Embed presentation
Downloaded 33 times


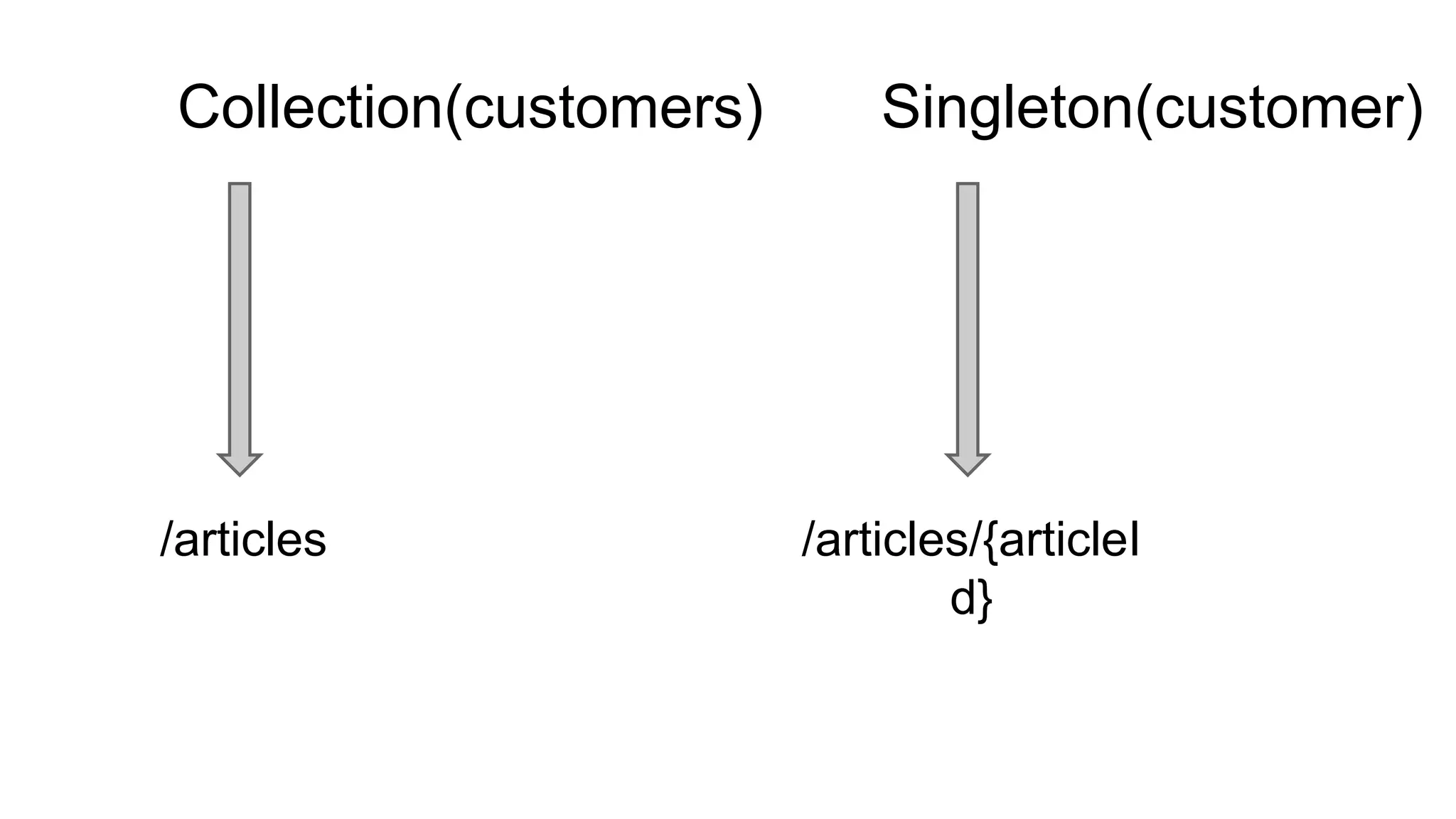












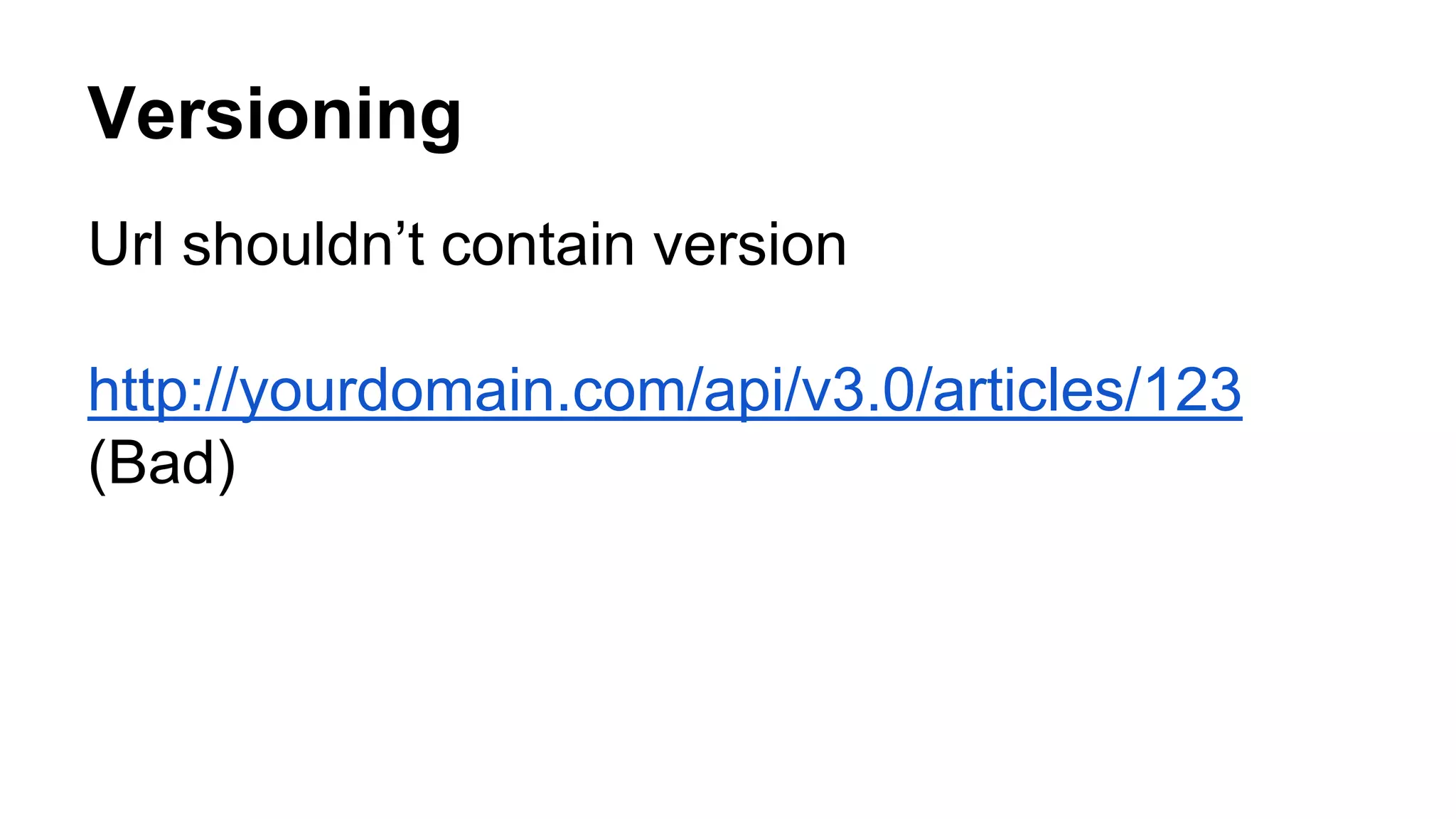




The document discusses fundamentals of RESTful API design including resources, representations, HTTP verbs, and versioning. Key points include: - Resources can be collections like customers or singletons like a specific customer and are identified by URIs. Sub-collections are also resources. - HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE map to common CRUD operations for resources. - Resources have representations, typically JSON or XML, that are transferred in requests and responses. - Choosing resources depends on domain analysis and consumer needs. Resources can be fine-grained with separate endpoints or coarse-grained with all details at once. - Versioning is best done by specifying the version in the Accept



















