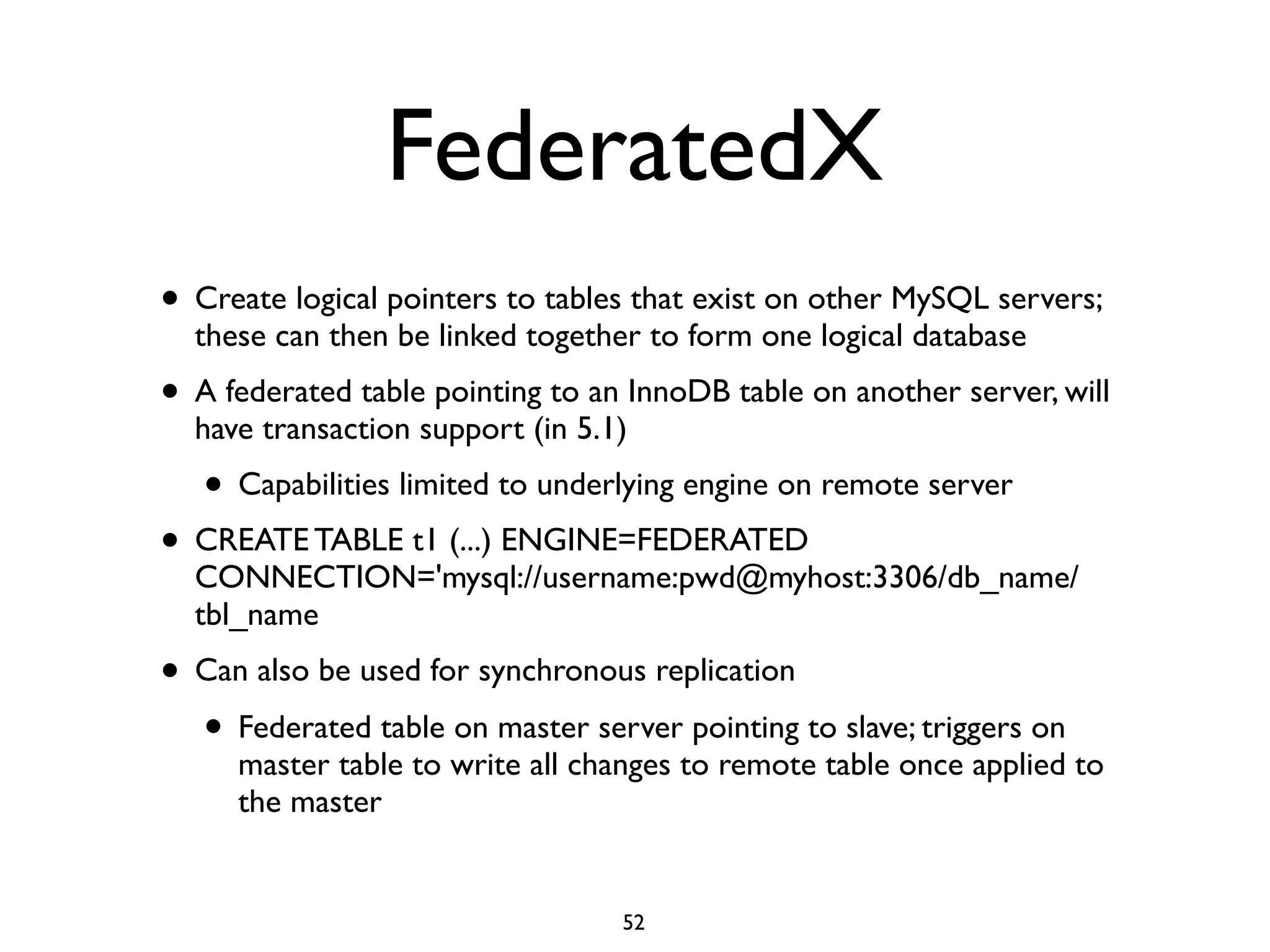
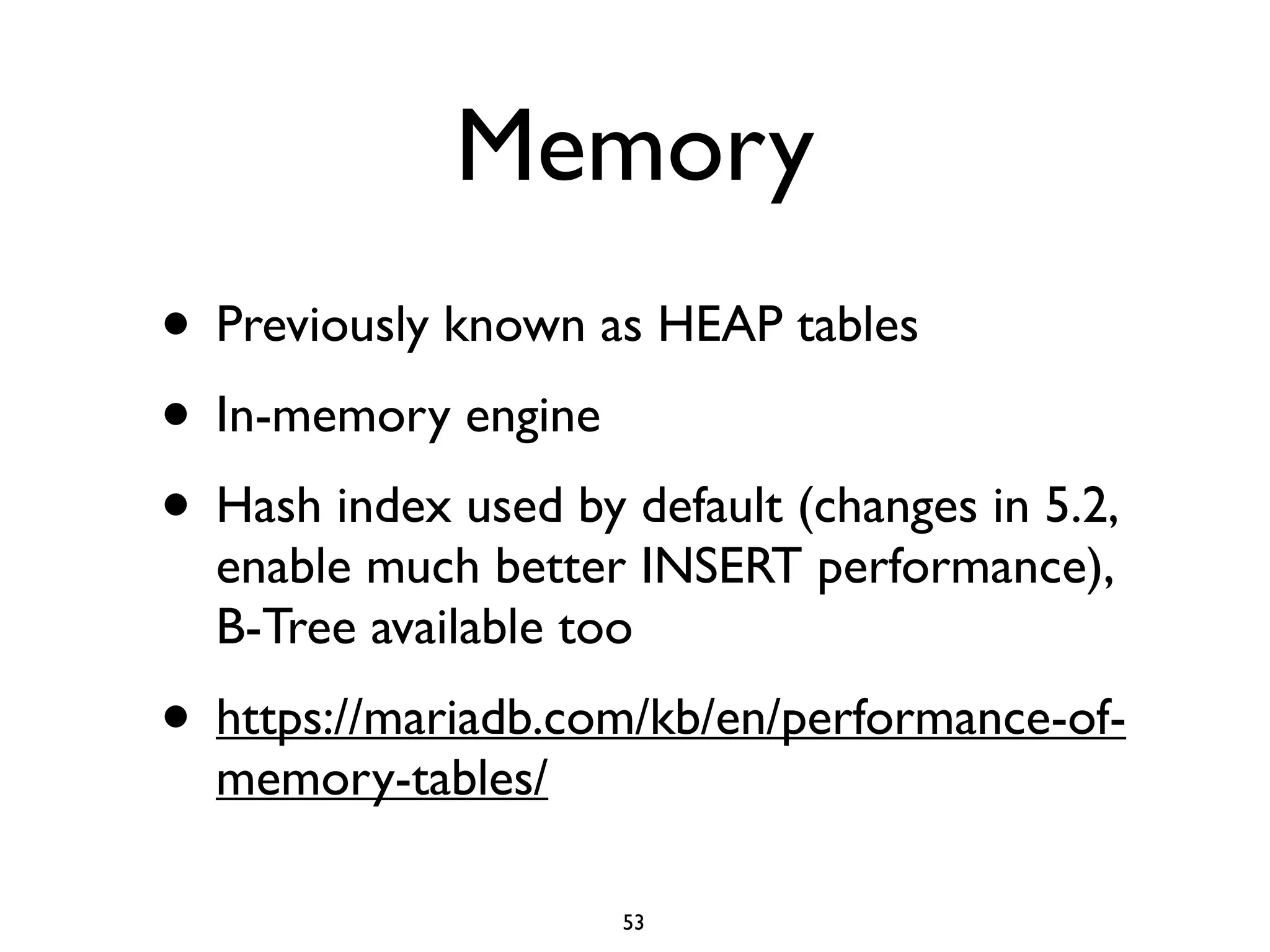
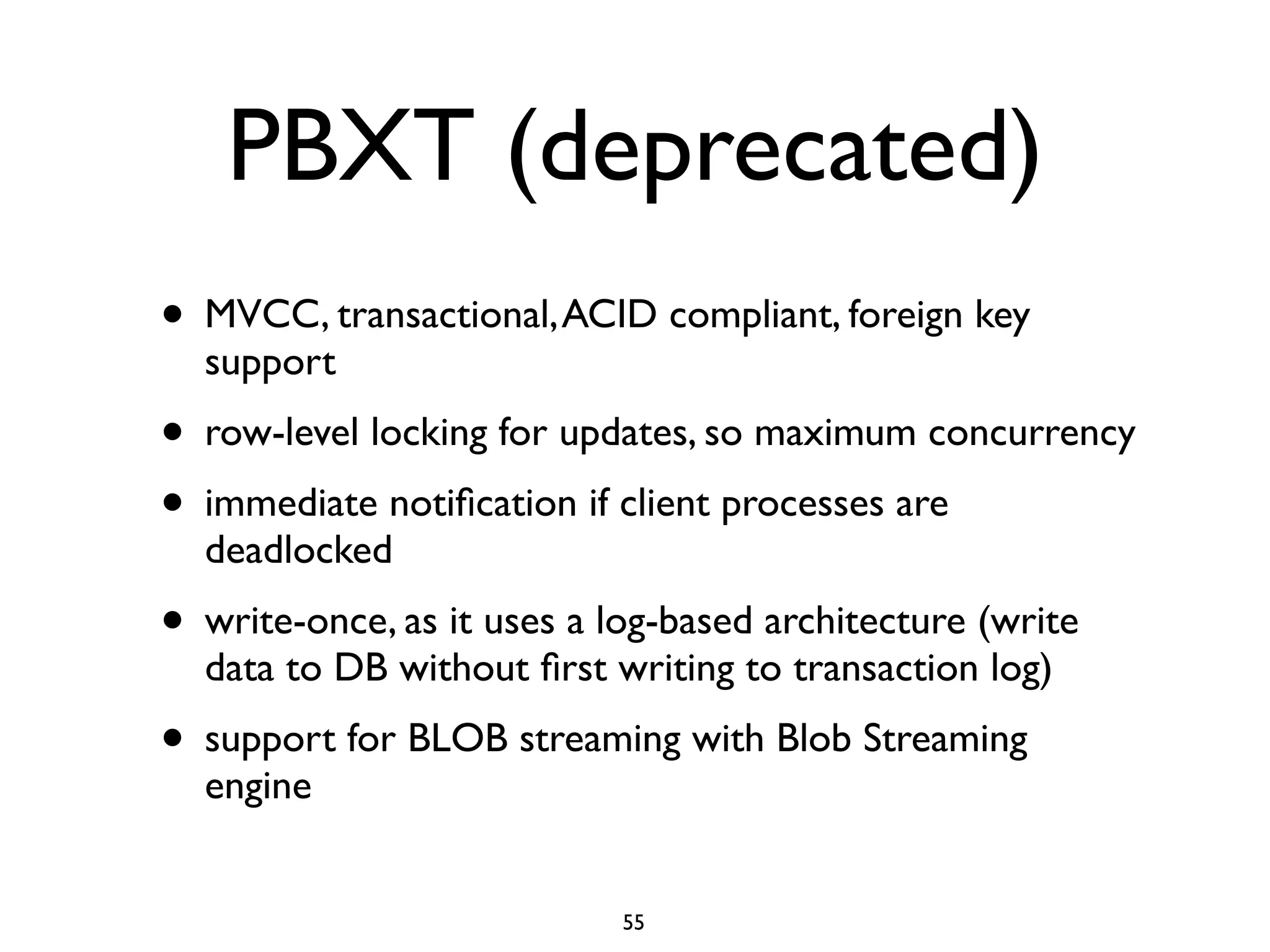
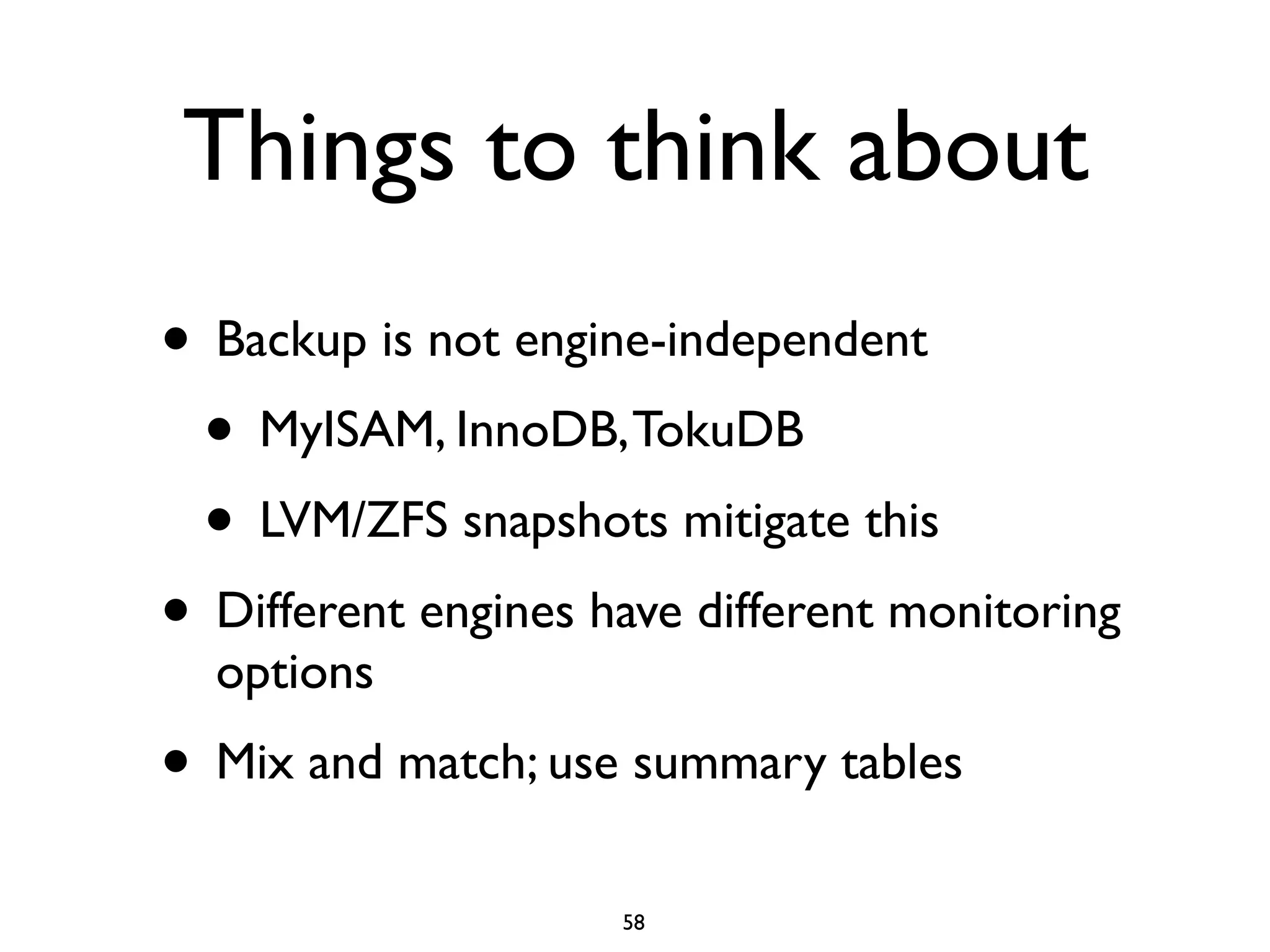
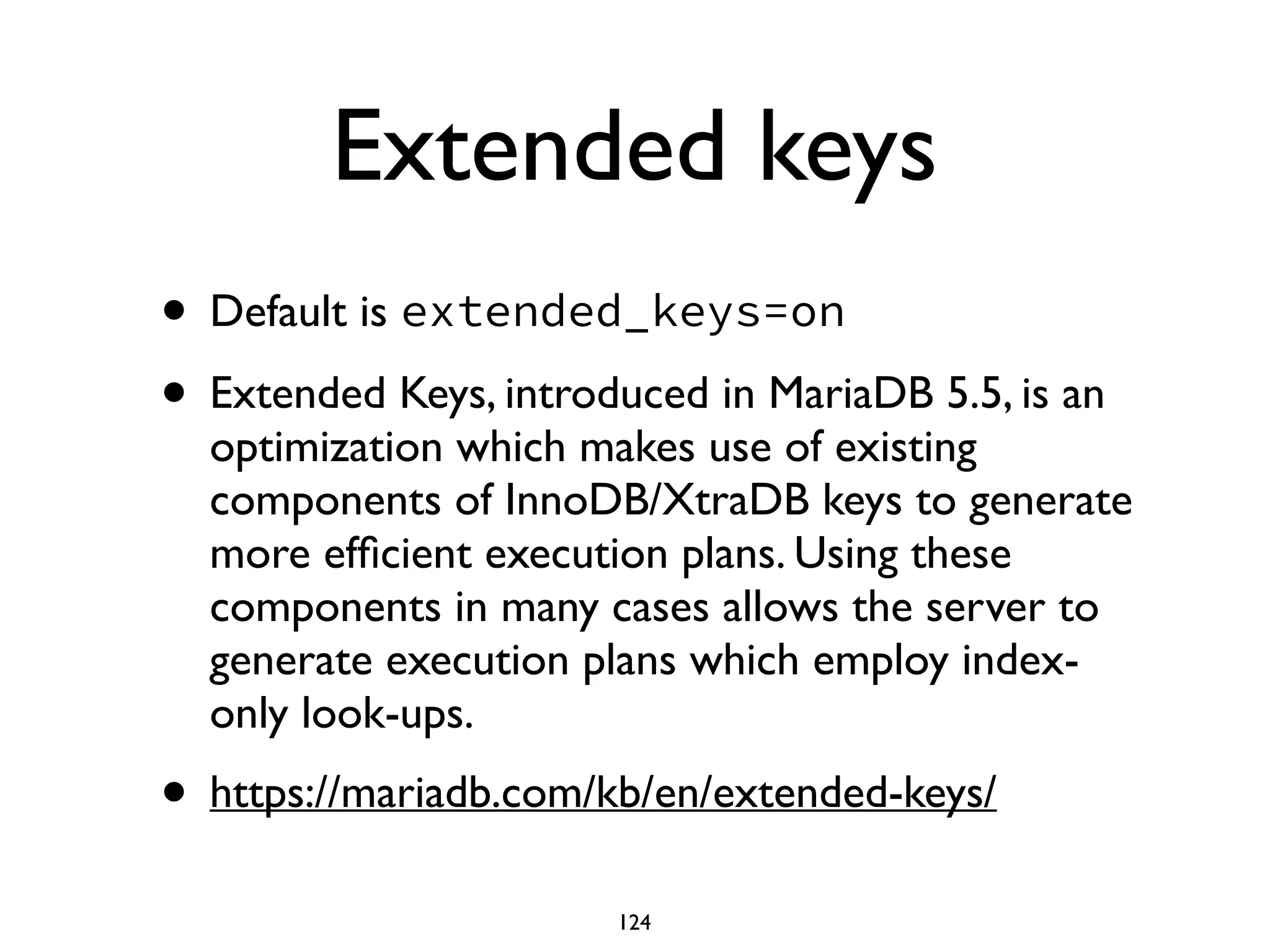
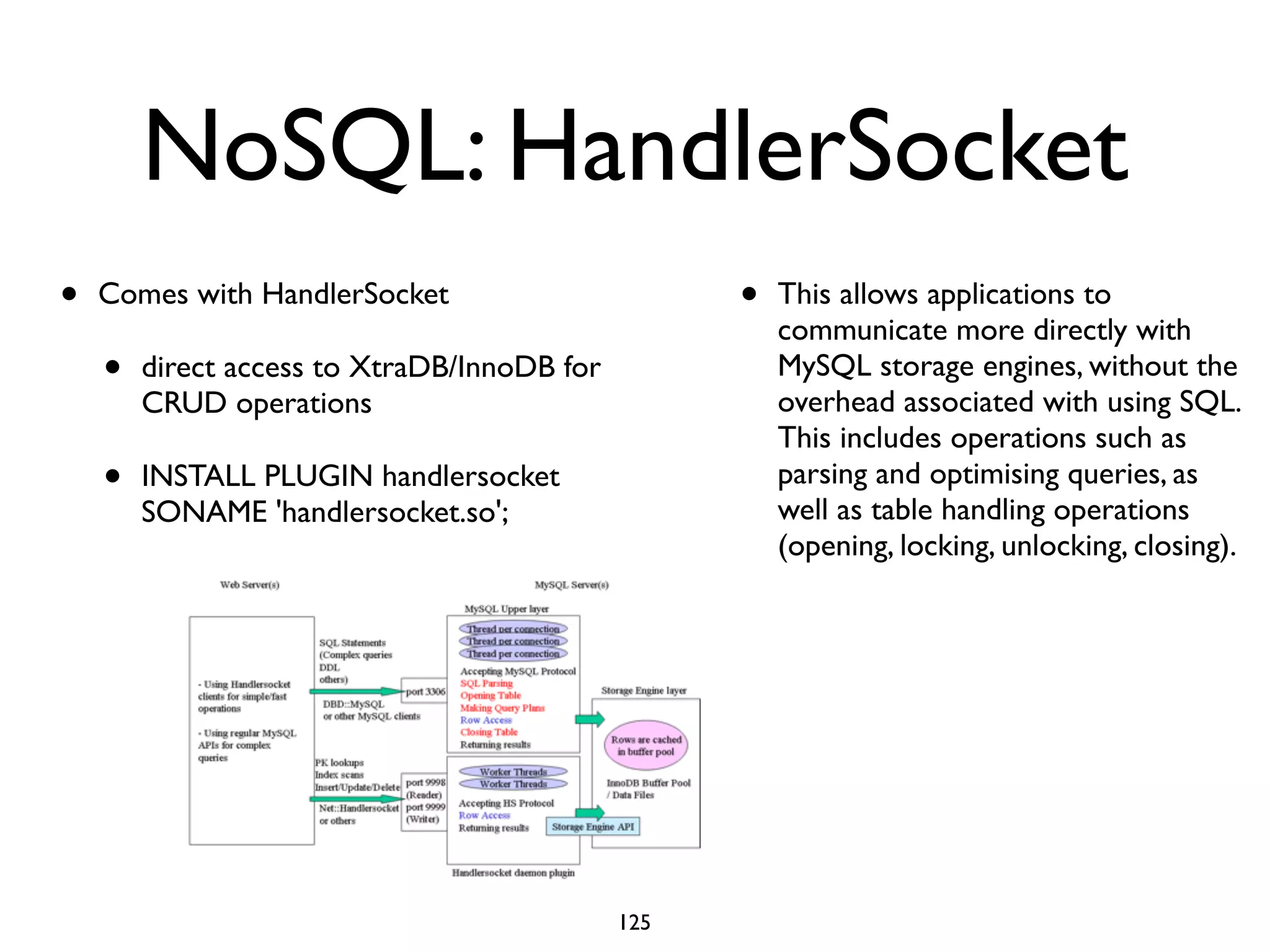
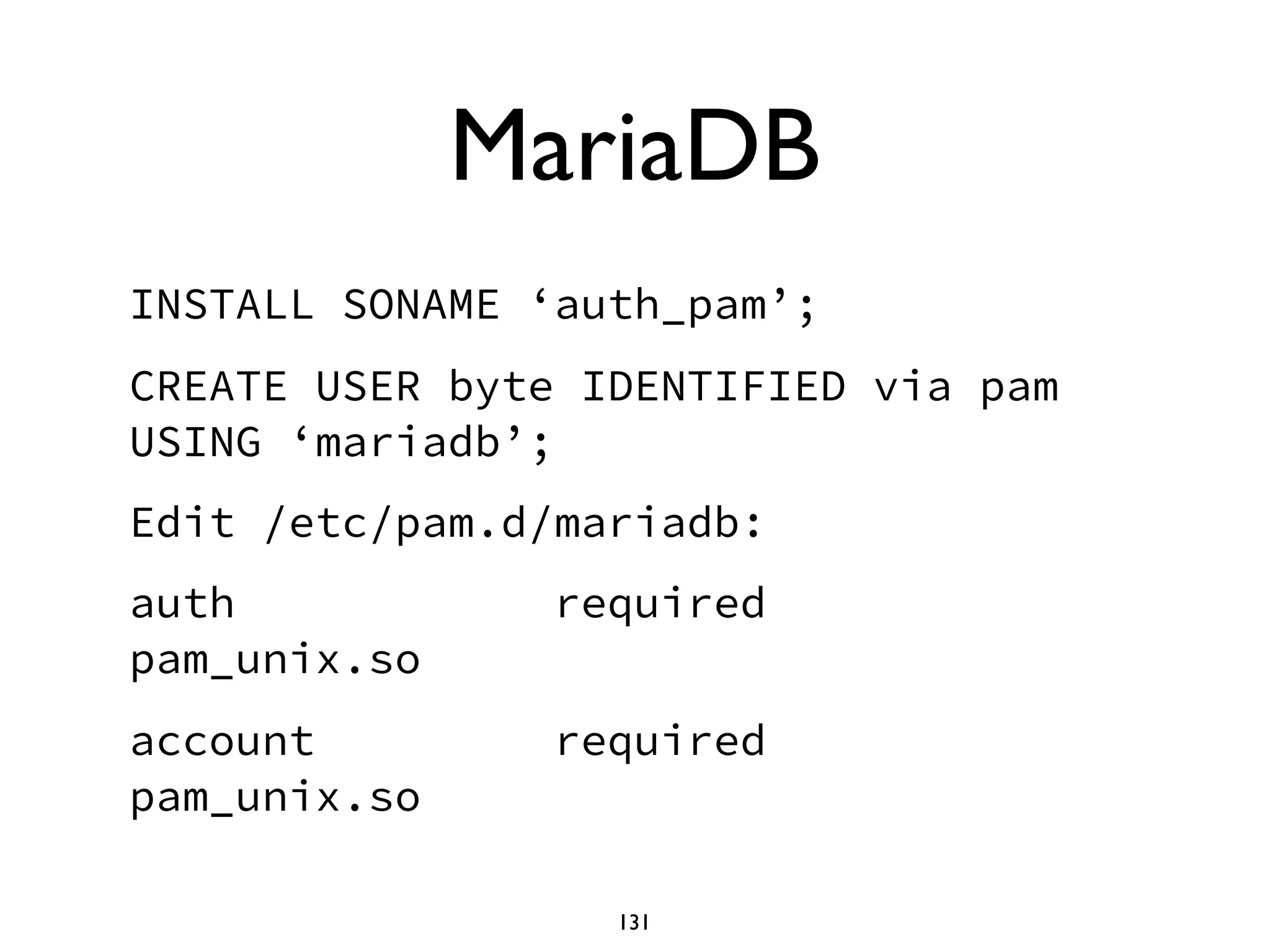
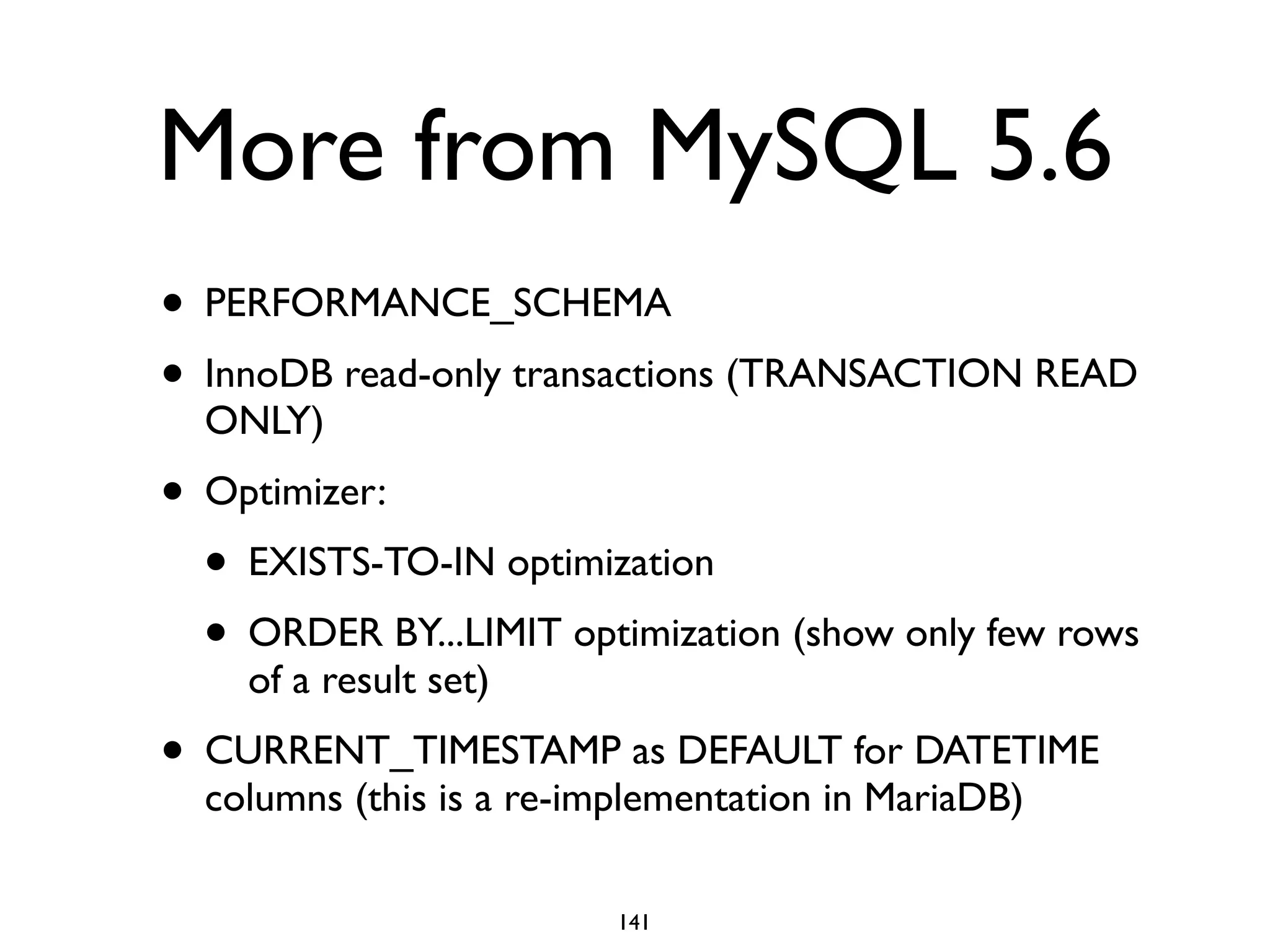
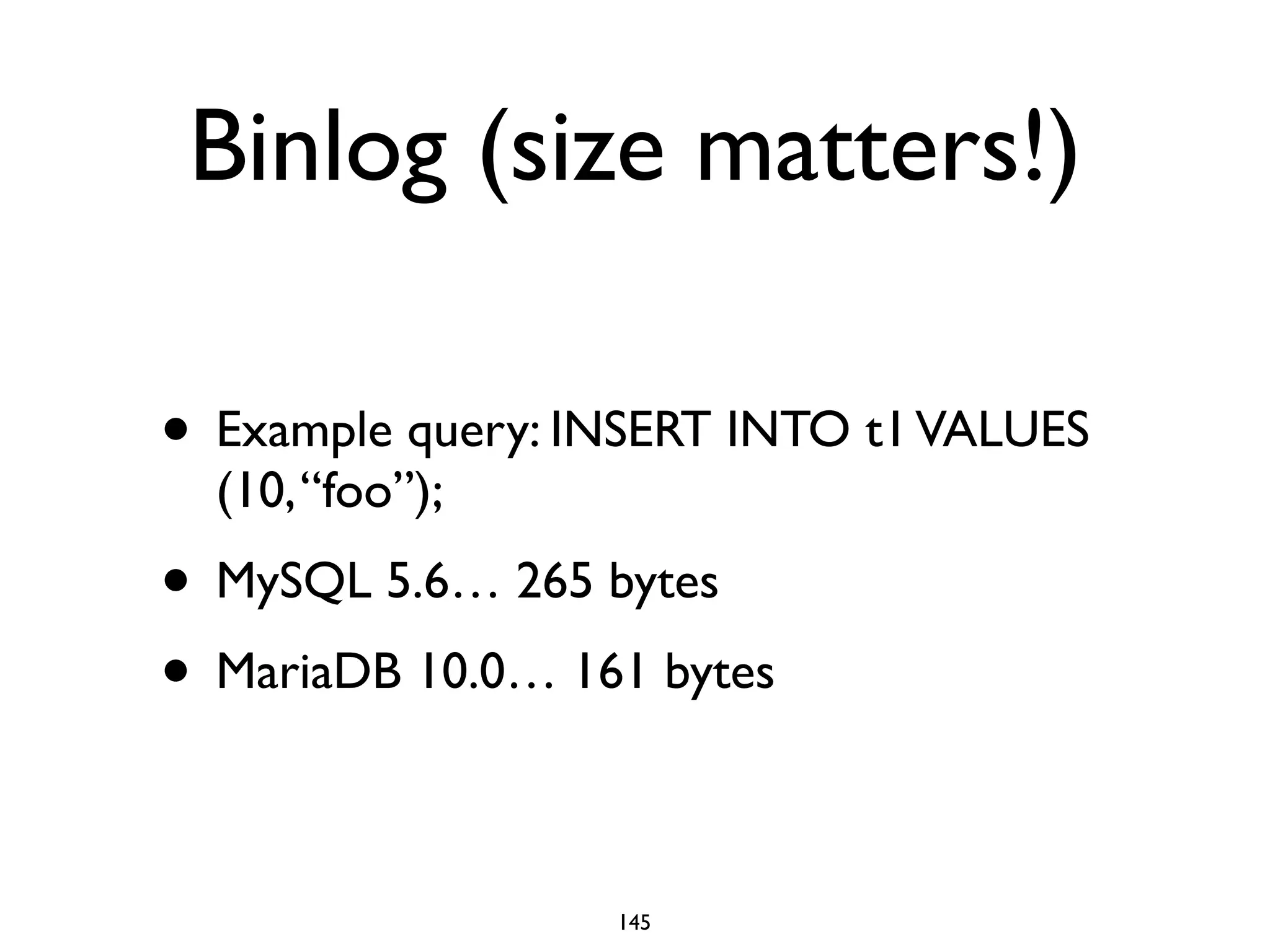
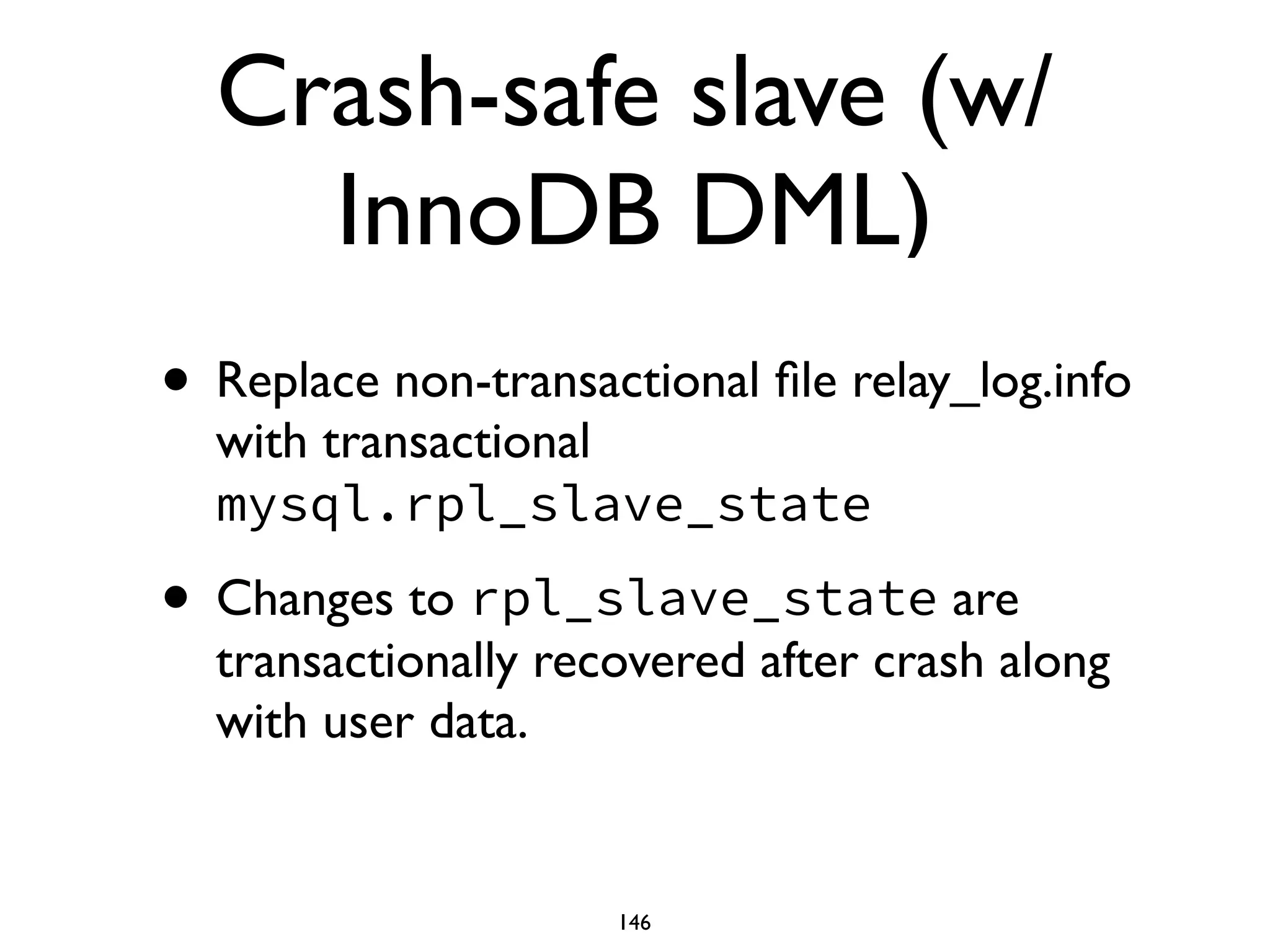
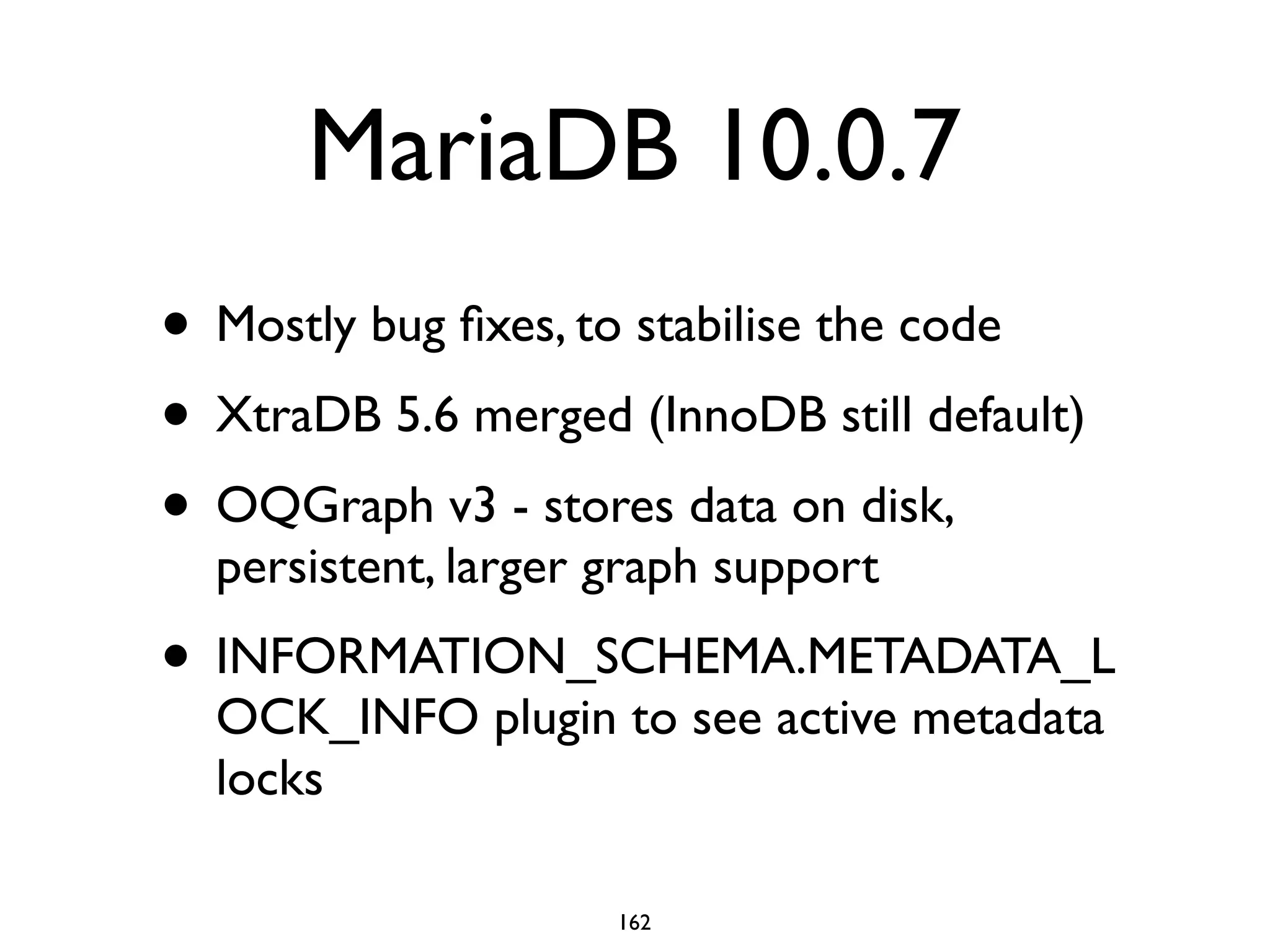
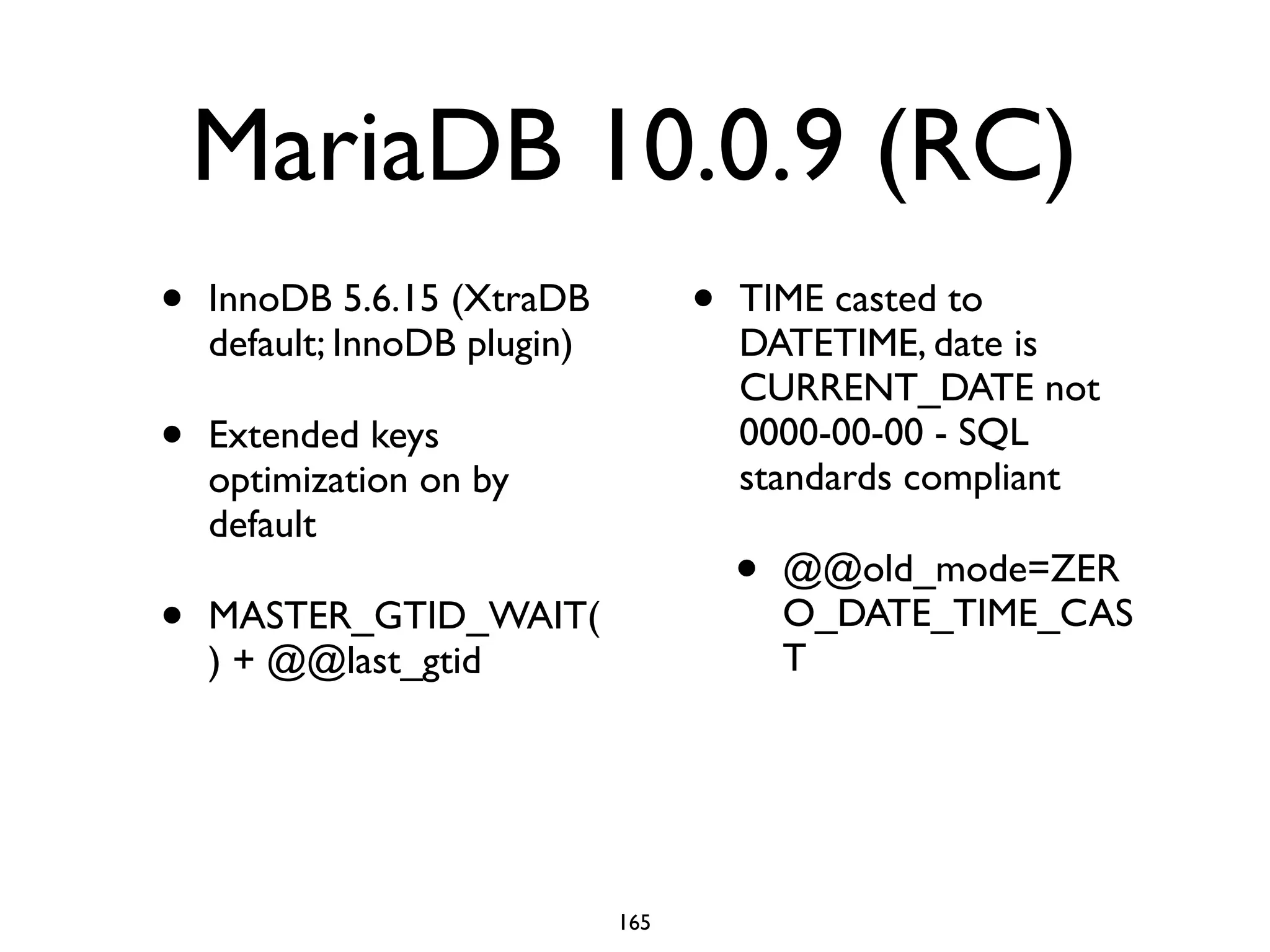
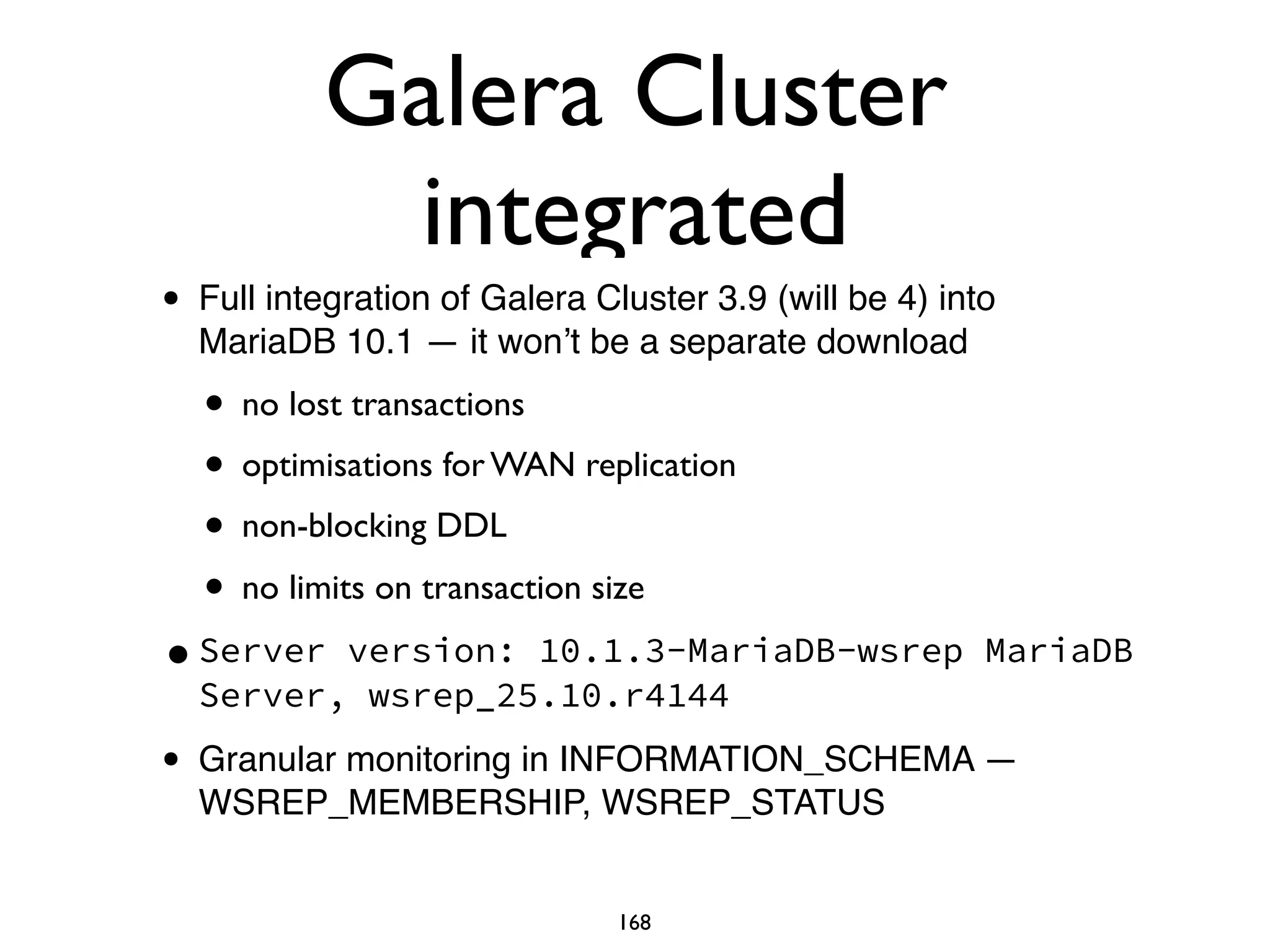
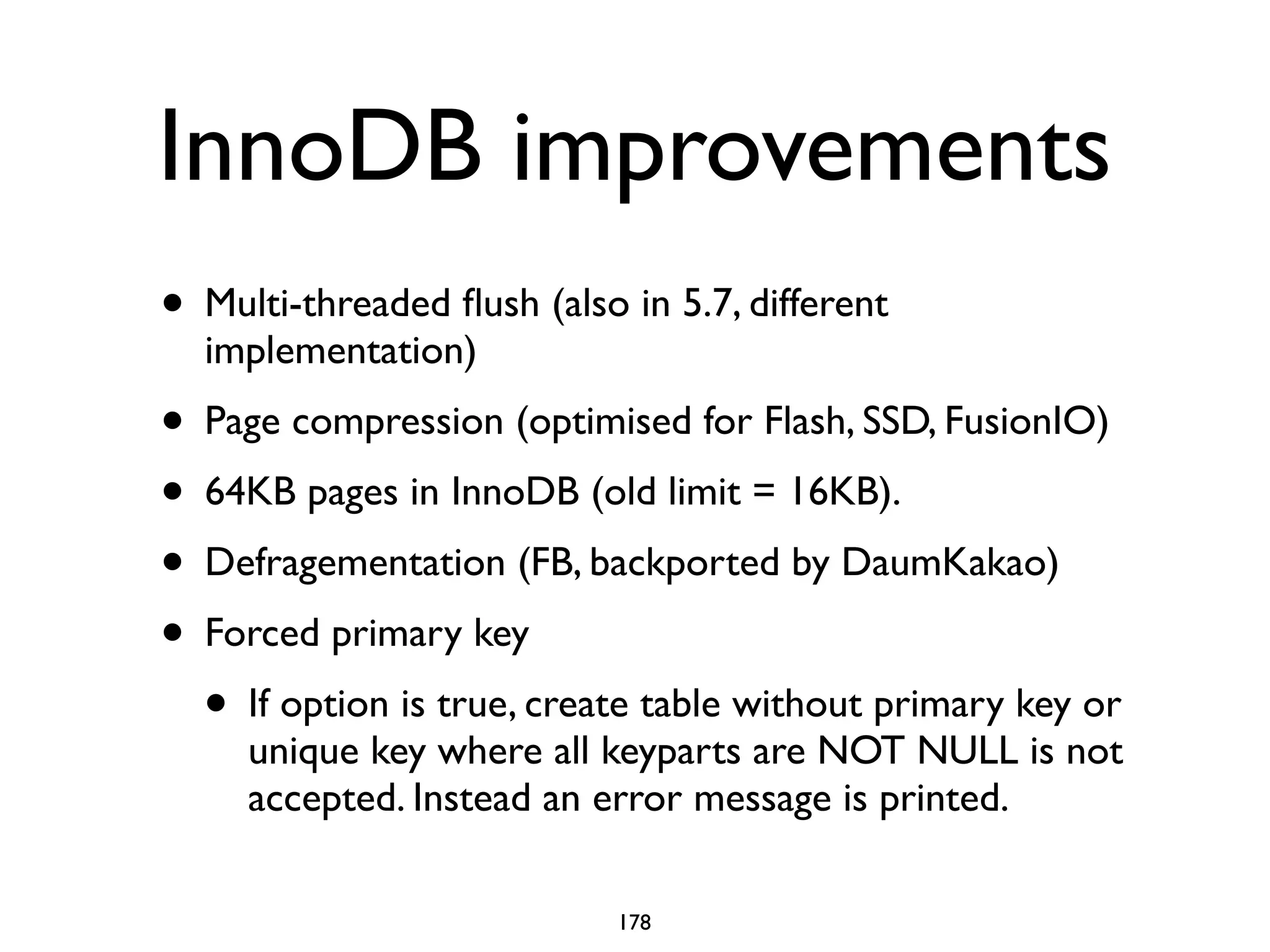
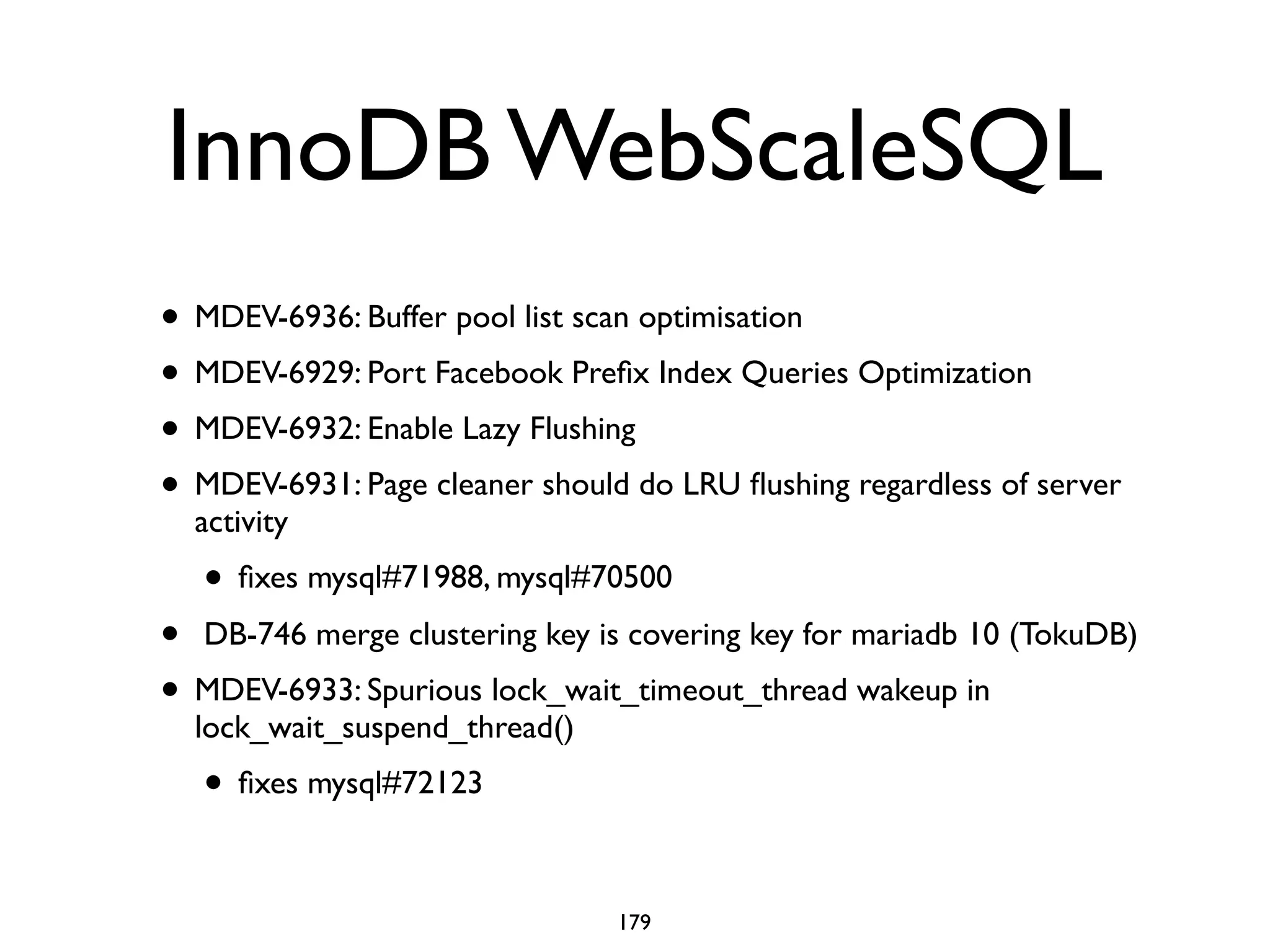
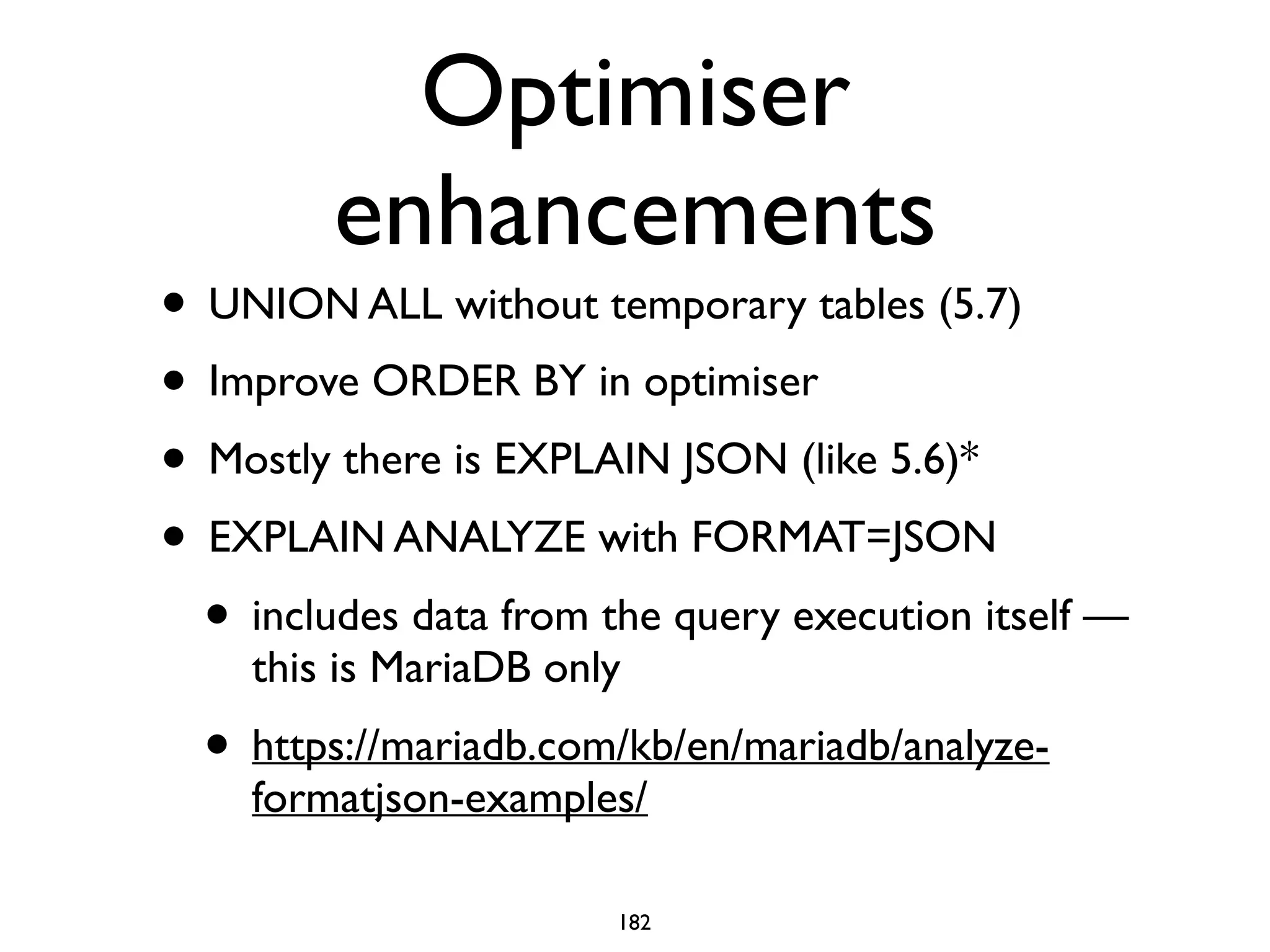
The document is a comprehensive tutorial about MariaDB, covering its features, installation, upgrade procedures, and architecture. It emphasizes the compatibility of MariaDB as a drop-in replacement for MySQL, highlighting its development history and community contributions. Various performance optimizations, storage engines, and best practices for database management are also discussed throughout the tutorial.













































![Switching between XtraDB & InnoDB mysqld --ignore-builtin-innodb --plugin- load=innodb=ha_innodb.so --plugin_dir=/usr/local/ mysql/lib/mysql/plugin Or in my.cnf [mysqld] ignore-builtin-innodb plugin-load=innodb=ha_innodb.so plugin_dir=/usr/local/mysql/lib/mysql/plugin 69](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-69-2048.jpg)




















![Progress reporting • ALTER TABLE & LOAD DATA INFILE MariaDB [mail]> alter table mail engine = maria; Stage: 1 of 2 'copy to tmp table' 17.55% of stage done MariaDB [mail]> select id, user, db, command, state, -> time_ms, progress from information_schema.processlist; +---------+-------------------+-----------+----------+ | command | state | time_ms | progress | +---------+-------------------+-----------+----------+ | Query | copy to tmp table | 23407.131 | 17.551 | +---------+-------------------+-----------+----------+ 1 row in set (0.47 sec) 94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-94-2048.jpg)

![New KILL syntax • HARD | SOFT & USER USERNAME are MariaDB-specific (5.3.2) • KILL QUERY ID query_id (10.0.5) - kill by query id, rather than thread id • SOFT ensures things that may leave a table in an inconsistent state aren’t interrupted (like REPAIR or INDEX creation for MyISAM or Aria) KILL [HARD | SOFT] [CONNECTION | QUERY] [thread_id | USER user_name] 98](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-98-2048.jpg)

















































![my.cnf config [mysqld] plugin-load-add=file_key_management.so file-key-management file-key-management-filename = /home/mdb/keys.enc innodb-encrypt-tables innodb-encrypt-log innodb-encryption-threads=4 aria-encrypt-tables=1 # PAGE row format encrypt-tmp-disk-tables=1 # this is for Aria 171](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-171-2048.jpg)








![EXPLAIN ANALYZE MariaDB [information_schema]> explain format=json select * from all_pluginsG *************************** 1. row *************************** EXPLAIN: { "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "table": { "table_name": "all_plugins", "access_type": "ALL" } } } 1 row in set (0.01 sec) 183](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-183-2048.jpg)







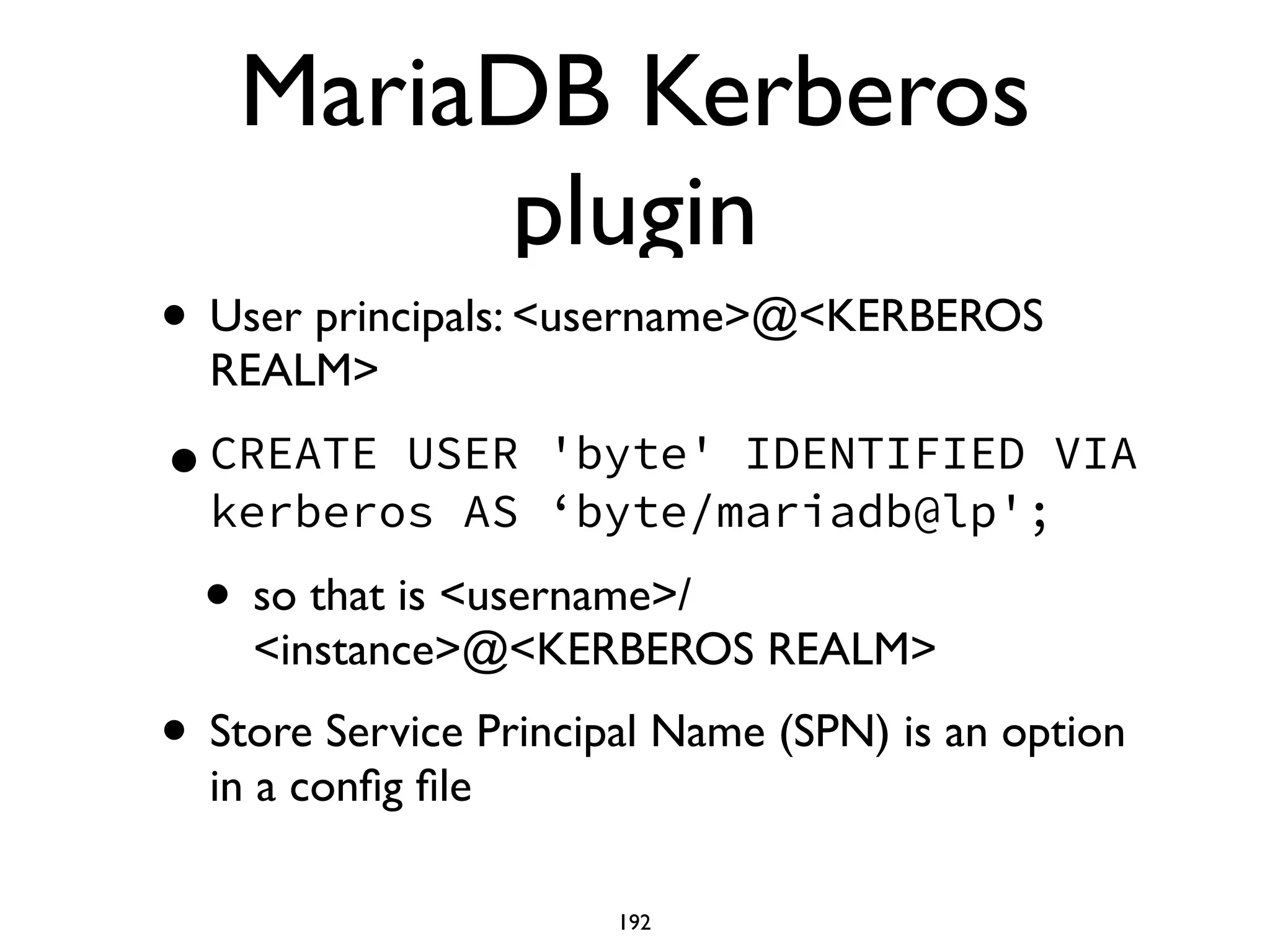



![Query response time • (range_base ^ n; range_base ^ (n+1)] • INSTALL SONAME ‘query_response_time'; • SHOW QUERY_RESPONSE_TIME; • https://www.percona.com/doc/percona- server/5.6/diagnostics/ response_time_distribution.html 196](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecompletemariadbservertutorialamsterdam2016-161011020714/75/The-Complete-MariaDB-Server-tutorial-196-2048.jpg)