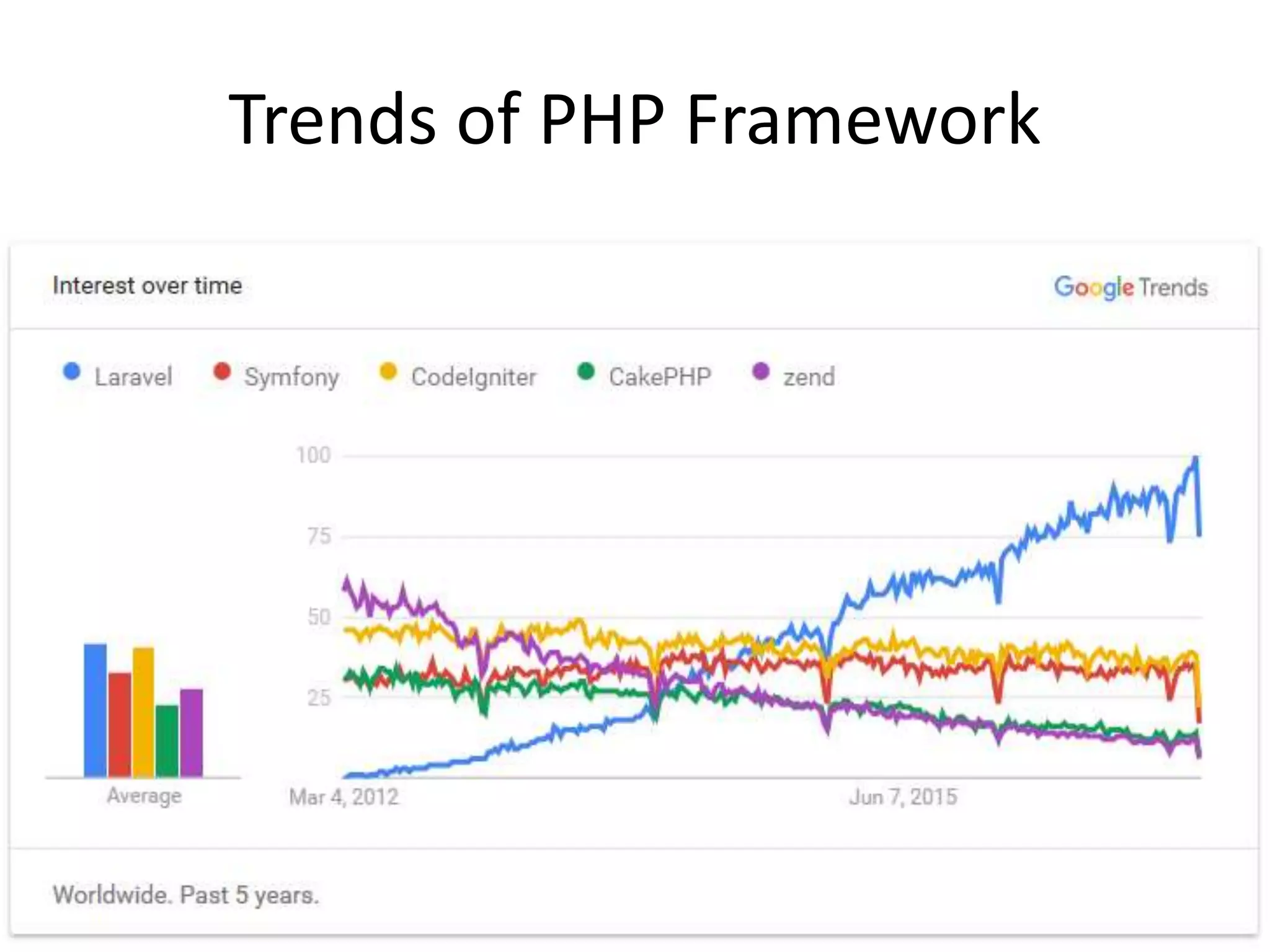
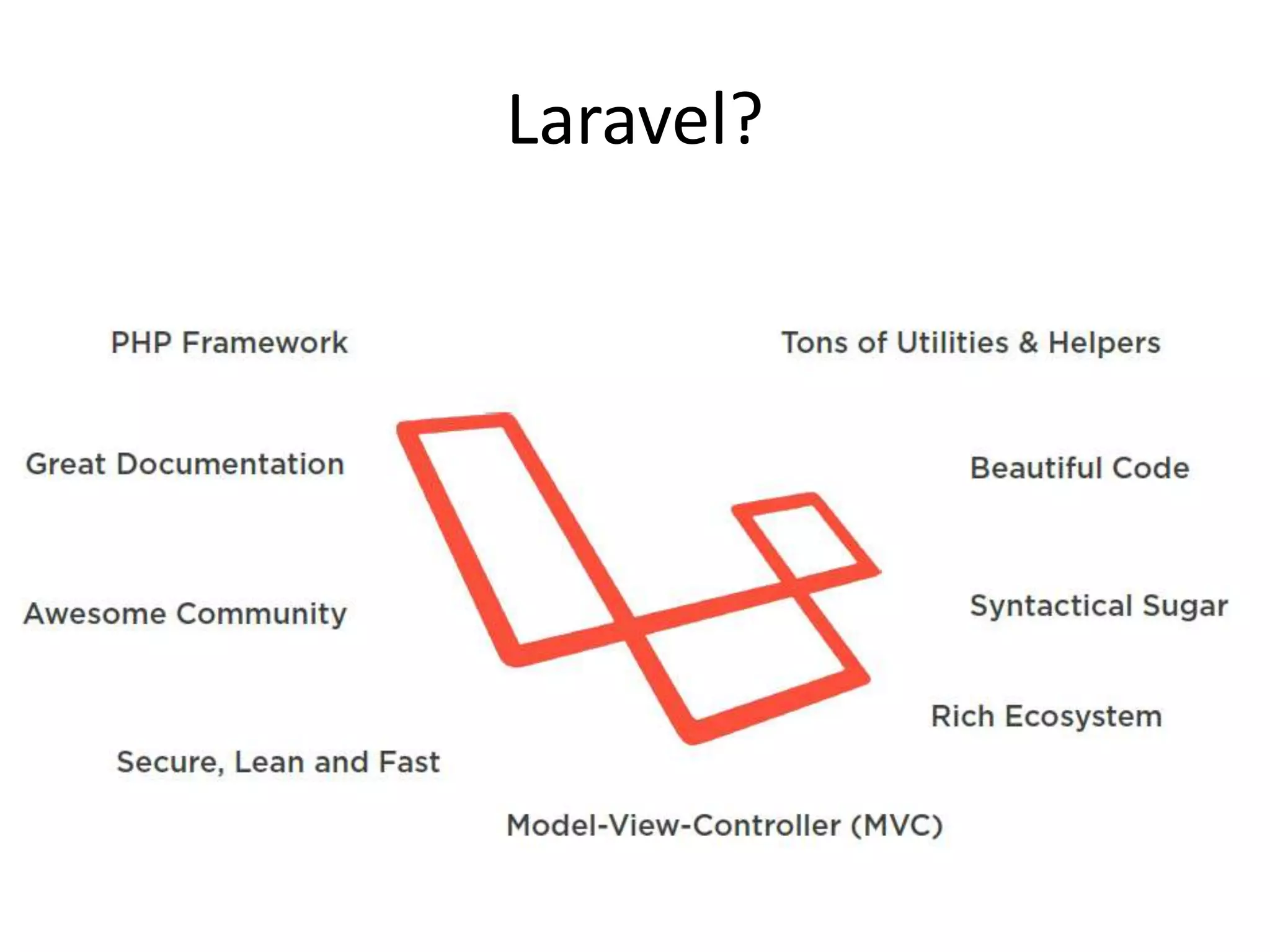
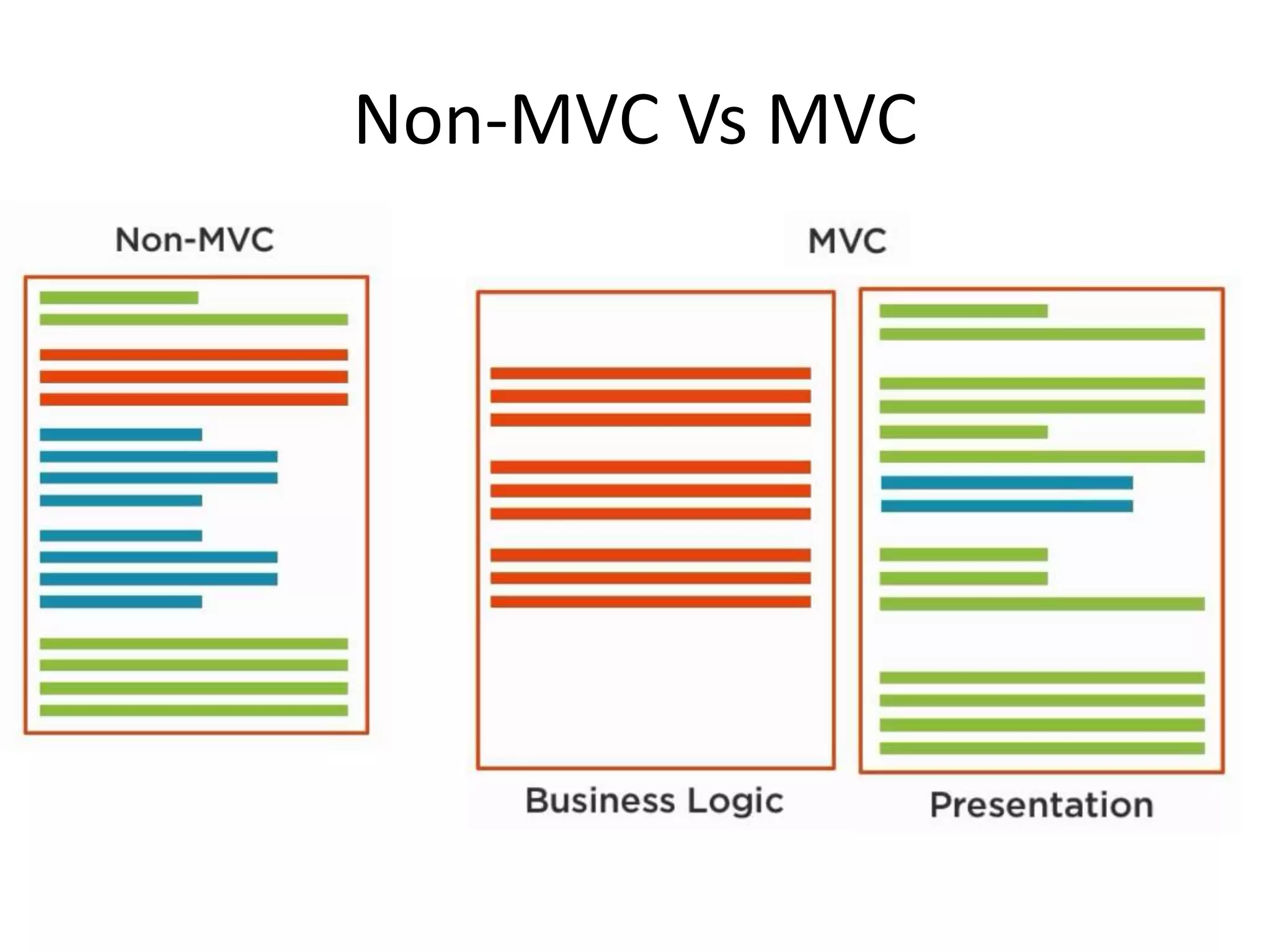
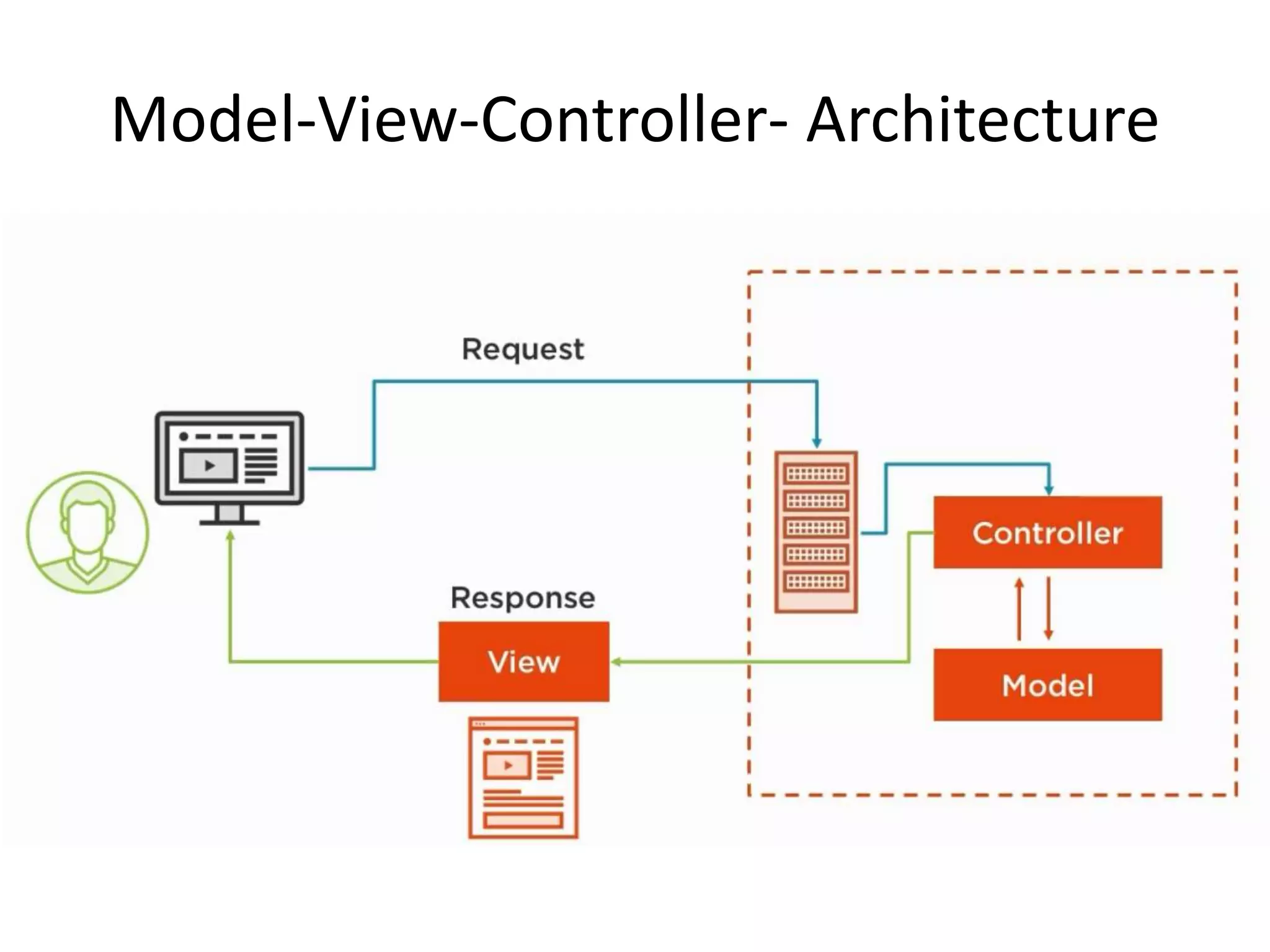
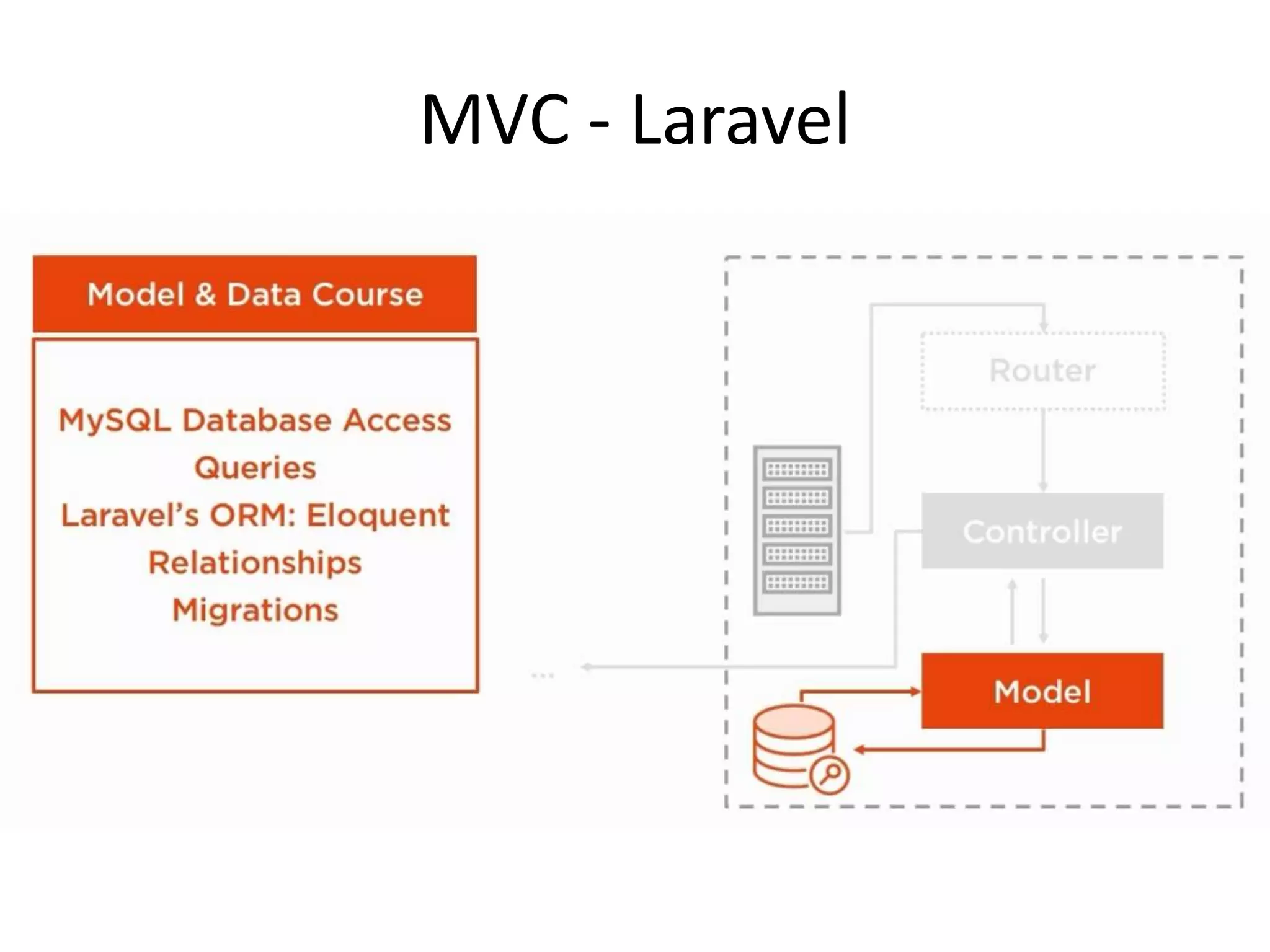
The document discusses Laravel, a PHP framework designed to overcome issues associated with legacy code, such as security vulnerabilities and limited code reuse. It explains the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architectural pattern essential to Laravel, its evolution, and key benefits like faster development, SEO-friendliness, and easy modifications. Additionally, it outlines prerequisites for learning Laravel and installation requirements via Composer.