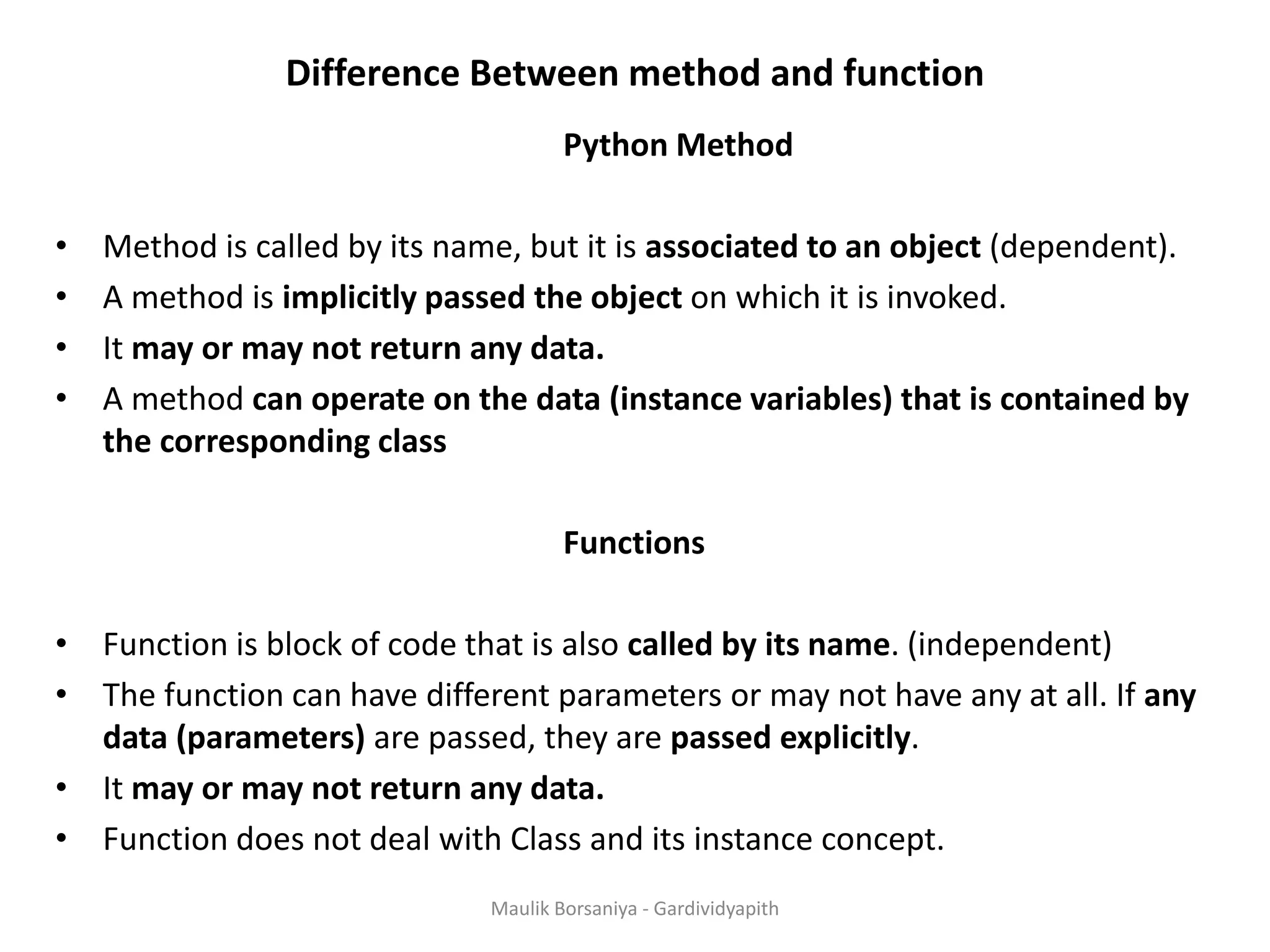
The document provides a comprehensive overview of functions and methods in Python, explaining their definitions, rules for creation, and examples of their usage, including built-in functions and exception handling. It also discusses Python's file handling capabilities, such as opening, reading, writing, and removing files, along with the use of loops and lambda functions. The content is presented with various code snippets to illustrate how to implement the concepts in real scenarios.
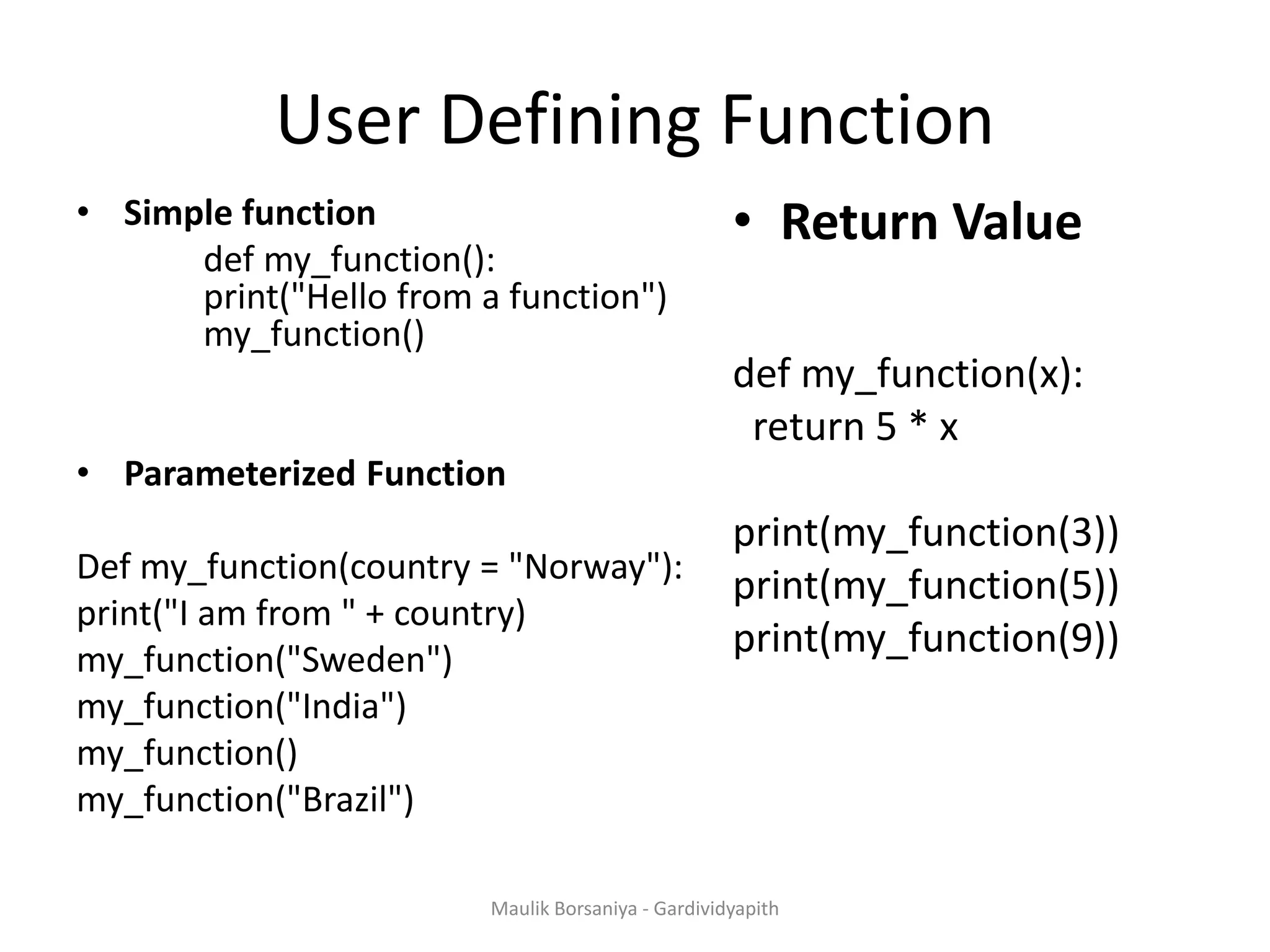
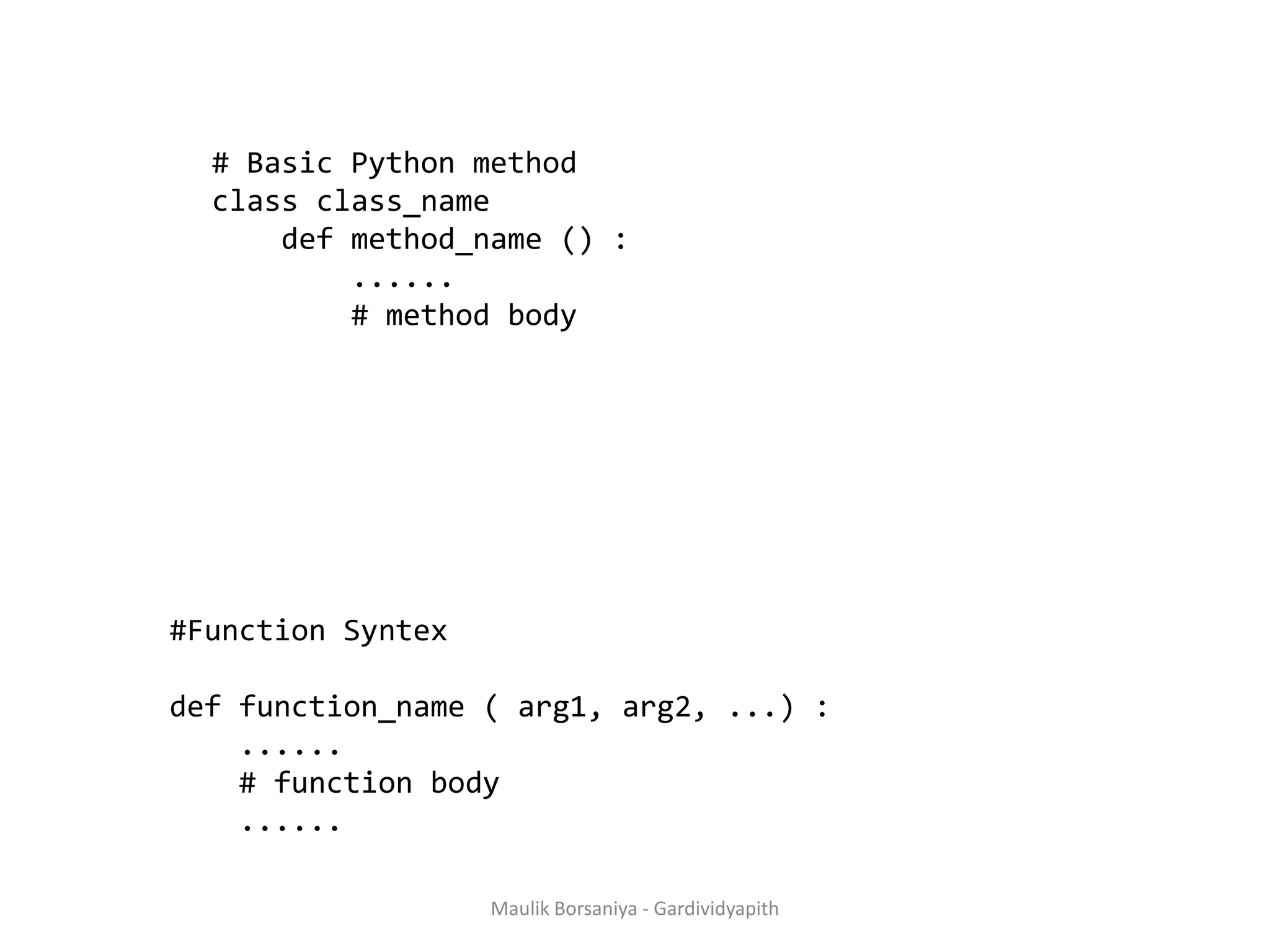
![A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action. Functions provide better modularity for your application and a high degree of code reusing. Function Defining a Function You can define functions to provide the required functionality. Here are simple rules to define a function in Python. Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ). Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these parentheses. You can also define parameters inside these parentheses. The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is indented. The statement return [expression] exits a function, Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-1-2048.jpg)
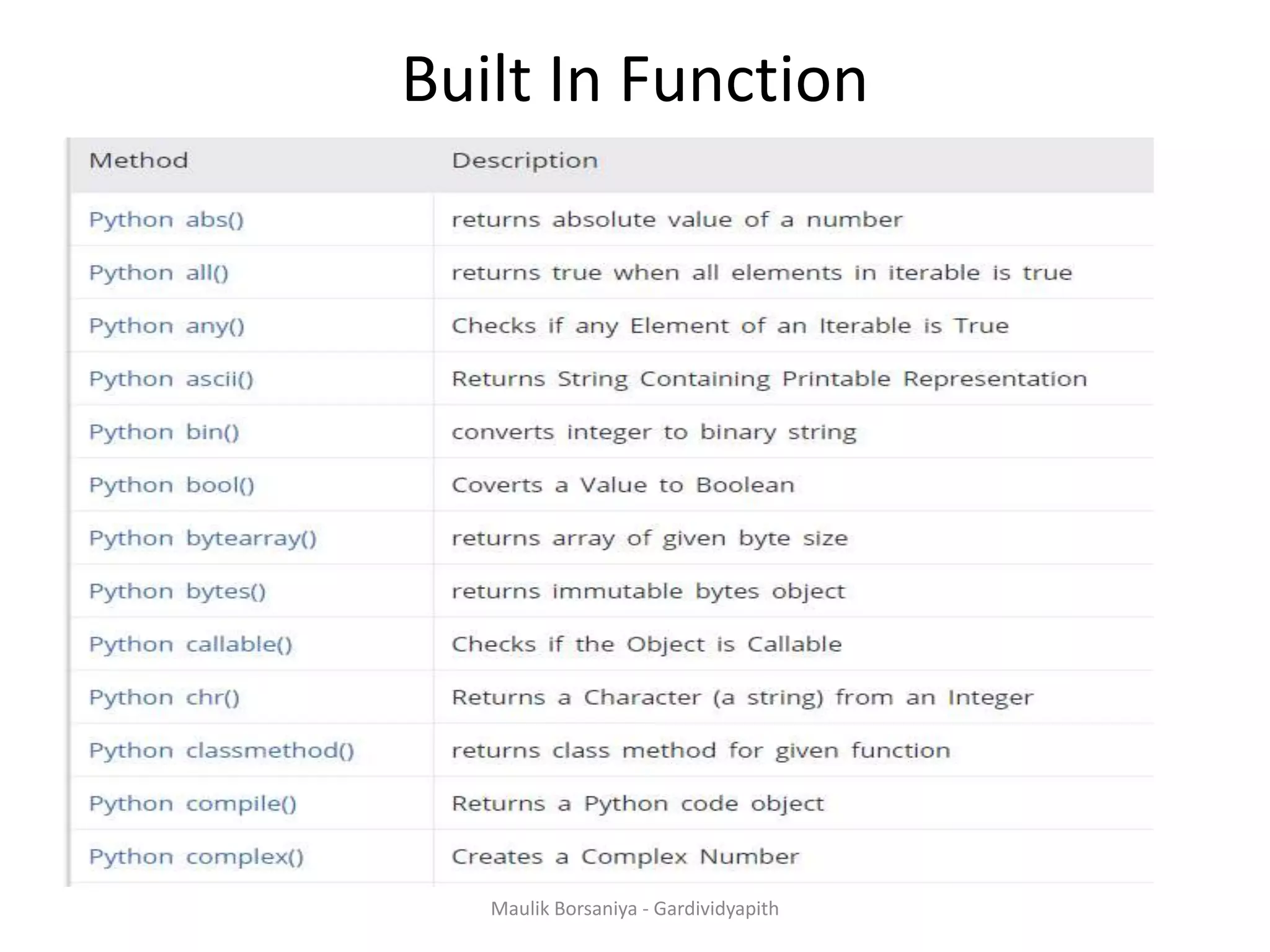
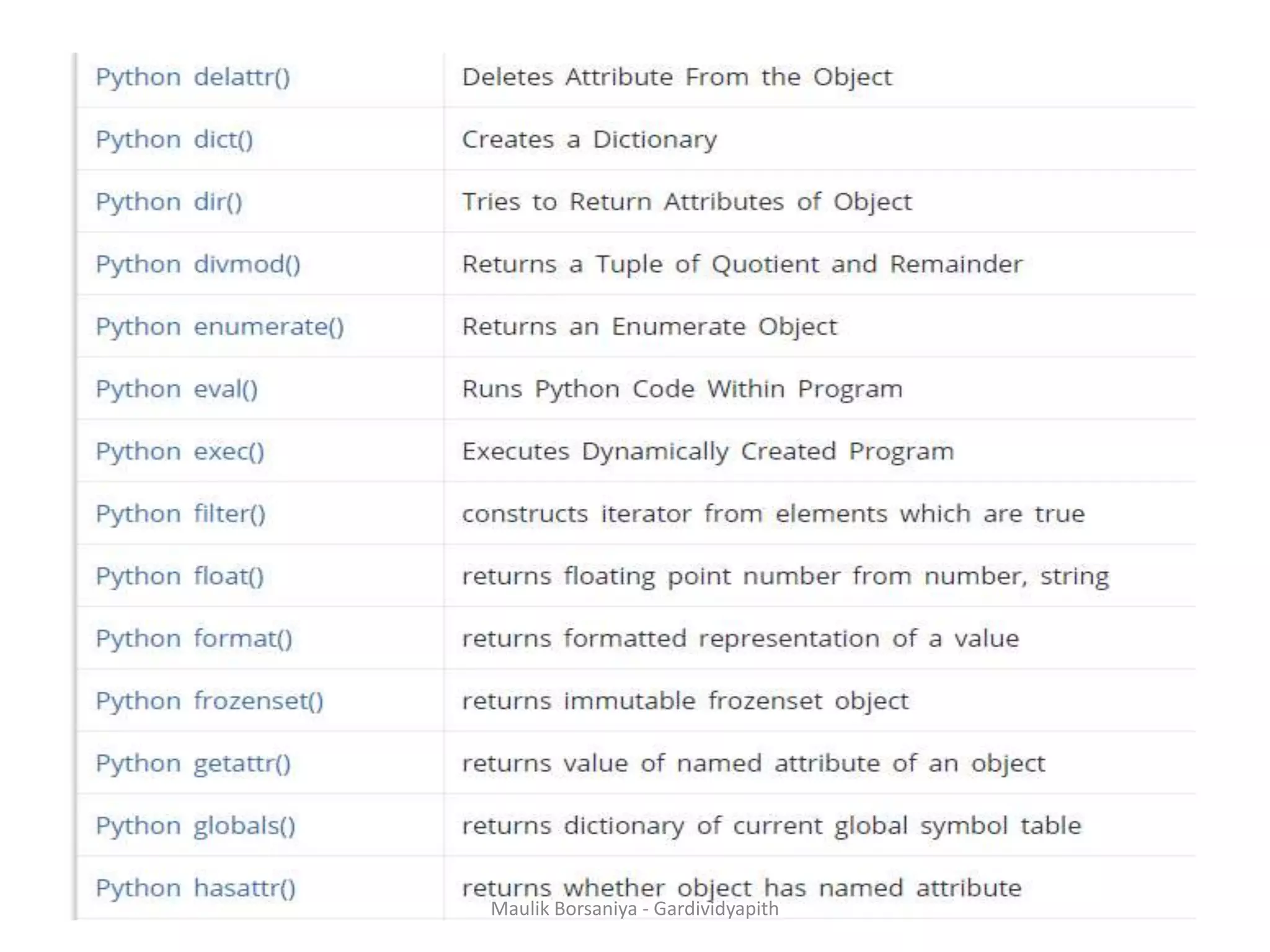
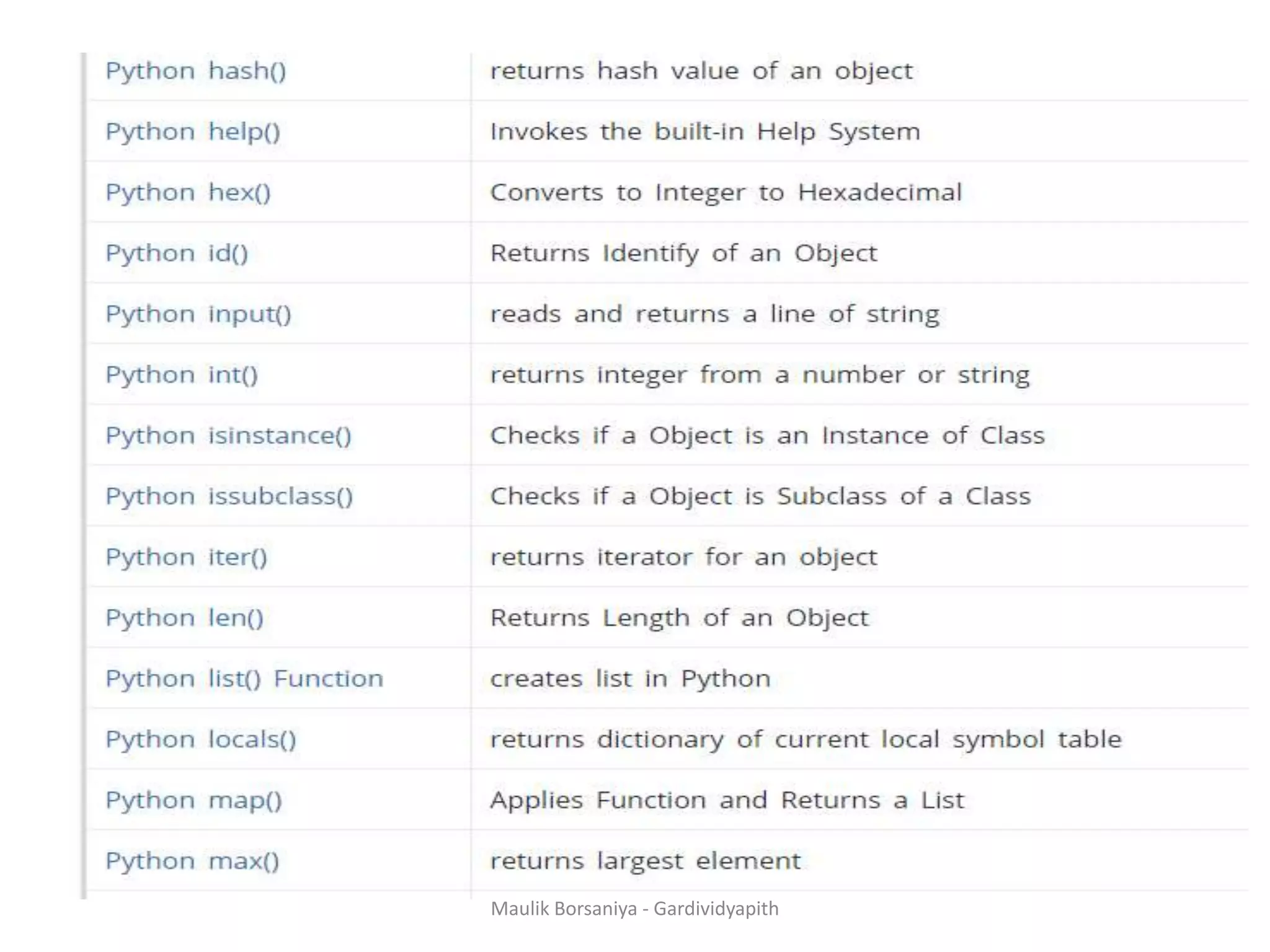
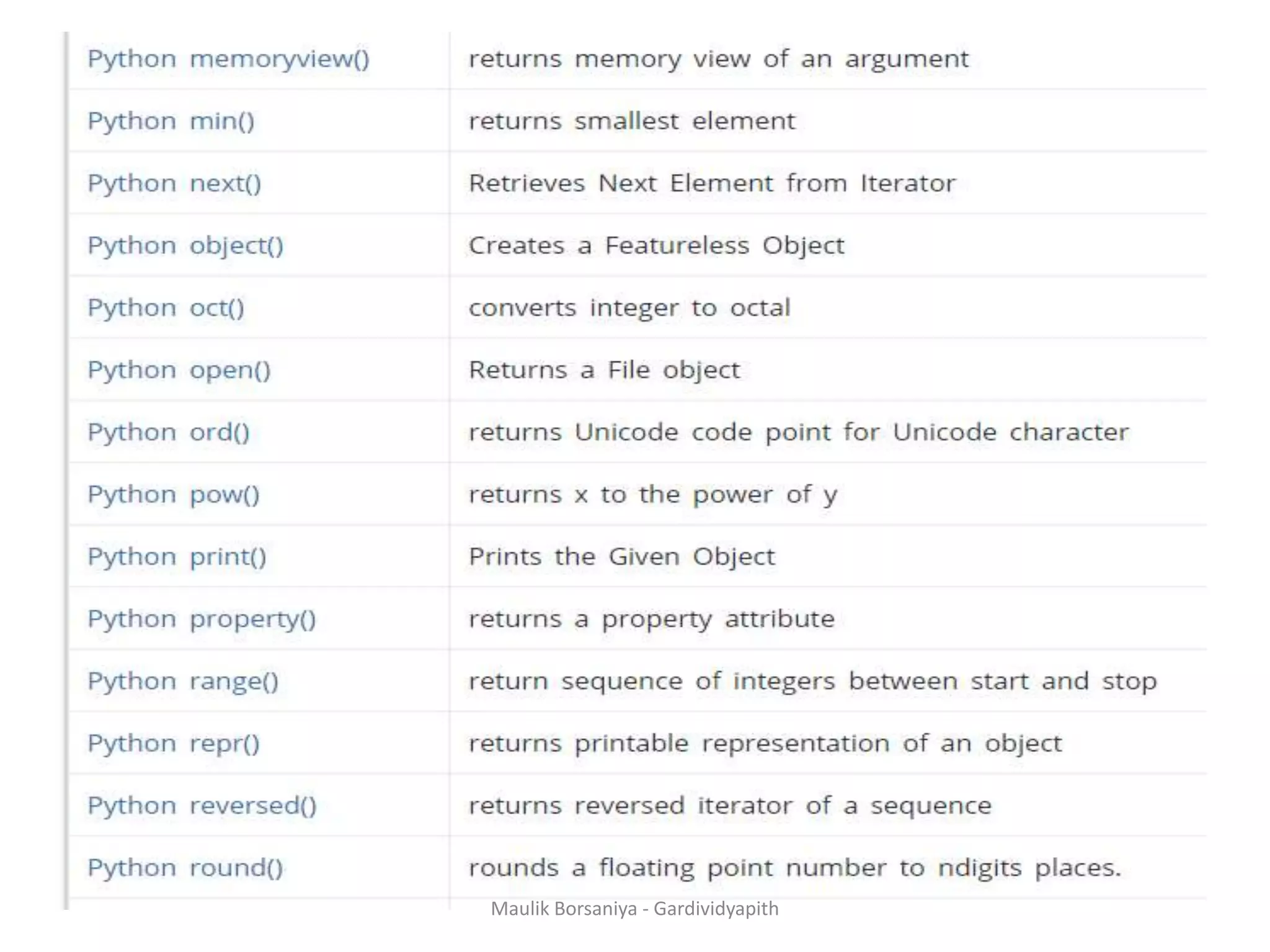

![ABS() integer = -20 print('Absolute value of -20 is:',abs(integer)) Chr() print(chr(97)) print(chr(65)) Max & Min # using max(arg1, arg2, *args) print('Maximum is:', max(1, 3, 2, 10, 4)) # using min(iterable) num = [1, 3, 2, 8, 5, 10, 6] print('Maximum is:', min(num)) Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-8-2048.jpg)
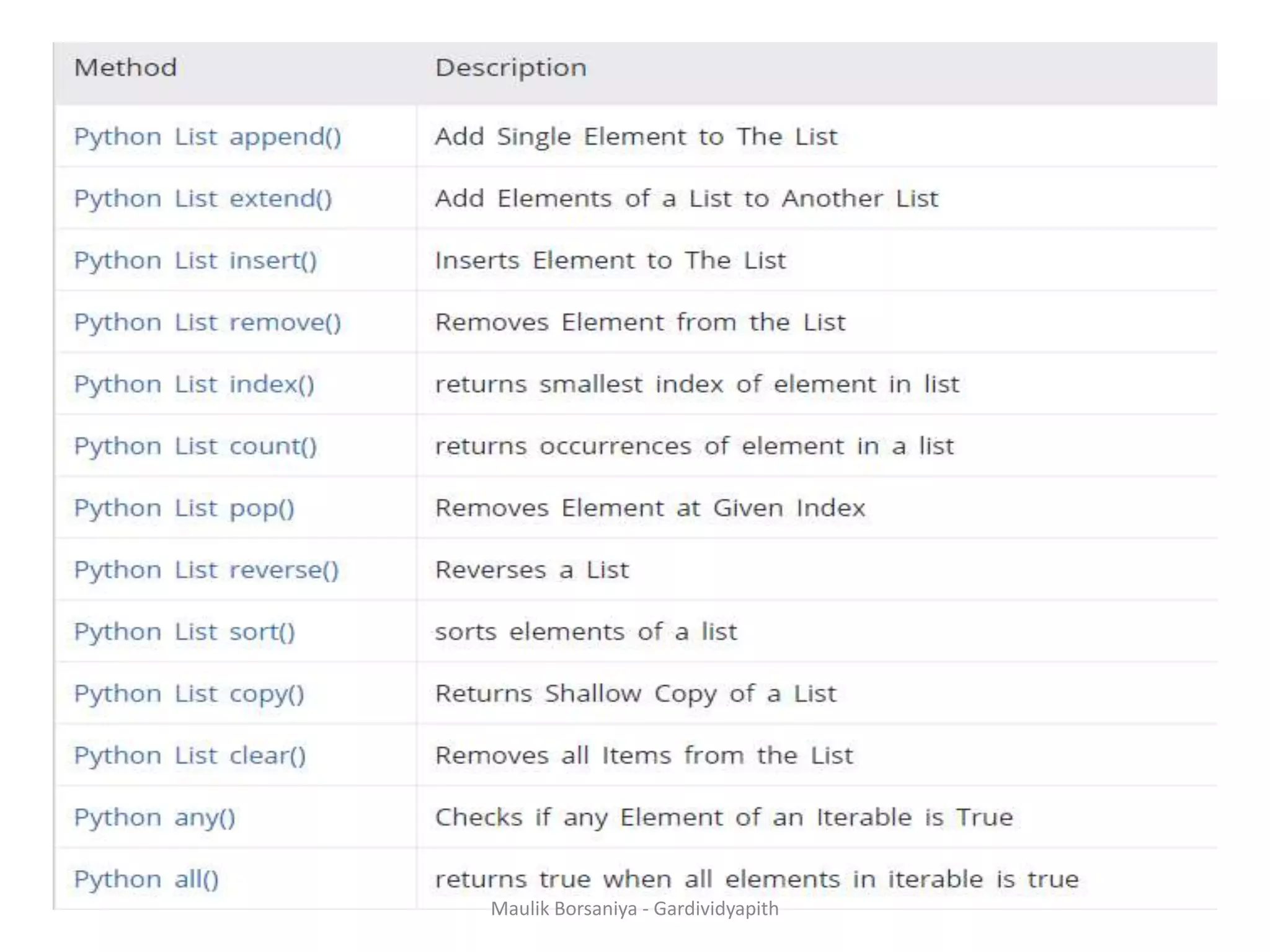
![Method • Python has some list methods that you can use to perform frequency occurring task (related to list) with ease. For example, if you want to add element to a list, you can use append() method. Simple Example animal = ['cat', 'dog', 'rabbit'] animal.append('pig') #Updated Animal List print('Updated animal list: ', animal) • Eg-1 Eg-2 numbers = [2.5, 3, 4, -5] numbersSum = sum(numbers) print(numbersSum) Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-9-2048.jpg)
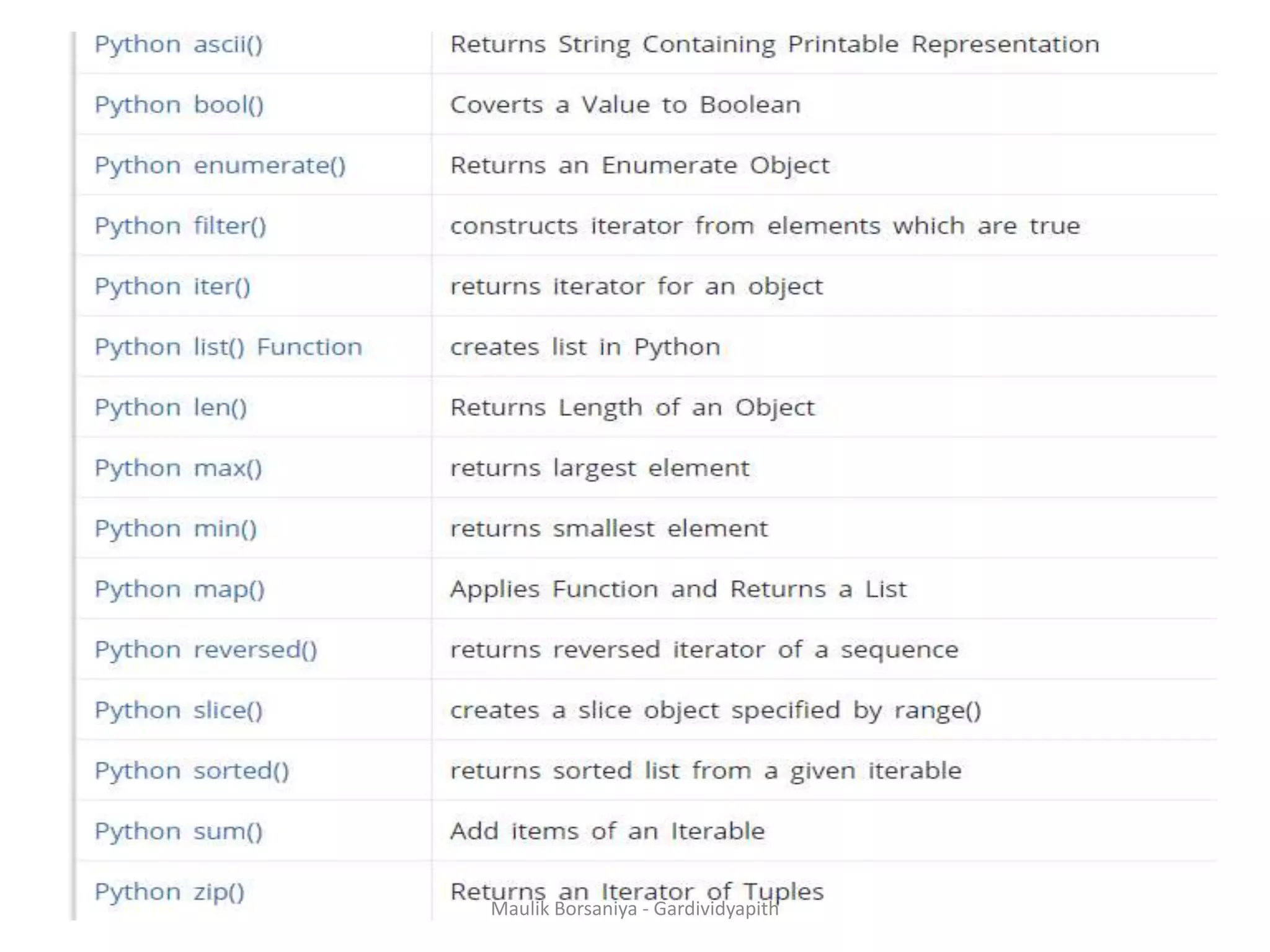
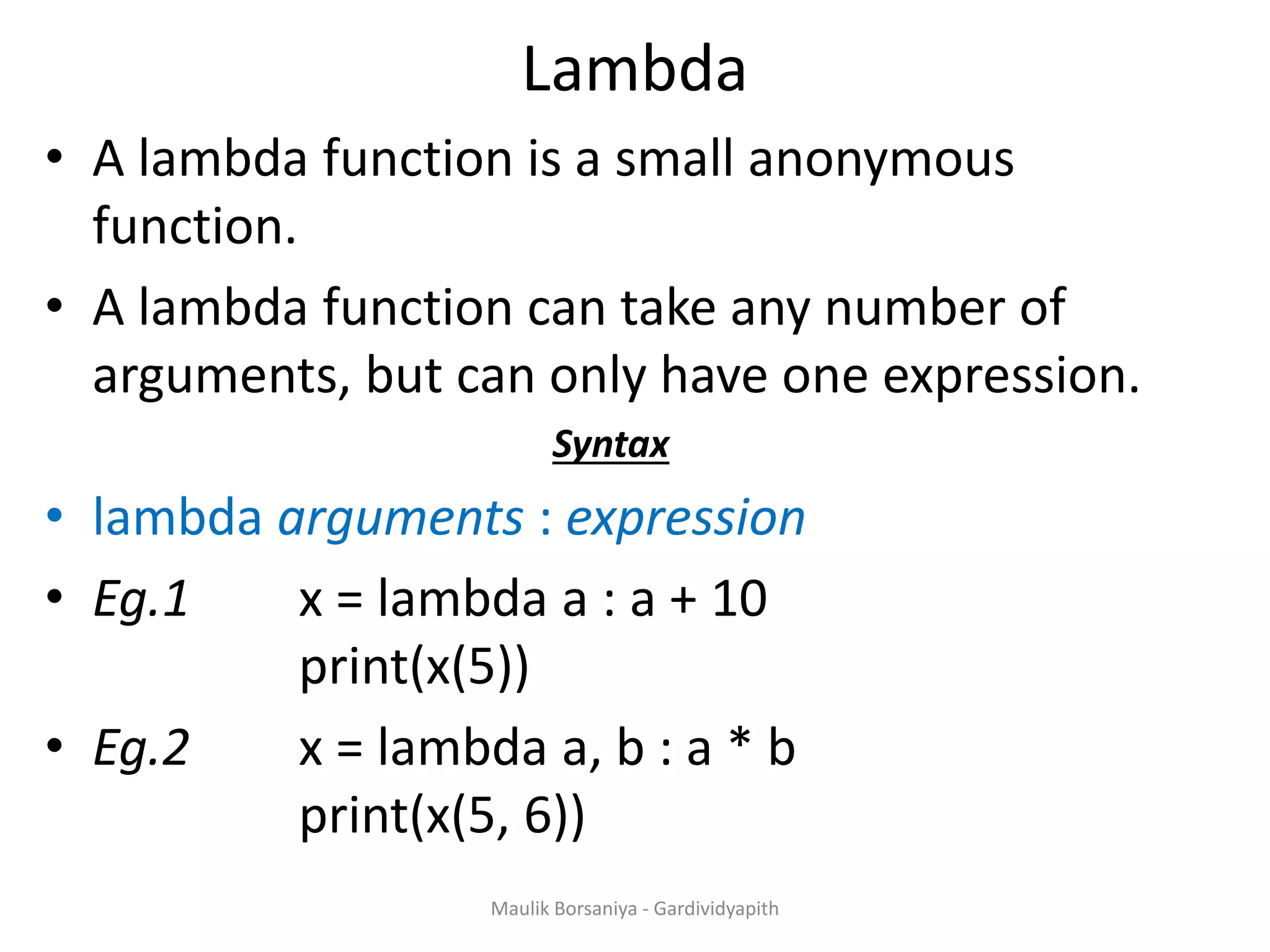
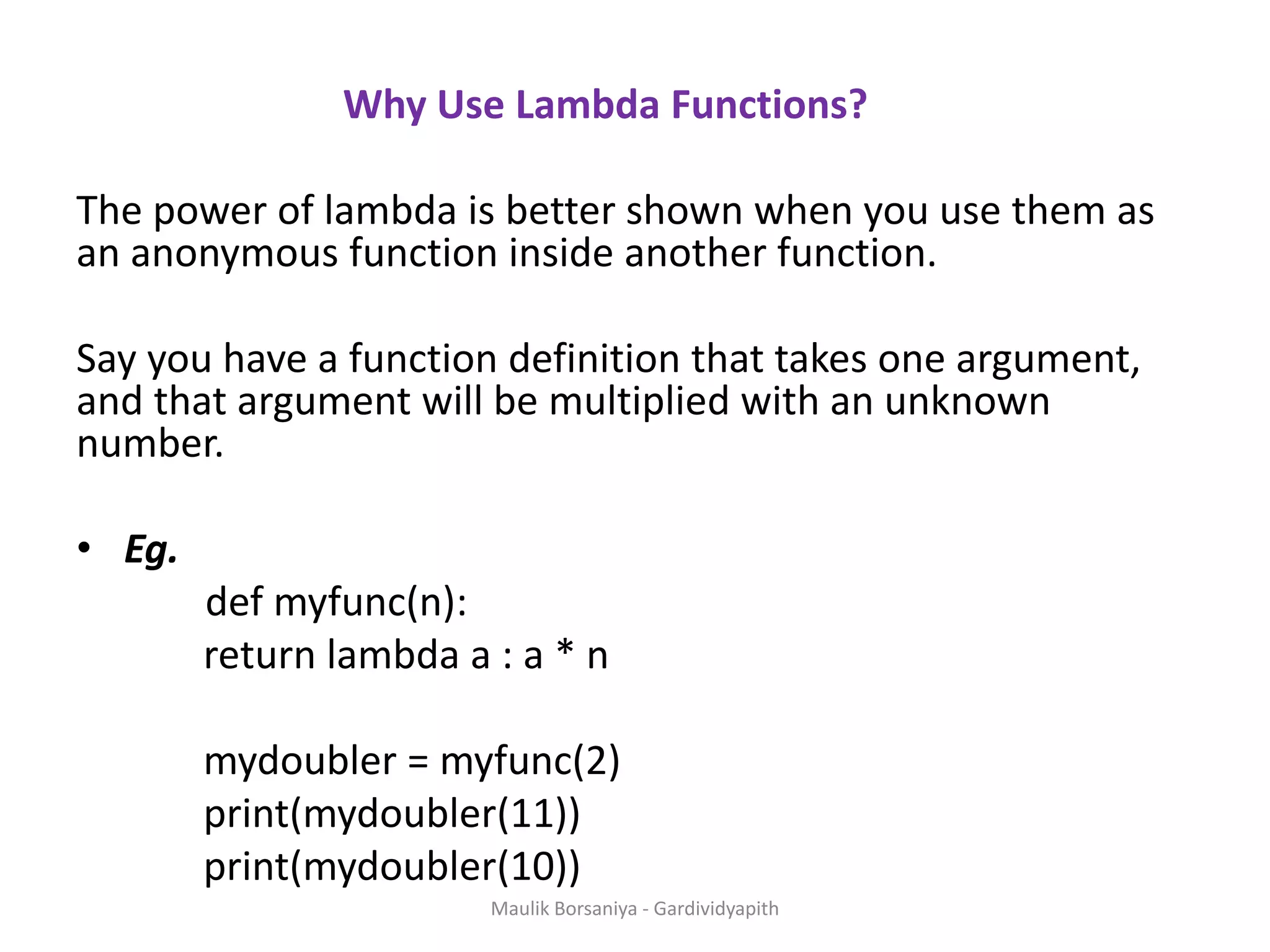
![Filter With Lambda • The filter() function in Python takes in a function and a list as arguments. • The function is called with all the items in the list and a new list is returned which contains items for which the function evaluates to True. • Here is an example use of filter() function to filter out only even numbers from a list. • Eg.1 my_list = [1, 5, 4, 6, 8, 11, 3, 12] new_list = list(filter(lambda x: (x%2 == 0) , my_list)) print(new_list) Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-16-2048.jpg)
![Map With Lambda • The map() function in Python takes in a function and a list. • The function is called with all the items in the list and a new list is returned which contains items returned by that function for each item. • Here is an example use of map() function to double all the items in a list. • Eg.1 my_list = [1, 5, 4, 6, 8, 11, 3, 12] new_list = list(map(lambda x: x * 2 , my_list)) print(new_list) Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-17-2048.jpg)
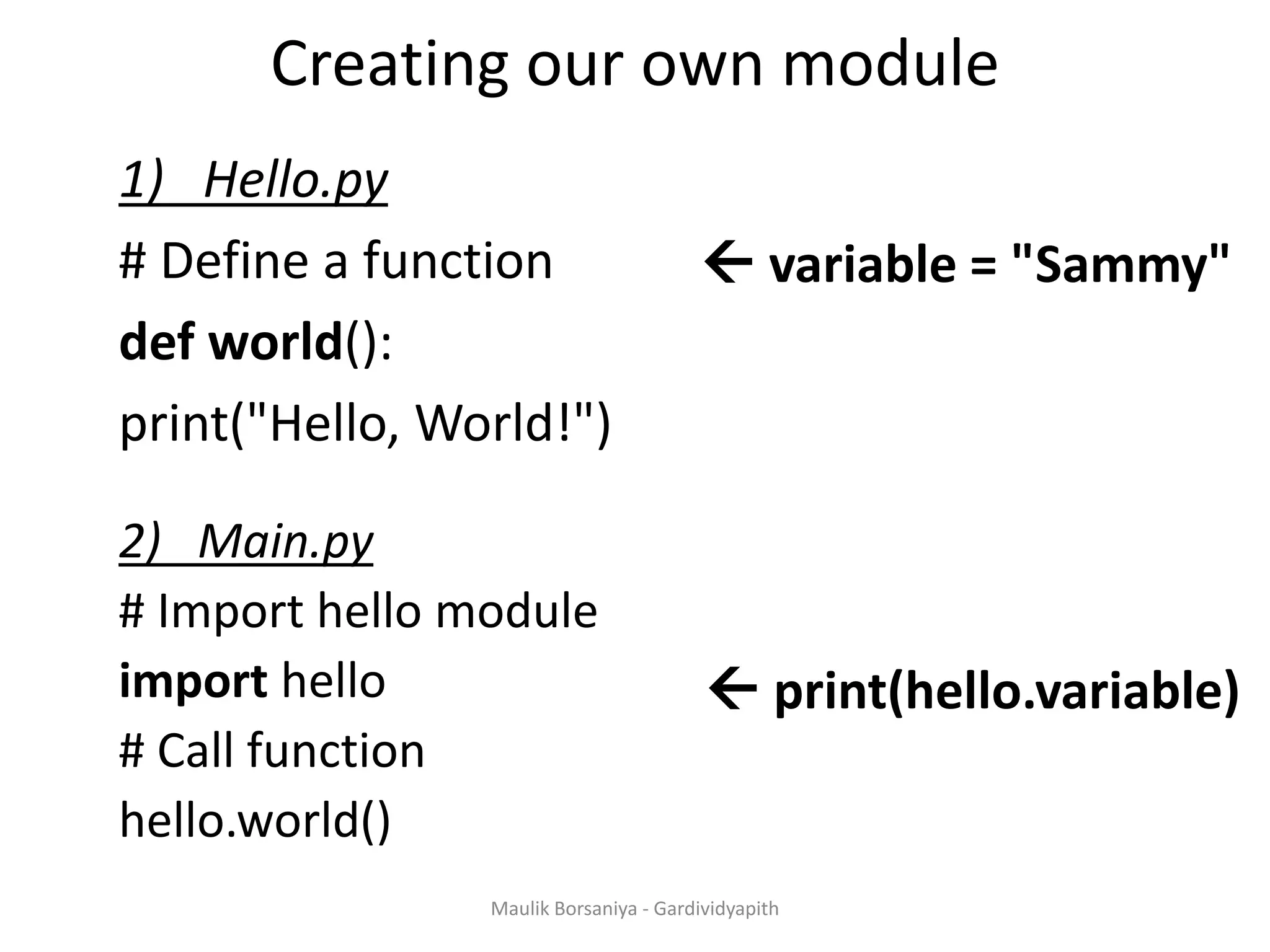



![Exception Handling With Assert Statement • Syntex : assert expression, argument, messag Eg . assert 2 + 2 == 4 assert 2 + 3 == 3, ’’error is here’’ Eg.2 def avg(marks): assert len(marks) != 0,"List is empty.“ return sum(marks)/len(marks) mark2 = [55,88,78,90,79] print("Average of mark2:",avg(mark2)) mark1 = [] print("Average of mark1:",avg(mark1)) • Python has built-in assert statement to use assertion condition in the program. • assert statement has a condition or expression which is supposed to be always true. • If the condition is false assert halts the program and gives an AssertionError. Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-22-2048.jpg)


![File Positions • The tell() method tells you the current position within the file; in other words, the next read or write will occur at that many bytes from the beginning of the file. • The seek(offset[, from]) method changes the current file position. The offset argument indicates the number of bytes to be moved. The from argument specifies the reference position from where the bytes are to be moved. • If from is set to 0, it means use the beginning of the file as the reference position and 1 means use the current position as the reference position and if it is set to 2 then the end of the file would be taken as the reference position. Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-27-2048.jpg)




![Python For Loops • A for loop is used for iterating over a sequence (that is either a list, a tuple or a string). • This is less like the for keyword in other programming language, and works more like an iterator method as found in other object-orientated programming languages. • With the for loop we can execute a set of statements, once for each item in a list, tuple, set etc. Example • fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] for x in fruits: print(x) Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-32-2048.jpg)
![• fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] for x in fruits: if x == "banana": break print(x) • for x in range(2, 30, 3): print(x) • i = 1 while i < 6: print(i) i += 1 Maulik Borsaniya - Gardividyapith](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-181201113316/75/PYTHON-Chapter-2-Functions-Exception-Modules-and-Files-MAULIK-BORSANIYA-33-2048.jpg)