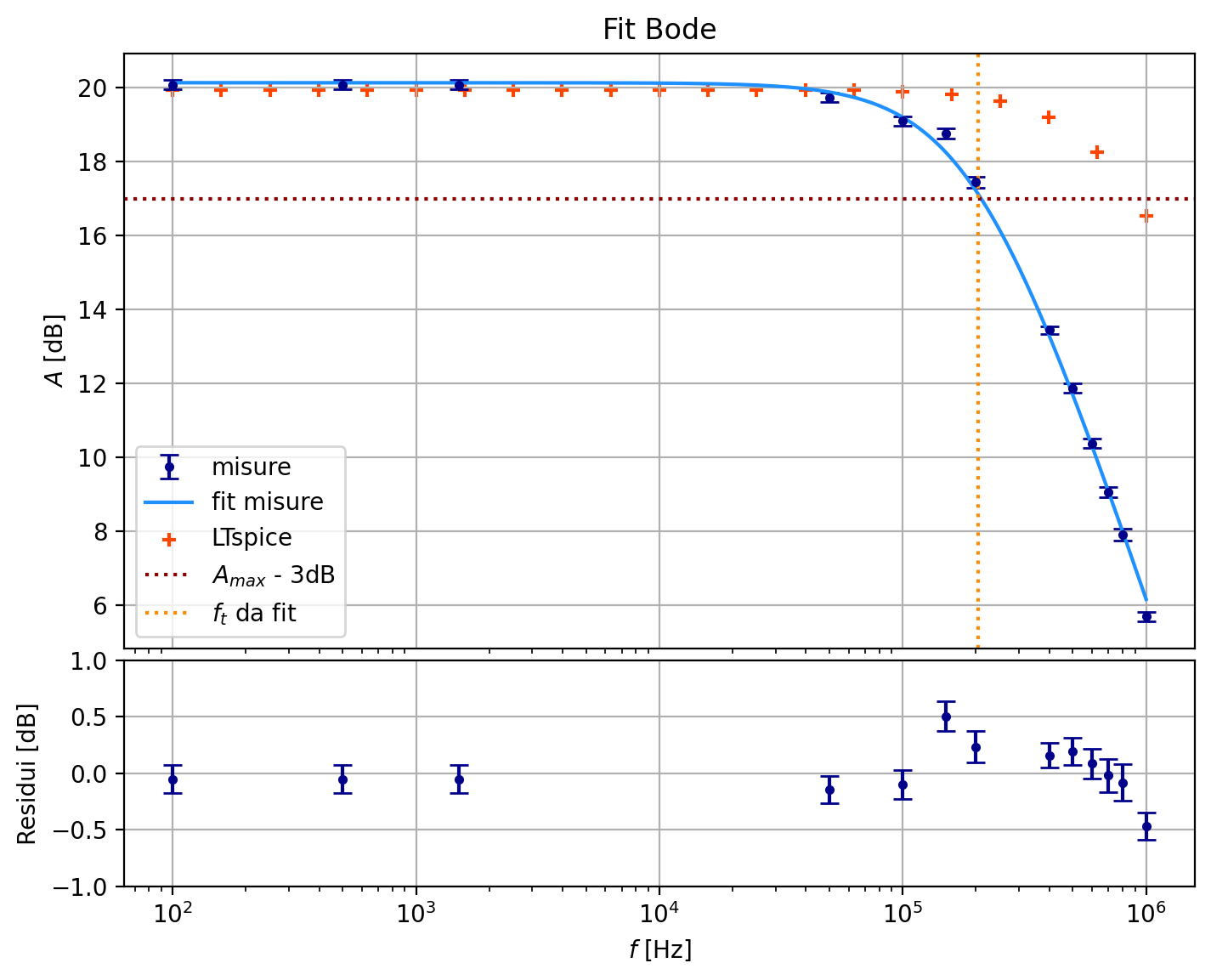
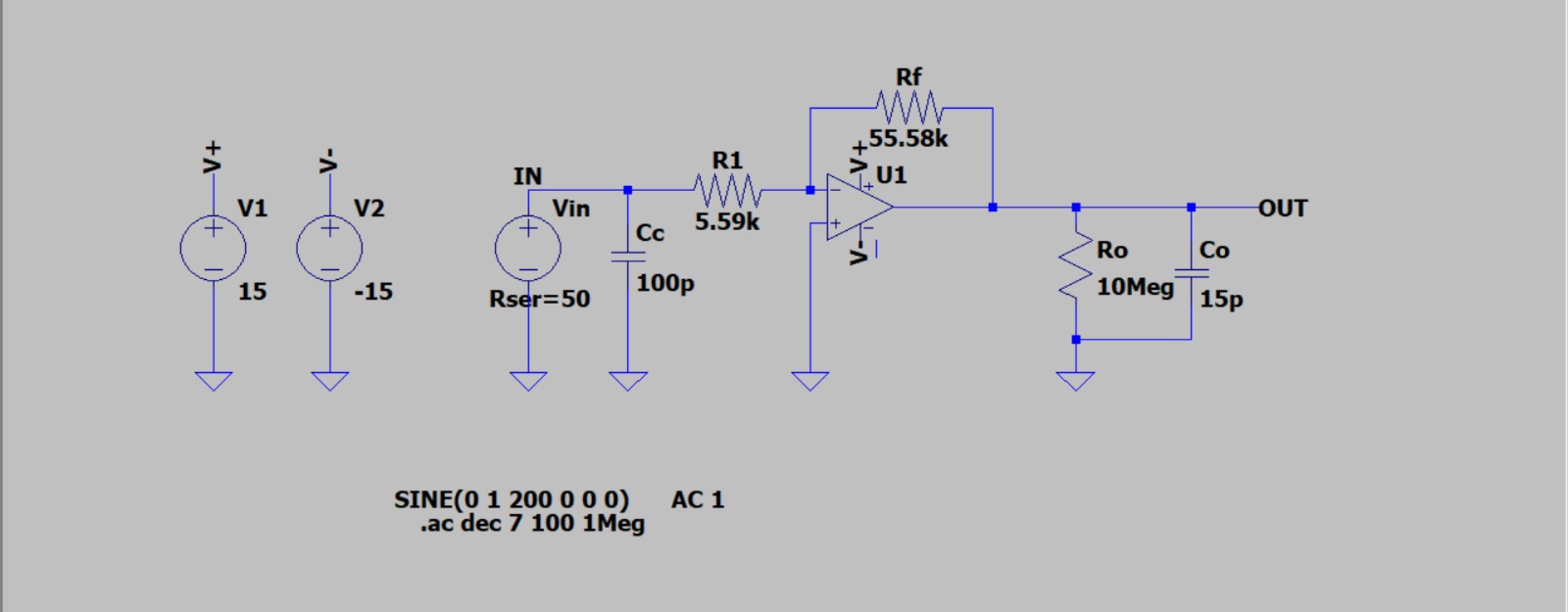
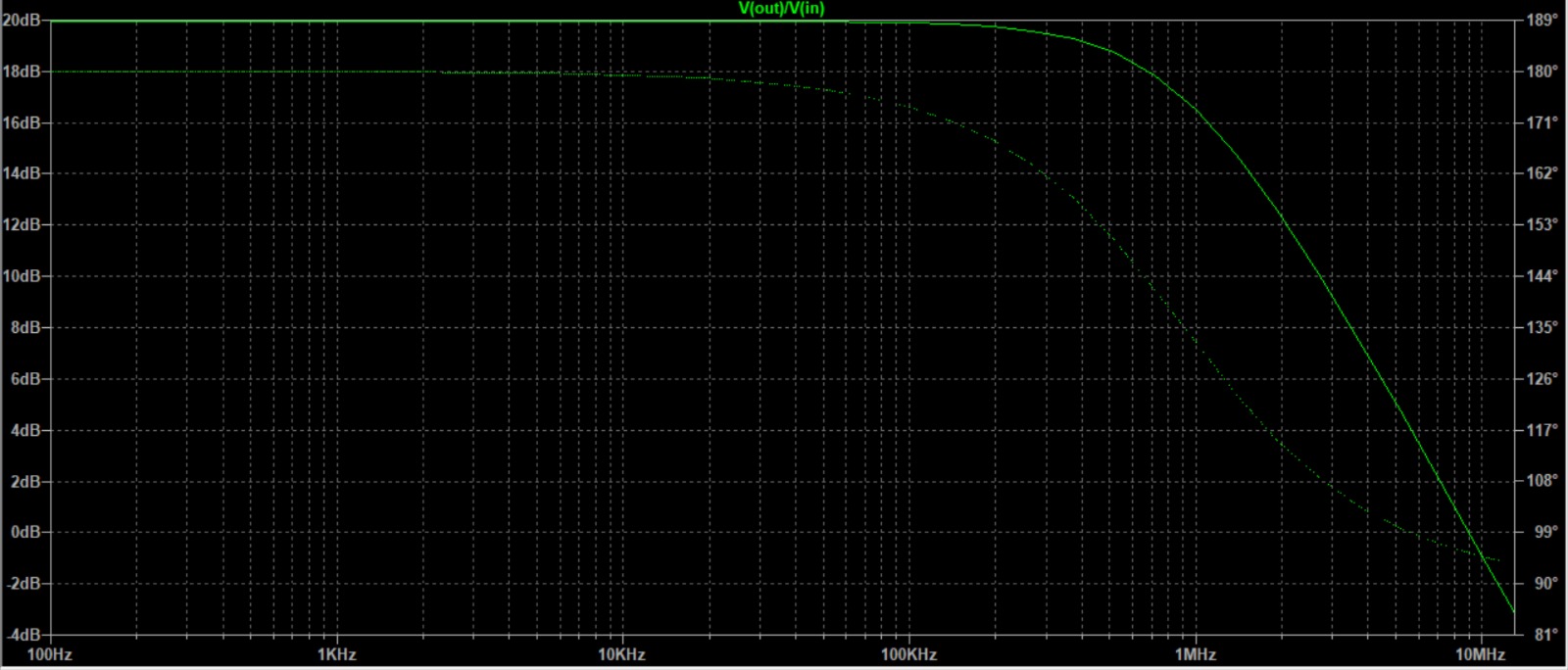
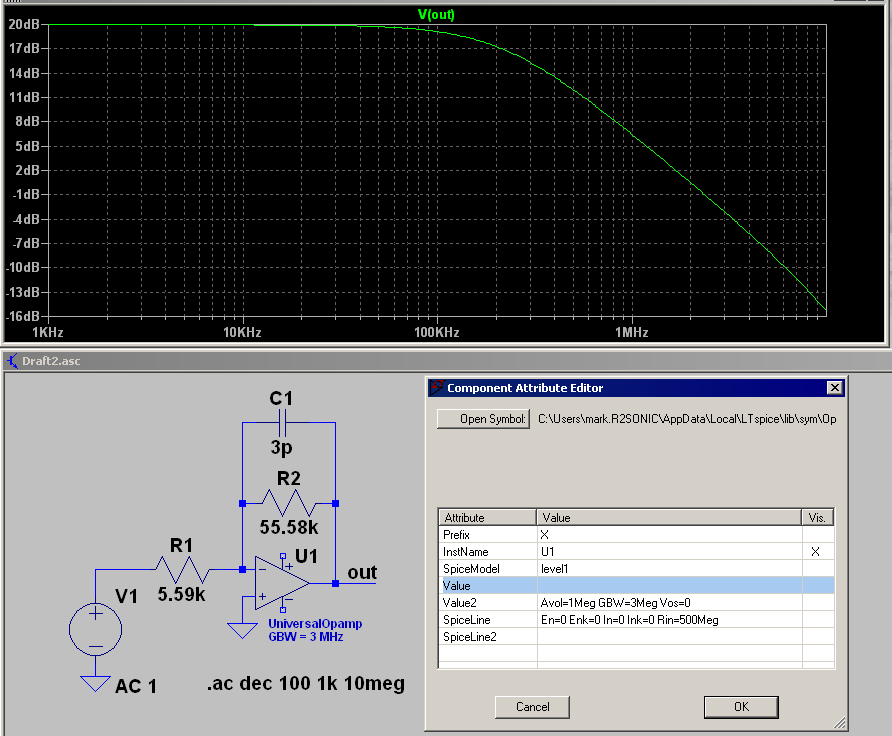
I have a simple inverting opamp amplifier and I want to study the frequency response of the circuit and finally calculate the frequency band (or cutoff frequency). Unfortunately the model created in LTspice gives very different output from the data I collected doing the circuit manually in laboratory.
What I get is a very different cutoff frequency, but the amplification is okay. I'm gonna link to you the pictures of our frequency response with our data, and then also the circuit we use in LTspice and the output. As you can see in the LTspice simulation cutoff frequency is something like 1MHz but in our data we estimated it to be 200kHz more or less.