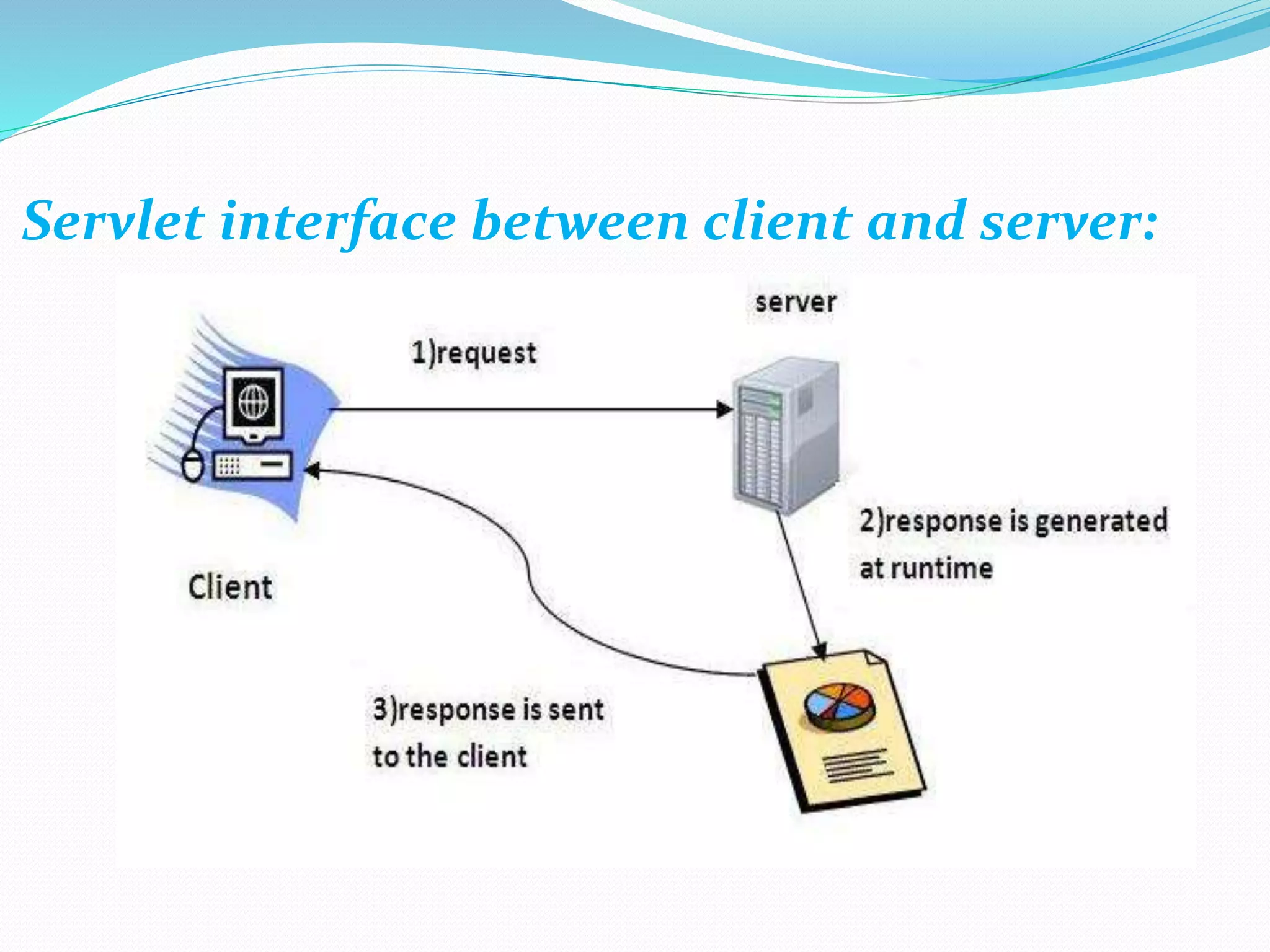
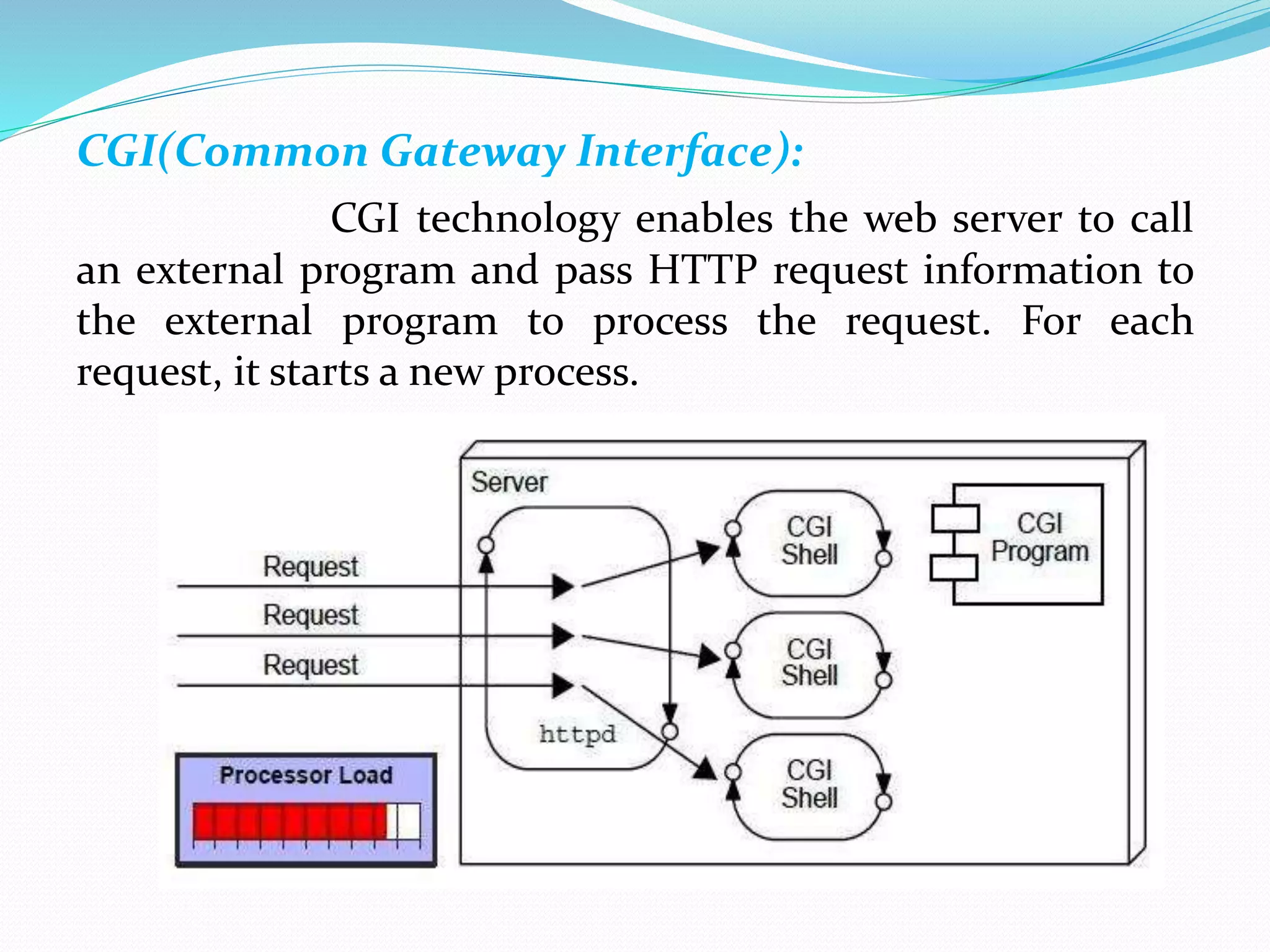
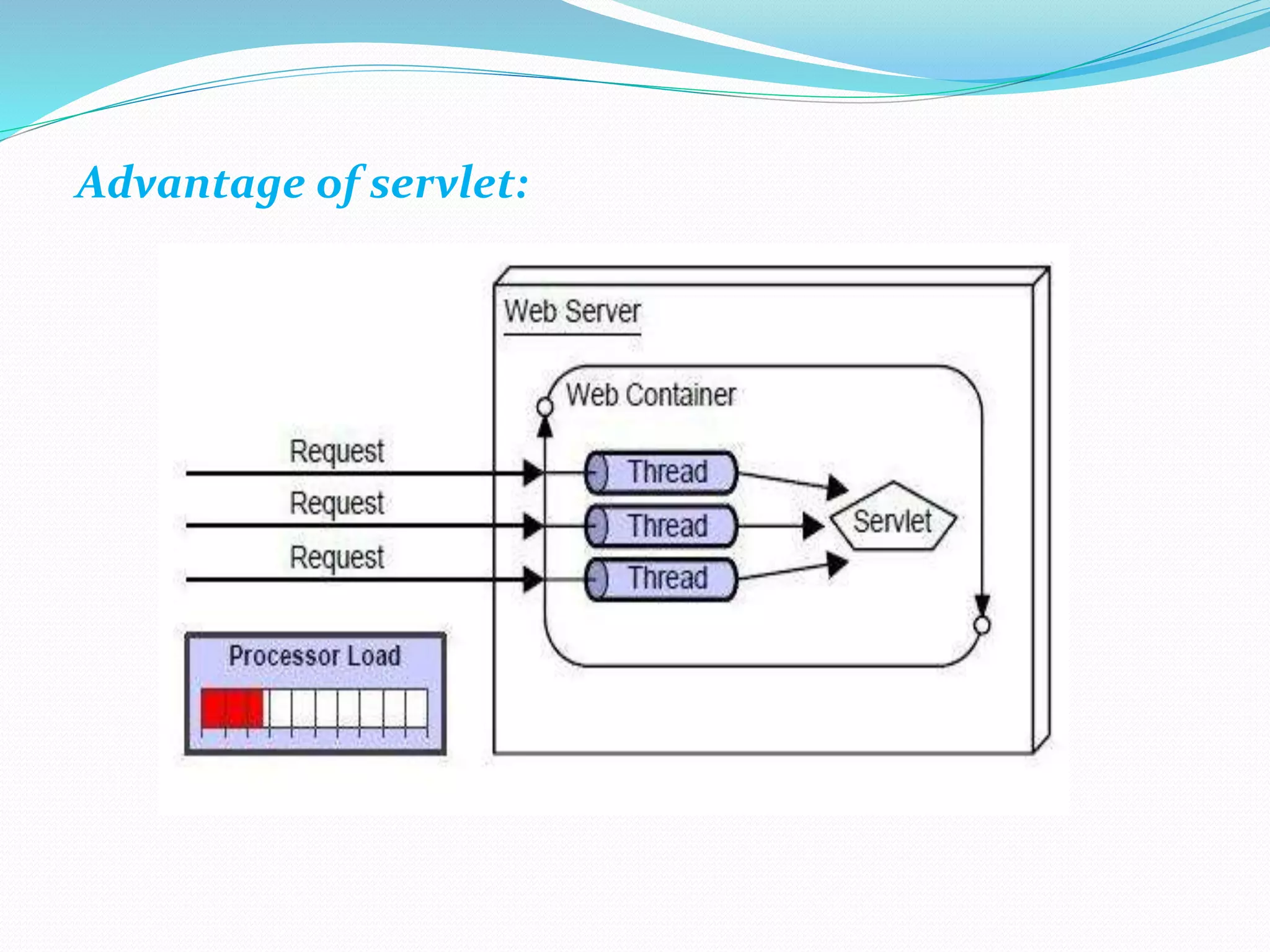
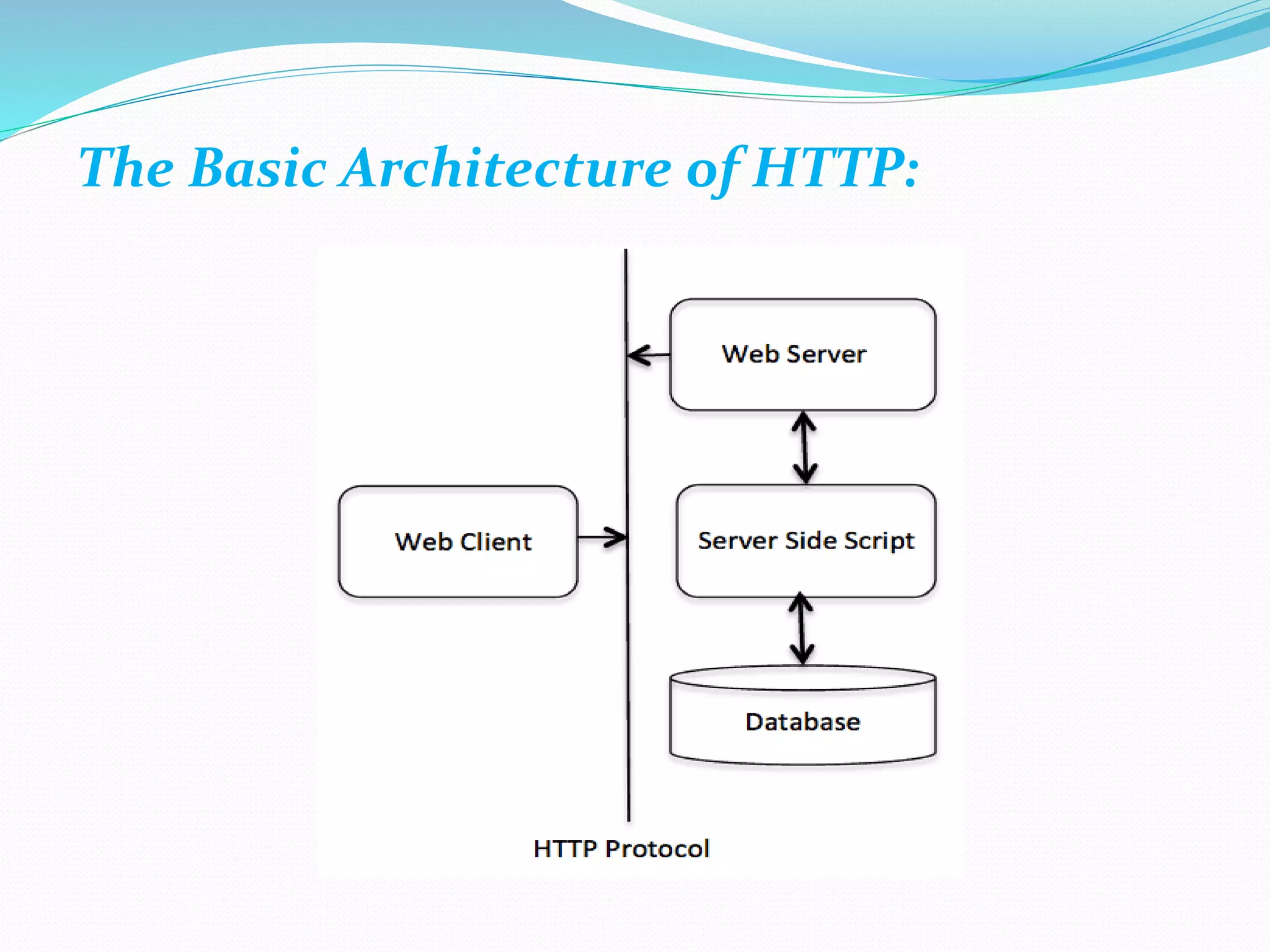
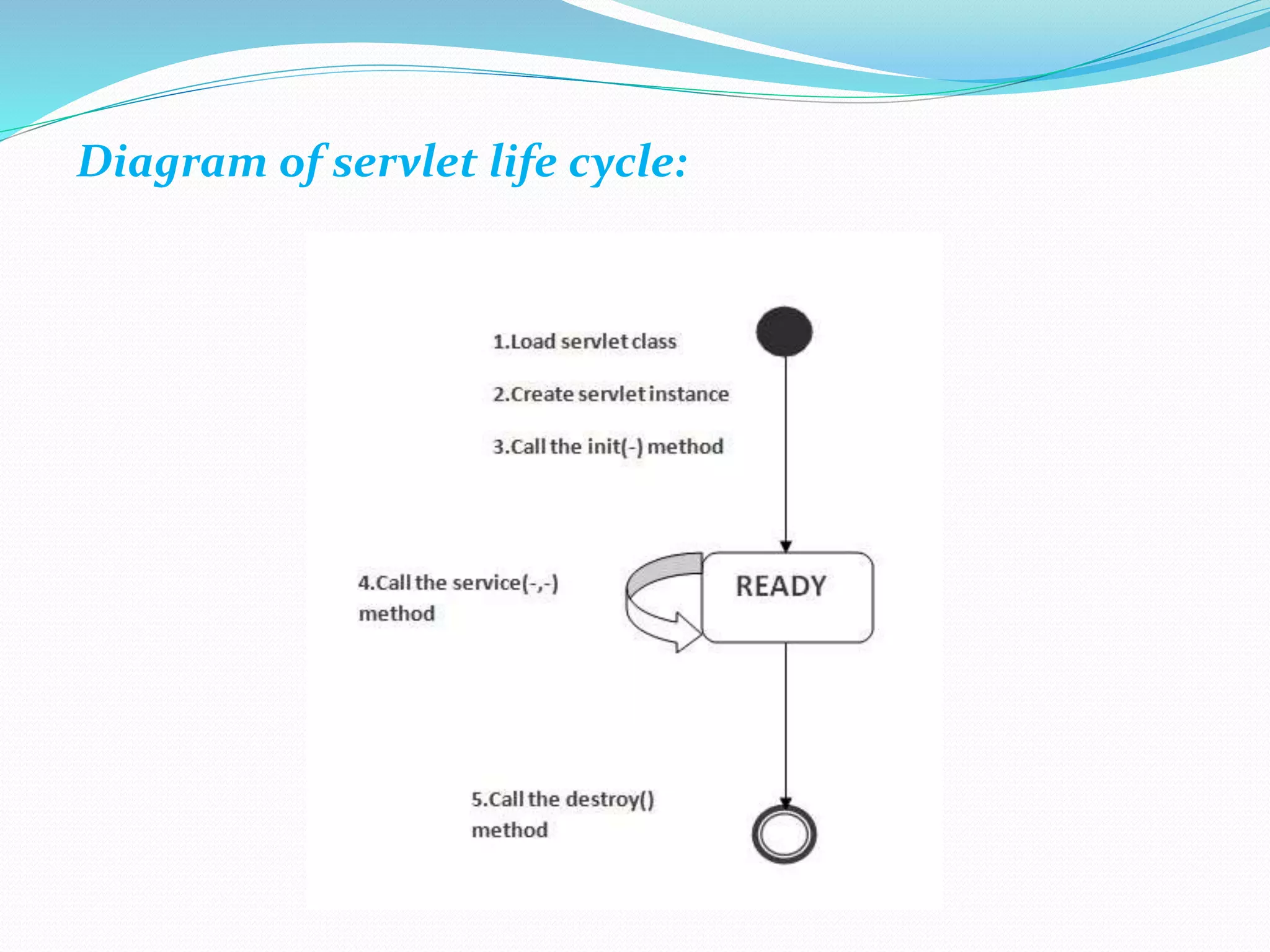
The document provides an overview of Java servlets, explaining their role as a middle layer between web clients and servers, highlighting their advantages over CGI including better performance and security. It discusses the servlet life cycle, the importance of the servlet API, and different classes and interfaces within the javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages. Additionally, it outlines fundamental concepts of websites and the HTTP protocol used for communication between clients and servers.