Embed presentation





The document discusses various division algorithms in computer architecture, focusing on both restoring and non-restoring methods for unsigned binary division. It highlights the implementation details and advantages of the non-restoring algorithm, including eliminating a test subtraction and efficient sign handling. The document also notes the necessity of adjusting the sign after converting to positive in the simplest solution.
Introduction to computer architecture focusing on ALU by S. Ciyamala Kushbu, ECE Assistant Professor.
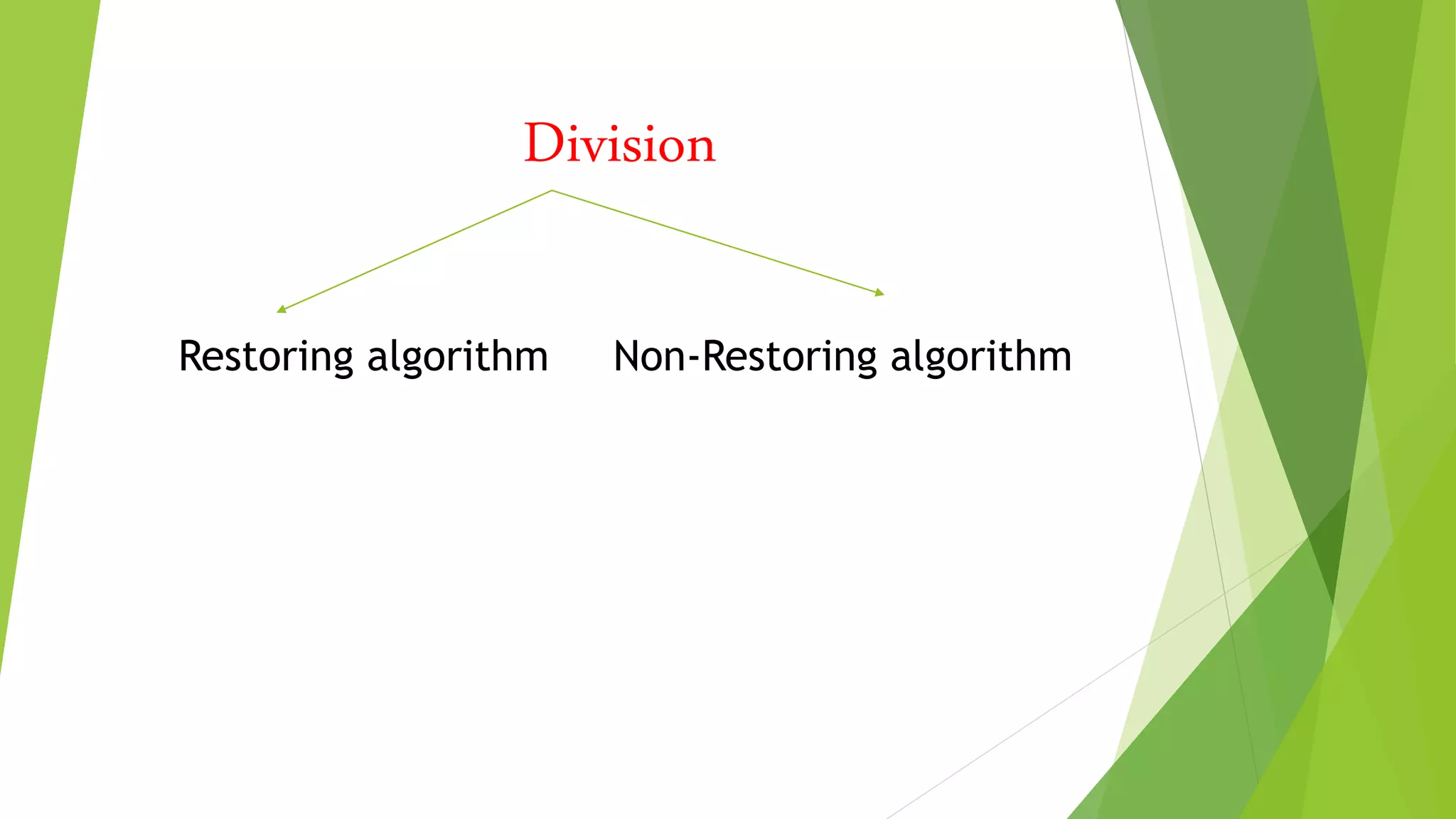
Introduction to the two types of division algorithms: Restoring and Non-Restoring.
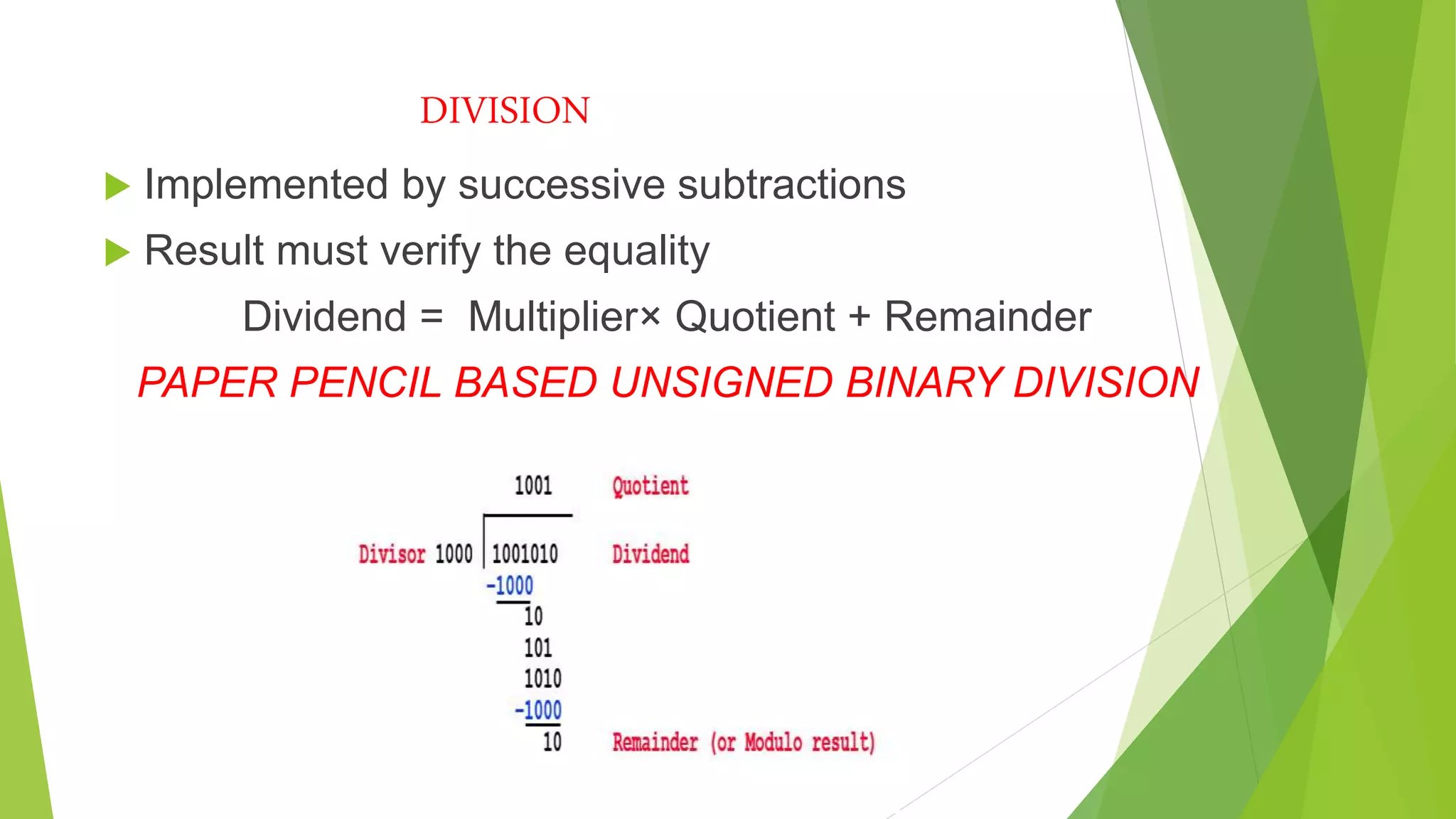
Detailed explanation of unsigned binary division using successive subtractions with a relation of dividend, multiplier, quotient, and remainder.
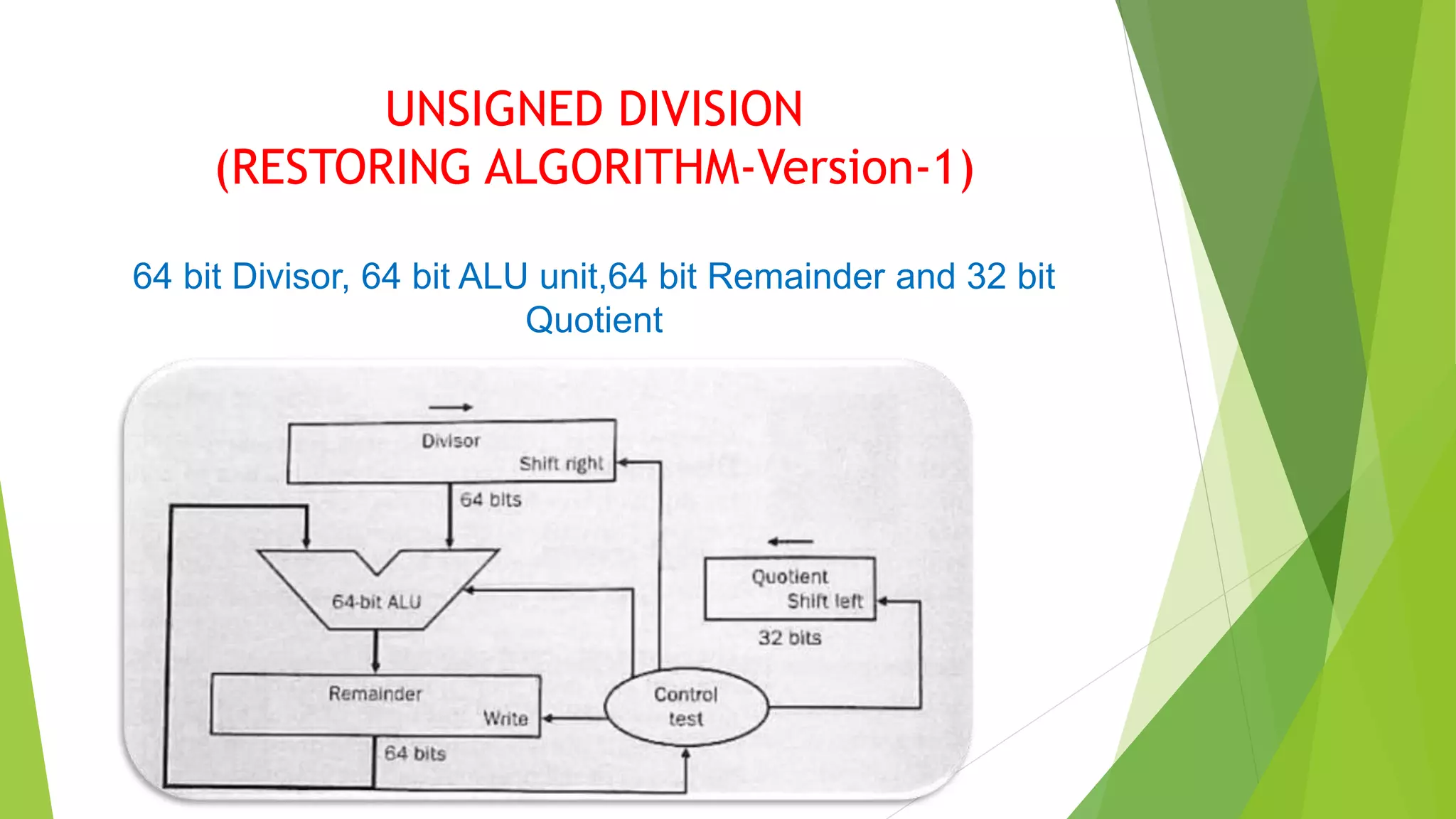
Outline of unsigned division using a restoring algorithm with specifications of 64-bit divisor, ALU unit, remainder, and 32-bit quotient.
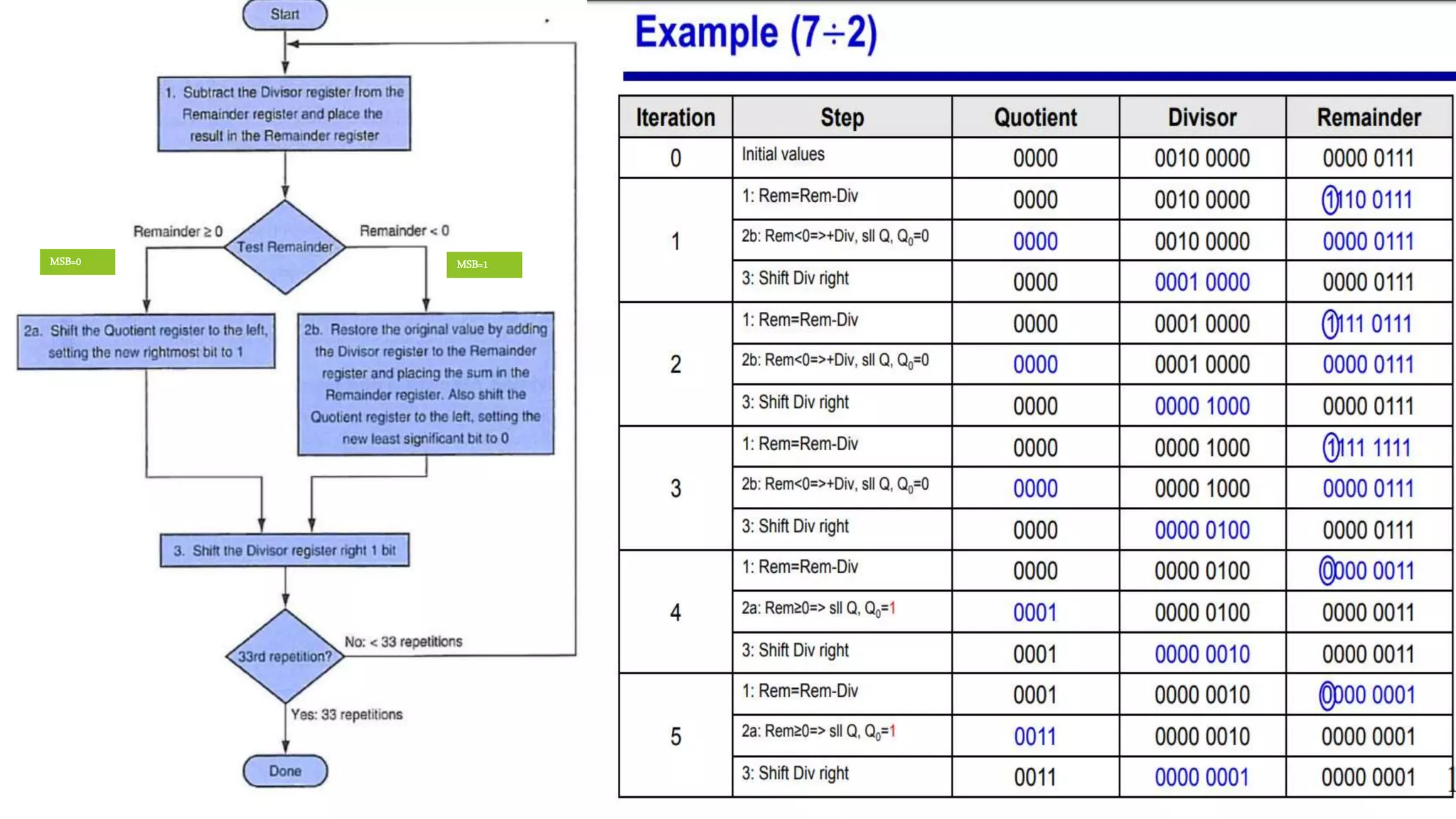
Illustration of the significance of the most significant bit (MSB) in the division.
Observations from the first version of the division algorithm highlighting efficiency losses due to zero bits.
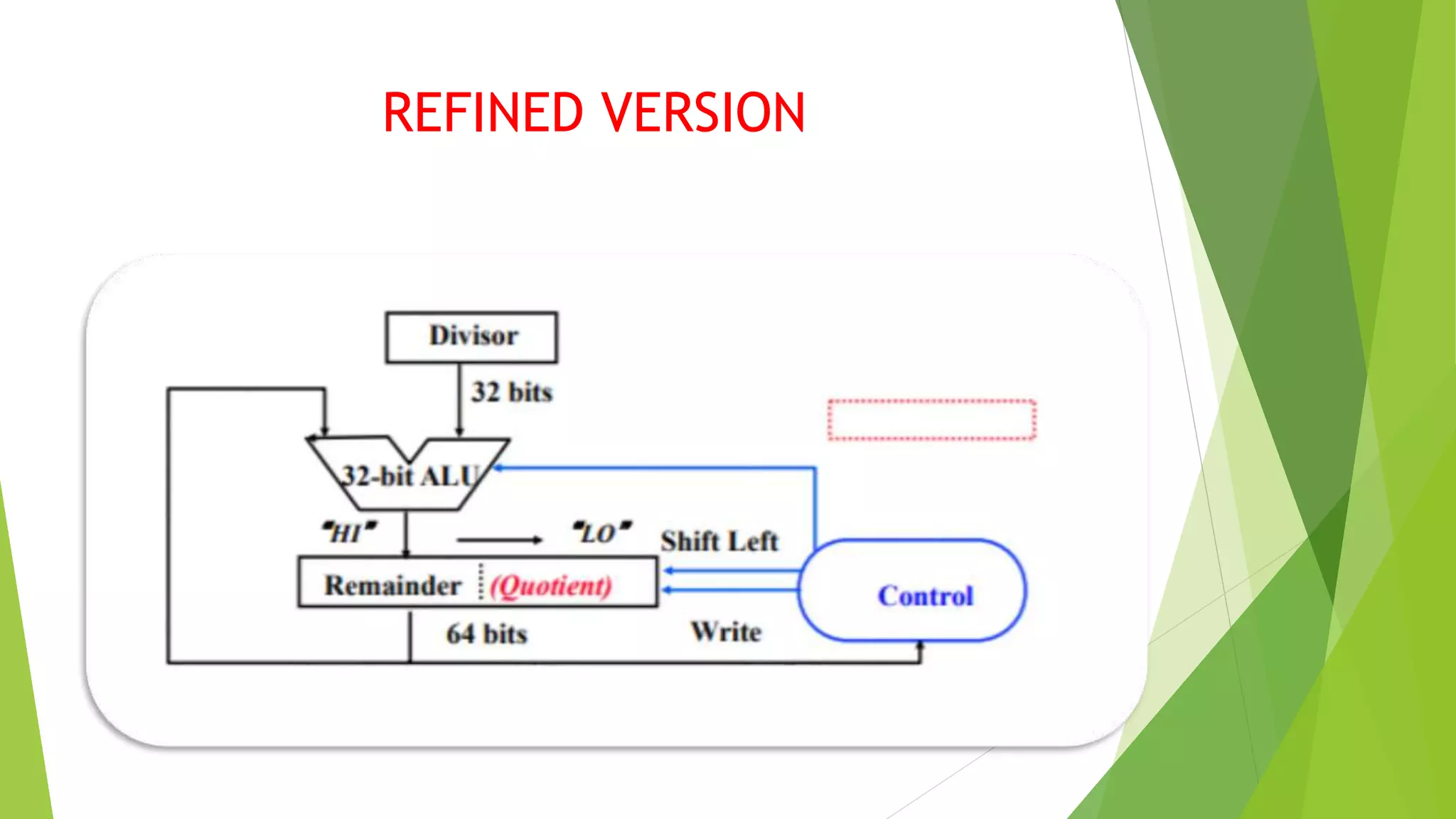
Introduction to a refined version of the division algorithm addressing previous issues.
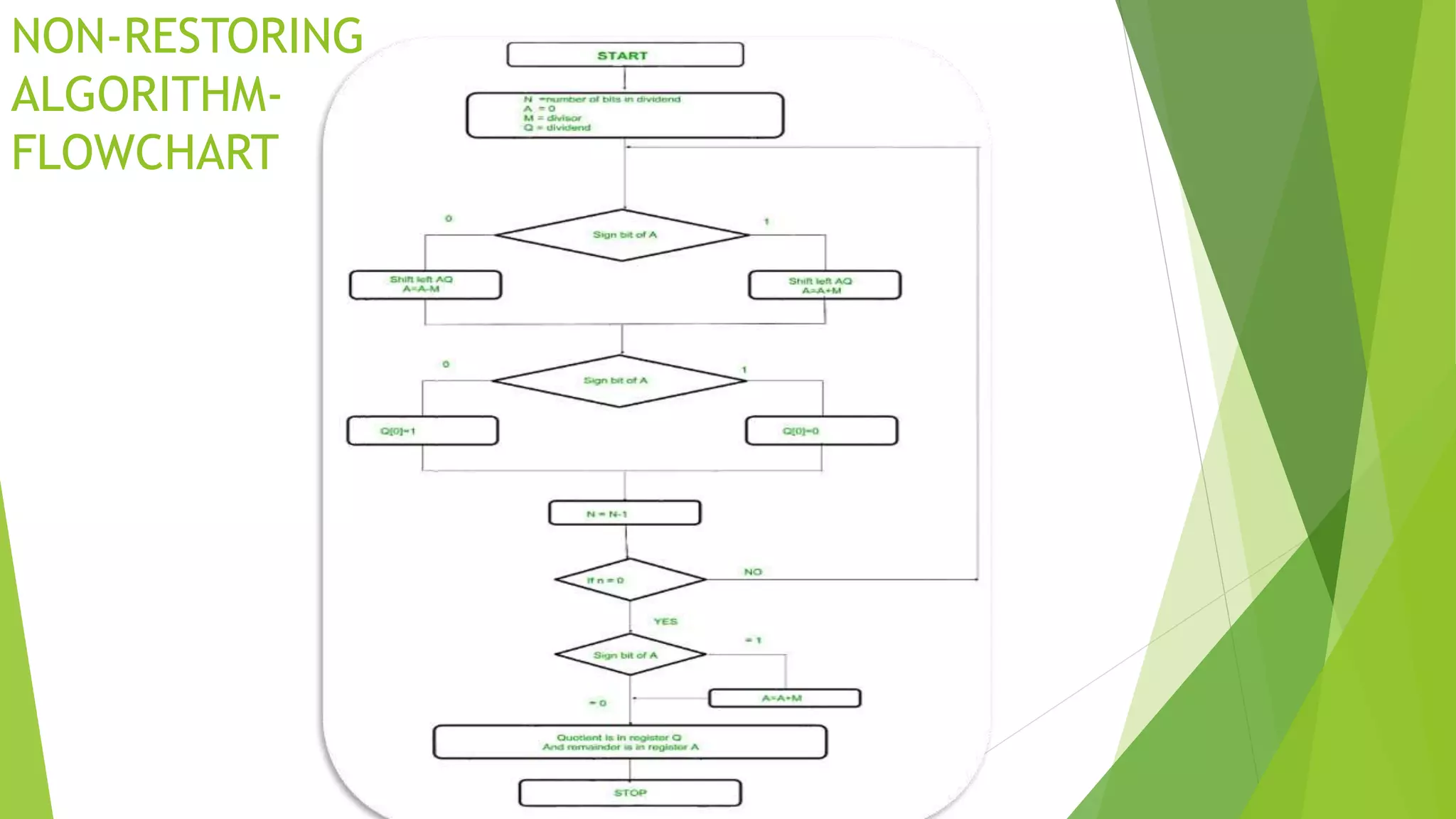
Overview of the Non-Restoring algorithm represented through a flowchart.
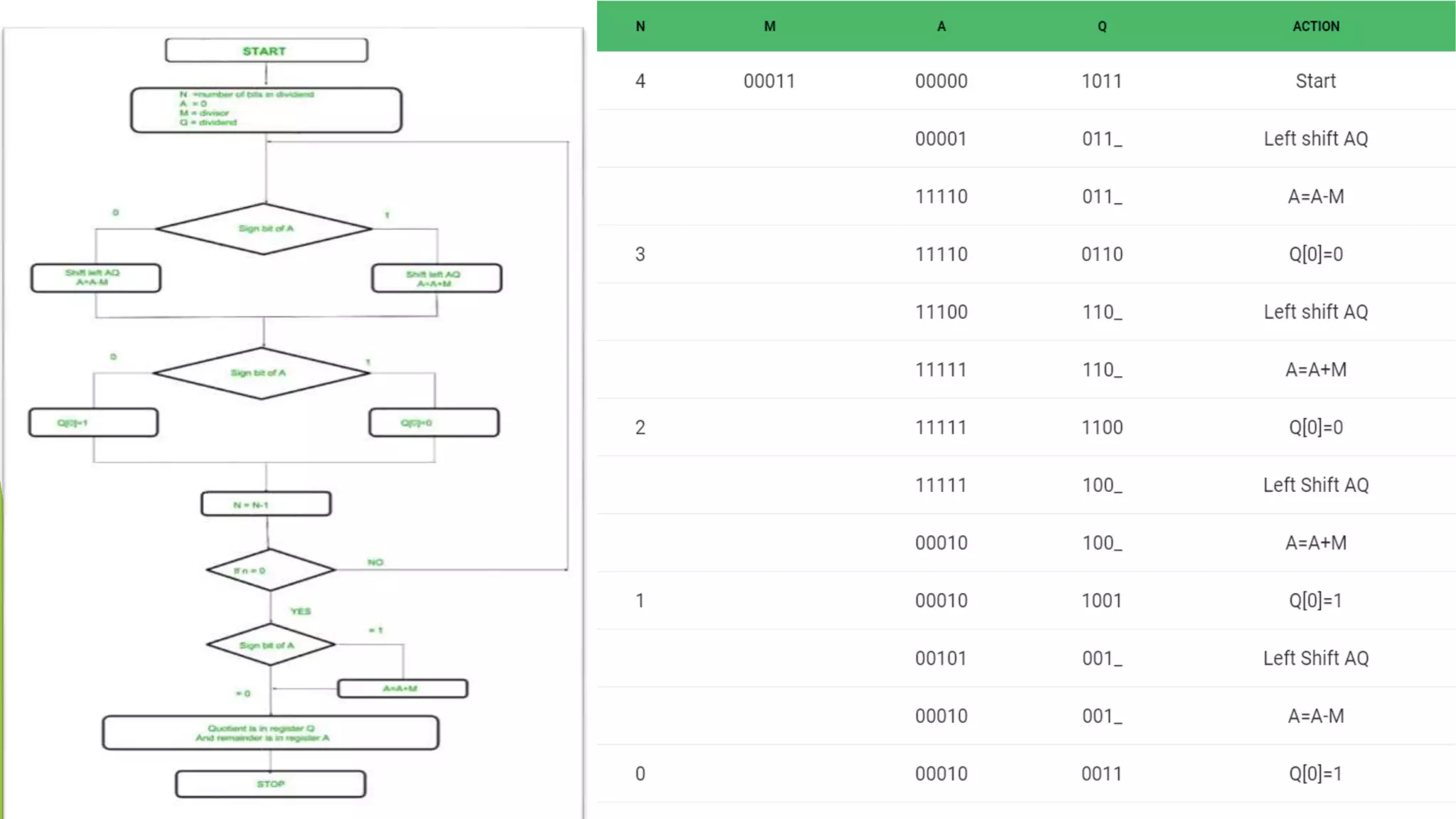
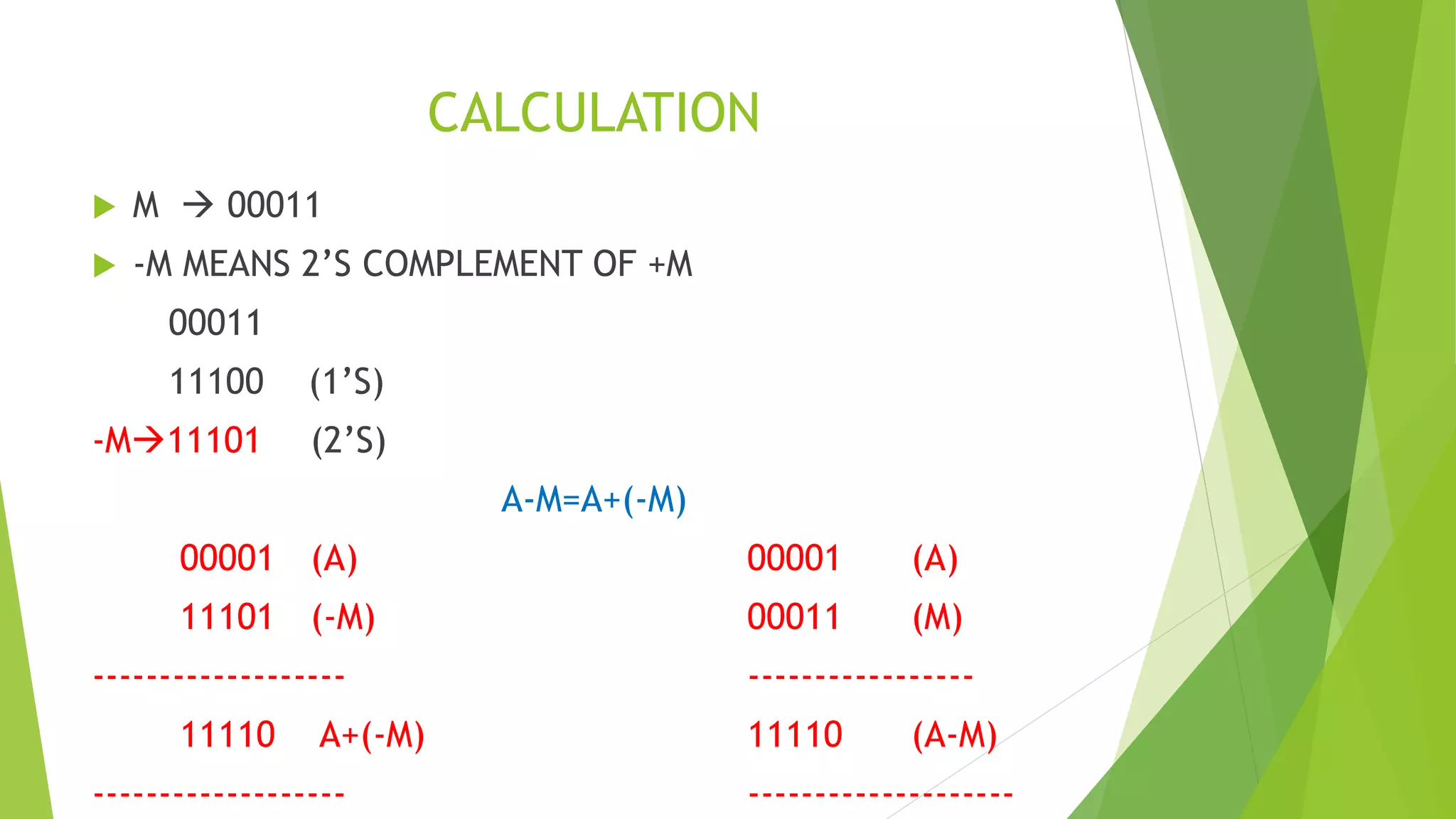
Detailed calculation process in the Non-Restoring algorithm demonstrating 2's complement logic.
Advantages of the non-restoring algorithm include less complexity; however, it requires an extra bit for sign tracking.
Overview of signed division strategies with emphasis on converting to positive and adjusting final signs thereafter.












