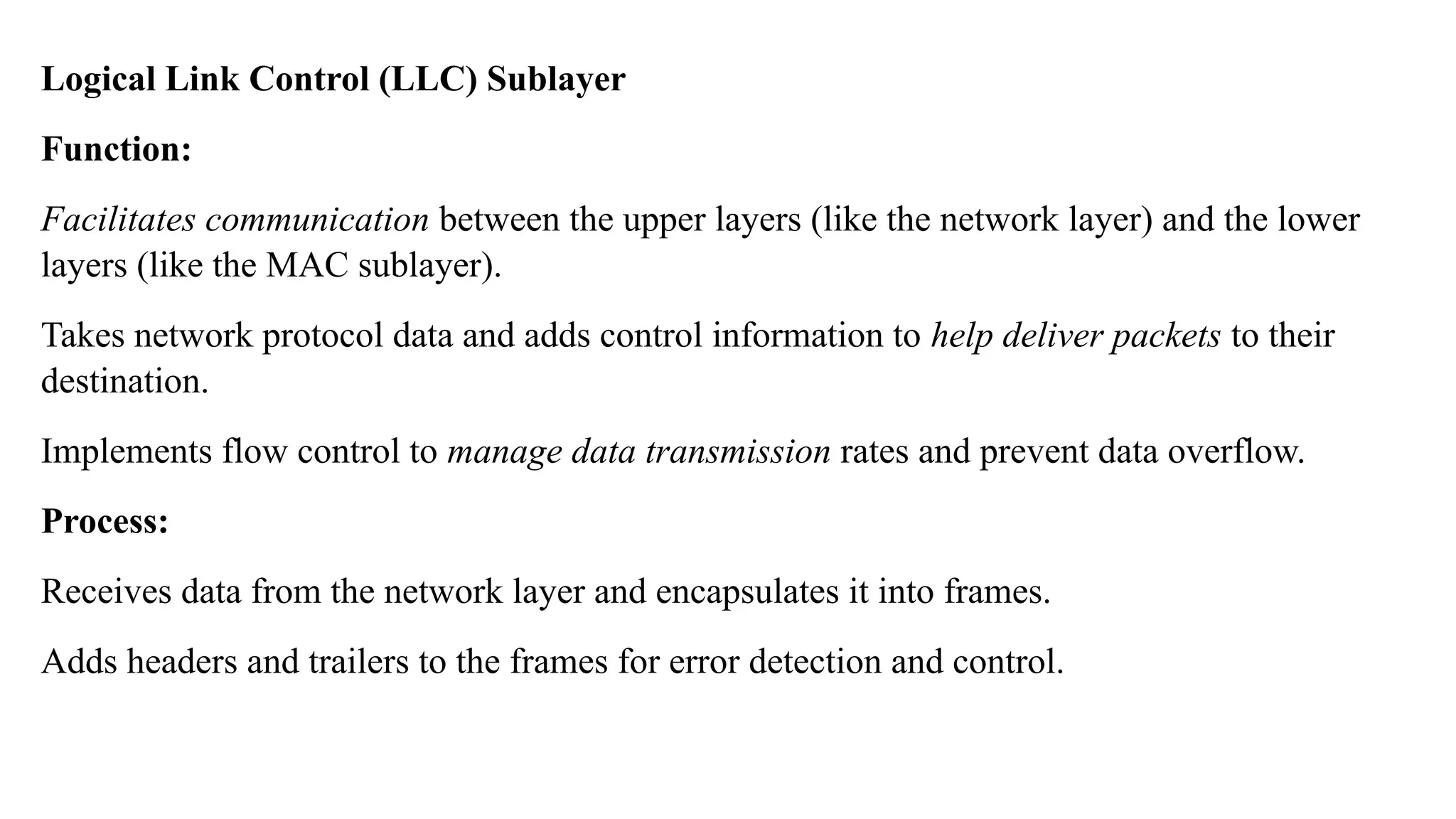
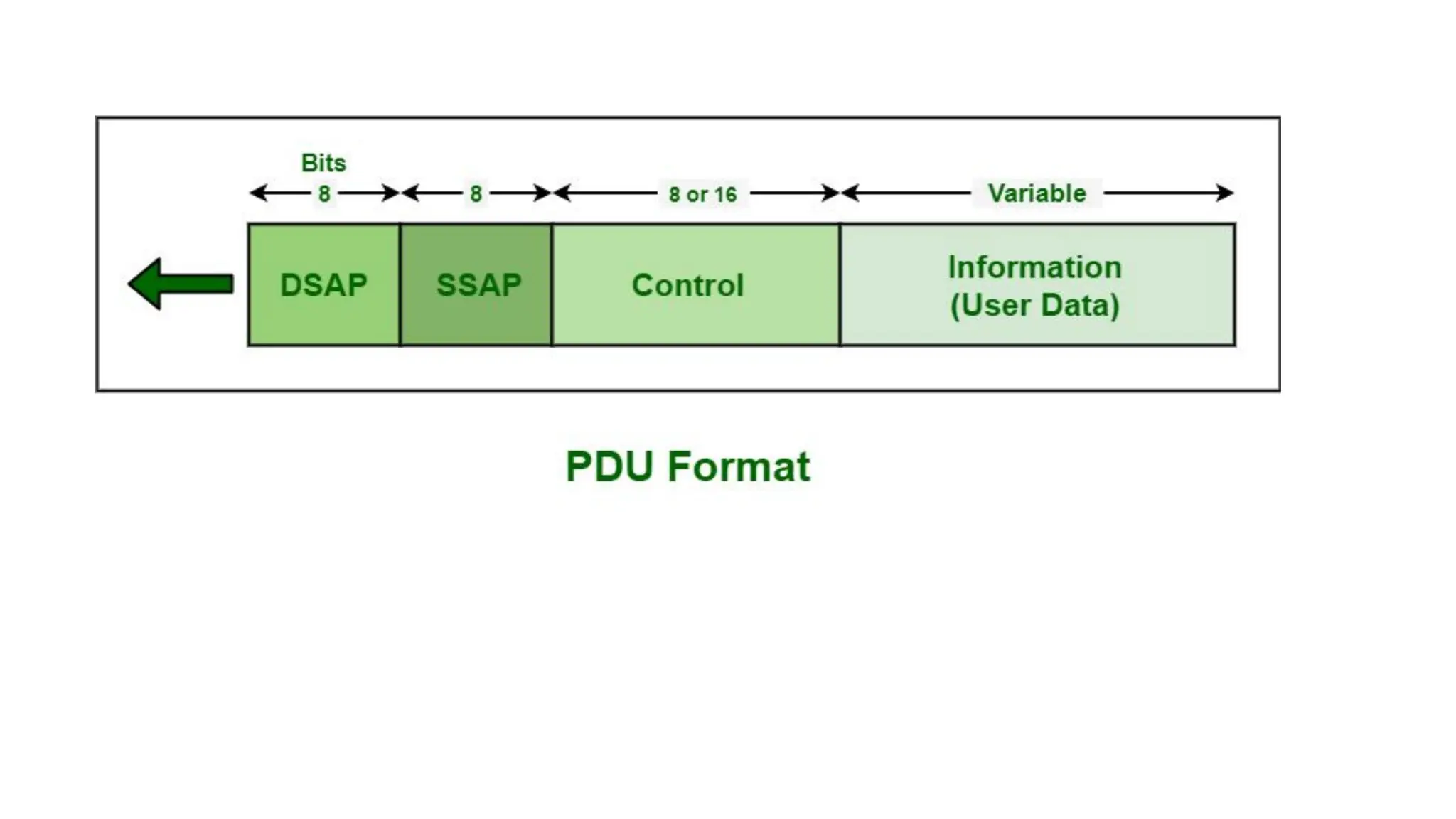
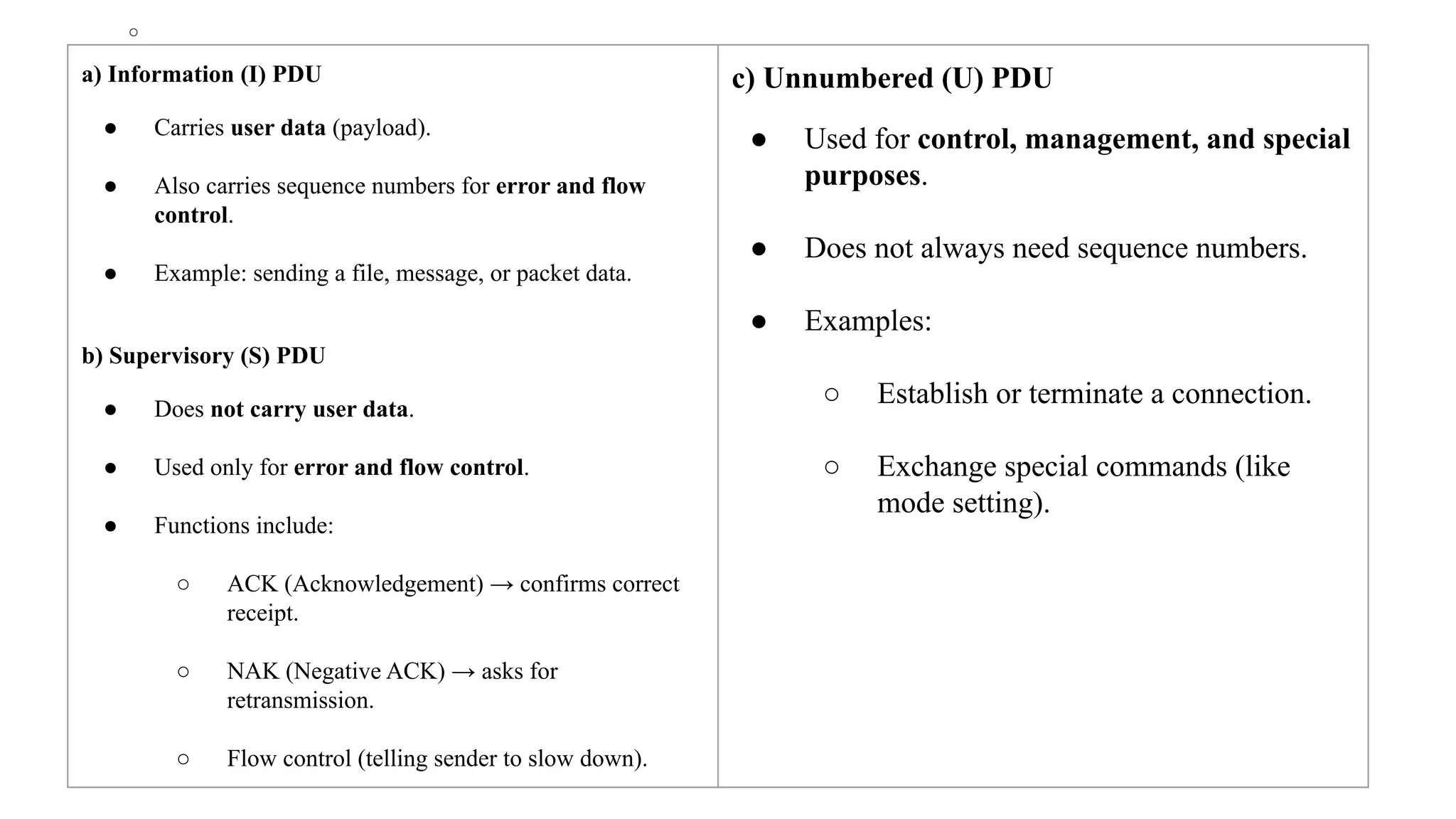
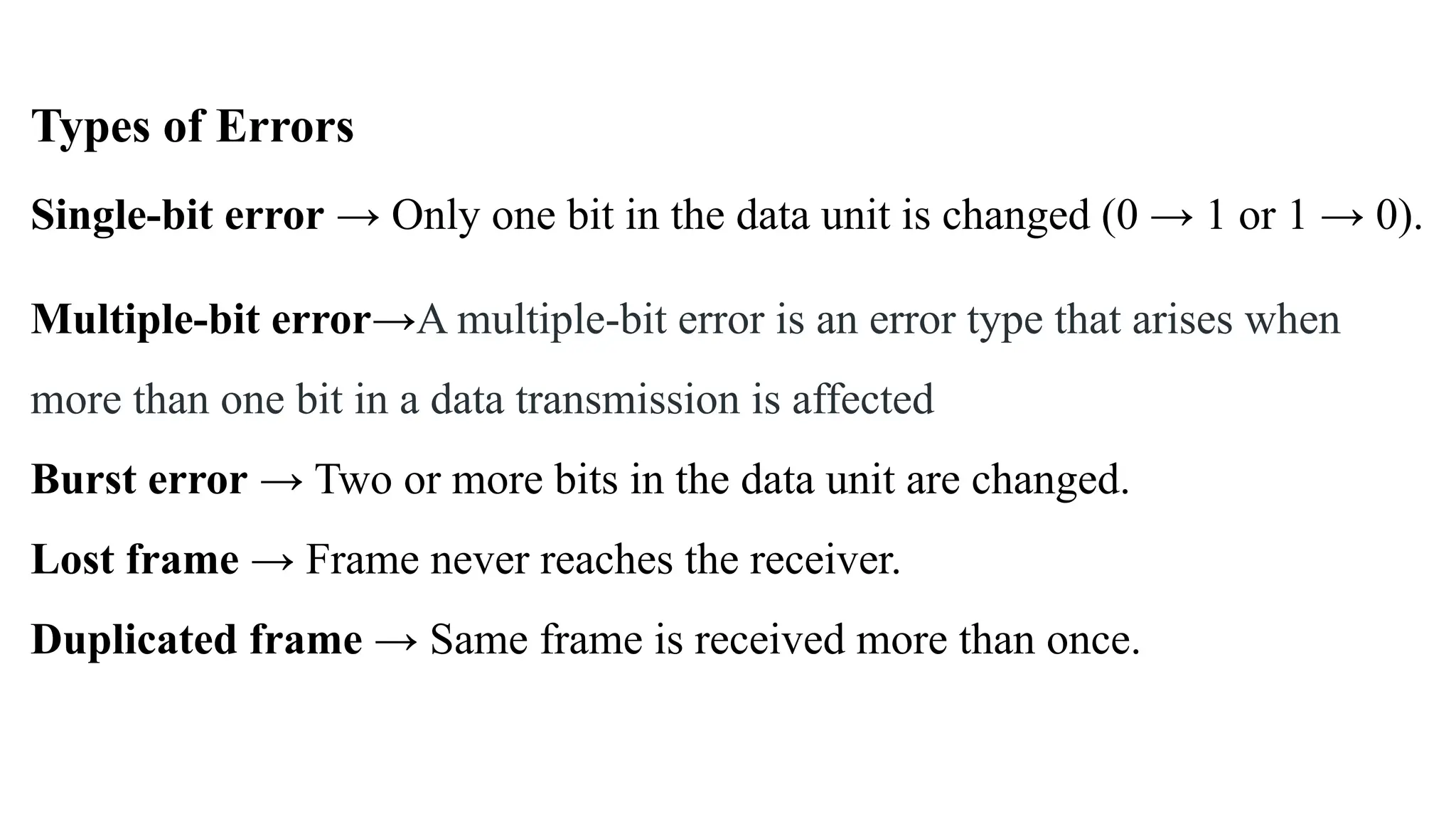
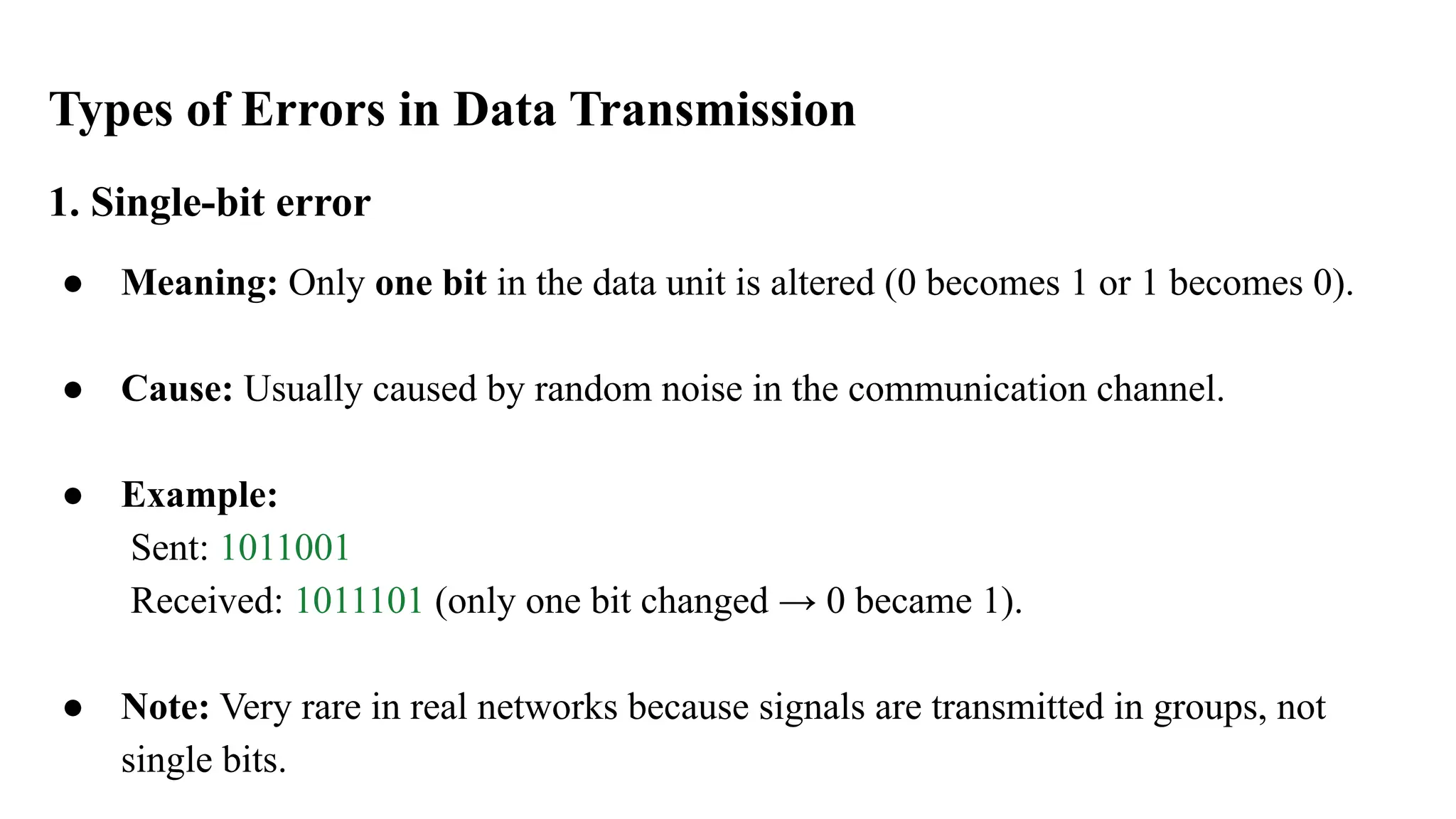
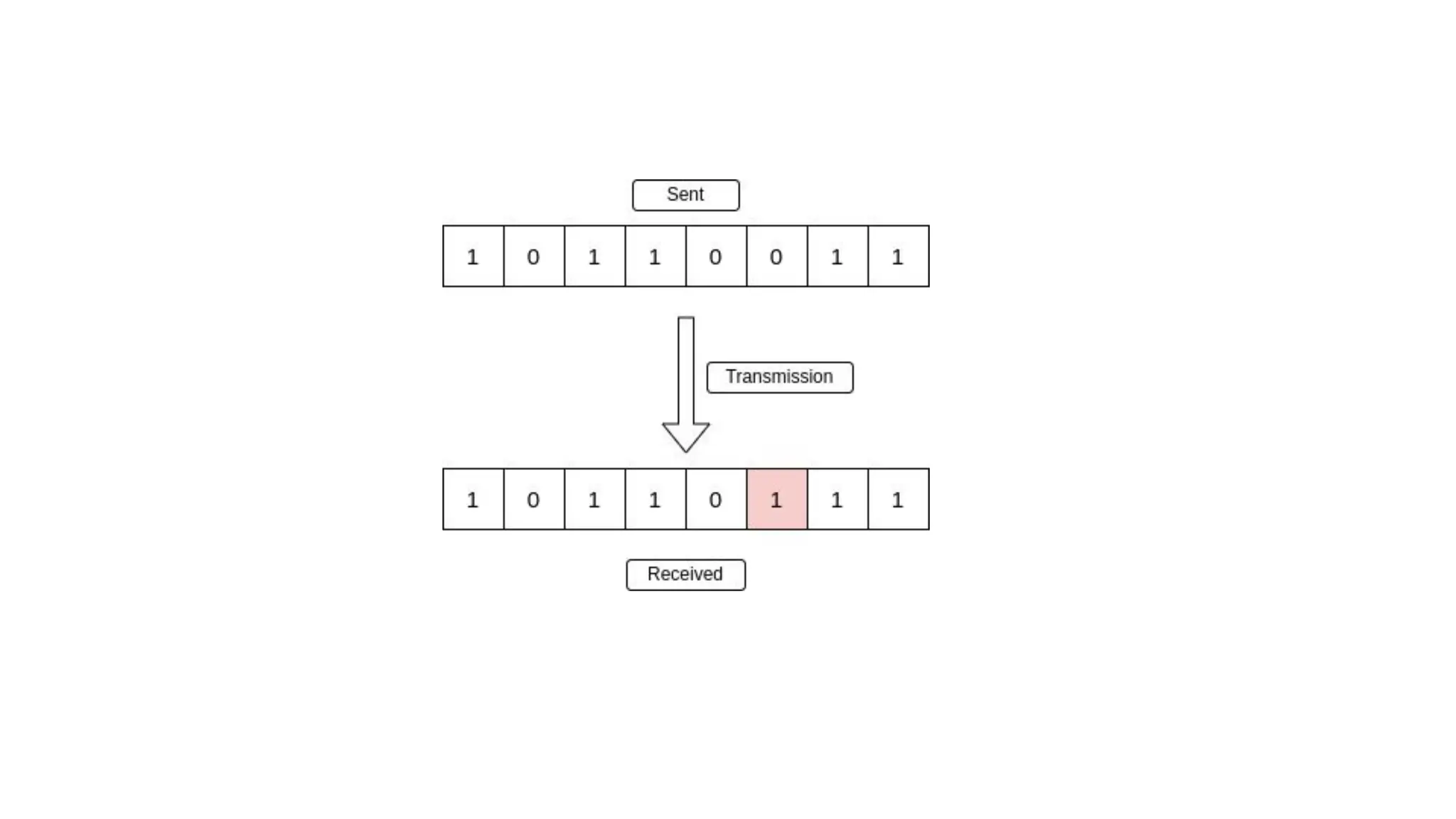
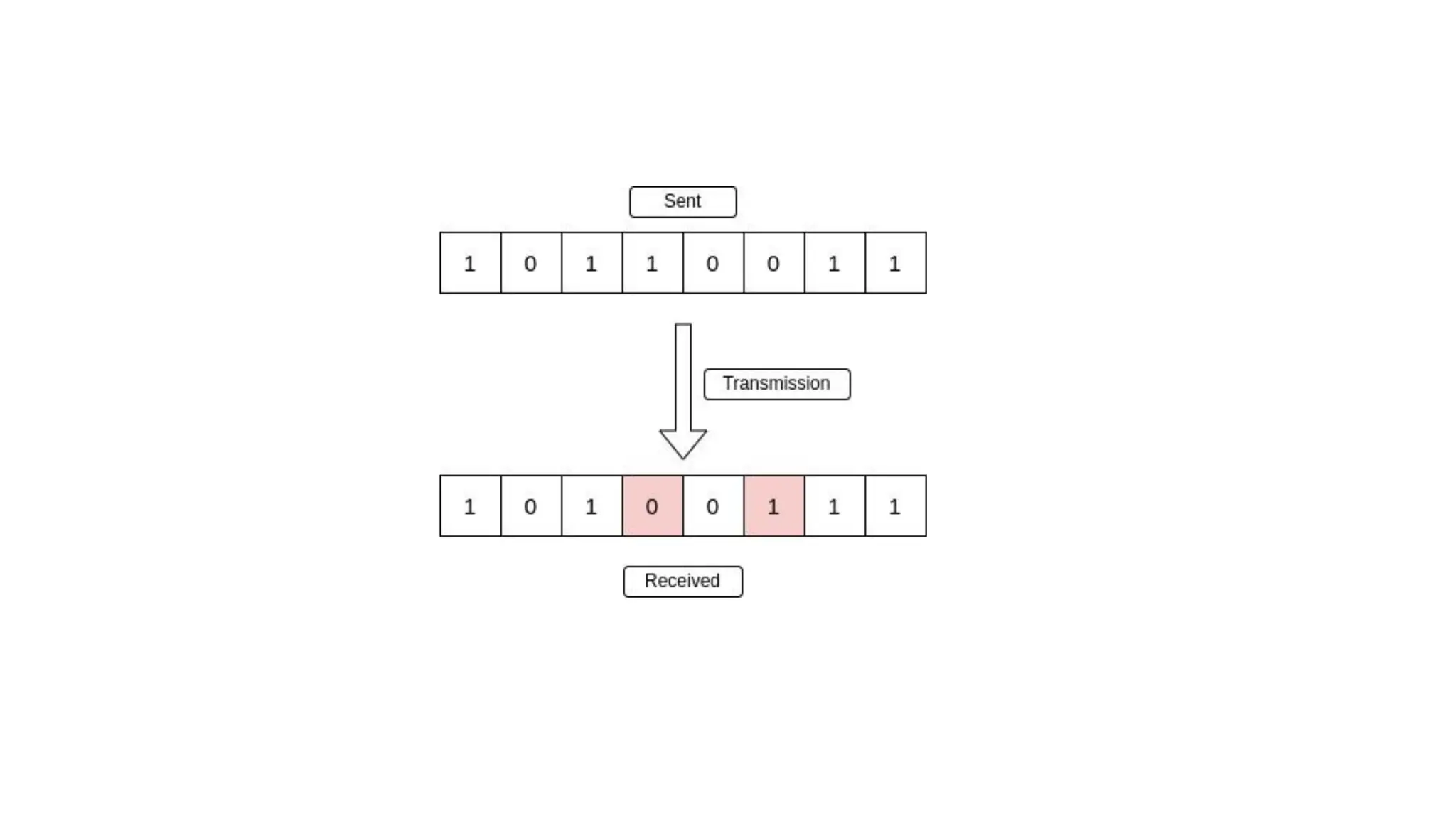
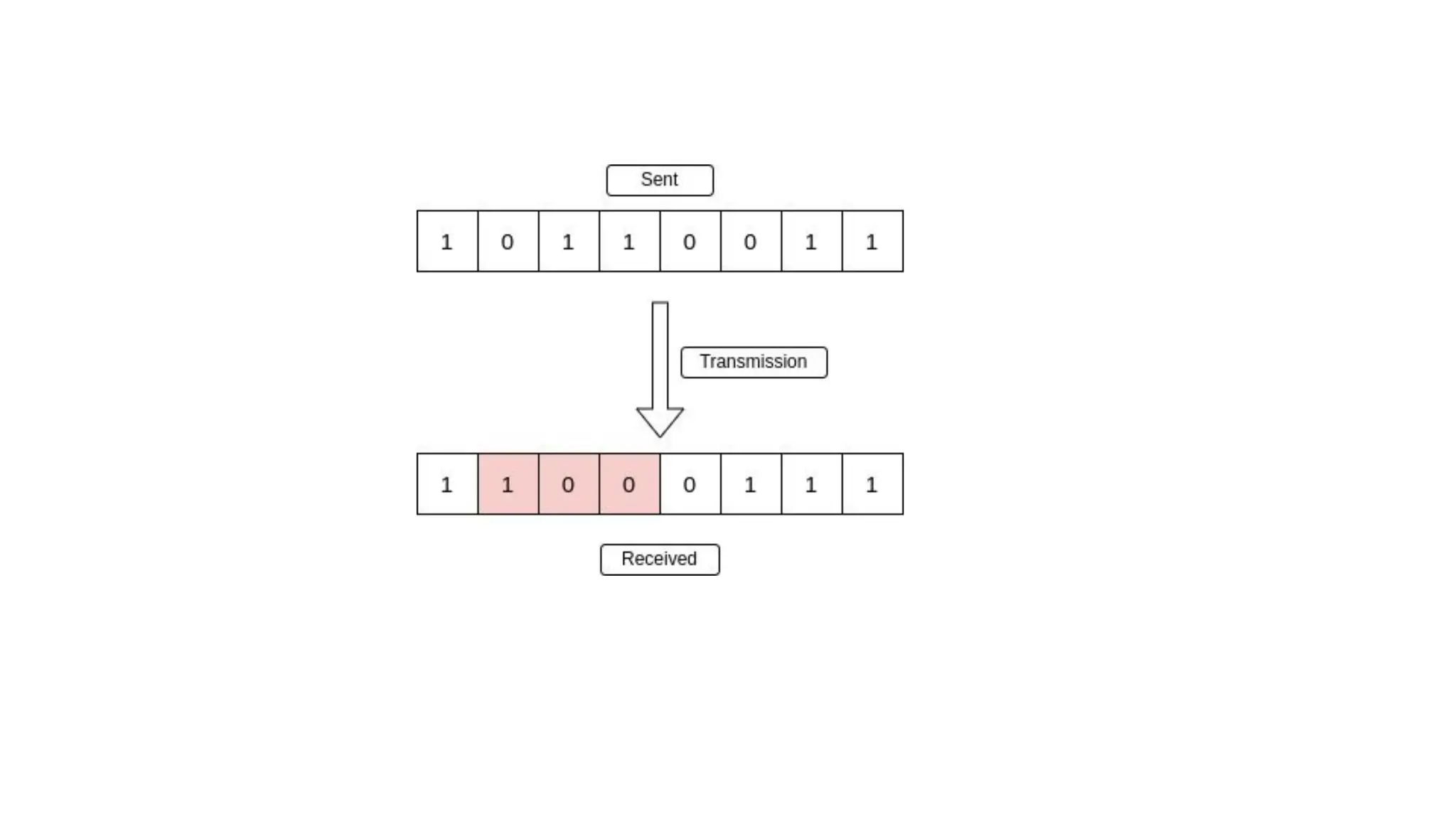
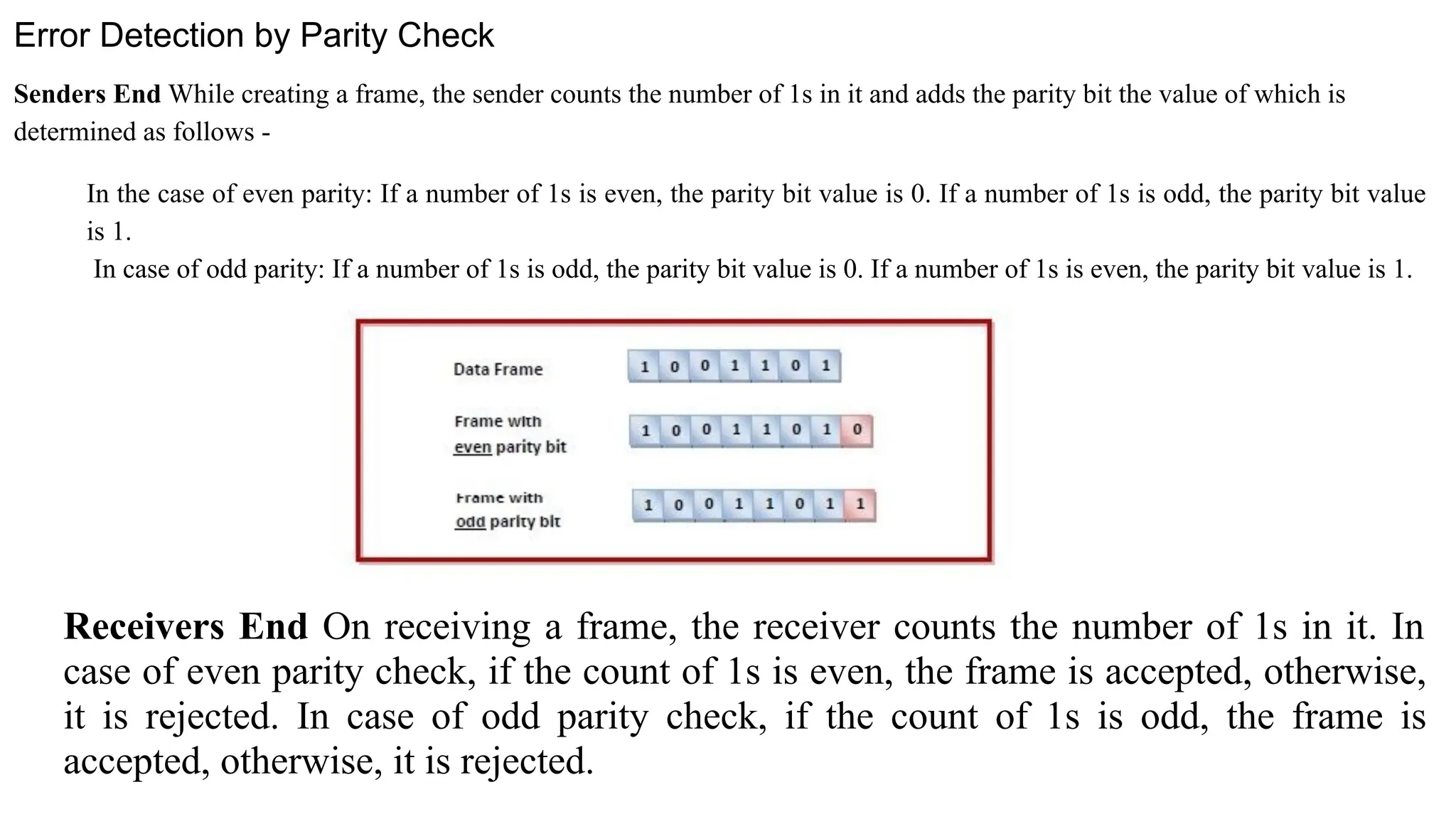
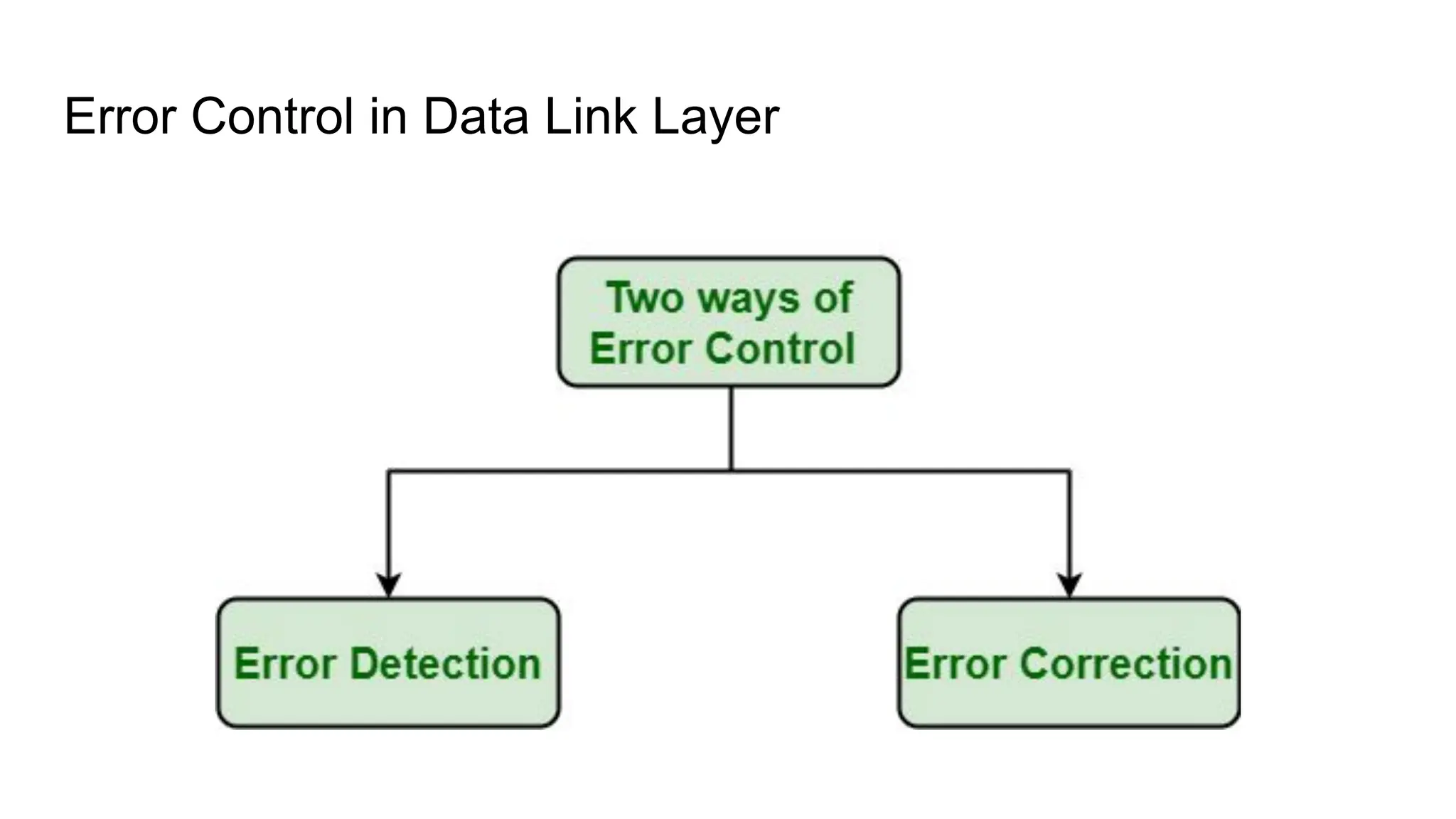
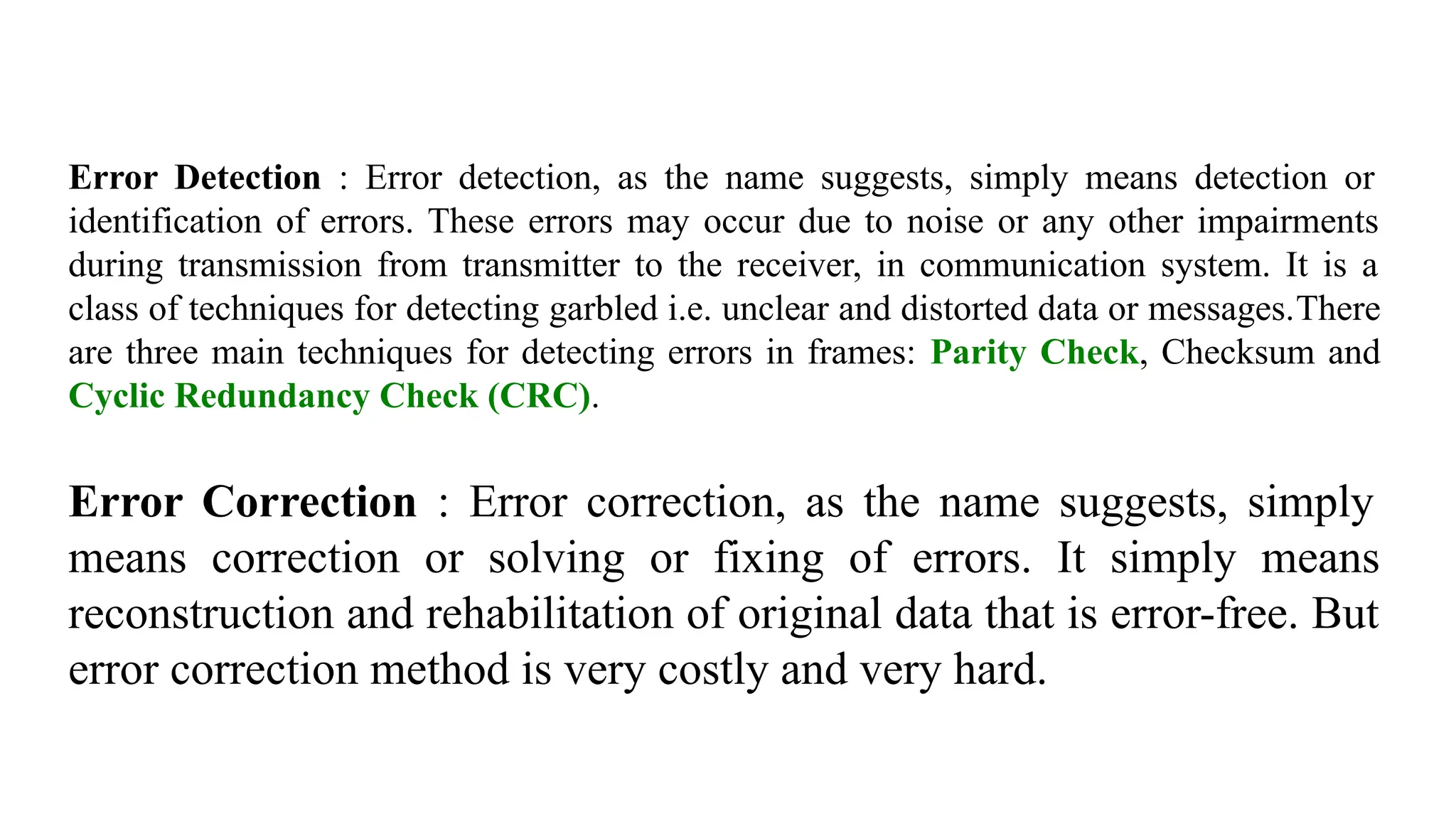
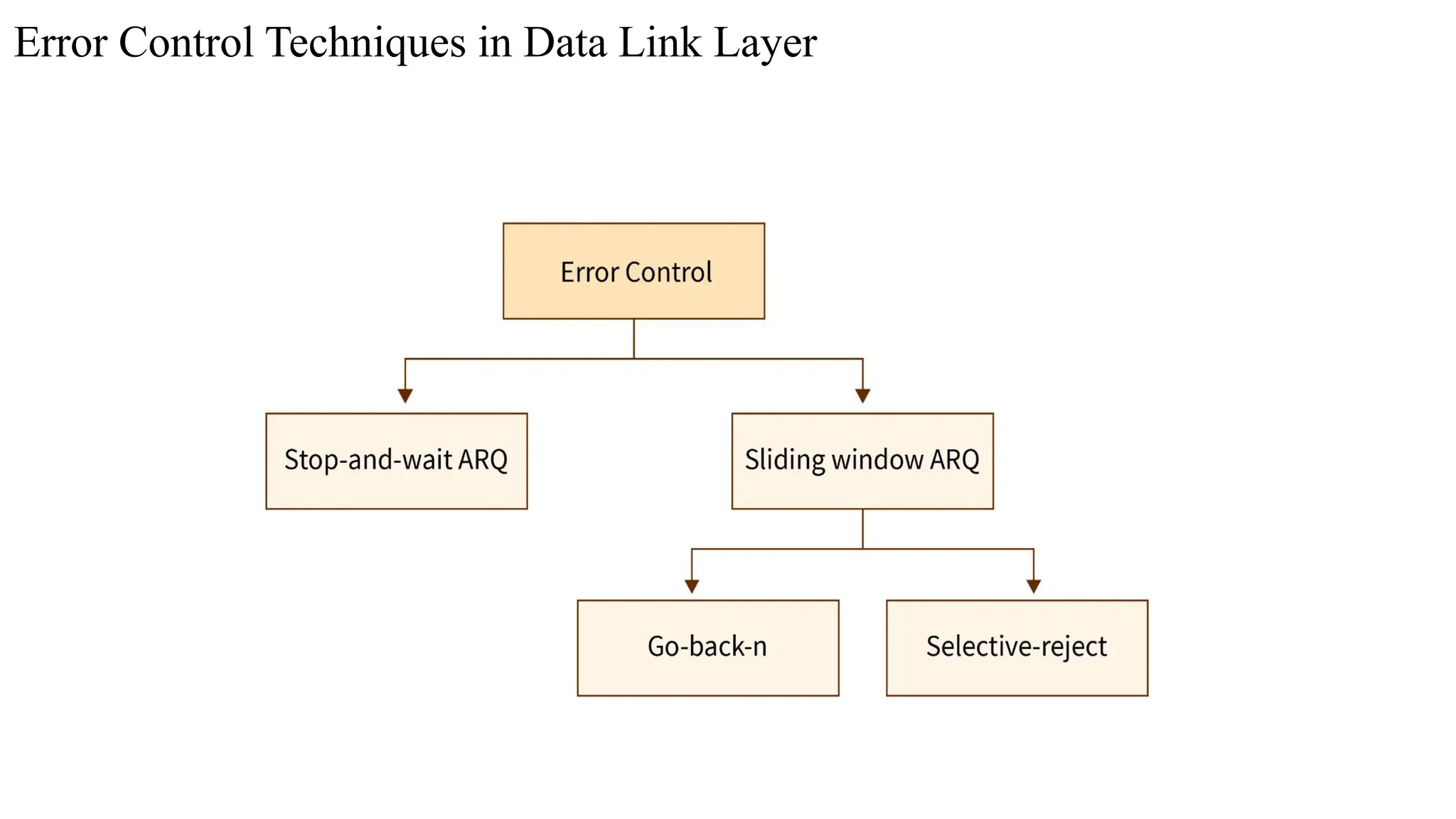
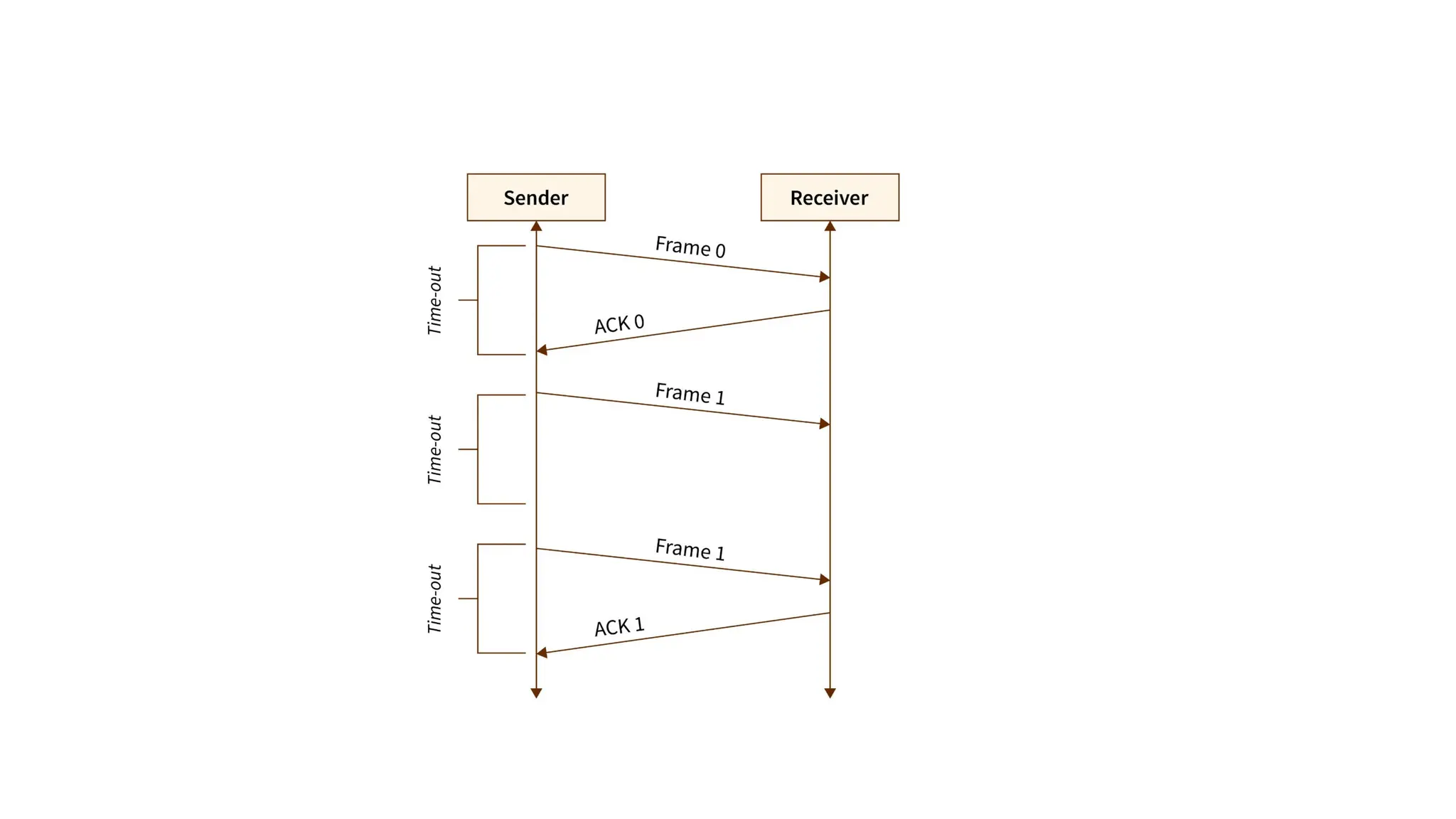
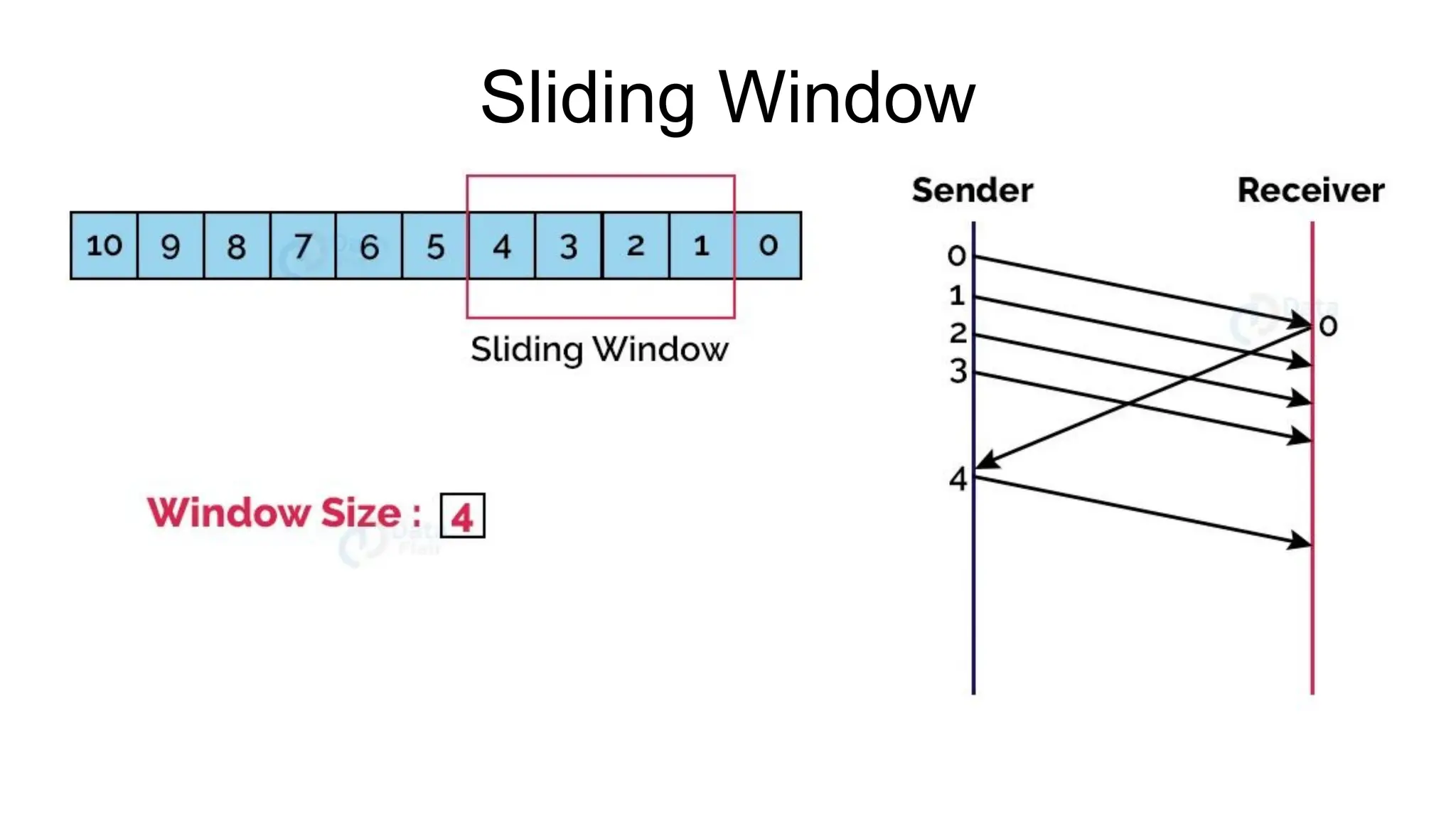
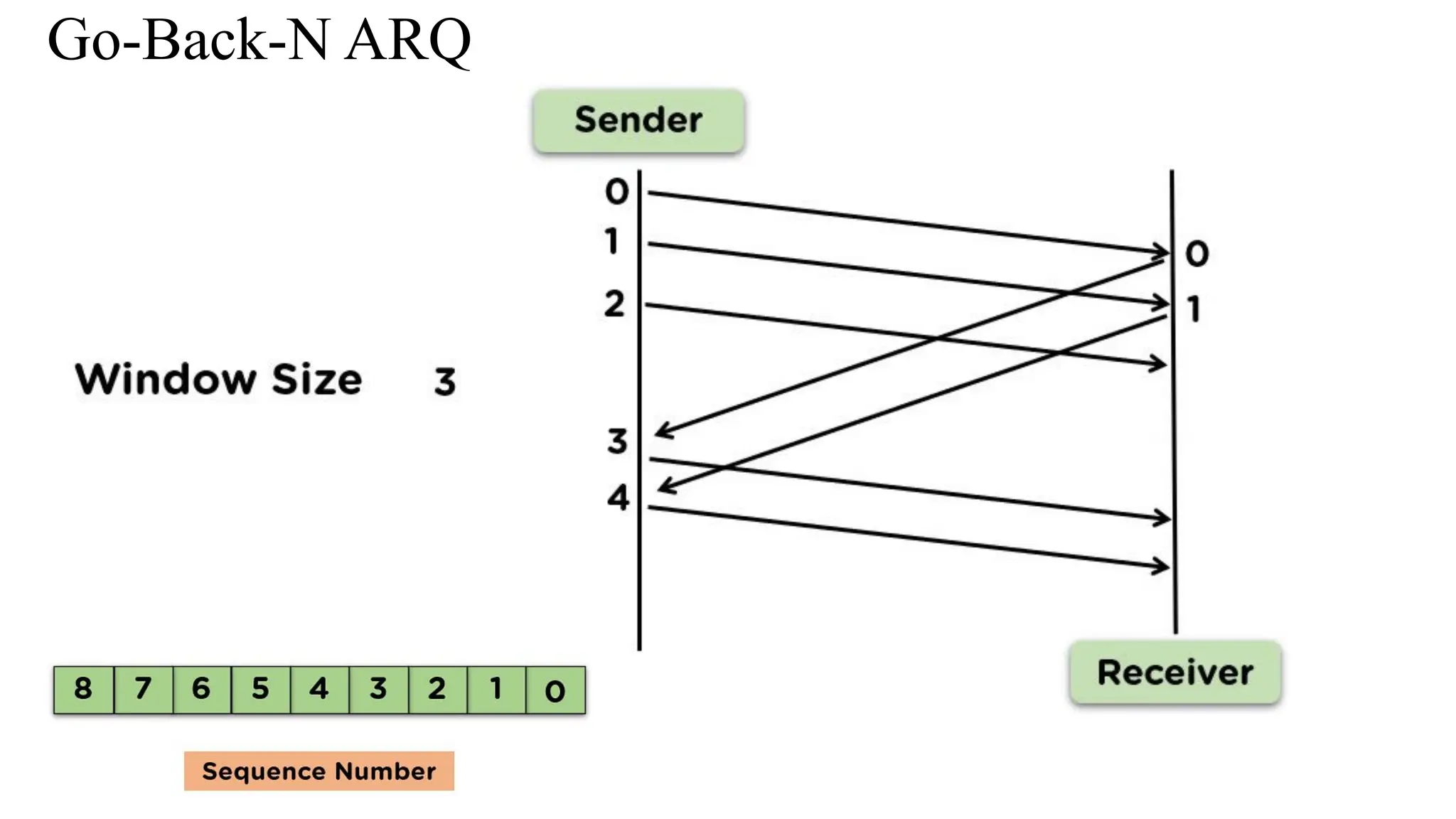
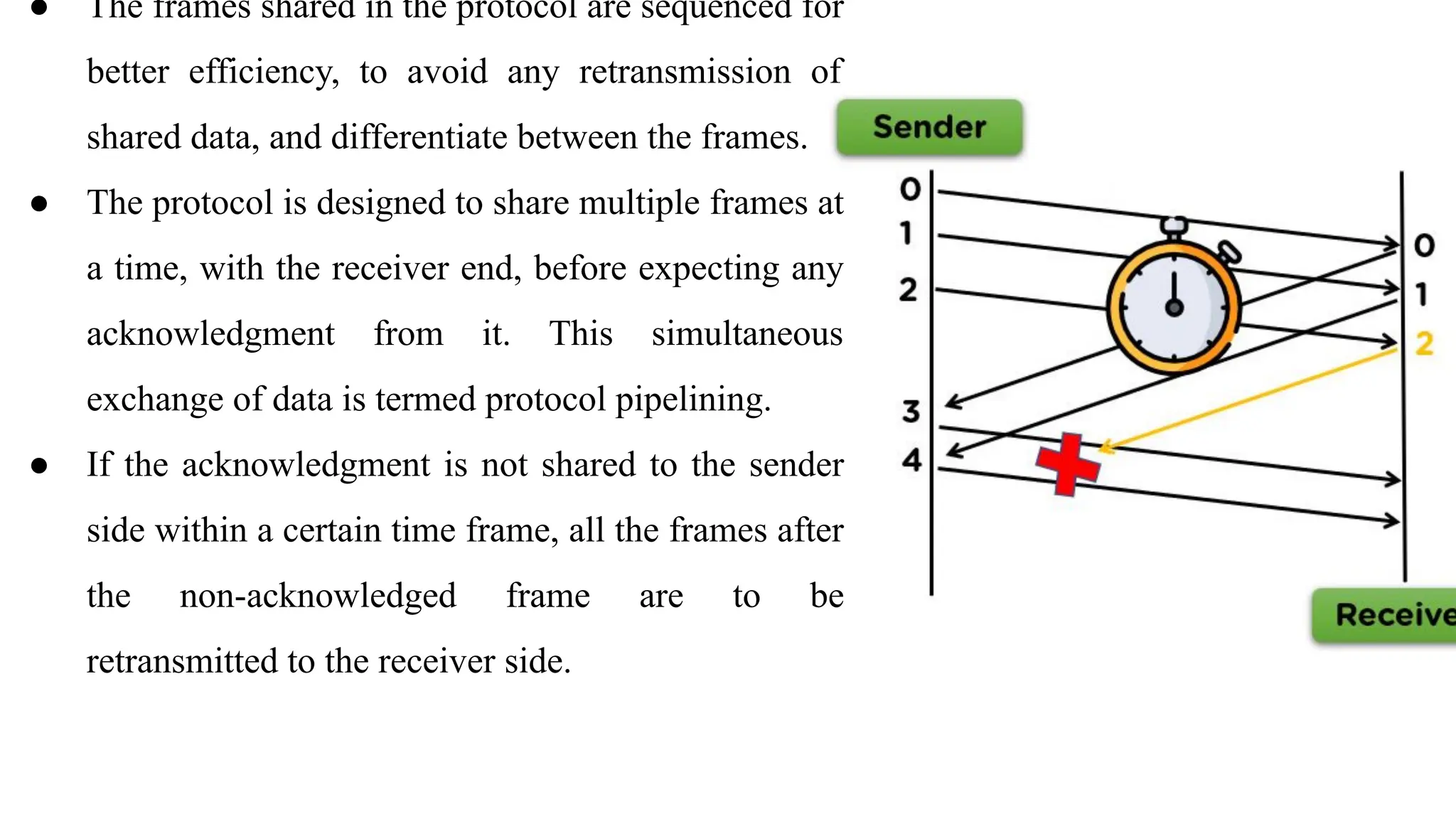
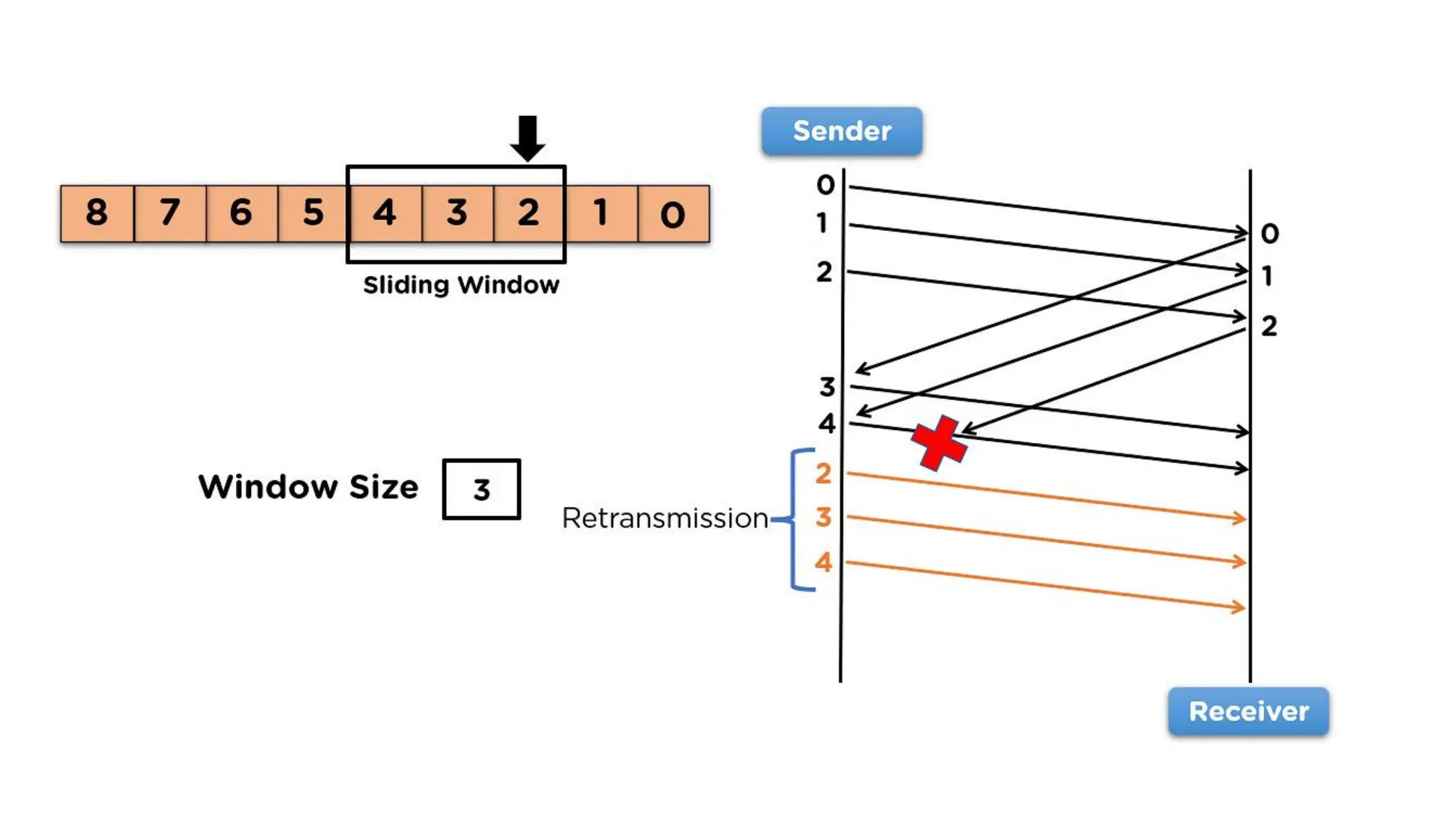
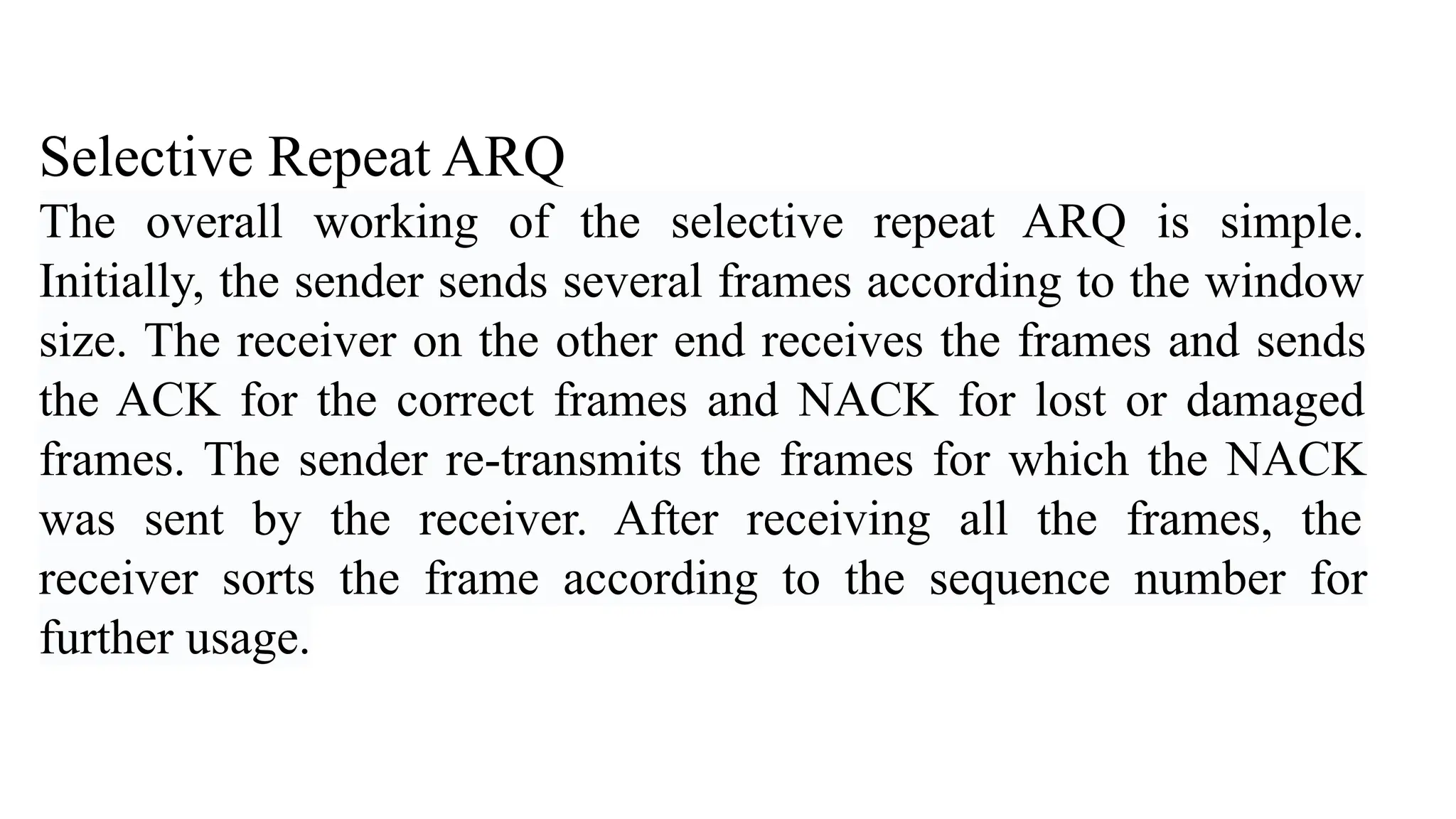
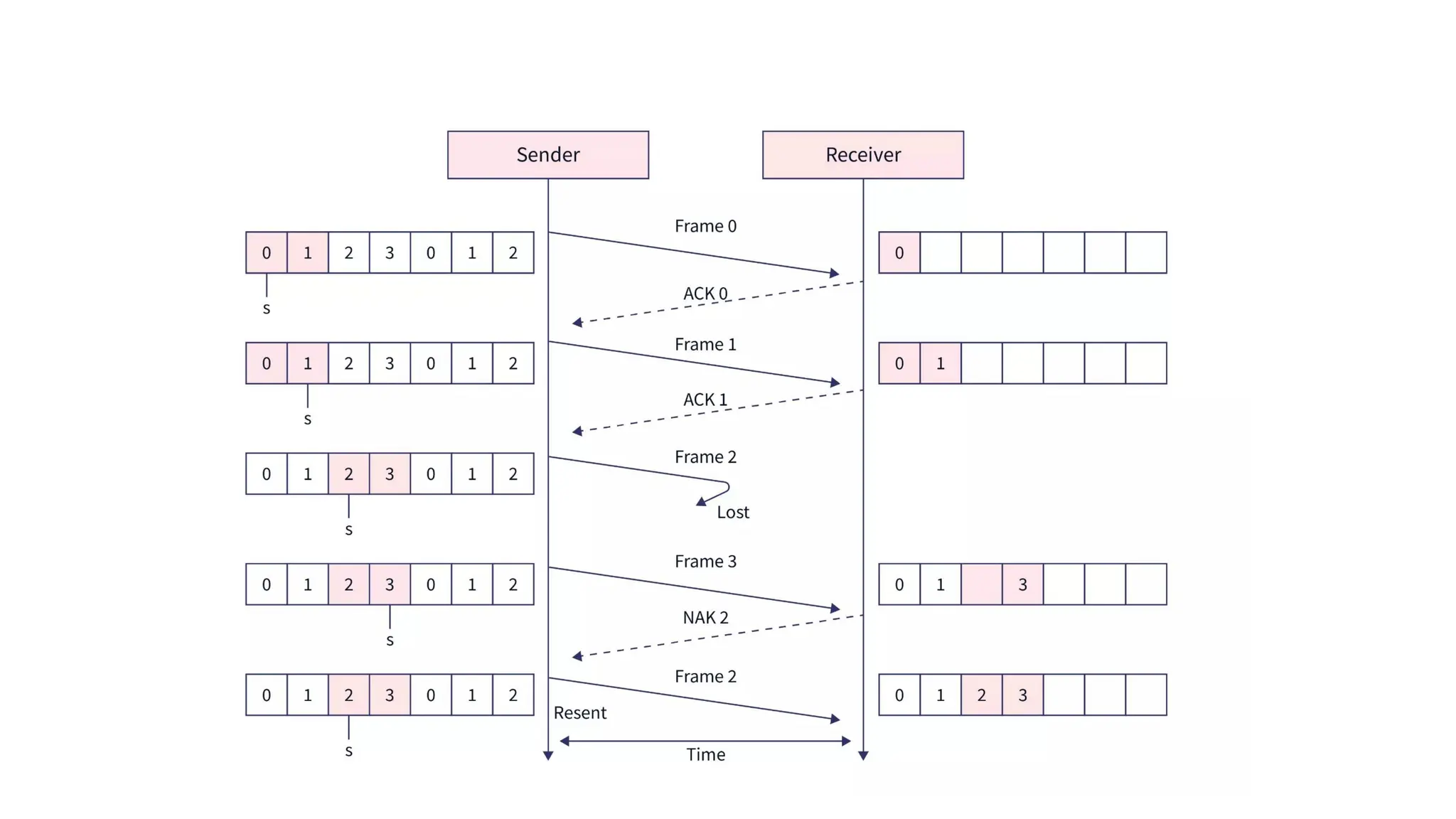
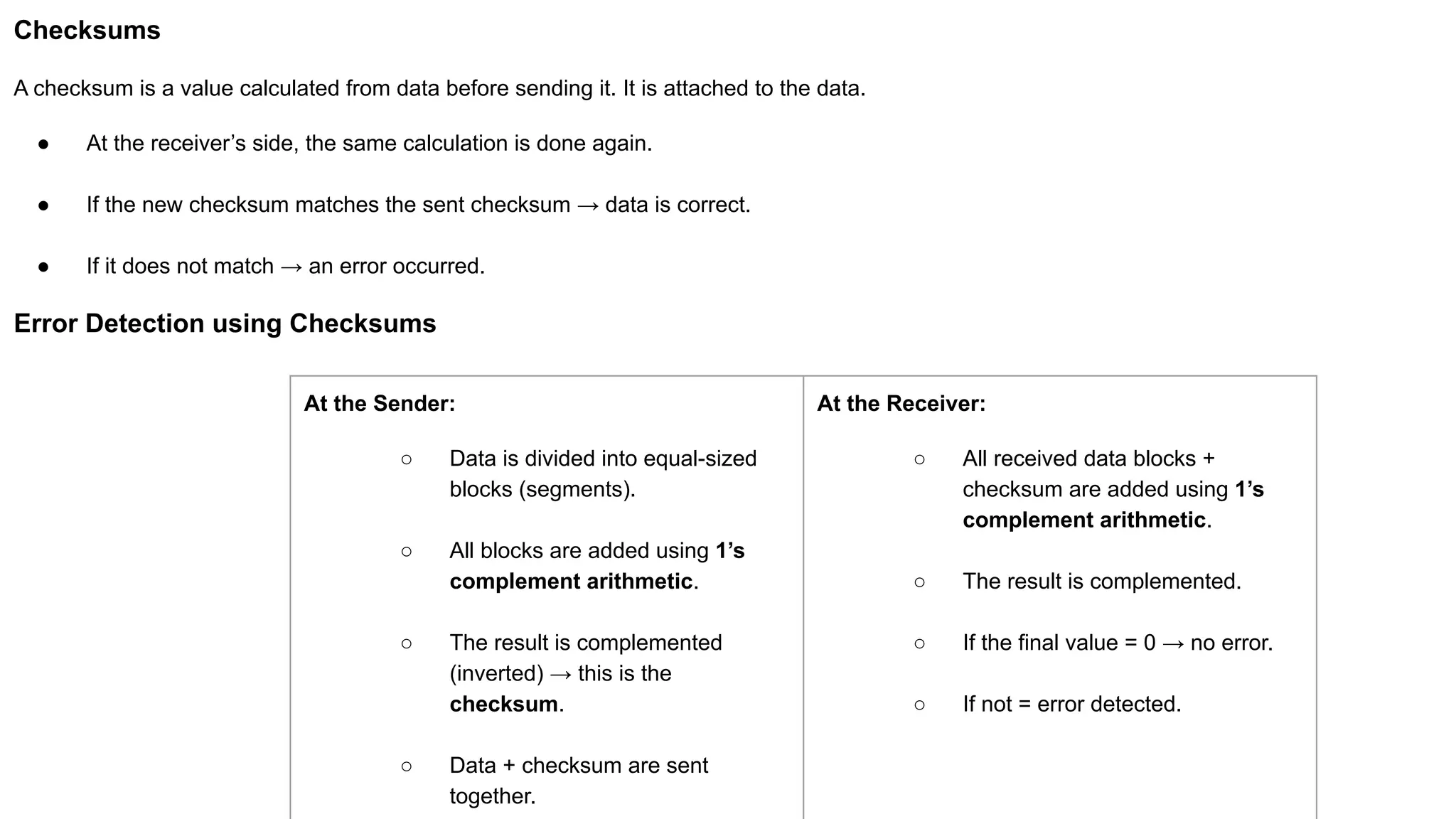
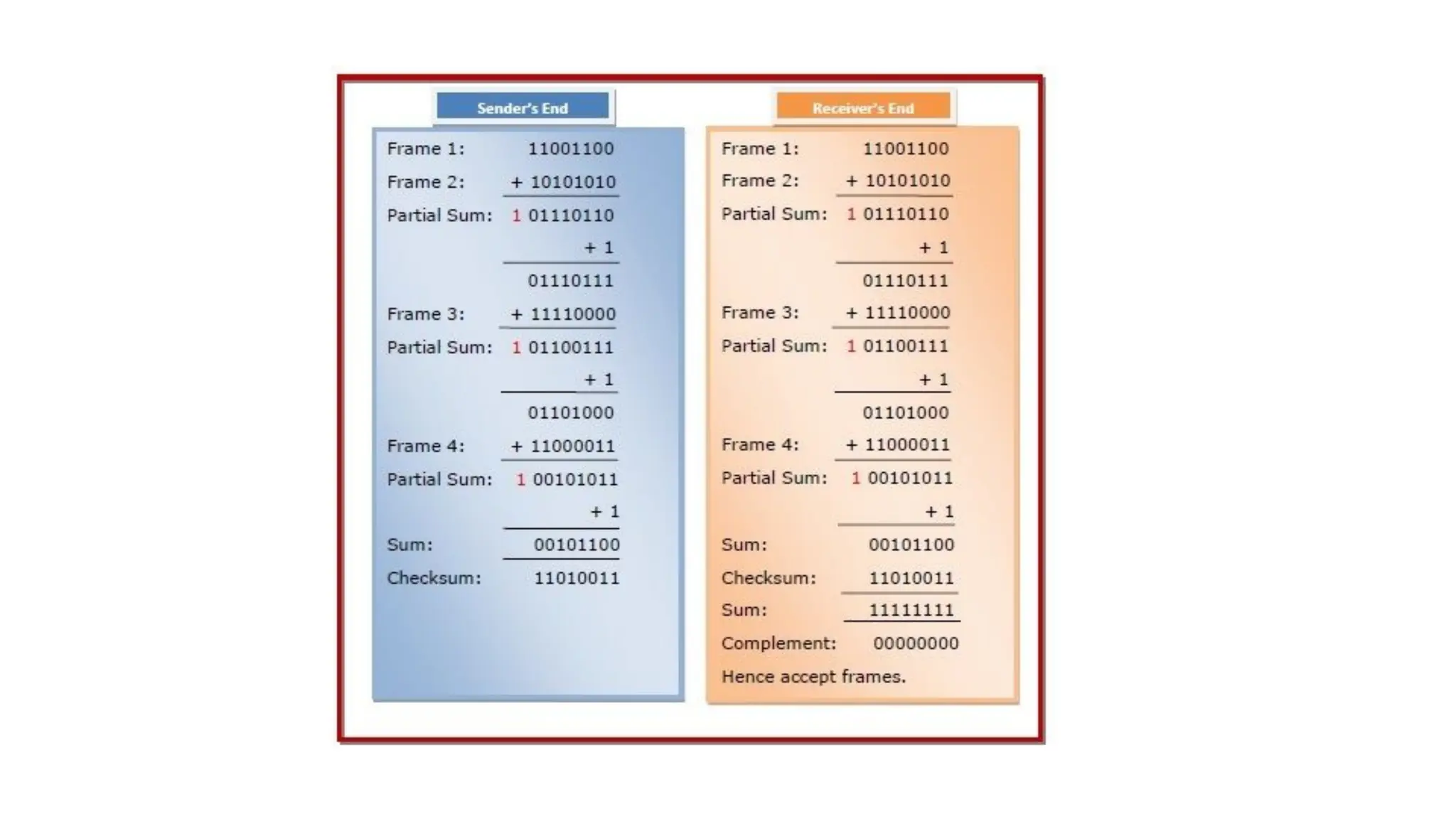
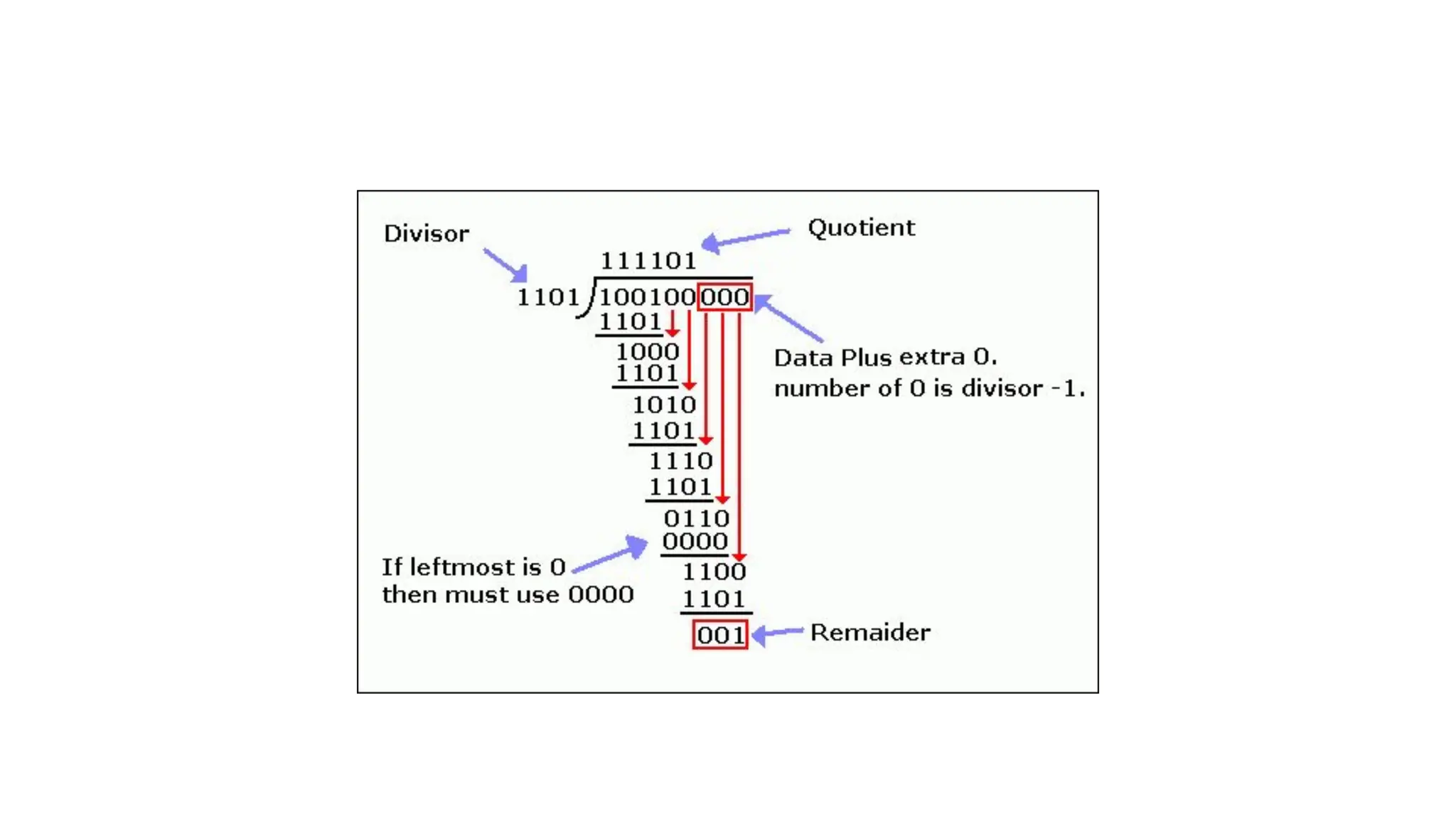
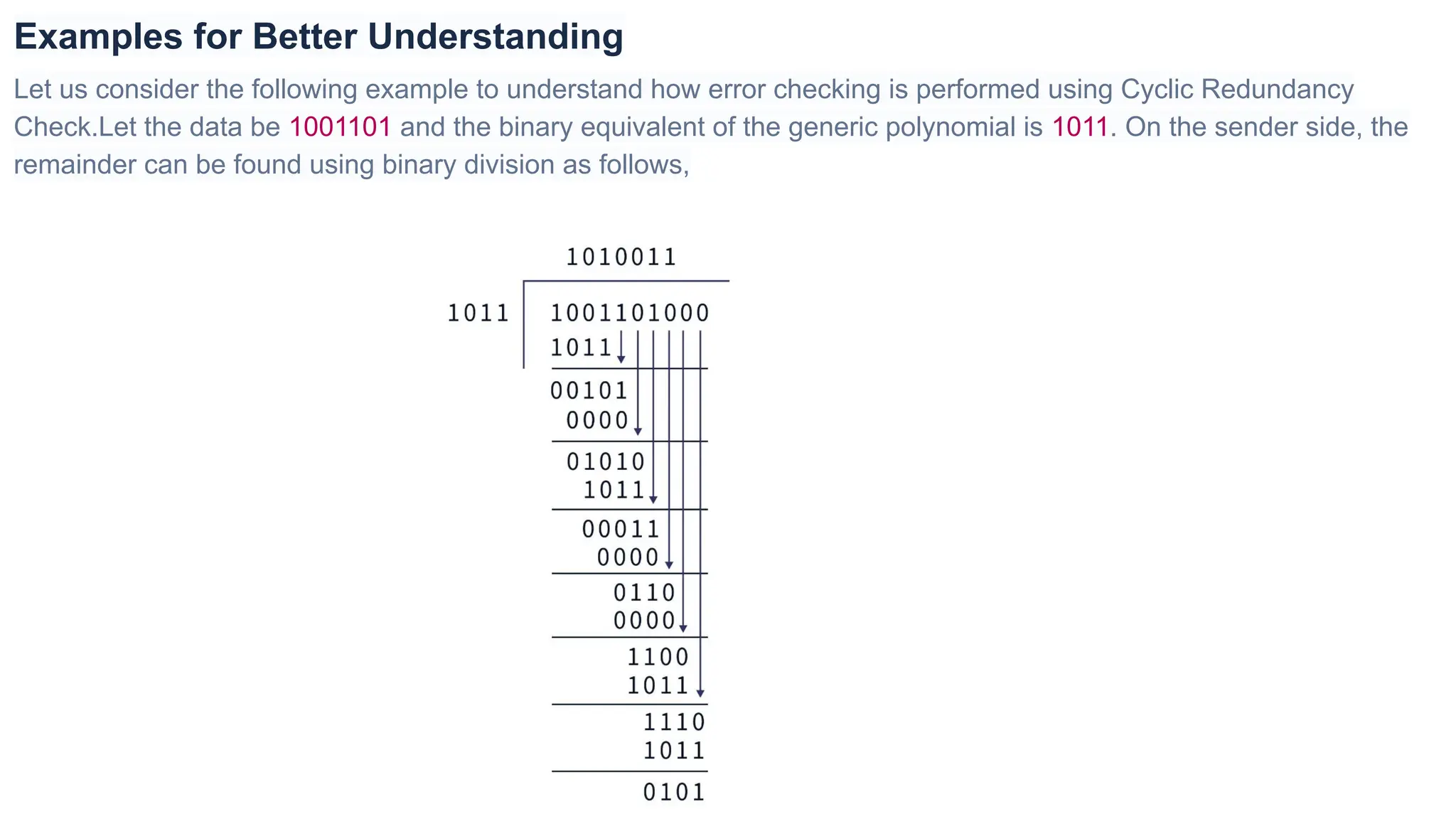
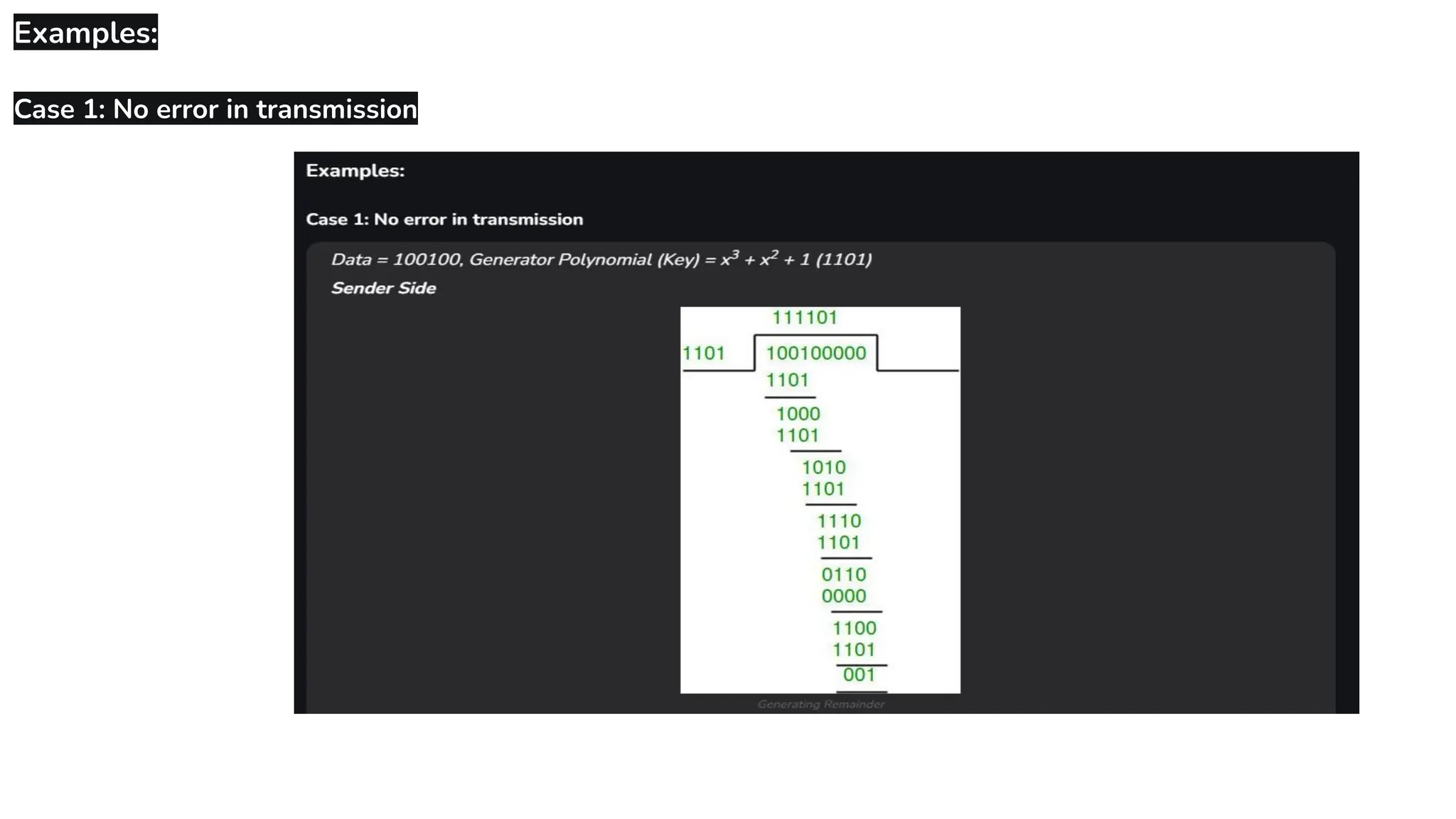
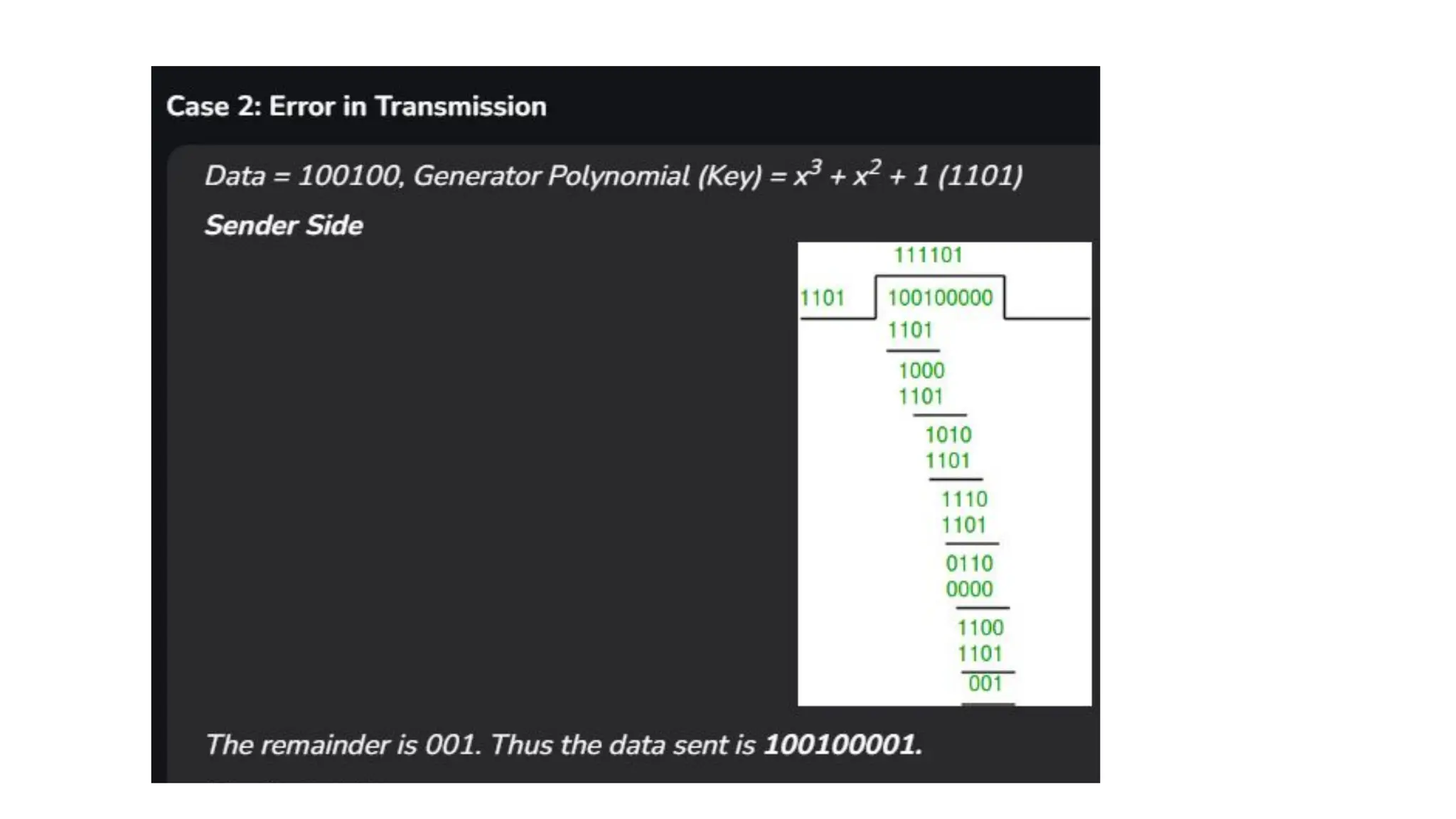
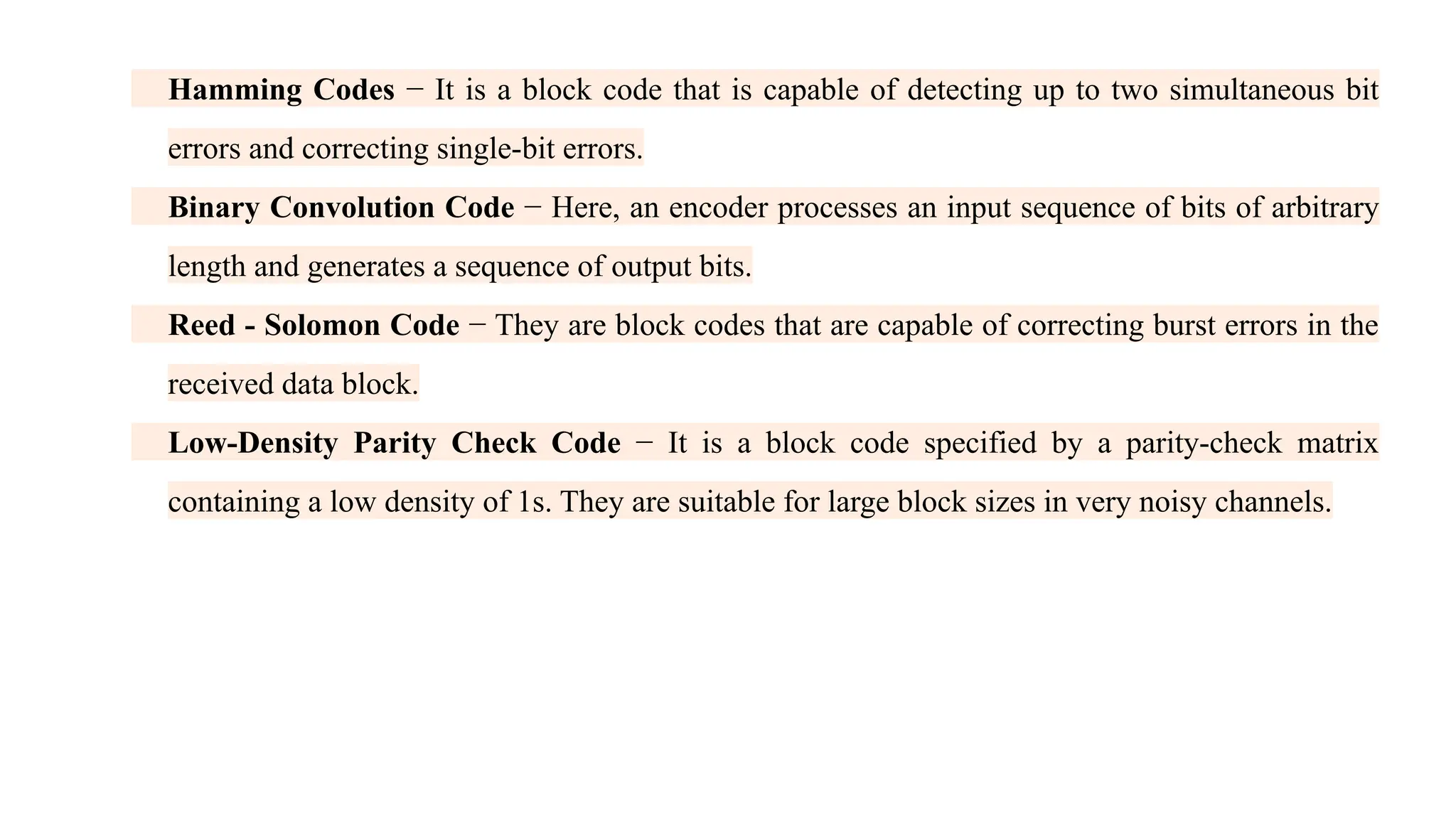
The Logical Link Layer (LLL), a crucial part of the data link layer in computer networks, ensures reliable and efficient communication between directly connected nodes. Unlike the physical layer, which transmits raw bits, the logical link layer provides mechanisms to detect and correct errors, manage data flow, and maintain proper sequencing of frames. Error control is a key function, addressing issues caused by noise, signal attenuation, or interference during data transmission. Errors are broadly classified into single-bit errors, burst errors, and multiple-bit errors, which can distort the transmitted data. To detect these errors, various techniques are employed, including the parity check method, checksum method, and cyclic redundancy check (CRC), each varying in complexity and effectiveness. Once detected, errors are corrected using methods like Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ), which retransmits corrupted frames, and Forward Error Correction (FEC), which allows the receiver to correct errors without retransmission. Alongside error control, flow control ensures that the sender does not overwhelm the receiver by regulating the rate of data transmission. Collectively, error control and flow control maintain the integrity, reliability, and efficiency of data transfer, making the logical link layer indispensable for robust network communication.