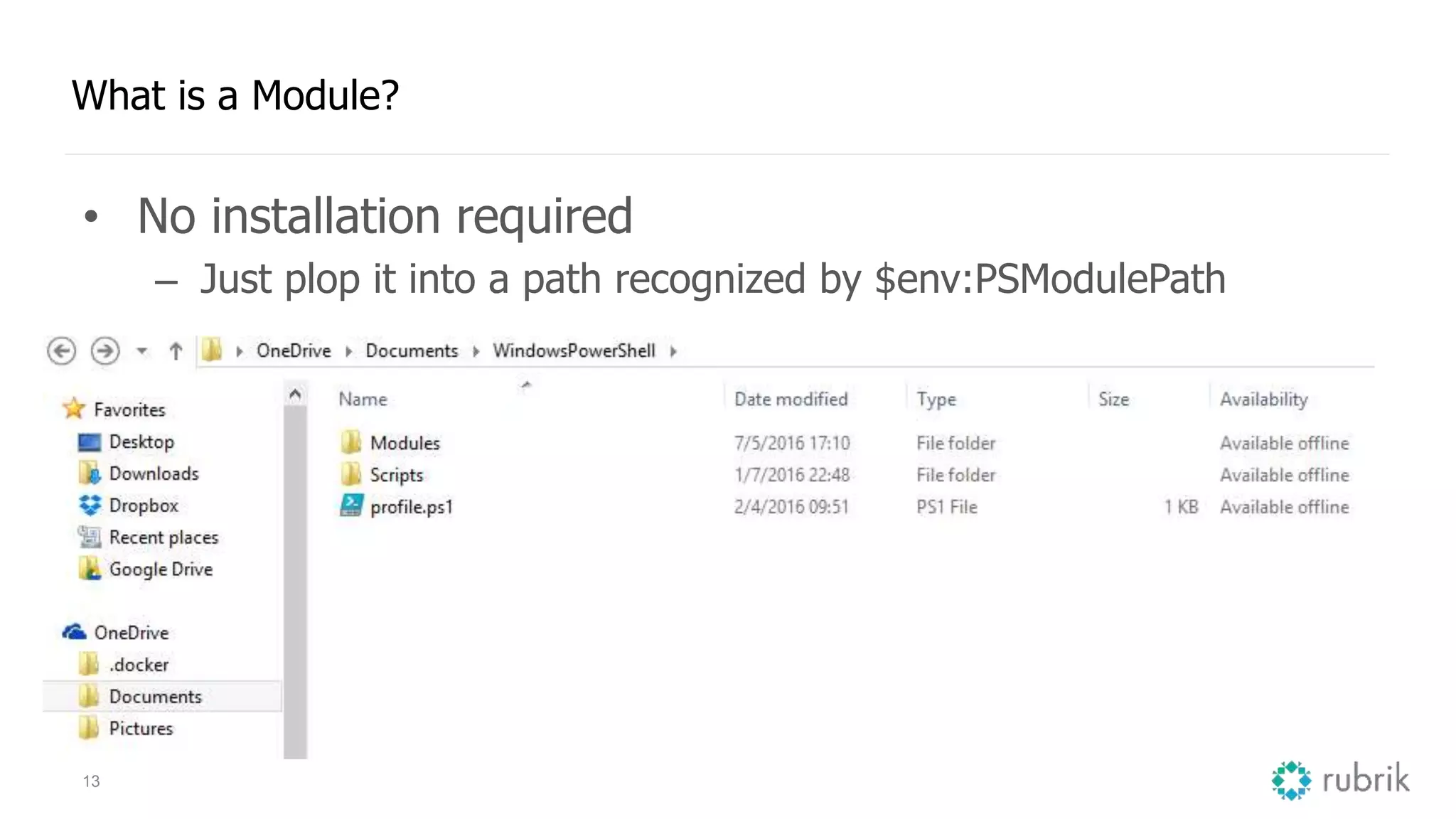
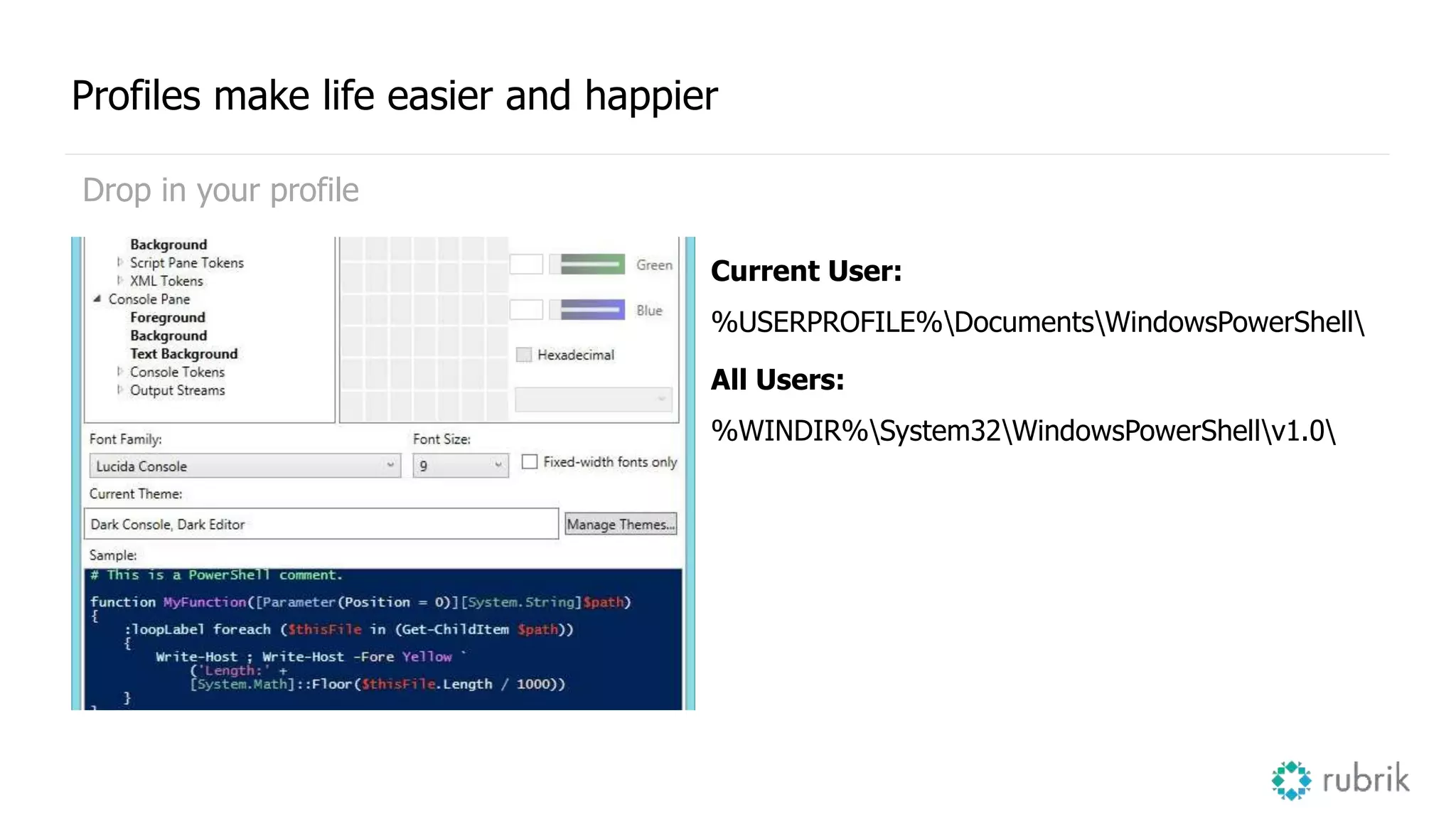
This document provides an overview and introduction to PowerShell and PowerCLI for managing VMware environments. It discusses what PowerShell and PowerCLI are, important terminology like modules and functions, how to set them up and configure profiles, and examples of how to start coding with PowerShell including gathering data, writing logic statements, and using cmdlets safely. The presenters are introduced and an agenda is provided covering these topics at a high level to get started with PowerShell and PowerCLI.