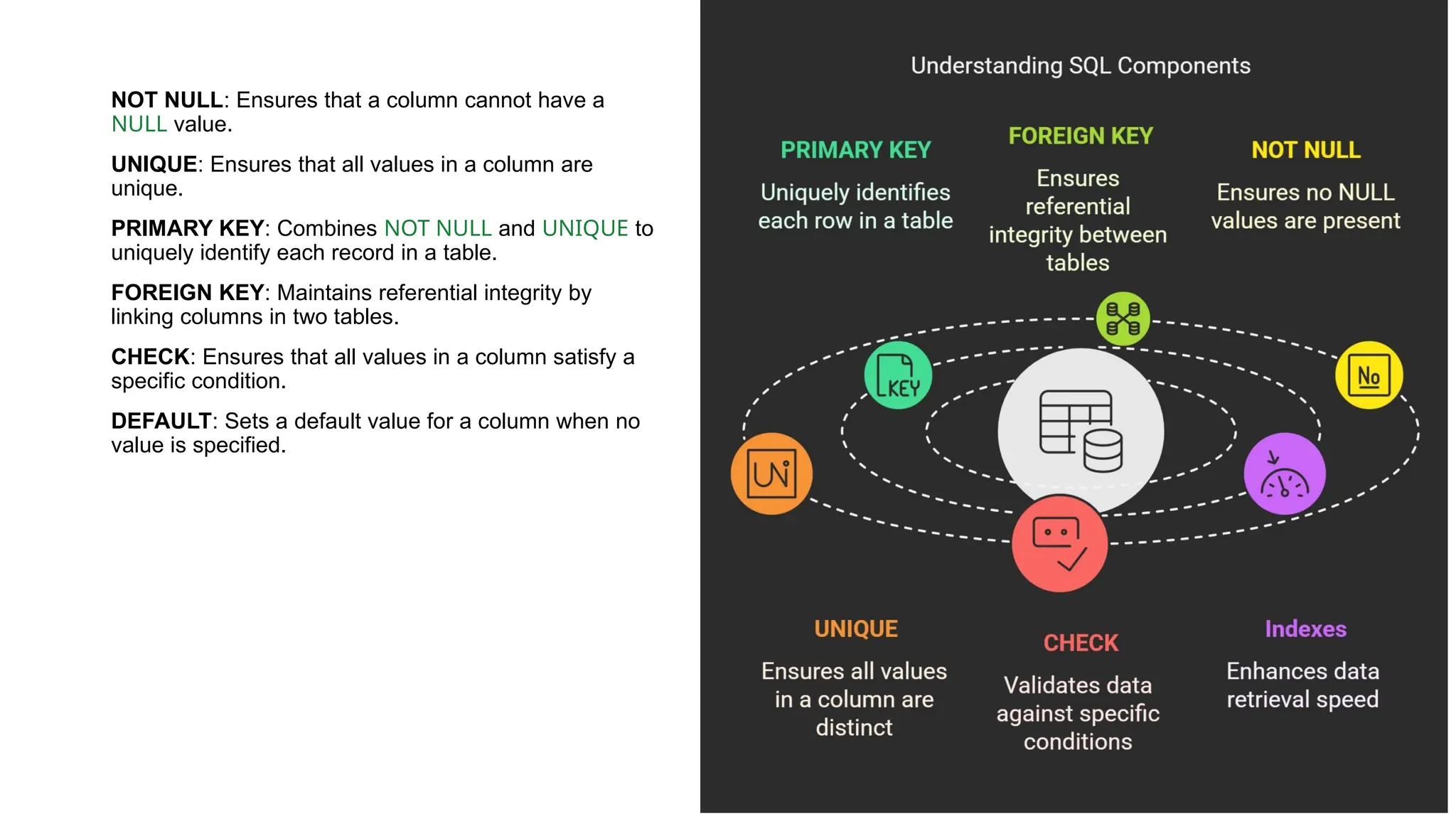
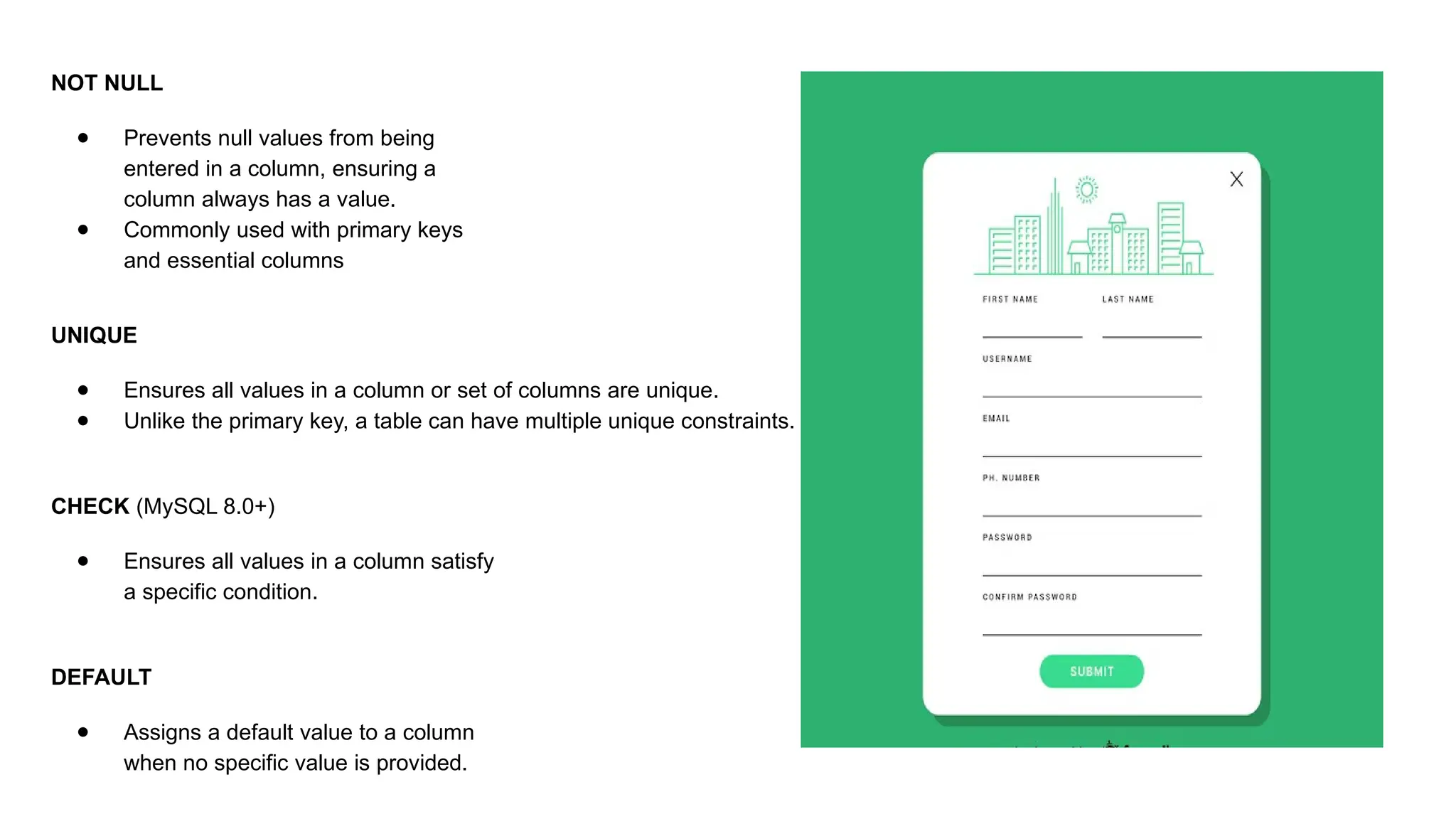
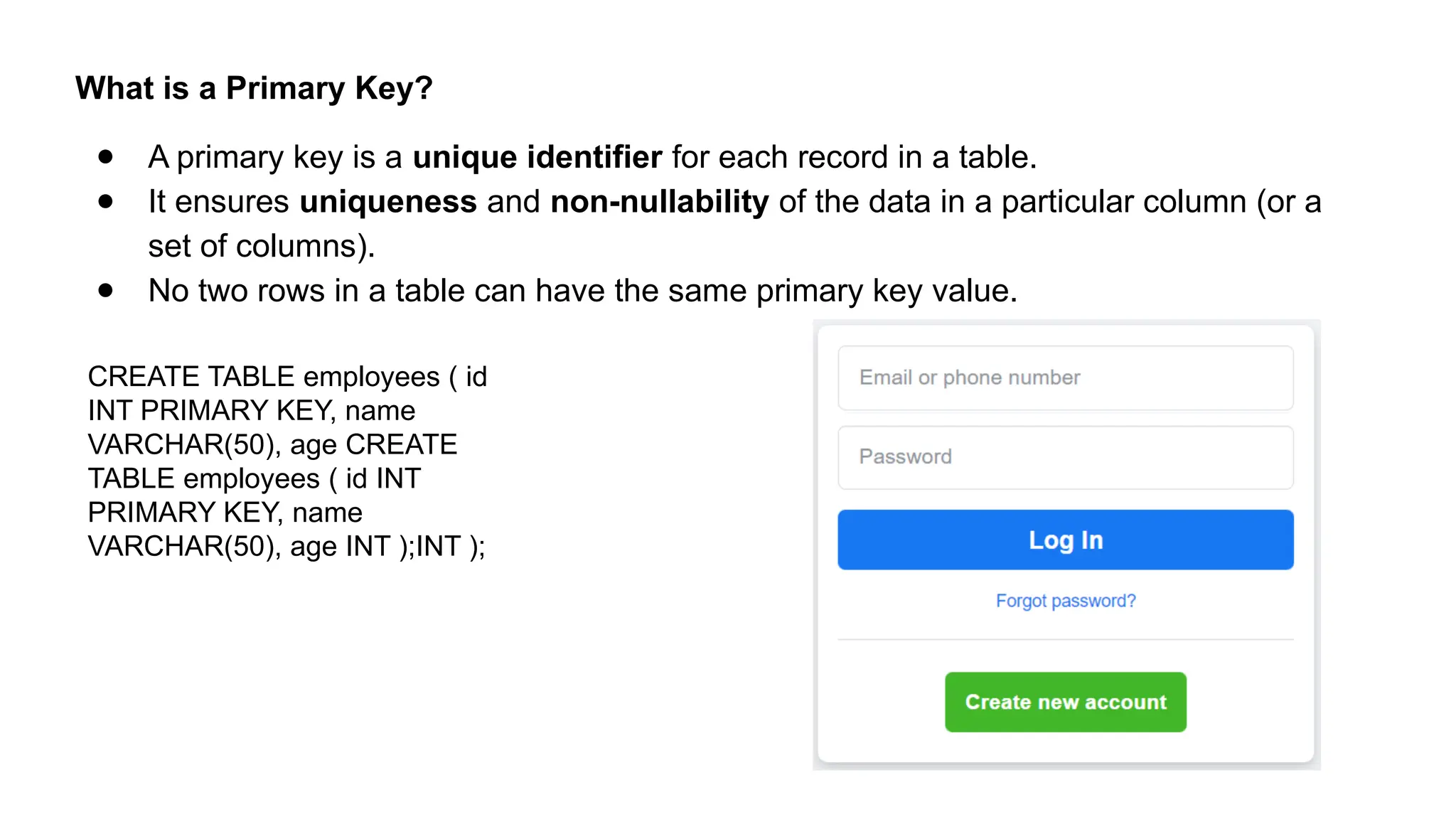
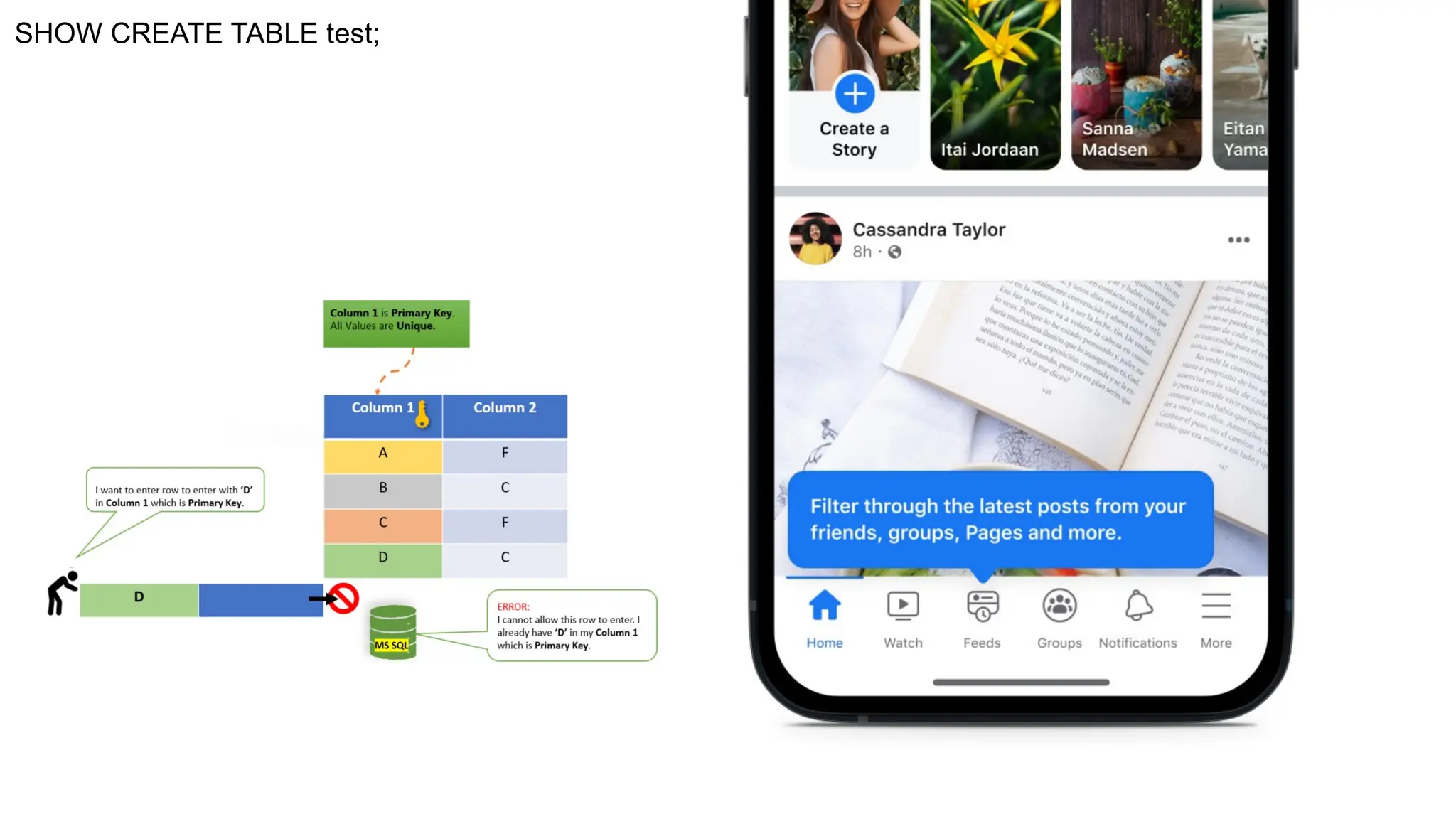
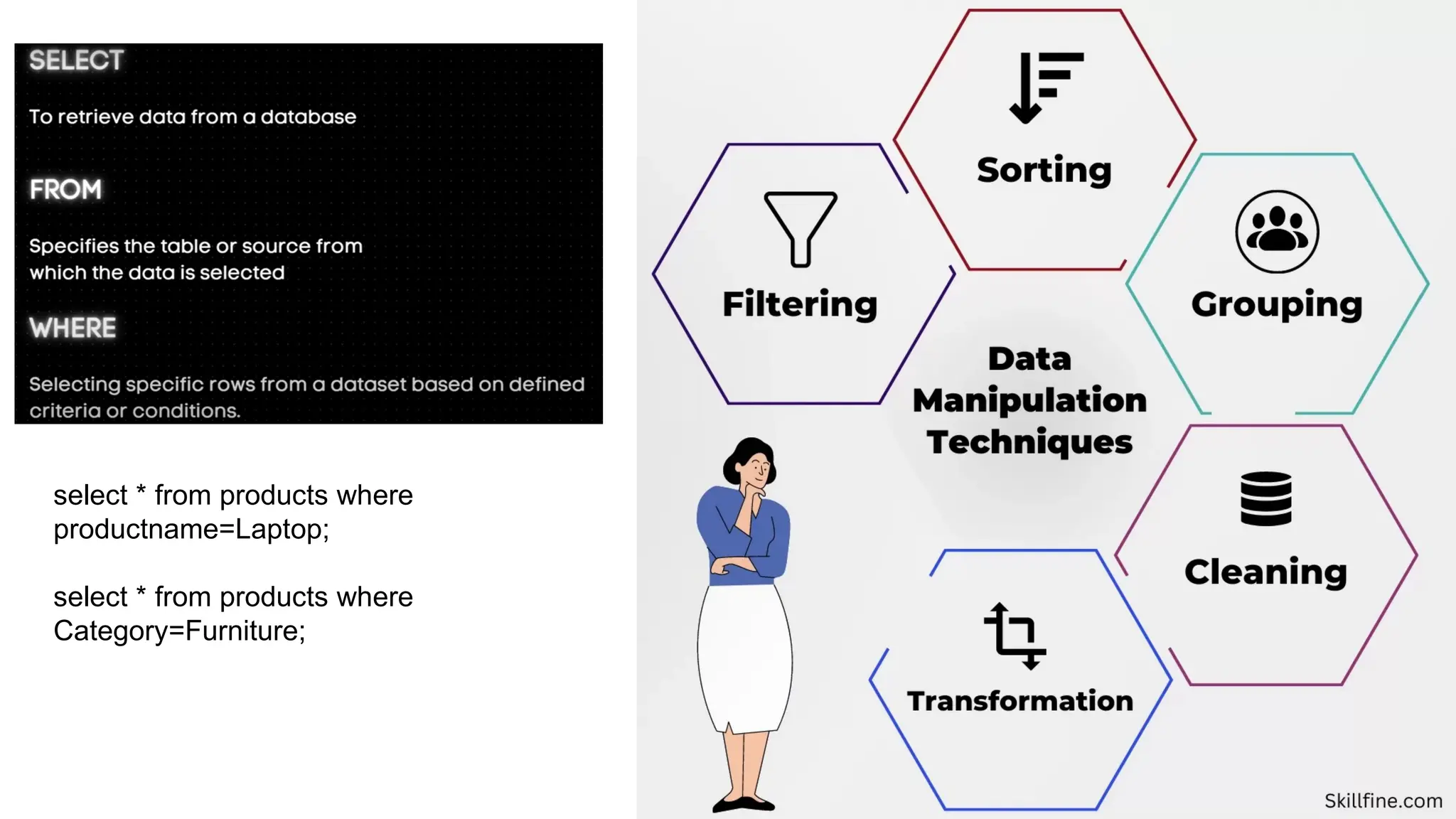
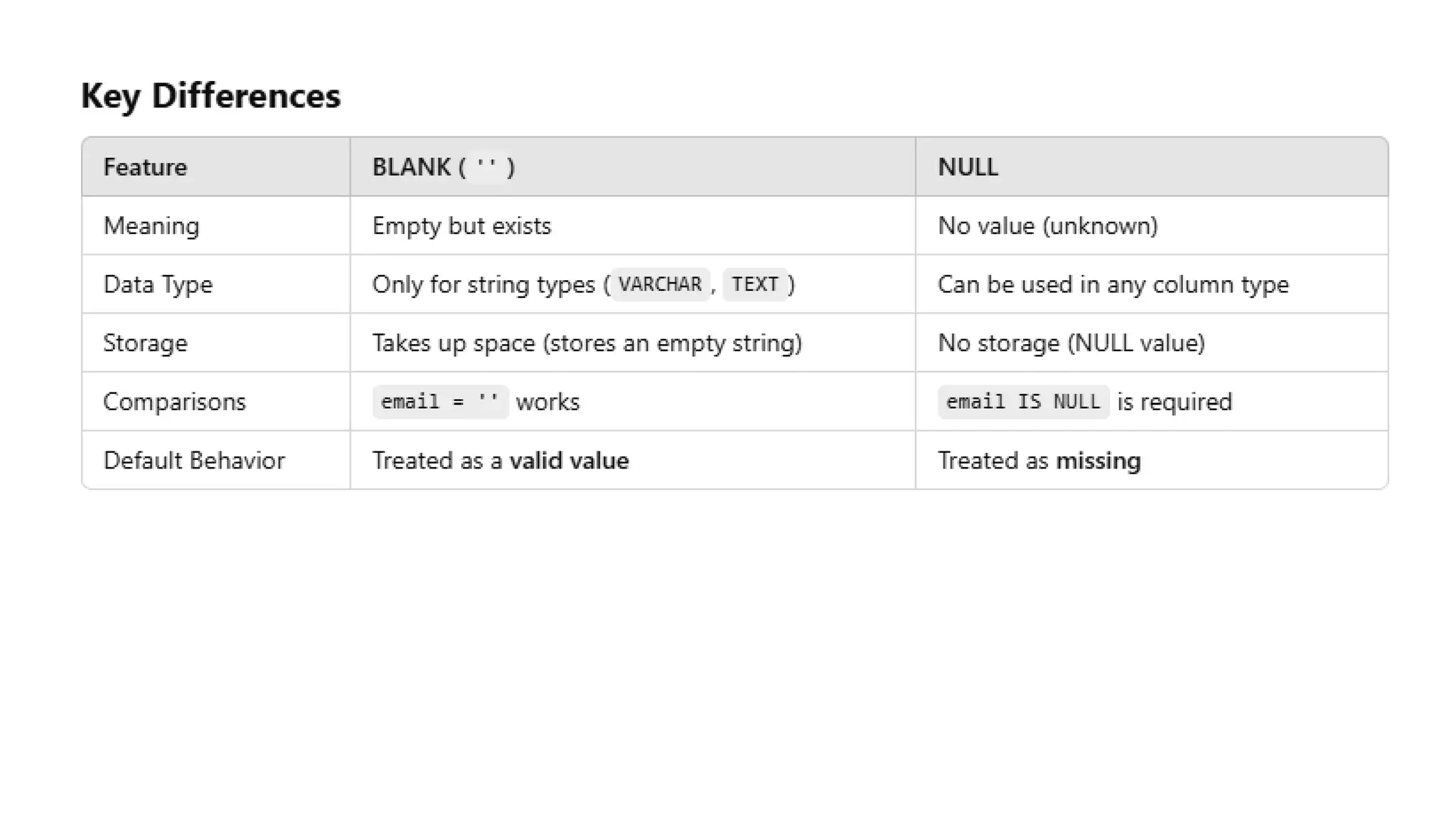
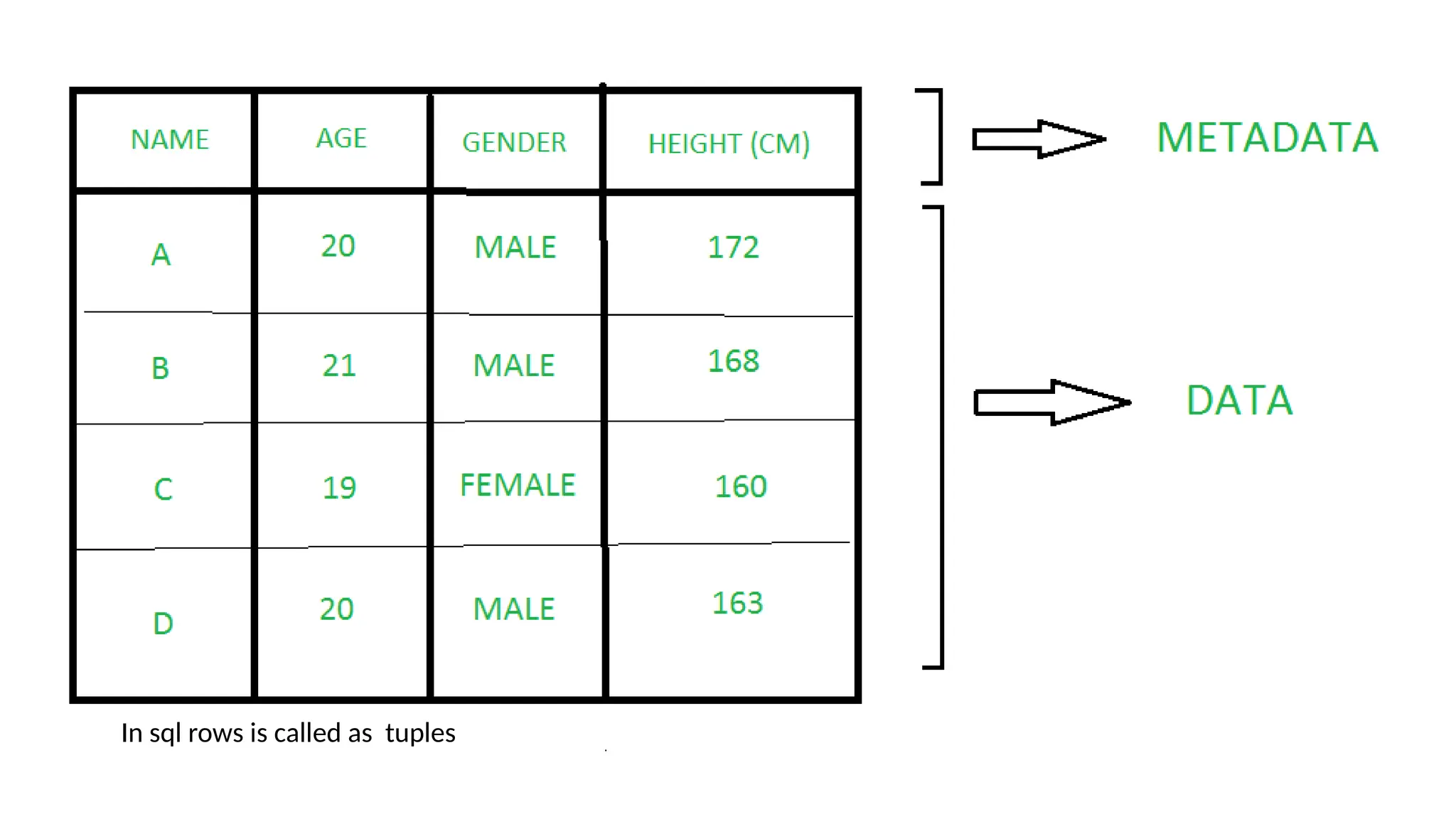
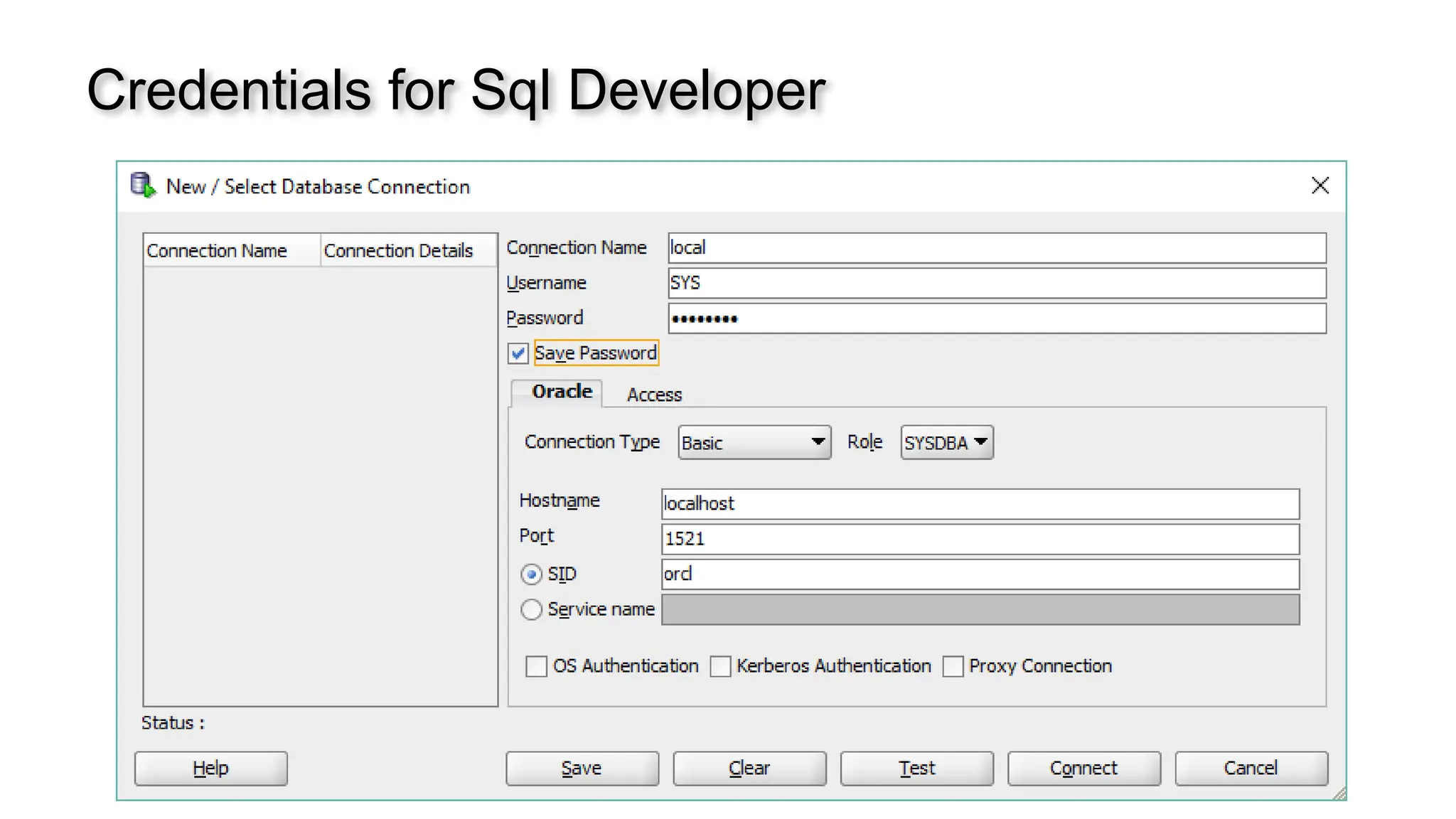
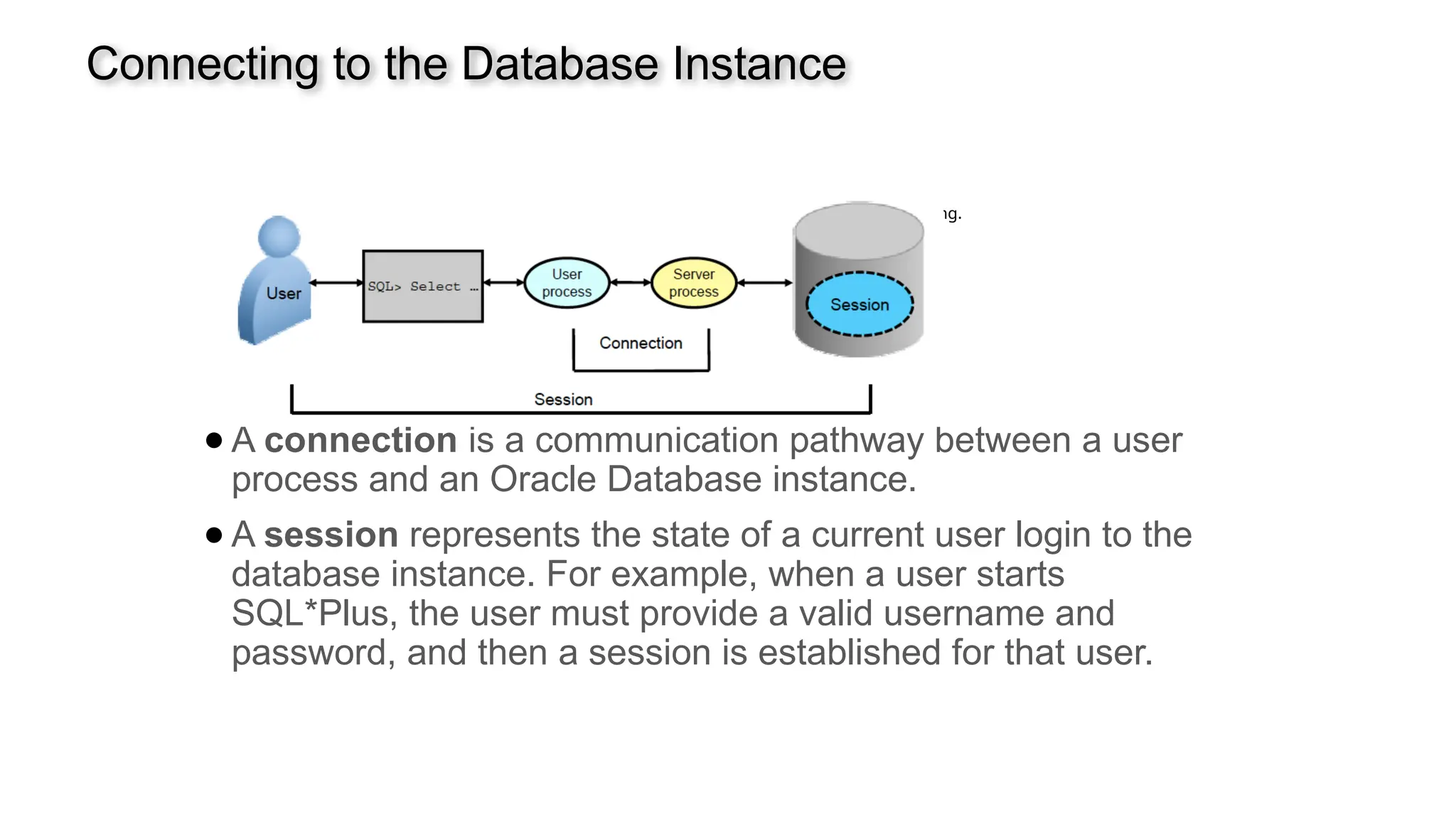
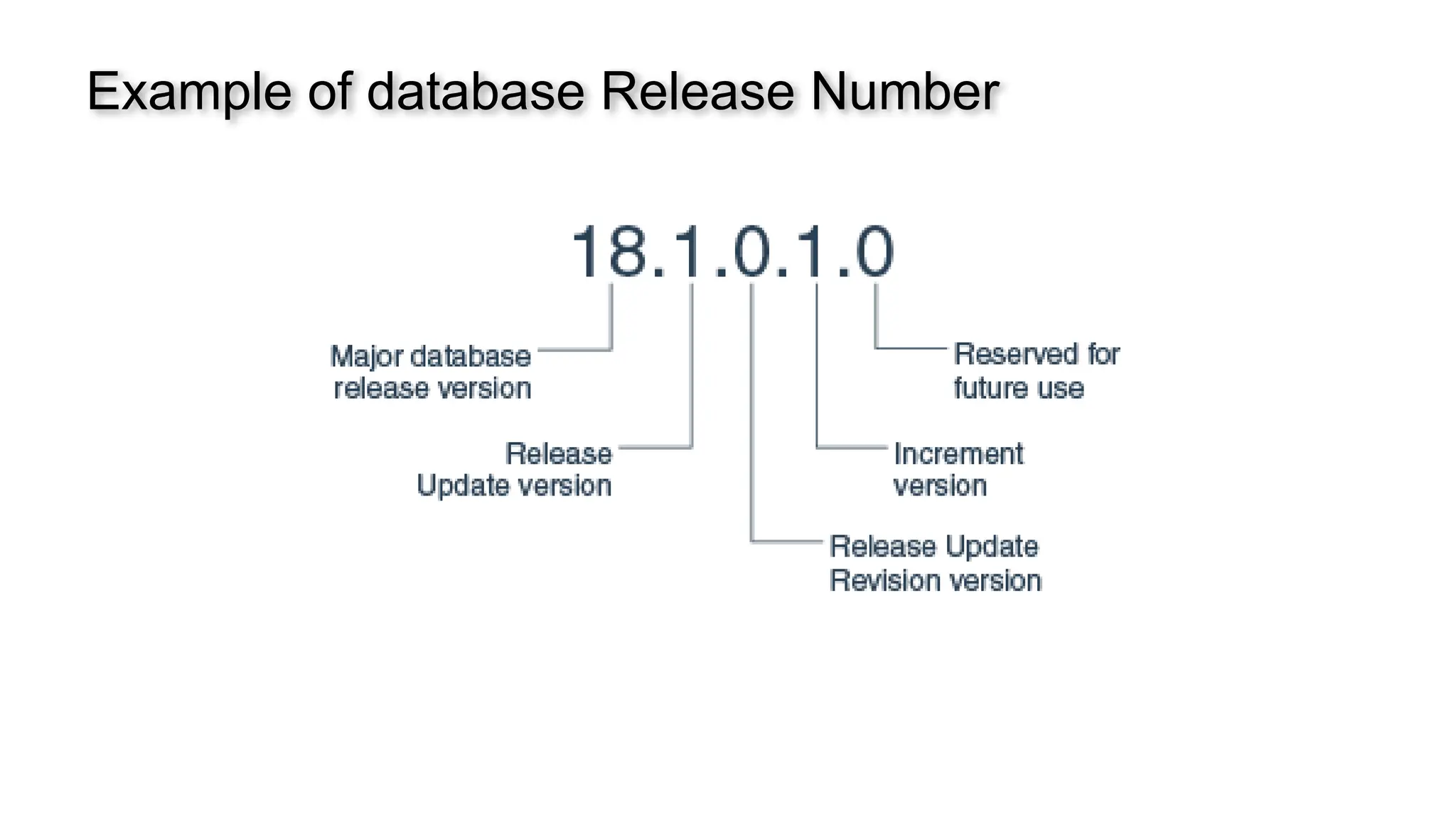
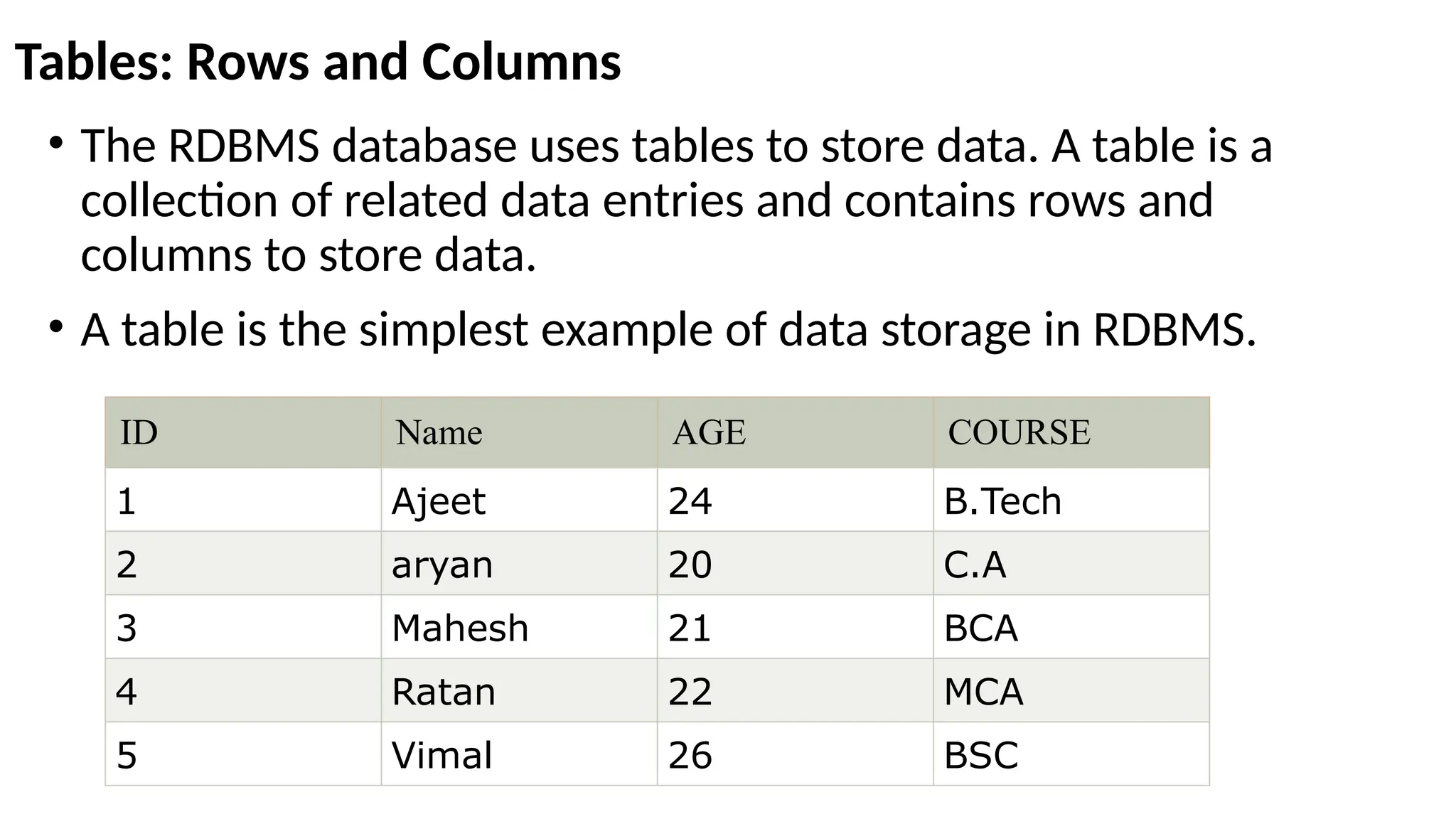
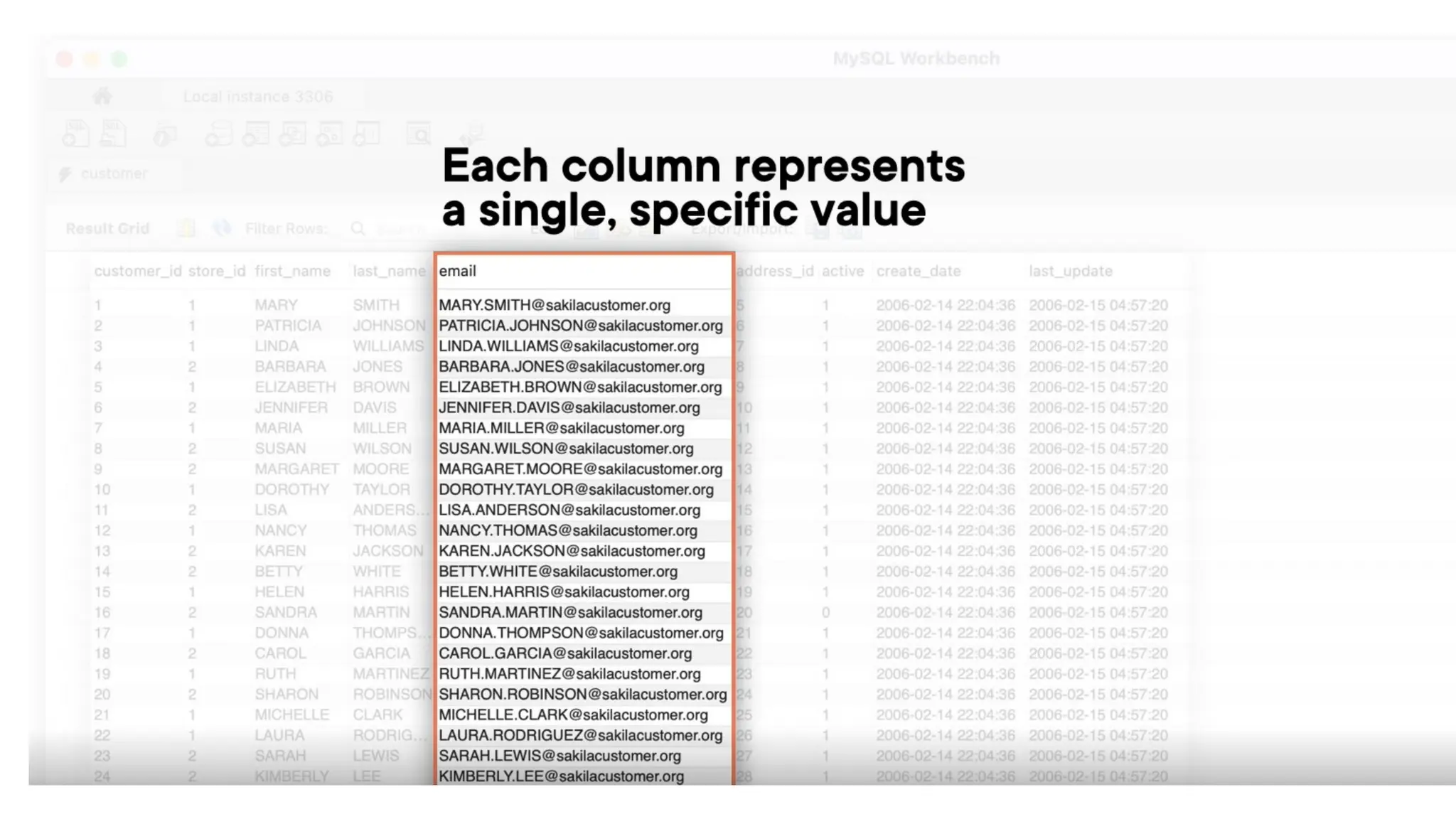
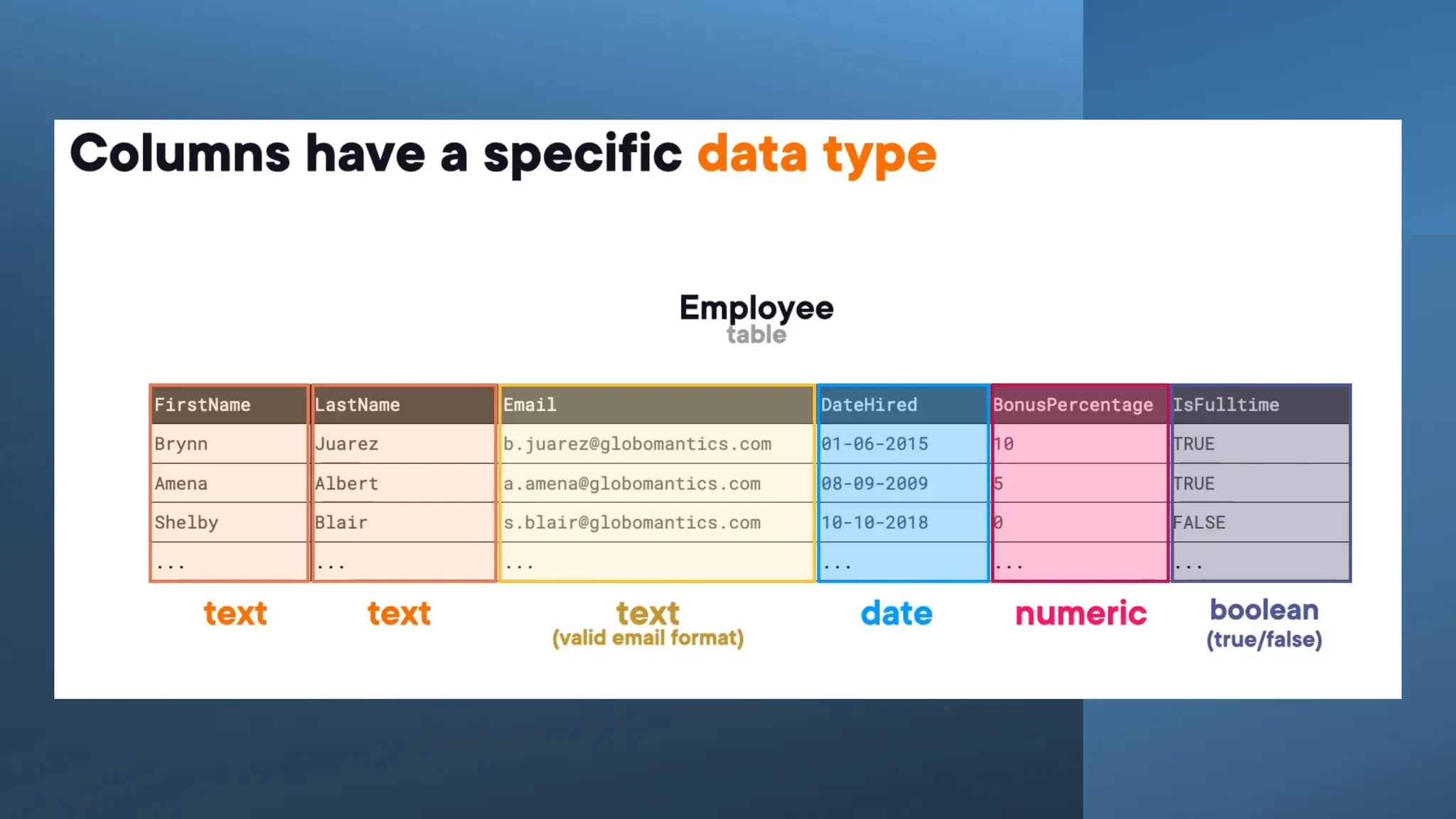
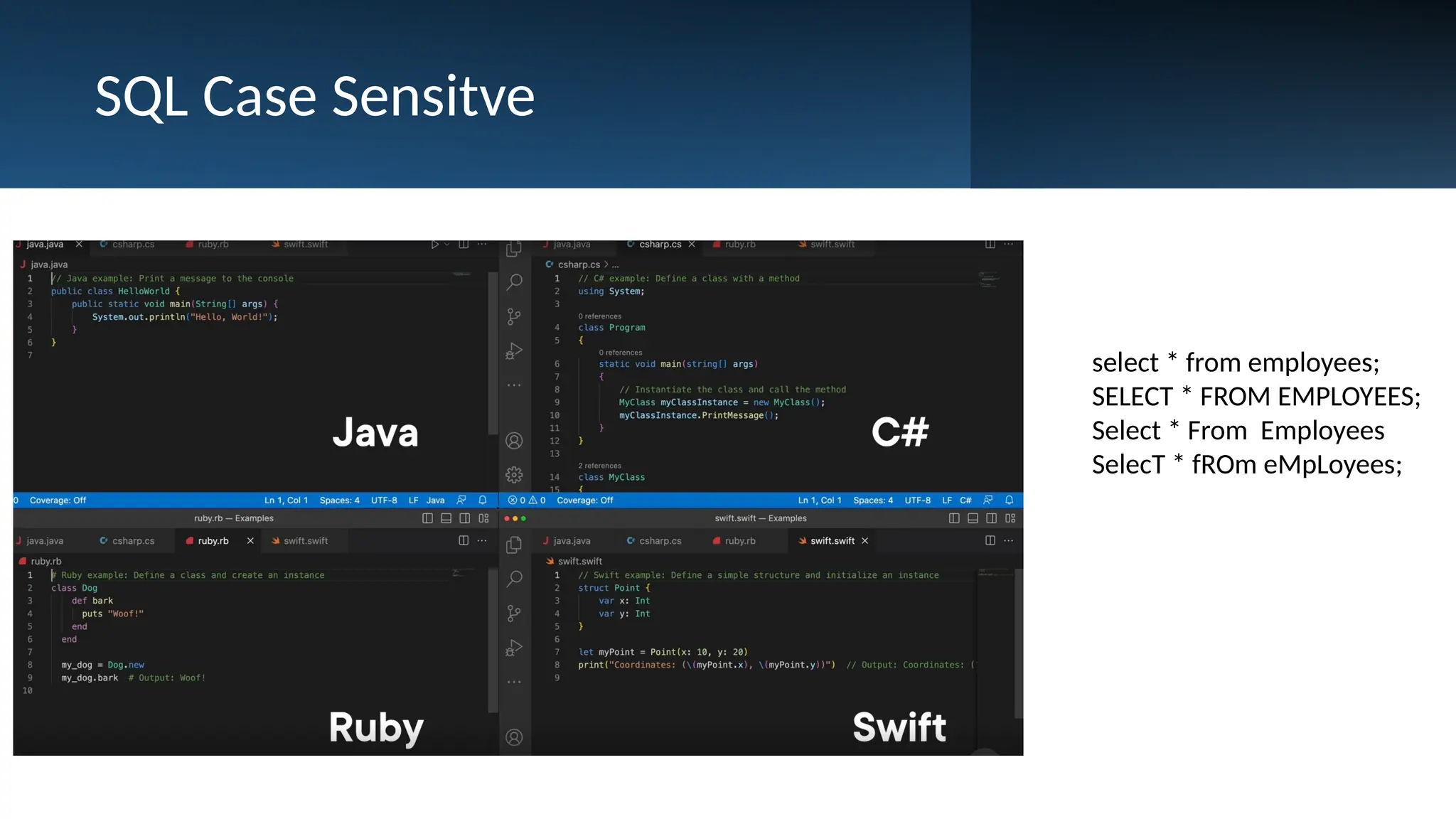
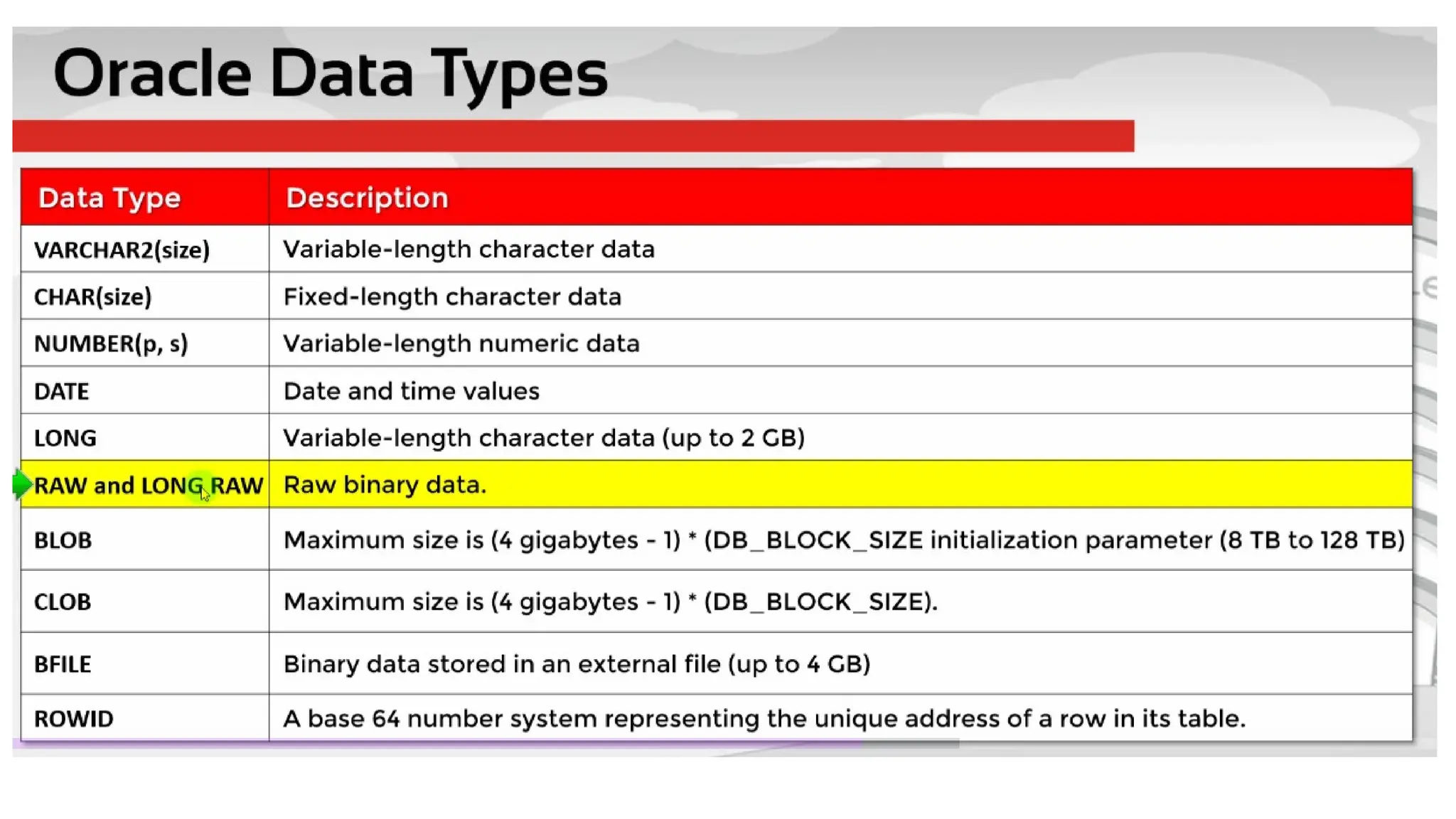
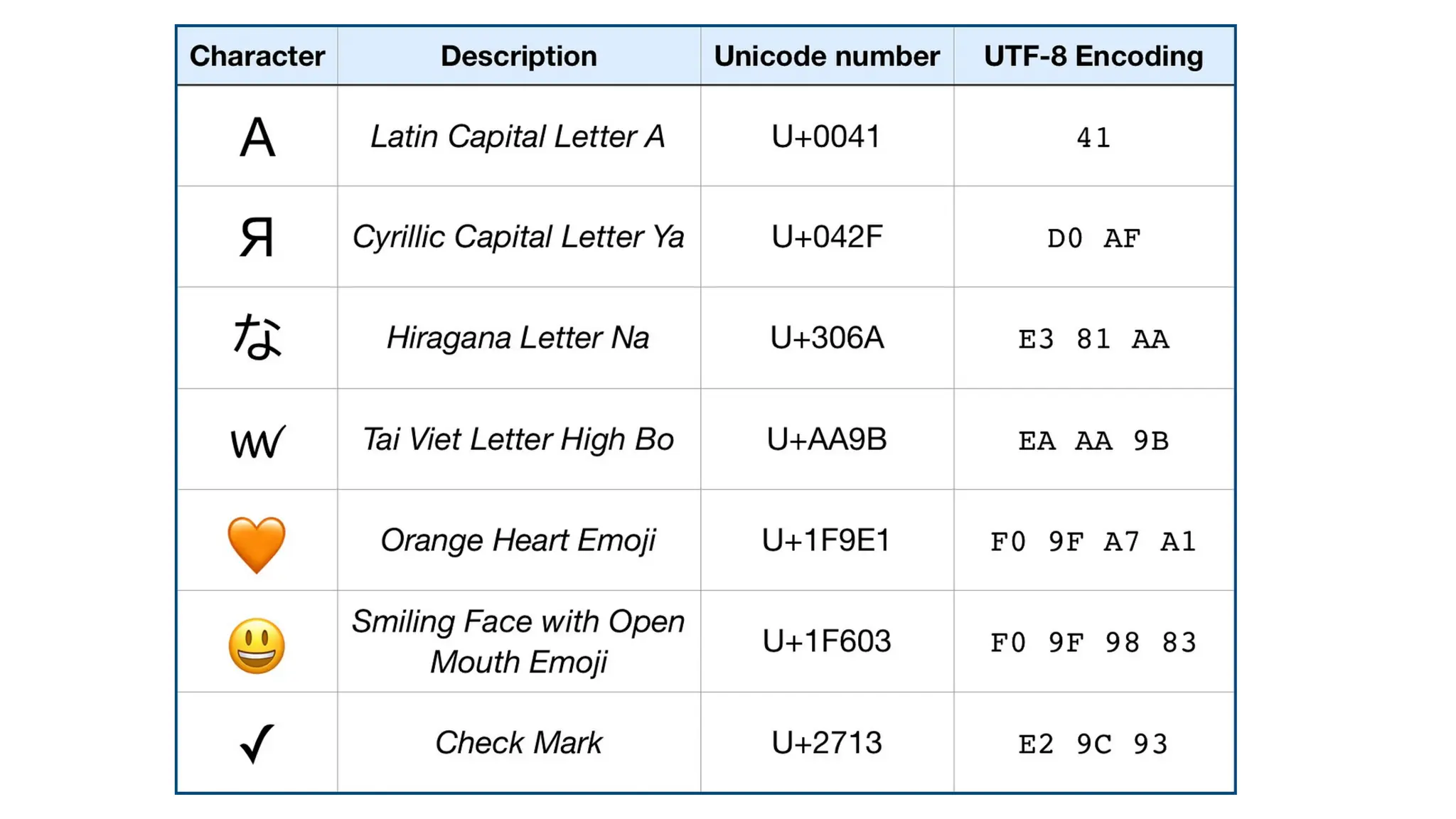
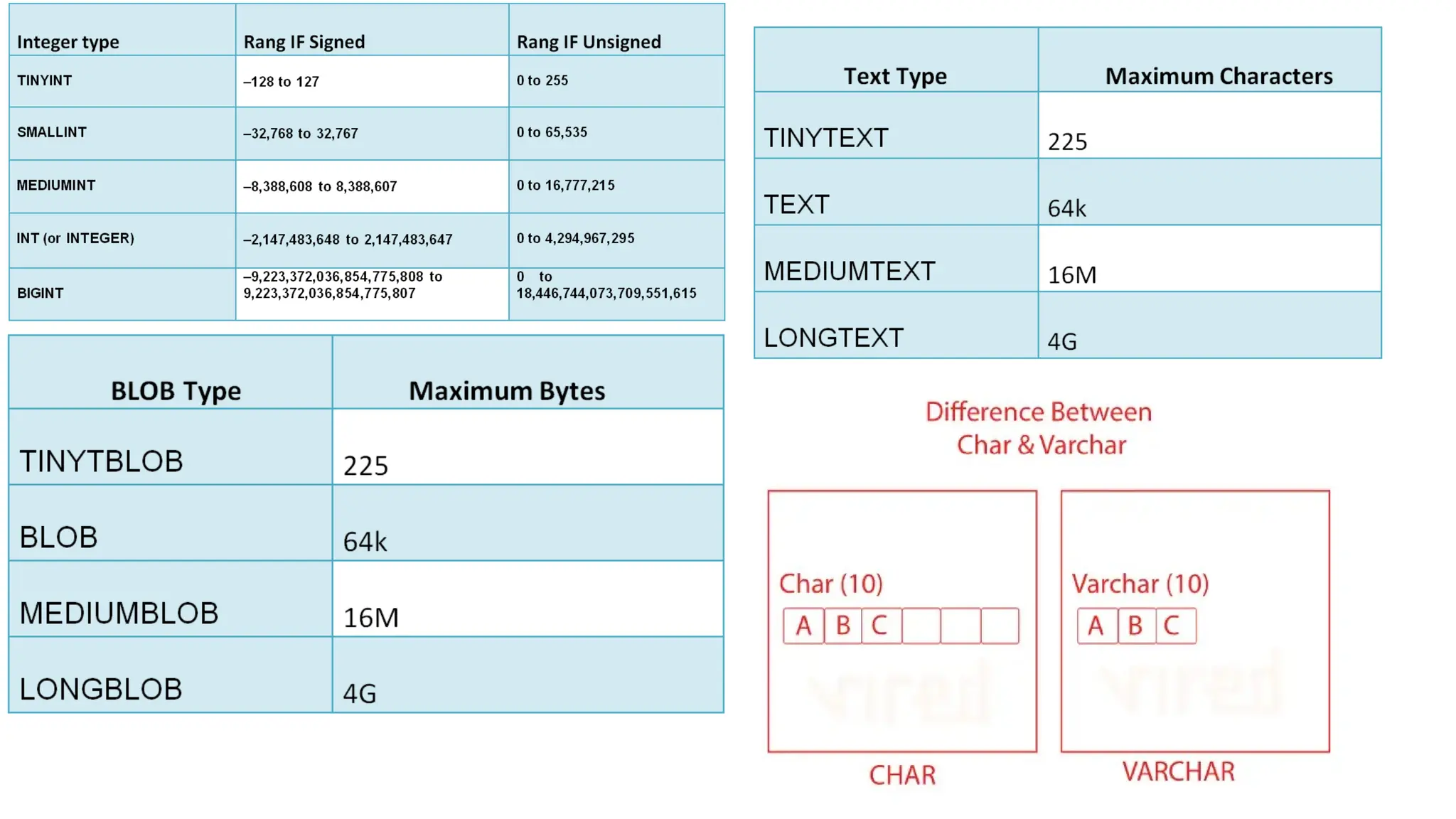
A database is a set of data stored in a computer. This data is usually structured in a way that makes the data easily accessible. A Database is a collection of information that is well organized so that it can be easily accessed ,managed and updated. Database Management system should provide systematics method of 1.Creating Database 2.Updating the database 3.Storing the database 4.Retrieving of data from Database. CREATE DATABASE my_database; Data is a collection of facts, such as numbers, words, measurements, observations or just descriptions of things. Data is any sort of information which is stored in computer memory. This information can later be used for a website, an application or can be used in future. Data can be structured OR unstructured. Structured-Student Name, Address Unstructured-Student Photo,AddrMap If you create a notepad file, then the content of that document is data. It can simply be a piece of information, a list of grocery items, or observations, a story or a description of a certain scenario.A connection is a communication pathway between a user process and an Oracle Database instance. A session represents the state of a current user login to the database instance. For example, when a user starts SQL*Plus, the user must provide a valid username and password, and then a session is established for that user.SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming language used to communicate with data stored in a relational database management system. SQL syntax is similar to the English language, which makes it relatively easy to write, read, and interpret. It’s used to perform data interacting tasks such as: Creating a table and inserting data into it. Querying and filtering data. Modifying and updating data. Delete data or table. NOT NULL: Ensures that a column cannot have a NULL value. UNIQUE: Ensures that all values in a column are unique. PRIMARY KEY: Combines NOT NULL and UNIQUE to uniquely identify each record in a table. FOREIGN KEY: Maintains referential integrity by linking columns in two tables. CHECK: Ensures that all values in a column satisfy a specific condition. DEFAULT: Sets a default value for a column when no value is specified. A primary key is a unique identifier for each record in a table. It ensures uniqueness and non-nullability of the data in a particular column (or a set of columns). No two rows in a table can have the same primary key value. A foreign key is a column or a set of columns in one table that references the primary key of another table. It establishes a relationship between two tables, enforcing referential integrity by linking records across tables. A NULL value represents missing or undefined data.Something being empty, missing, or not applicable.In MySQL, NULL represents missing , unknown, or undefined data. It is not the same as zero (0) or an empty string (''). Comparisons using = or != with NULL return FALSE; instead, use IS NULL or IS NOT NULL and Functions



















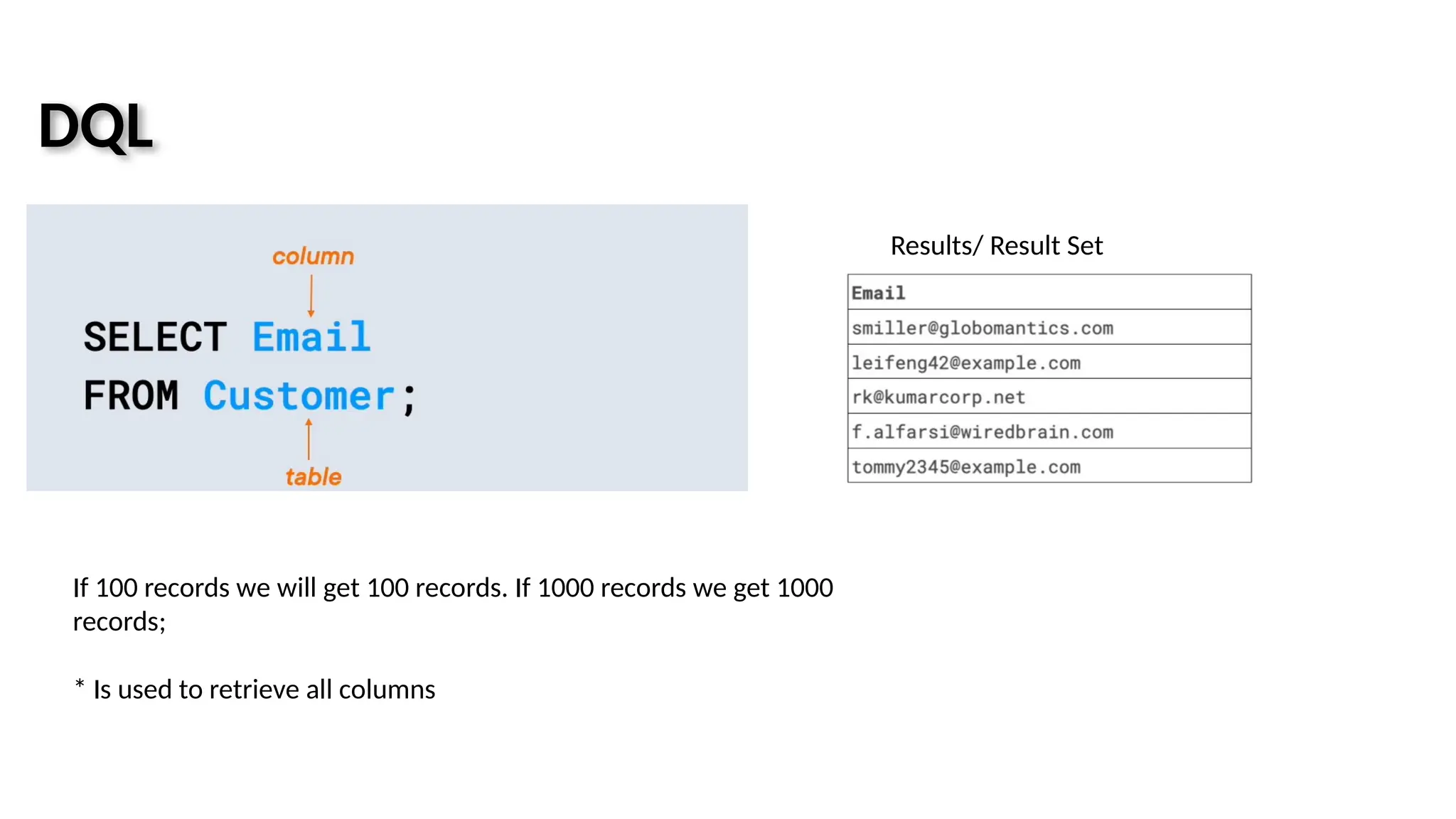
![Query • It is an operation that retrieves data from one or more tables or views • Select statement is used to Retrieves data from one or more tables/views/Mviews. Synatax: SELECT [COLUMNS] FROM [Table_Name] WHERE [Condtions] GROUP BY ORDER BY 1. SELECT * FROM employees; 2. SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary > 10000; 3. SELECT * FROM employees WHERE job_id = 'IT_ROG';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-251107164540-66f989a1/75/SQL-pptx-Data-Types-Database-Operations-Types-38-2048.jpg)
![SQL Aliases • SQL aliases are used to give a table, or a column in a table, a temporary name. • Aliases are often used to make column names more readable. • An alias only exists for the duration of that query. • An alias is created with the AS keyword. • SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name; • SELECT column_name AS ”new name” FROM table_name; • select * from dual; • select 'My Name is Adam' as "Output" from dual; • select 'I''m using quote operator in SQL statements' as "Output" from dual; • select q'[I'm using quote operator in SQL statements]' as "Quote Operator" from dual; • select q'<I'm using quote operator in SQL >' as "Quote Operator" from dual; • select q'dI'm using quote operator in statementsd' as "Quote Operator" from dual;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-251107164540-66f989a1/75/SQL-pptx-Data-Types-Database-Operations-Types-39-2048.jpg)