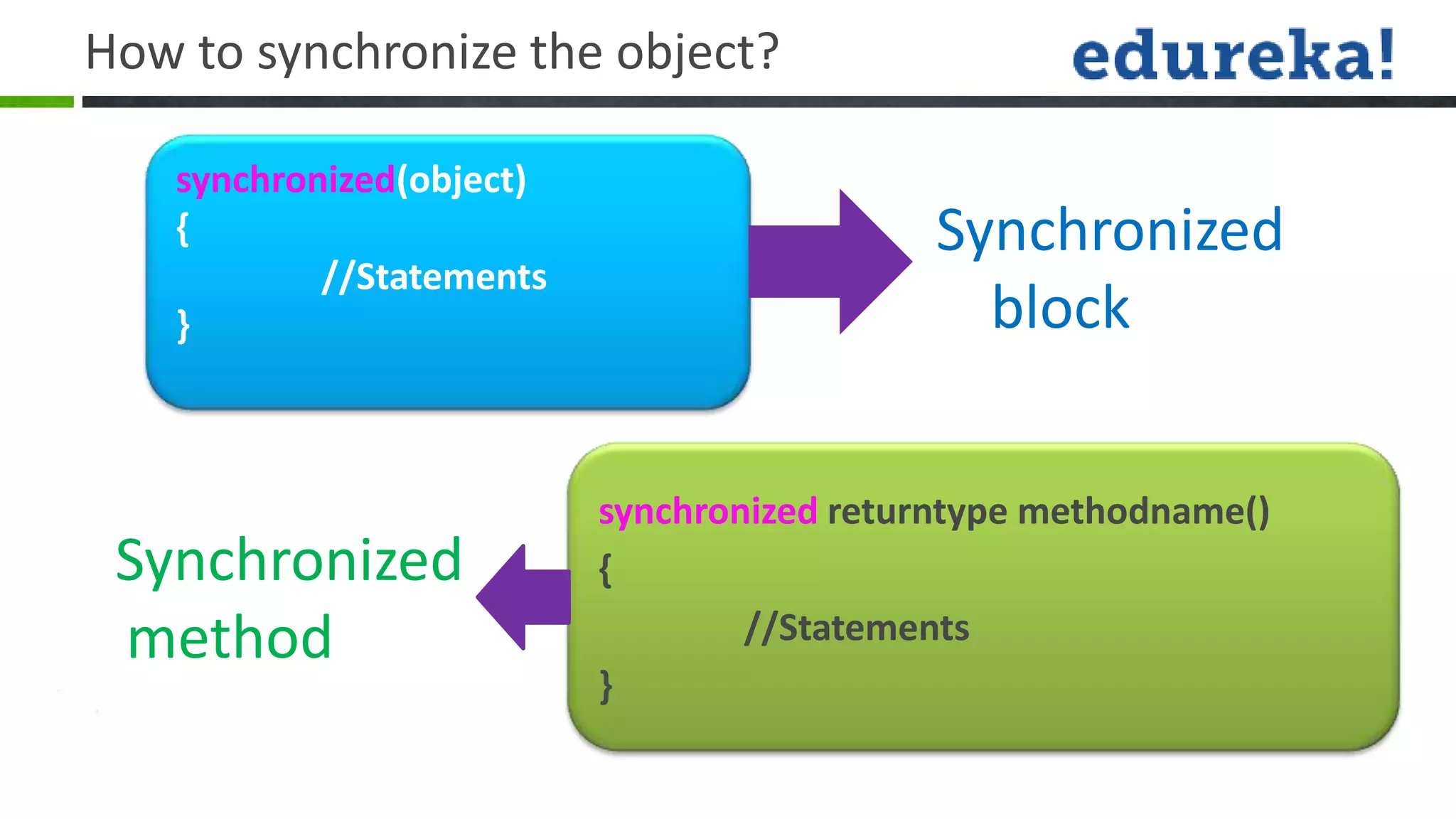
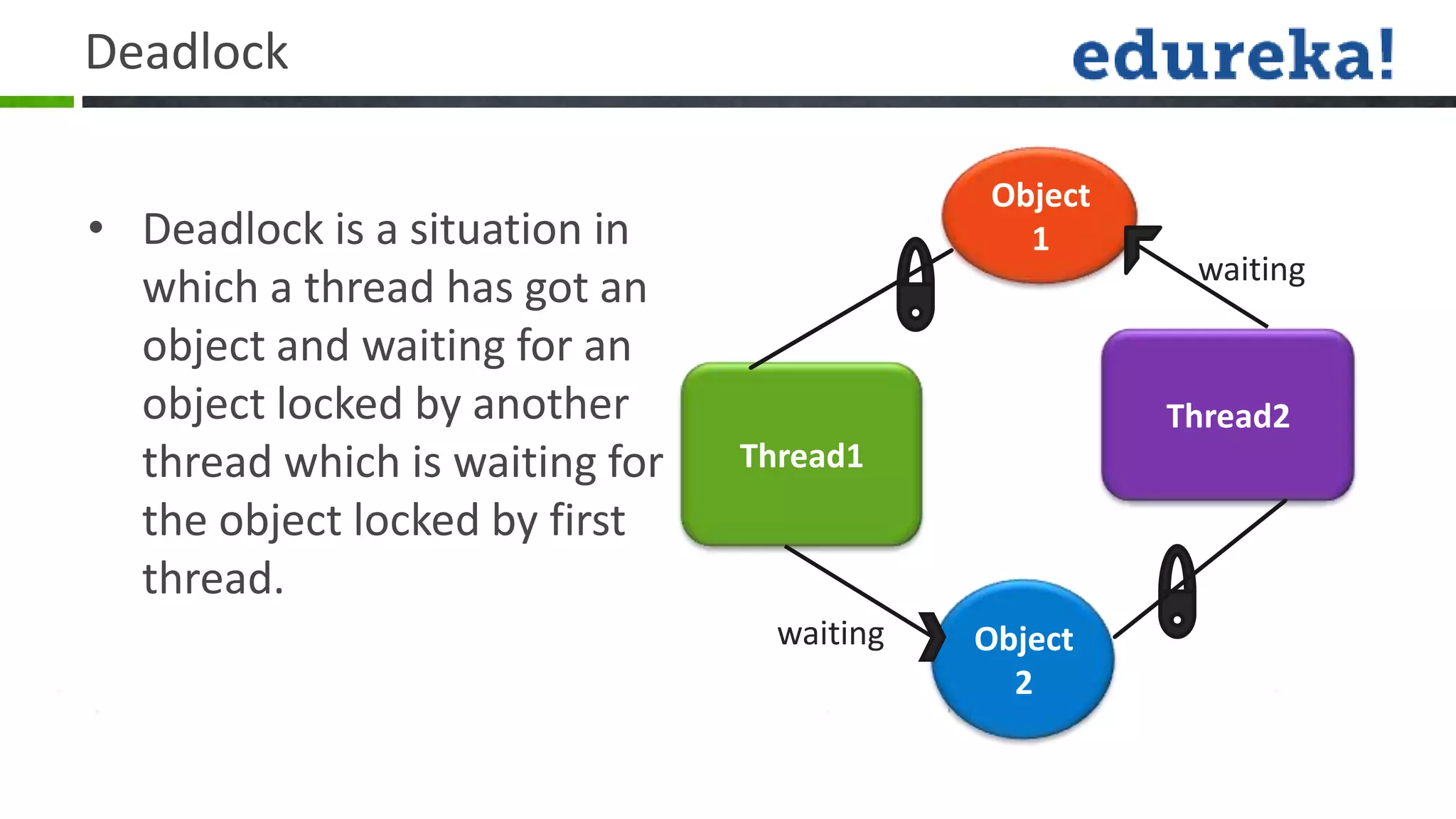
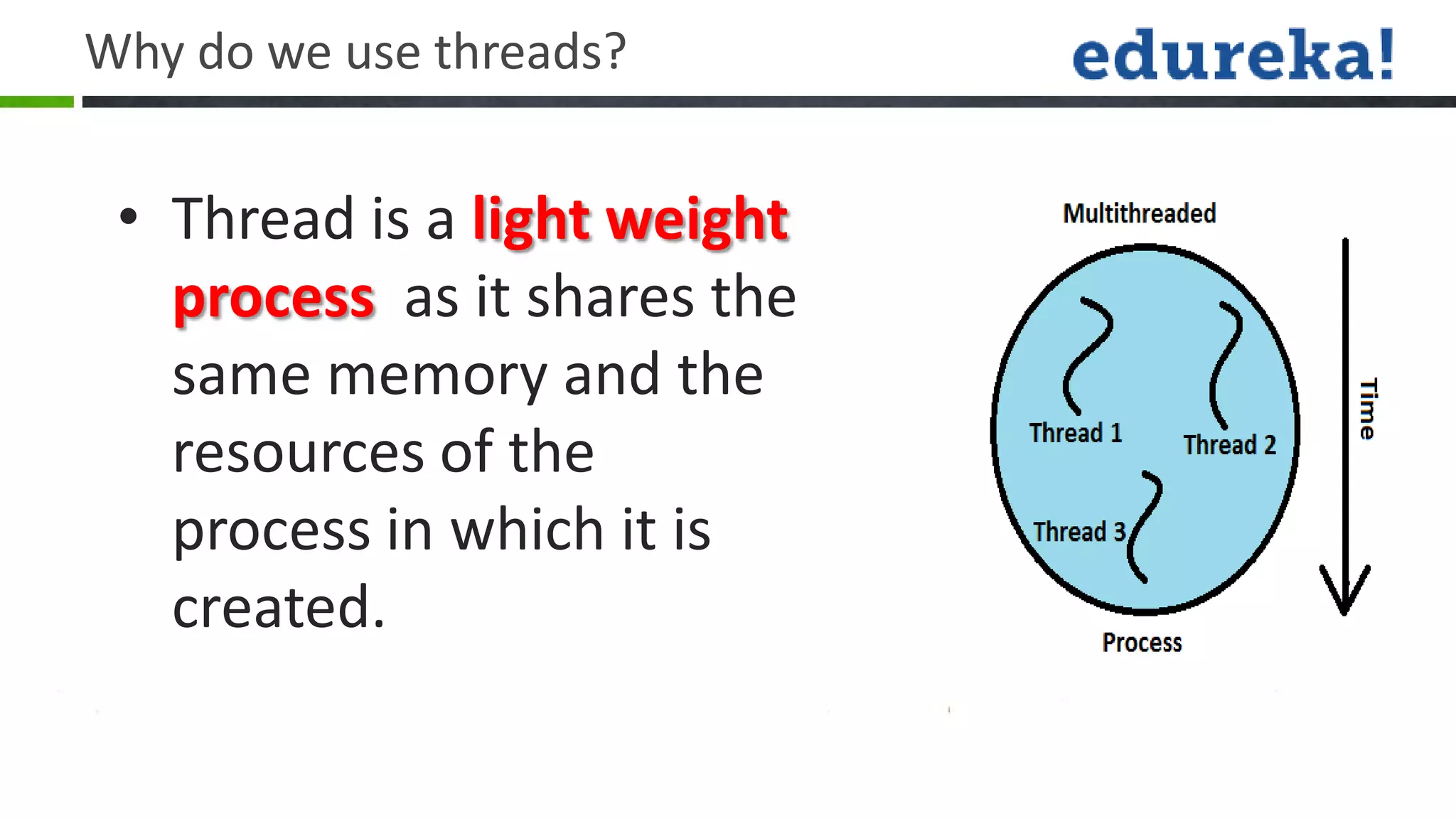
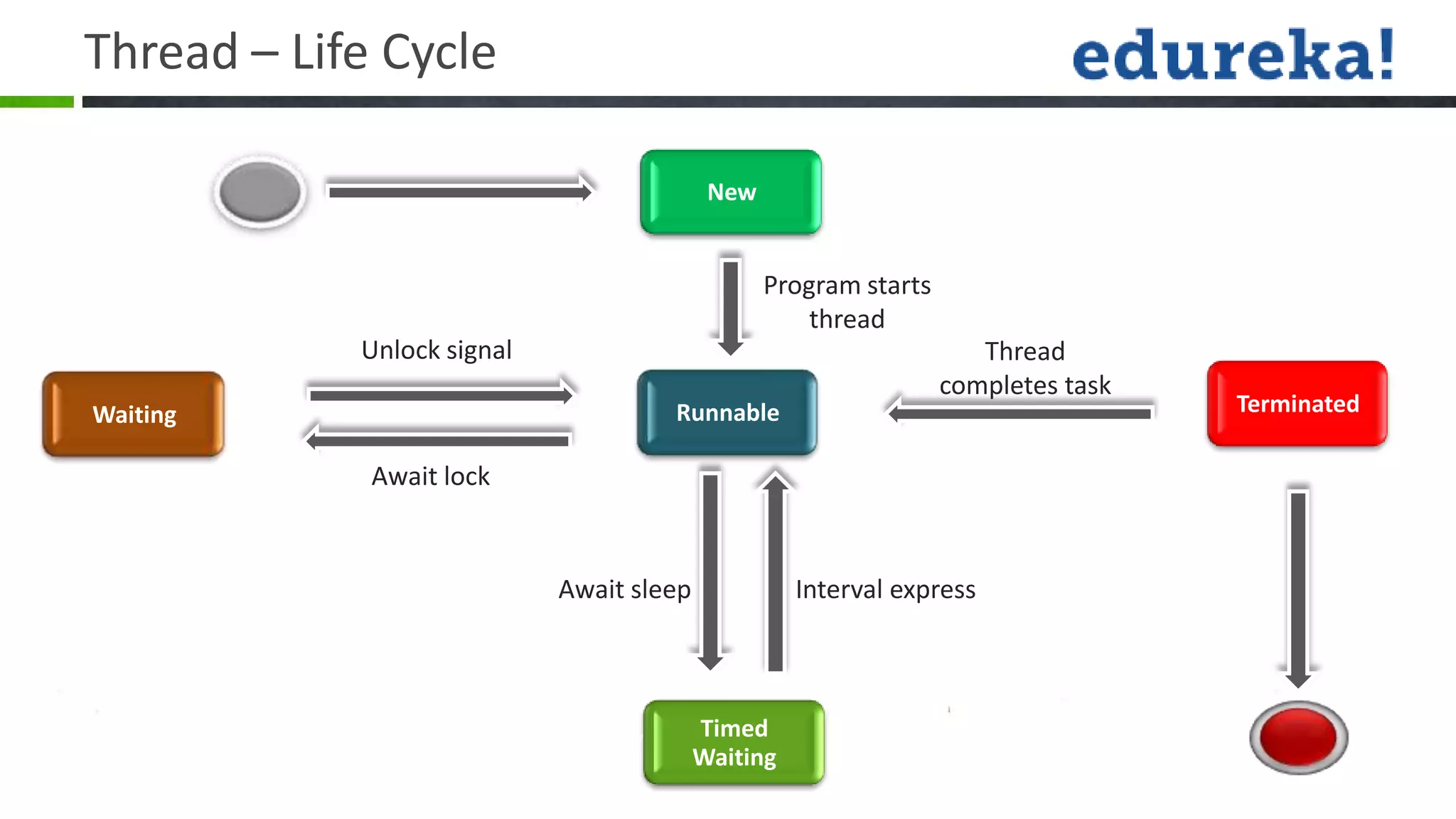
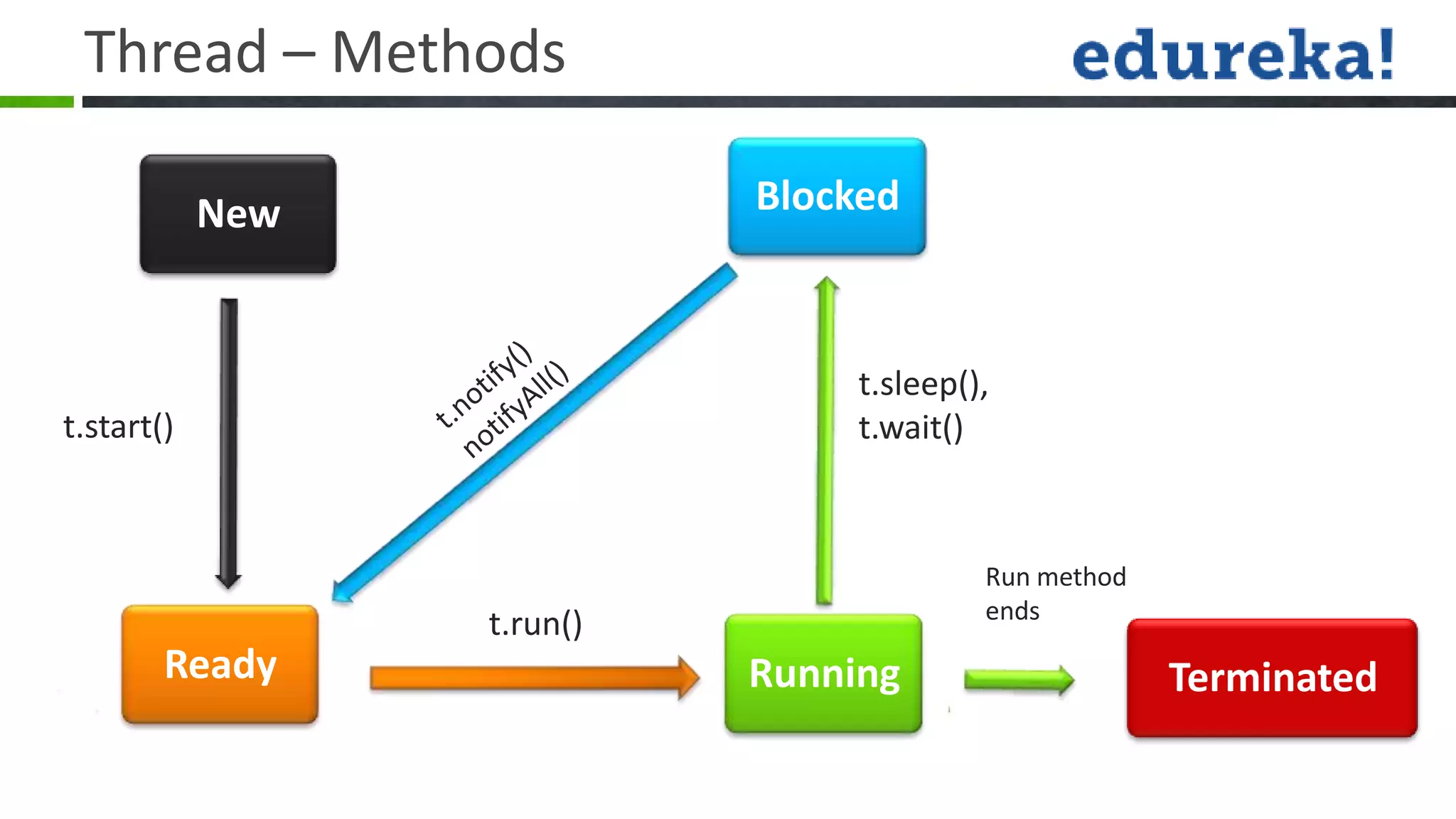
Threads allow a program to split into multiple threads that can run concurrently. A thread is a lightweight subprocess that shares memory and resources with other threads in a process. Threads allow programs to perform multiple tasks simultaneously or asynchronously. Threads have a life cycle and priority levels that determine their order of execution. Threads can be created by implementing the Runnable interface or extending the Thread class. Synchronization ensures that only one thread can access a shared resource at a time to prevent race conditions. Inter-thread communication allows threads to coordinate using wait(), notify(), and notifyAll() methods. Deadlocks can occur when threads are waiting indefinitely for resources held by each other.




![Implementing Runnable Interface package com.edureka.threadsrunnable; public class ThreadClass implements Runnable { public void run() { System.out.println("Hello from a thread!"); } } package com.edureka.threadsrunnable; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadClass obj = new ThreadClass(); //object of class ThreadClass Thread thread_runnable = new Thread(obj); thread_runnable.start(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass6-130416015944-phpapp02/75/Java-class-6-10-2048.jpg)
![Extending Thread Class package com.edureka.threads; public class ThreadClass extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println("Hello from a thread!"); } } package com.edureka.threads; public class Main{ public static void main(String args[]) { ThreadClass obj = new ThreadClass(); //object of class ThreadT Thread thread_extend = new Thread(obj); thread_extend.start(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass6-130416015944-phpapp02/75/Java-class-6-11-2048.jpg)


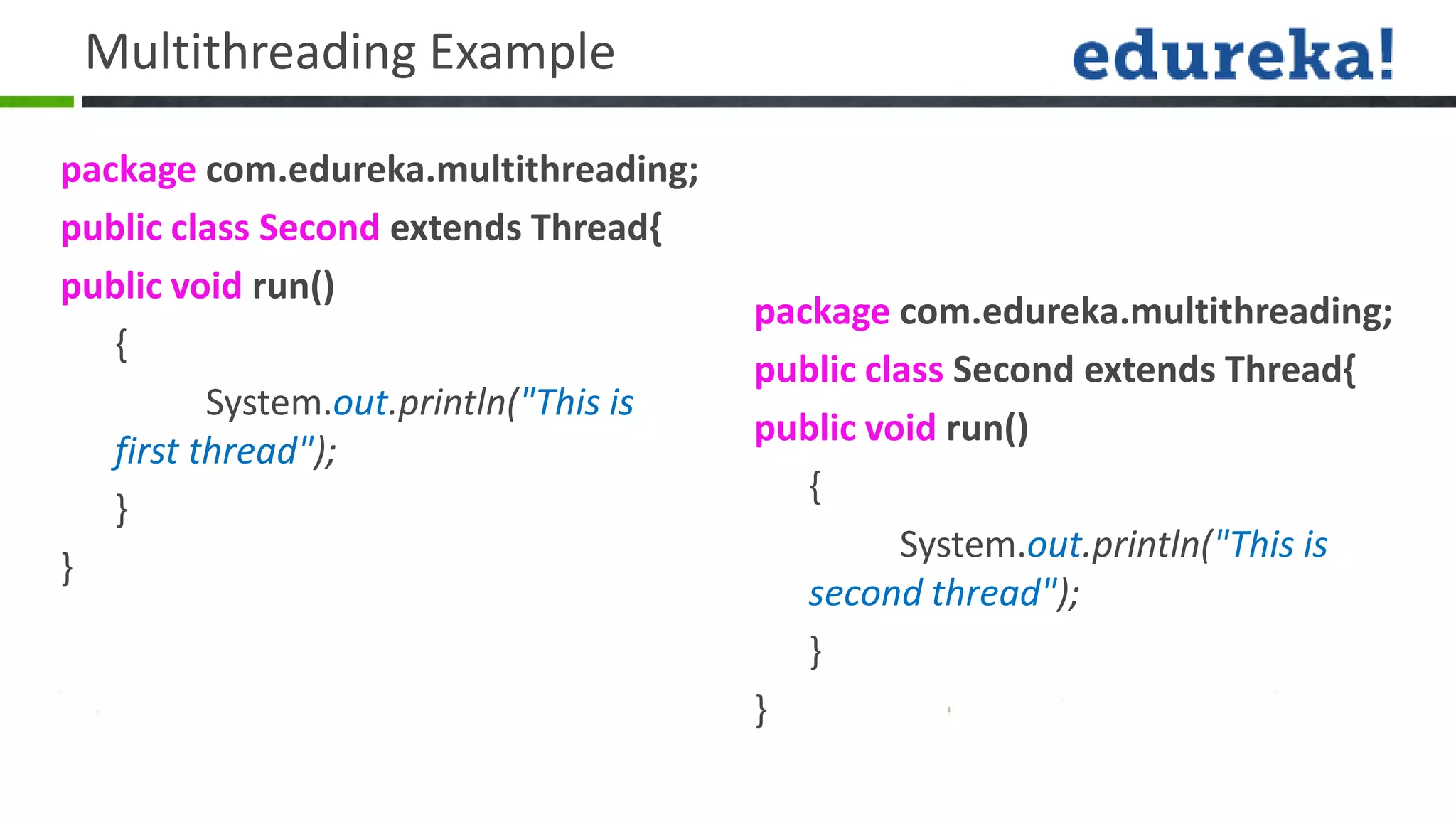
![Multithreading Example package com.edureka.multithreading; public class Main extends Thread{ public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new One()); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Second()); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass6-130416015944-phpapp02/75/Java-class-6-15-2048.jpg)