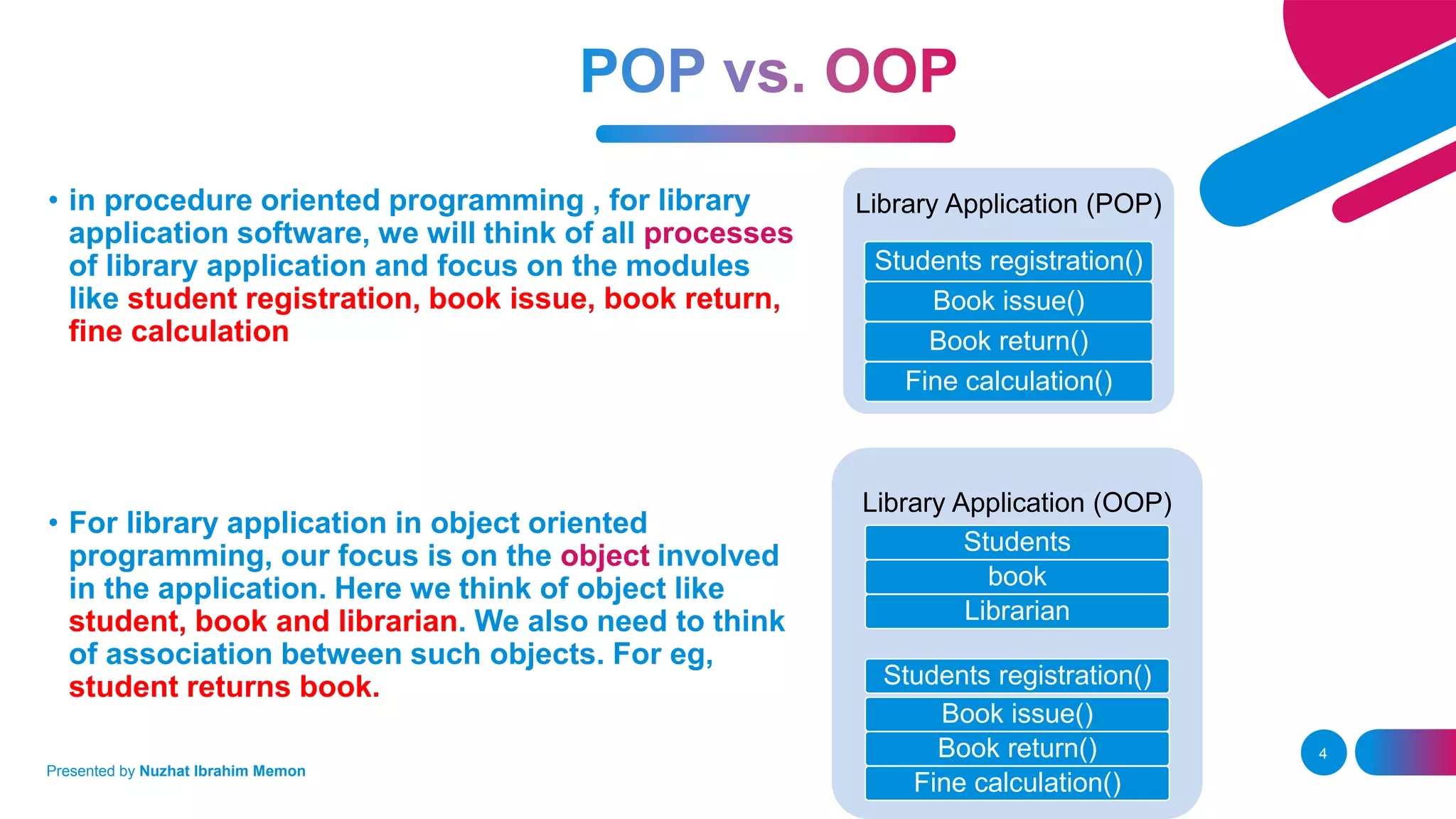
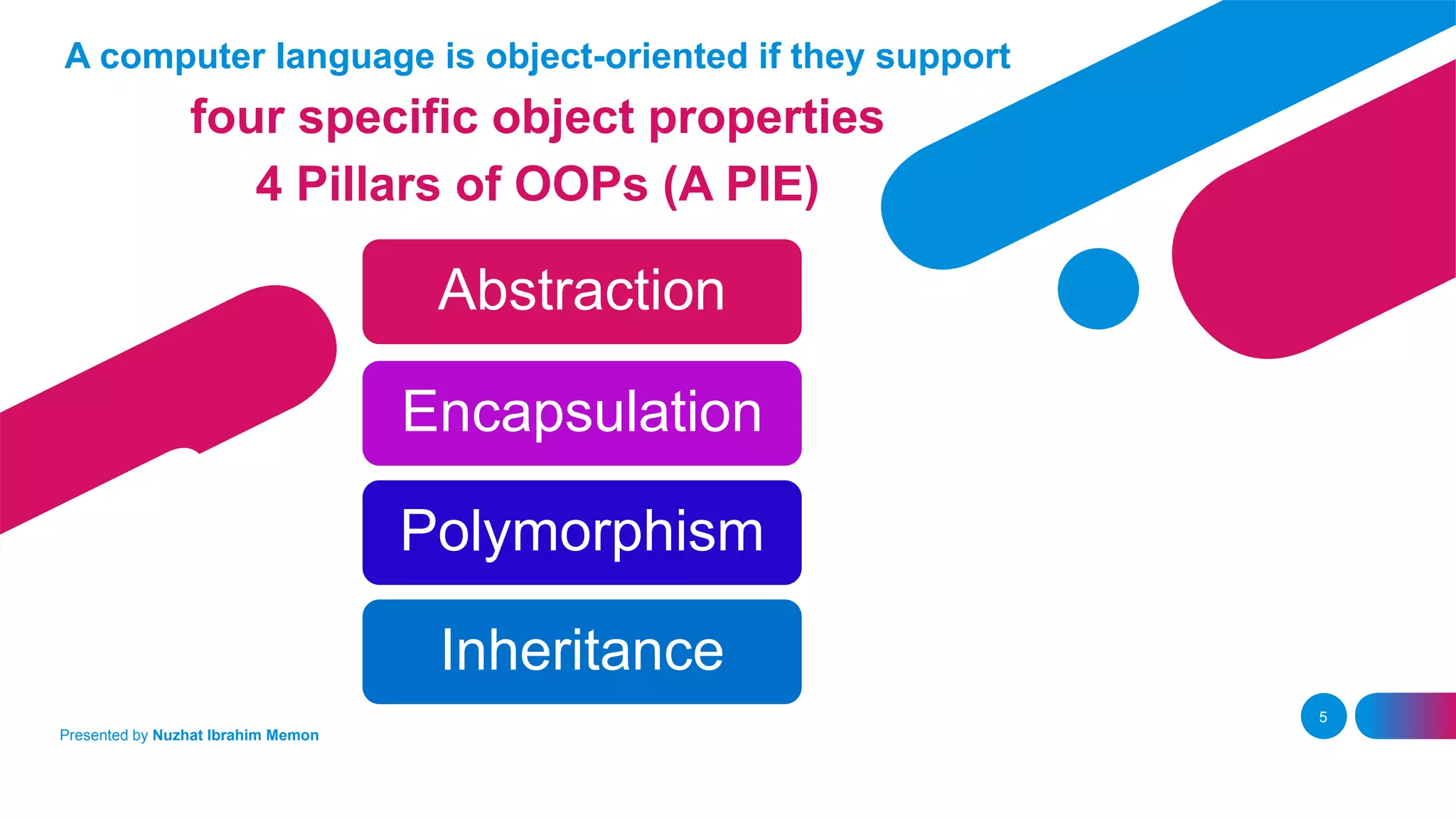
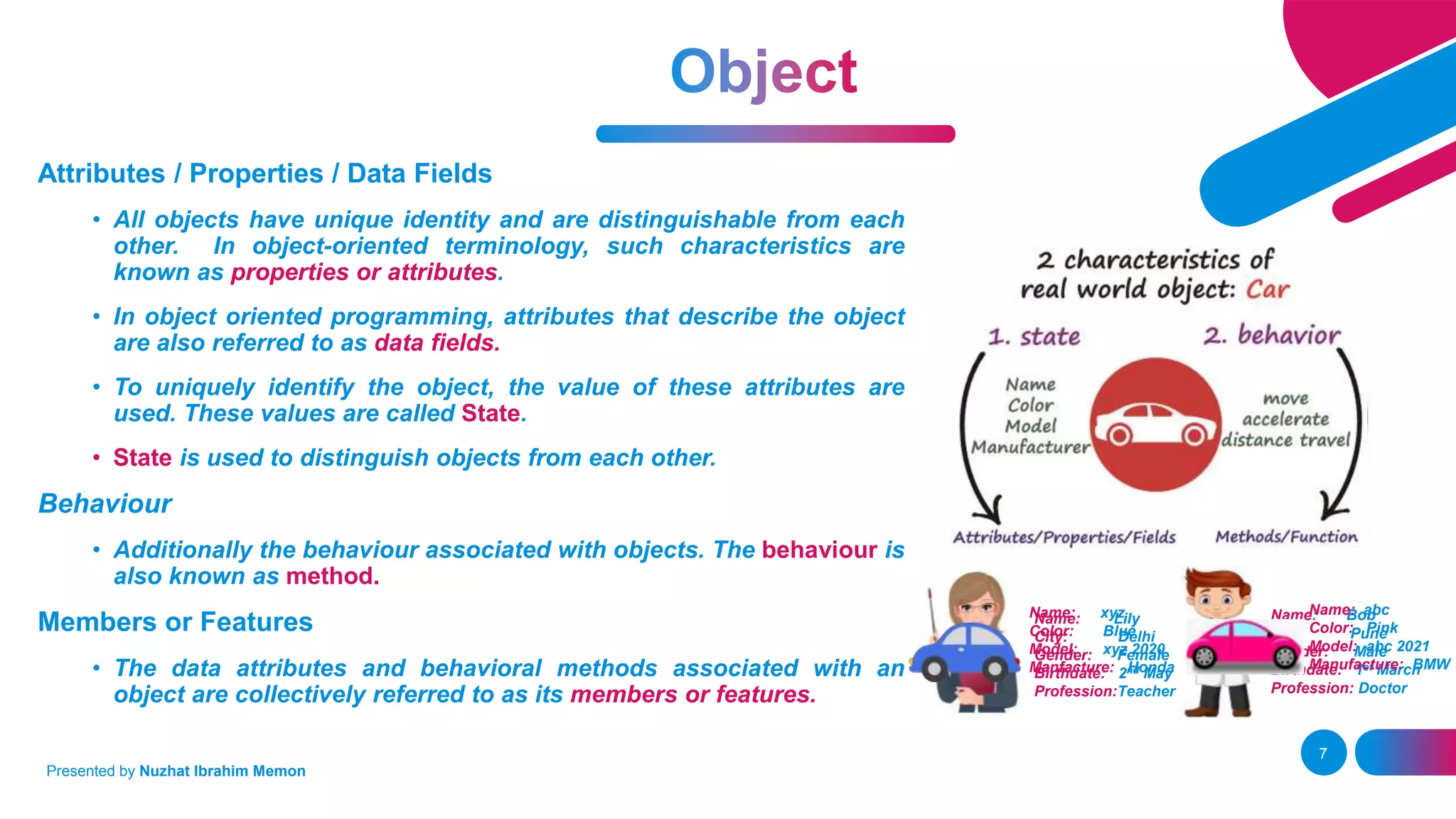
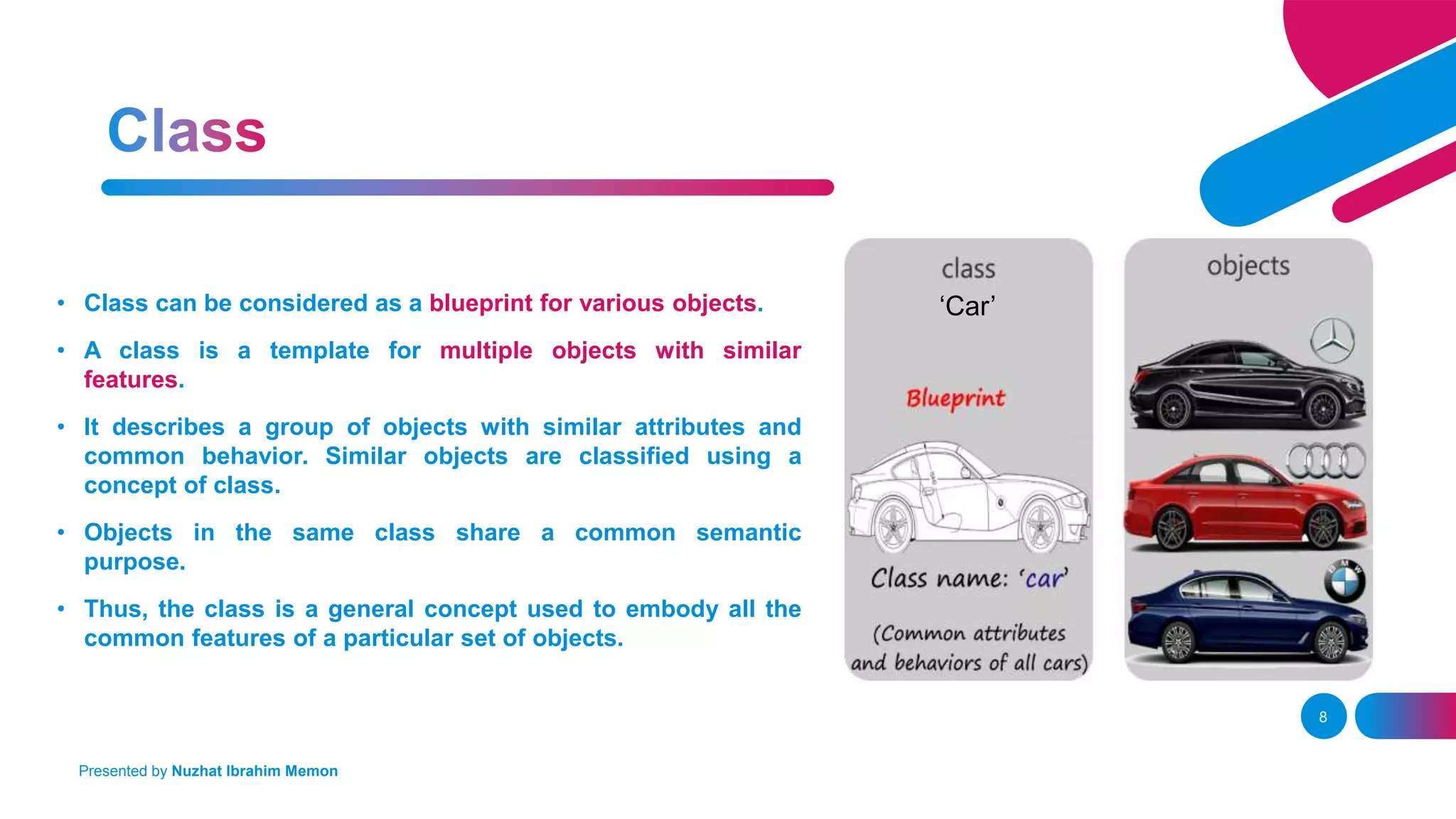
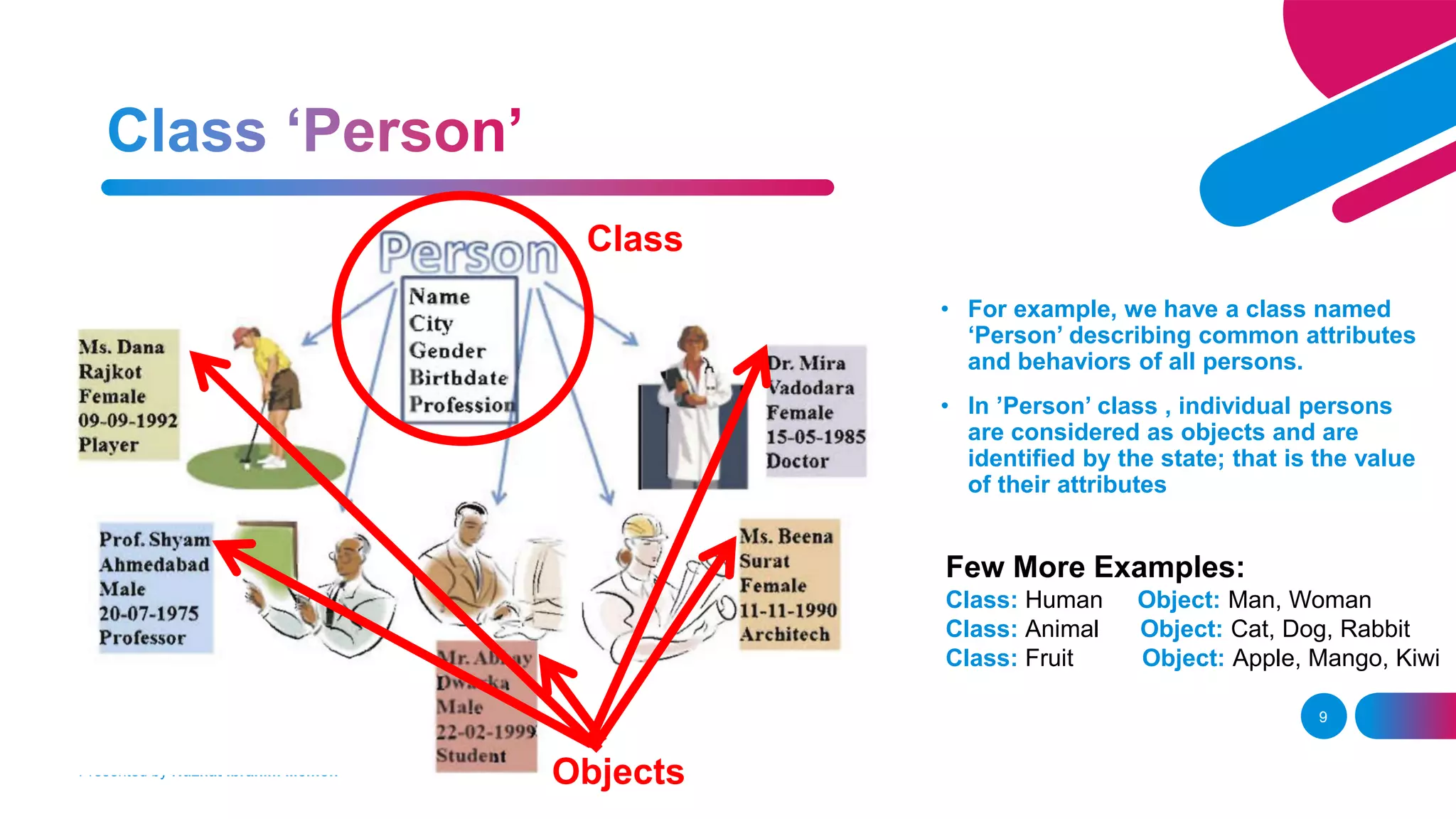
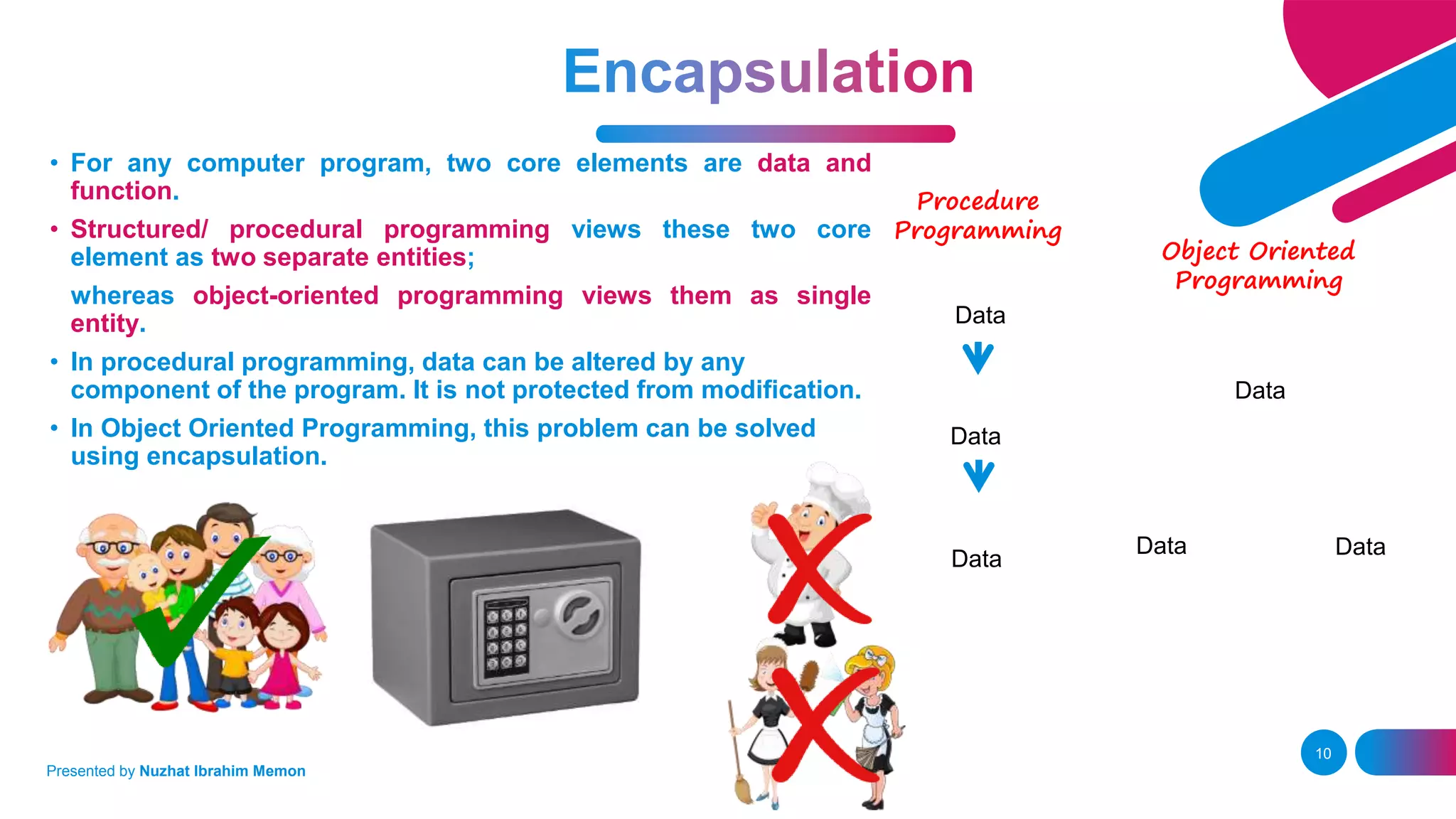
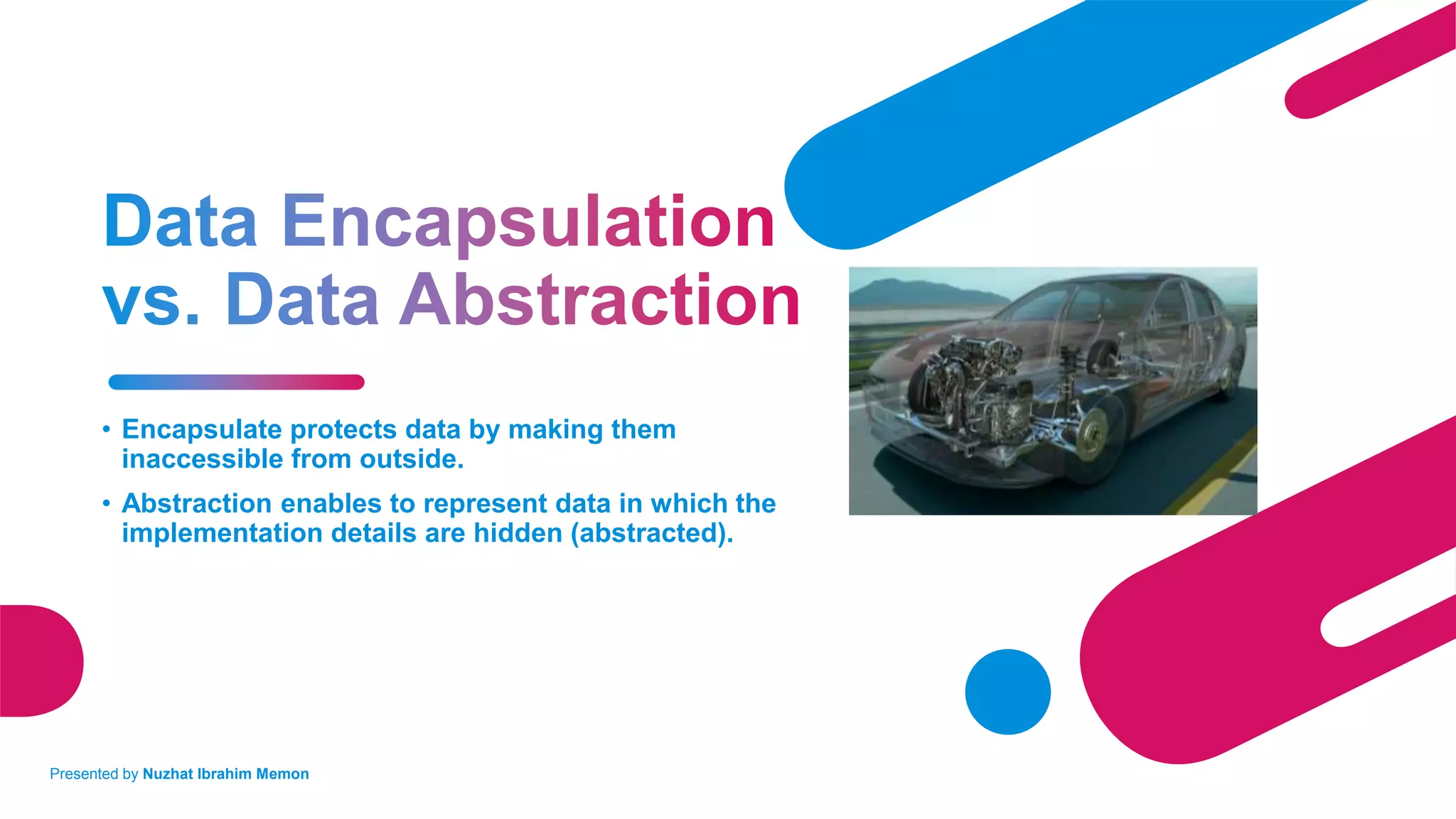
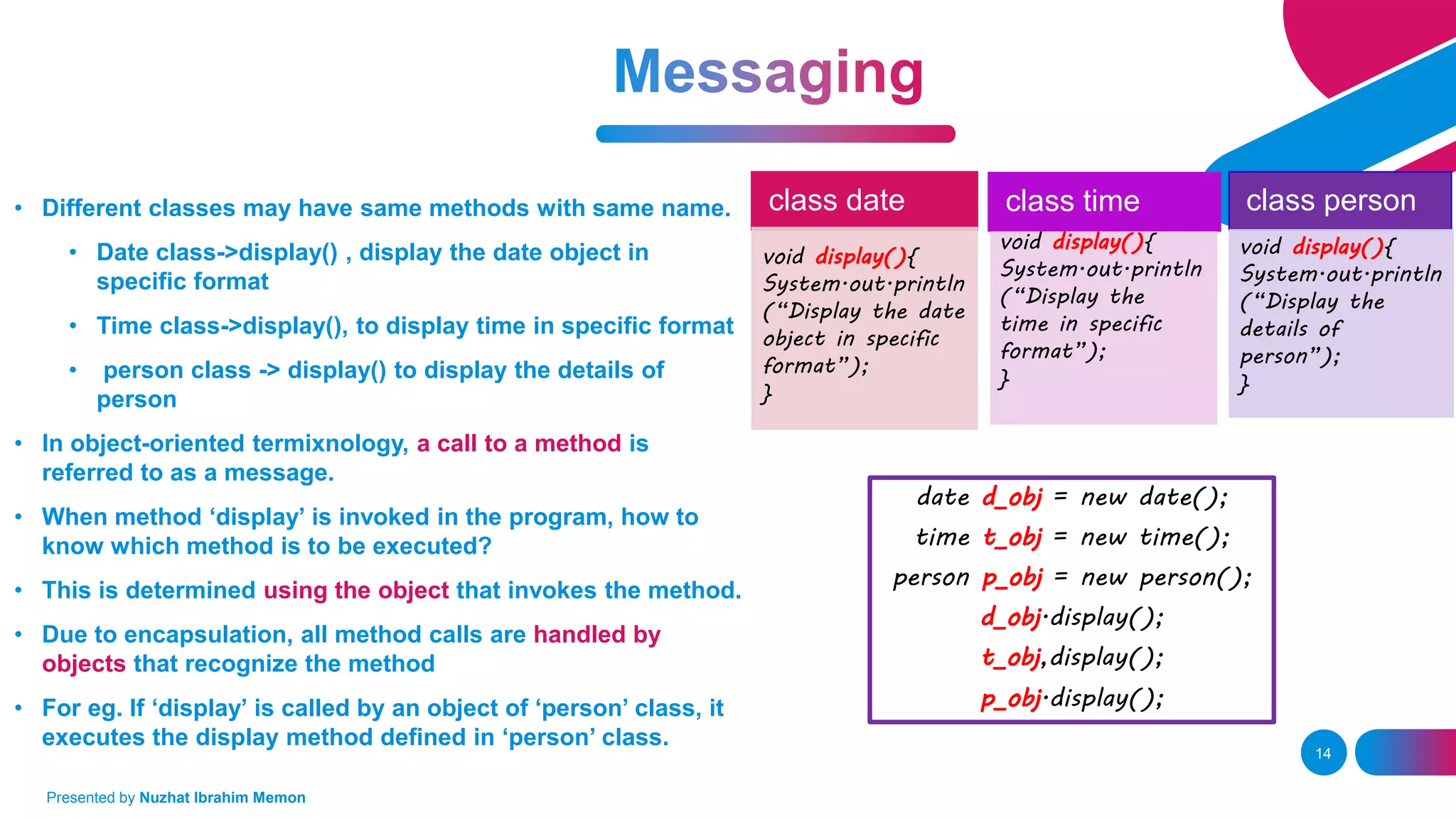
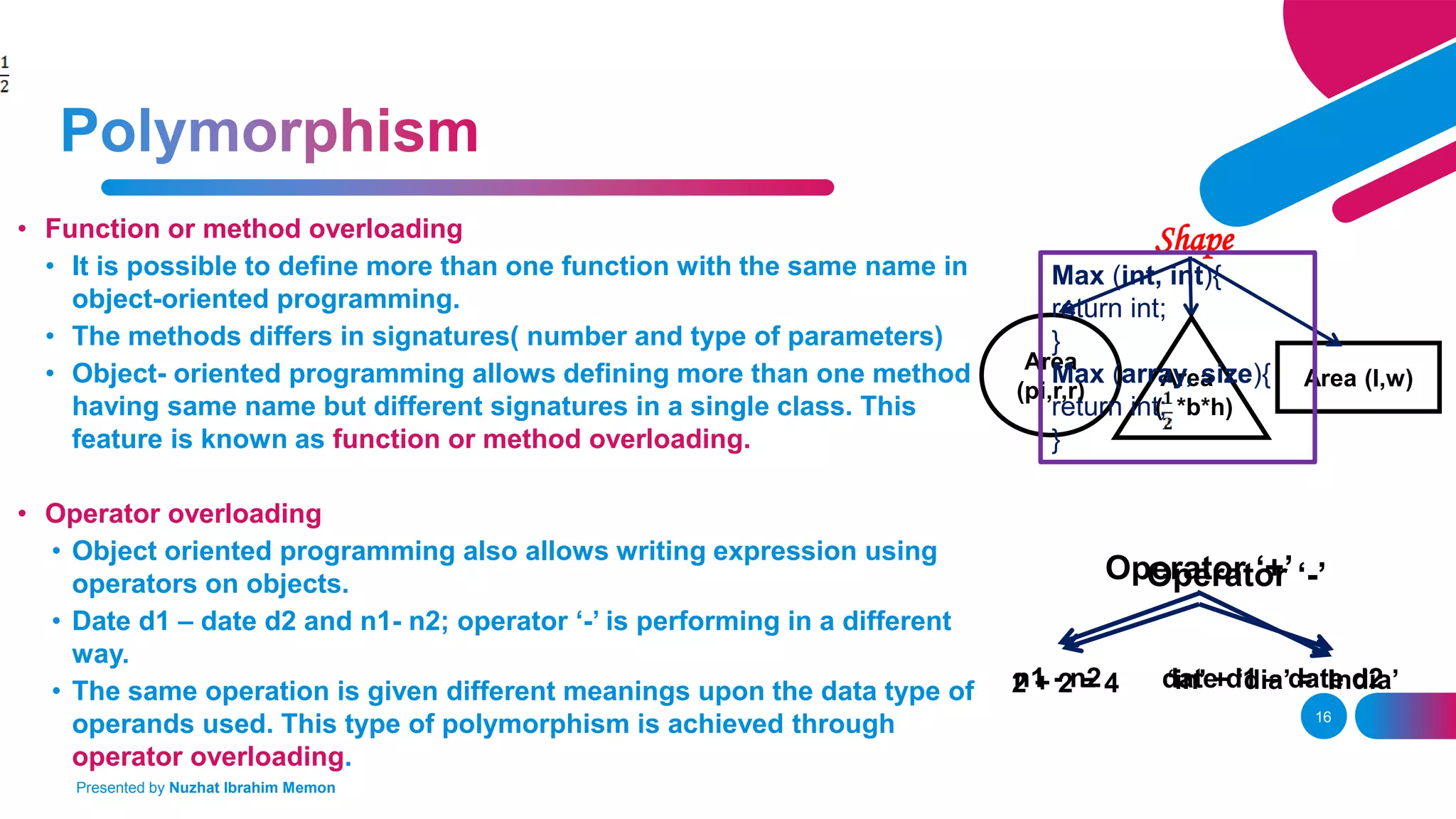
The document presents an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) and its fundamental concepts, including encapsulation, abstraction, polymorphism, and inheritance. It explains how OOP enables the development of reliable, maintainable software by organizing data and methods into classes and objects, contrasting this approach with procedural programming. The document also discusses the significance of OOP in modern software development and lists popular programming languages that support these paradigms.