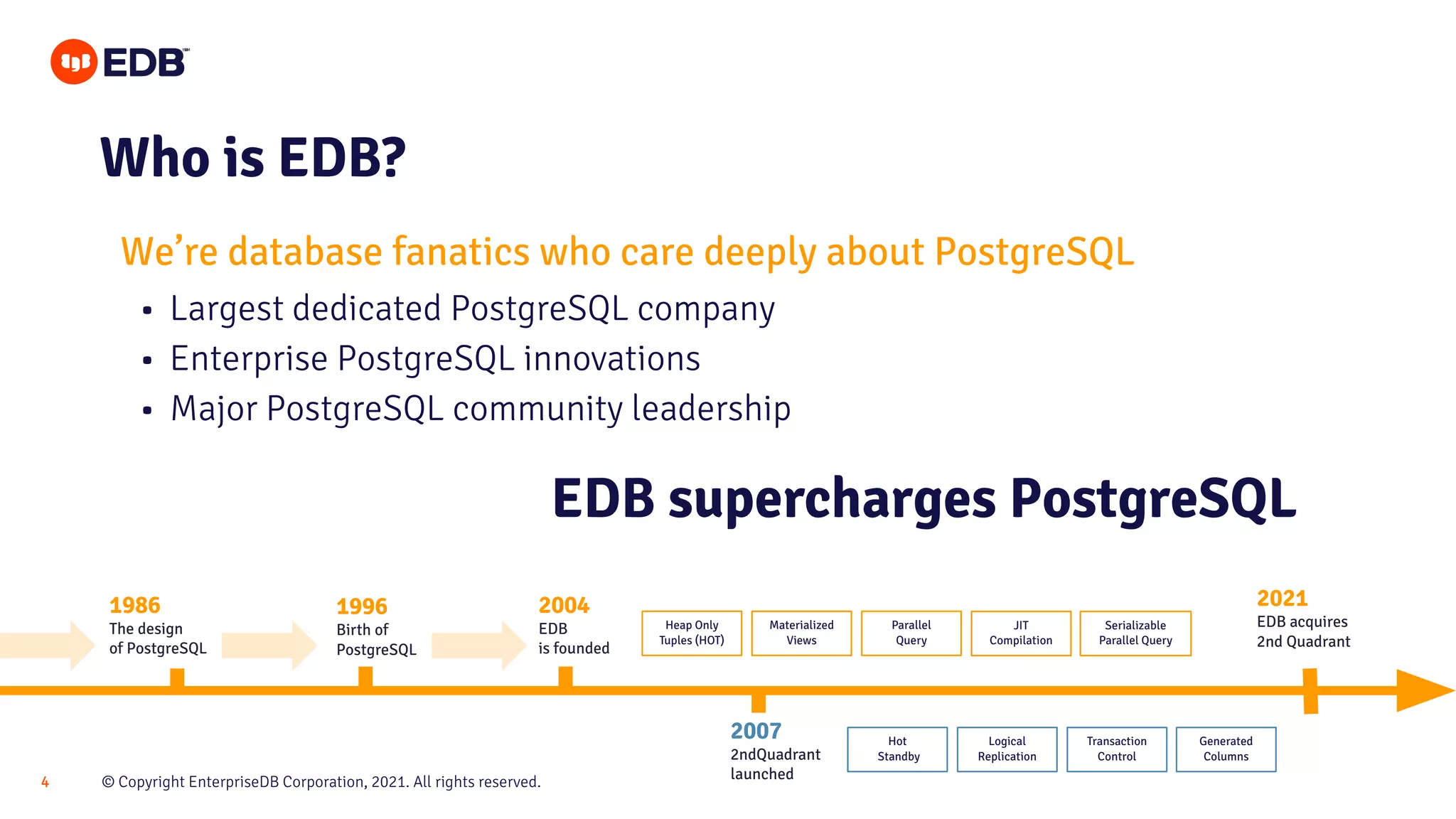
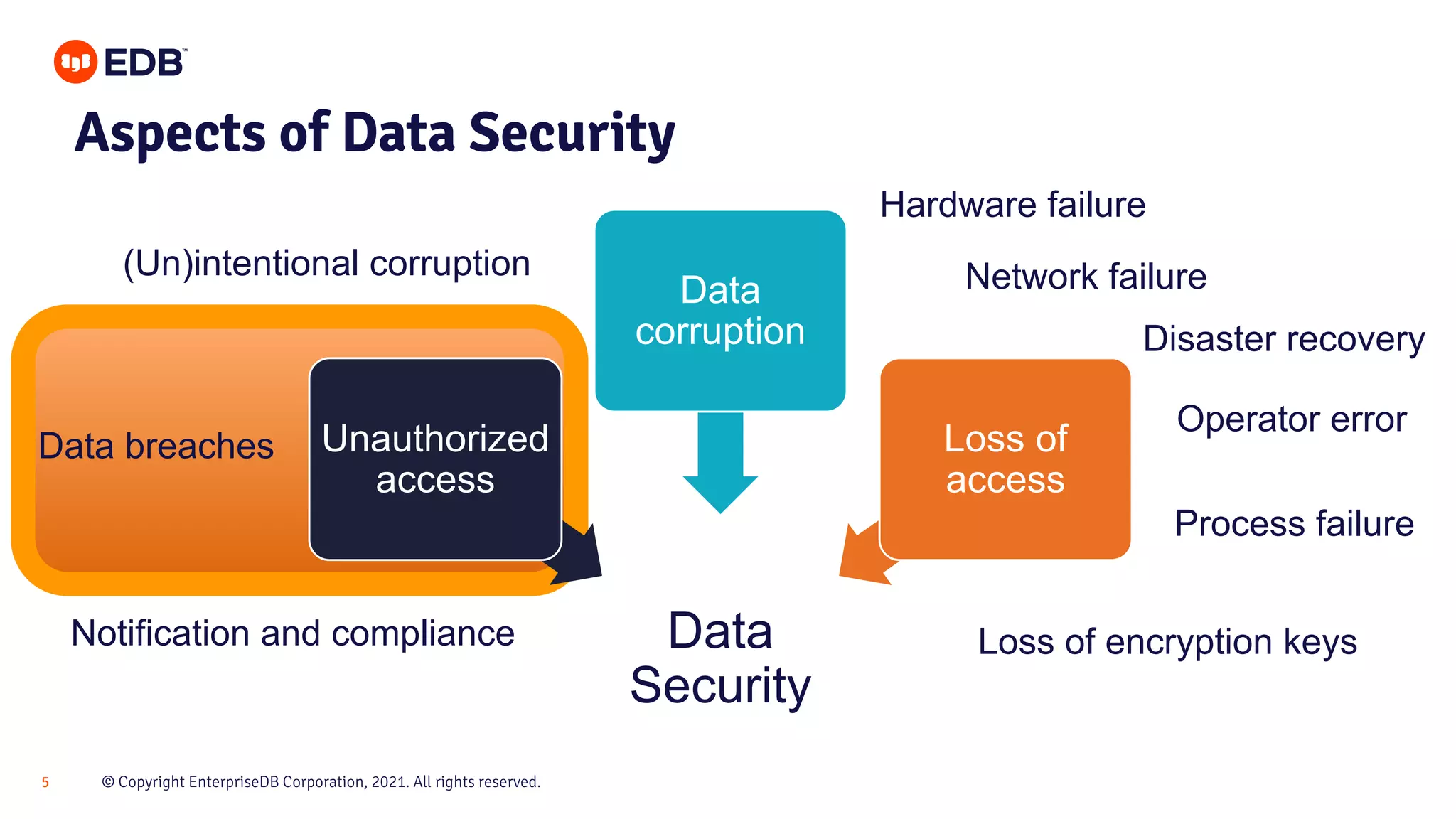
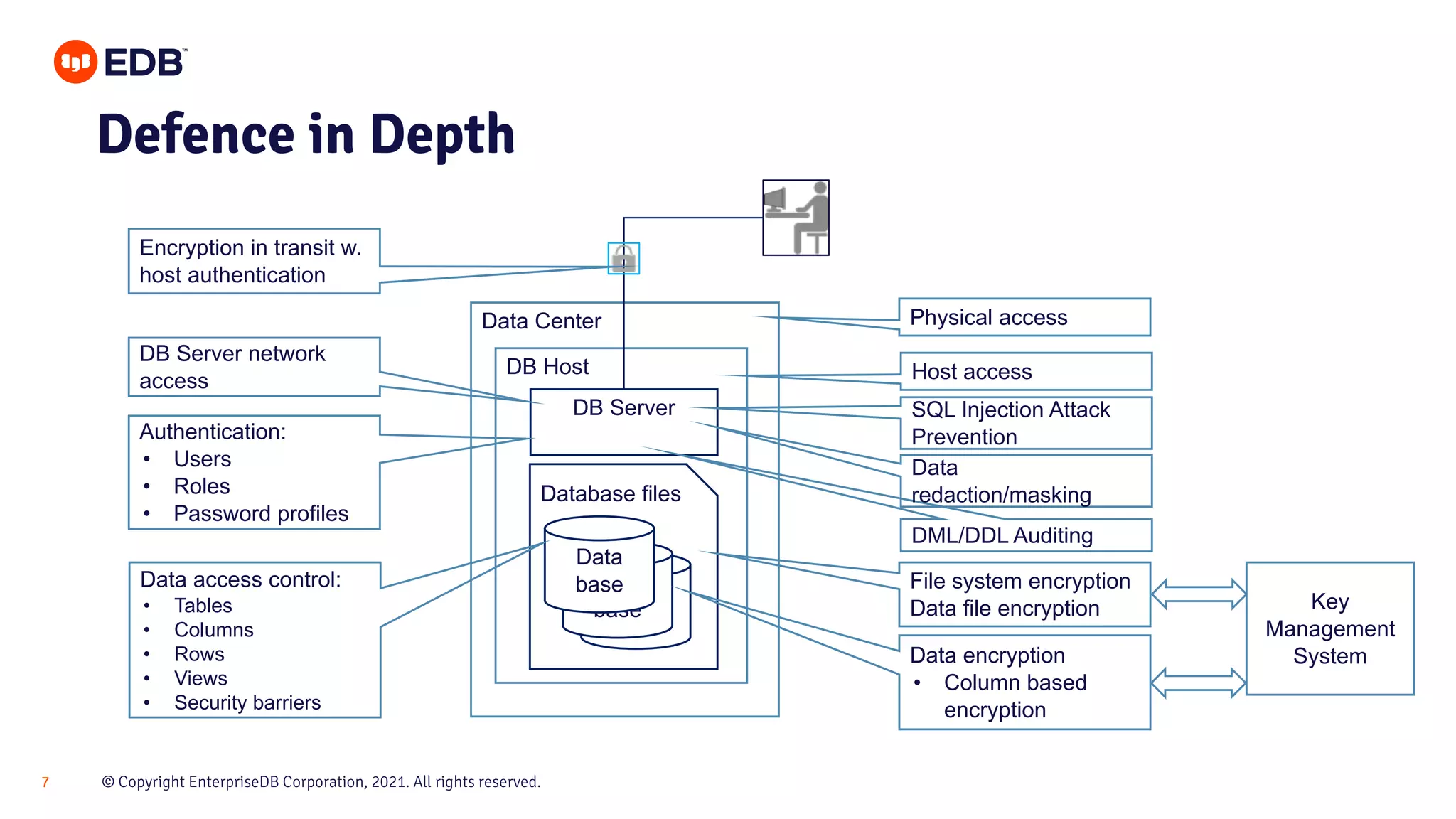
The document presents best practices for securing PostgreSQL databases, covering key concepts such as authentication, authorization, auditing, and data encryption. It provides general recommendations, detailed explanations of security models, and techniques to prevent unauthorized access and SQL injection attacks. Key takeaways include implementing the principle of least privilege, keeping systems updated, and utilizing encryption for data protection.















![© Copyright EnterpriseDB Corporation, 2021. All rights reserved. 21 Data Redaction Username [enterprisedb]: privilegeduser mycompany=> select * from employees; id | name | ssn | phone | birthday ----+--------------+-------------+------------+-------------------- 1 | Sally Sample | 020-78-9345 | 5081234567 | 02-FEB-61 00:00:00 1 | Jane Doe | 123-33-9345 | 6171234567 | 14-FEB-63 00:00:00 1 | Bill Foo | 123-89-9345 | 9781234567 | 14-FEB-63 00:00:00 (3 rows) Username [enterprisedb]: redacteduser mycompany=> select * from employees; id | name | ssn | phone | birthday ----+--------------+-------------+------------+-------------------- 1 | Sally Sample | xxx-xx-9345 | 5081234567 | 02-FEB-02 00:00:00 1 | Jane Doe | xxx-xx-9345 | 6171234567 | 14-FEB-02 00:00:00 1 | Bill Foo | xxx-xx-9345 | 9781234567 | 14-FEB-02 00:00:00 (3 rows)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kangarootpartnerwebinarbestpracticesinsecuritywithpostgresql-210311144131/75/Kangaroot-EDB-Webinar-Best-Practices-in-Security-with-PostgreSQL-21-2048.jpg)