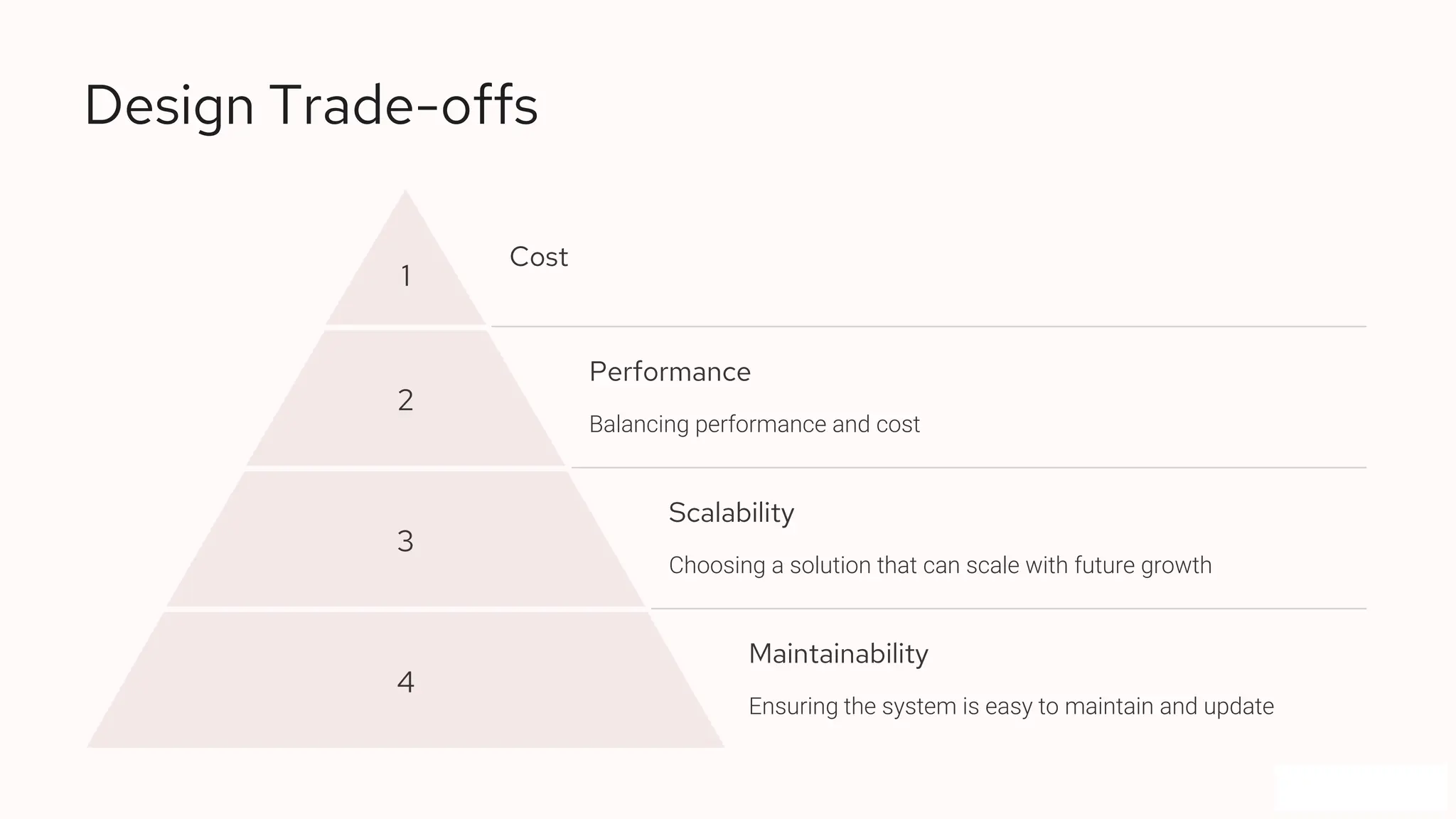
The presentation outlines the process of capturing software requirements and developing a robust system design, covering problem statements, functional and non-functional requirements. It includes details on API design, data representation, database structures, security measures, and design trade-offs. Next steps involve documentation, prototyping, and incorporating feedback for refinement.