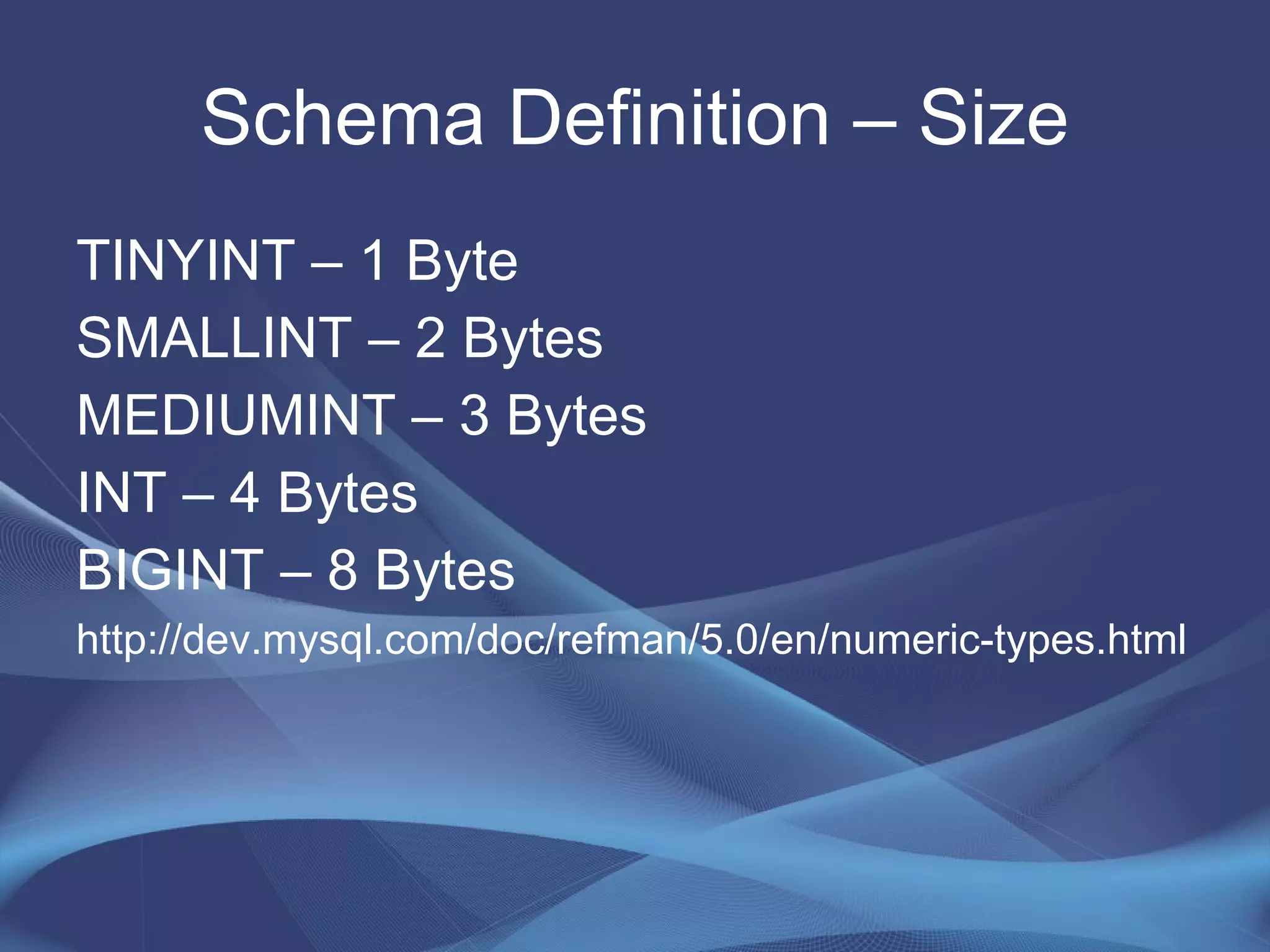
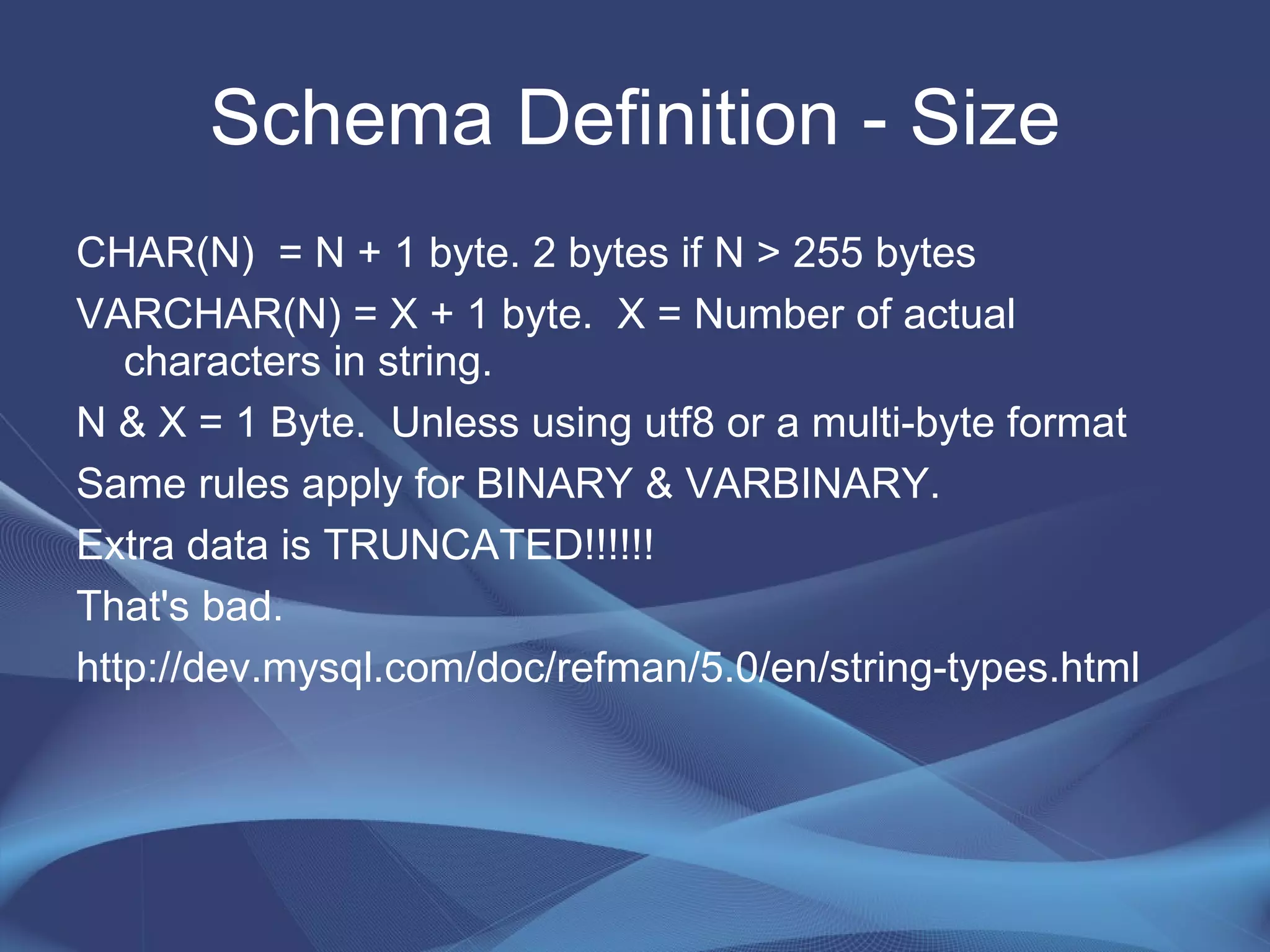
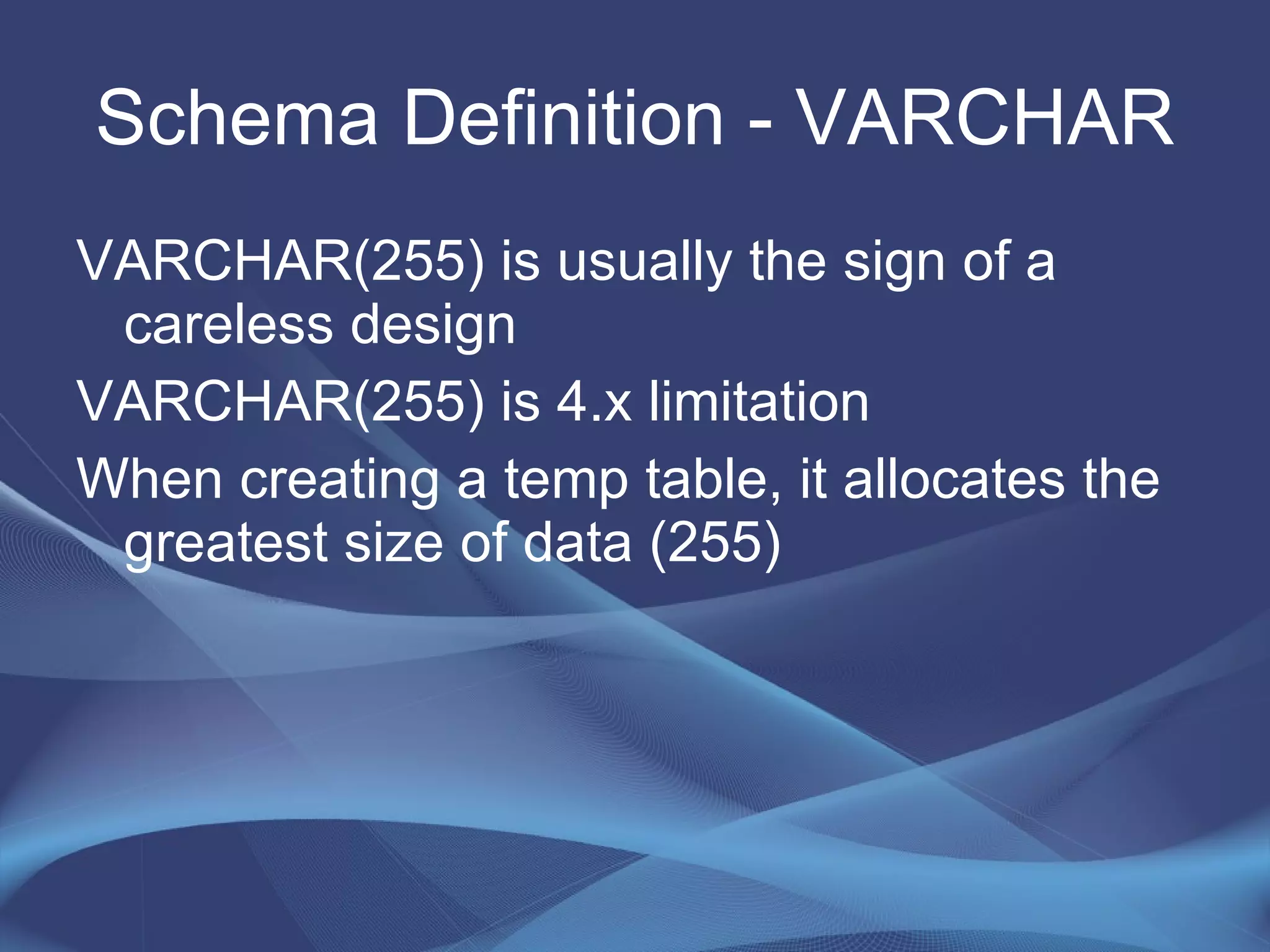
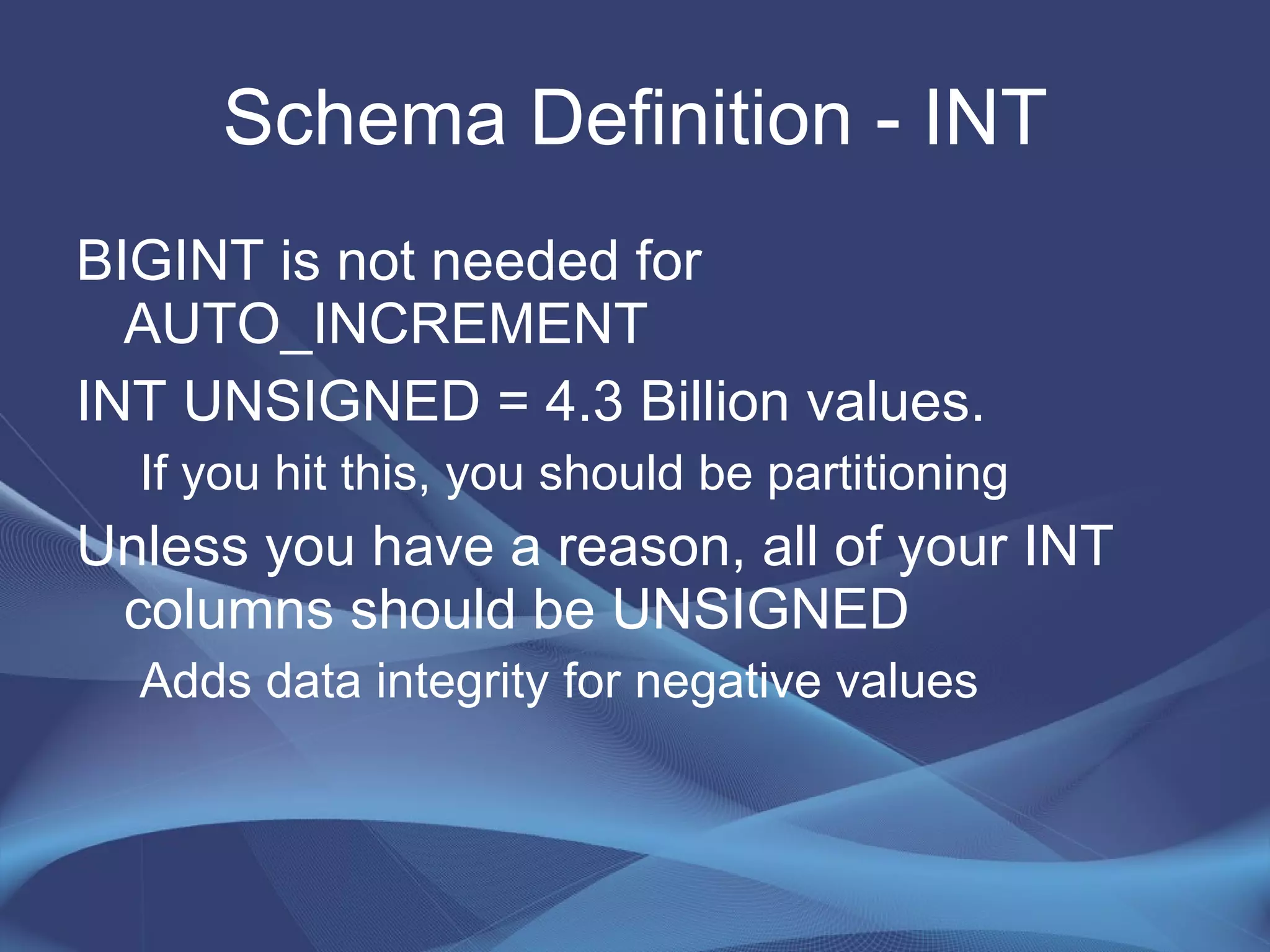
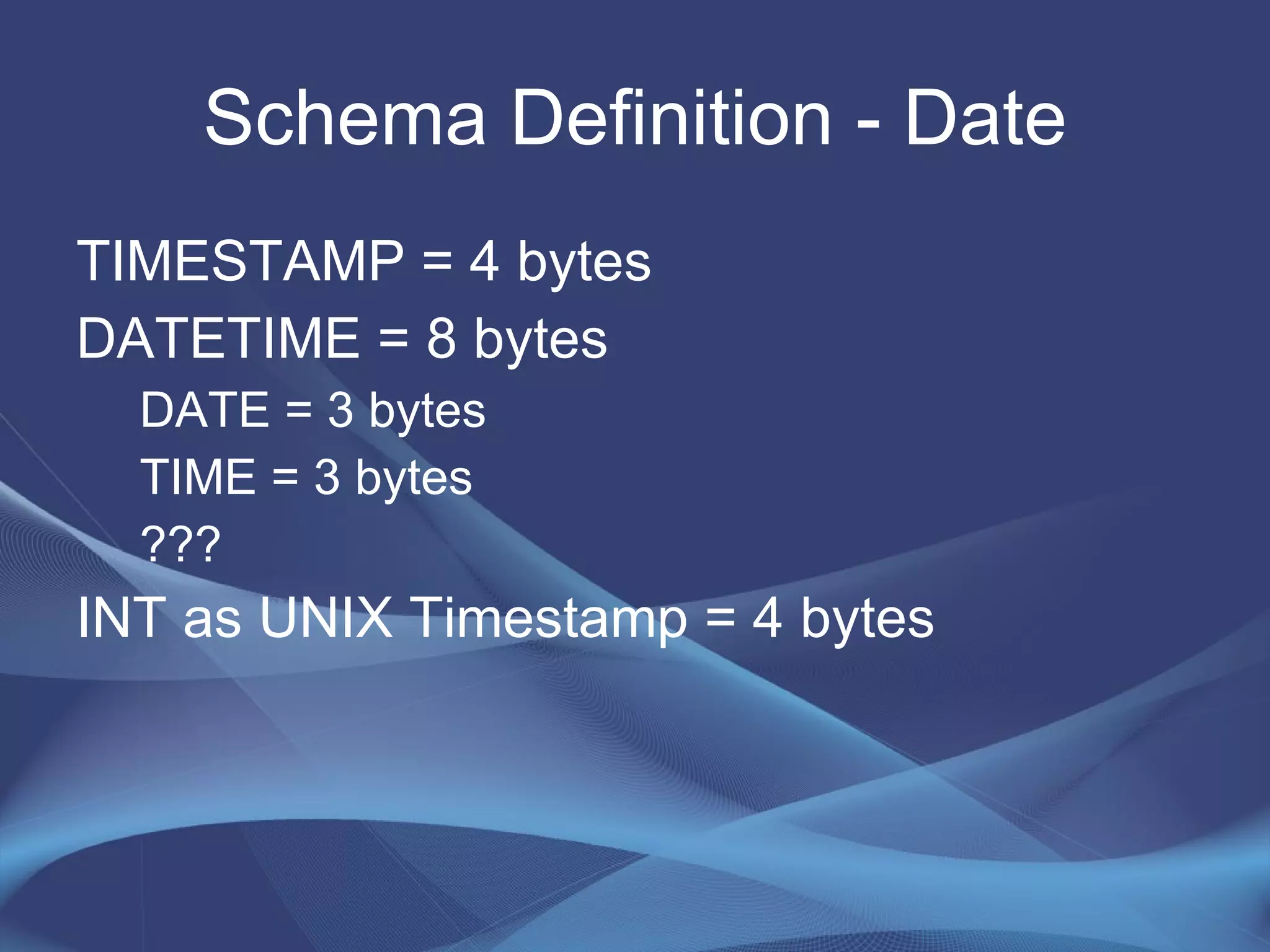
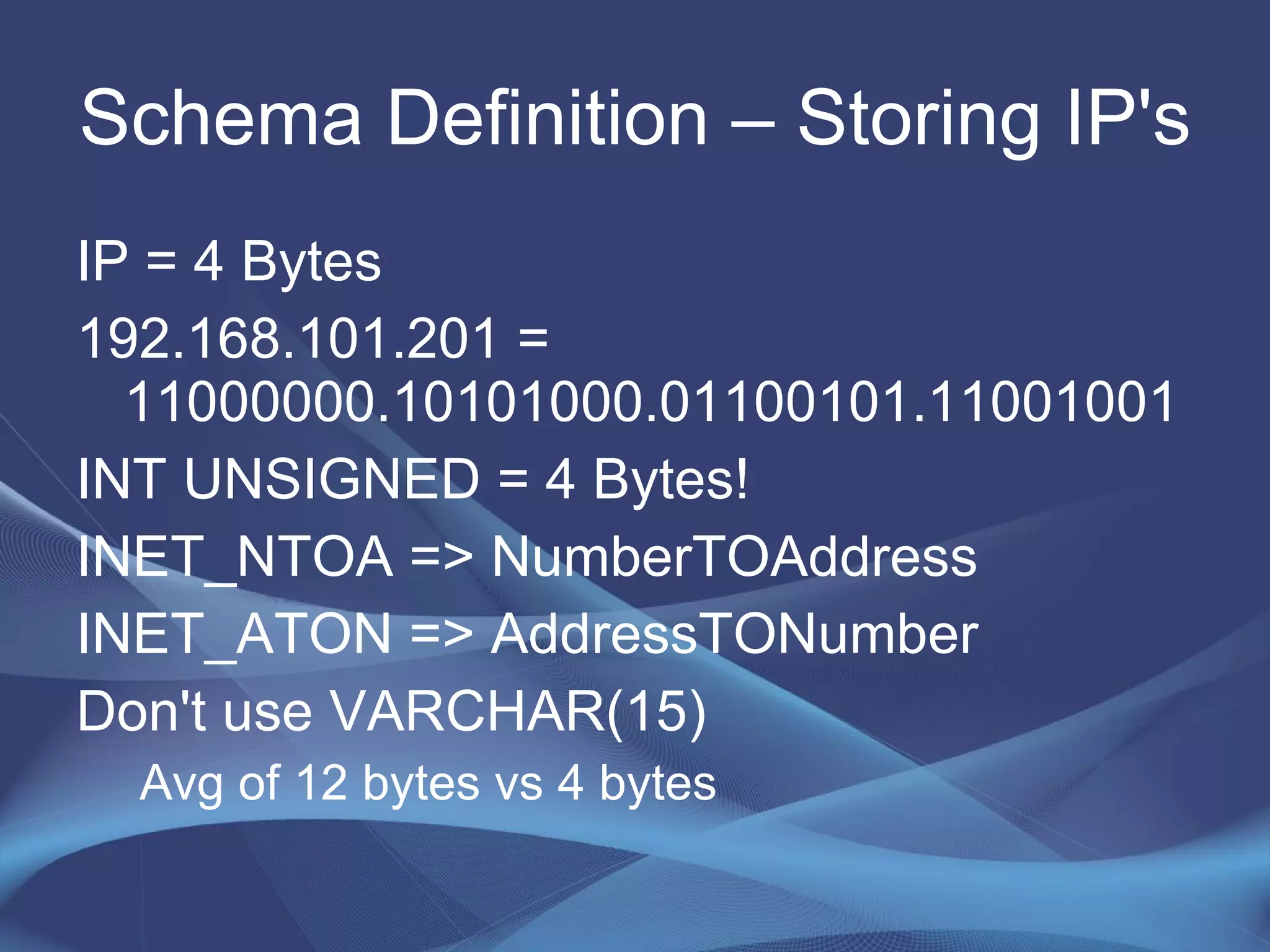
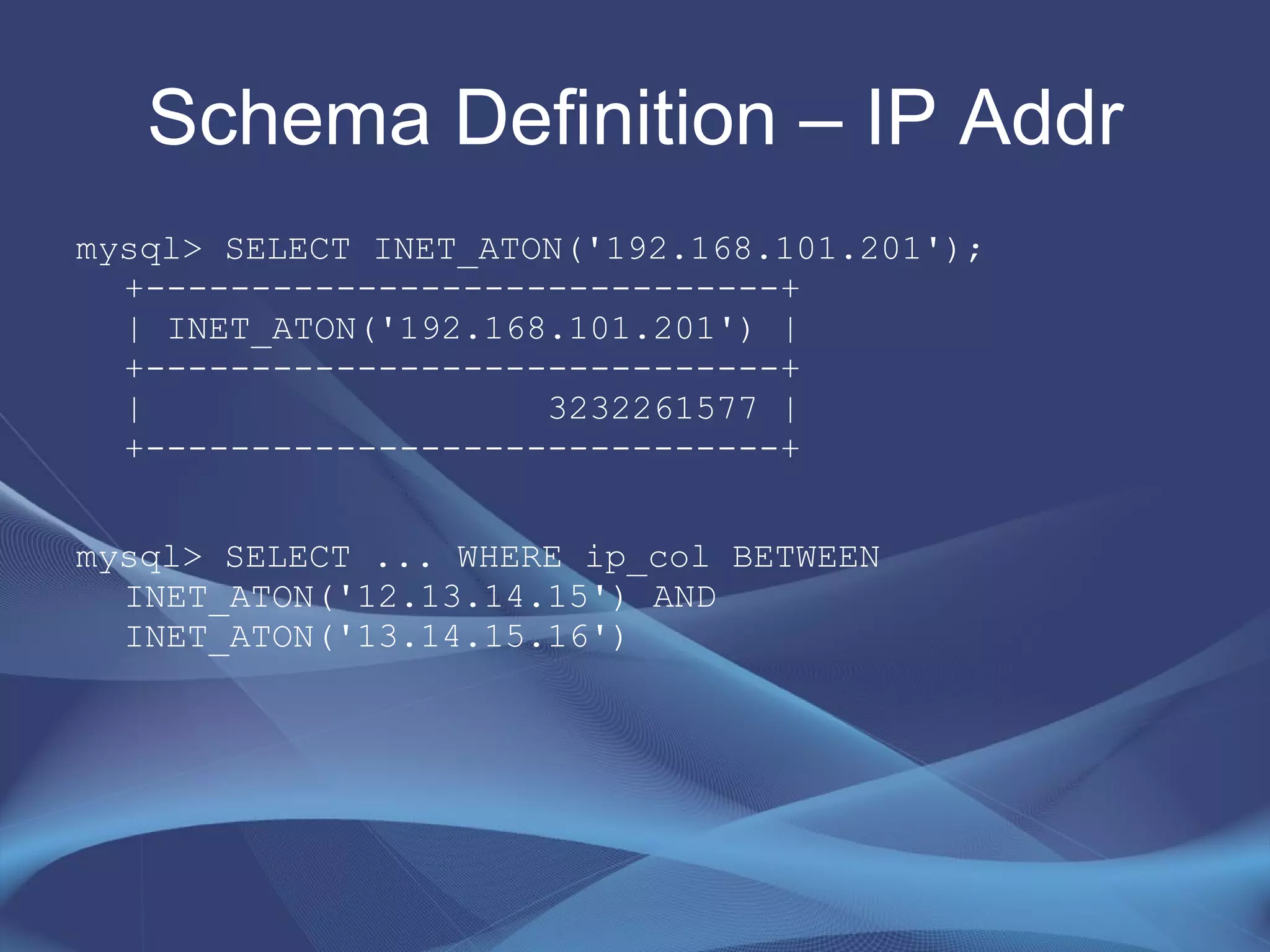
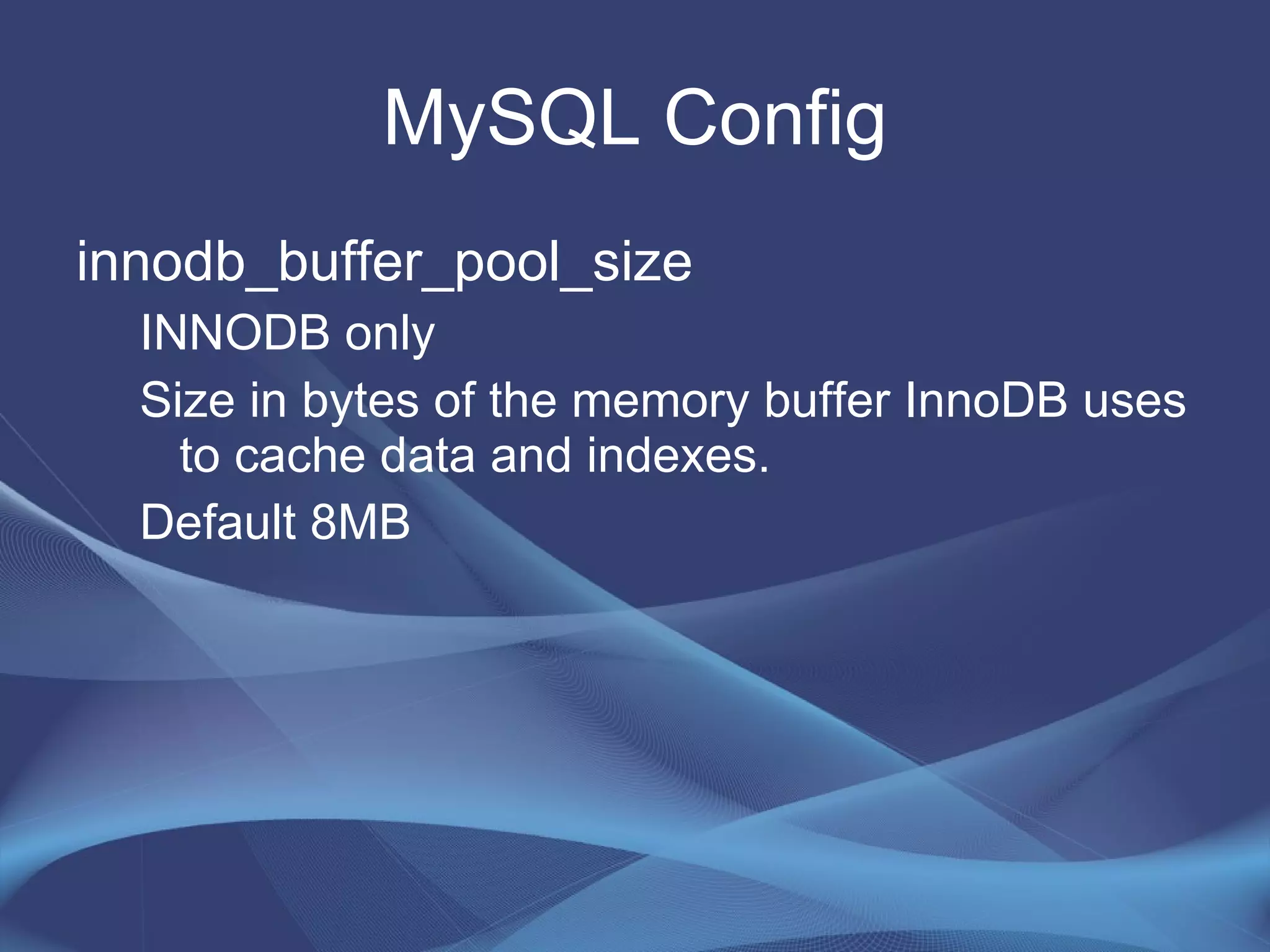
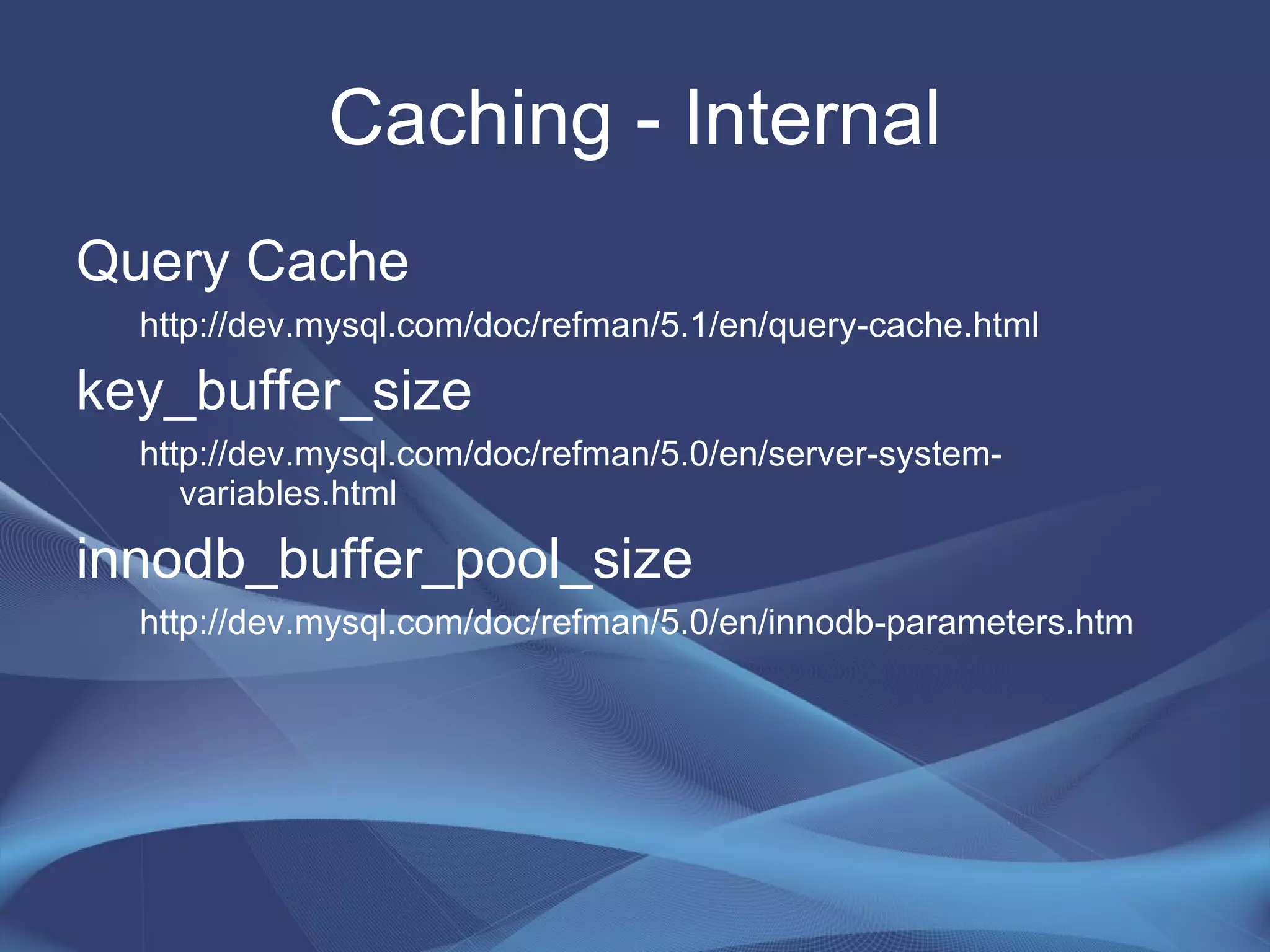
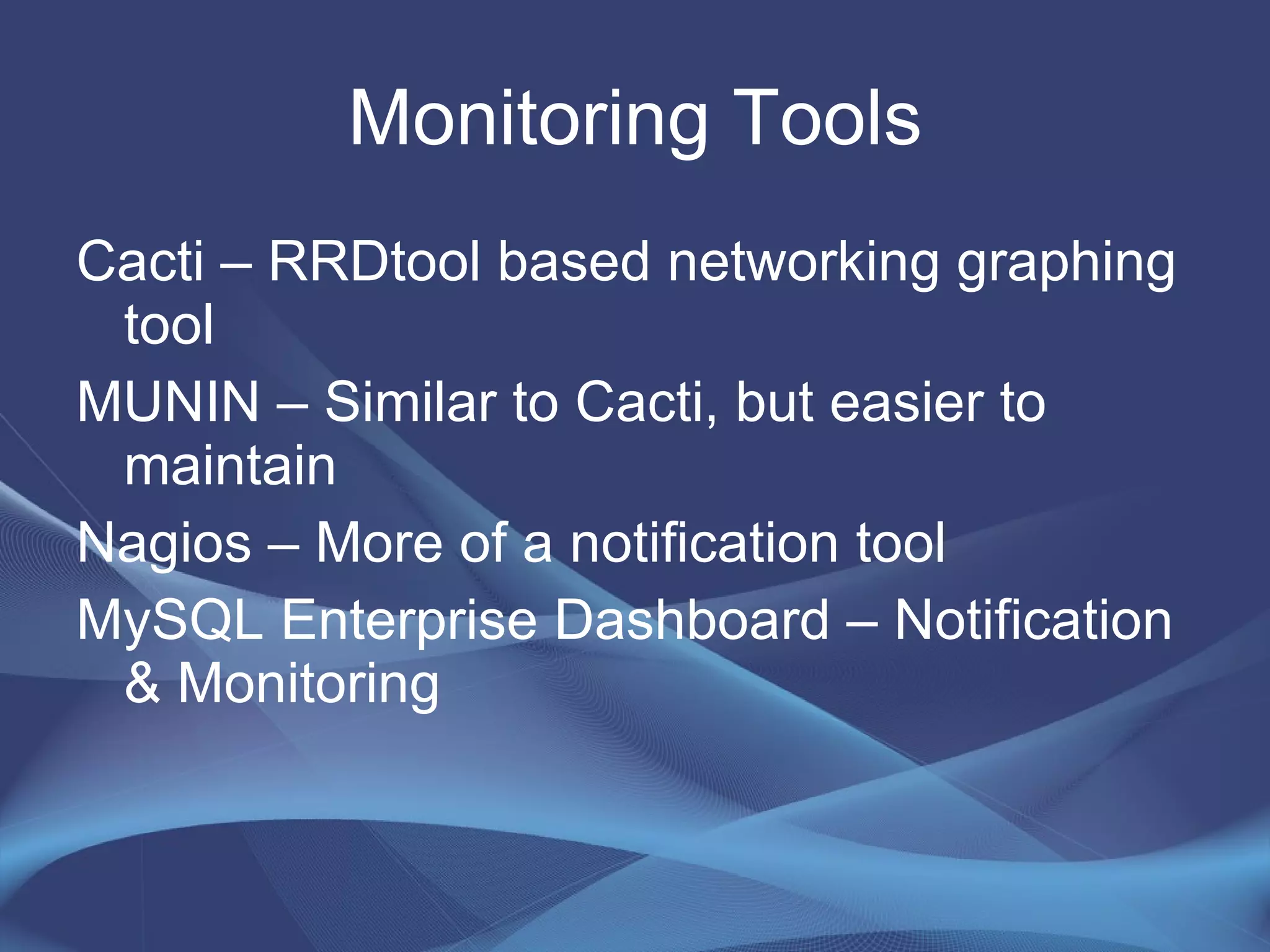
This document provides strategies for optimizing MySQL performance as databases grow in complexity and size. It discusses ways to optimize queries, schemas, hardware, software configuration, caching, and monitoring. The key lessons are to optimize queries, choose appropriate data types and storage engines, configure MySQL and cache settings properly, benchmark and monitor performance, and scale reads and writes separately.