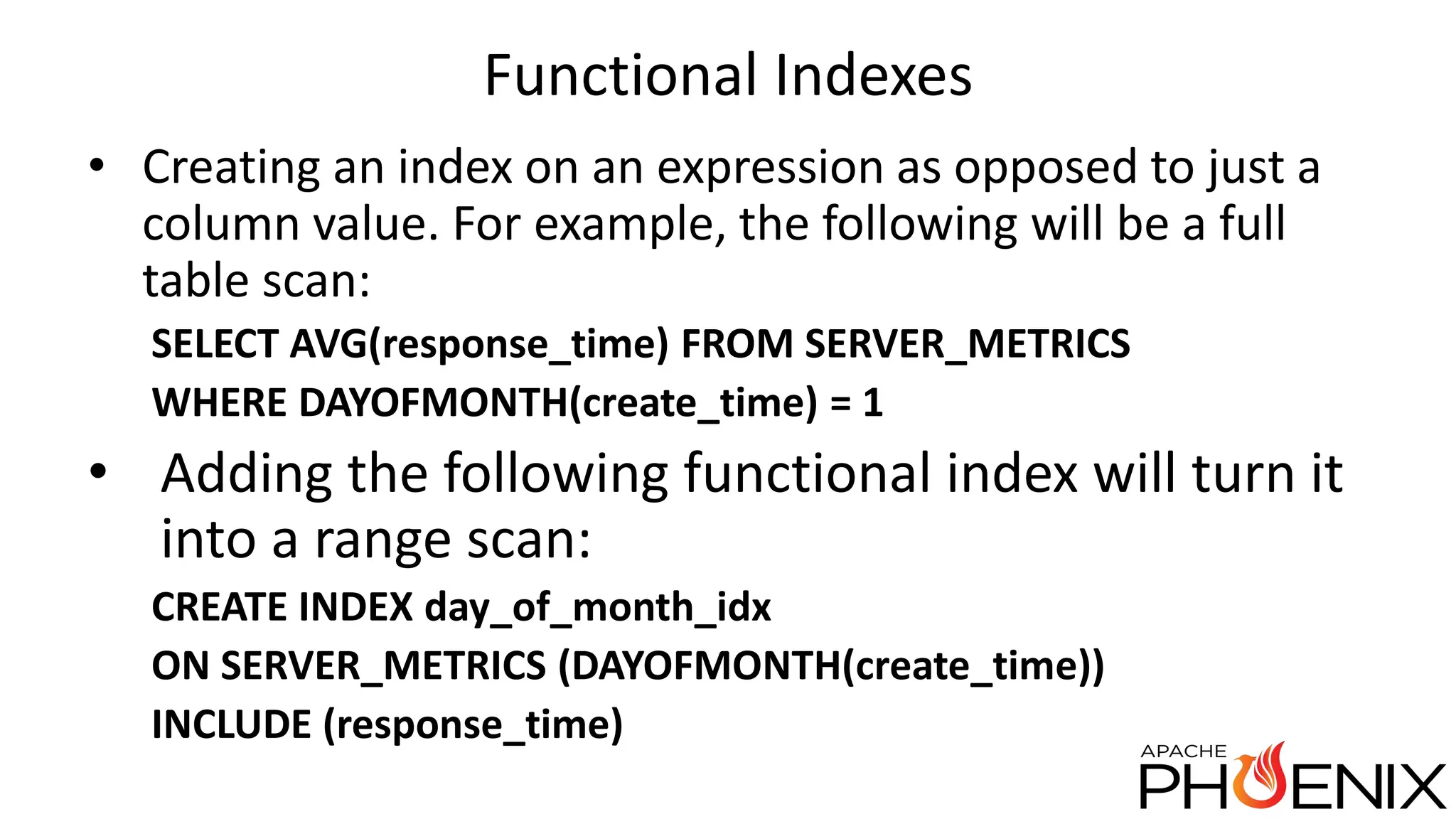
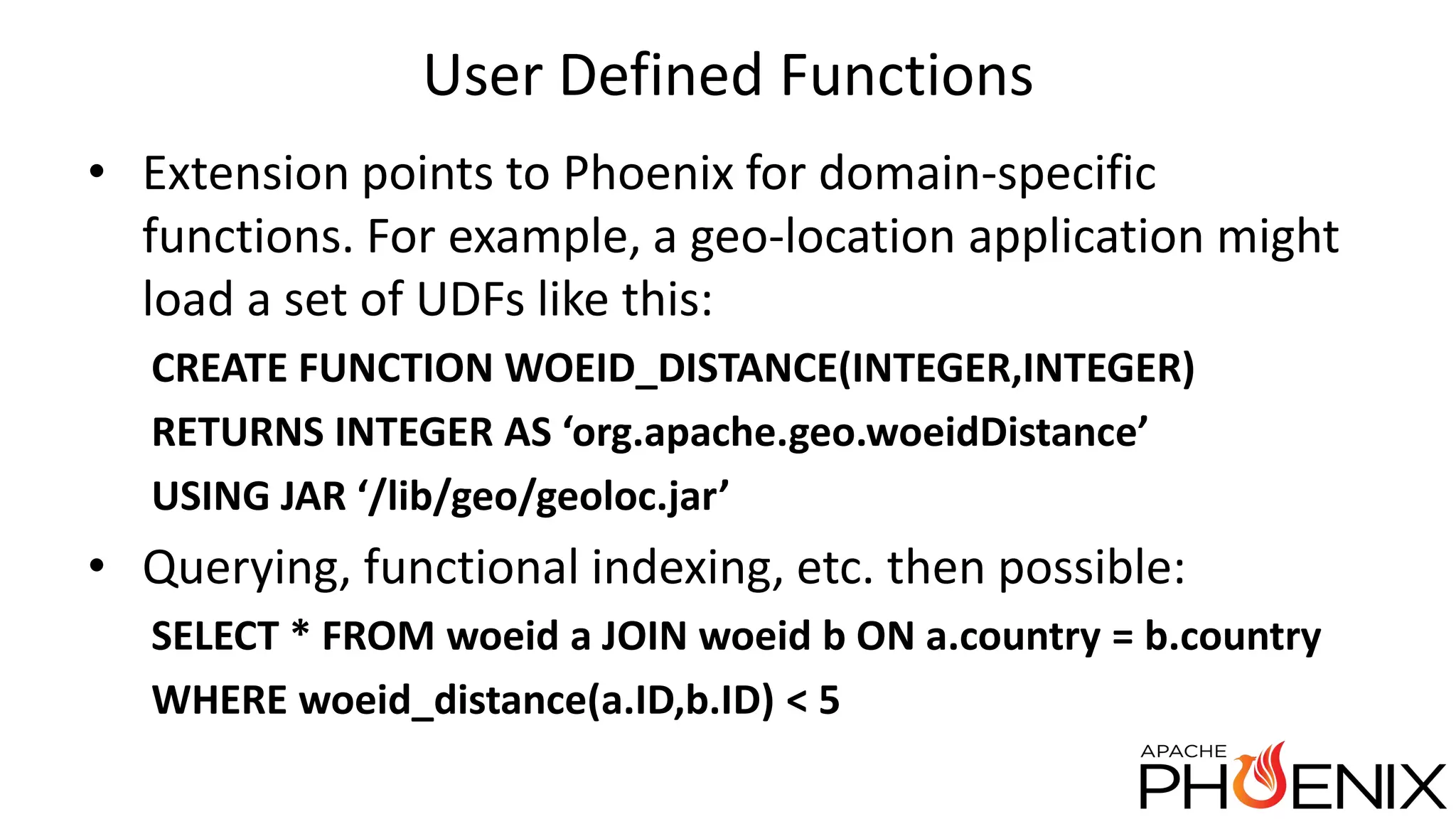
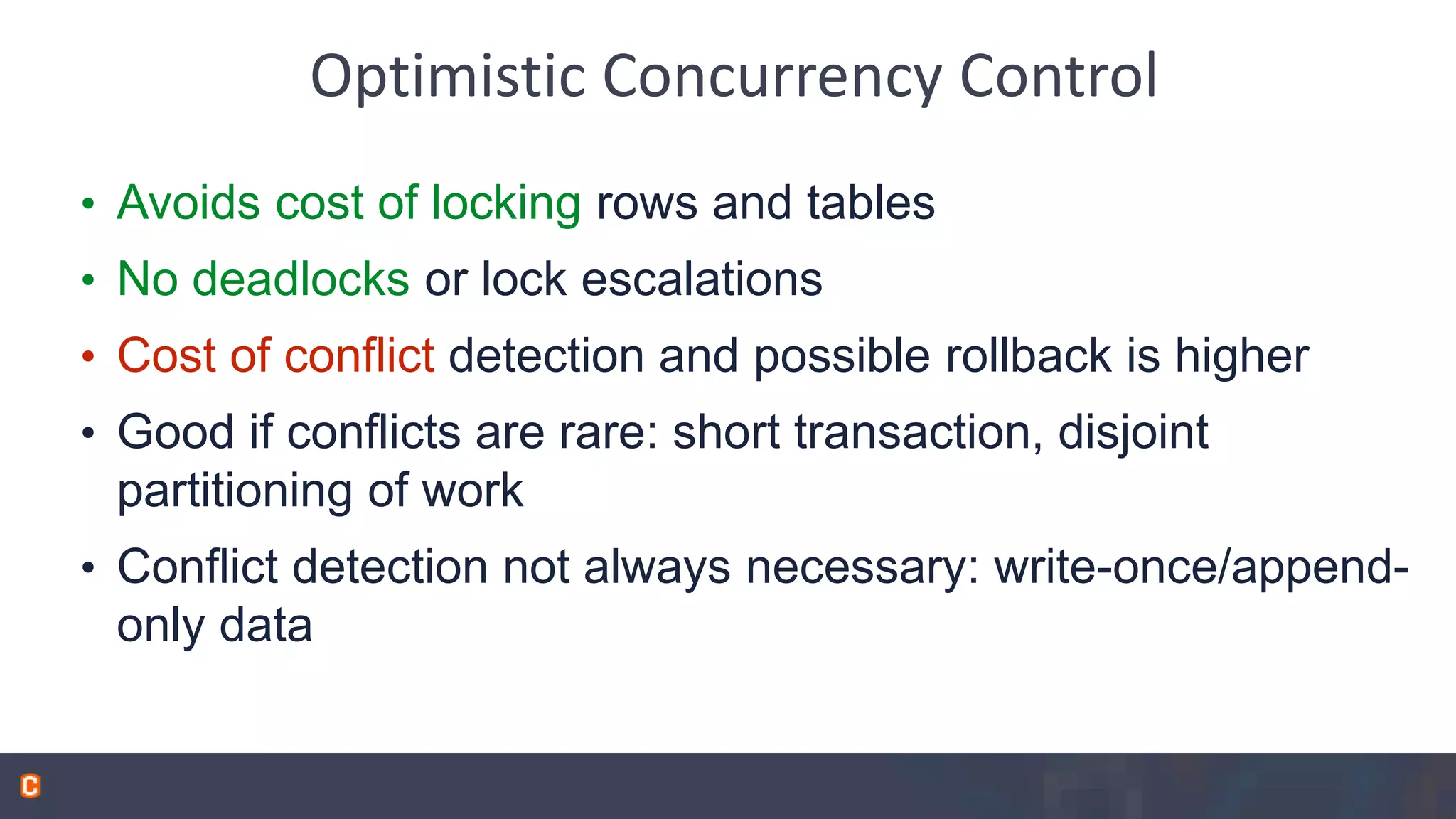
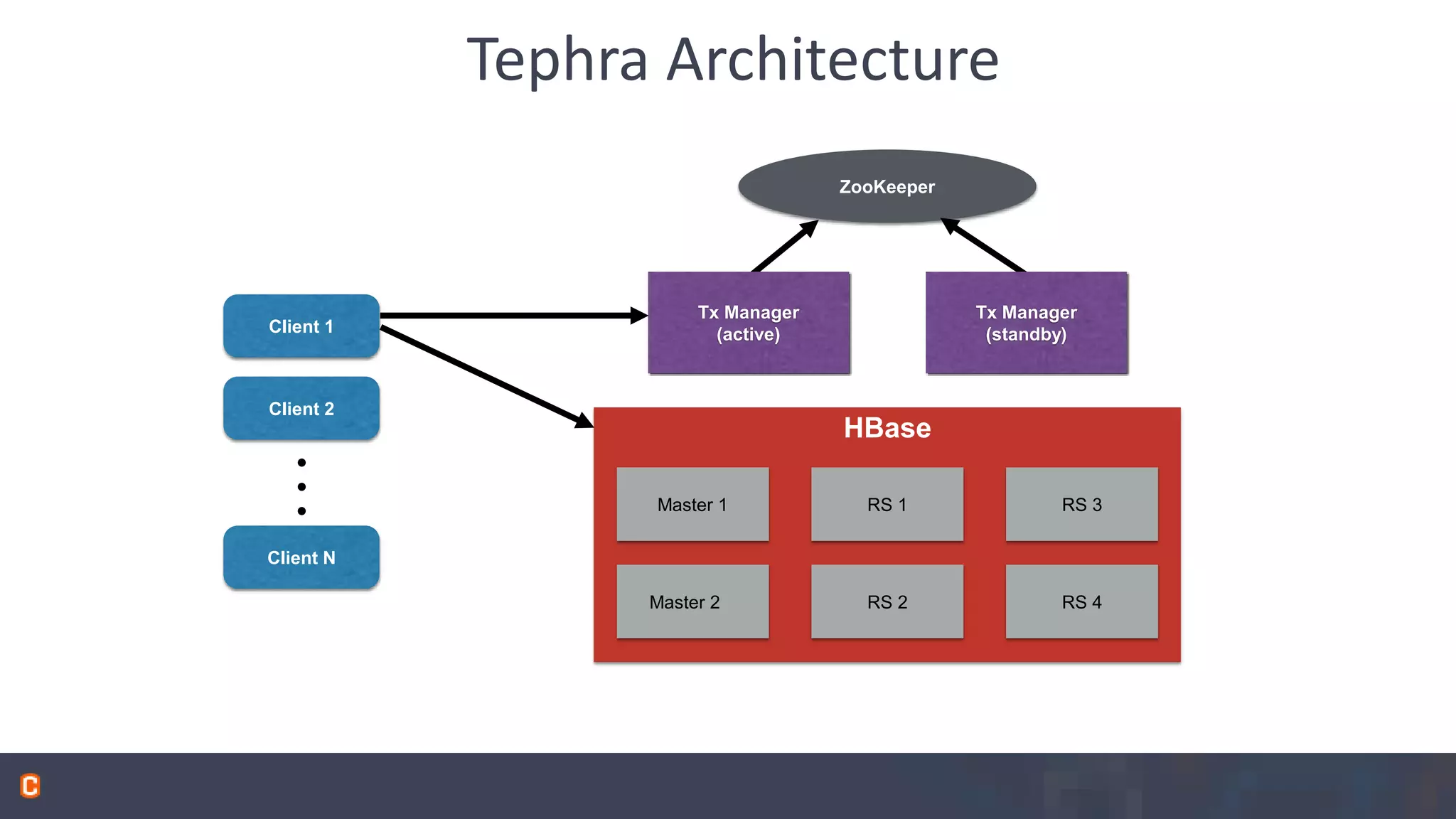
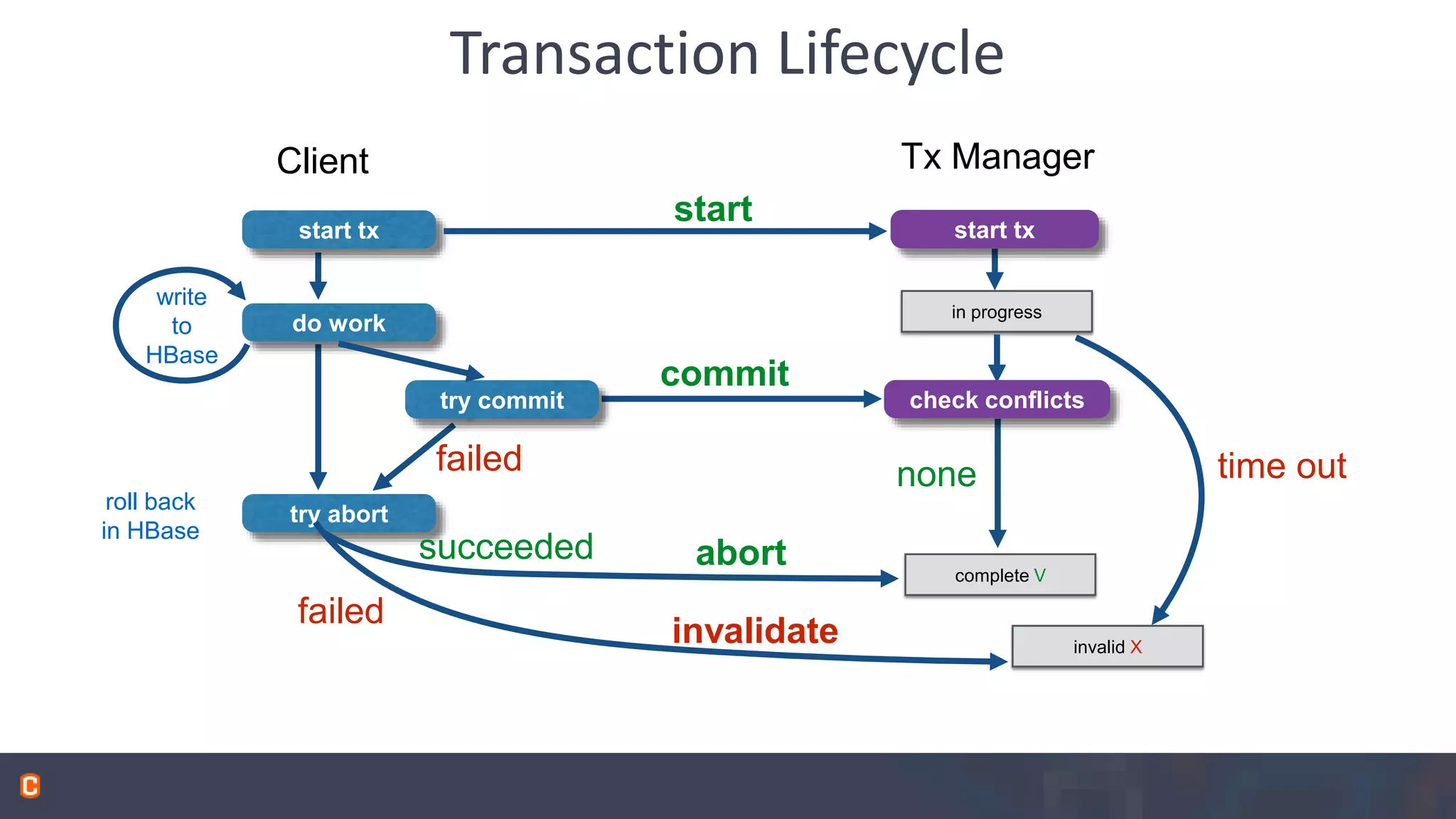
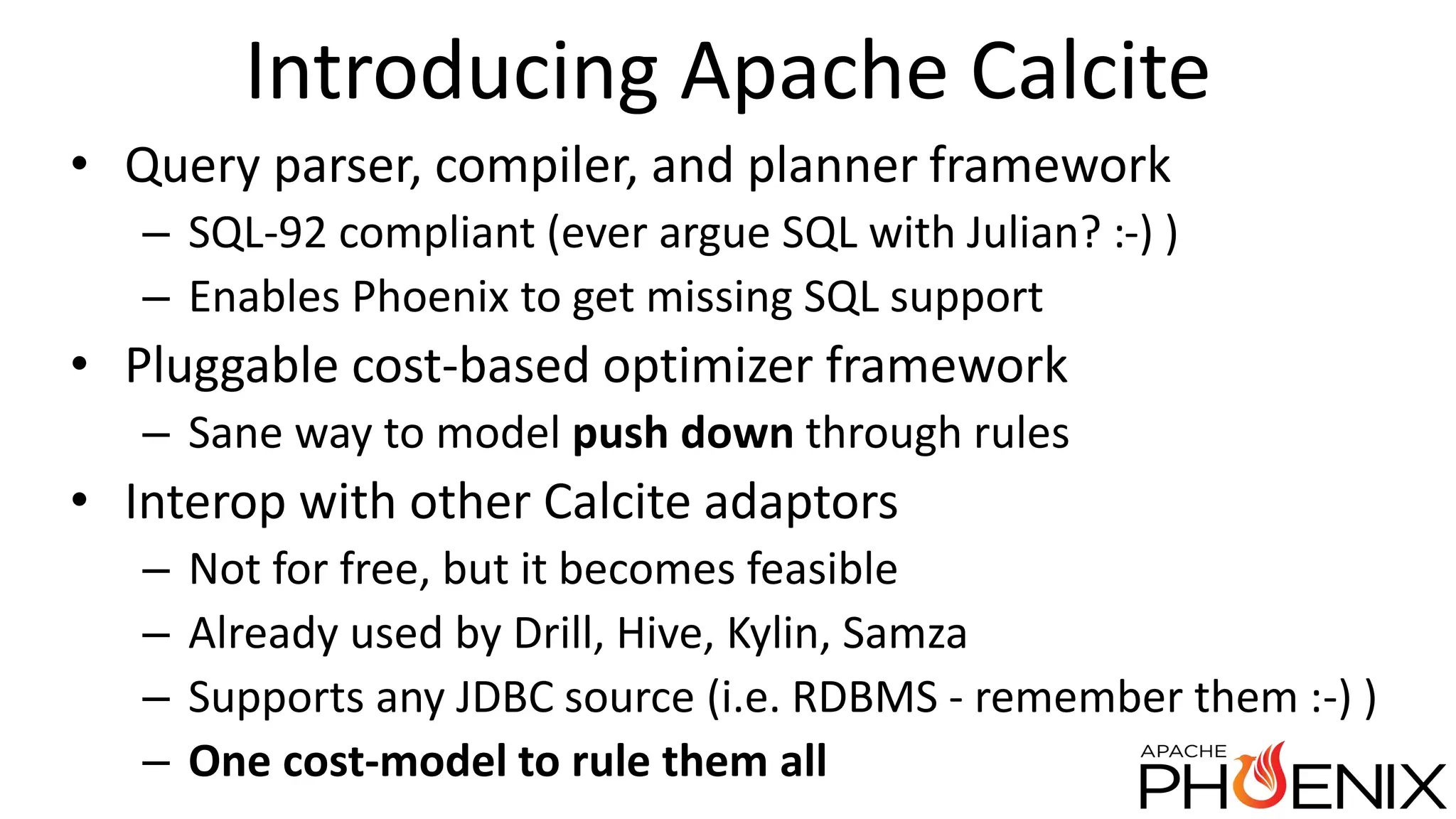
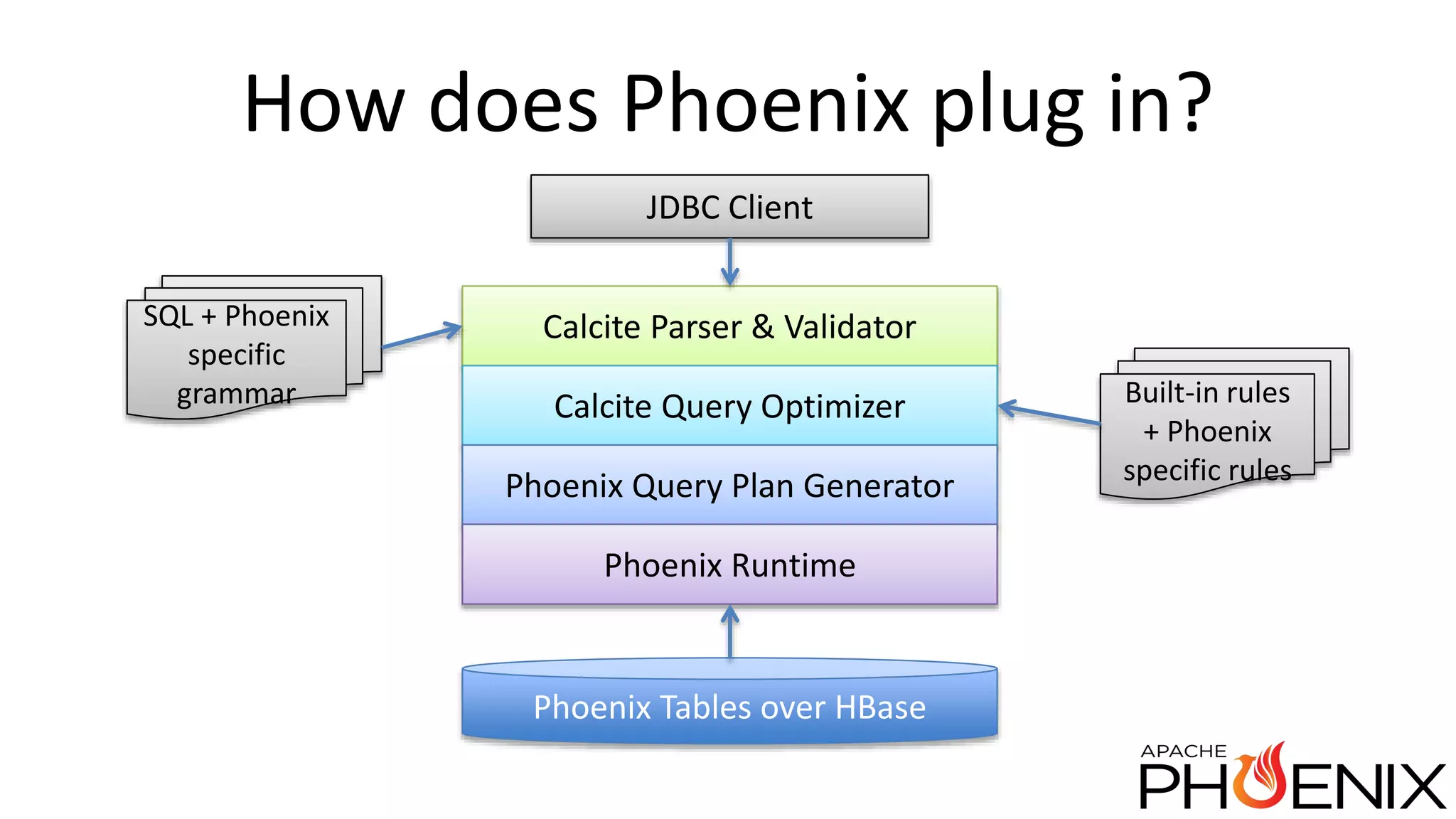
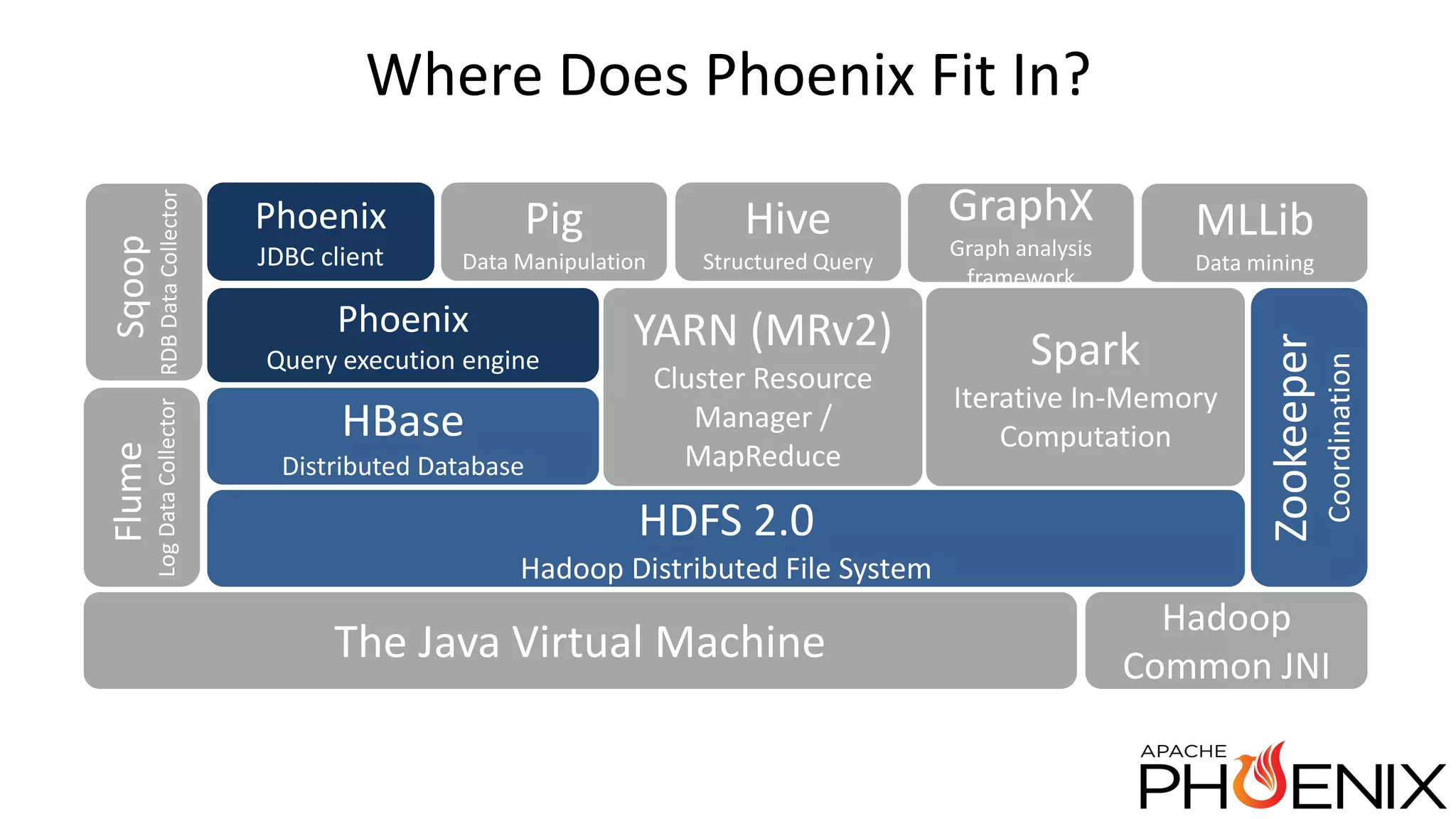
Apache Phoenix is a SQL query layer over Apache HBase that allows users to interact with HBase through JDBC and SQL. It transforms SQL queries into native HBase API calls for efficient parallel execution on the cluster. Phoenix provides metadata storage, SQL support, and a JDBC driver. It is now a top-level Apache project after originally being developed at Salesforce. The speaker discussed Phoenix's capabilities like joins and subqueries, new features like HBase 1.0 support and functional indexes, and future plans like improved optimization through Calcite and transaction support.




![TPC Example 1 Small-Quantity-Order Revenue Query (Q17) select sum(l_extendedprice) / 7.0 as avg_yearly from lineitem, part where p_partkey = l_partkey and p_brand = '[B]' and p_container = '[C]' and l_quantity < ( select 0.2 * avg(l_quantity) from lineitem where l_partkey = p_partkey ); CLIENT 4-WAY FULL SCAN OVER lineitem PARALLEL INNER JOIN TABLE 0 CLIENT 1-WAY FULL SCAN OVER part SERVER FILTER BY p_partkey = ‘[B]’ AND p_container = ‘[C]’ PARALLEL INNER JOIN TABLE 1 CLIENT 4-WAY FULL SCAN OVER lineitem SERVER AGGREGATE INTO DISTINCT ROWS BY l_partkey AFTER-JOIN SERVER FILTER BY l_quantity < $0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june10435pmsalesforce-150618233408-lva1-app6891/75/The-Evolution-of-a-Relational-Database-Layer-over-HBase-8-2048.jpg)
![TPC Example 2 Order Priority Checking Query (Q4) select o_orderpriority, count(*) as order_count from orders where o_orderdate >= date '[D]' and o_orderdate < date '[D]' + interval '3' month and exists ( select * from lineitem where l_orderkey = o_orderkey and l_commitdate < l_receiptdate ) group by o_orderpriority order by o_orderpriority; CLIENT 4-WAY FULL SCAN OVER orders SERVER FILTER o_orderdate >= ‘[D]’ AND o_orderdate < ‘[D]’ + 3(d) SERVER AGGREGATE INTO ORDERED DISTINCT ROWS BY o_orderpriority CLIENT MERGE SORT SKIP-SCAN JOIN TABLE 0 CLIENT 4-WAY FULL SCAN OVER lineitem SERVER FILTER BY l_commitdate < l_receiptdate DYNAMIC SERVER FILTER BY o_orderkey IN l_orderkey](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june10435pmsalesforce-150618233408-lva1-app6891/75/The-Evolution-of-a-Relational-Database-Layer-over-HBase-9-2048.jpg)