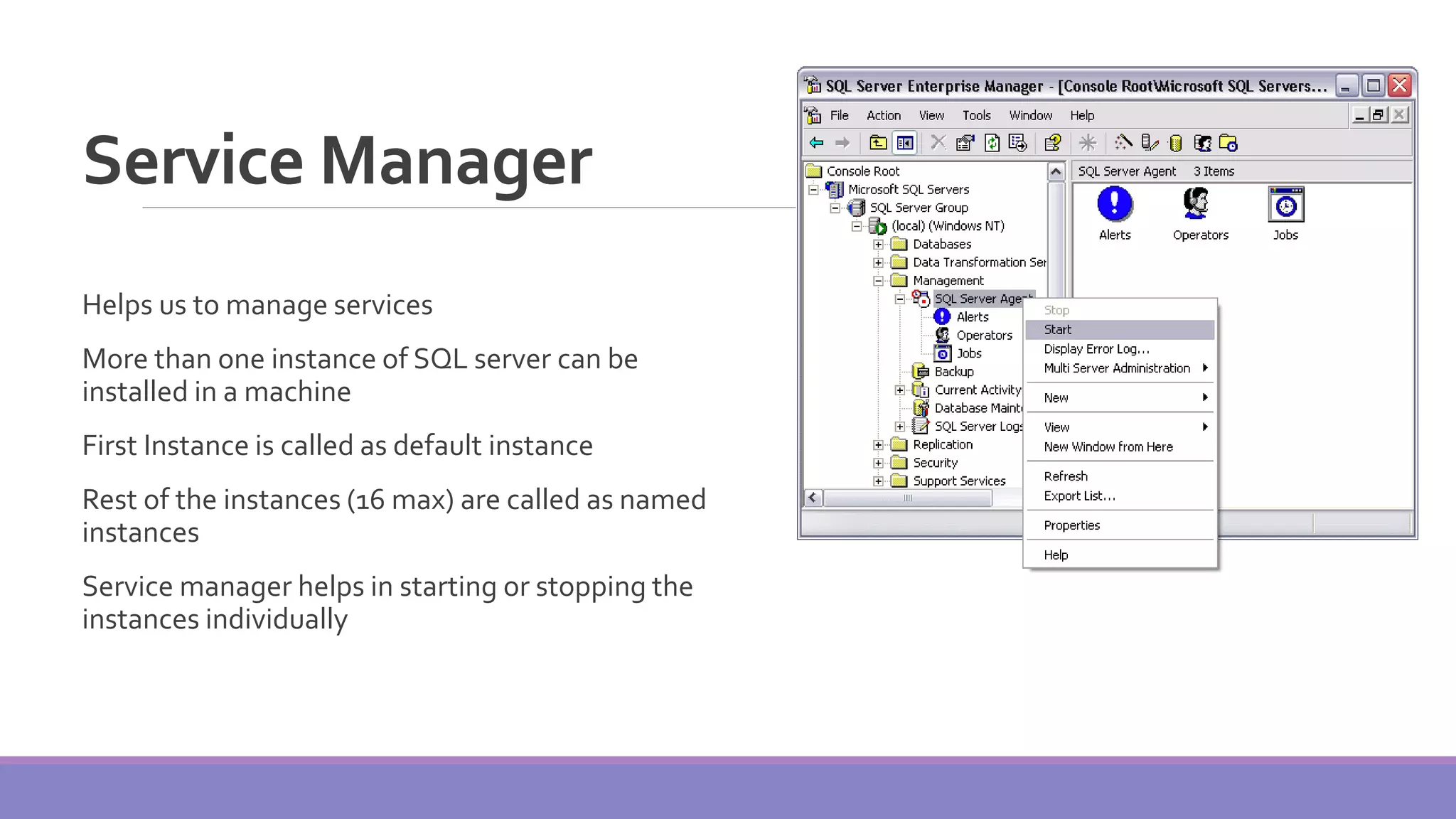
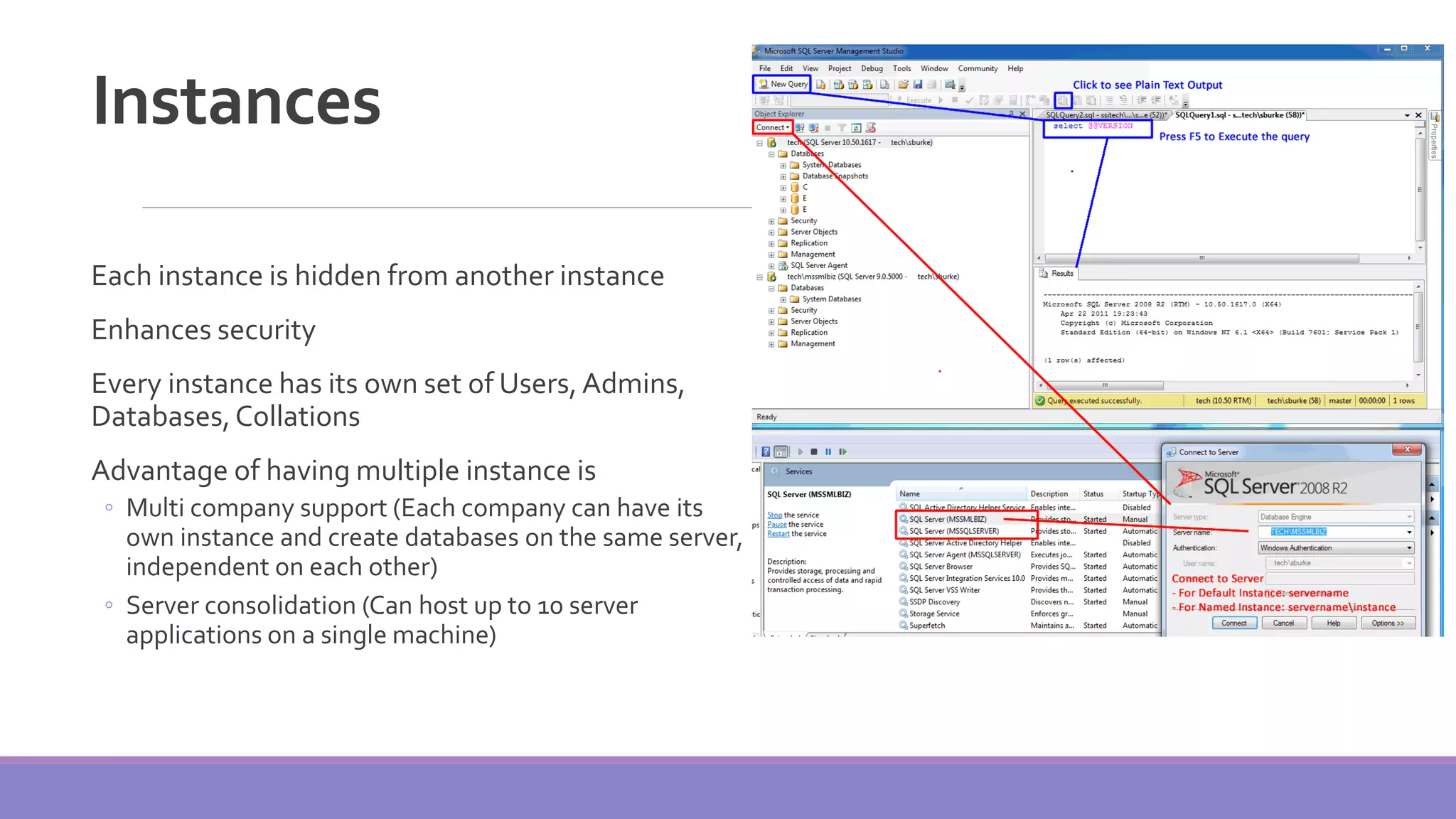
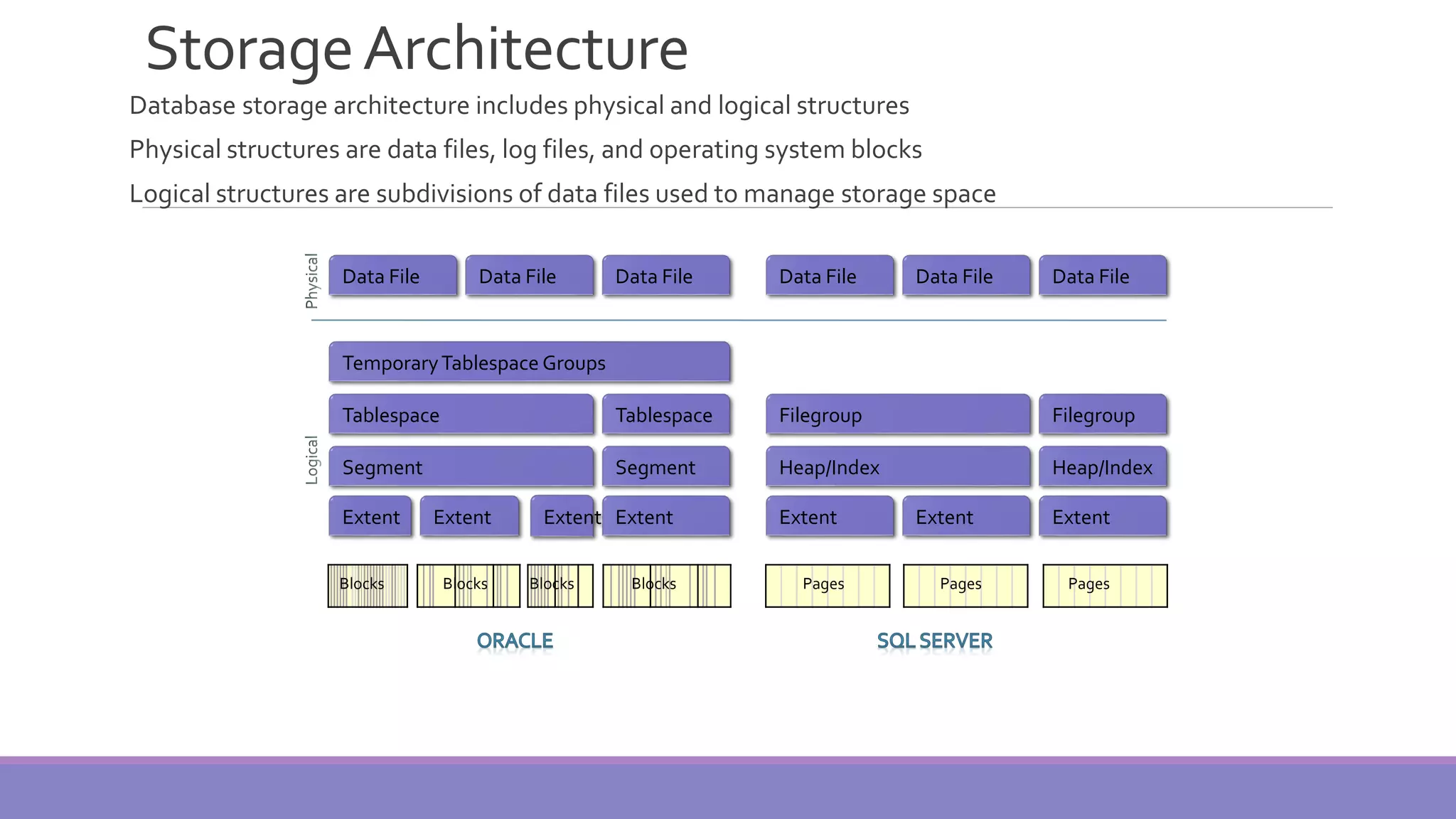
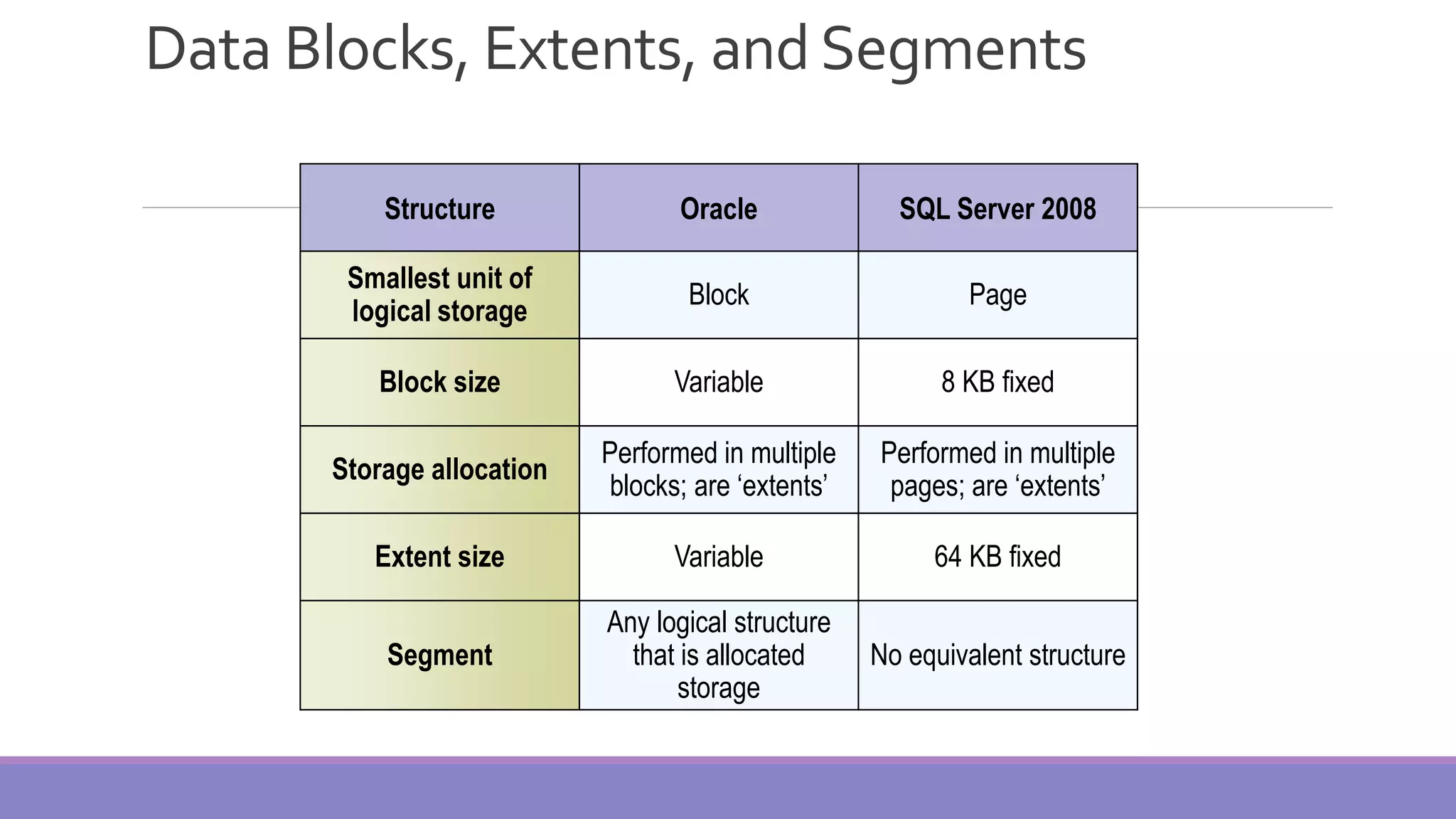
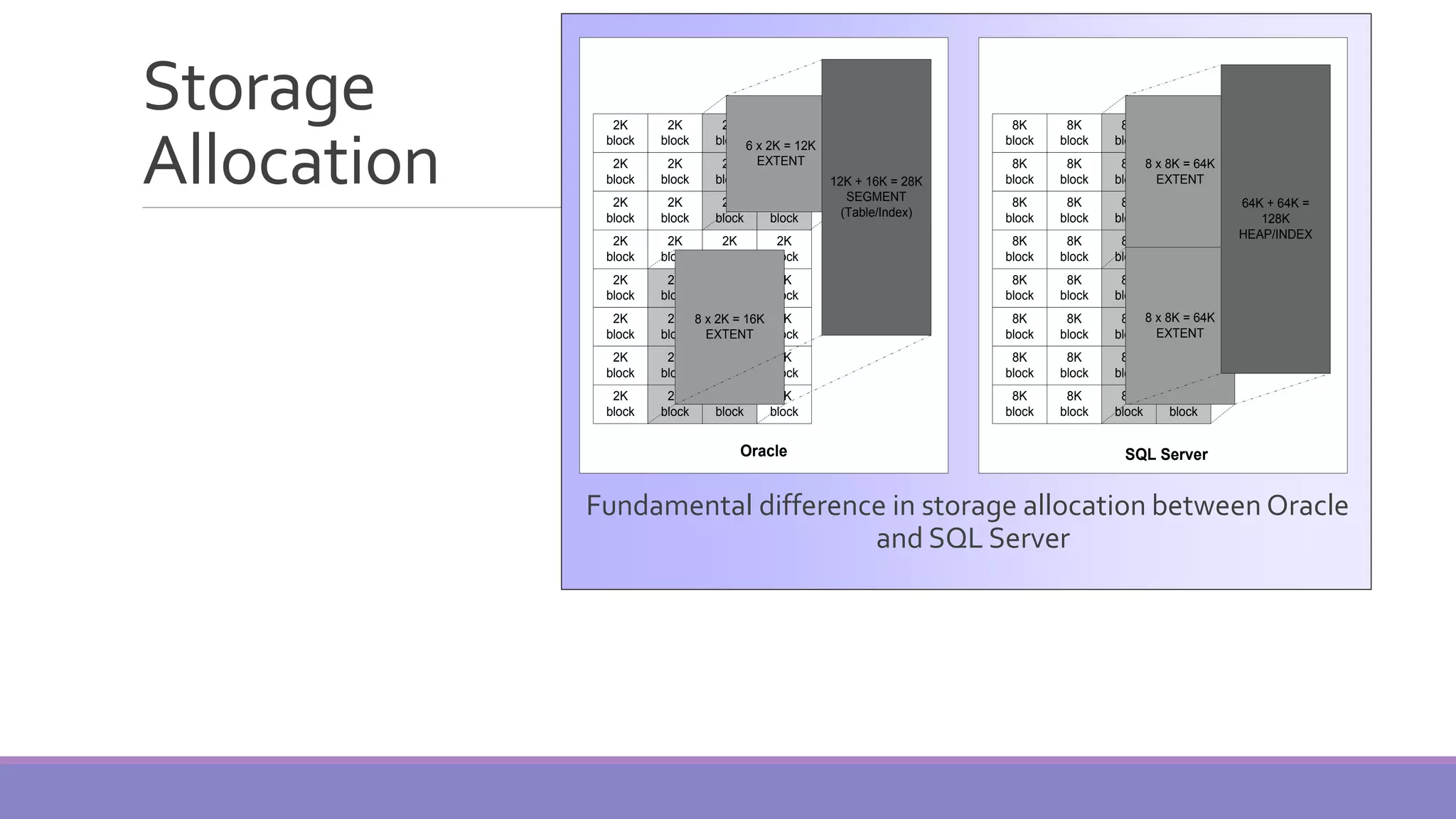
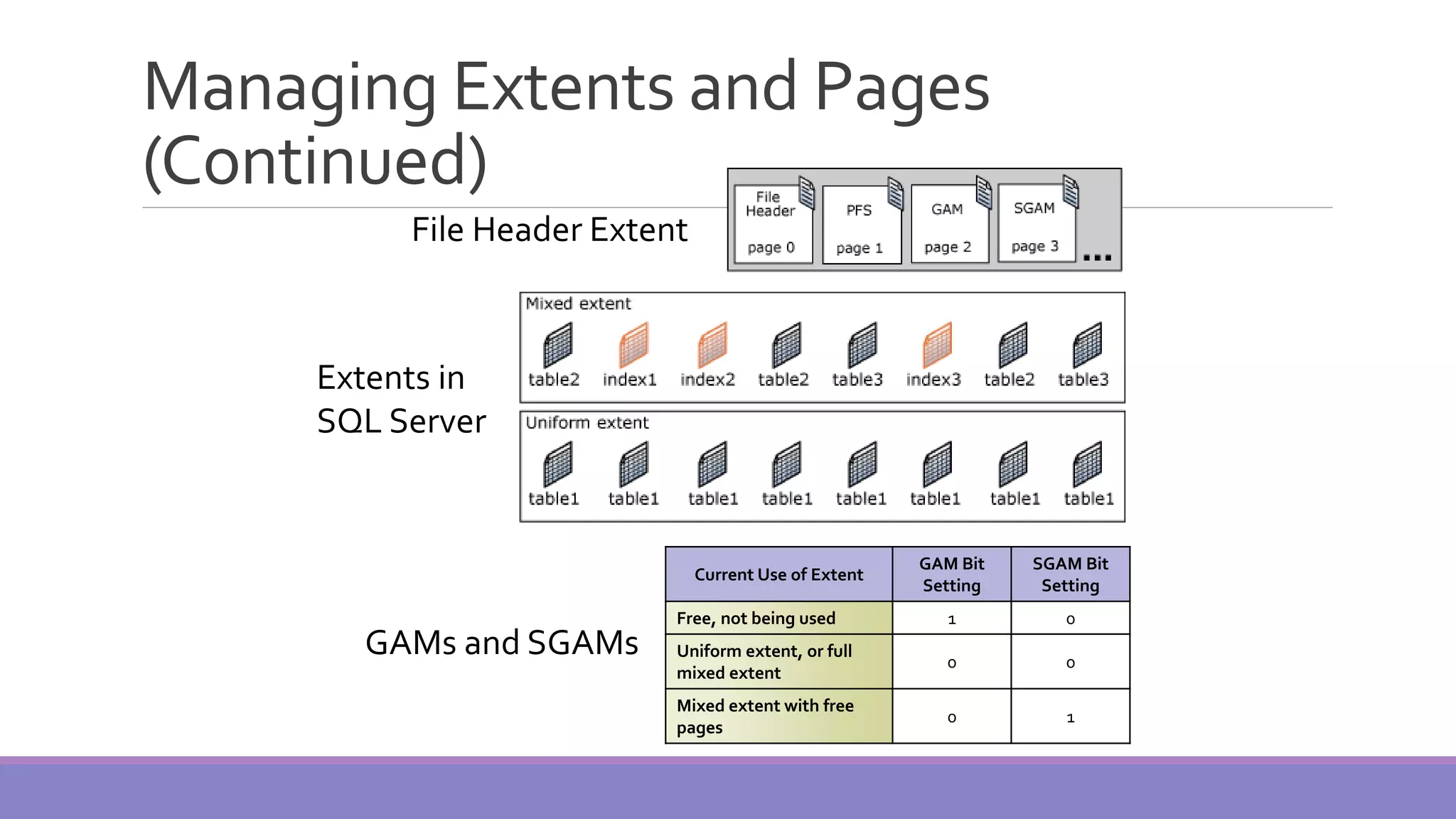
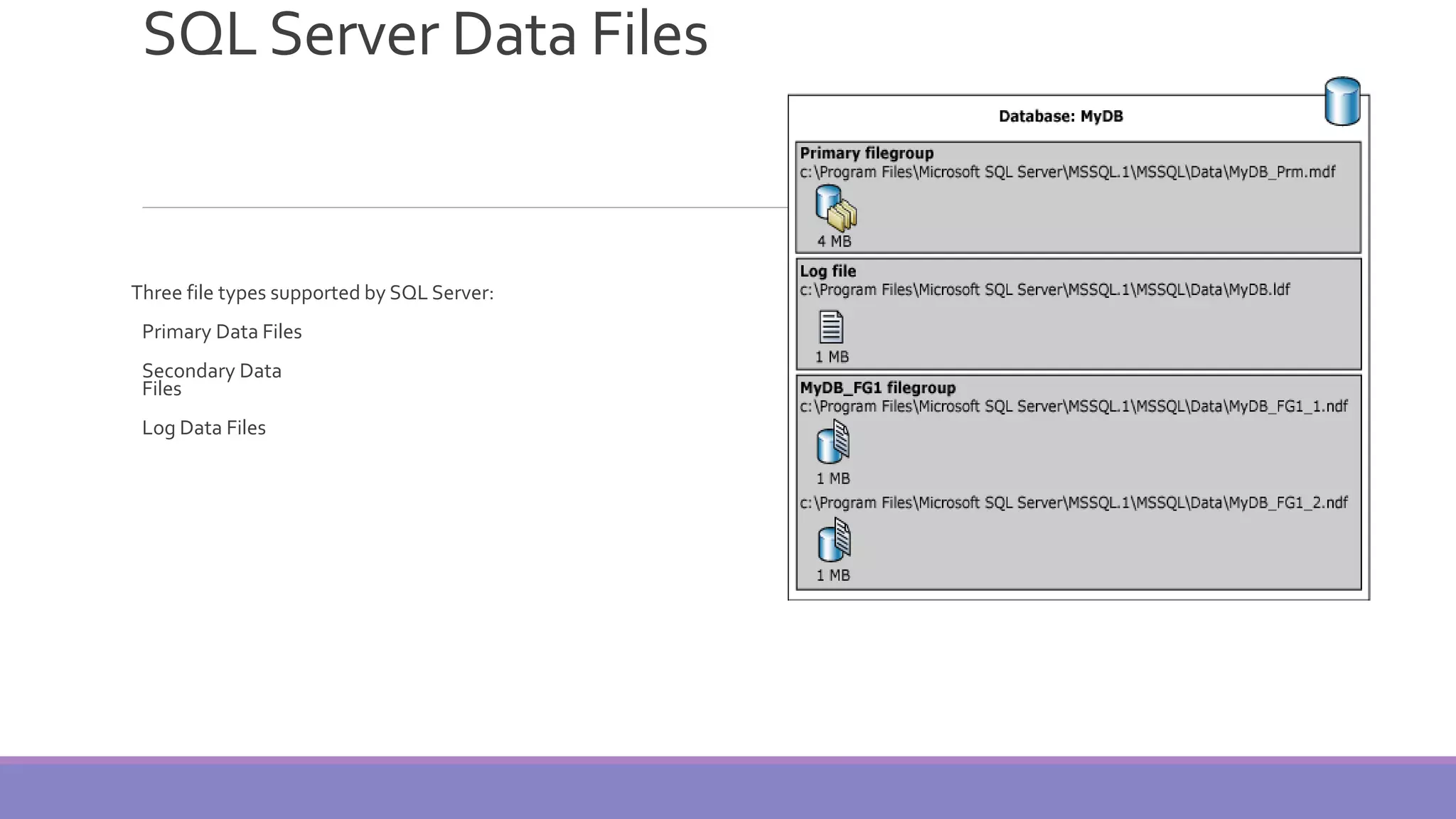
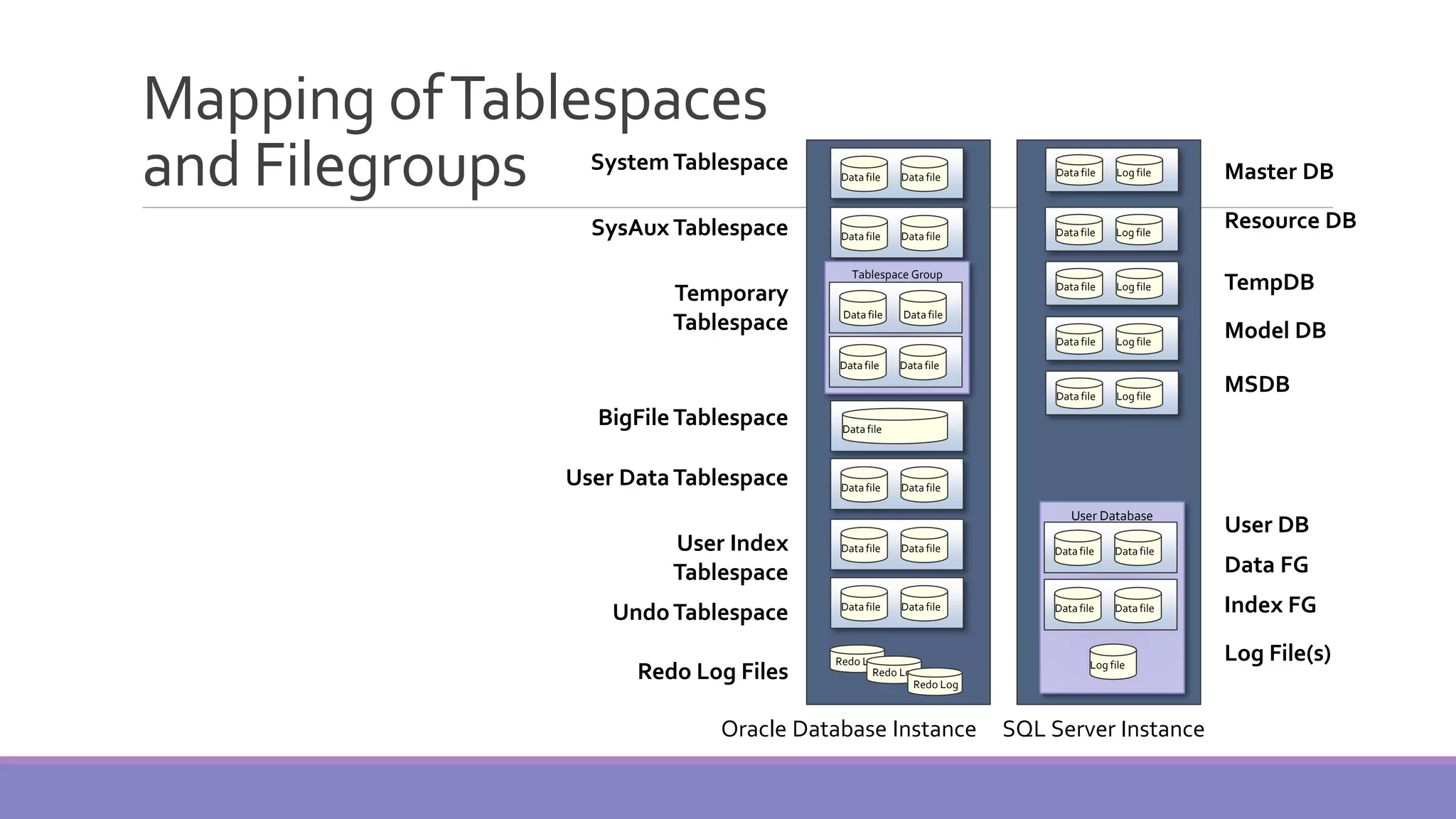
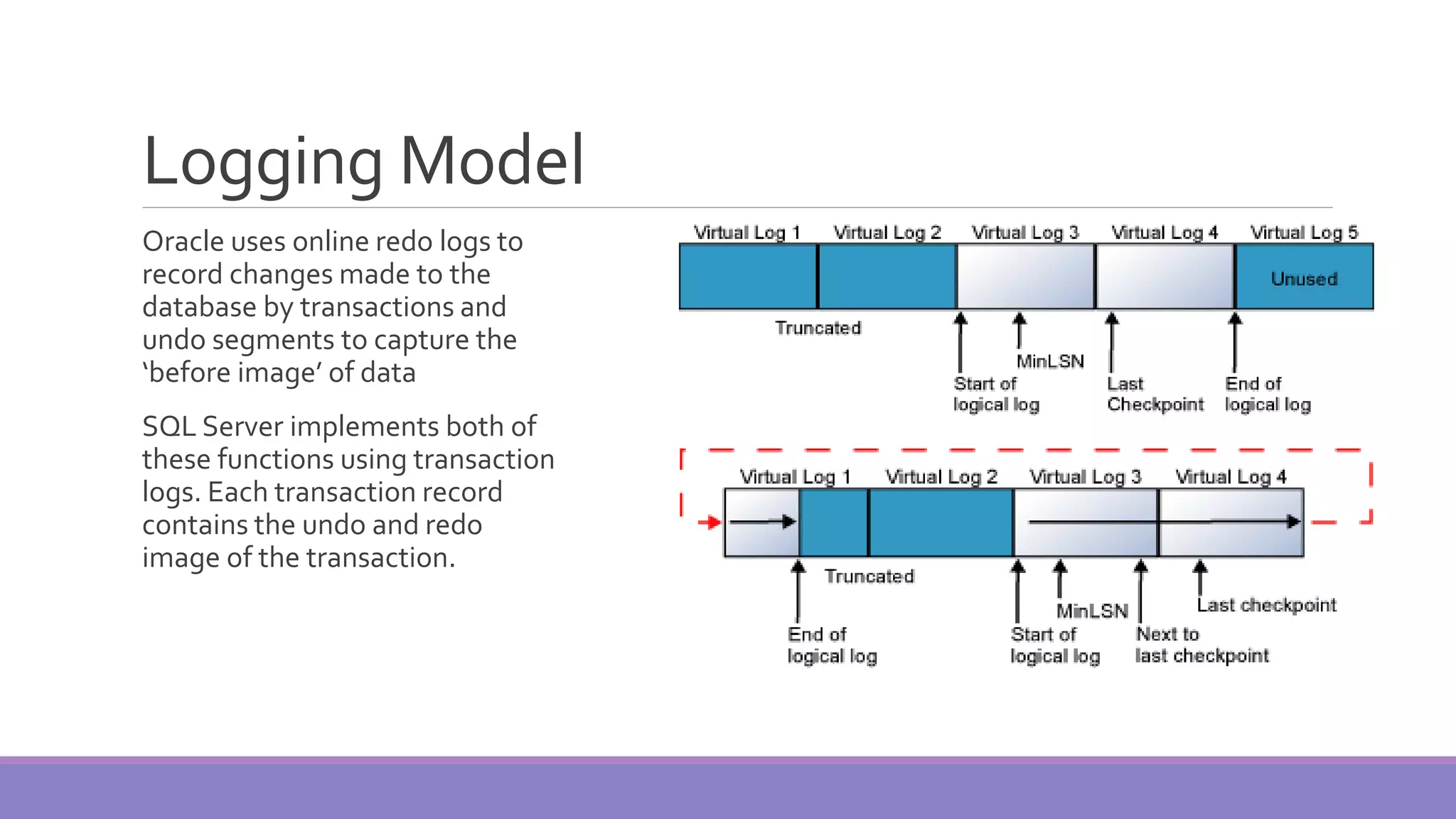
MS SQL Server is a database server produced by Microsoft that enables users to write and execute SQL queries and statements. It consists of several features like Query Analyzer, Profiler, and Service Manager. Multiple instances of SQL Server can be installed on a machine, with each instance having its own set of users, databases, and other objects. SQL Server uses data files, filegroups, and transaction logs to store database objects and record transactions. The data dictionary contains metadata about database schemas and is stored differently in Oracle and SQL Server.