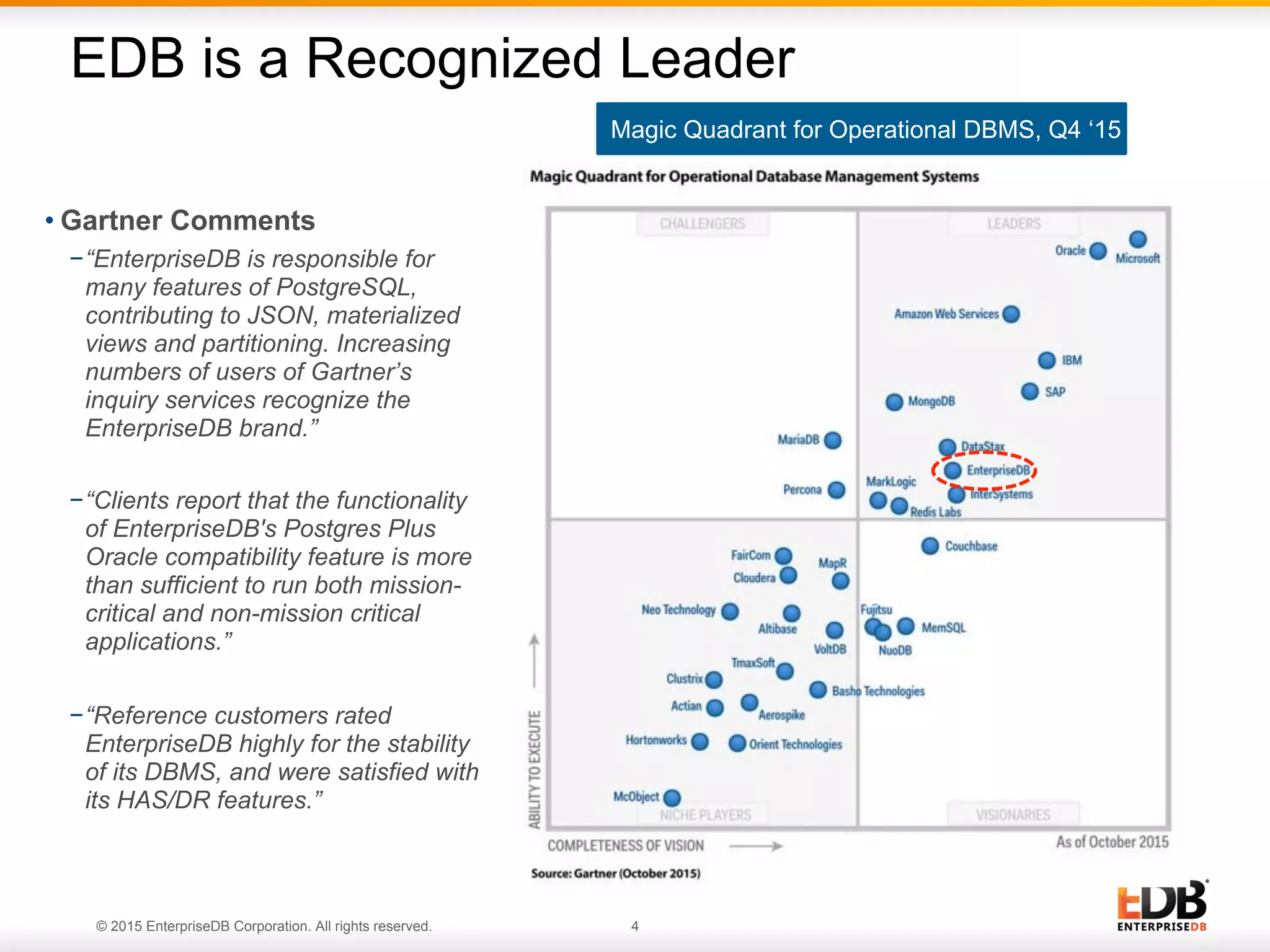
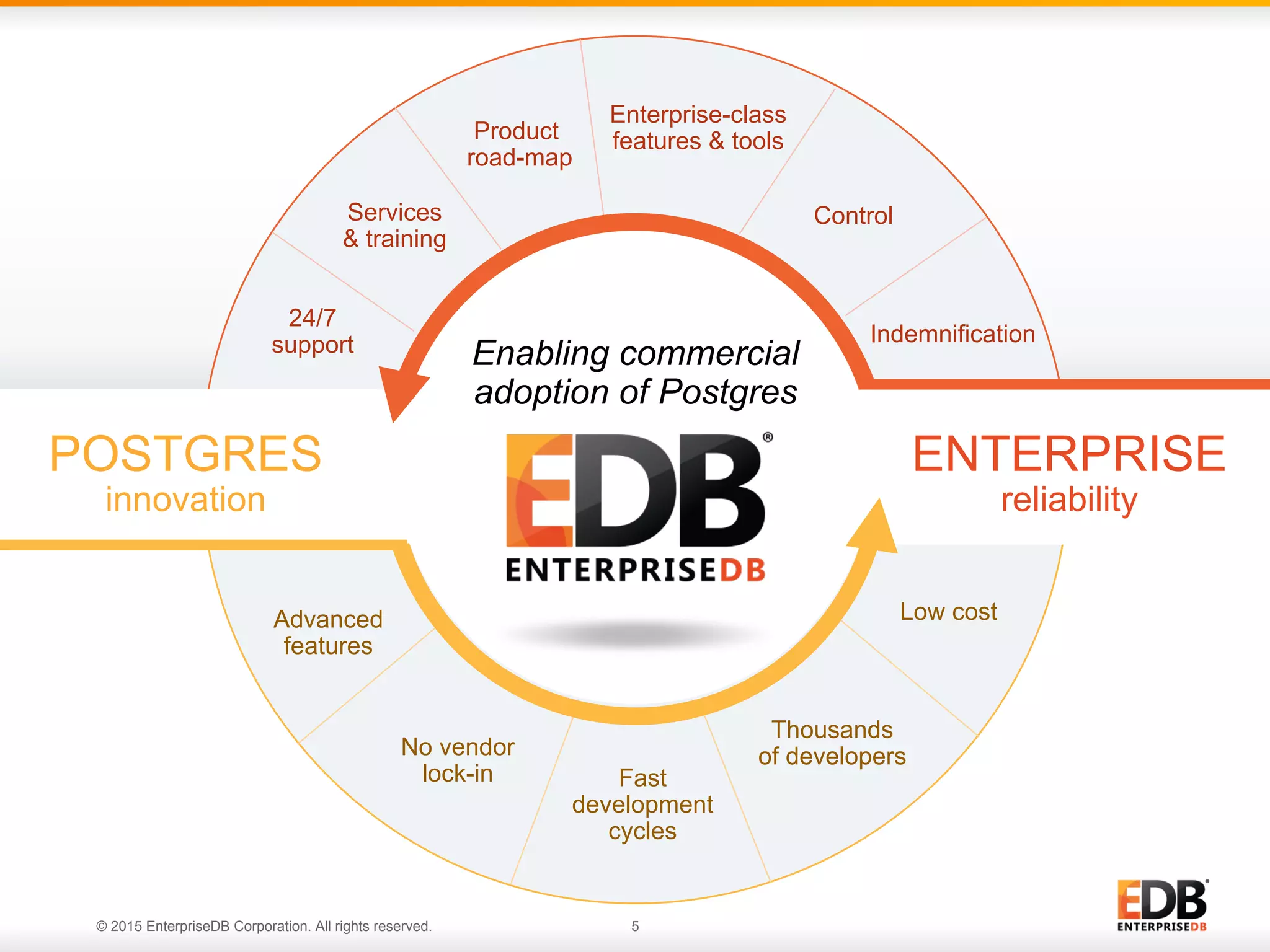
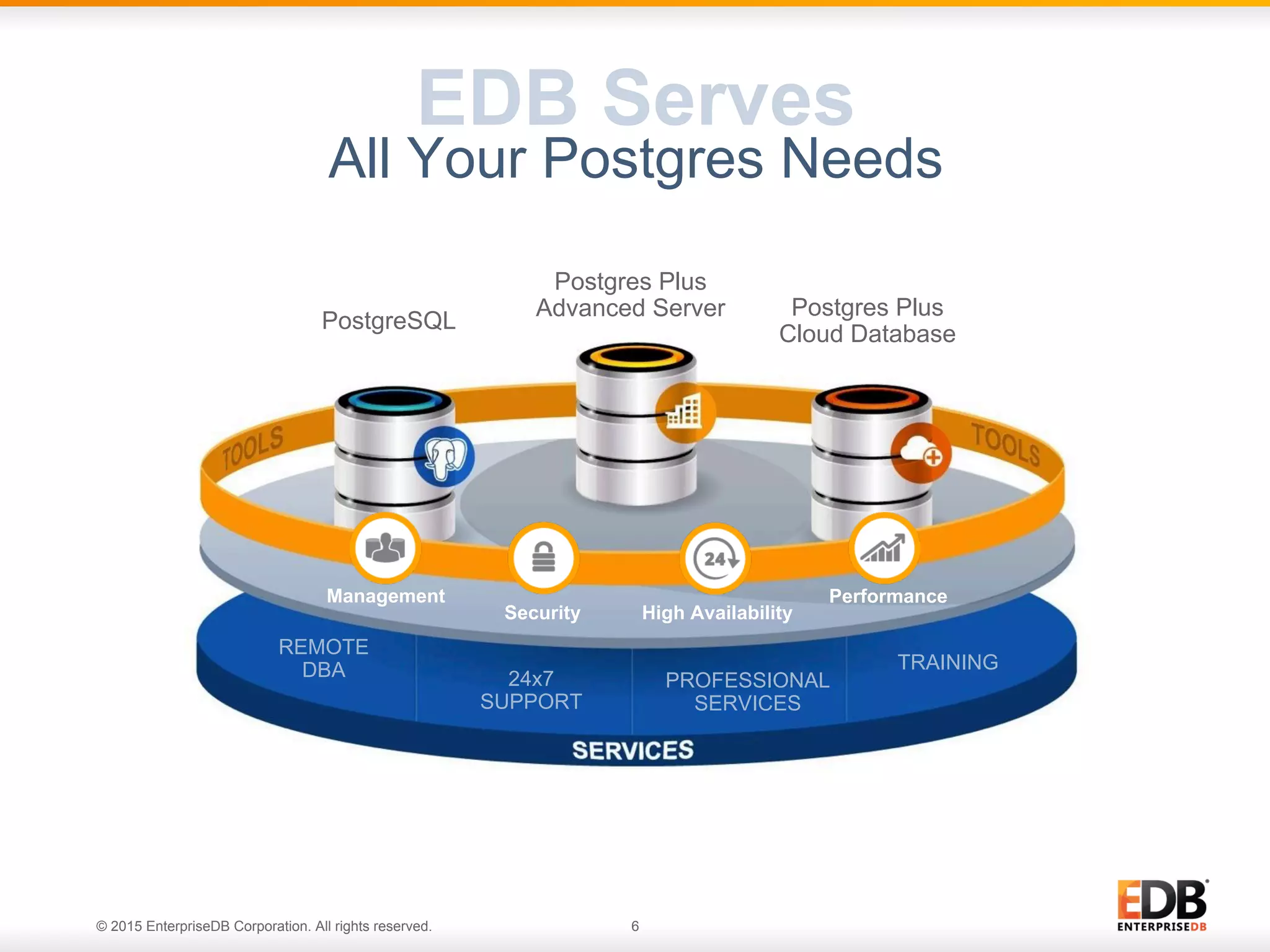
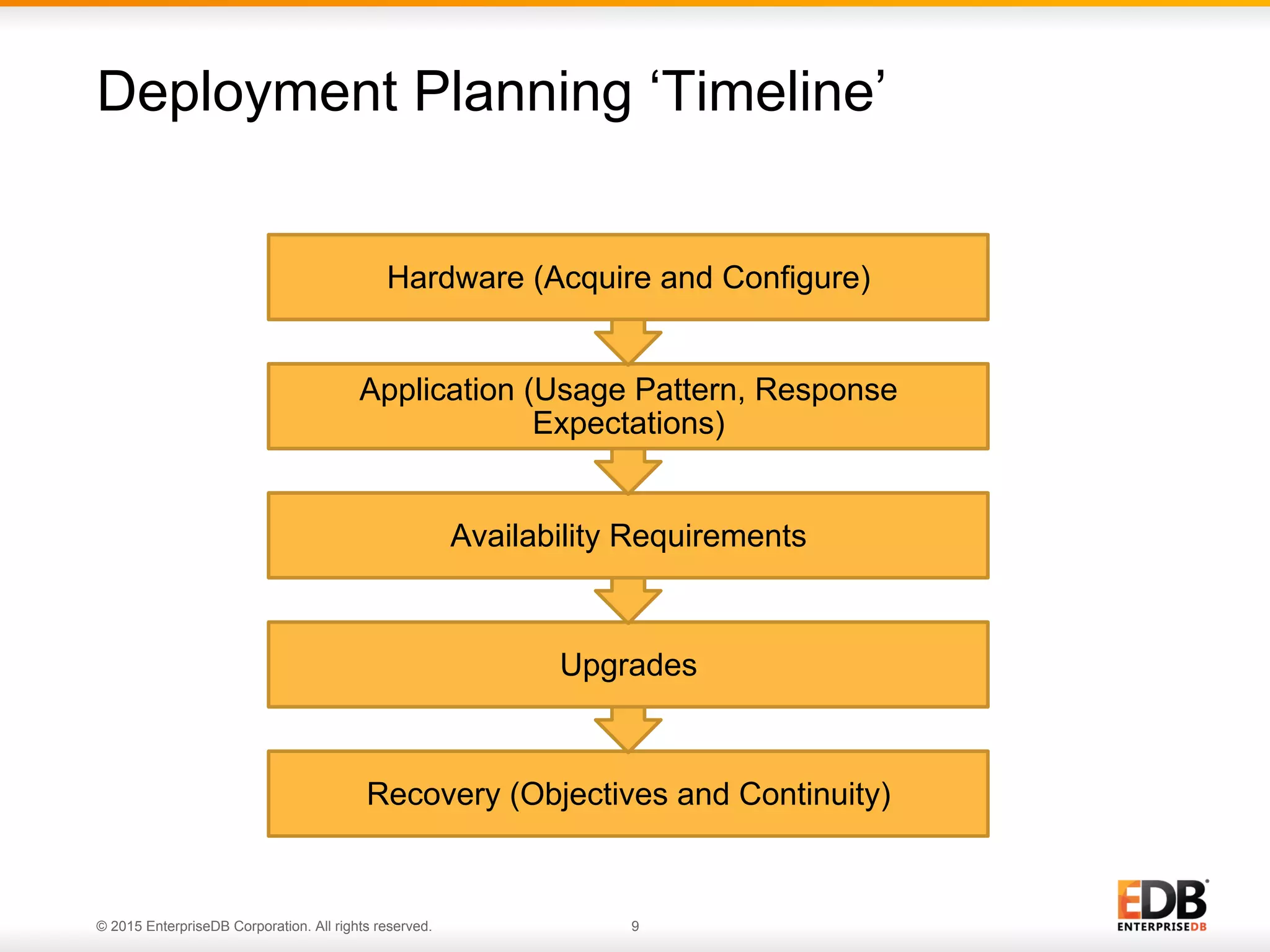
The document provides a comprehensive guide for effective PostgreSQL deployment, covering essential areas such as preparation, planning, questions to ask during deployment, uptime requirements, backups, and ongoing evaluation. It includes insights on hardware requirements, replication strategies, upgrade policies, and recovery options, emphasizing the importance of communication among teams and continuous adjustments. EDB's expertise and resources are highlighted, along with customer satisfaction regarding their PostgreSQL solutions.