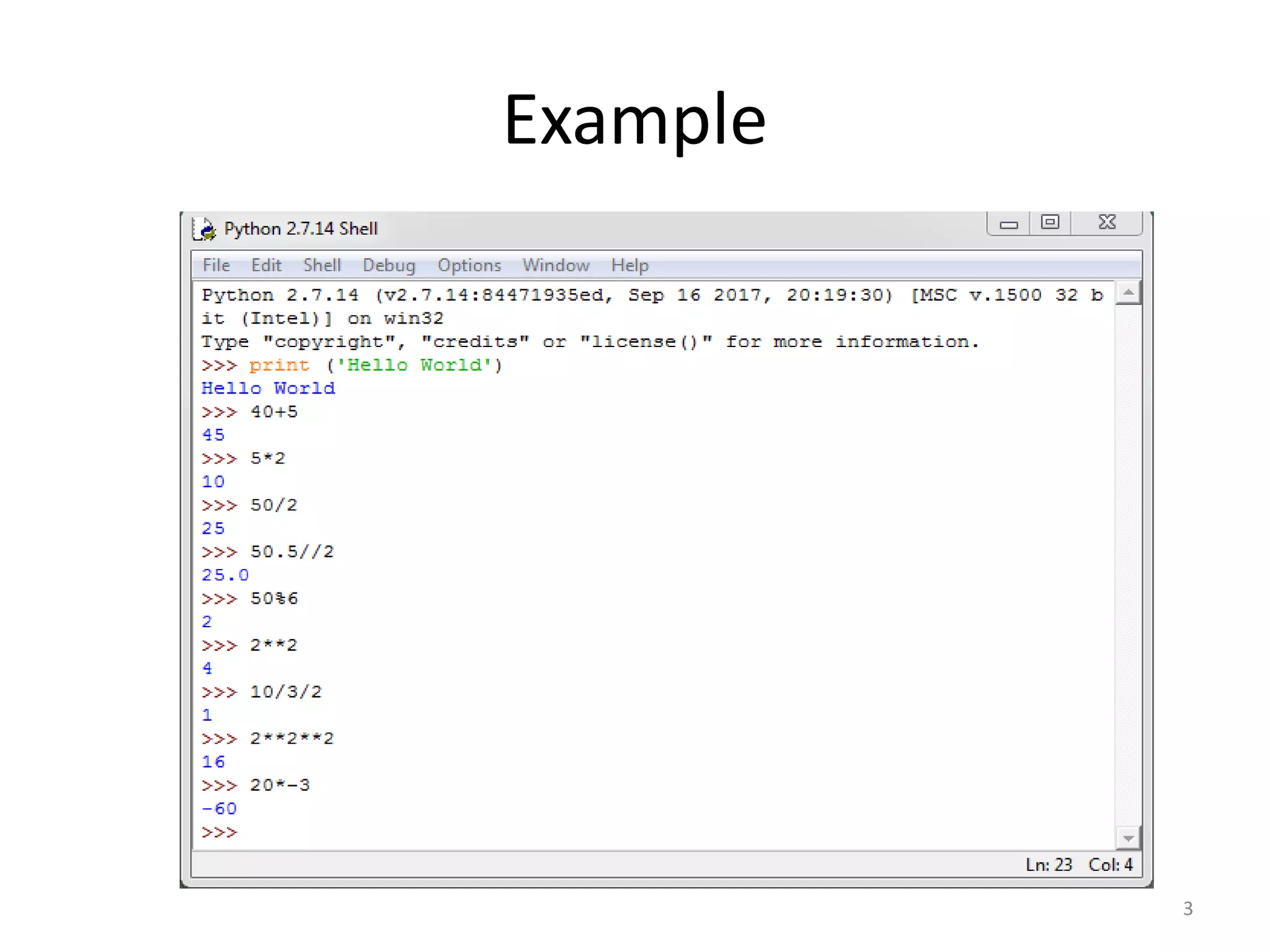
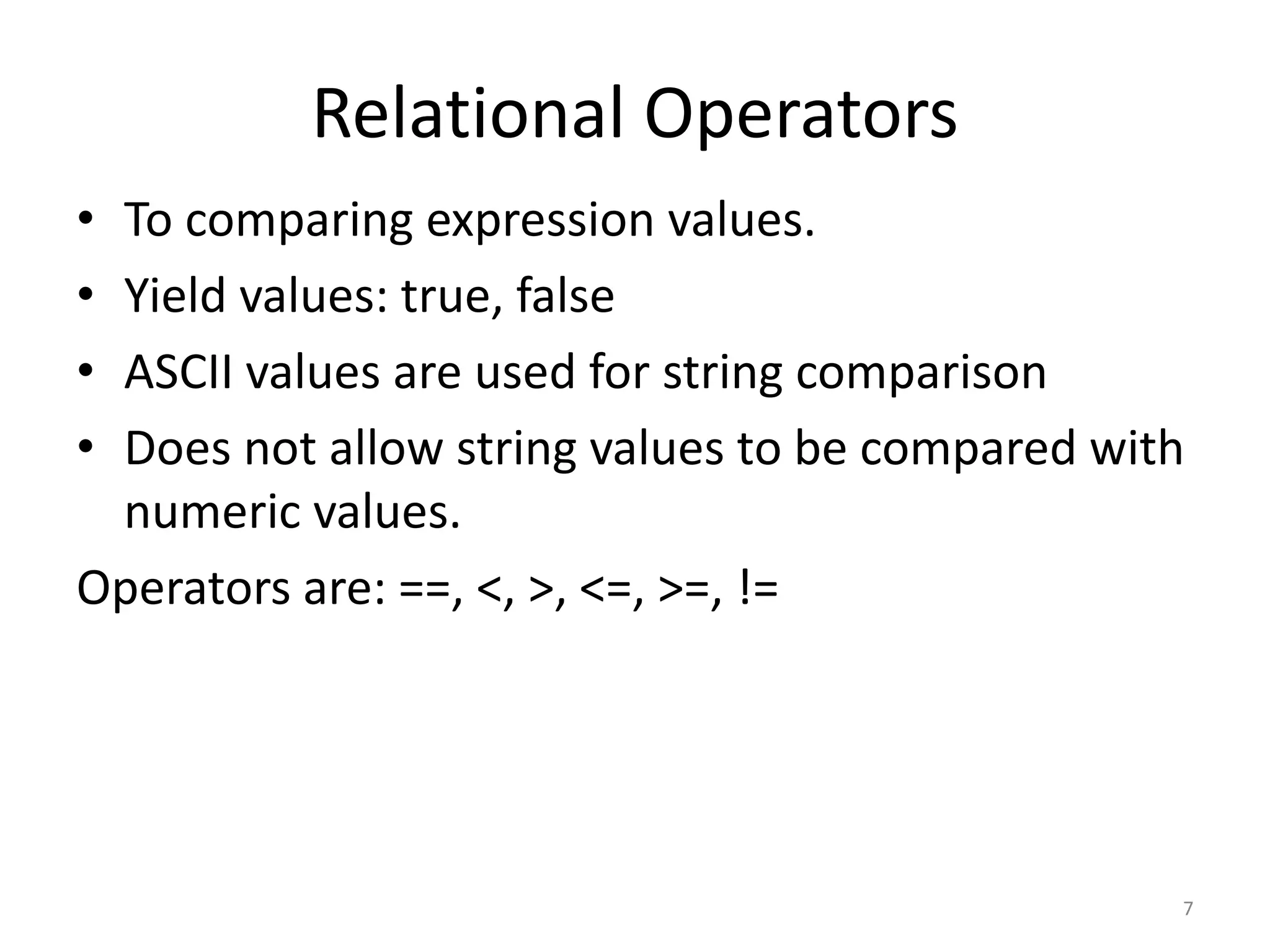
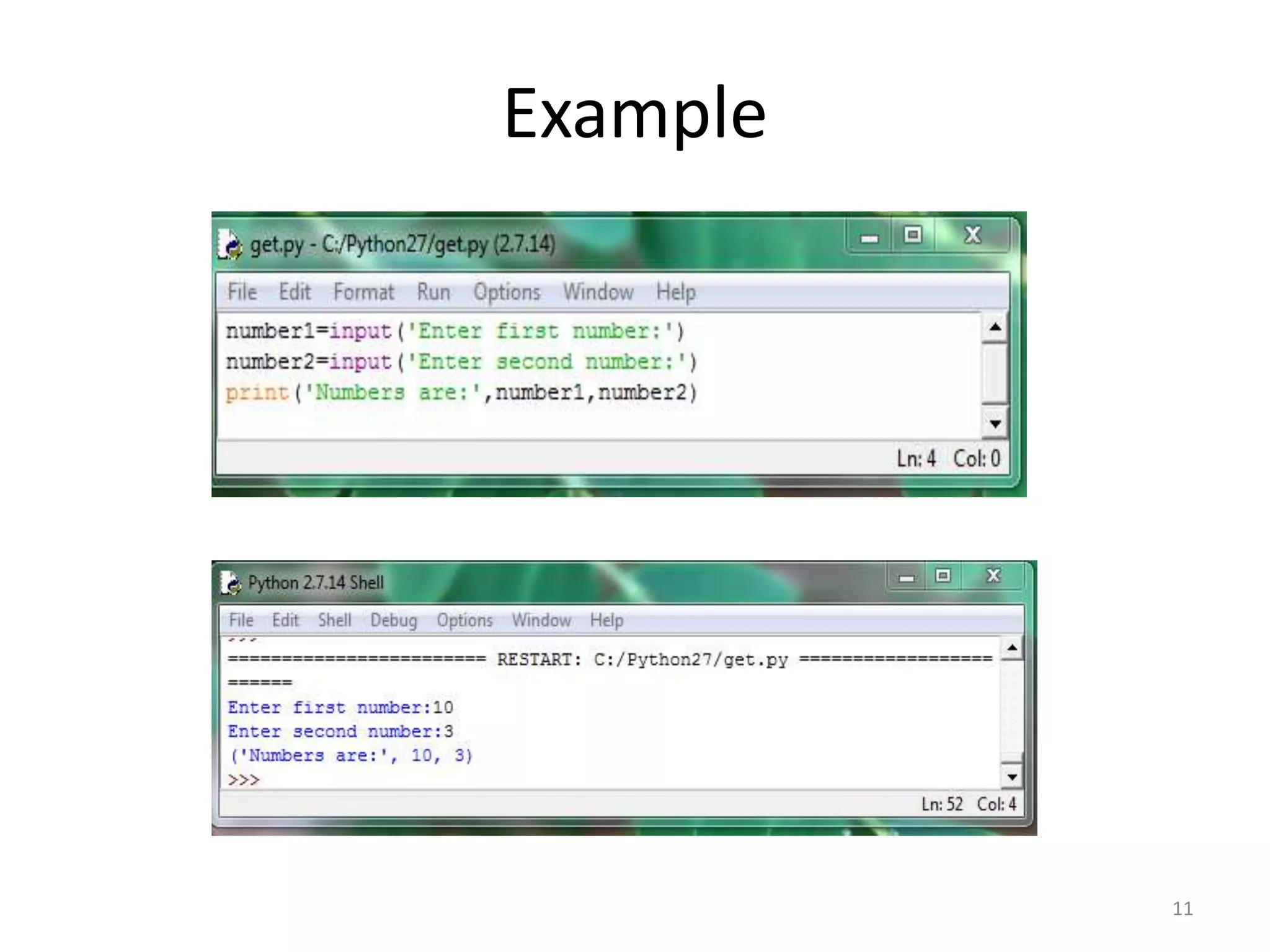
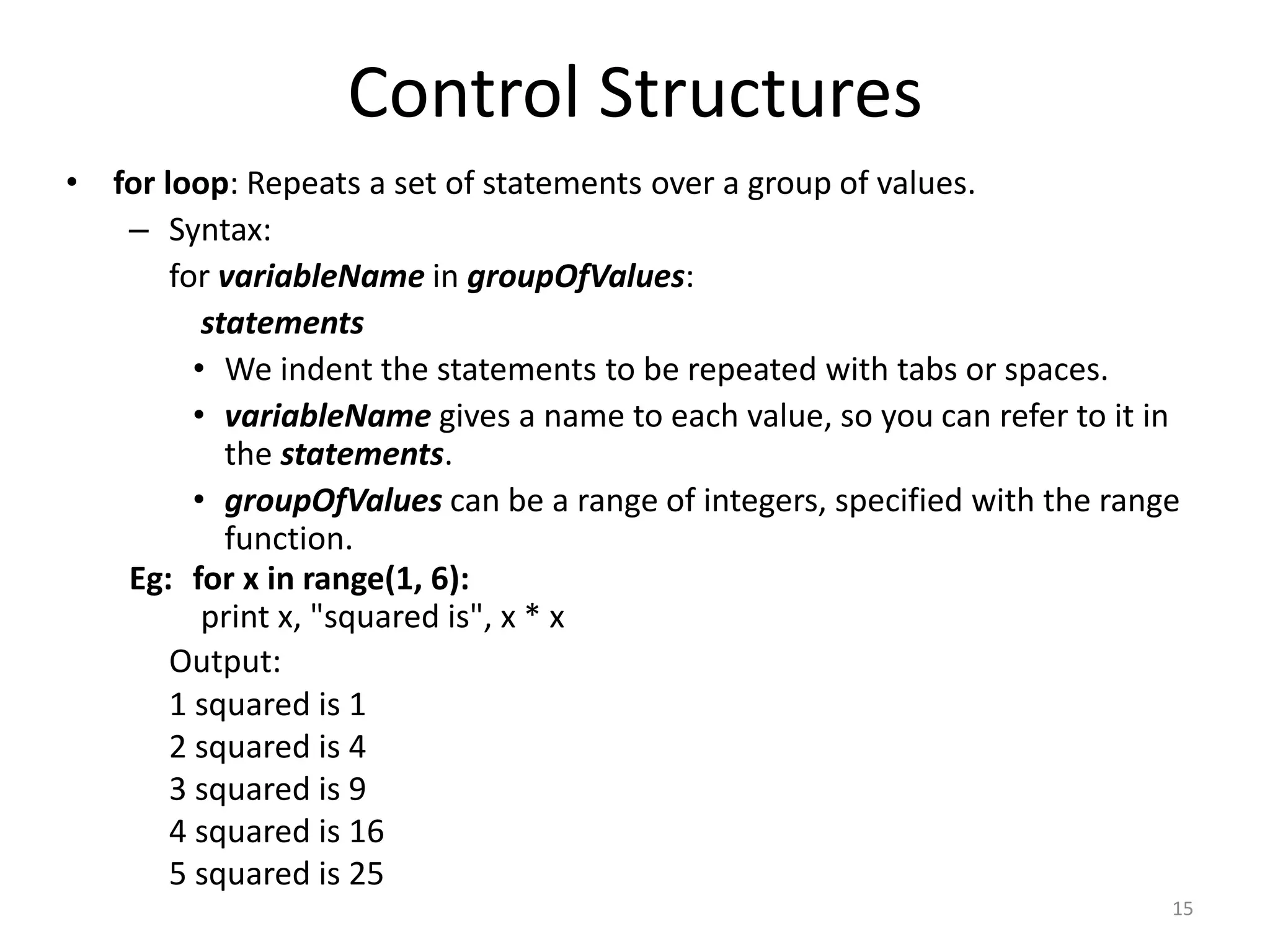
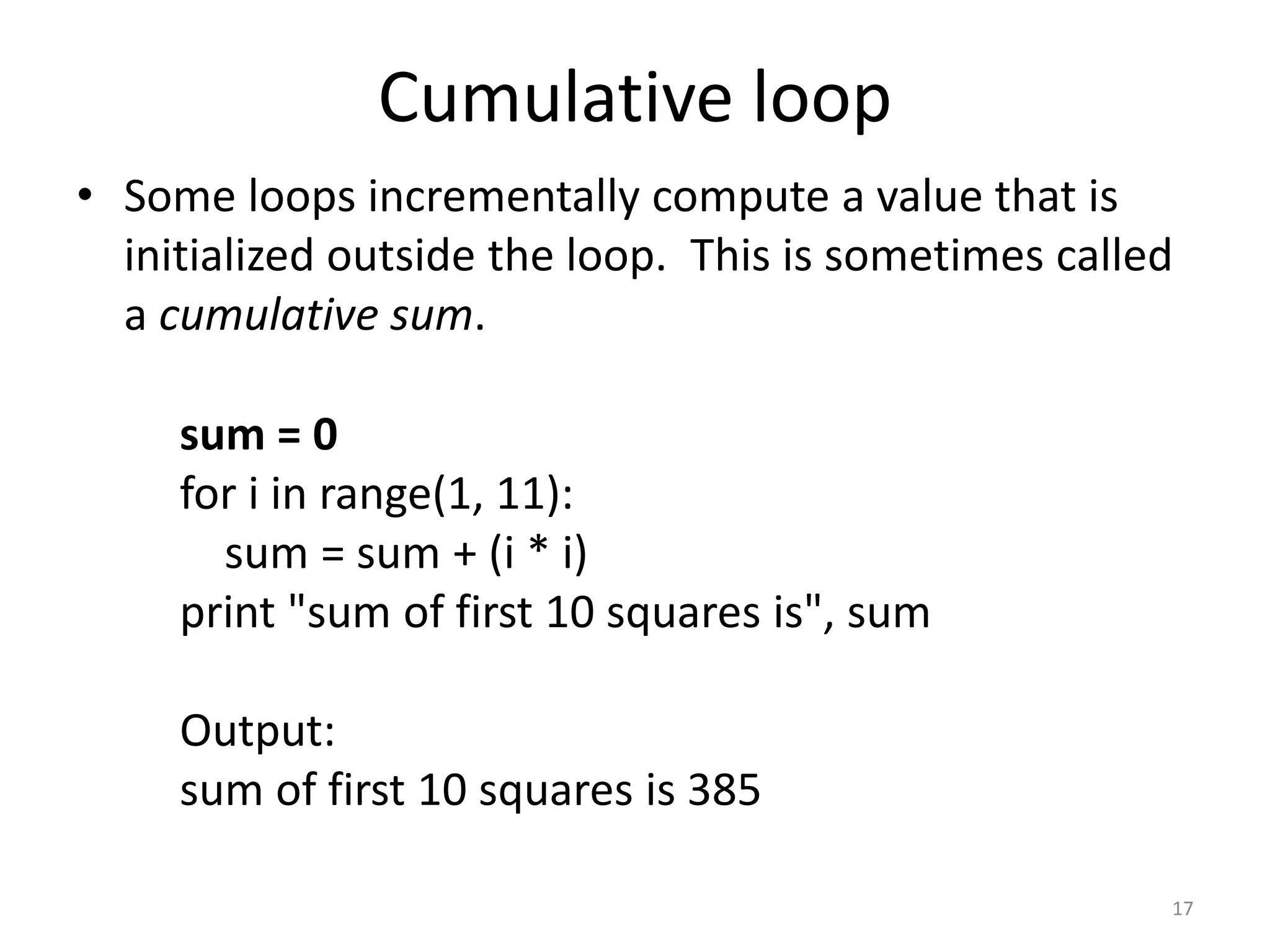
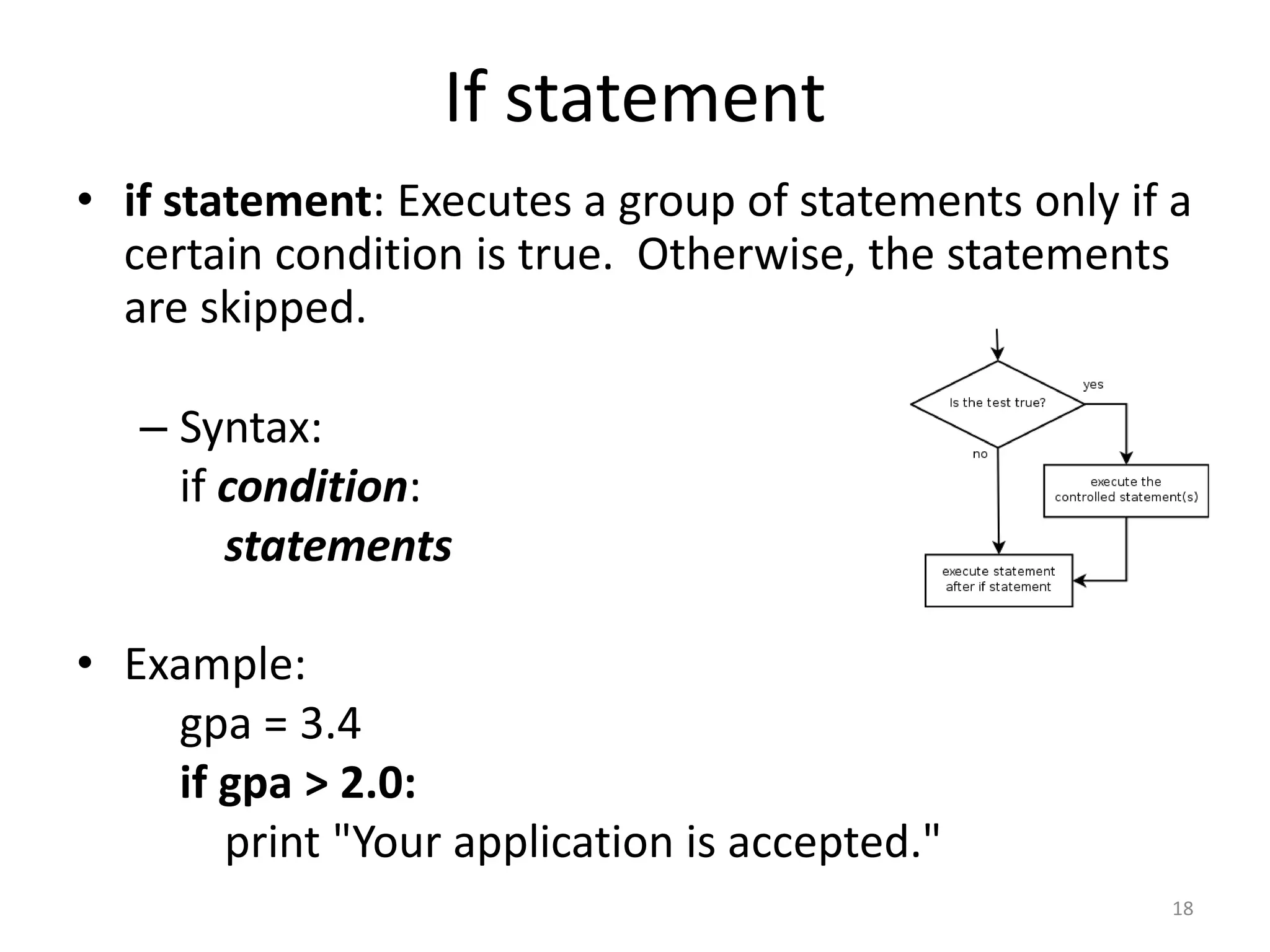
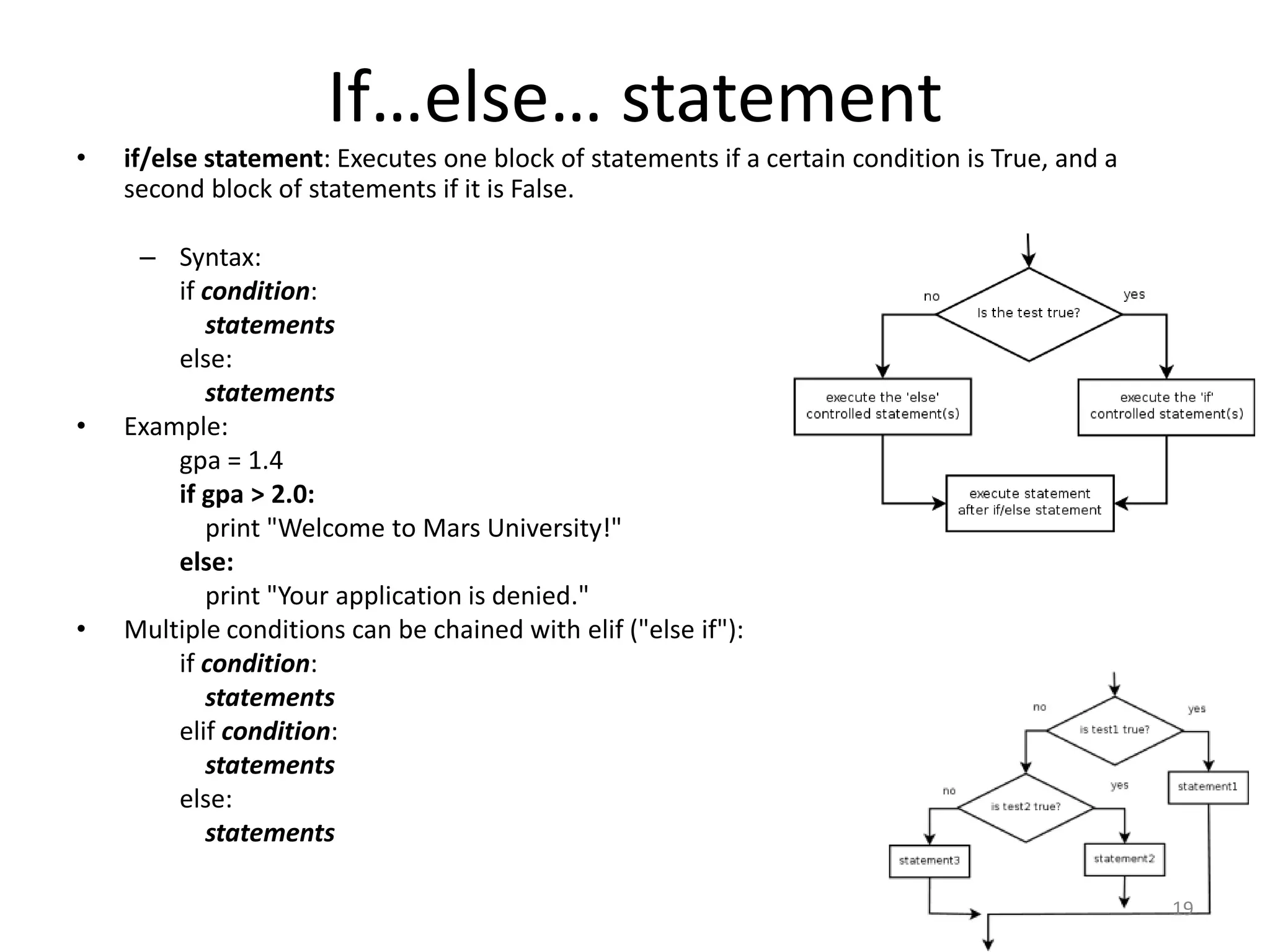
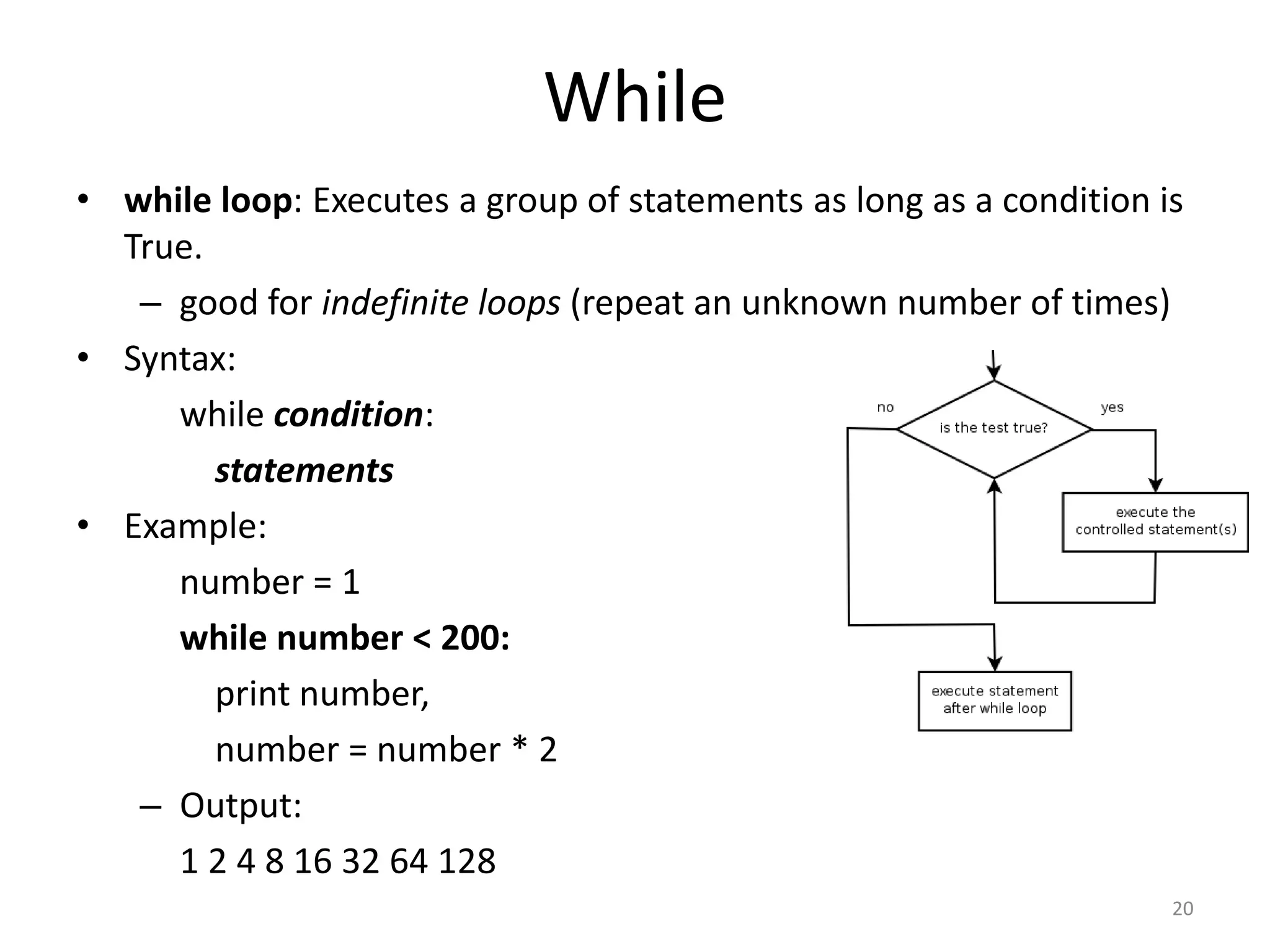
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Python programming including: - The IDLE integrated development environment and print statement syntax. - Operator precedence and common error messages. - Data types like strings and numeric types. - Relational, logical, and bitwise operators for comparisons. - Variables, keywords, and assignment statements. - Built-in functions, function definition syntax, and calling functions. - Control structures like for loops, if/else conditional statements, and while loops for iteration.