Java is an object-oriented, class-based, concurrent, secured and general-purpose computer-programming language. It is a widely used robust technology. Object-Oriented Programming is a methodology or paradigm to design a program using classes and objects


![Introduction to Java • Java is an object-oriented, class-based, concurrent, secured and general-purpose computer-programming language. It is a widely used robust technology. • Java was developed by Sun Microsystems (which is now the subsidiary of Oracle) in the year 1995. James Gosling is known as the father of Java. Before Java, its name was Oak. • Platform: Any hardware or software environment in which a program runs, is known as a platform. Since Java has a runtime environment (JRE) and API, it is called a platform. class Simple{ public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Hello Java"); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3rdsem-programminginjavappt-251114152500-b2d64349/75/Unit-1-Introduction-to-Java-Basic-Concepts-of-Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-3-2048.jpg)

















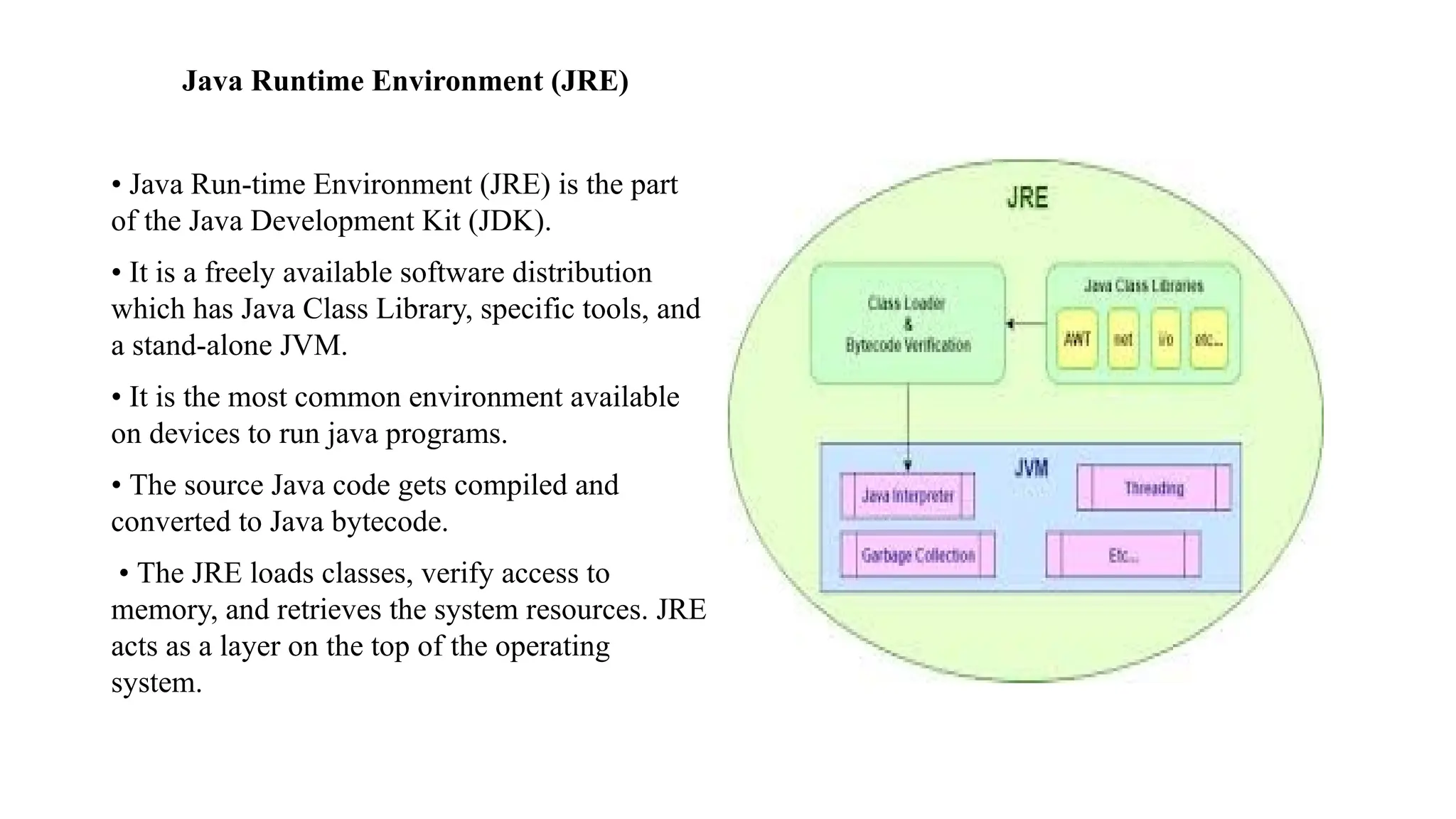


![Anatomy of a class • When the JVM starts running, it looks for the class you give it at the command line. Then it starts looking for a specially-written method that looks exactly like: public static void main (String[] args) { // your code goes here } • Next, the JVM runs everything between the curly braces { } of your main method. Every Java application has to have at least one class, and at least one main method (not one main per class; just one main per application).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3rdsem-programminginjavappt-251114152500-b2d64349/75/Unit-1-Introduction-to-Java-Basic-Concepts-of-Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-28-2048.jpg)