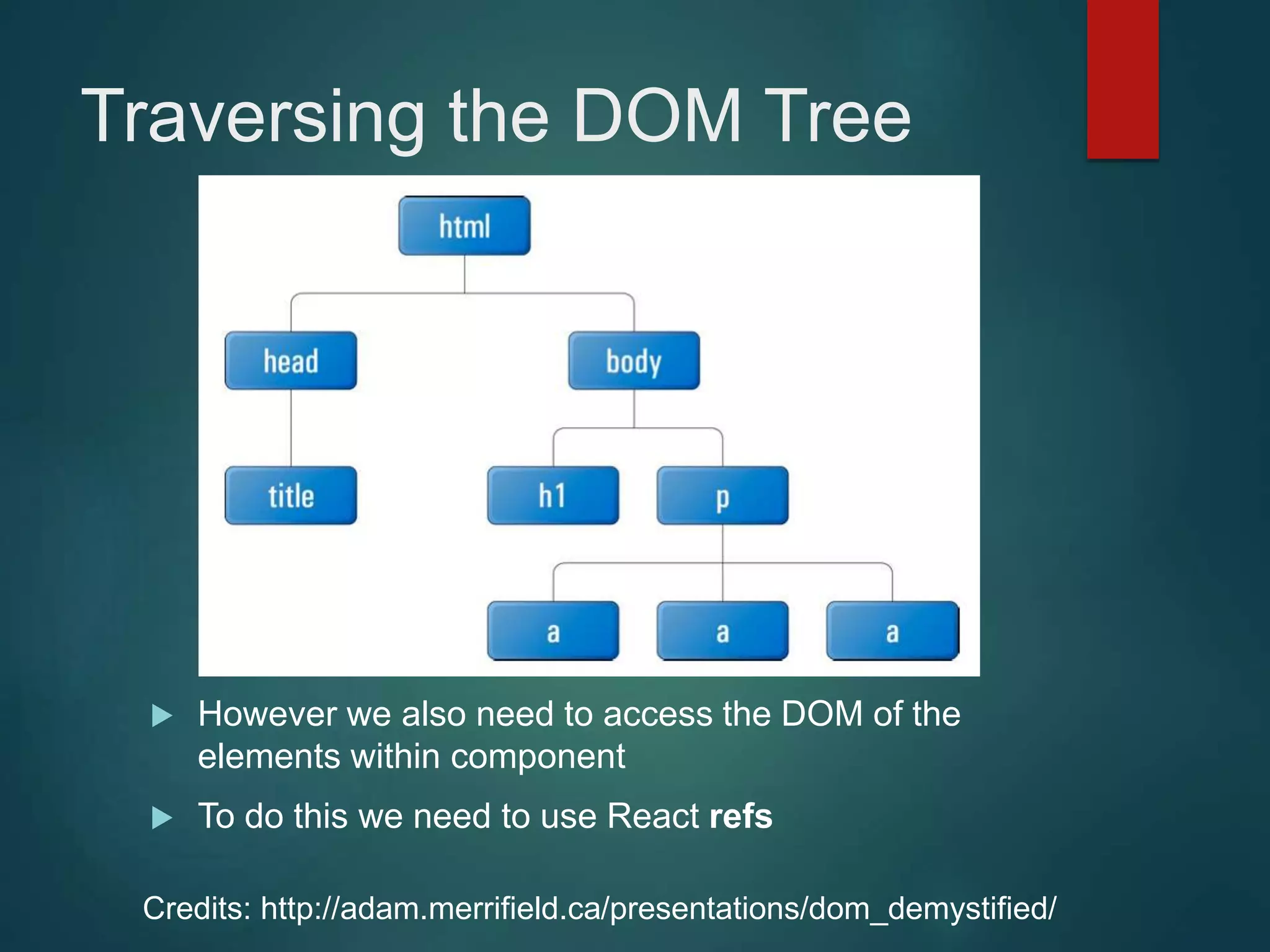
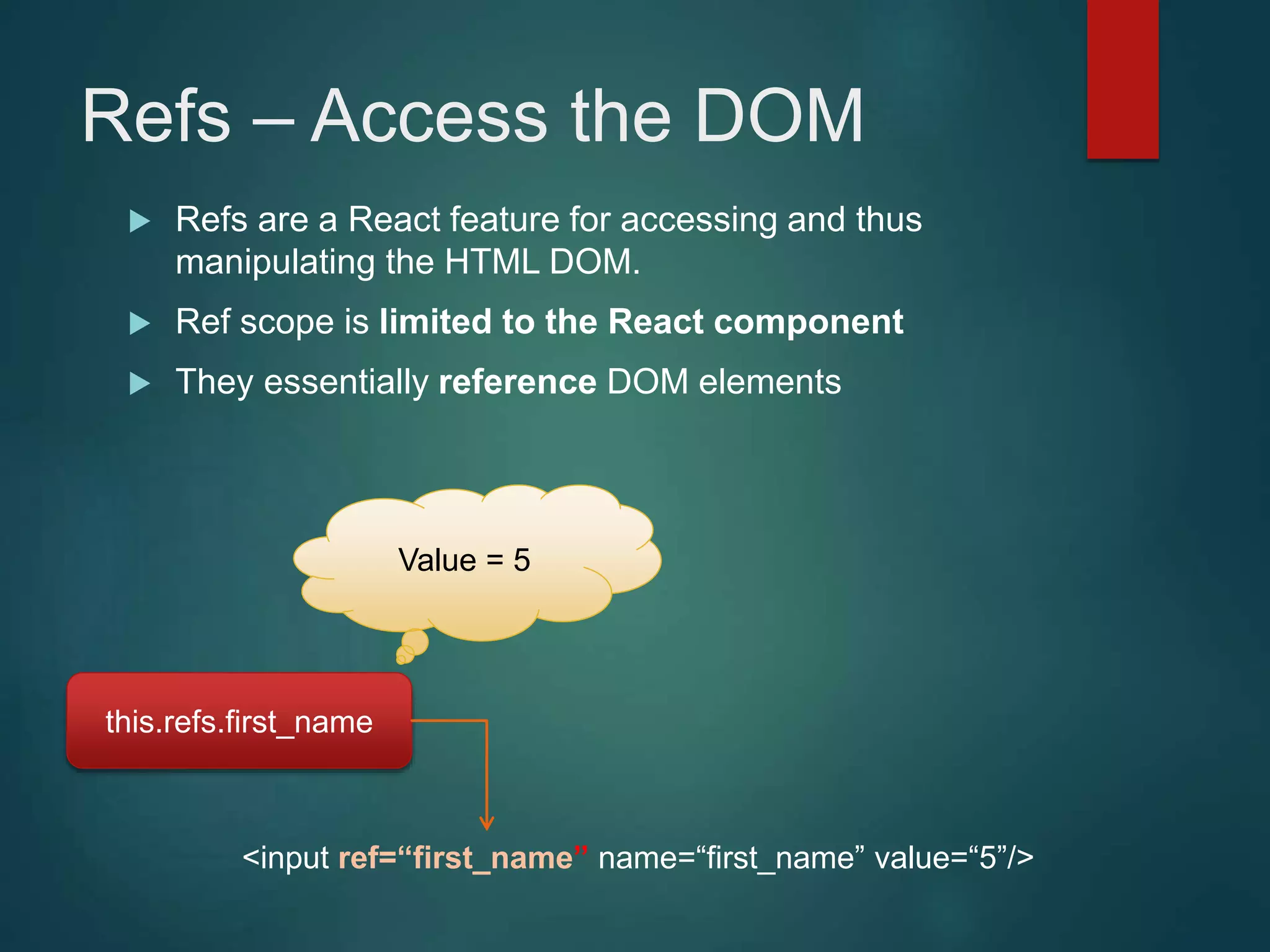
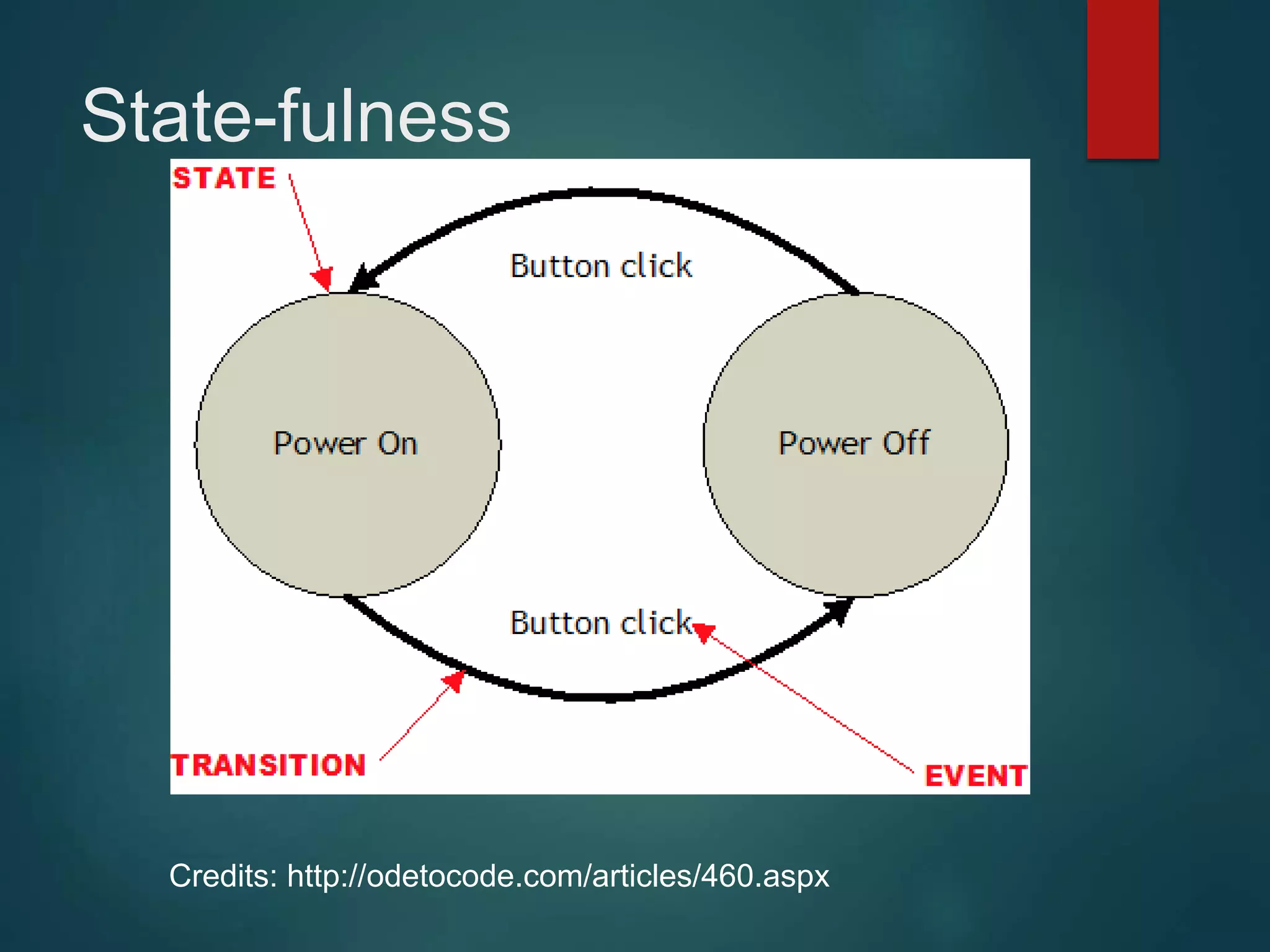
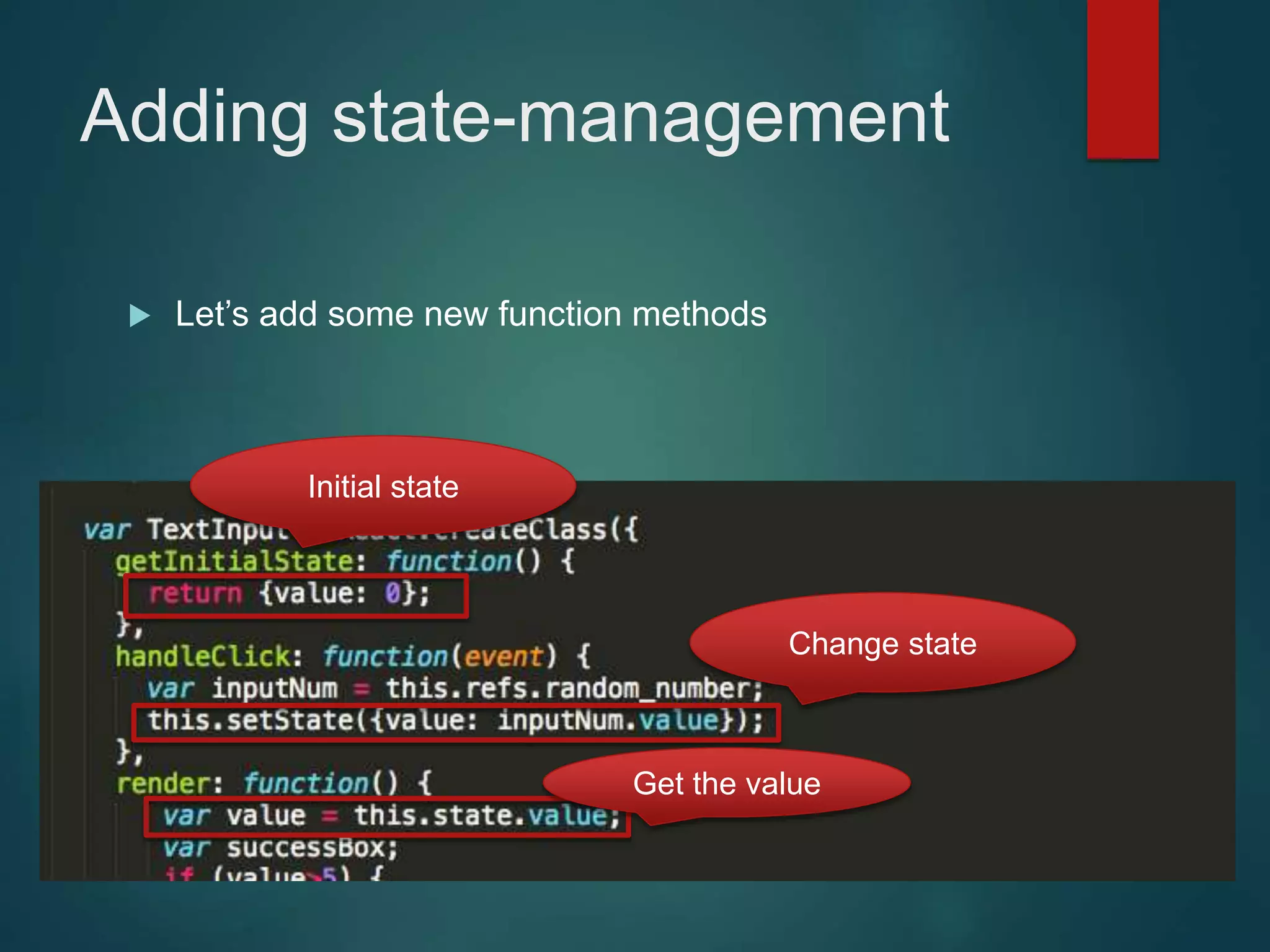
This document provides an introduction to ReactJS, including: - Why React is simple, declarative, and allows building of composable components - React's popularity, with over 900,000 downloads in the last month - How React addresses issues with traditional web development through its use of virtual DOM and componentization - An example component is demonstrated to show how to: render in JSX, make components dynamic and interactive through props and event handling, access the DOM through refs, and manage state.