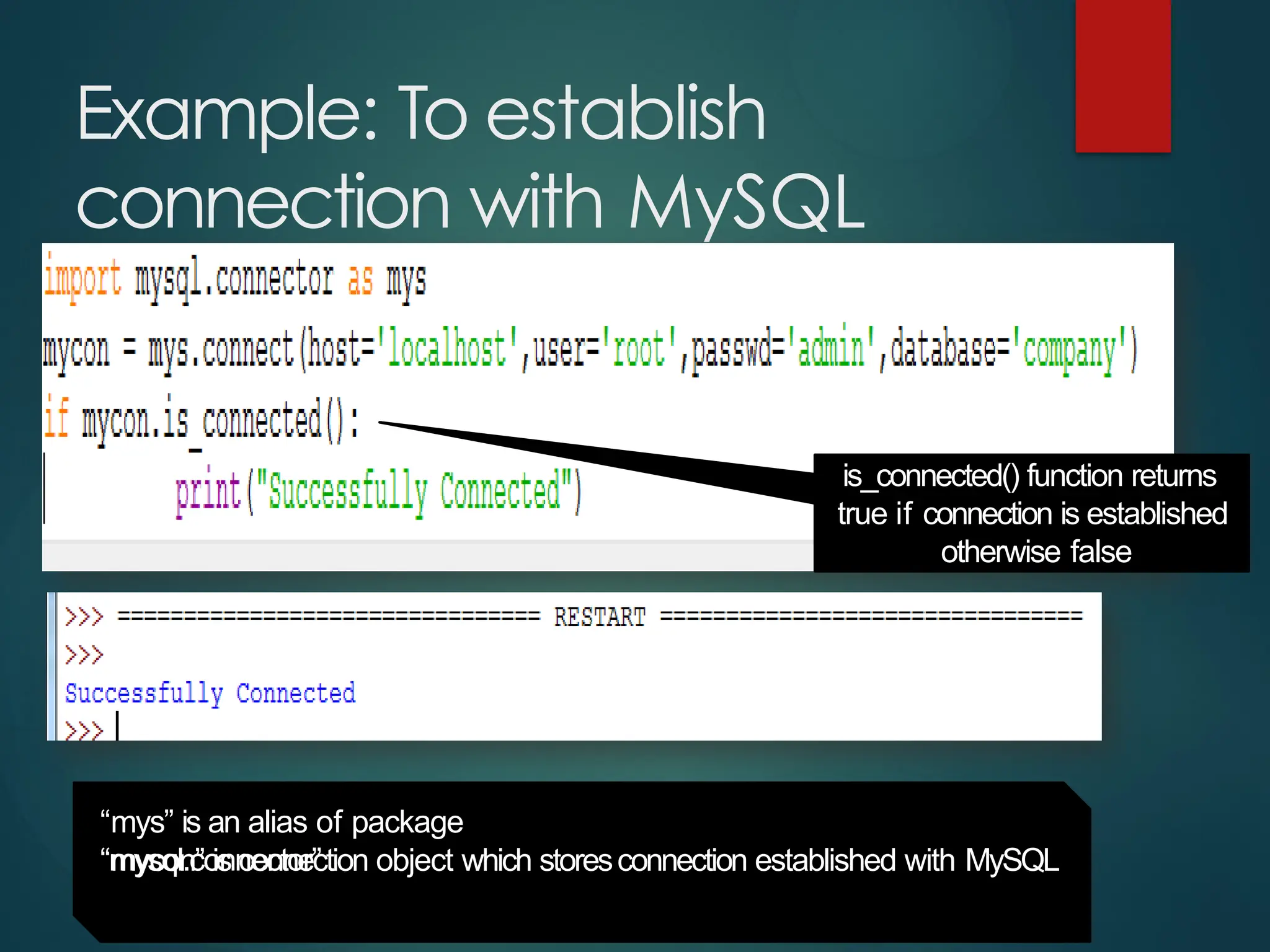
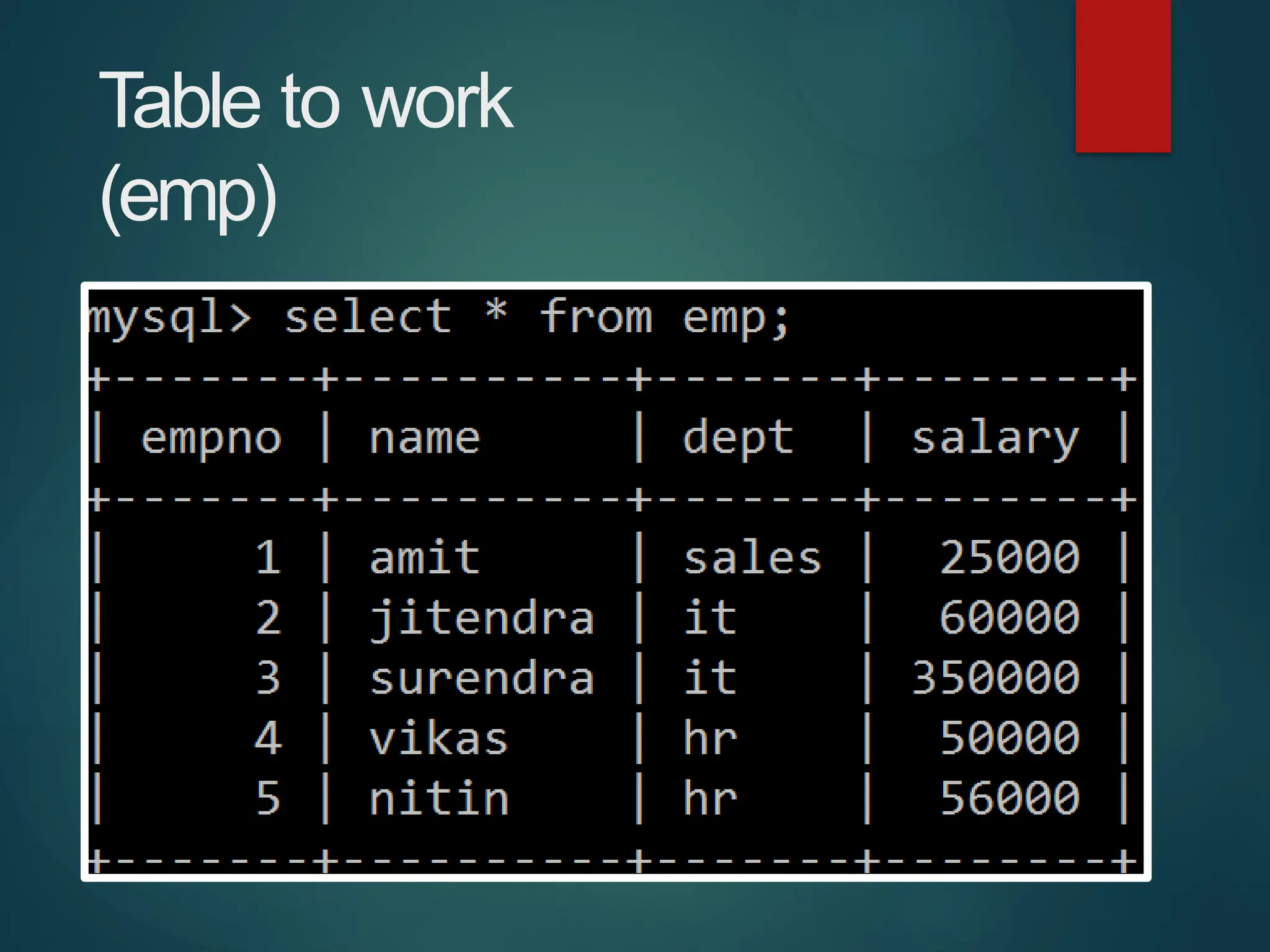
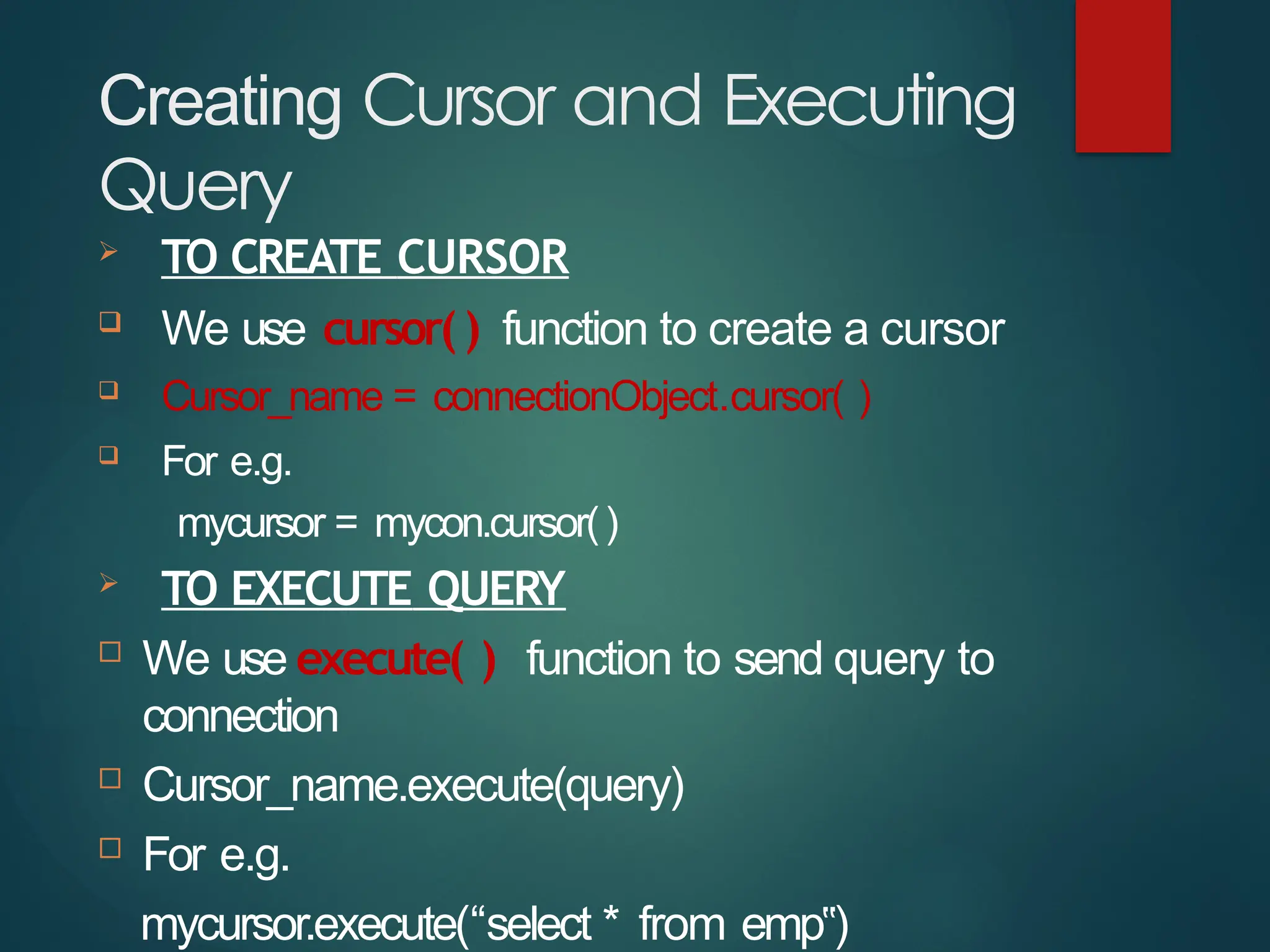
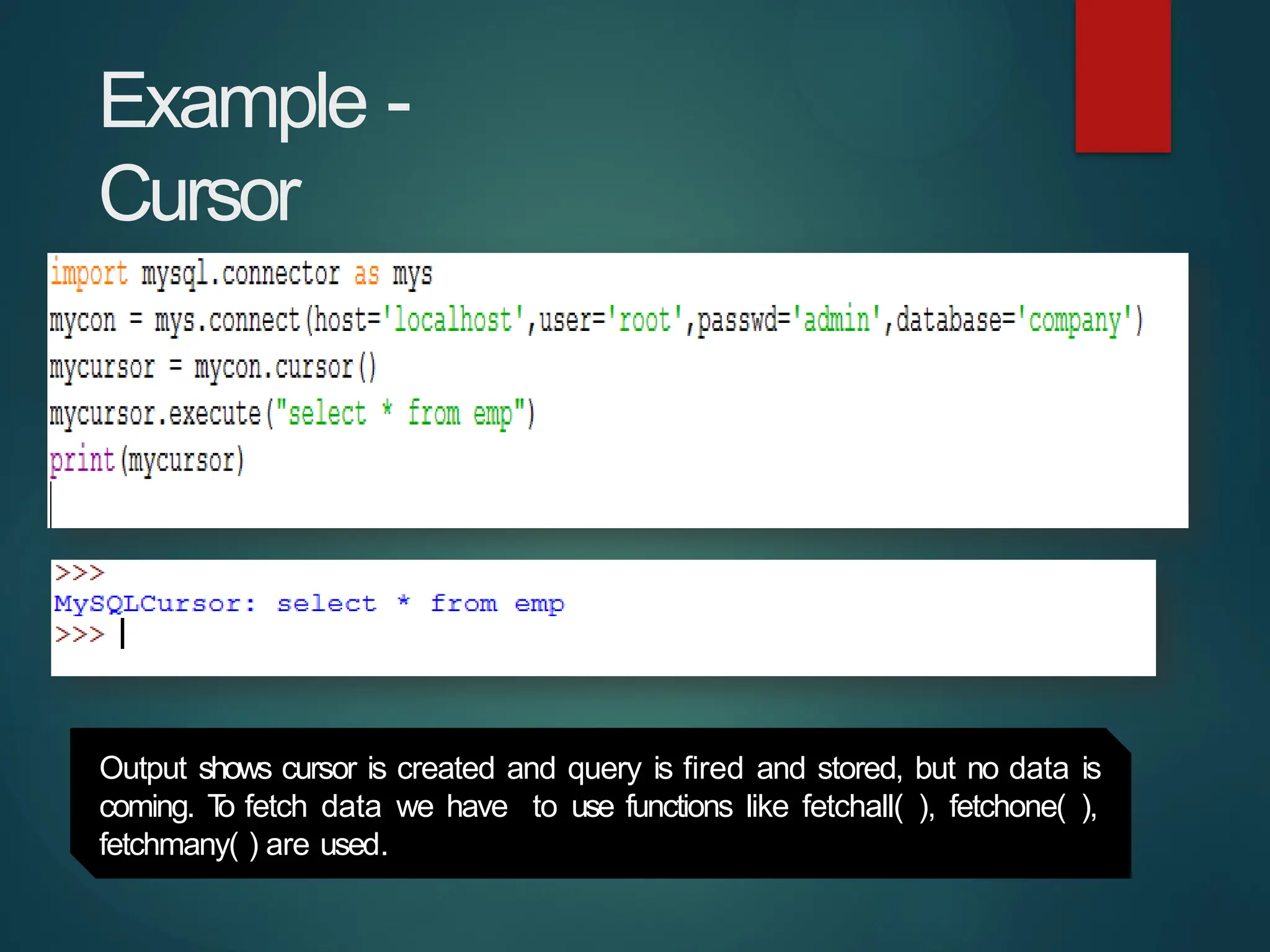
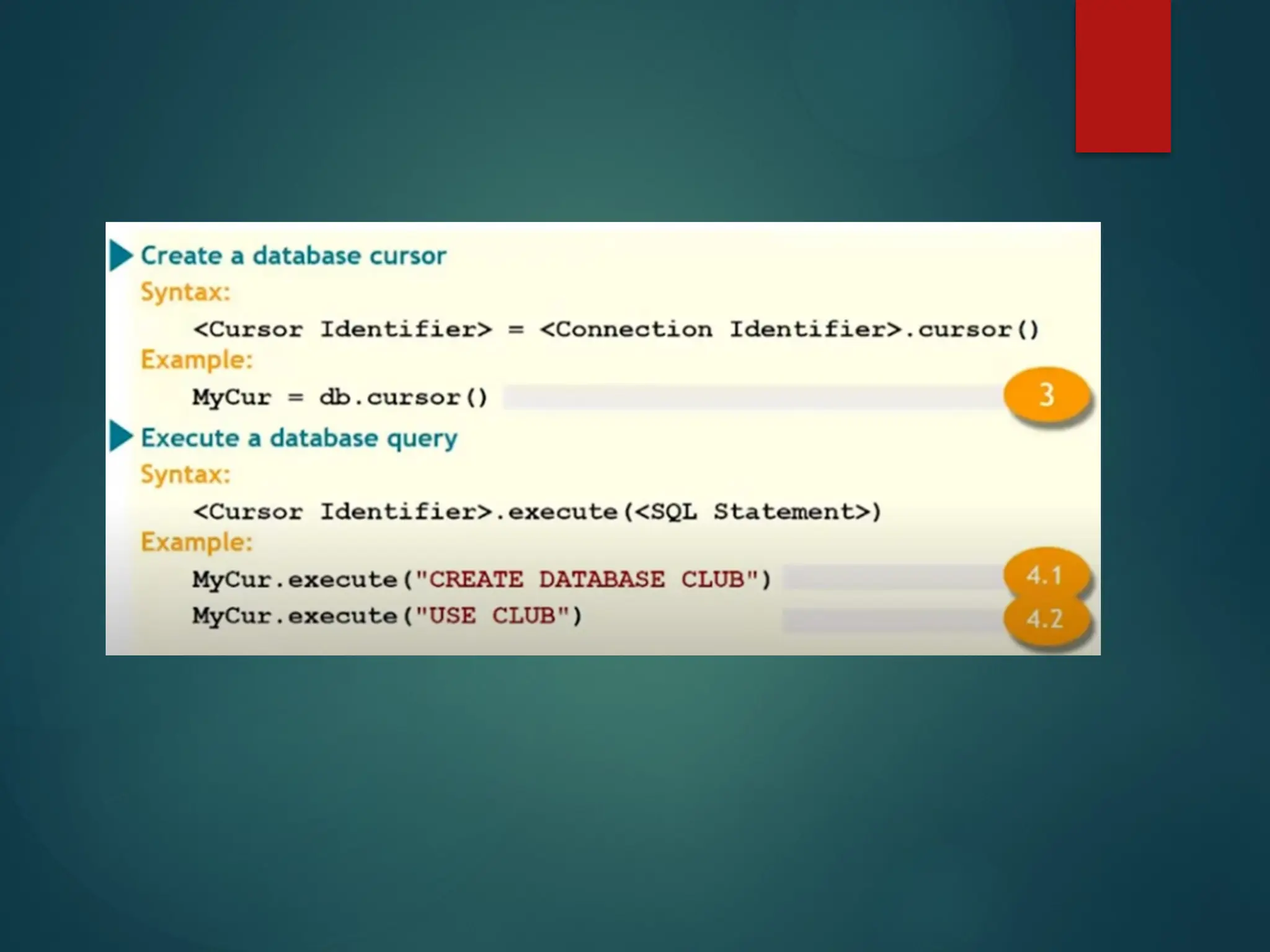
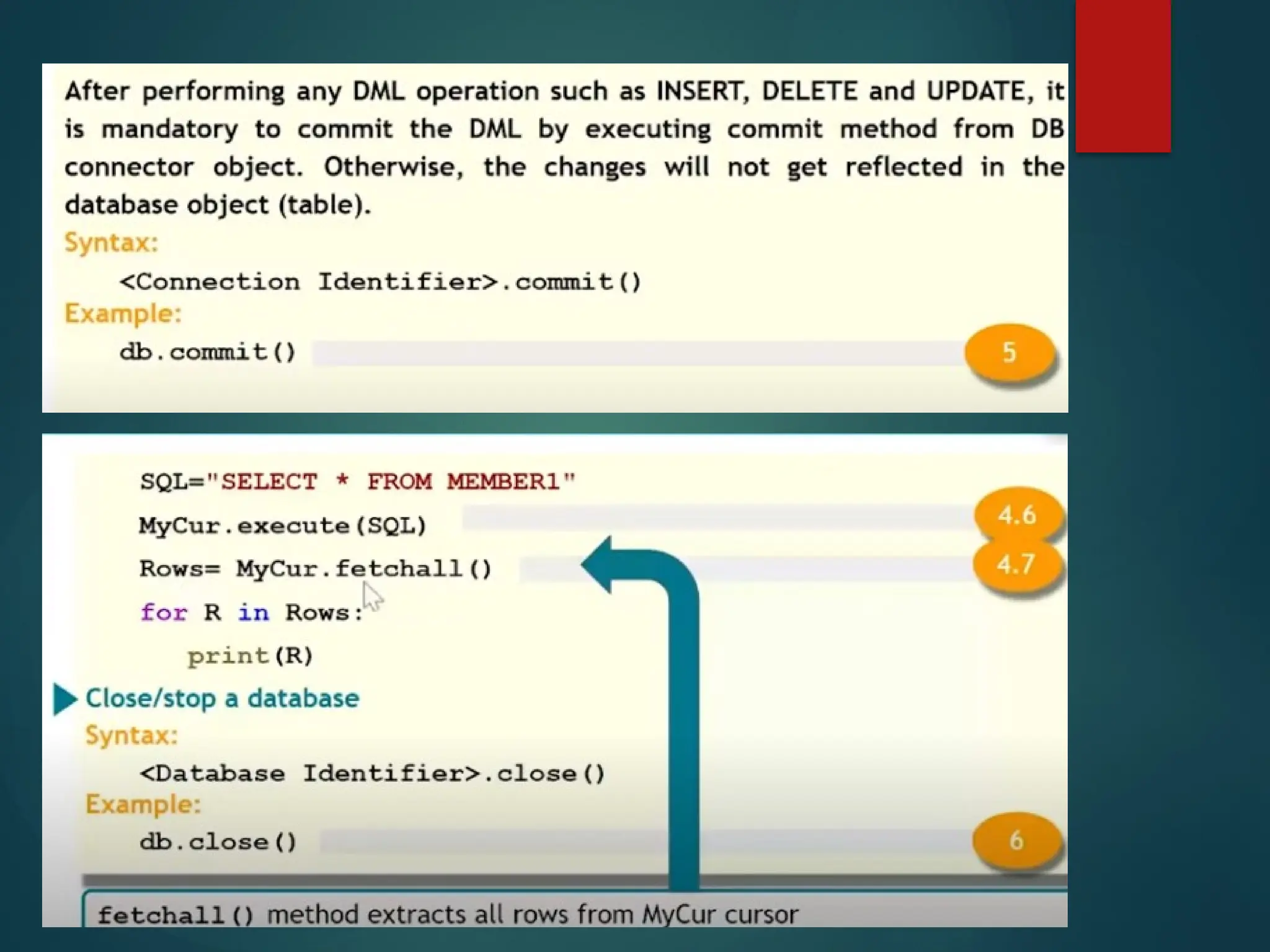
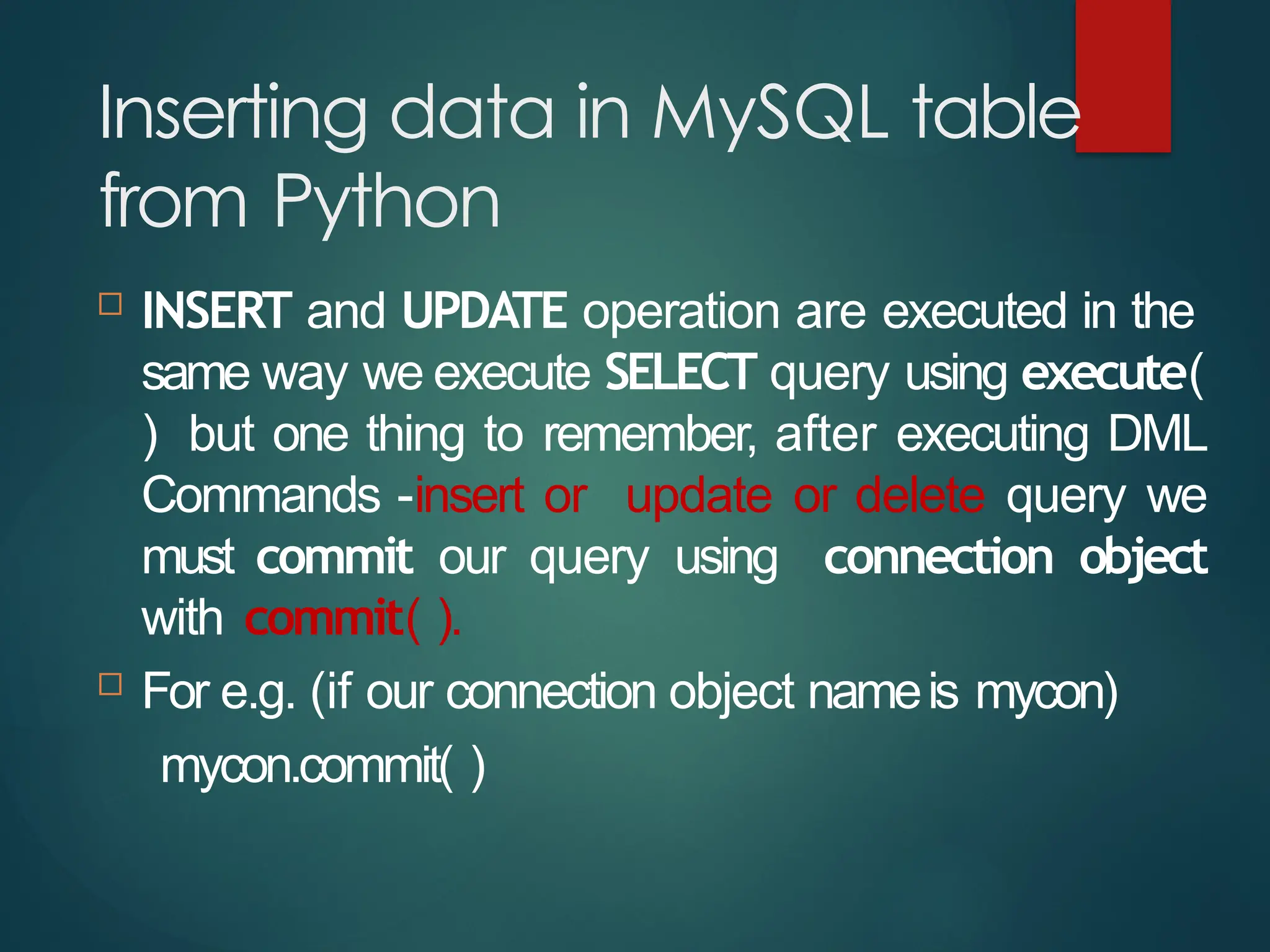
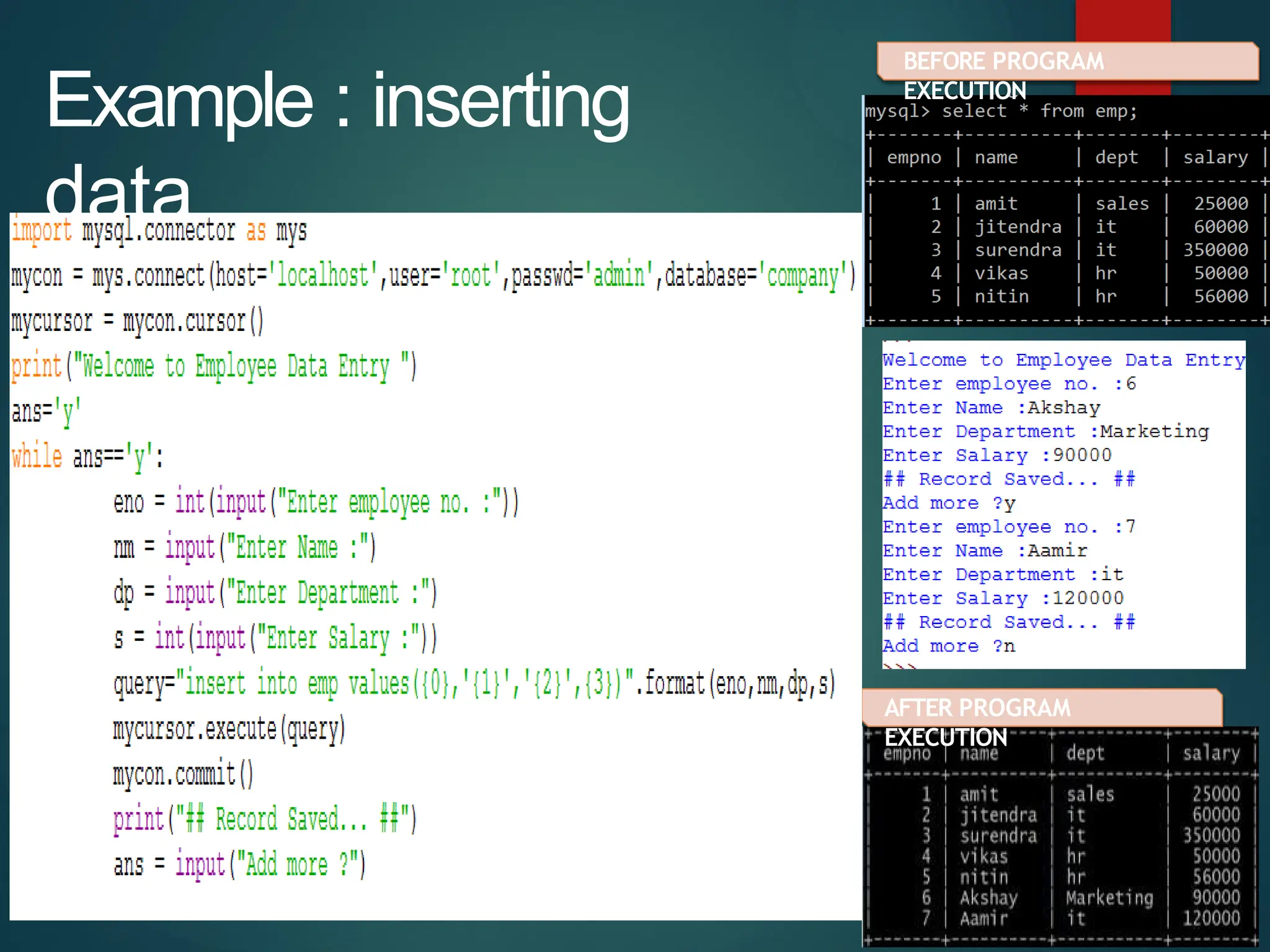
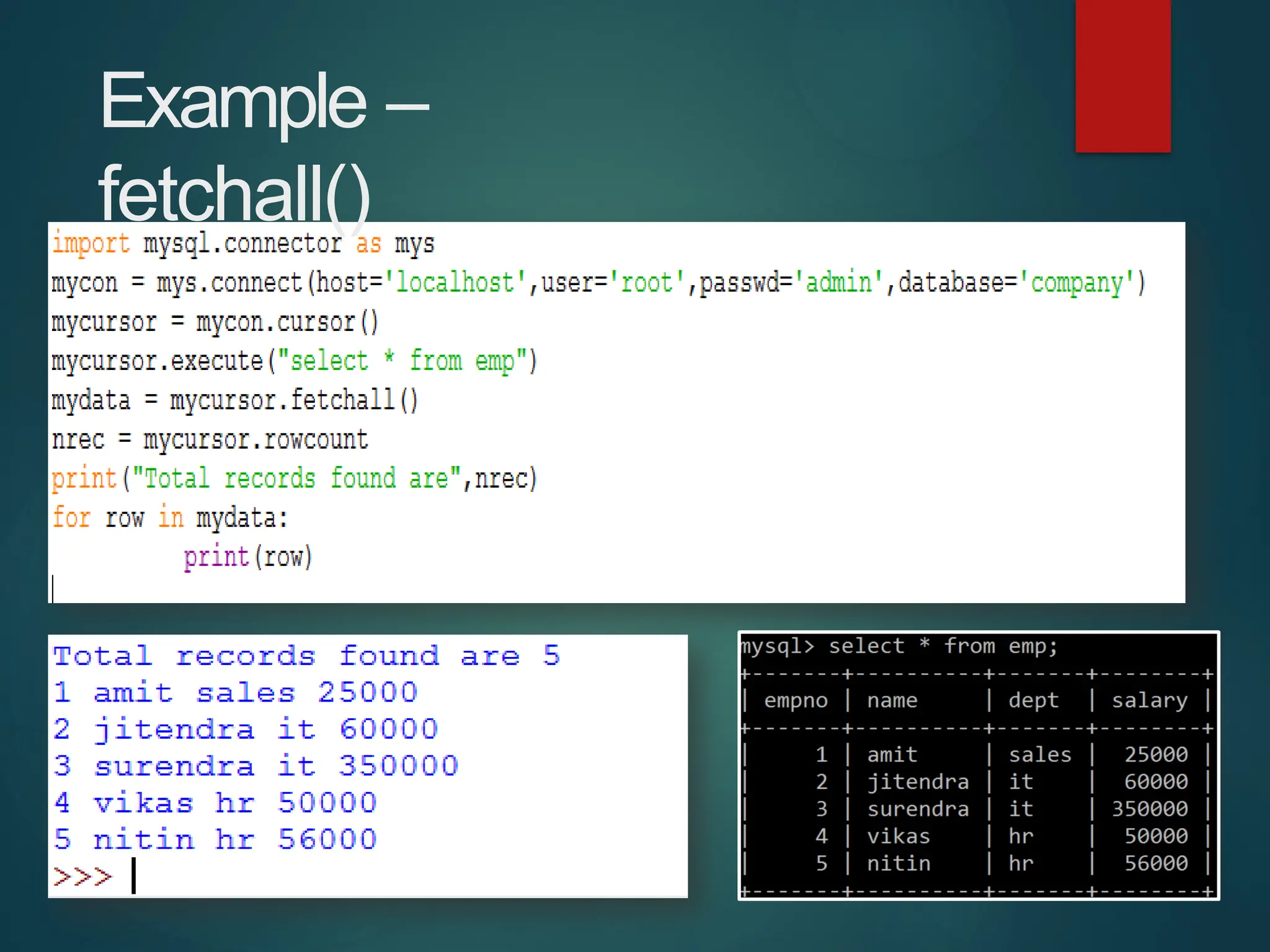
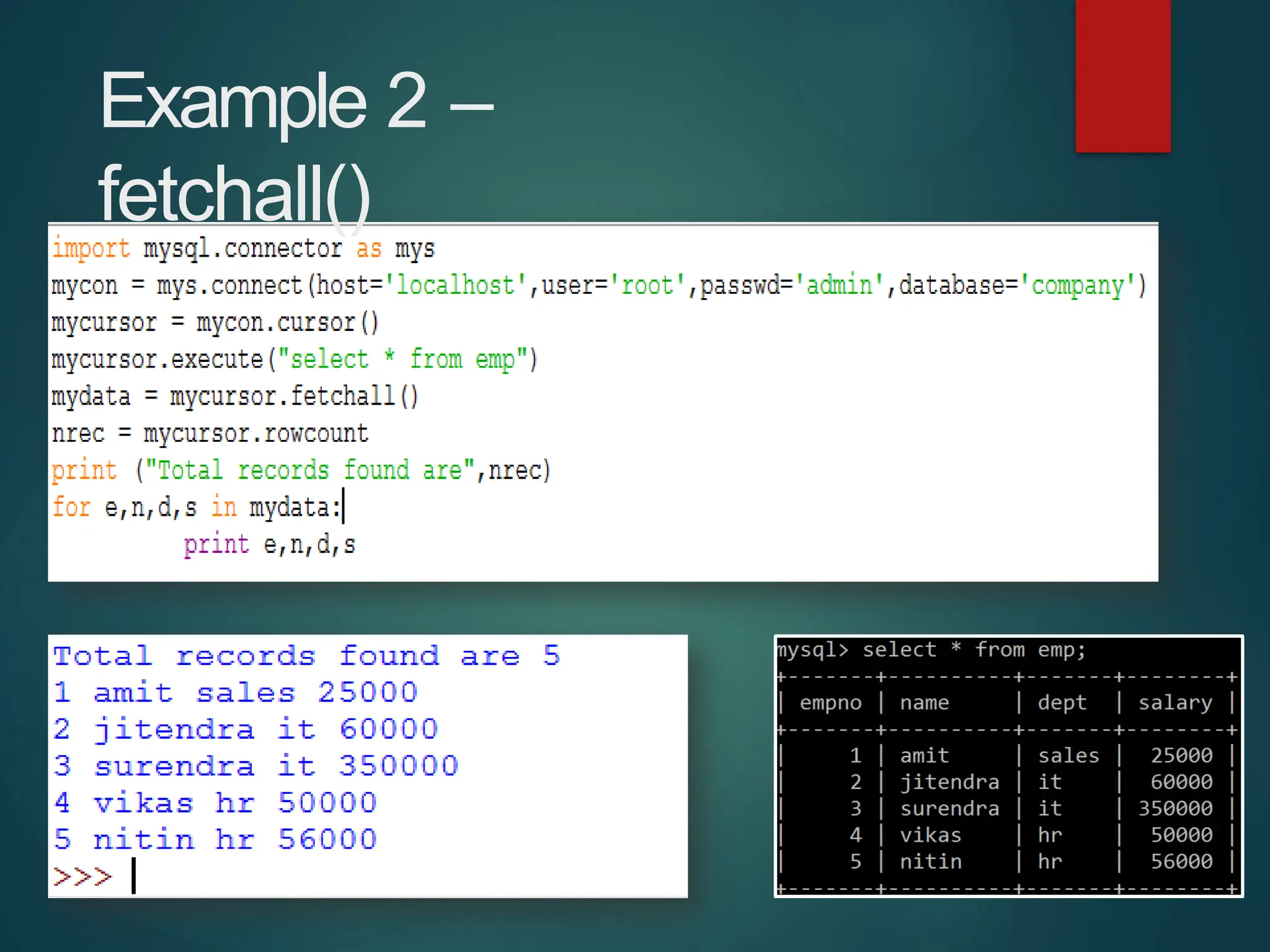
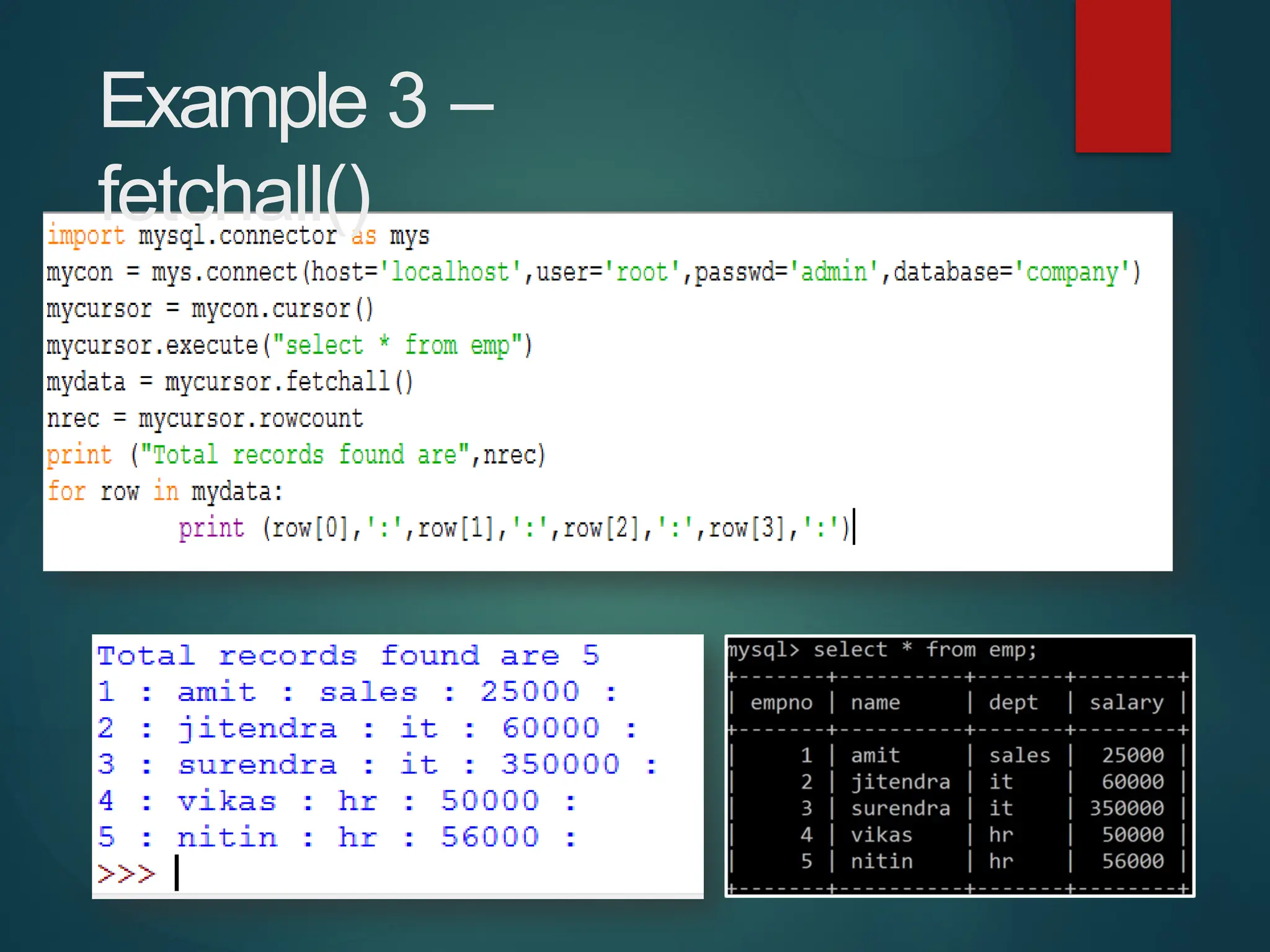
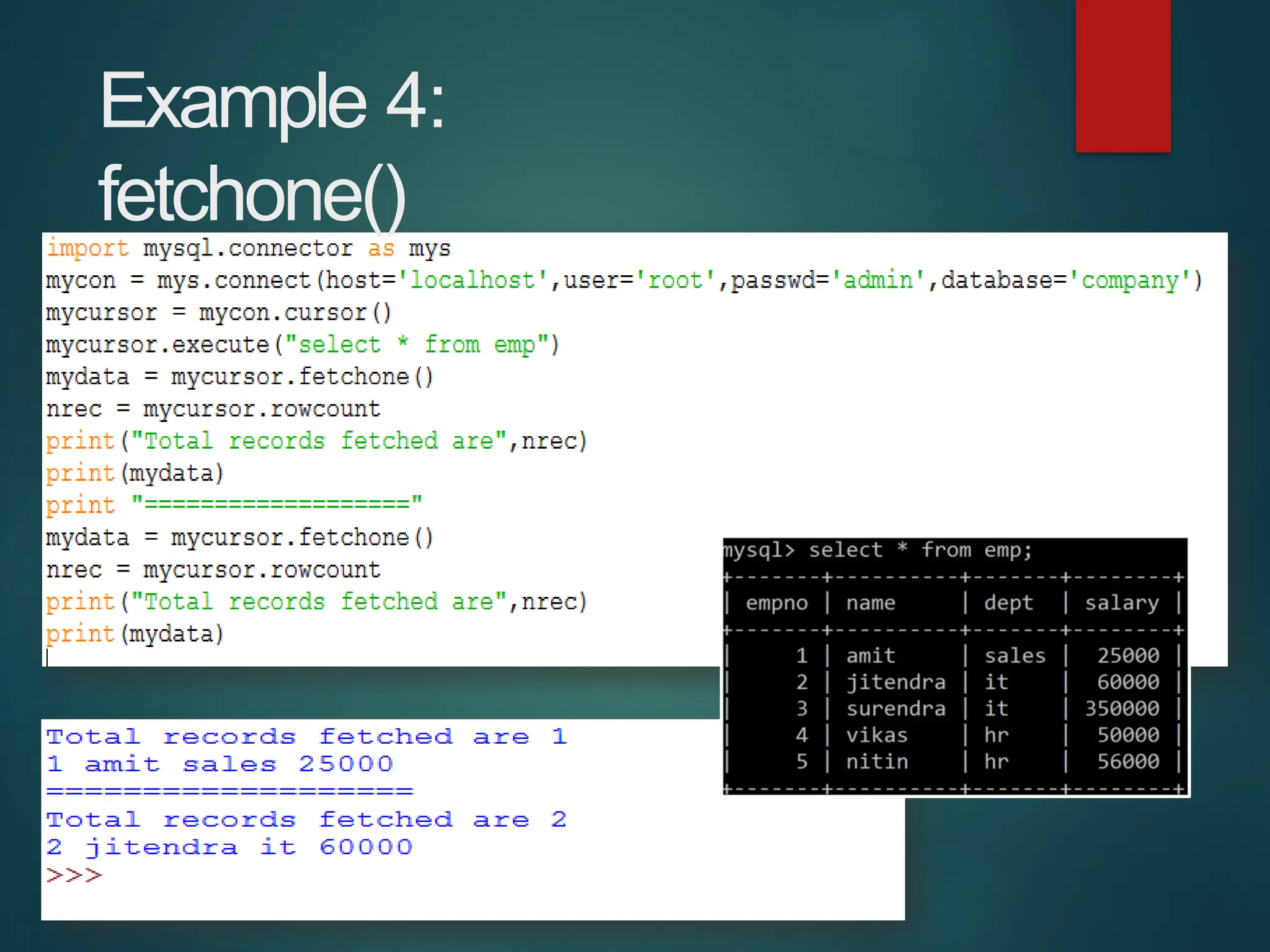
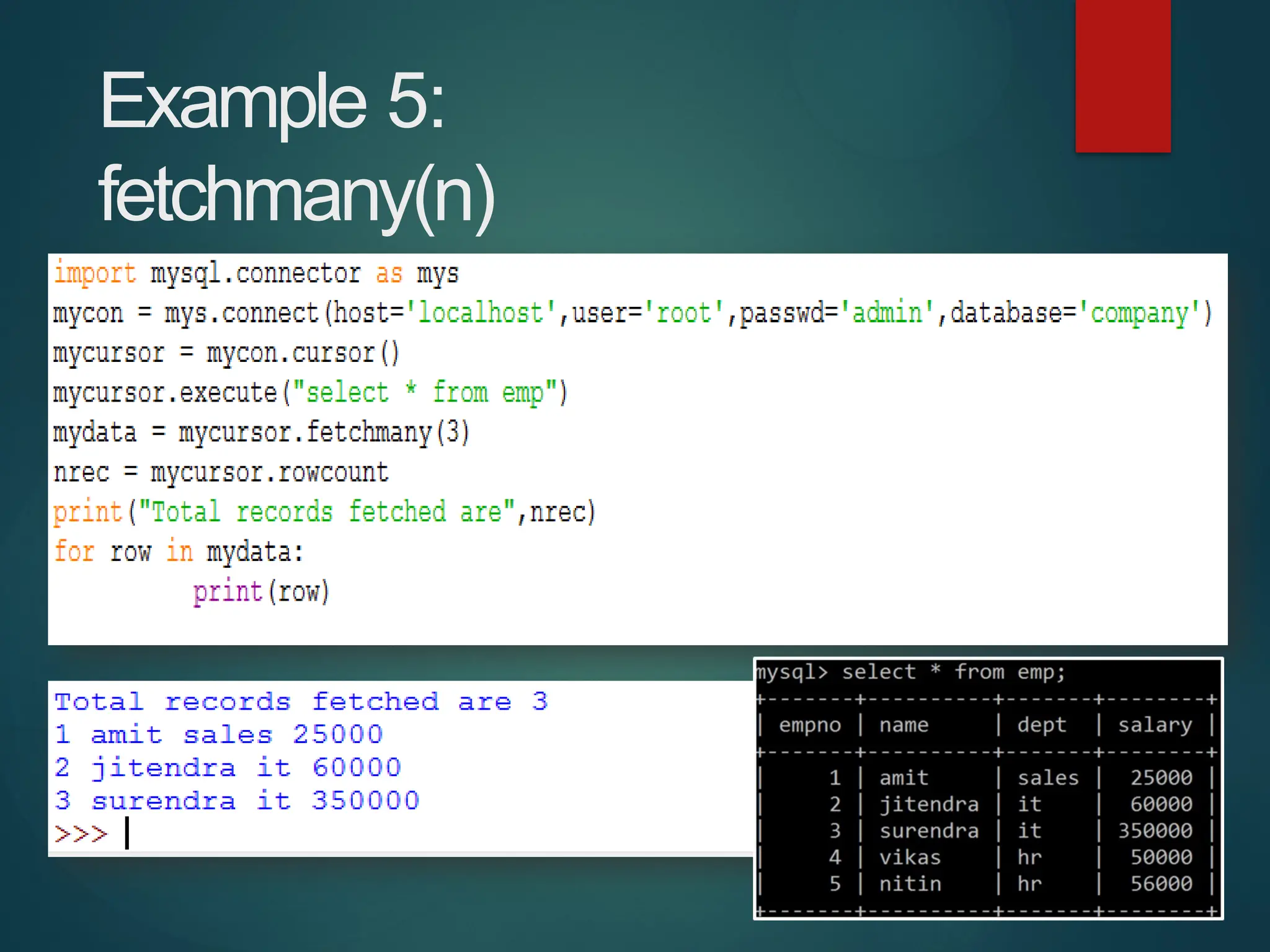
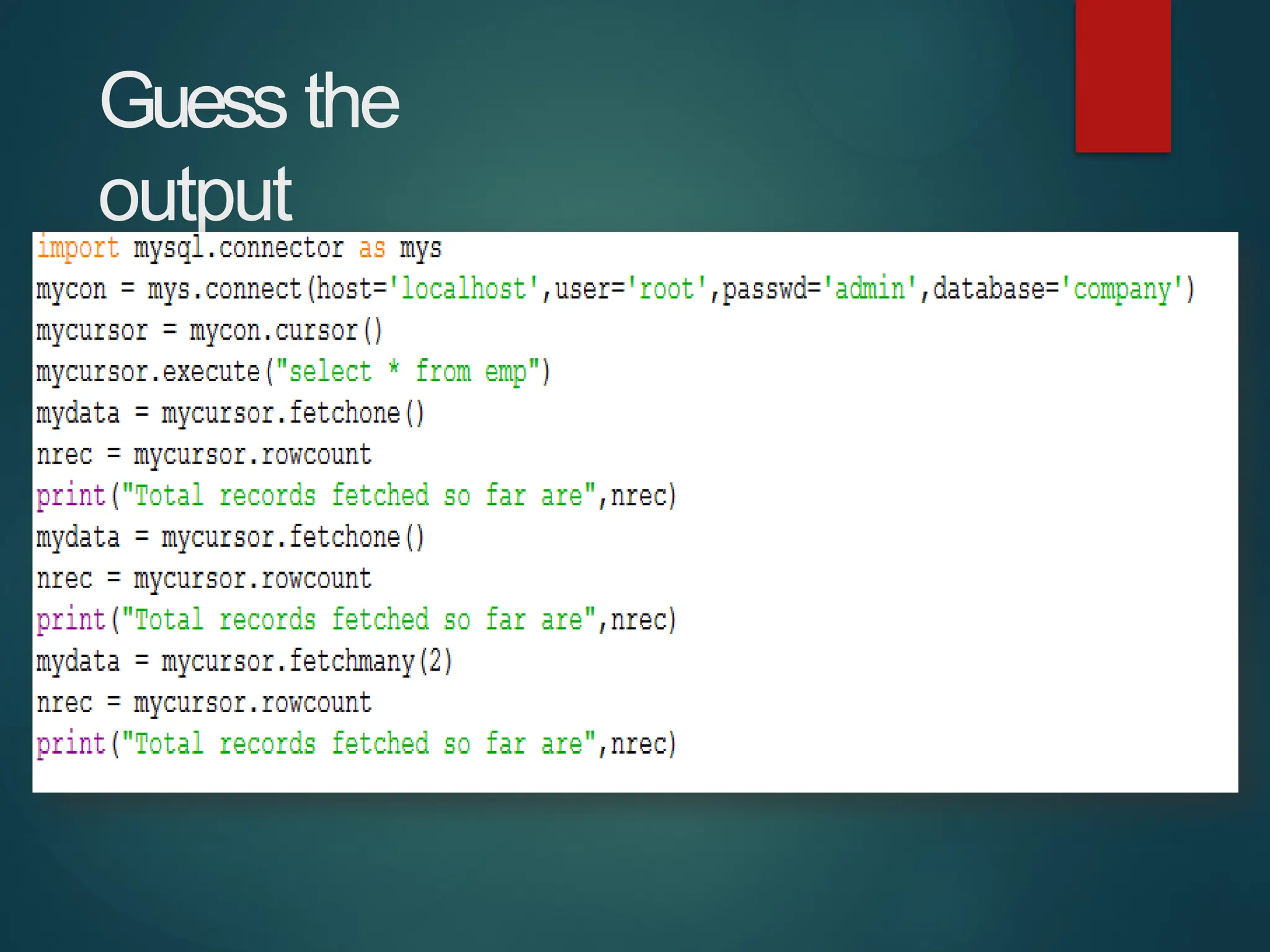
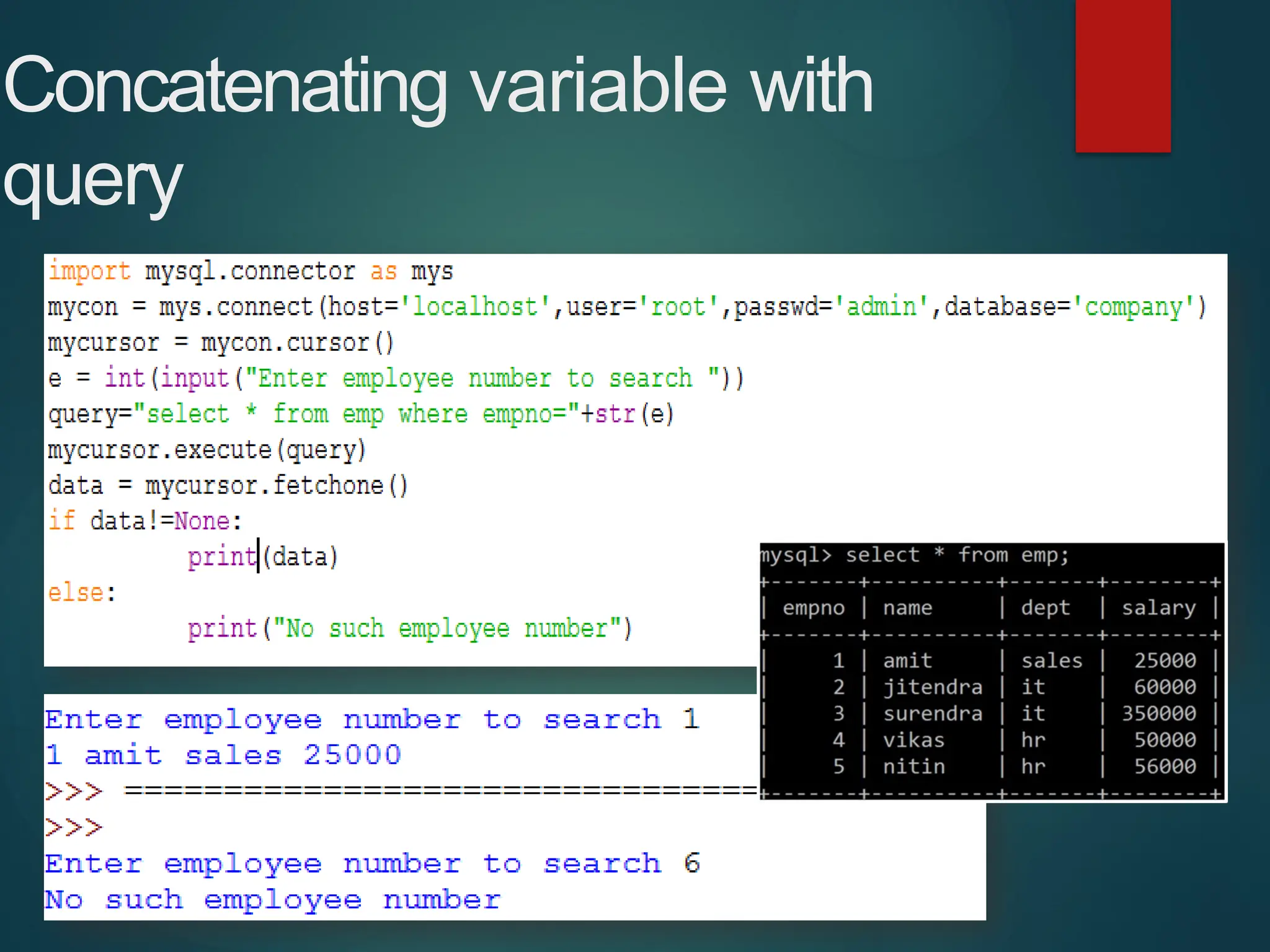
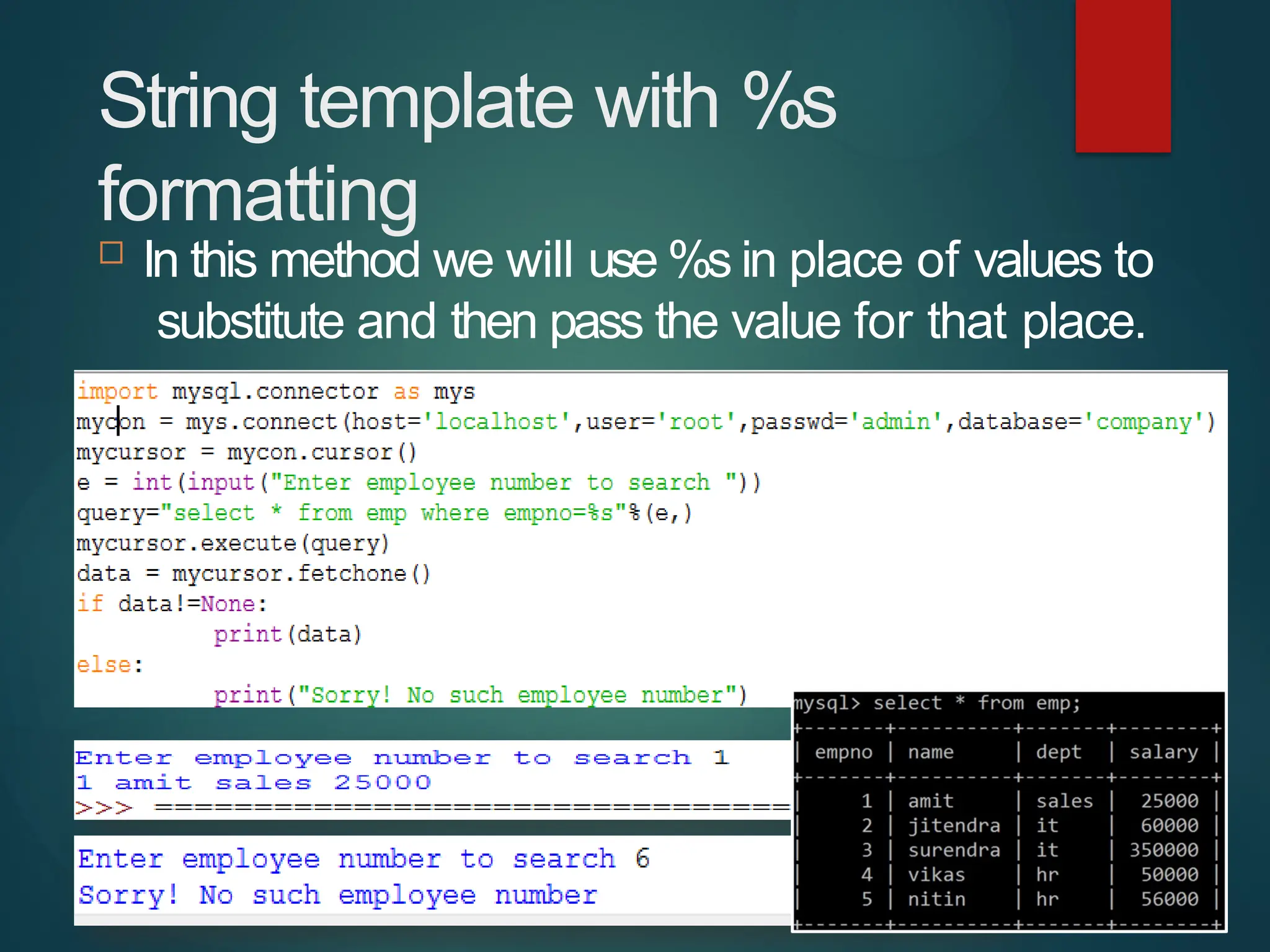
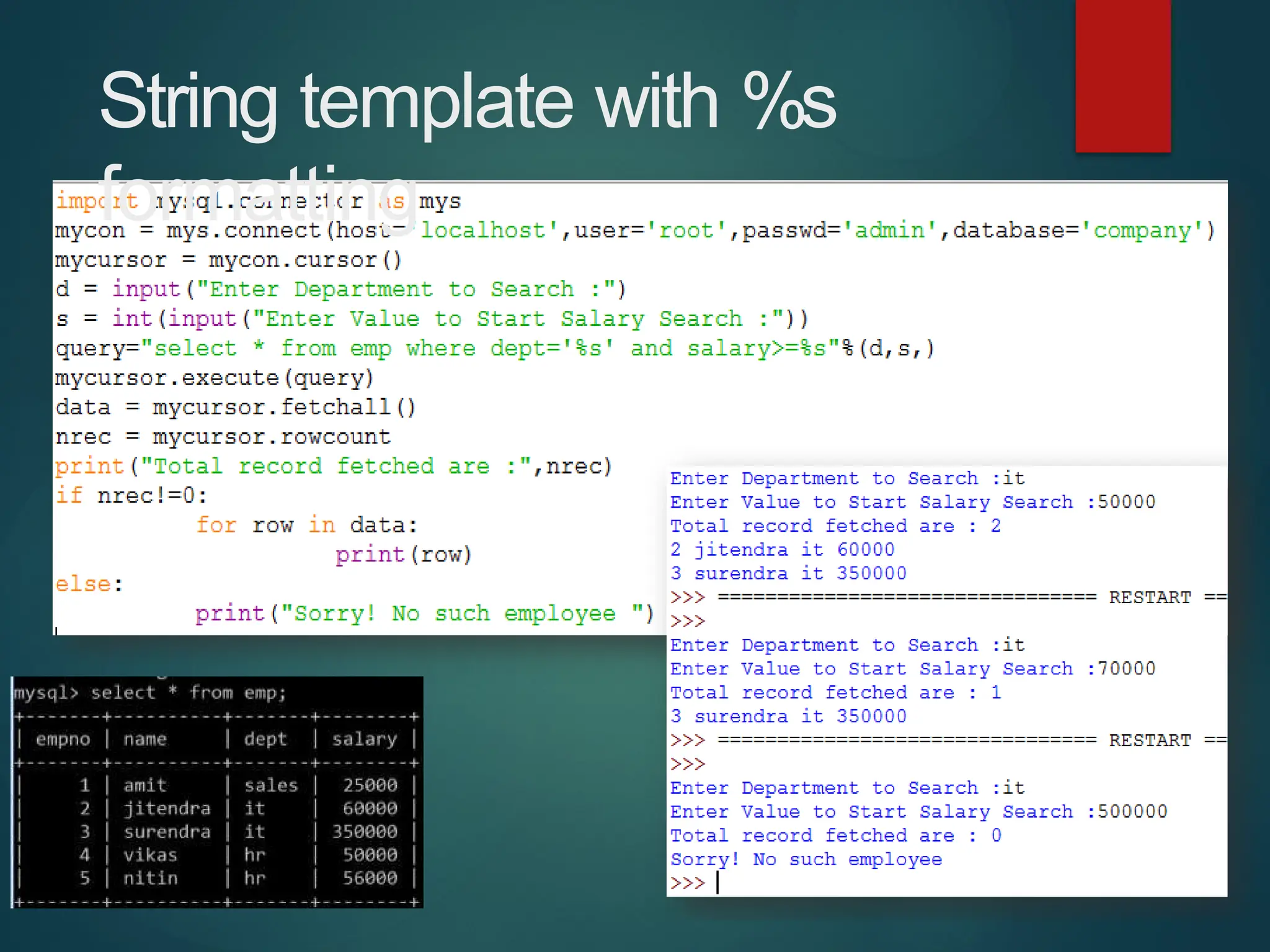
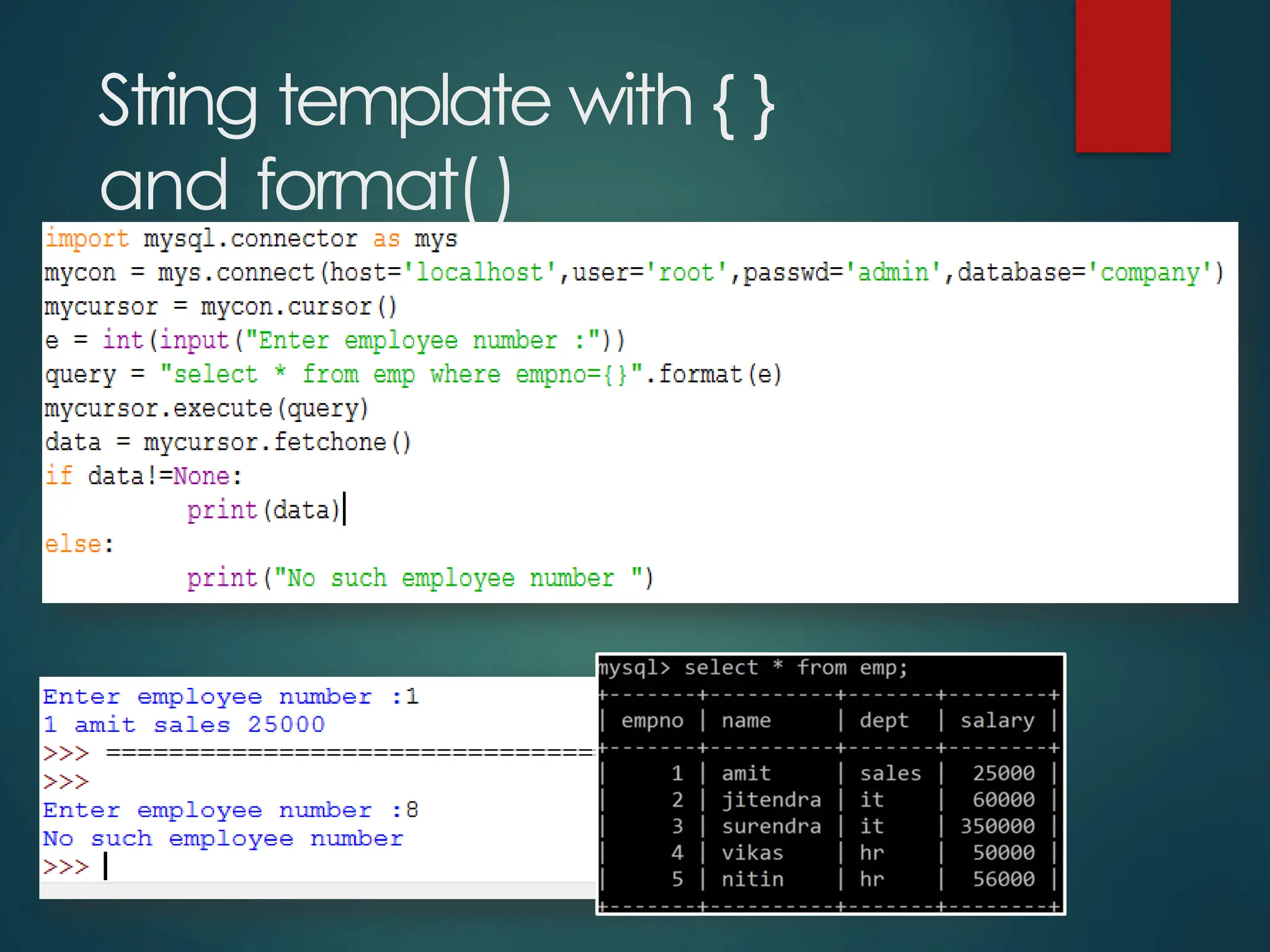
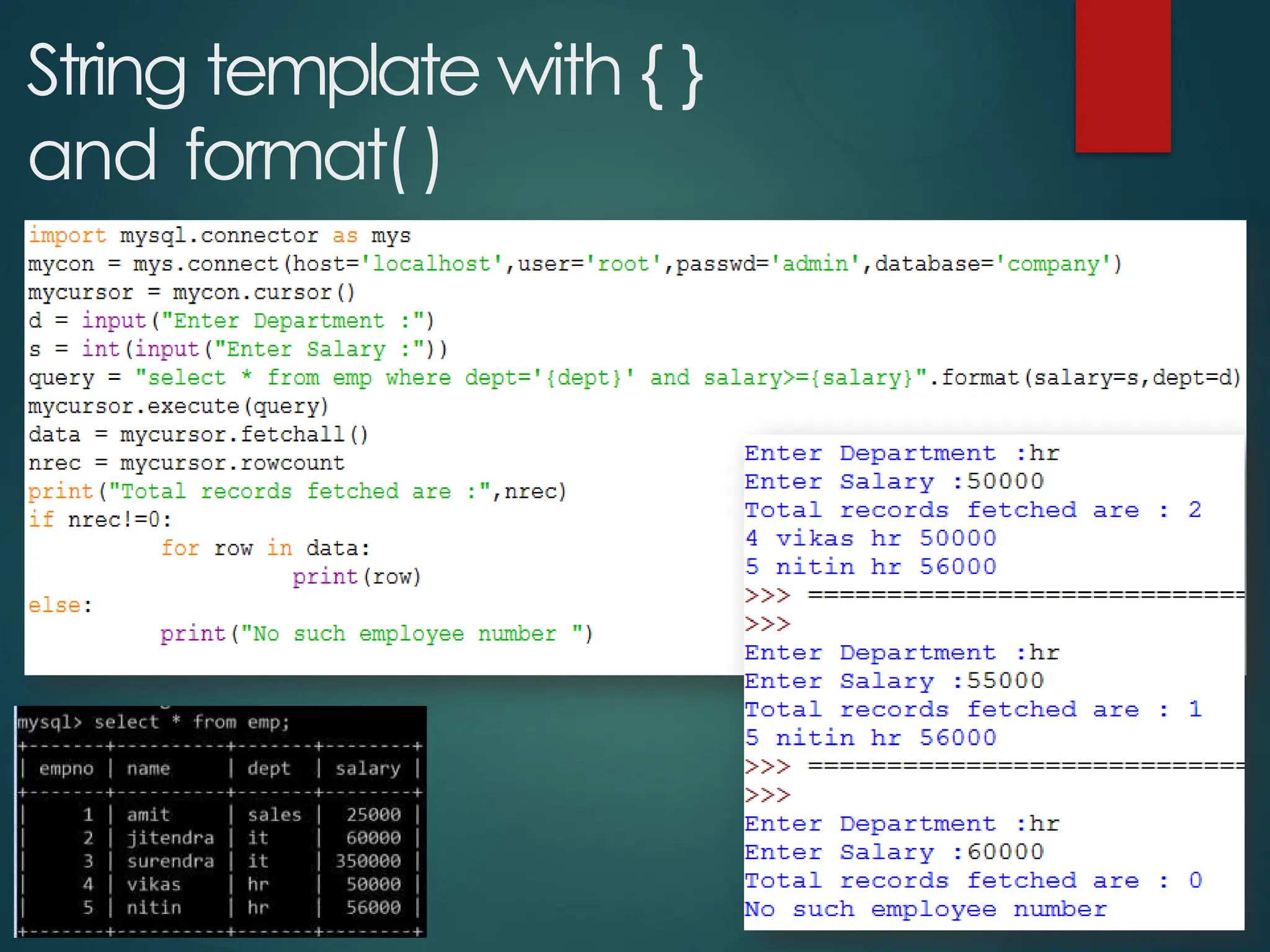
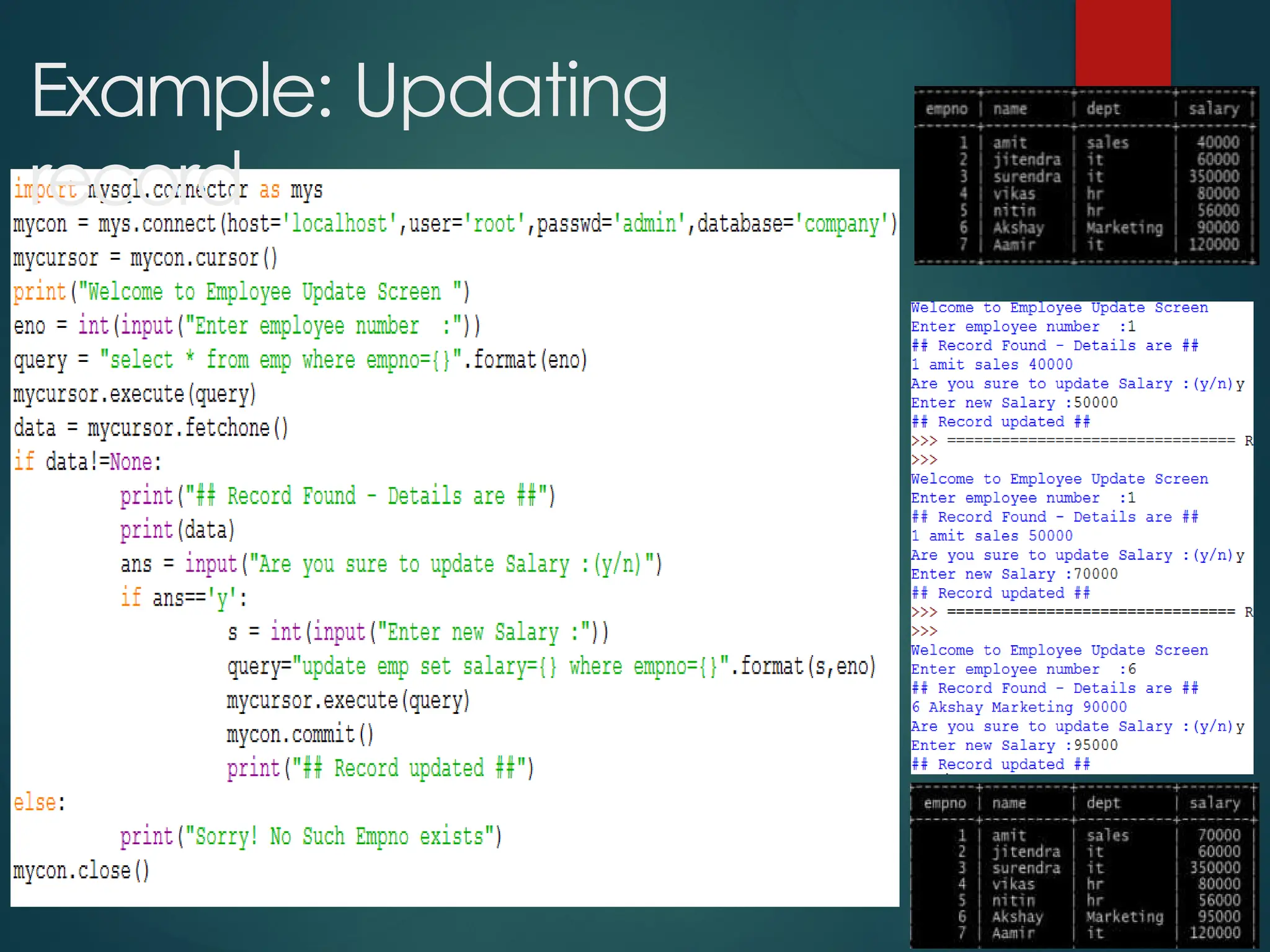
The document provides a comprehensive overview of connecting Python applications with MySQL, emphasizing the use of the 'mysql.connector' library to facilitate database interactions. It includes installation instructions, connection setup steps, usage of cursors for query execution, data insertion, retrieval methods, and the construction of parameterized queries. Key operations like inserting, updating, and deleting records are also addressed, along with examples for better understanding.






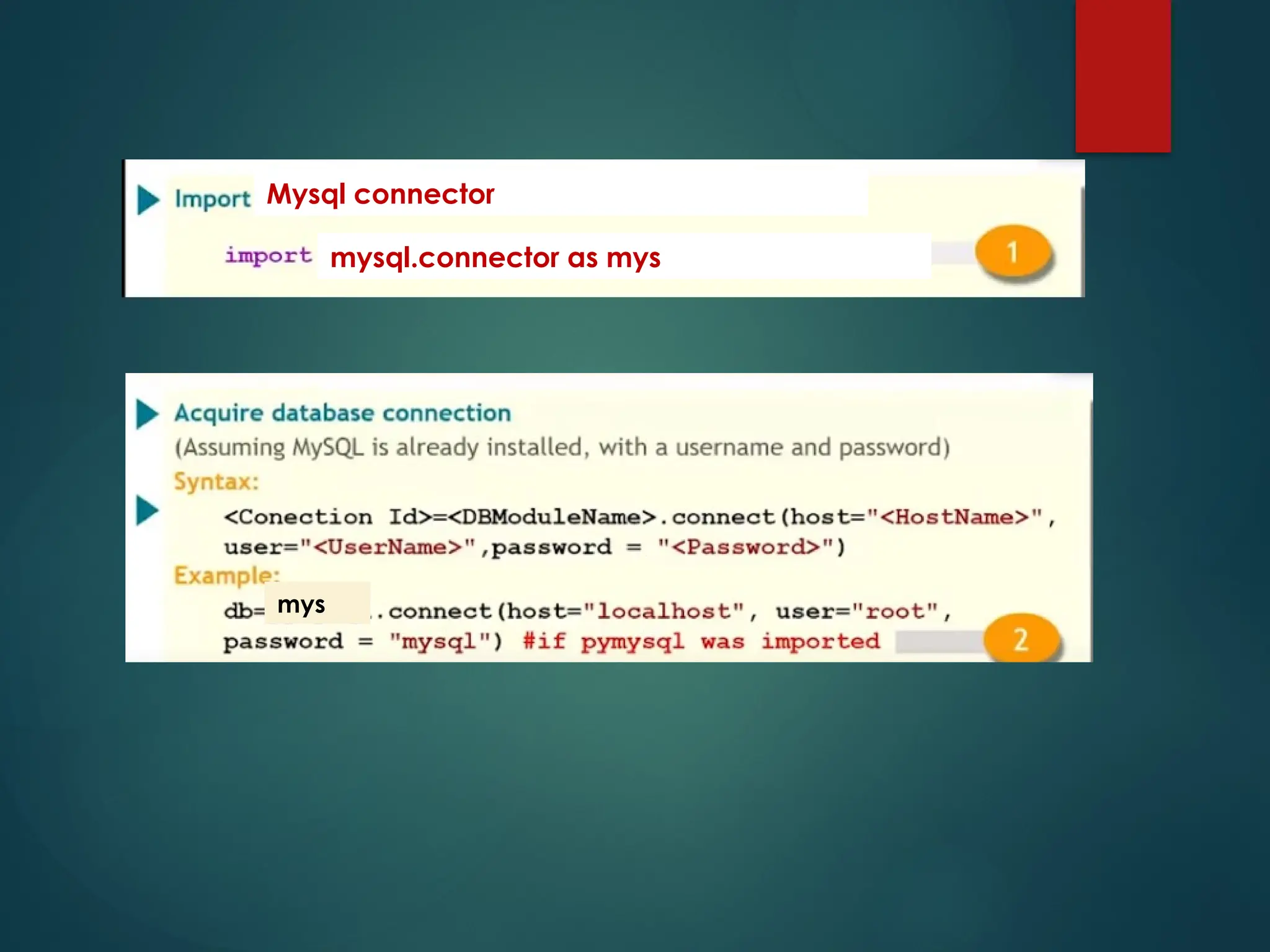
![Open a connection to MySQL Database T o create connection, connect( ) function is used Its syntax is: connect(host=<server_name>,user=<user_name>, passwd=<password>[,database=<database>]) Here server_name means database servername, generally it is given as “localhost” User_name means user by which we connect with mysql generally it is given as “root” Password is the password of user “root” Database is the name of database whose data(table) we want to use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-241225040346-bf470b64/75/SQL-Connectivity-python-for-beginners-easy-explanation-with-concepts-and-output-pptx-7-2048.jpg)