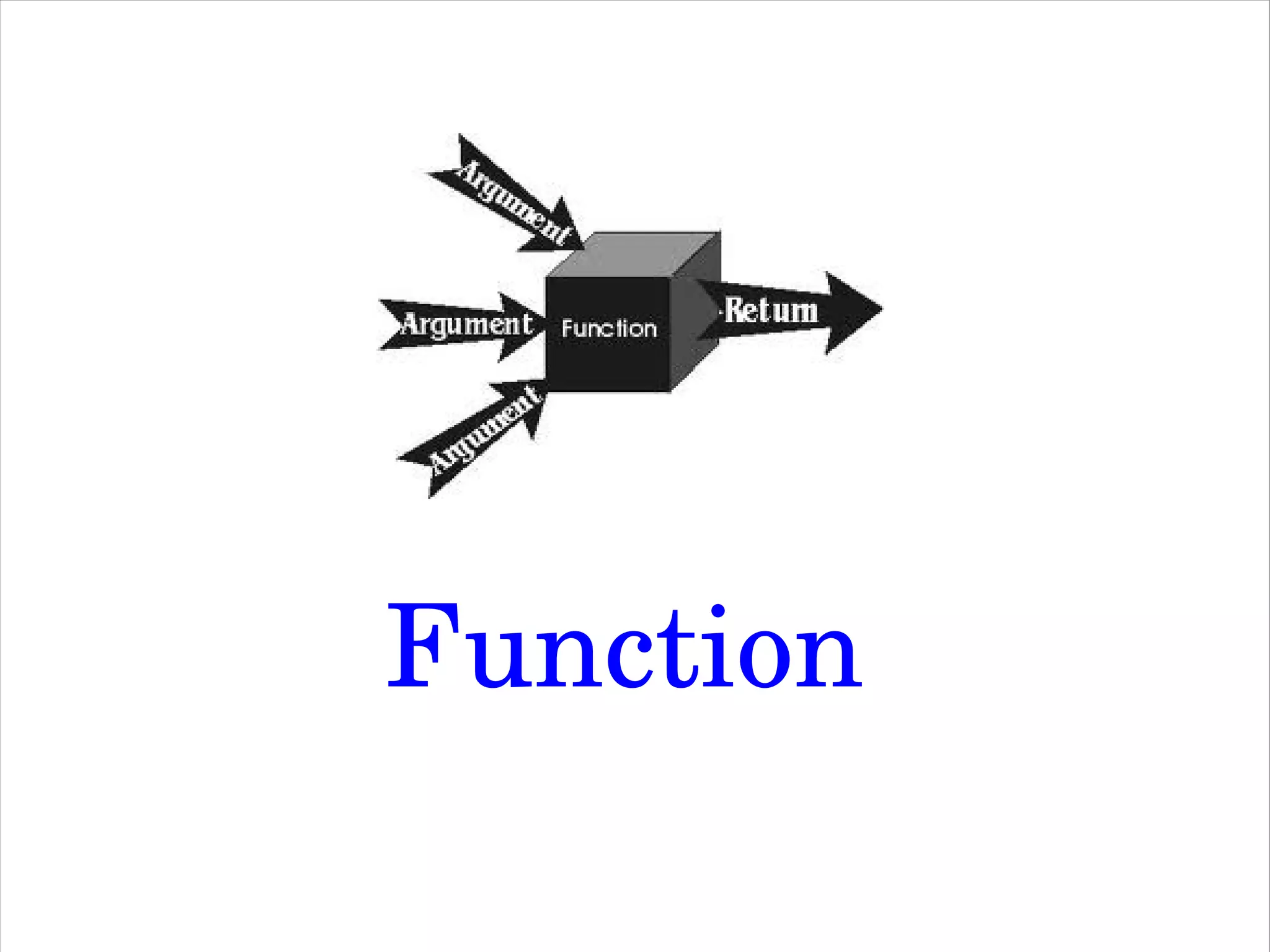
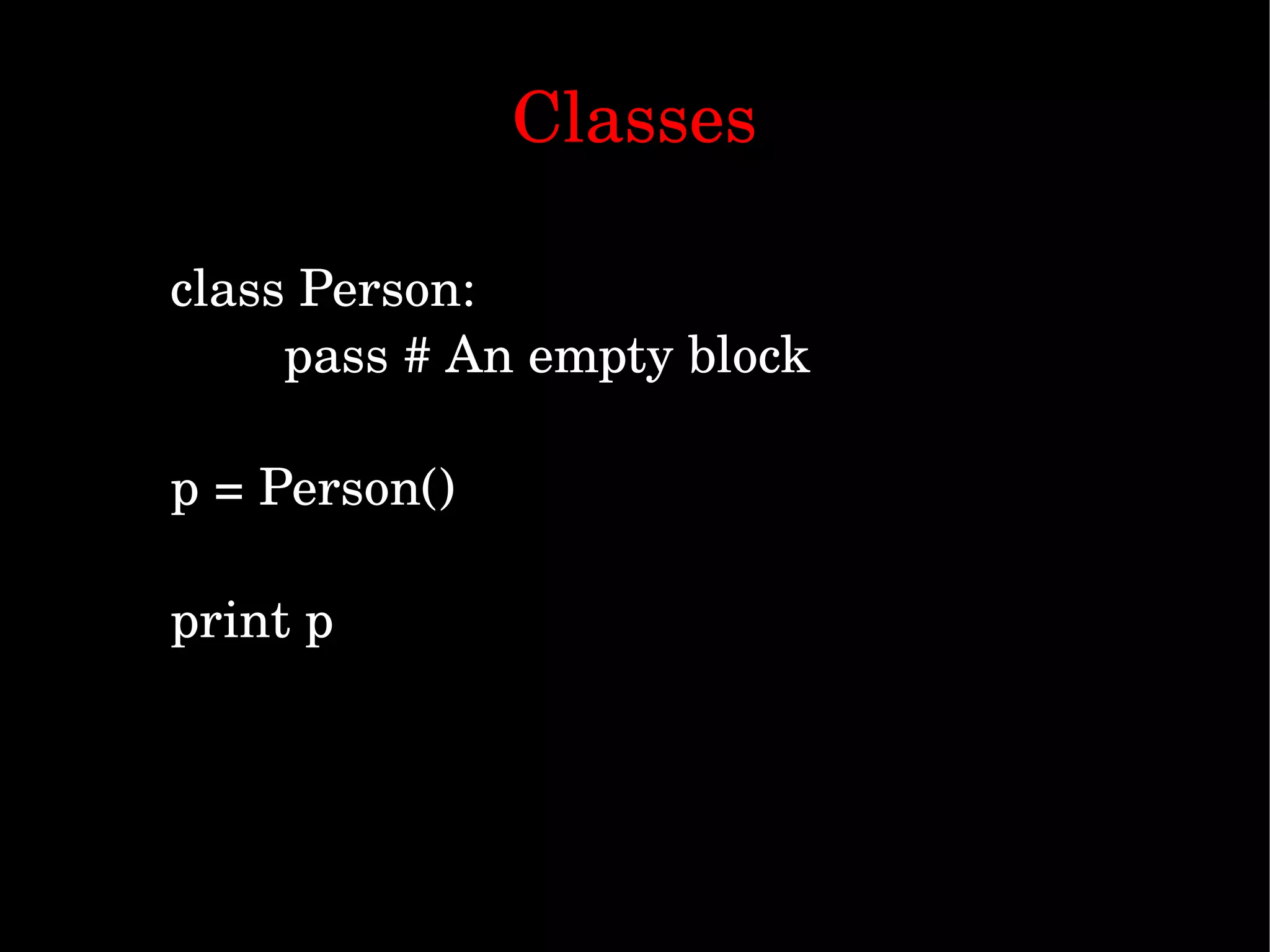
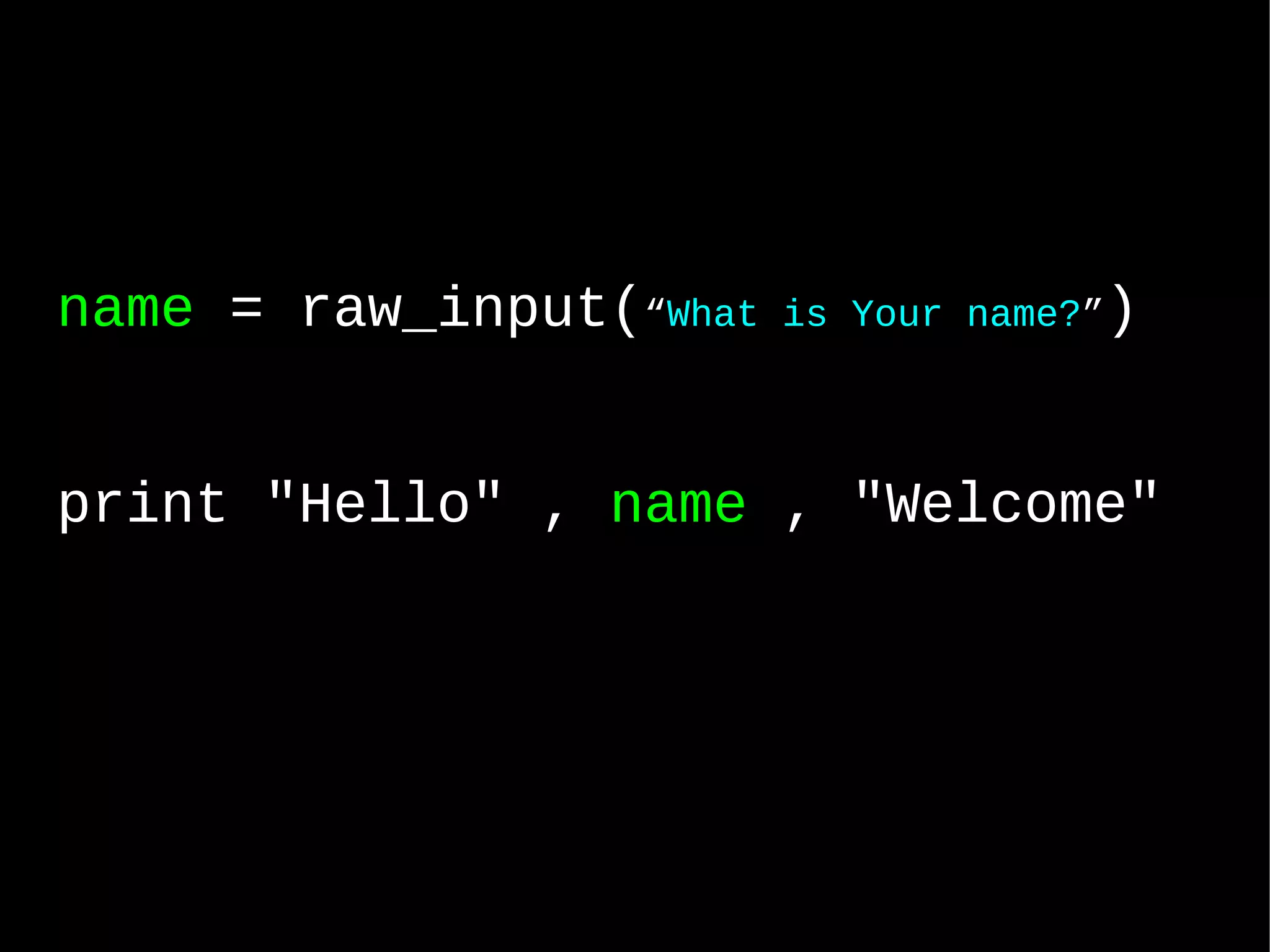
Python is a simple yet powerful programming language that can be used for a wide range of tasks. The document provides an introduction to Python, discussing why it is a good language to learn, its history and examples of common uses. It covers Python's syntax, data types, modules, object oriented programming and how to interface Python with databases and other languages. The goal is to illustrate Python's versatility and ease of use through examples.




























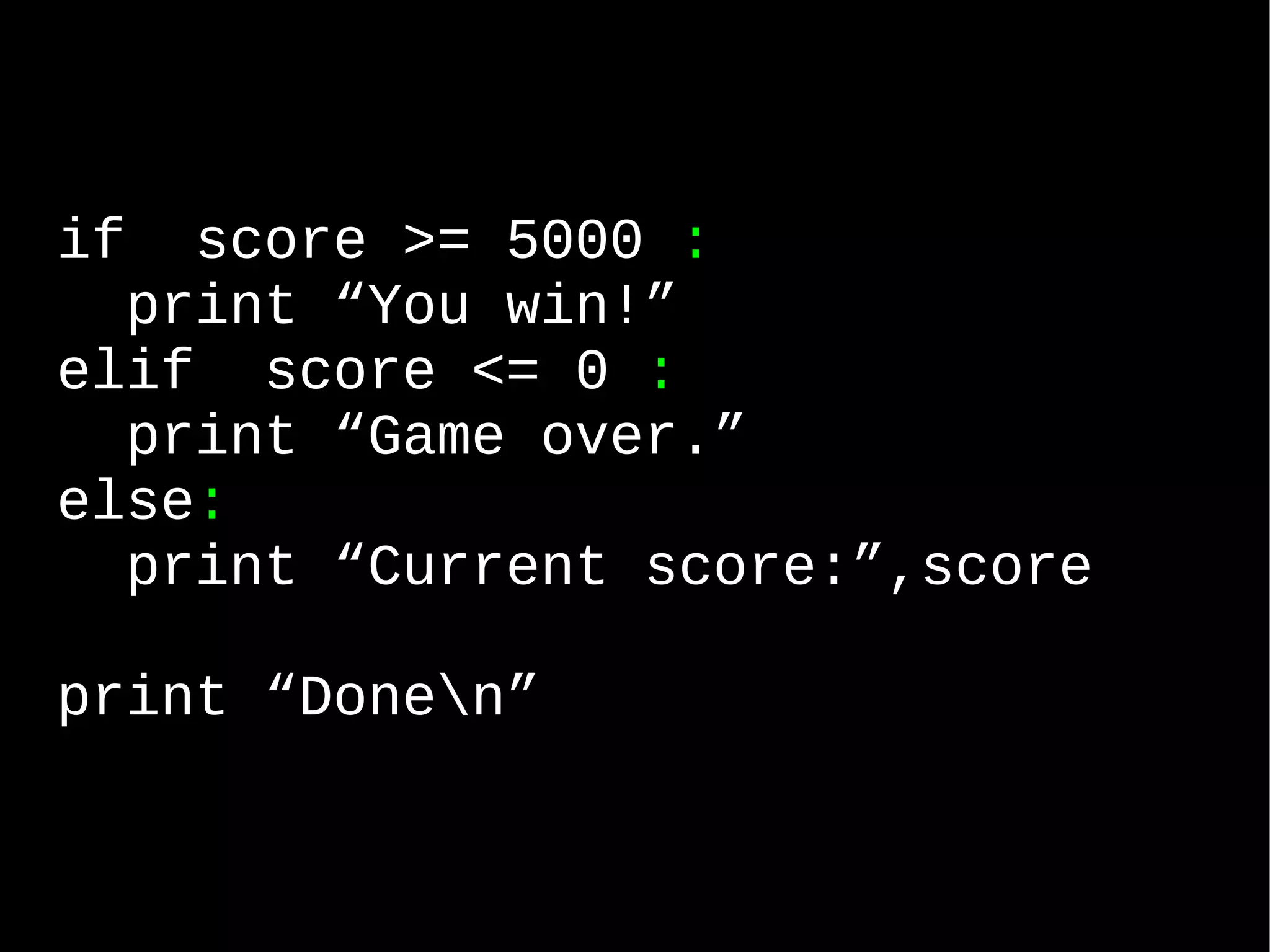



![List = Array numbers = [ "zero", "one", "two", "three", "FOUR" ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-36-2048.jpg)
![List = Array numbers = [ "zero", "one", "two", "three", "FOUR" ] numbers[0] >>> zero numbers[4] numbers[1] >>> FOUR >>> FOUR numbers[2] >>> three](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-37-2048.jpg)
![Multi Dimension List numbers = [ ["zero", "one"],["two", "three", "FOUR" ]] numbers[0] >>> ["zero", "one"] numbers[0][0] numbers[1][1] >>> zero >>> FOUR len(numbers) >>> 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-38-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-39-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ] primes.sort()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-40-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ] primes.sort() >>> [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-41-2048.jpg)
![Sort List names = [ "Shrini", "Bala", "Suresh", "Arul"] names.sort() >>> ["Arul", "Bala","Shrini","Suresh"] names.reverse() >>> ["Suresh","Shrini","Bala","Arul"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-42-2048.jpg)
![Mixed List names = [ "Shrini", 10, "Arul", 75.54] names[1]+10 >>> 20 names[2].upper() >>> ARUL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-43-2048.jpg)
![Mixed List names = [ "Shrini", 10, "Arul", 75.54] names[1]+10 >>> 20 names[2].upper() >>> ARUL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-44-2048.jpg)
![Append on List numbers = [ 1,3,5,7] numbers.append(9) >>> [1,3,5,7,9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-45-2048.jpg)



![name = 'Arul' name[0] >>>'A' myname = 'Arul' + 'alan' >>> 'Arulalan'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-49-2048.jpg)
![split name = 'This is python string' name.split(' ') >>>['This','is','python','string'] comma = 'Shrini,Arul,Suresh' comma.split(',') >>> ['Shrini','Arul','Suresh']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-50-2048.jpg)
![join li = ['a','b','c','d'] s = '' new = s.join(li) >>> abcd new.split('') >>>['a','b','c','d']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-51-2048.jpg)


![menu = { “idly” : 2.50, “dosai” : 10.00, “coffee” : 5.00, “ice_cream” : 5.00, 100 : “Hundred” } menu[“idly”] 2.50 menu[100] Hundred](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1pythonanintroduction-110525114205-phpapp01/75/Lesson1-python-an-introduction-54-2048.jpg)