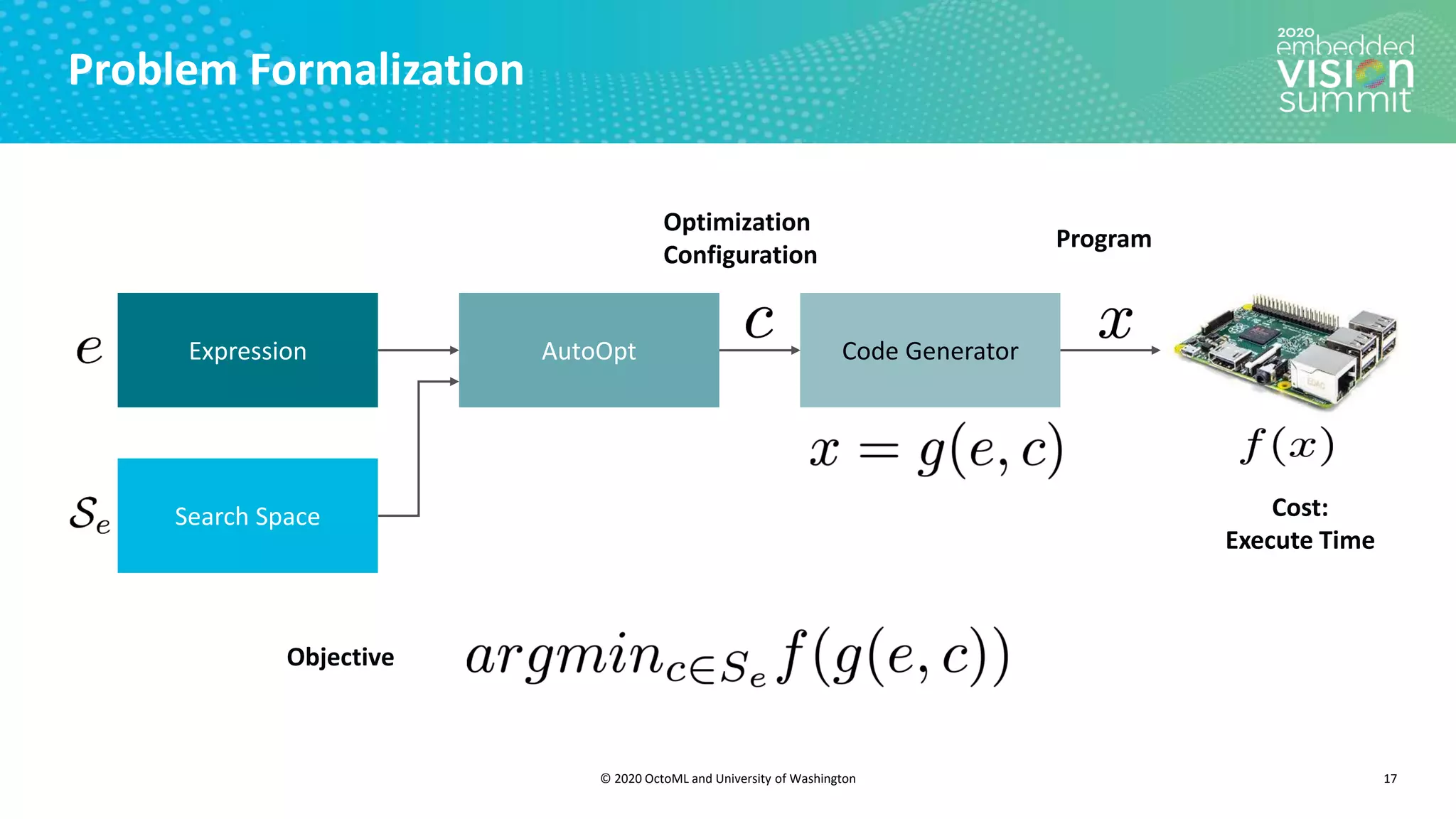
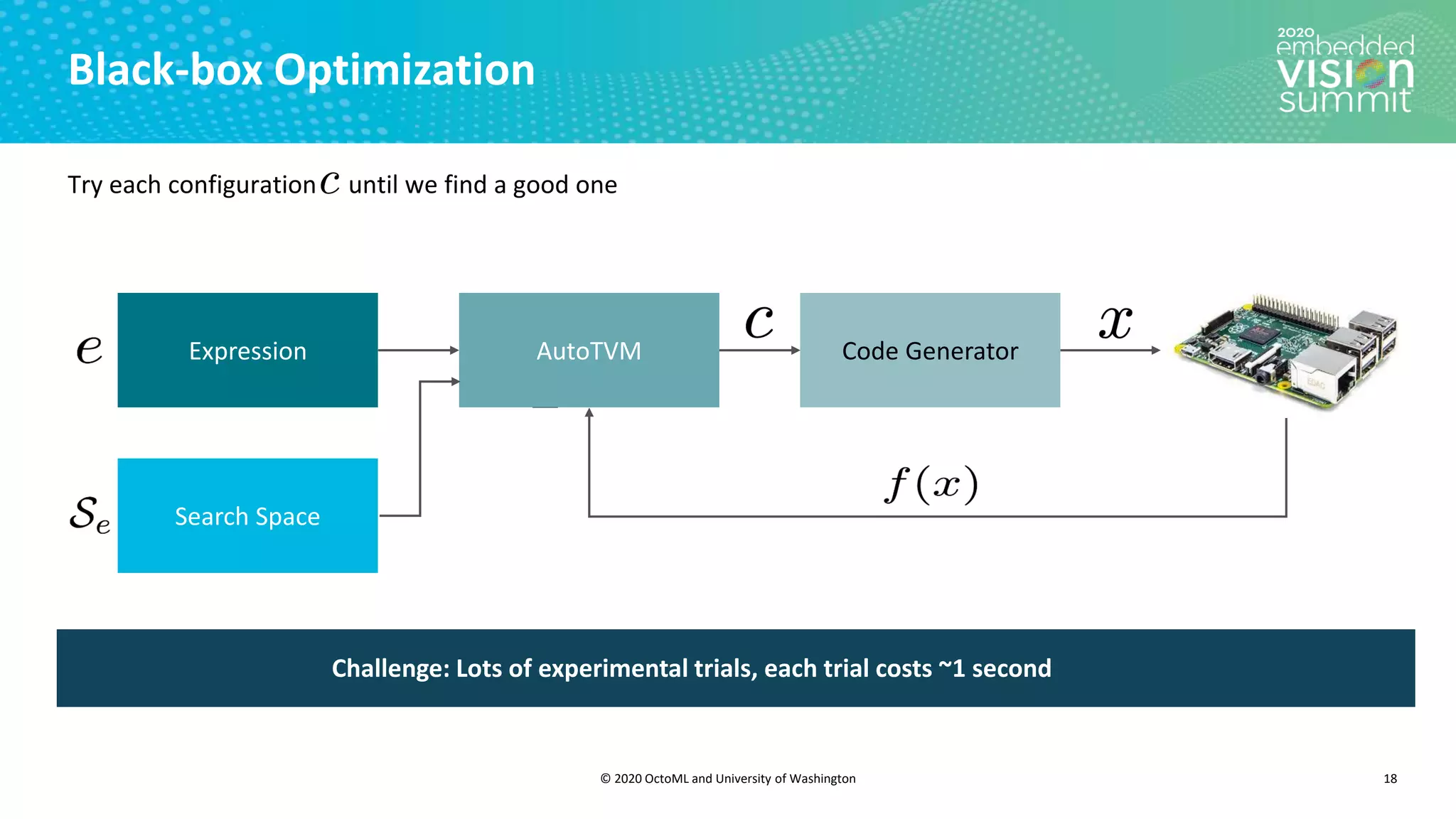
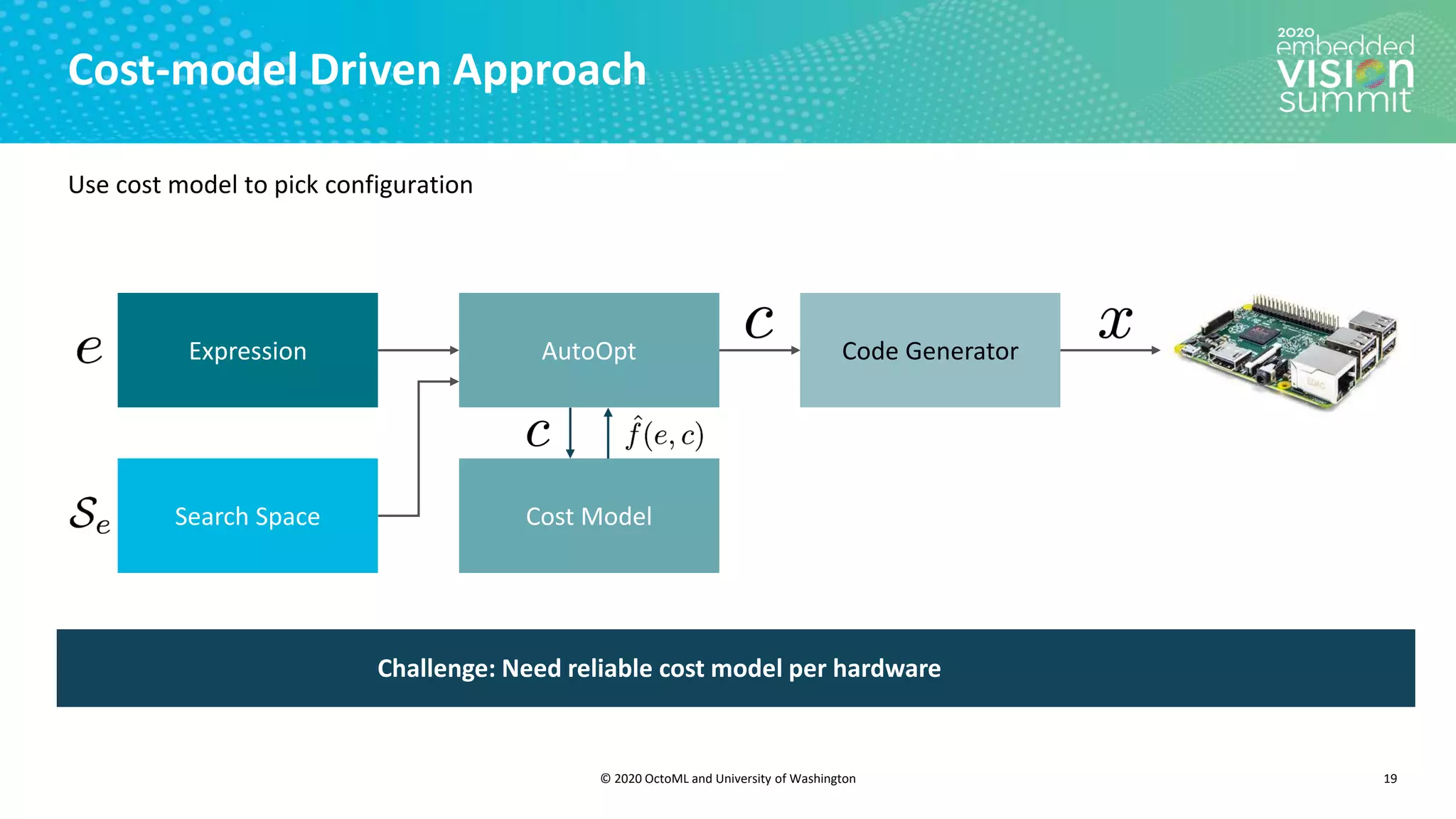
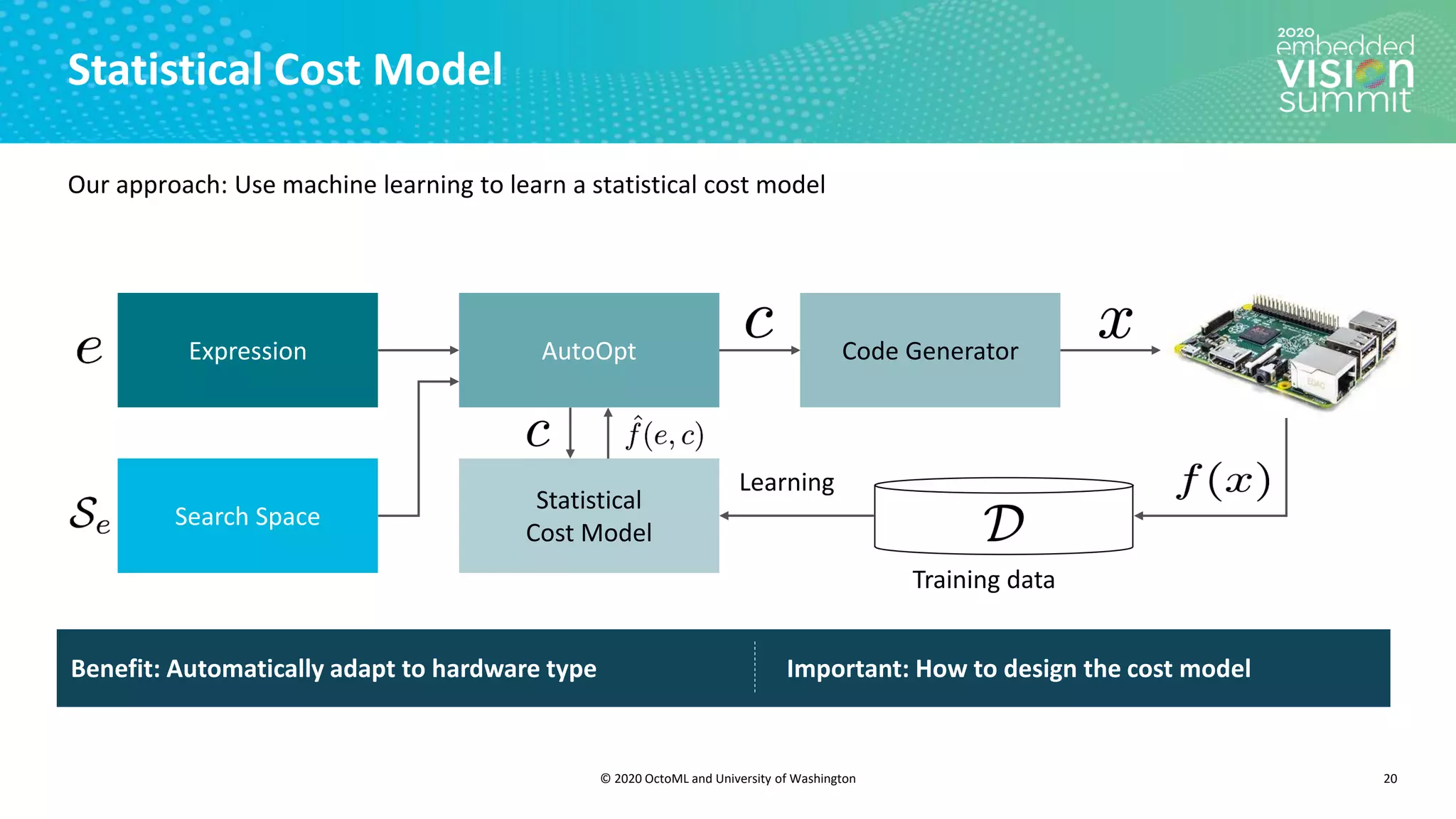
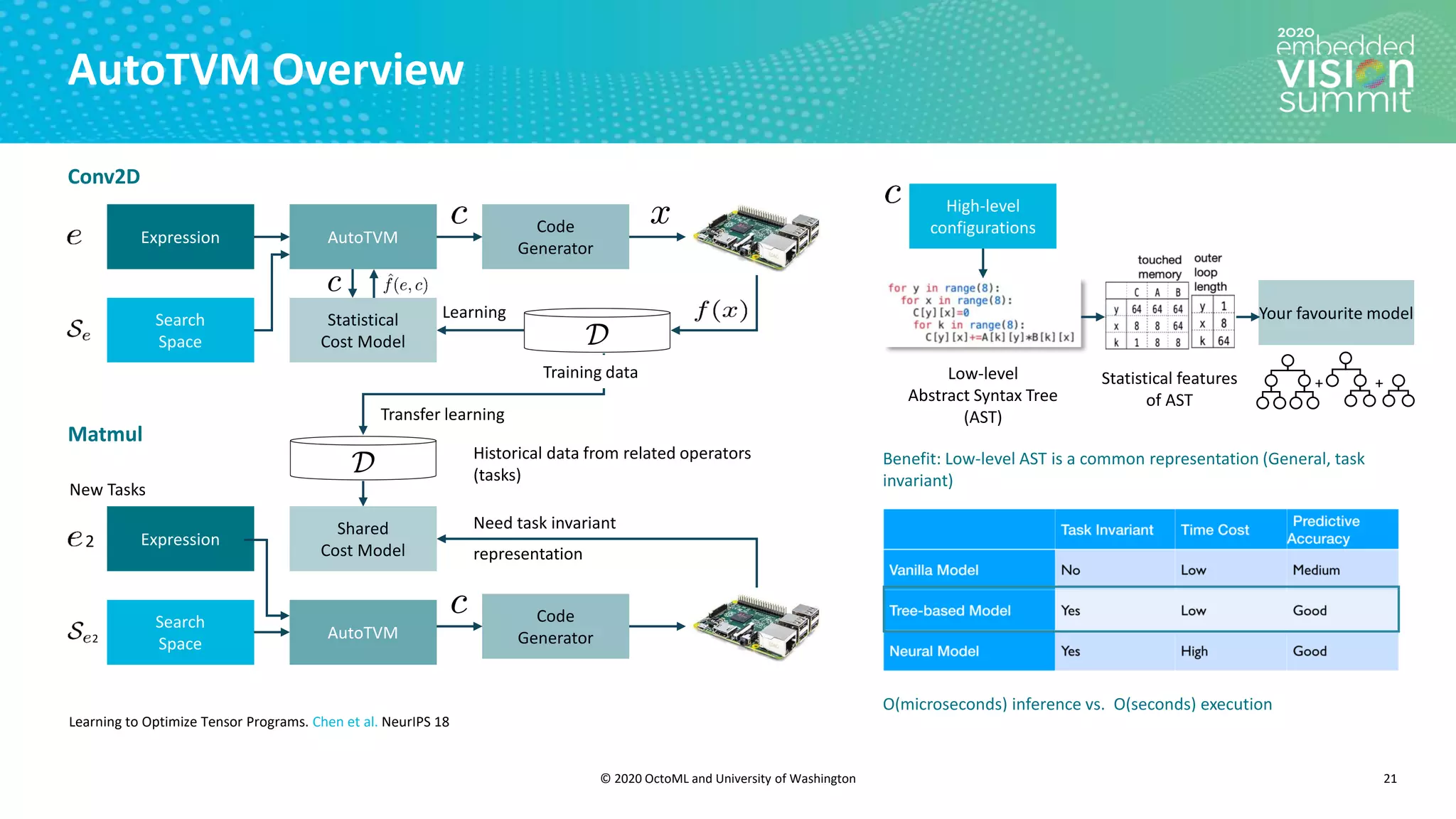
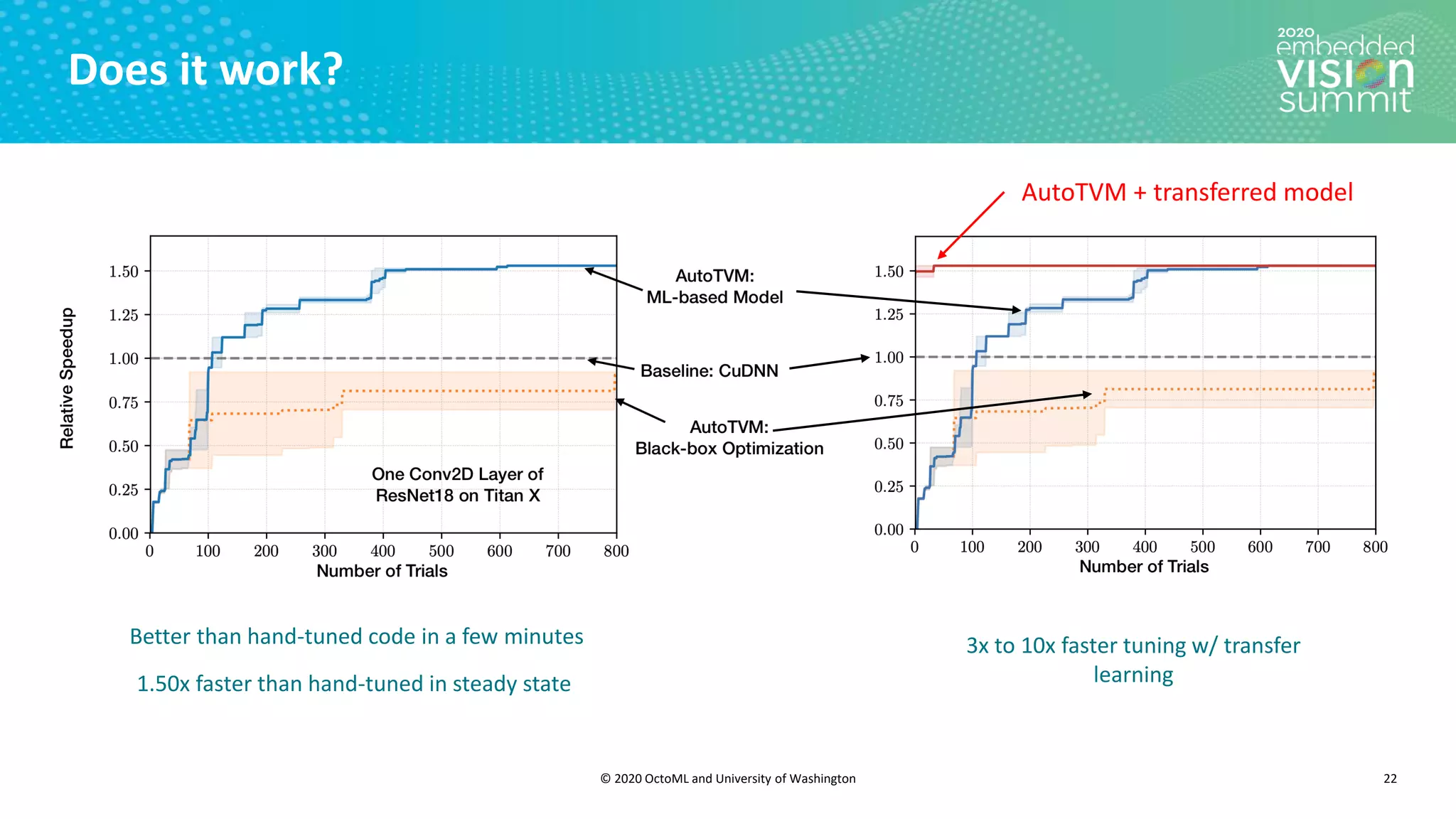
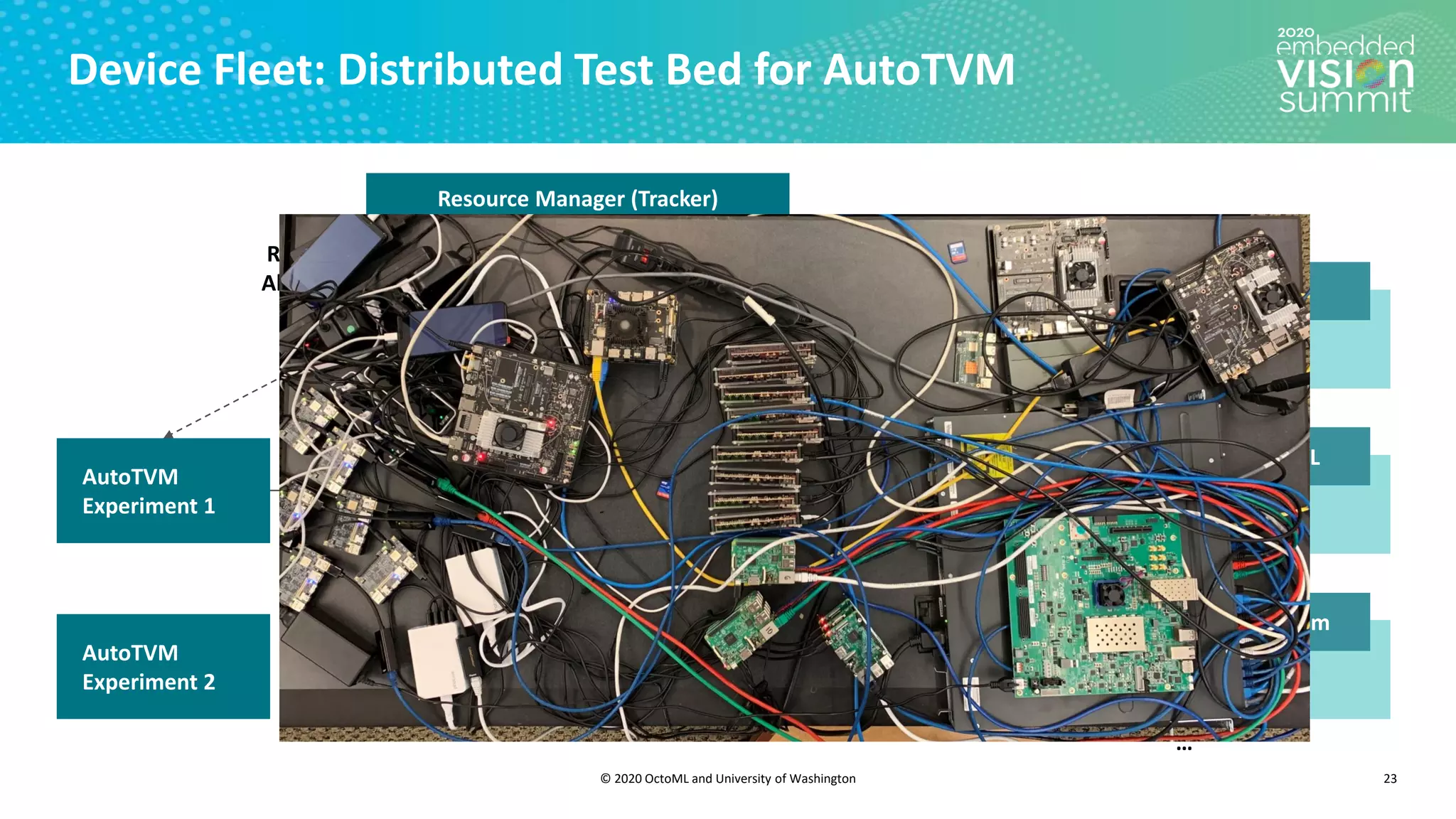
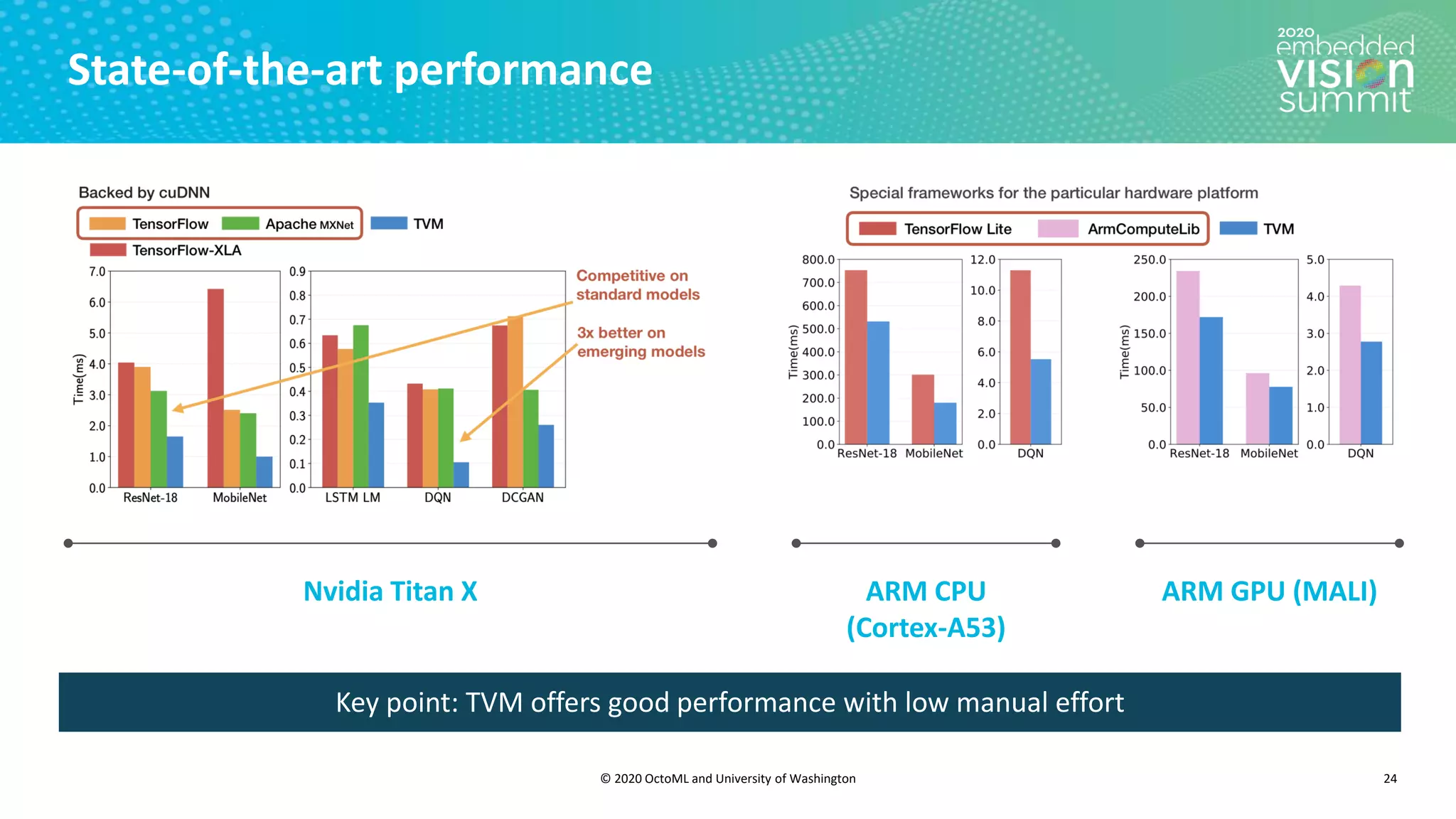
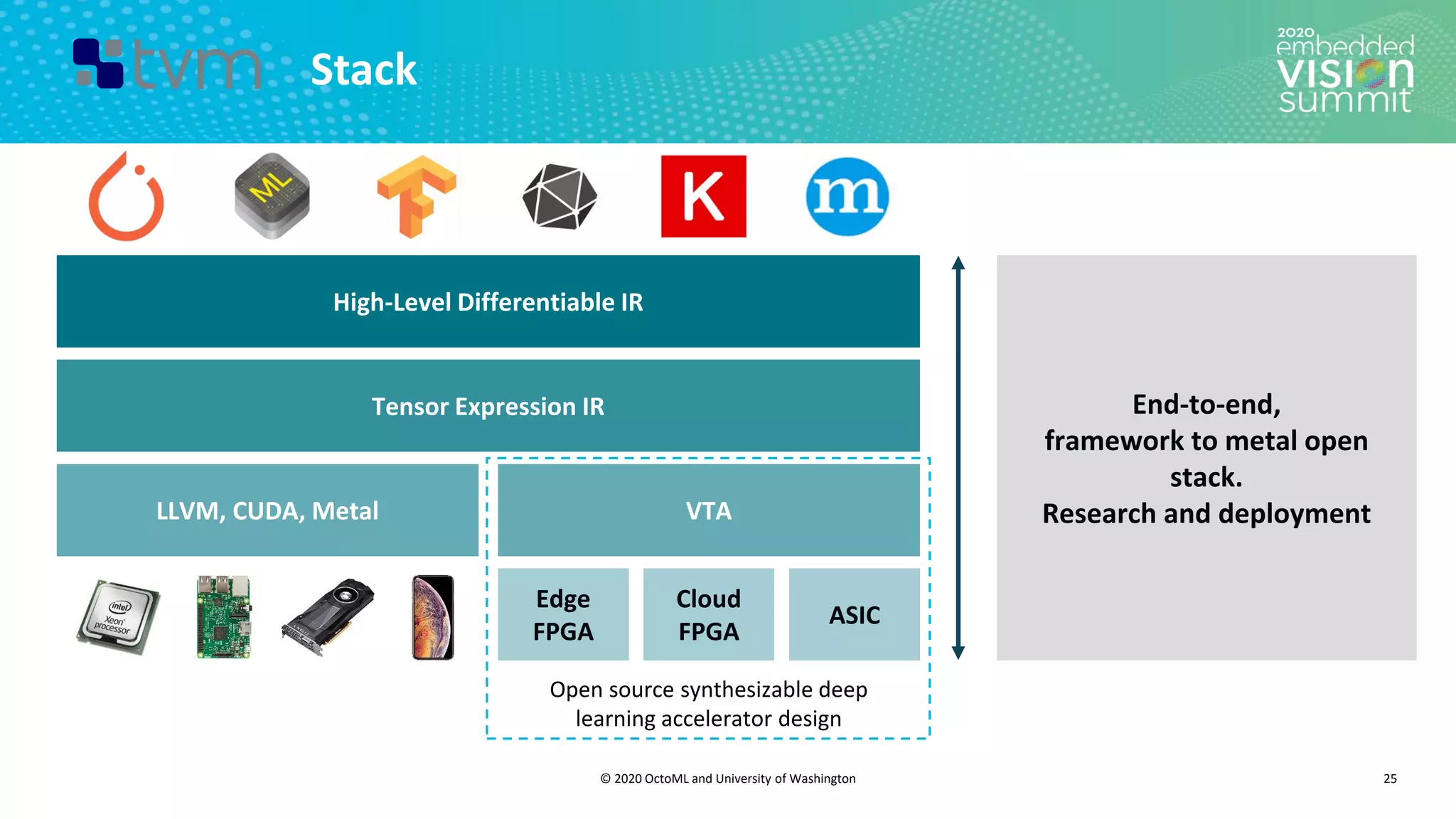
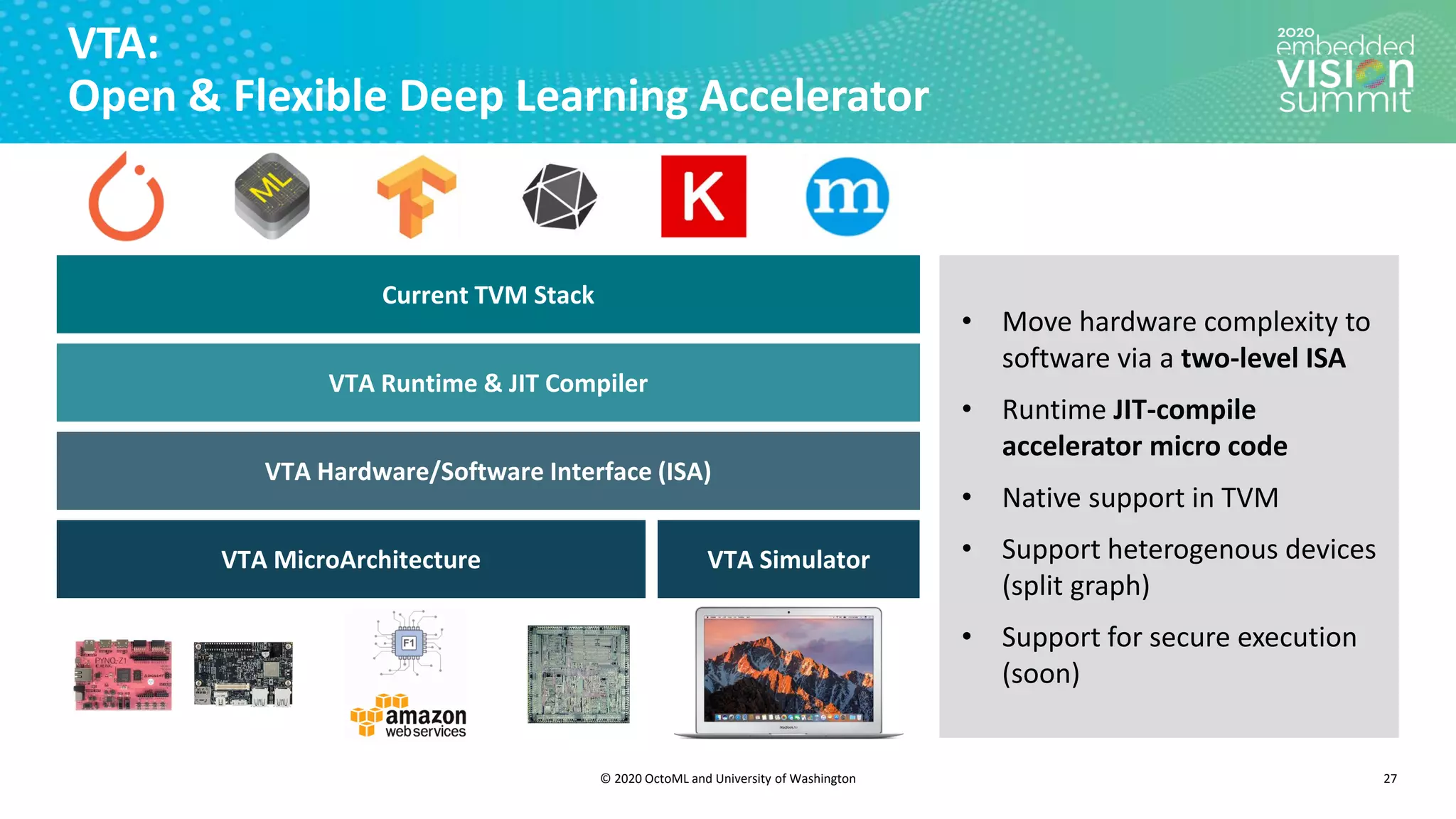
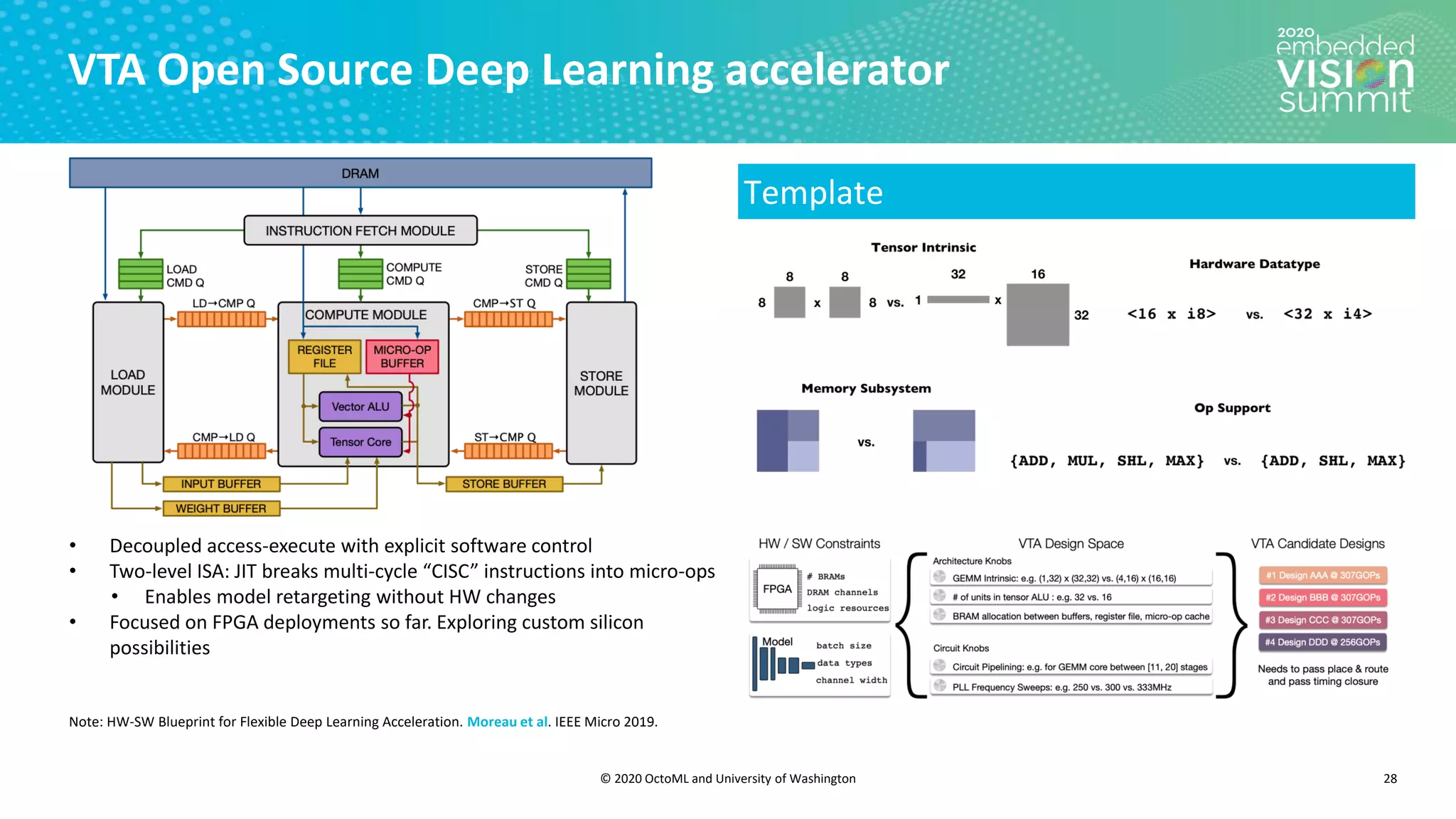
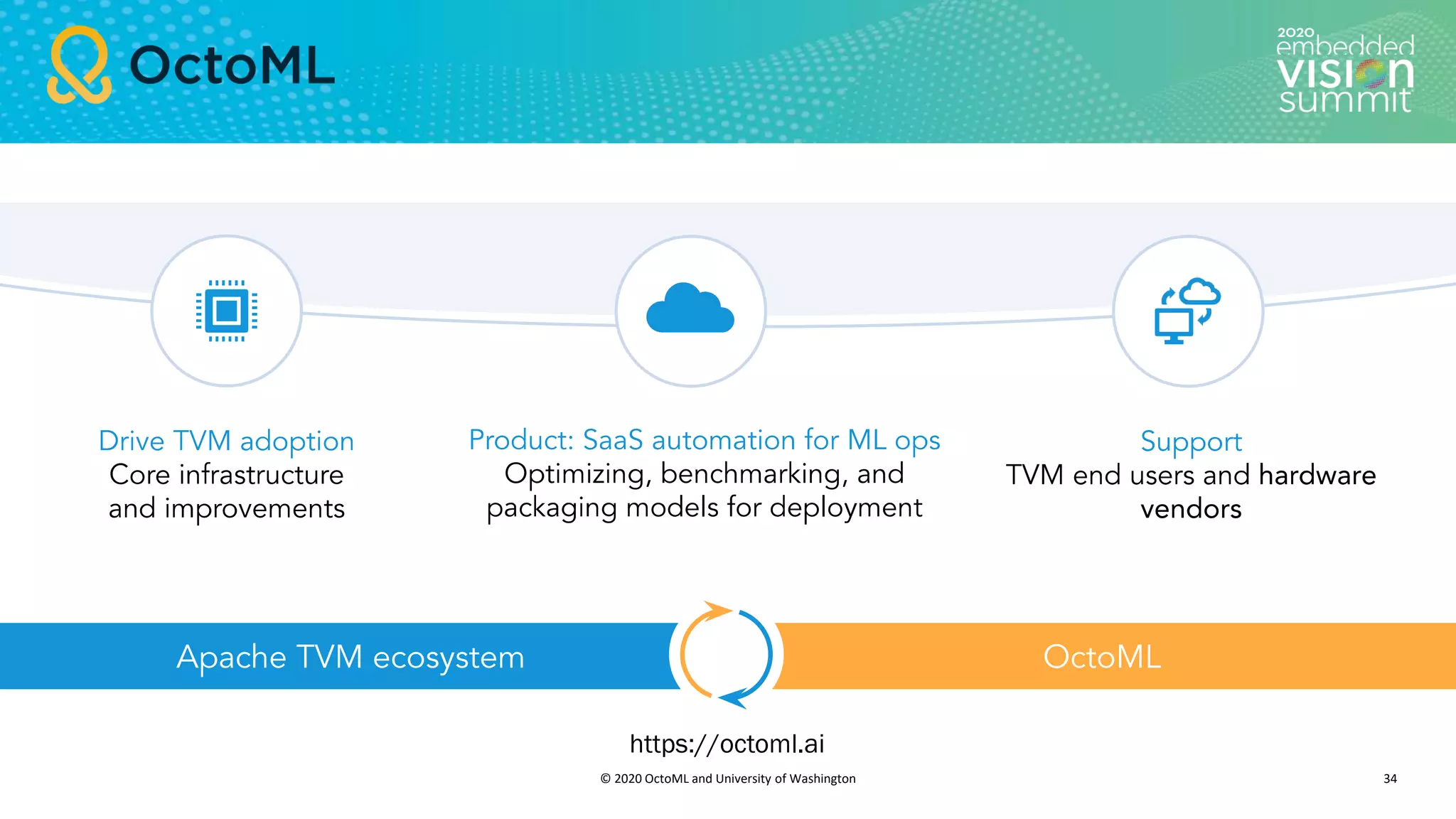
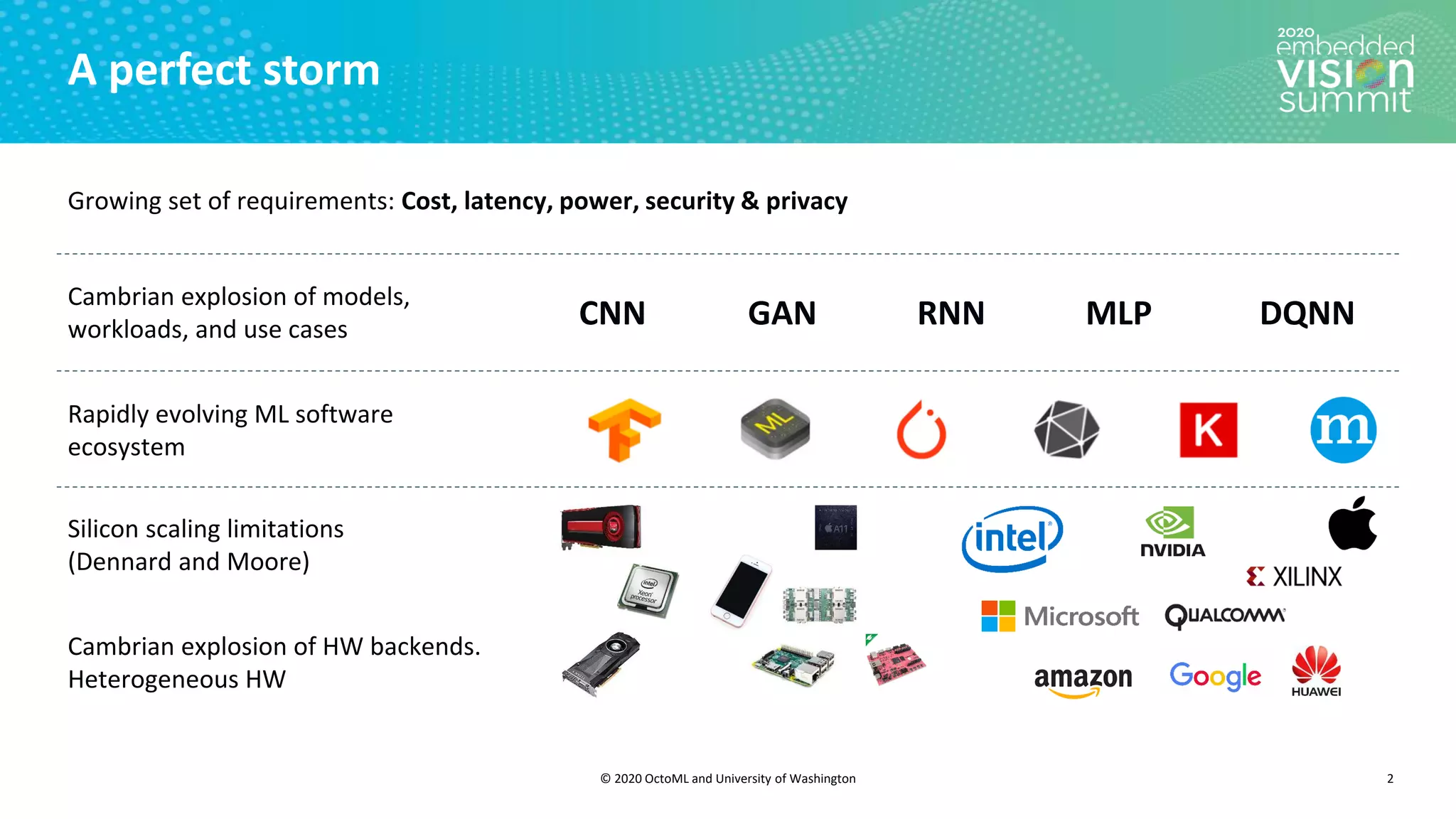
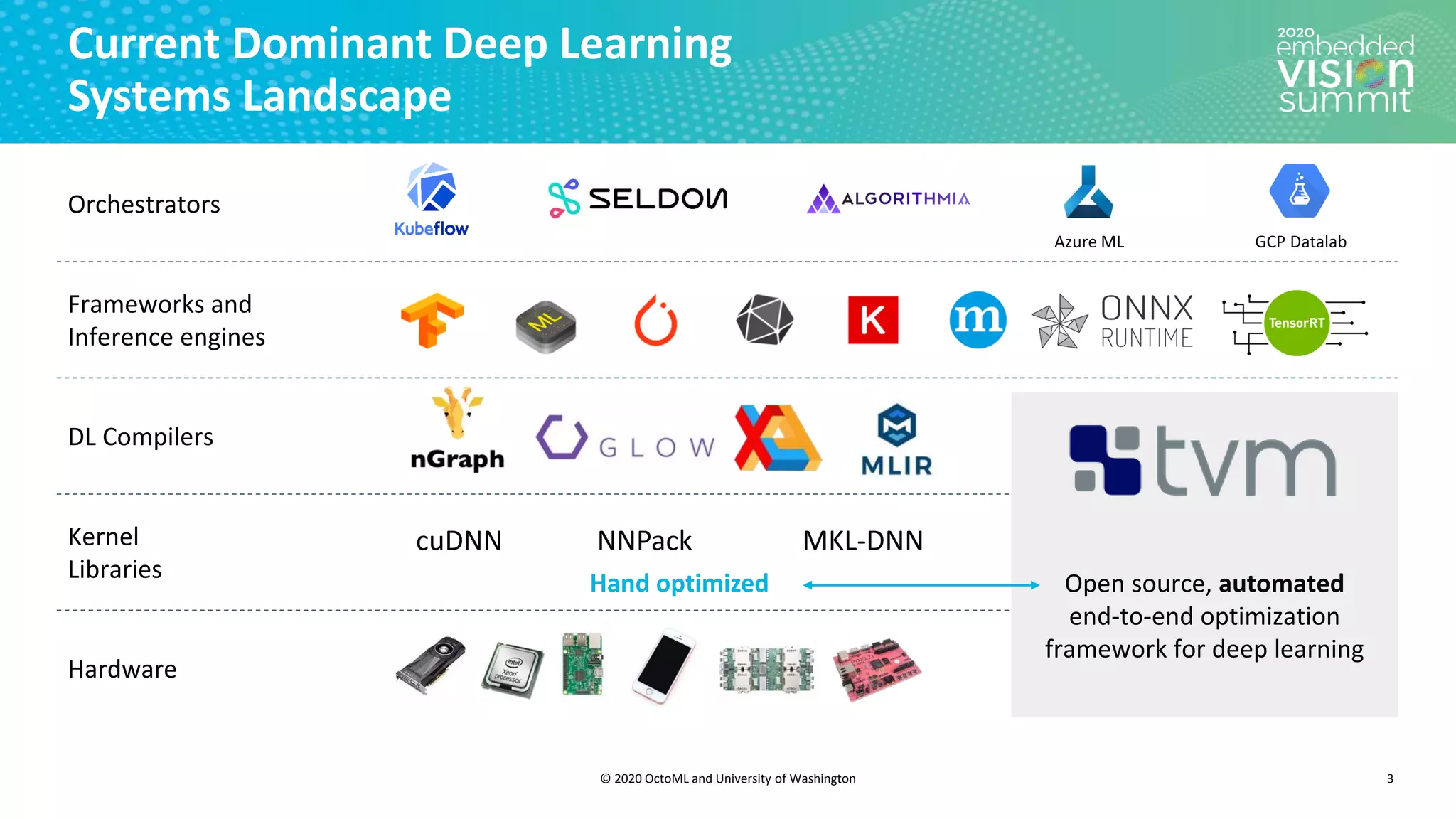
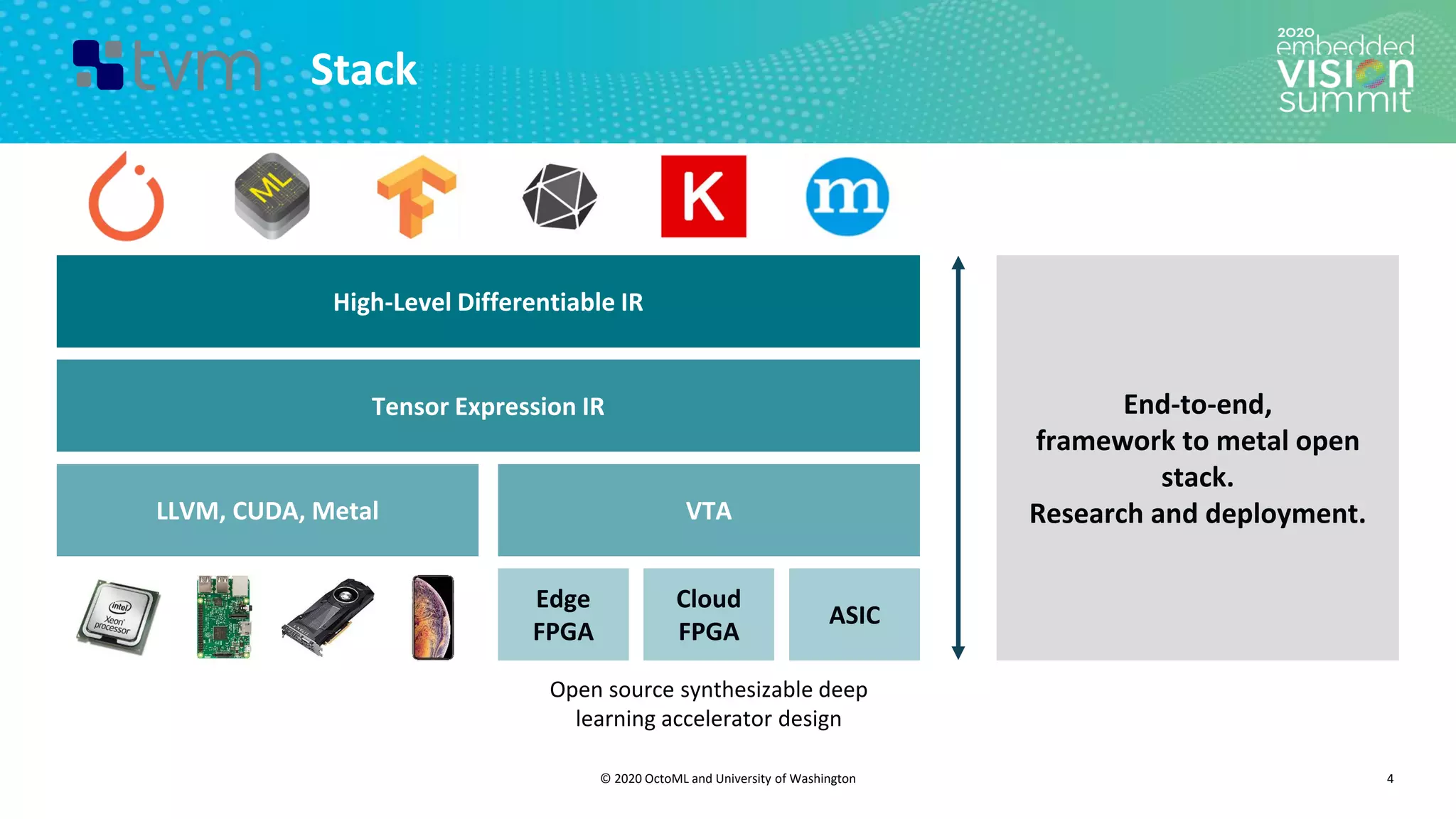
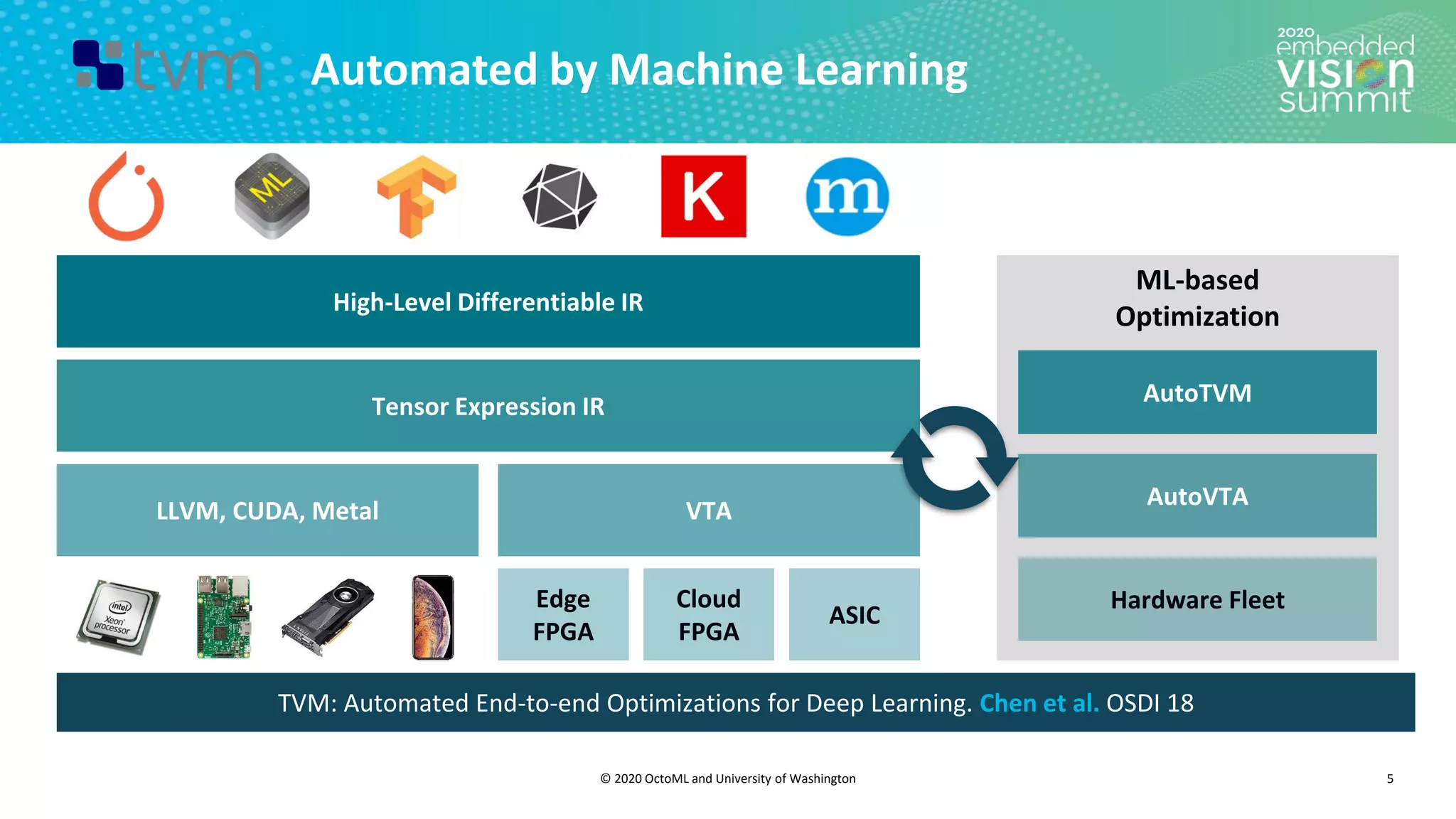
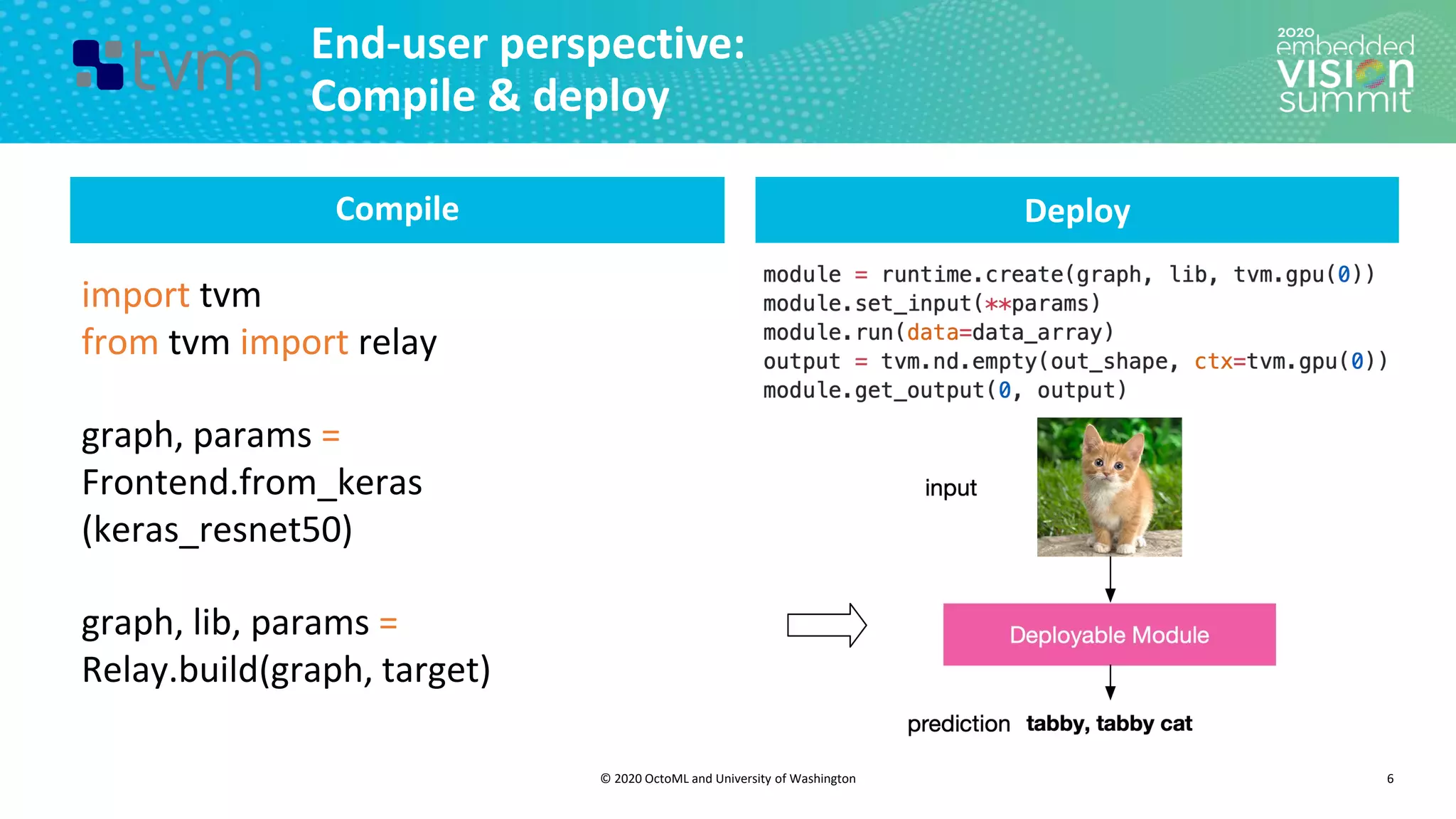
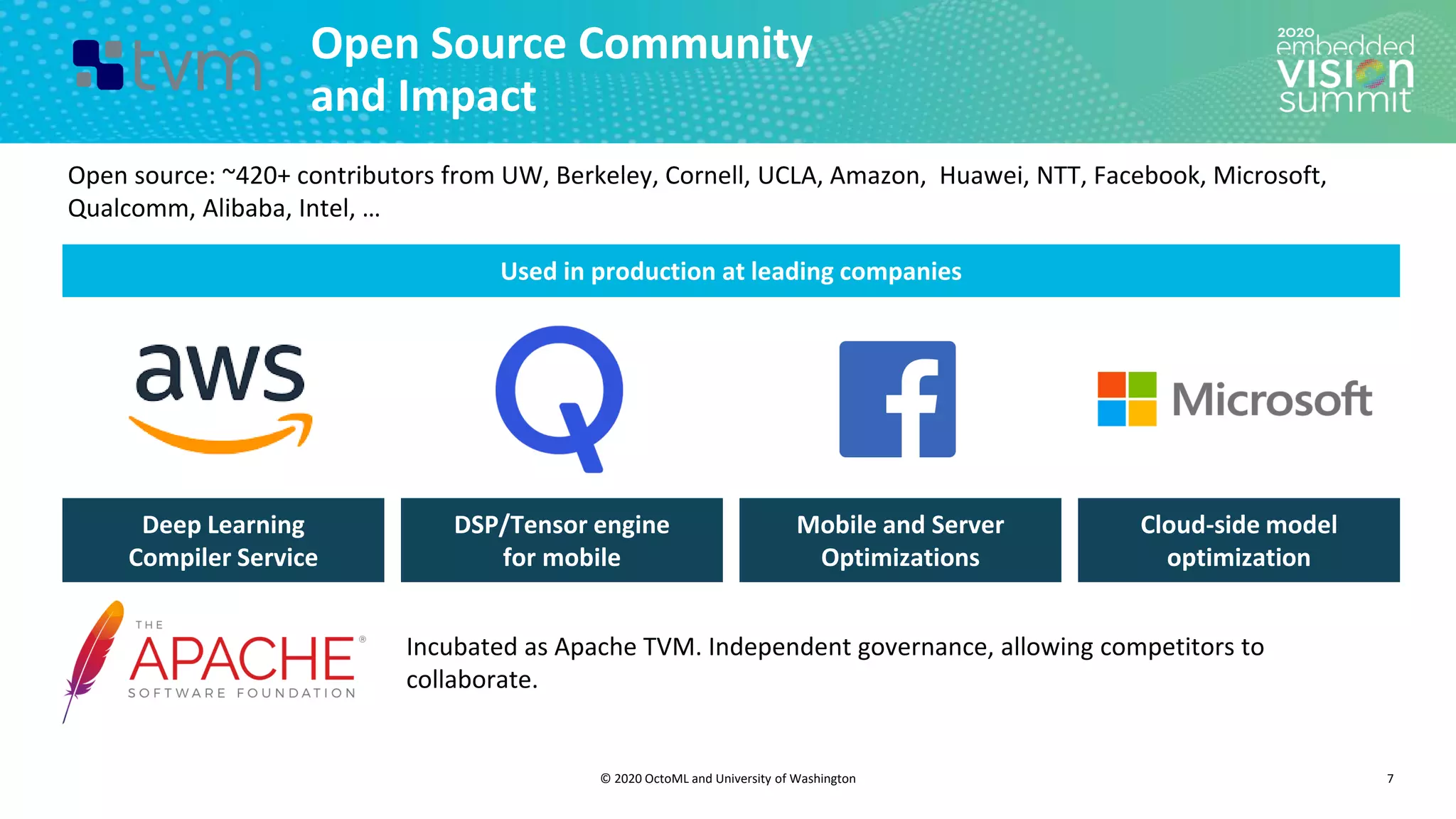
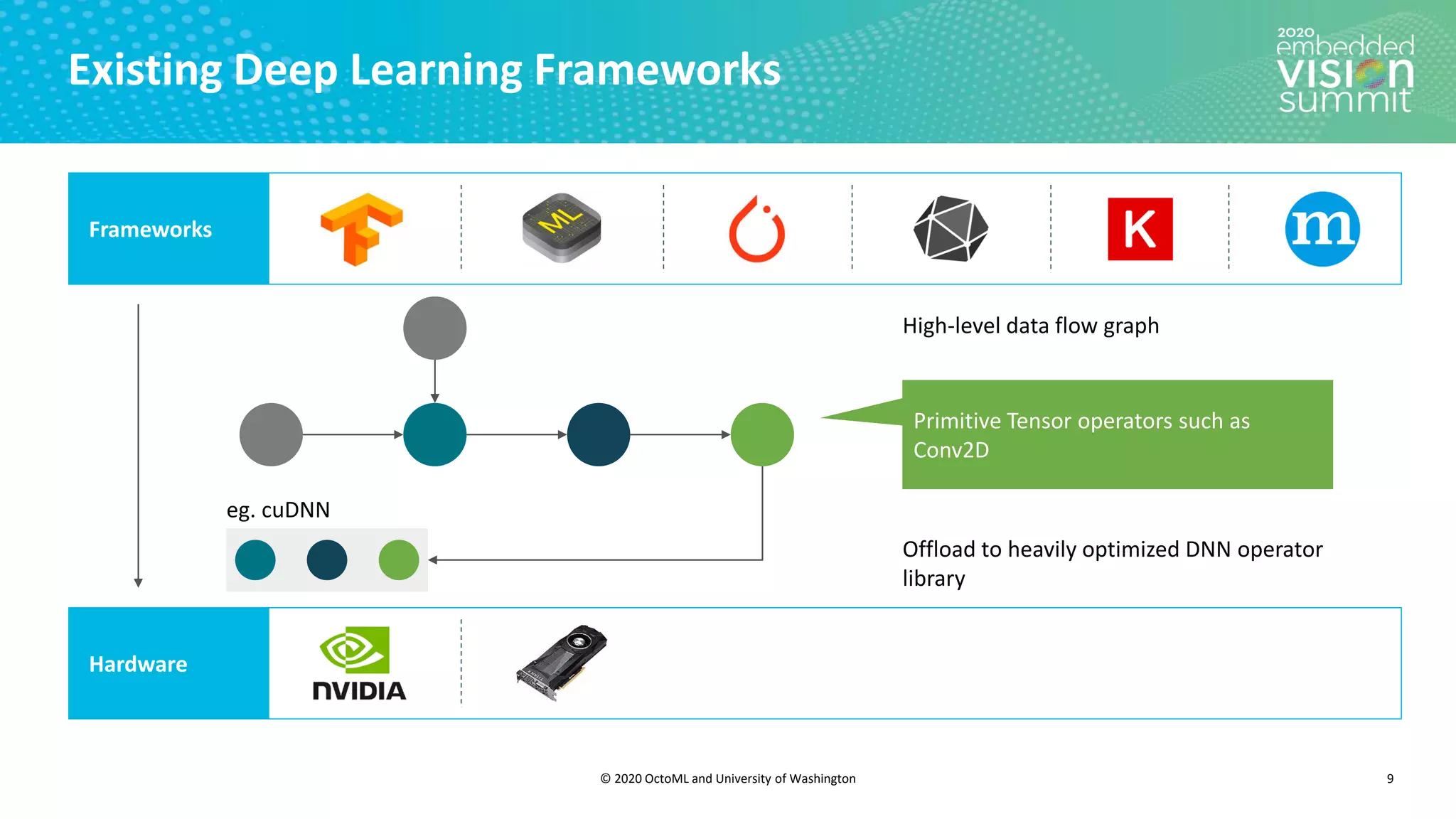
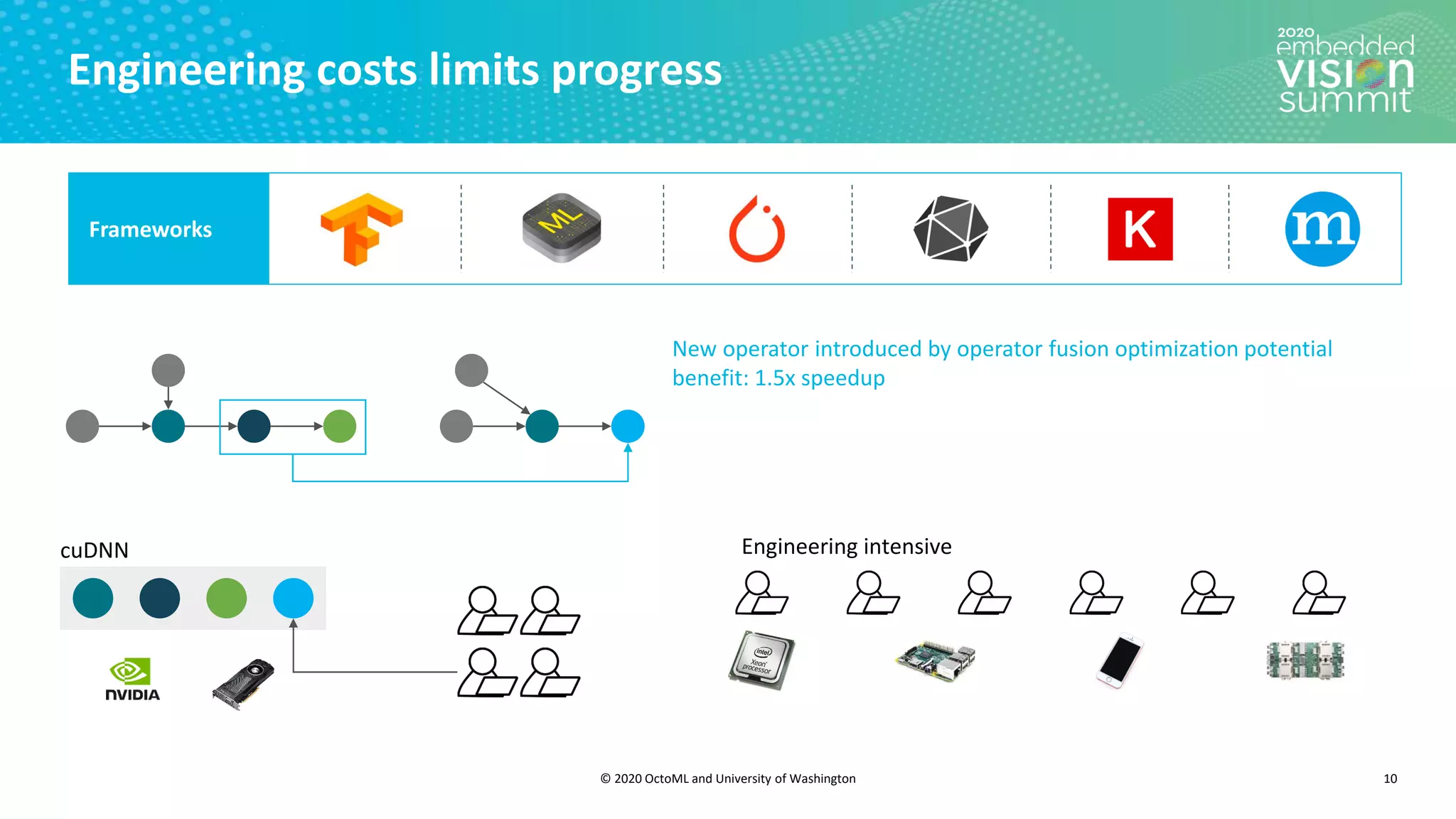
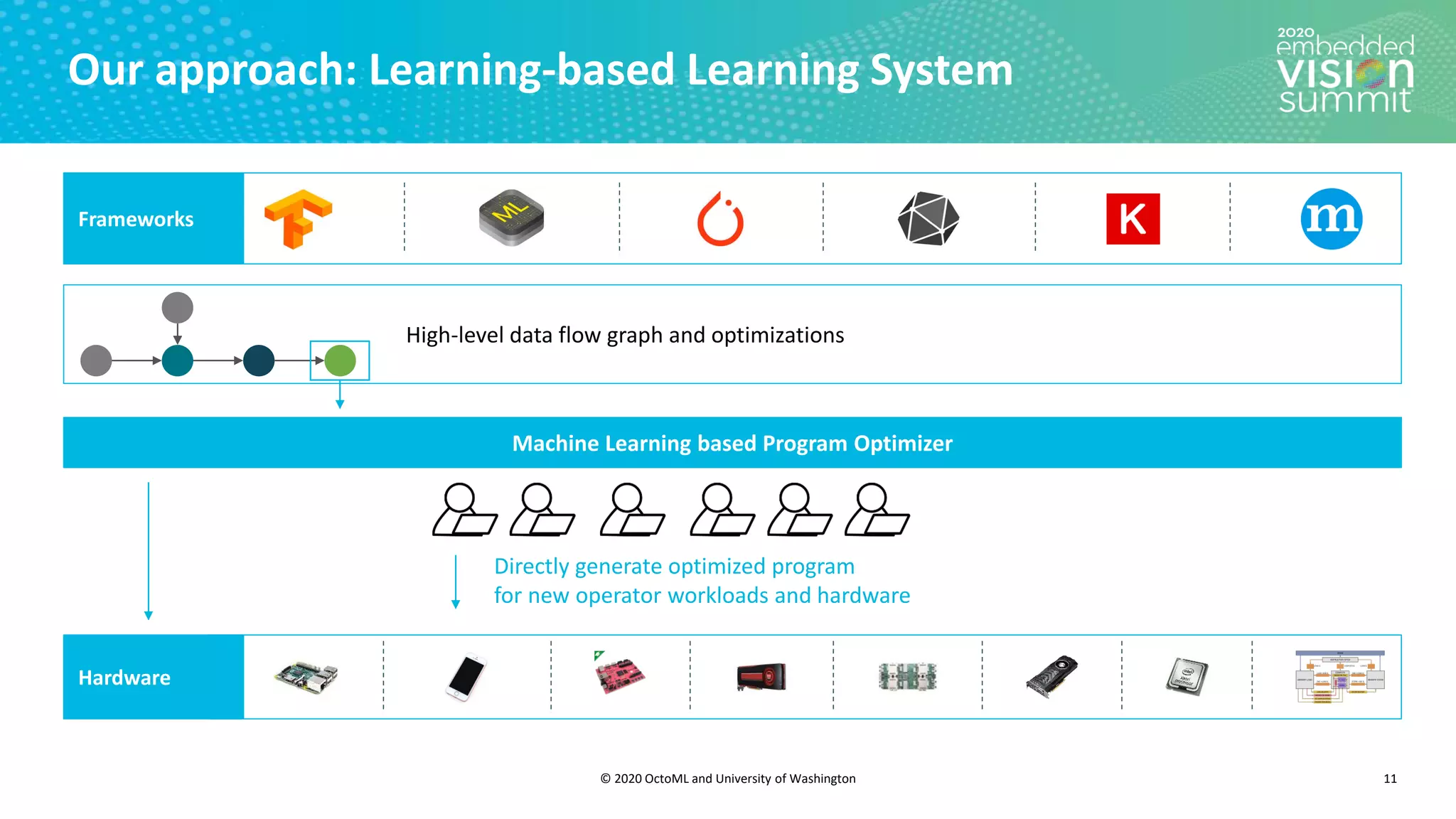
The document introduces the TVM open source deep learning compiler stack developed by OctoML and the University of Washington, highlighting its role in optimizing machine learning frameworks for various hardware backends. It discusses the challenges of deep learning compilation, including cost and performance optimization, and explains TVM's automated end-to-end optimization process using machine learning. The document emphasizes TVM's collaborative open-source community and its broad application across leading tech companies for efficient deployment of deep learning models.


![© 2020 OctoML and University of Washington Tensor Compilation/Optimization as a search problem 12 Tensor Expression (Specification) C = tvm.compute((m, n), lambda y, x: tvm.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k)) Search Space of Possible Program Optimizations Low-level Program Variants](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceze2020embeddedvisionsummitslidesfinal-210202163449/75/Introduction-to-the-TVM-Open-Source-Deep-Learning-Compiler-Stack-a-Presentation-from-OctoML-12-2048.jpg)
![© 2020 OctoML and University of Washington Search Space Example (1/3) 13 Search Space of Possible Program Optimizations Vanilla Code Tensor Expression (Specification) C = tvm.compute((m, n), lambda y, x: tvm.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceze2020embeddedvisionsummitslidesfinal-210202163449/75/Introduction-to-the-TVM-Open-Source-Deep-Learning-Compiler-Stack-a-Presentation-from-OctoML-13-2048.jpg)
![© 2020 OctoML and University of Washington Search Space Example (2/3) 14 Search Space of Possible Program Optimizations Loop Tiling for Locality Tensor Expression (Specification) C = tvm.compute((m, n), lambda y, x: tvm.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceze2020embeddedvisionsummitslidesfinal-210202163449/75/Introduction-to-the-TVM-Open-Source-Deep-Learning-Compiler-Stack-a-Presentation-from-OctoML-14-2048.jpg)
![© 2020 OctoML and University of Washington Search Space Example (3/3) 15 Search Space of Possible Program Optimizations Map to Accelerators Tensor Expression (Specification) C = tvm.compute((m, n), lambda y, x: tvm.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceze2020embeddedvisionsummitslidesfinal-210202163449/75/Introduction-to-the-TVM-Open-Source-Deep-Learning-Compiler-Stack-a-Presentation-from-OctoML-15-2048.jpg)
![© 2020 OctoML and University of Washington Optimization space is really large… 16 Loop Transformations Thread Bindings Cache Locality Thread Cooperation Tensorization Latency Hiding Typically explored via human intuition. How can we automate this? Auto-tuning is too slow. Billions of possible optimization choices Tensor Expression (Specification) C = tvm.compute((m, n), lambda y, x: tvm.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceze2020embeddedvisionsummitslidesfinal-210202163449/75/Introduction-to-the-TVM-Open-Source-Deep-Learning-Compiler-Stack-a-Presentation-from-OctoML-16-2048.jpg)