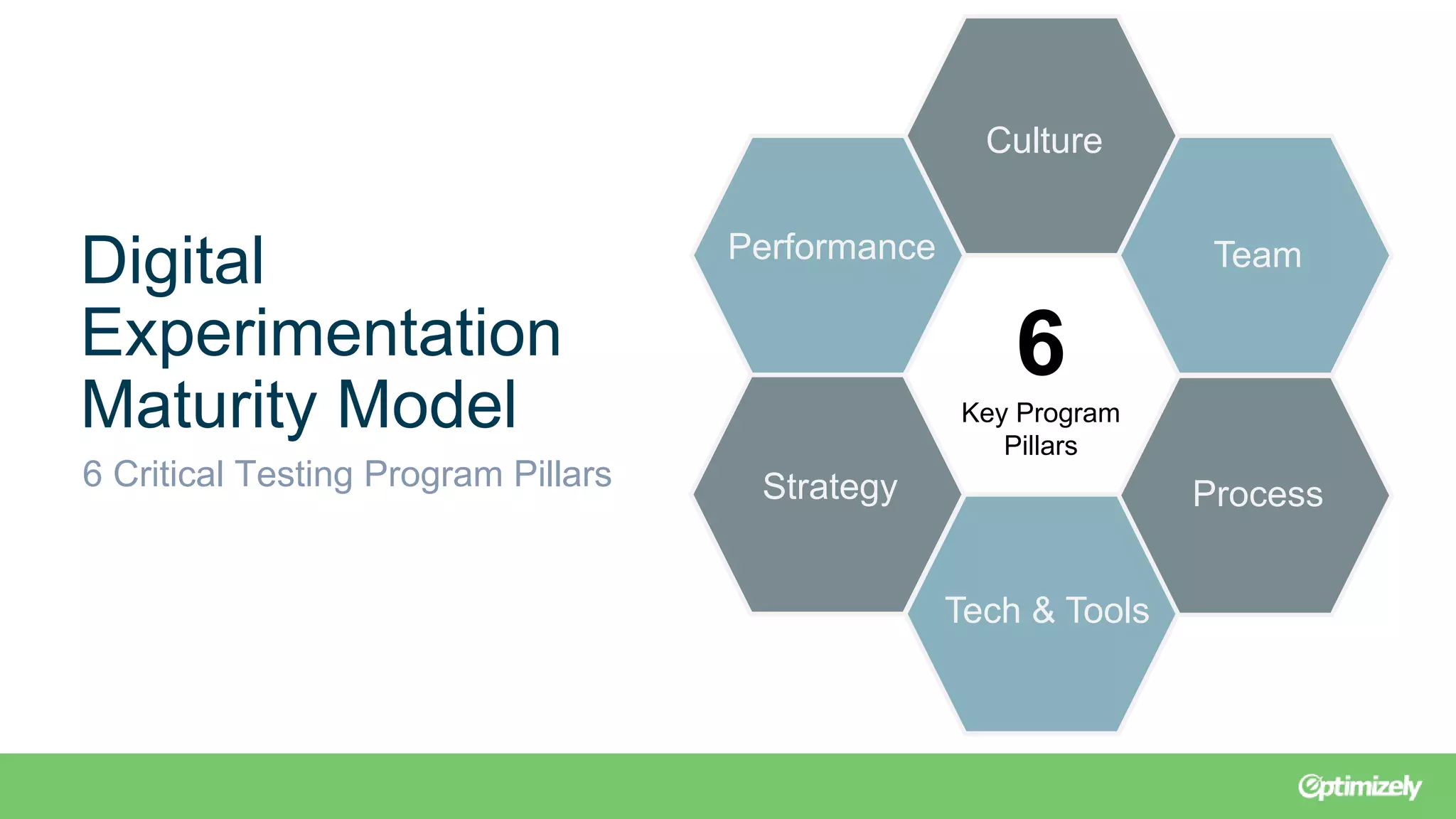
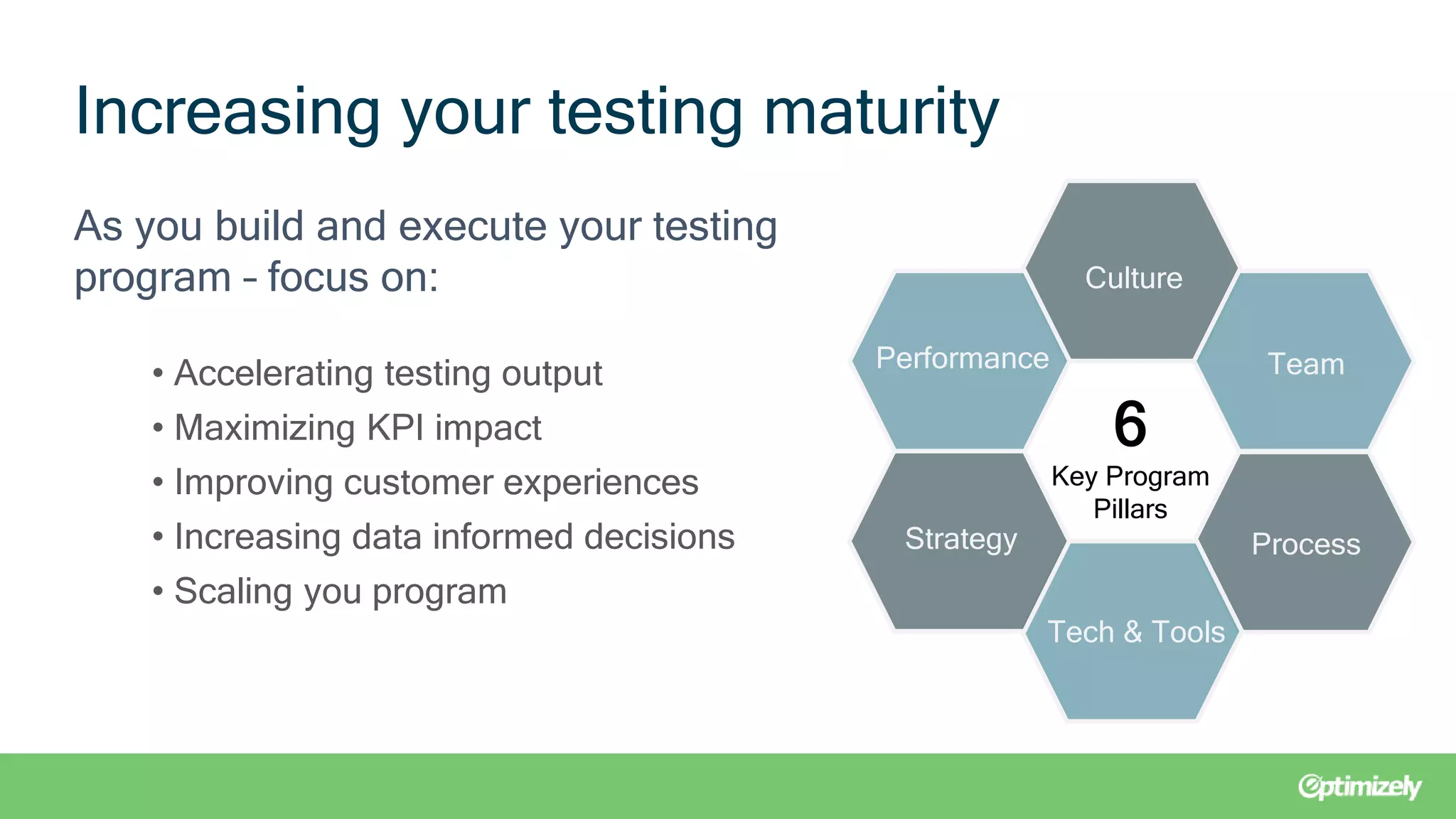
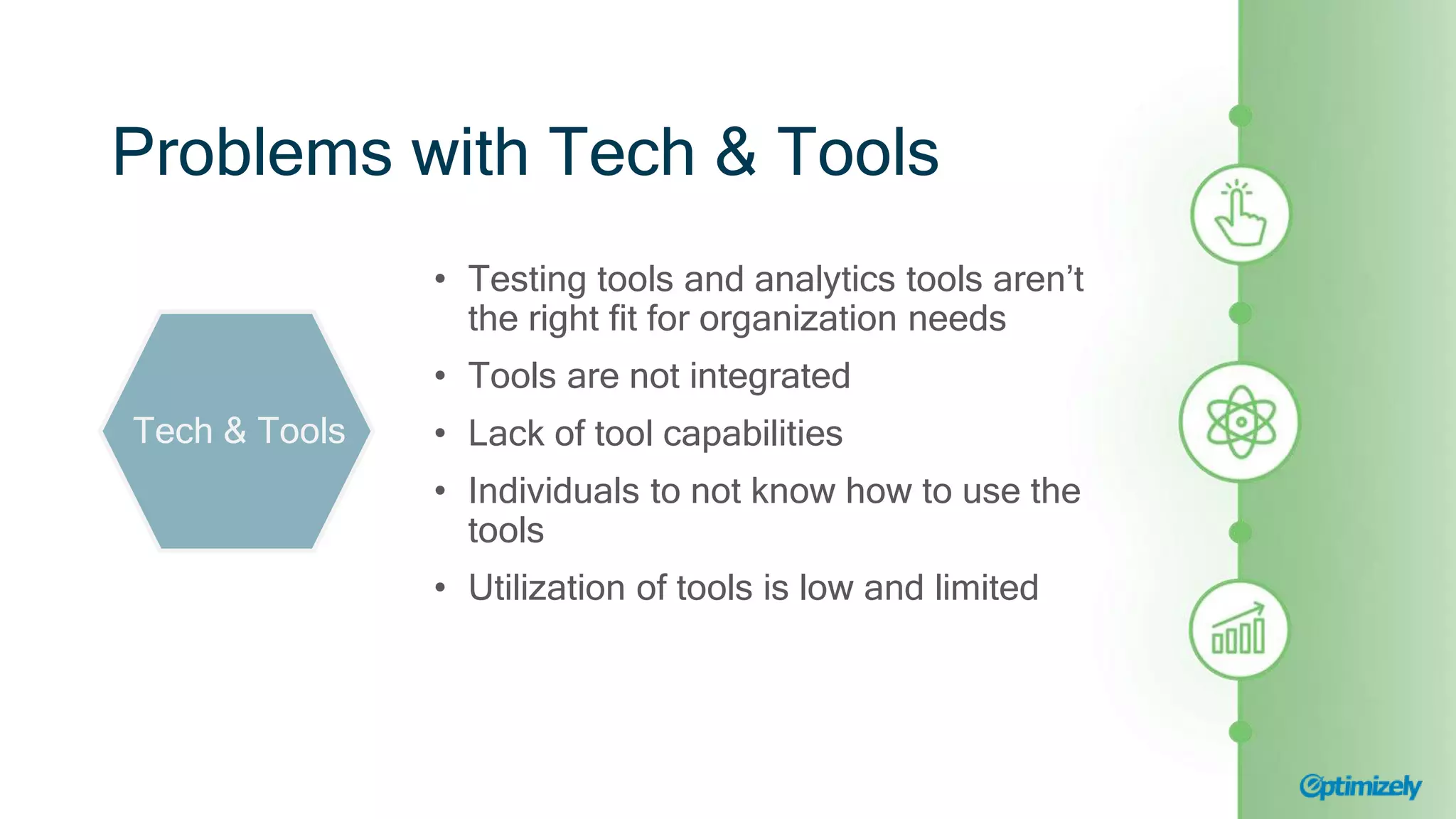
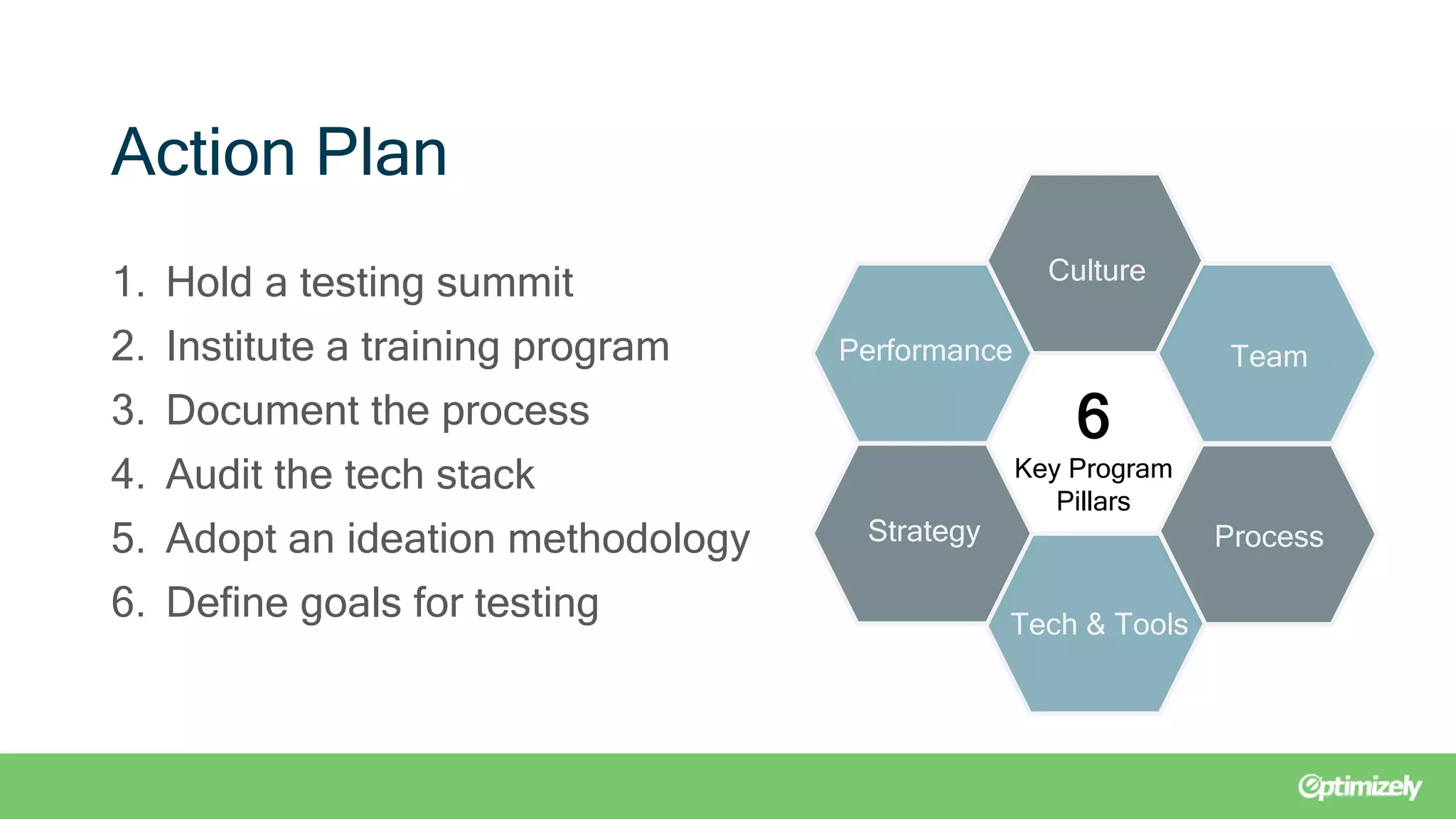
The document outlines a webinar presented by experts from Brooks Bell on maximizing testing programs through the Brooks Bell maturity model, which identifies six critical pillars: culture, team, process, tech & tools, strategy, and performance. It discusses common challenges within each pillar and offers solutions such as organizing training programs, documenting processes, and redefining goals to enhance testing maturity. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of continuous assessment to foster effective growth strategies in digital experimentation.