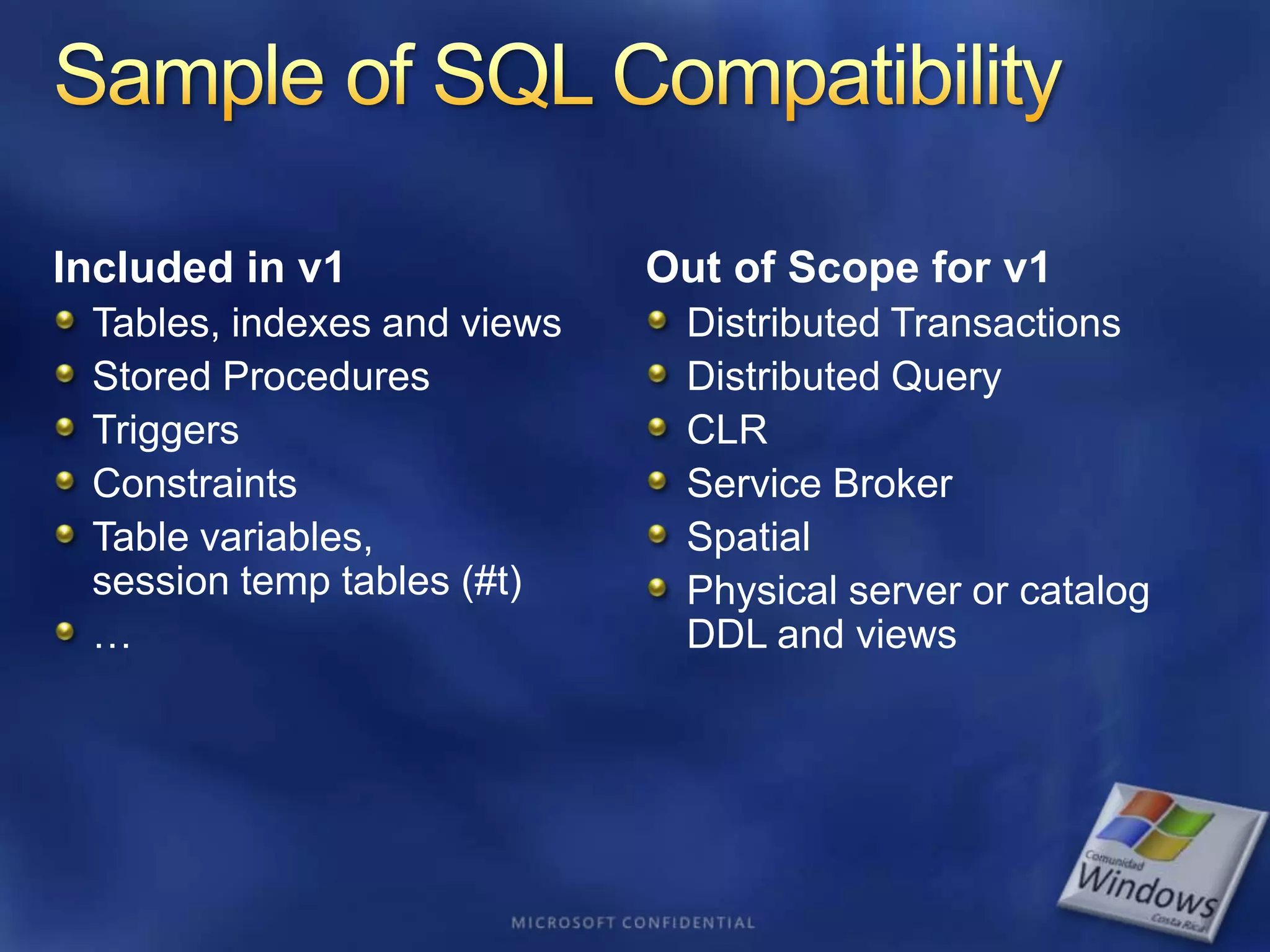
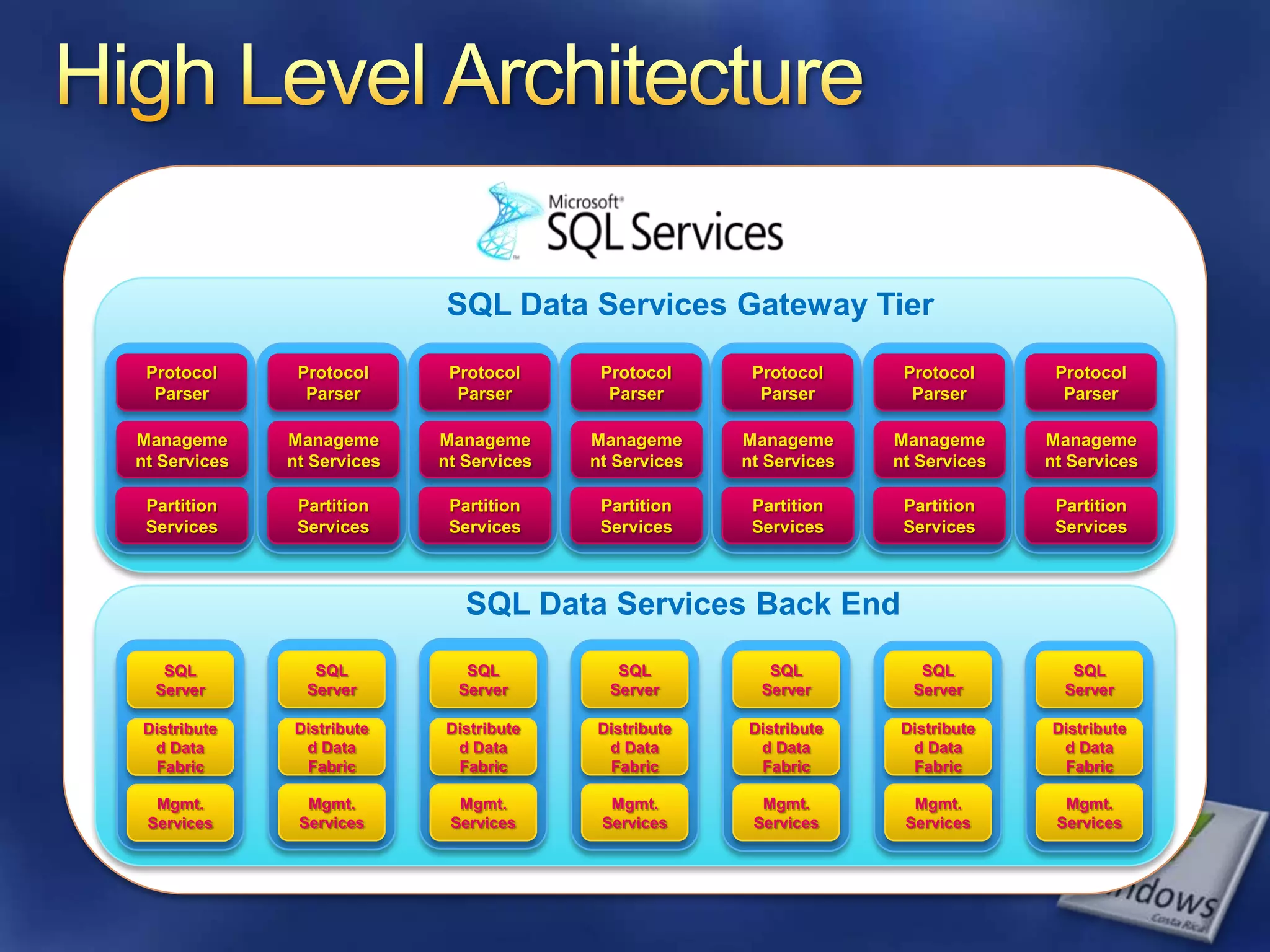
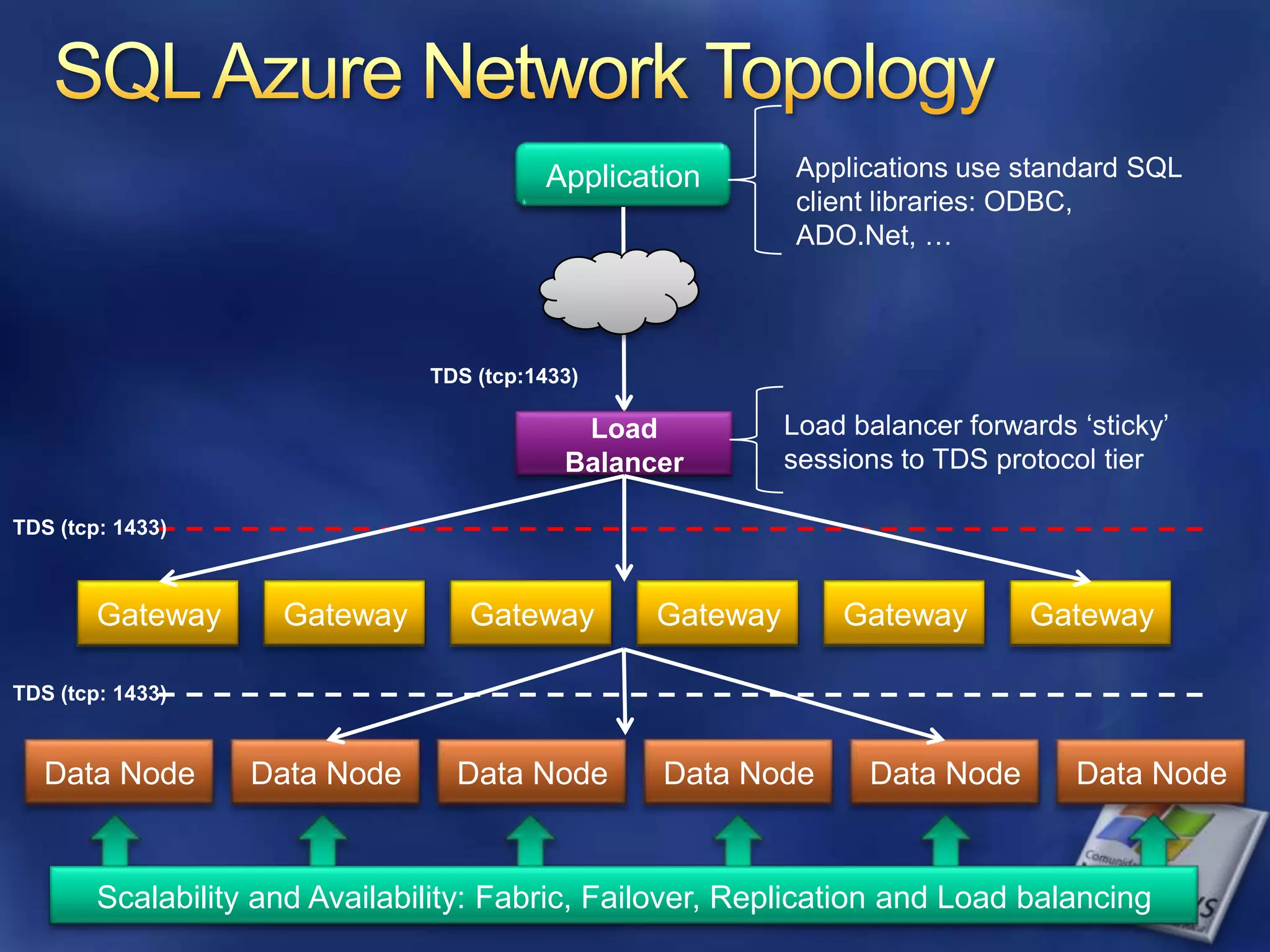
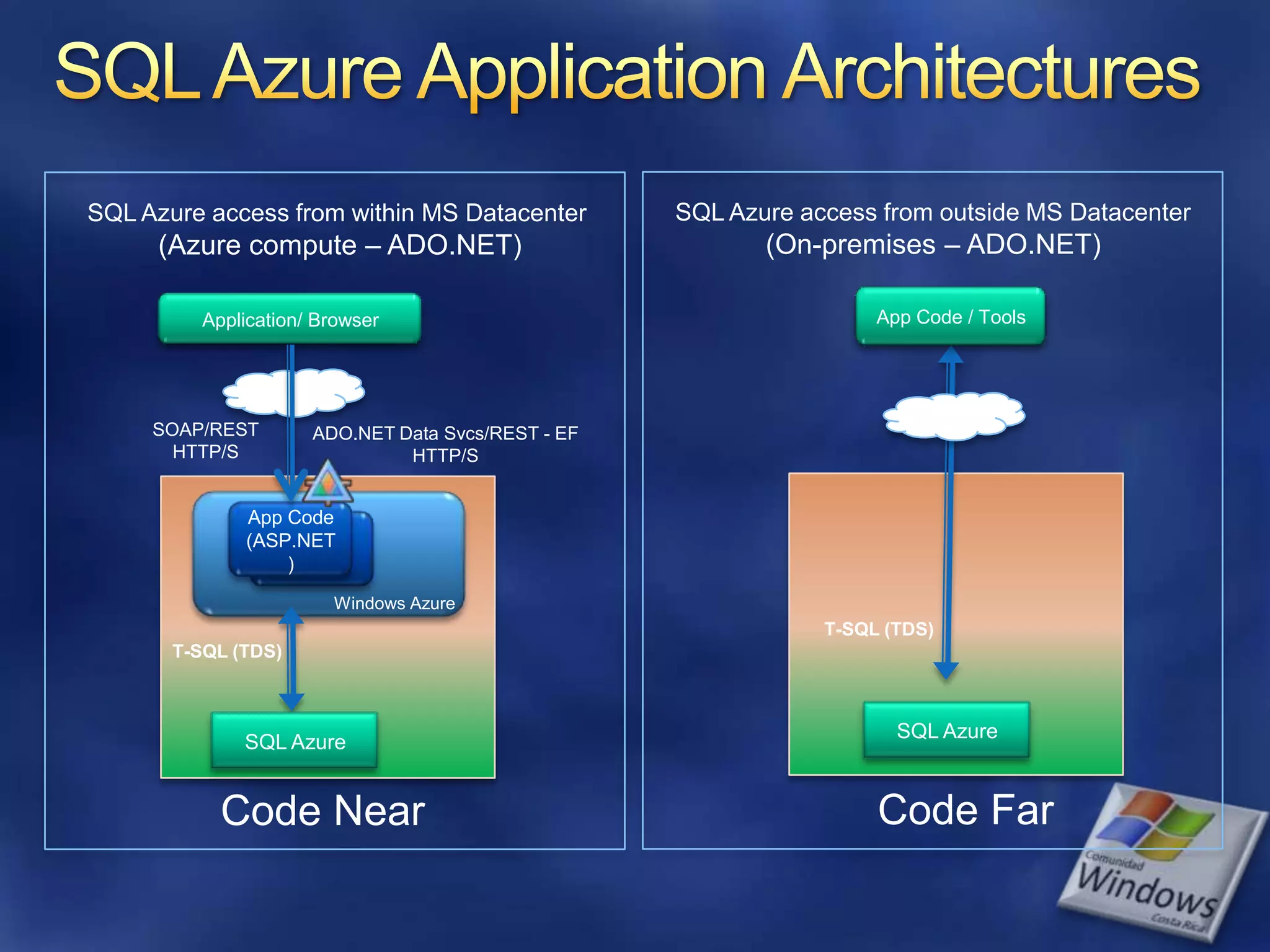
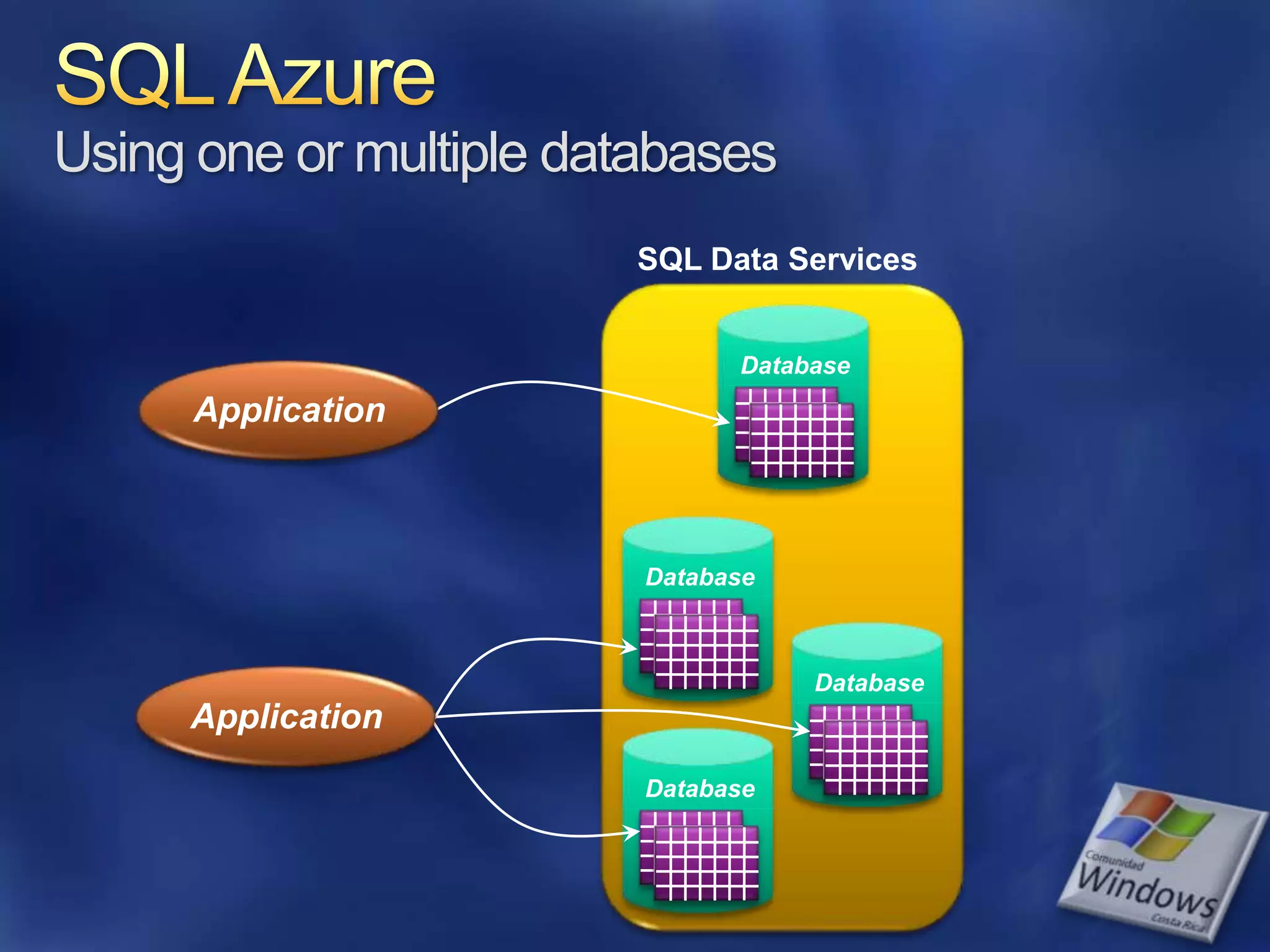
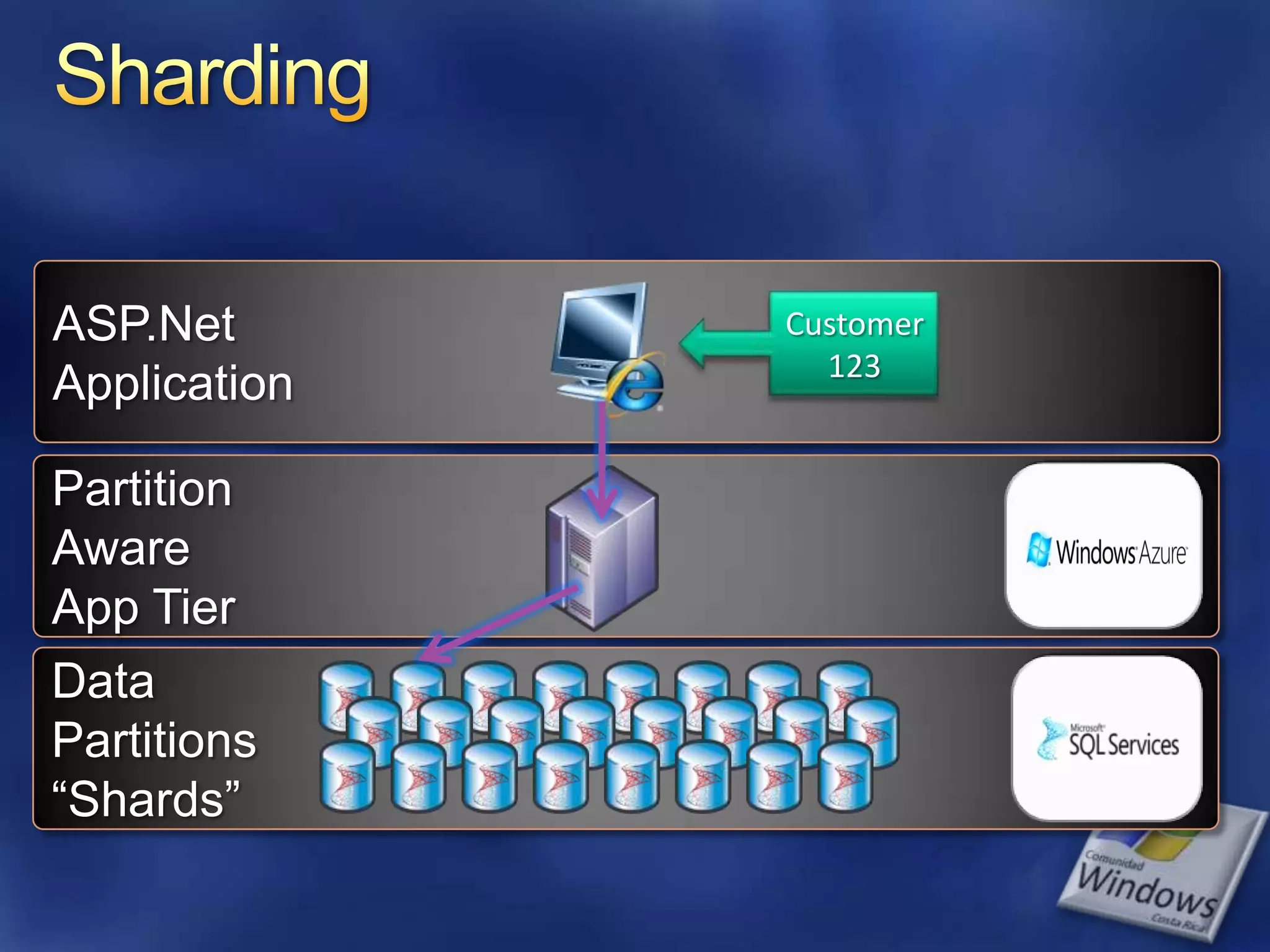
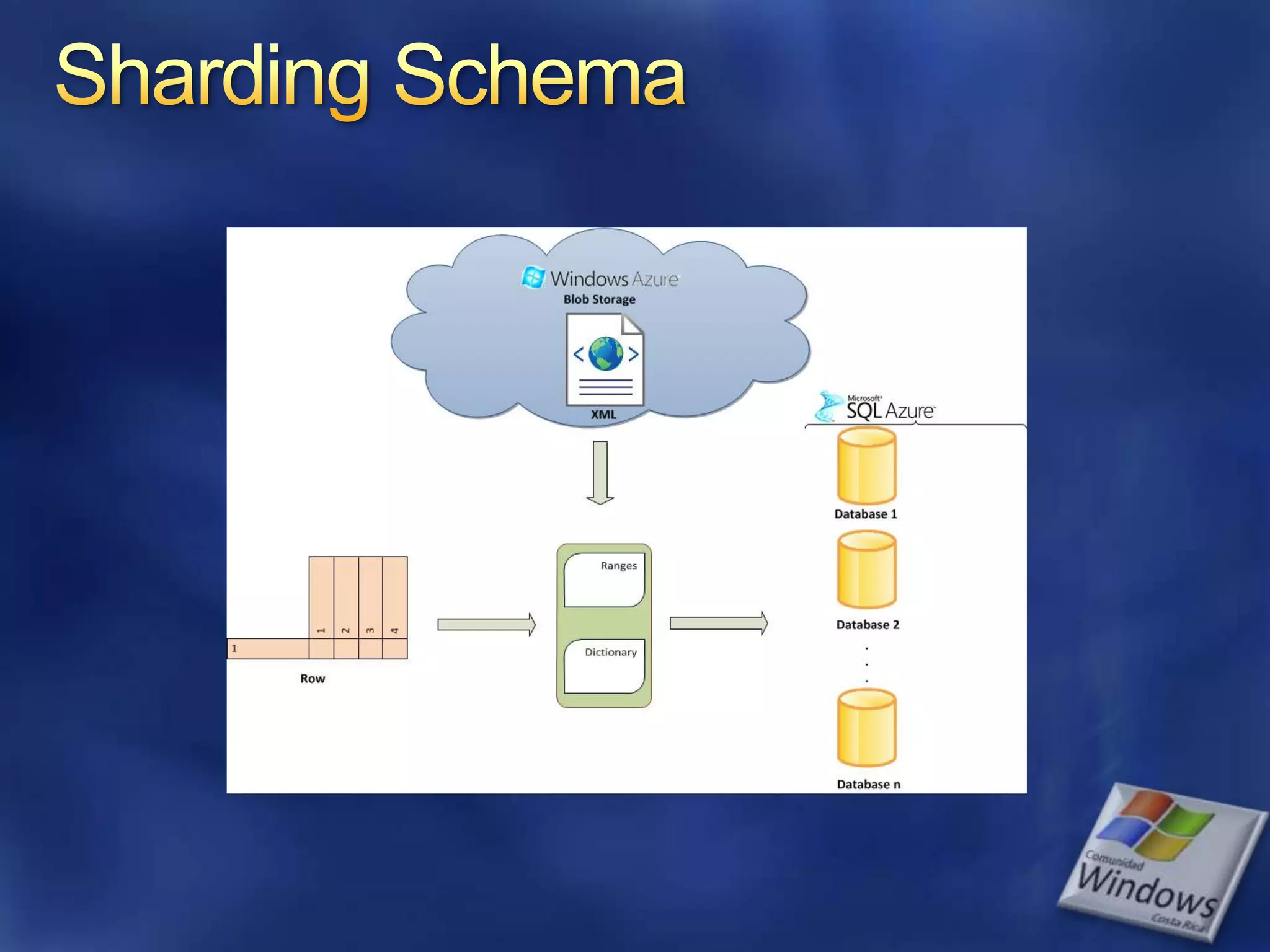
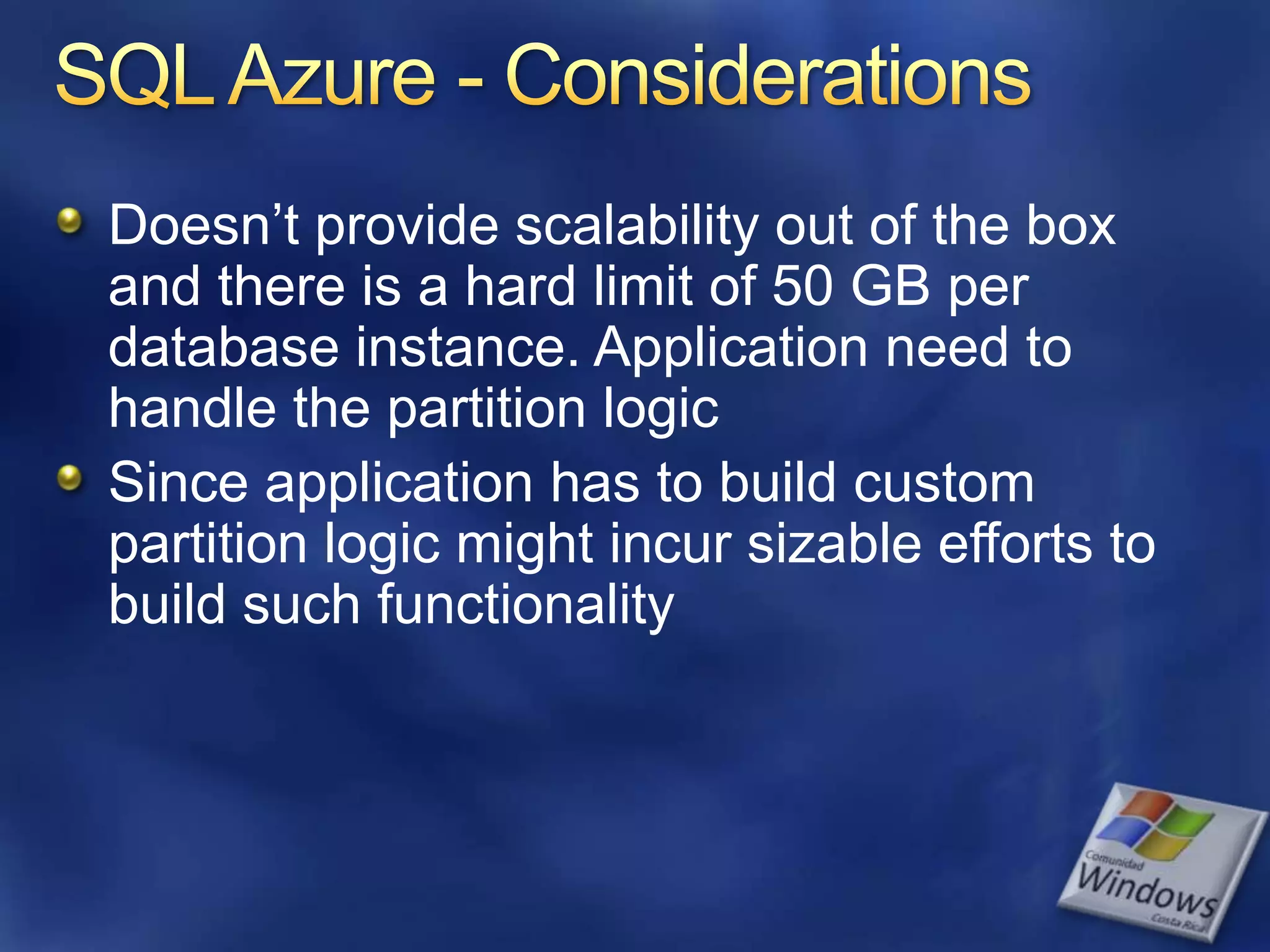
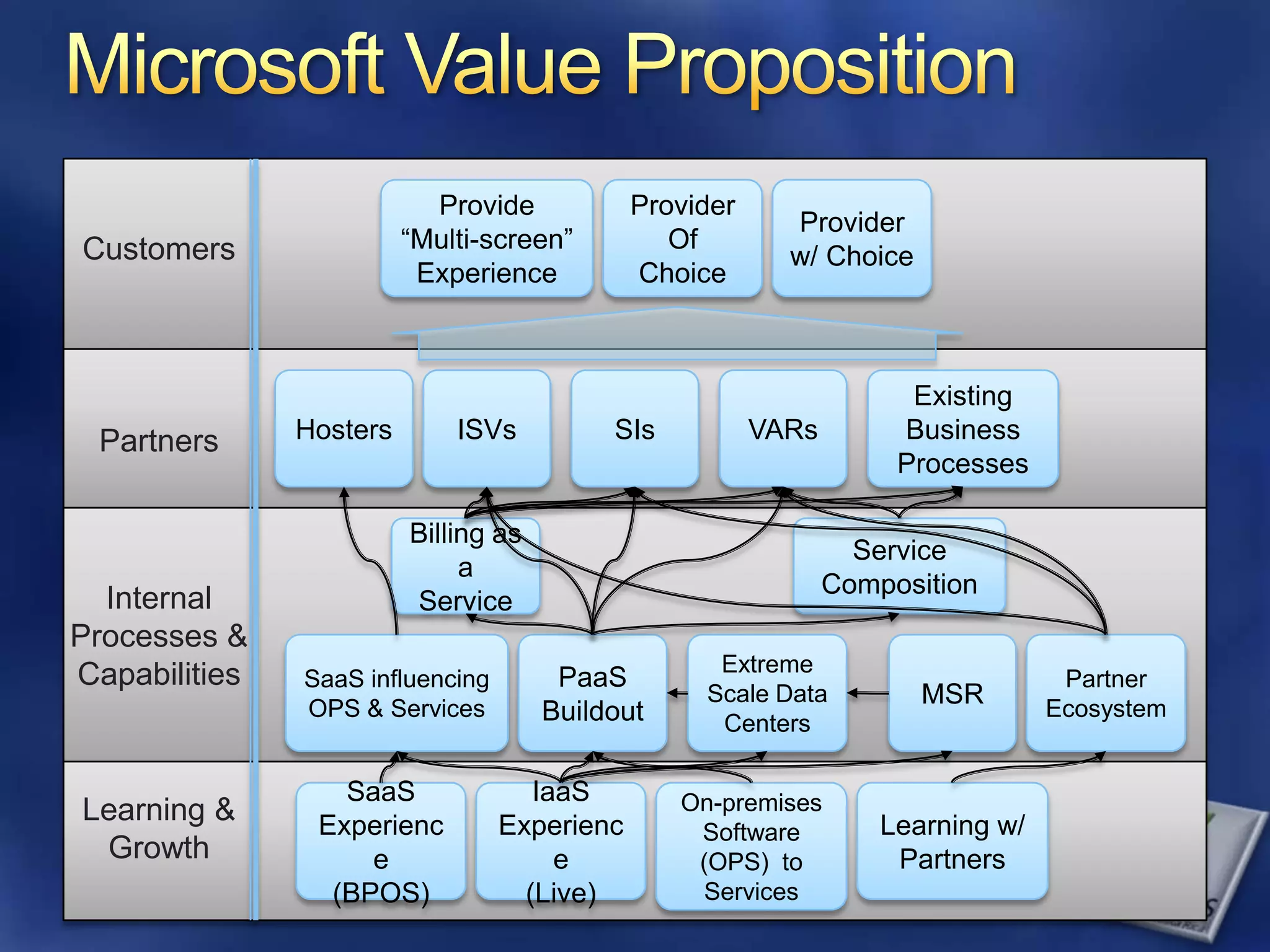
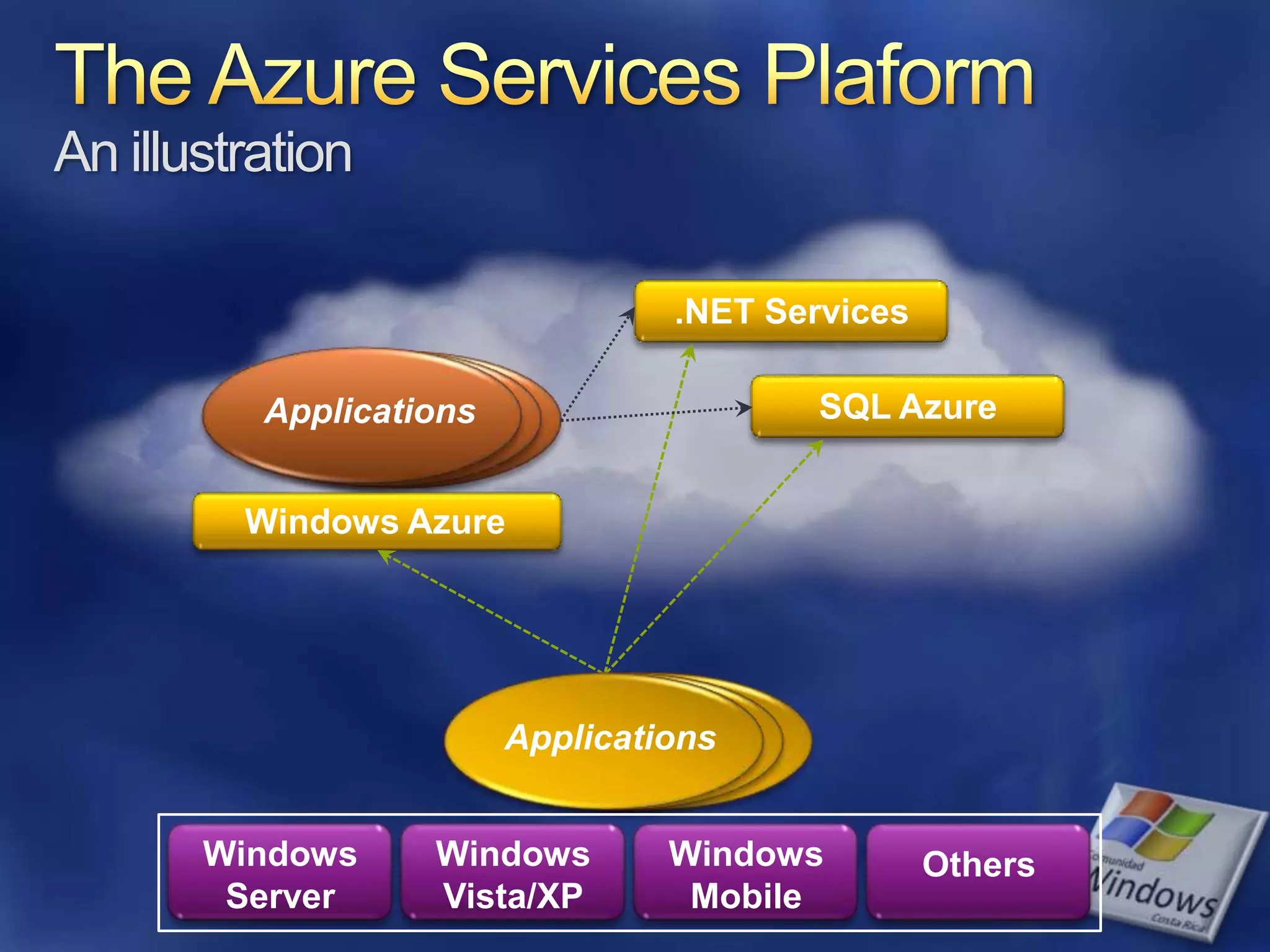
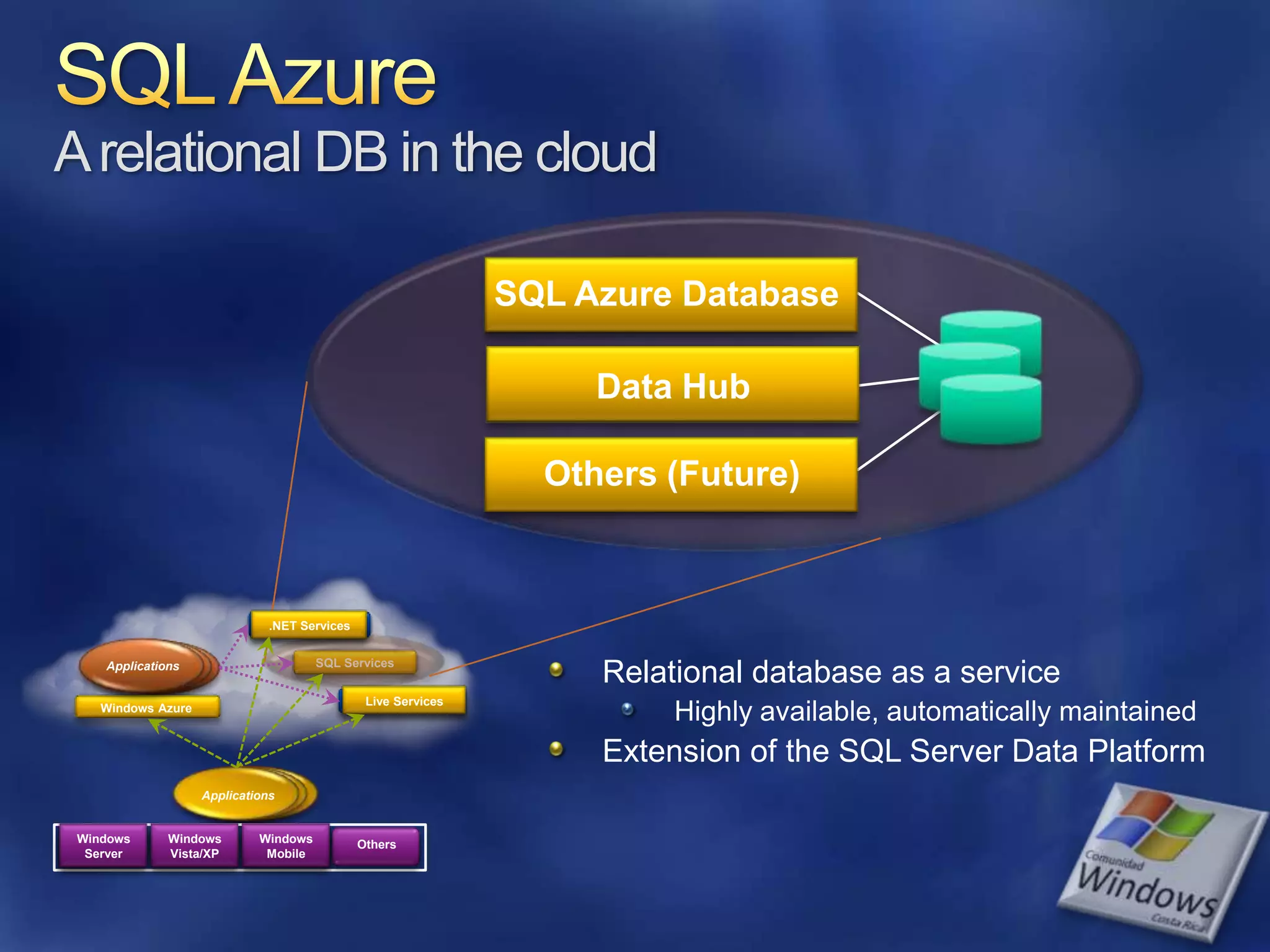
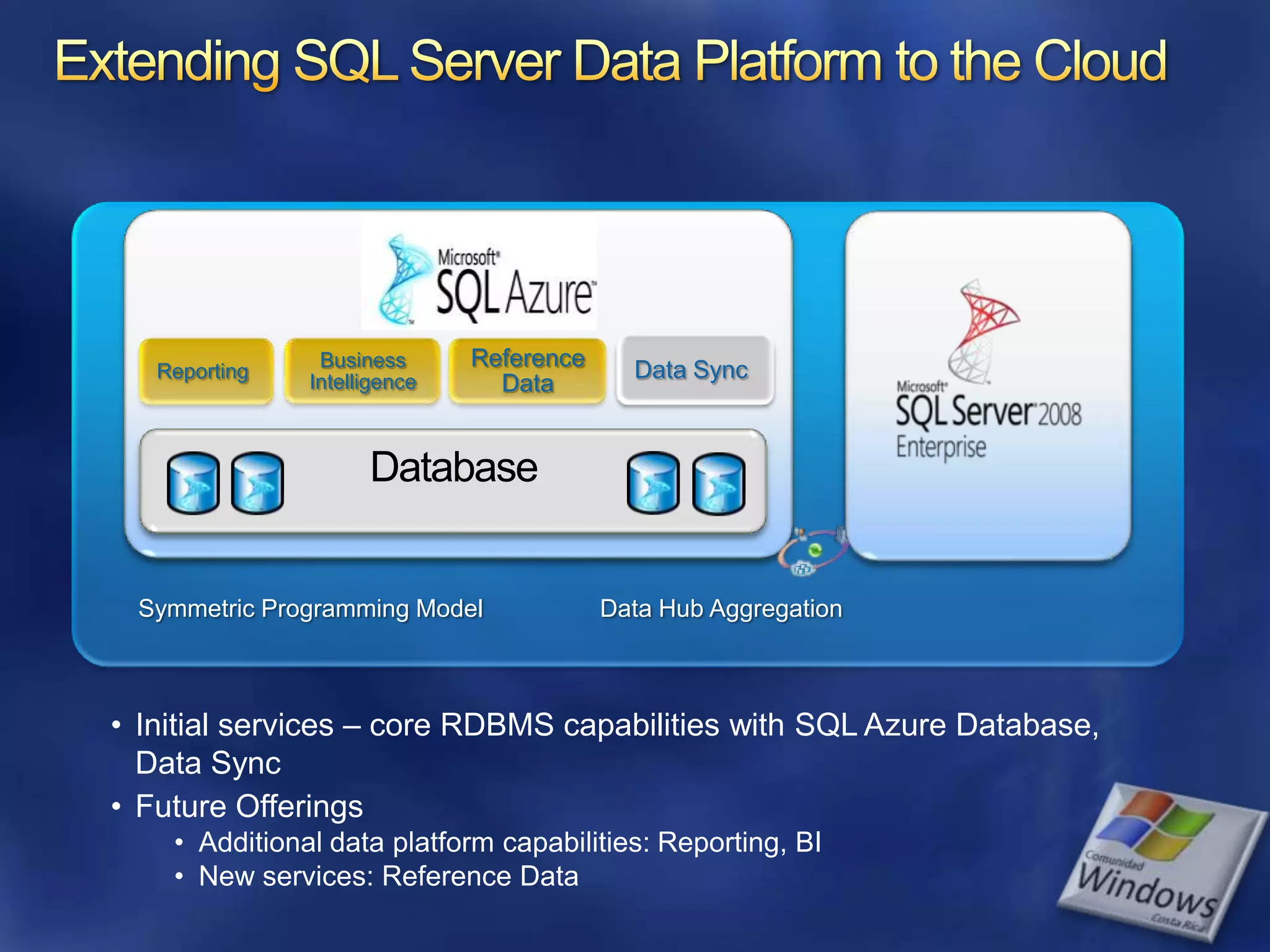
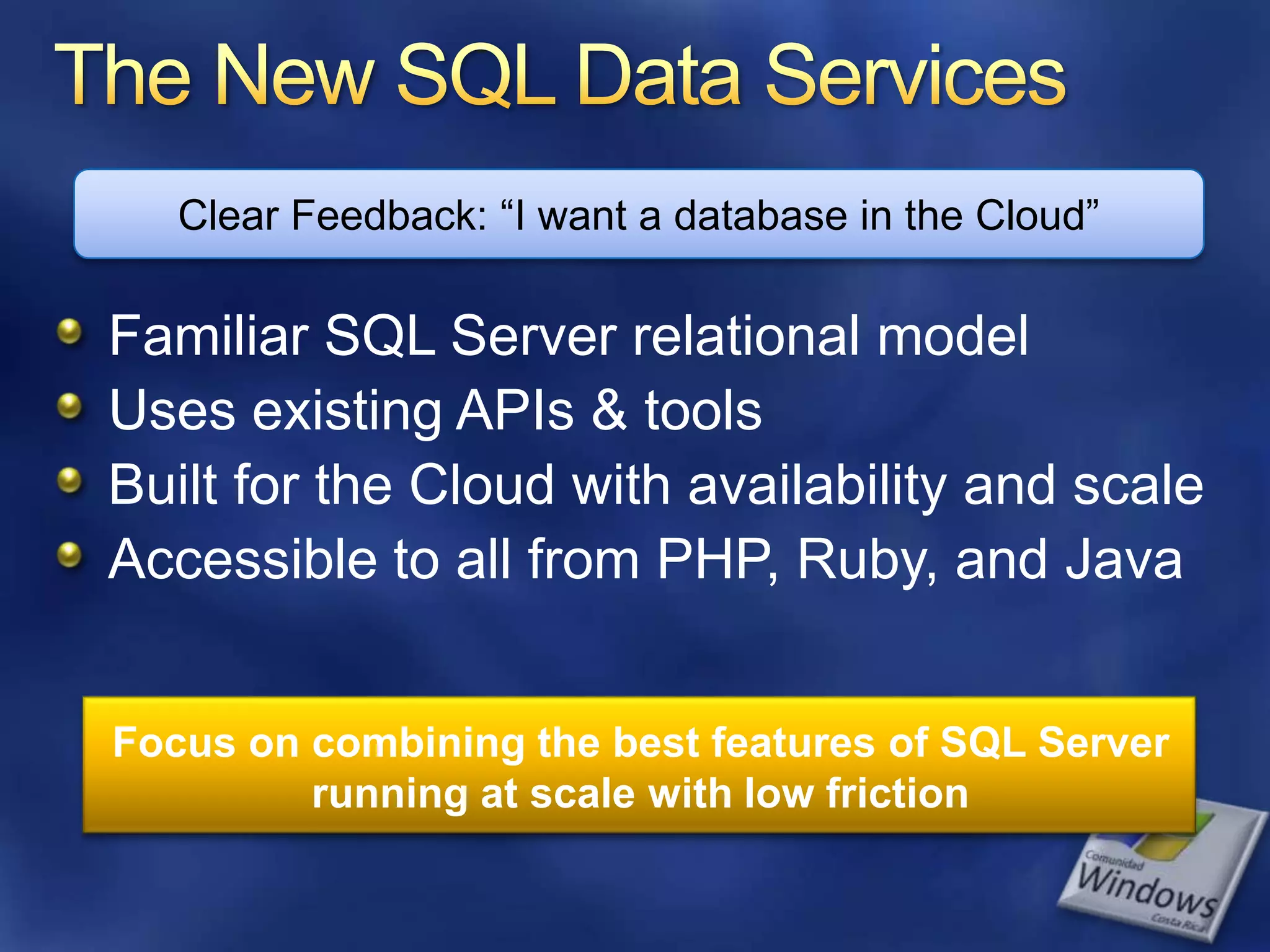
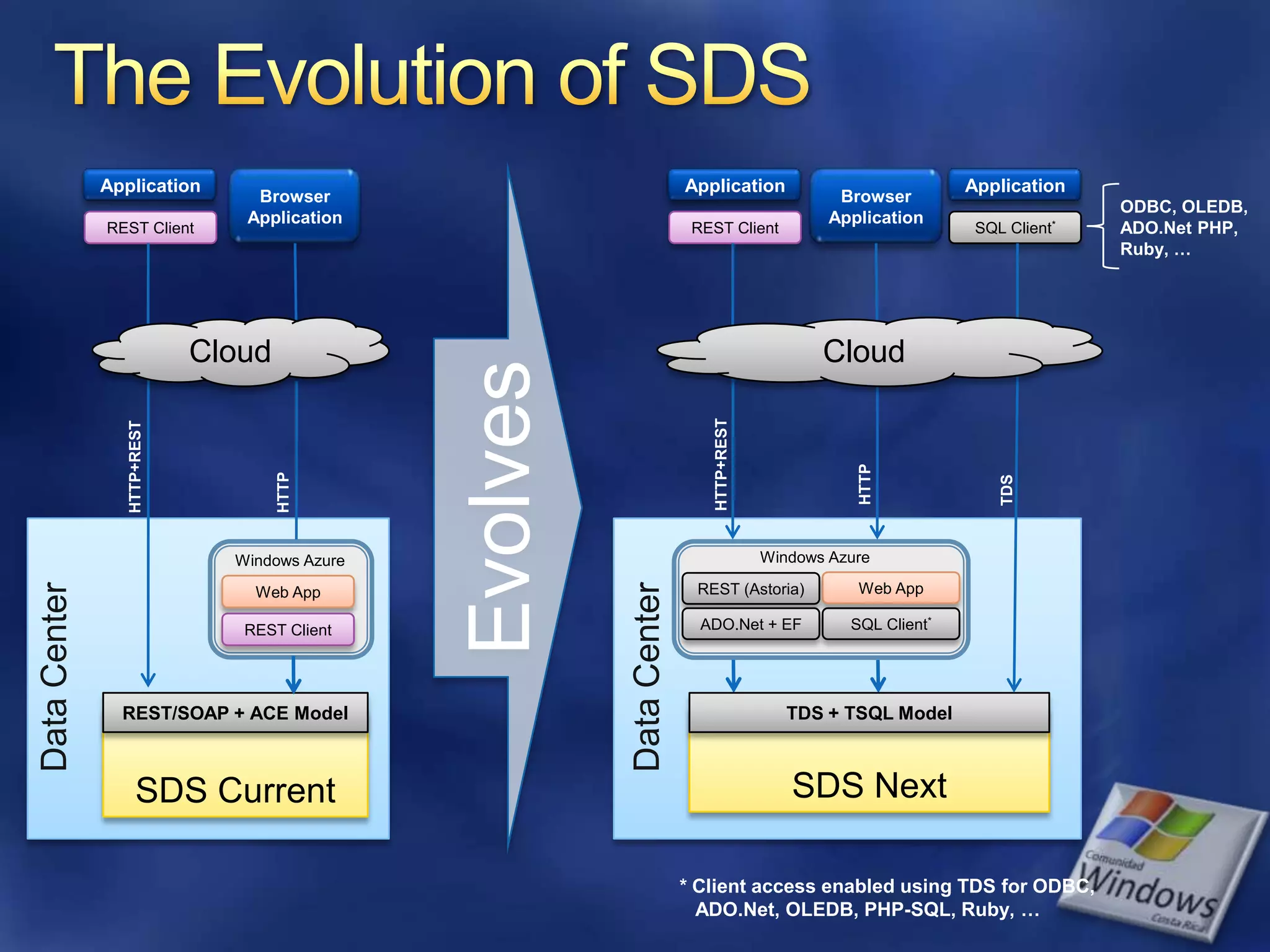
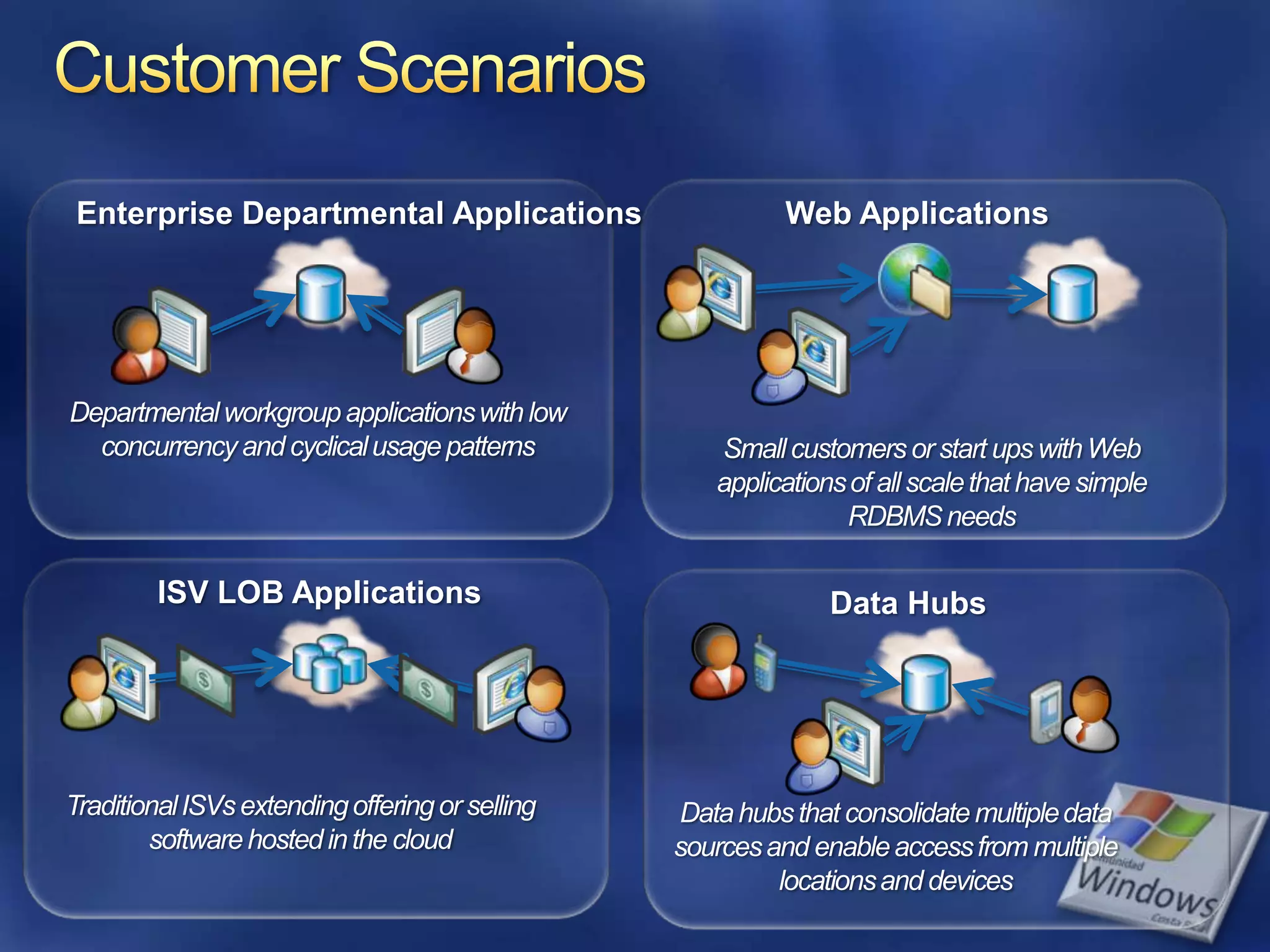
The document provides an overview of SQL Azure, a relational database service available on the Microsoft Azure platform. Key points include: - SQL Azure allows users to build applications that use a relational database in the cloud without having to manage infrastructure. - It is based on SQL Server and provides a familiar programming model, but is designed for the cloud with high availability and scalability. - The service has limitations on database size and does not provide built-in sharding capabilities, so applications need to implement custom partitioning logic for large datasets. - Future improvements may address limitations and open up new scenarios and opportunities through integration with other Azure services. SQL Azure is part of Microsoft's broader strategy around cloud-















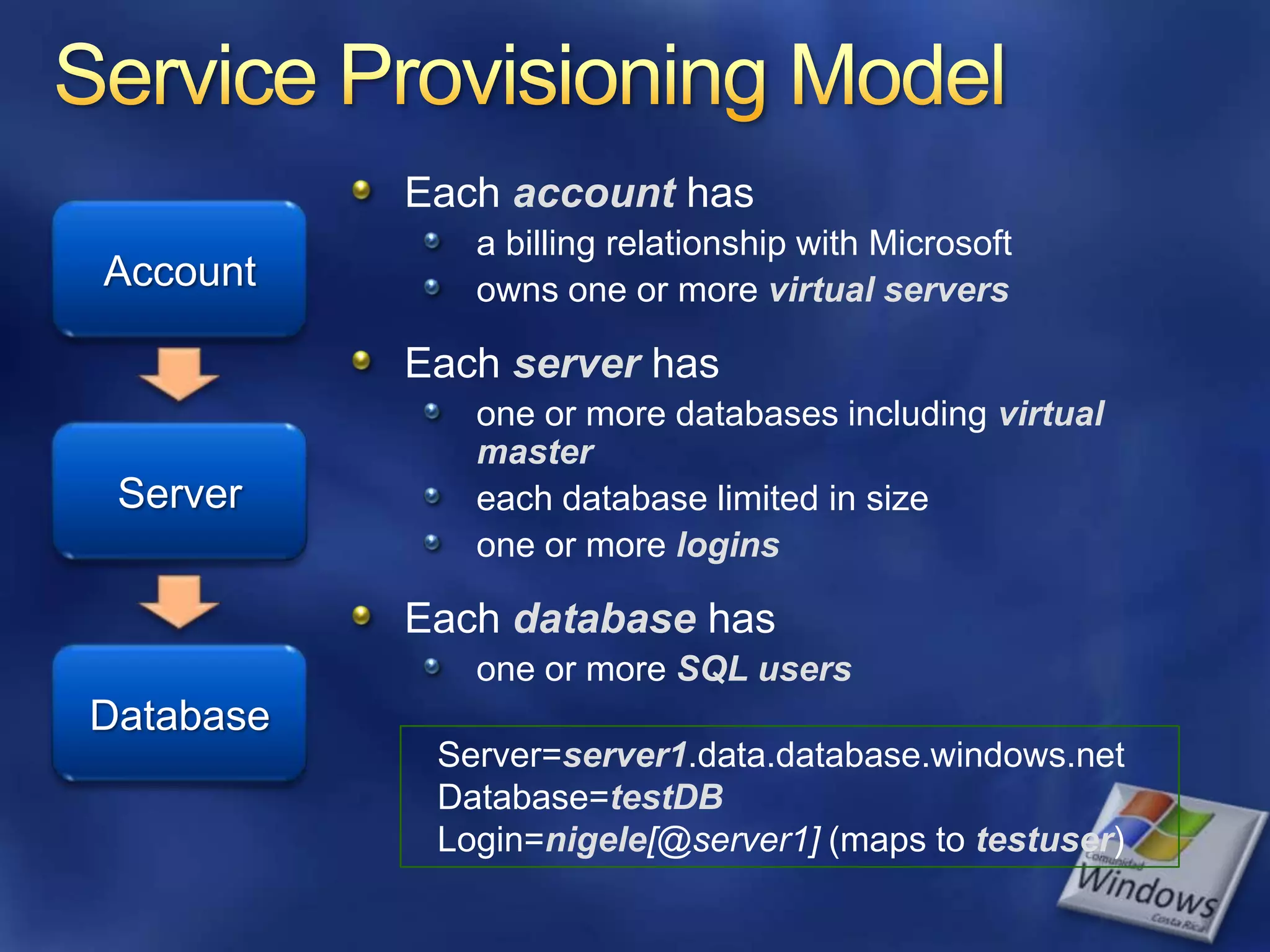
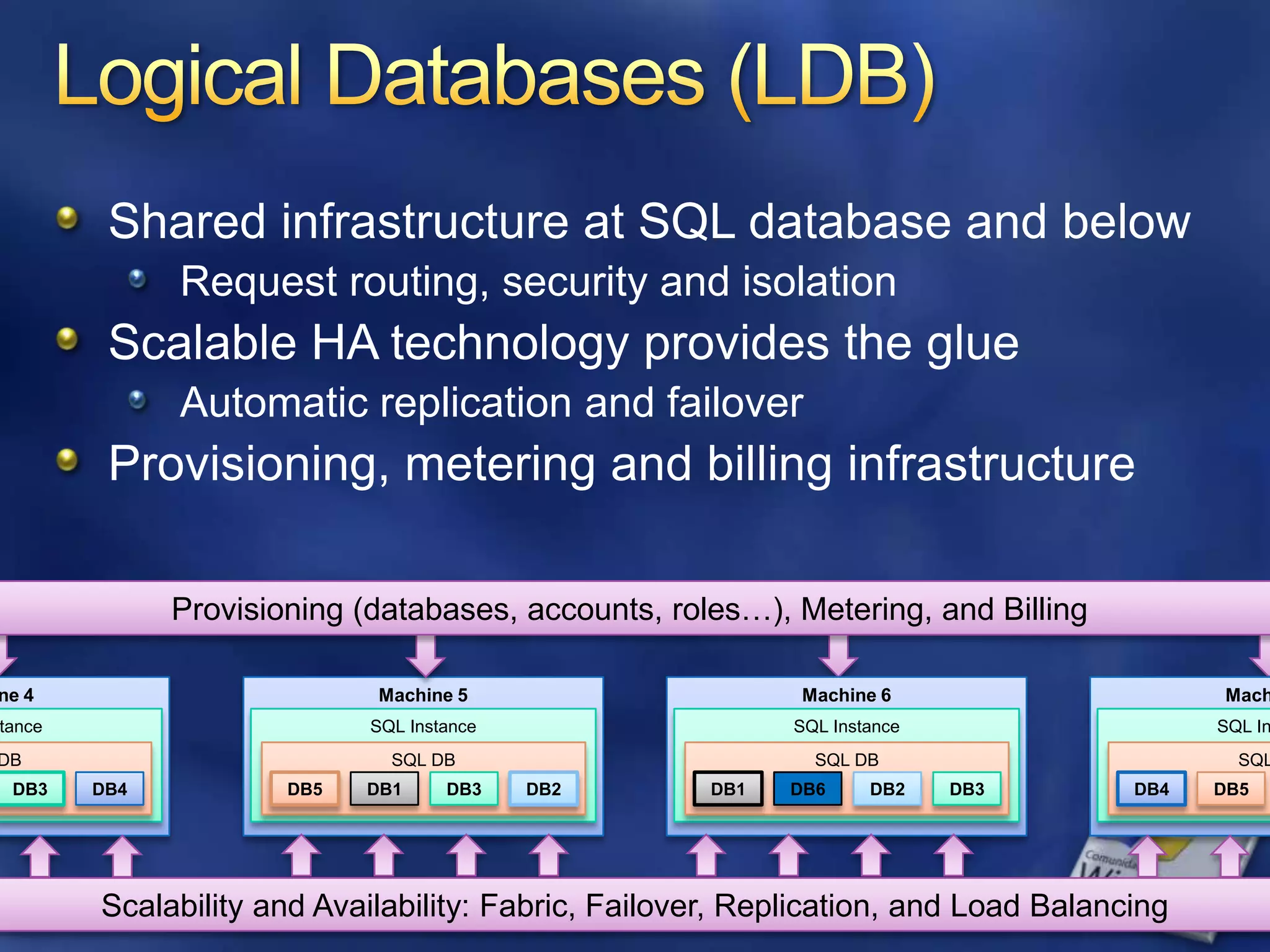
![Service Provisioning ModelEach account has a billing relationship with Microsoftowns one or more virtual serversEach server has one or more databases including virtual mastereach database limited in size one or more loginsEach database has one or more SQL usersAccountServerDatabaseServer=server1.data.database.windows.netDatabase=testDBLogin=nigele[@server1] (maps to testuser)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmsql01ppt2-100507102001-phpapp01/75/SQL-Azure-the-database-in-the-cloud-25-2048.jpg)