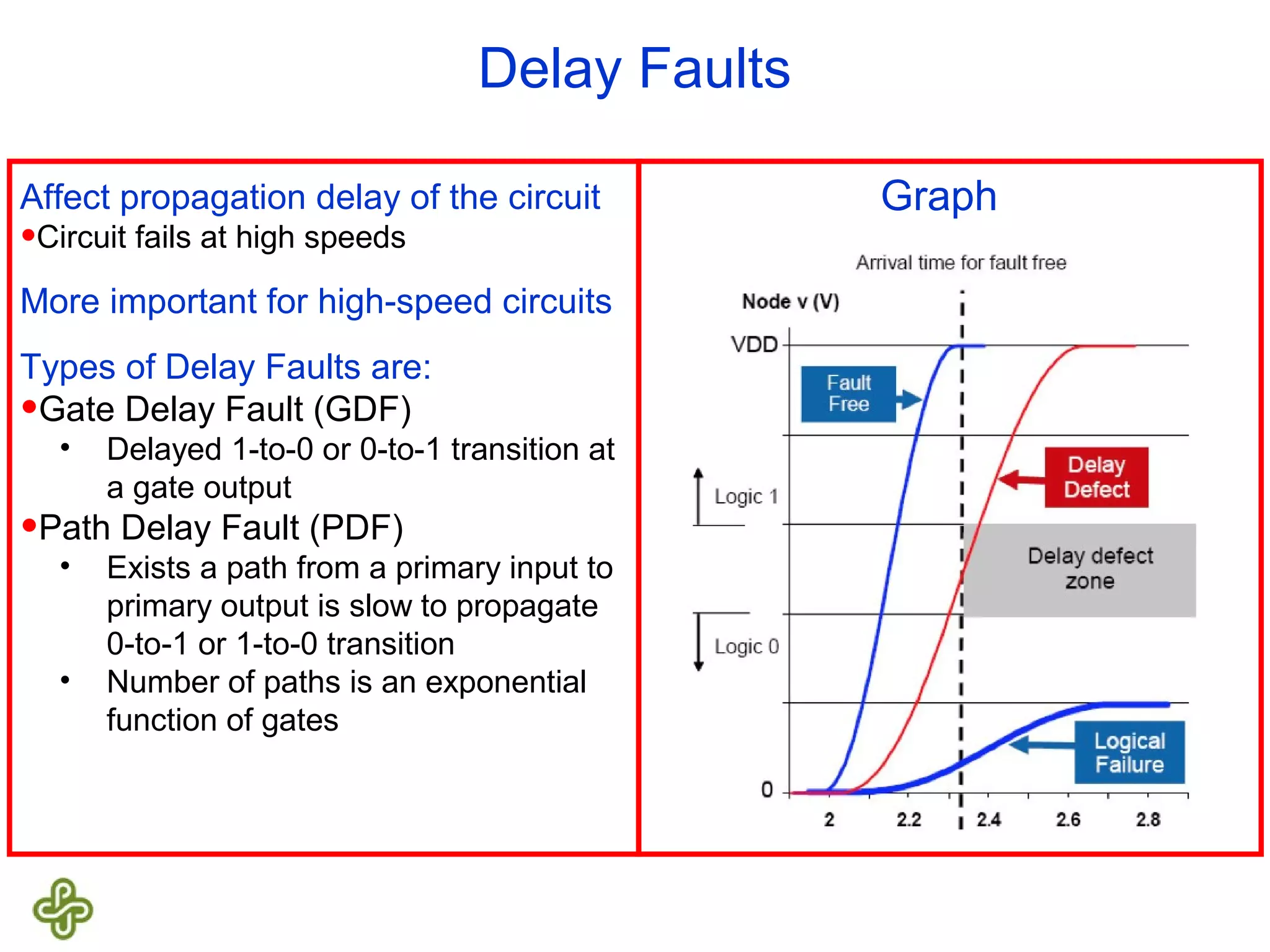
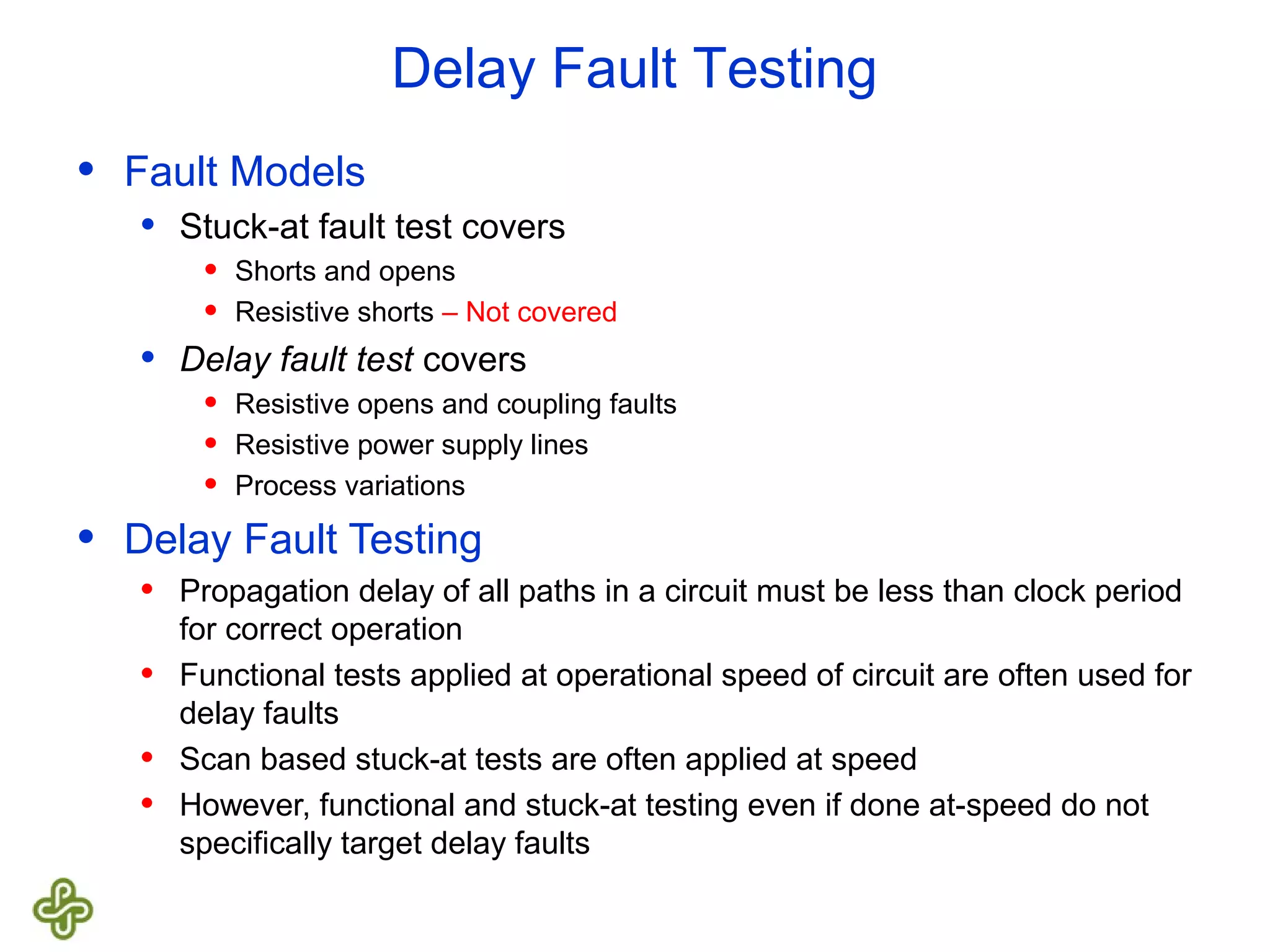
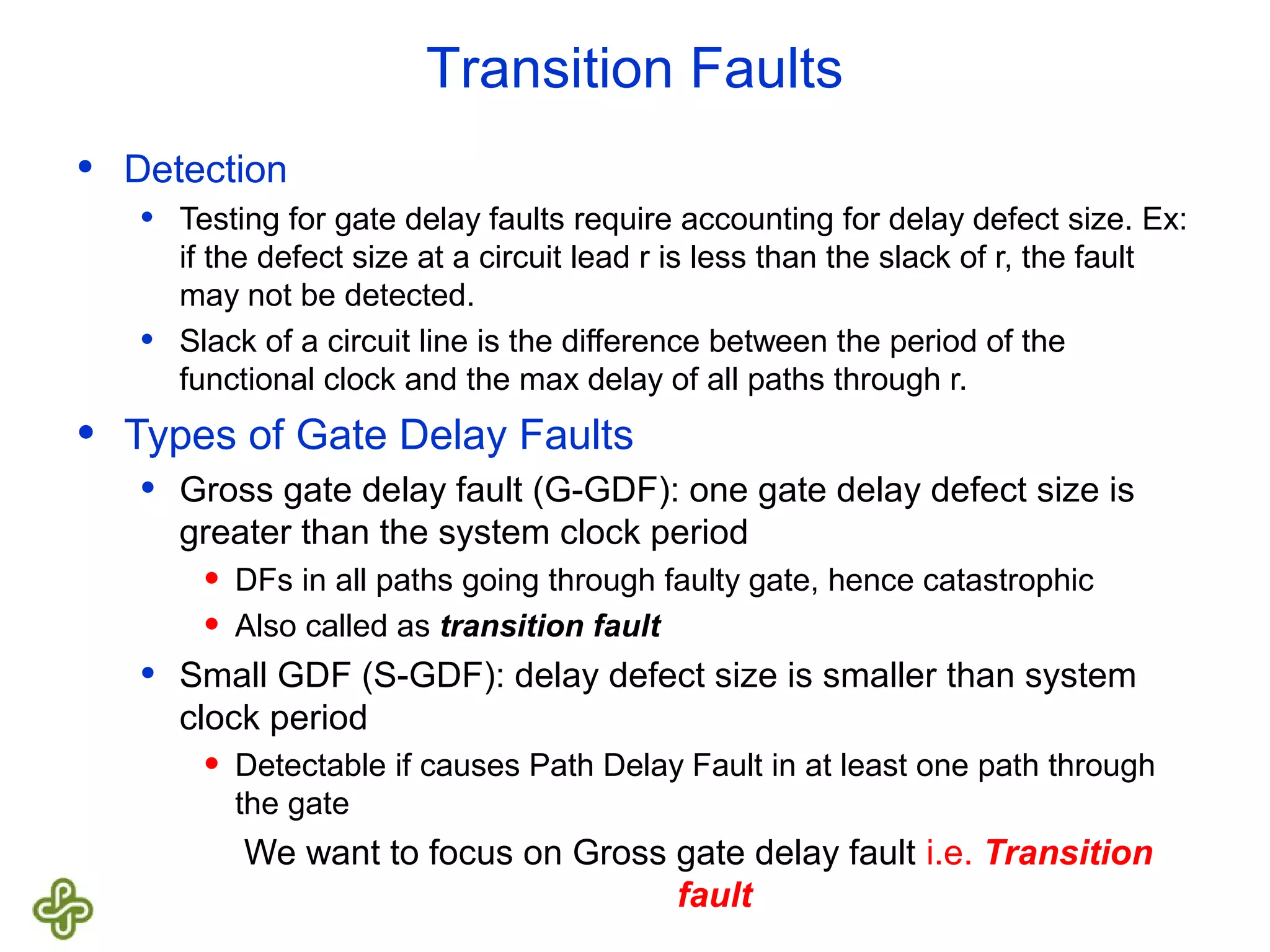
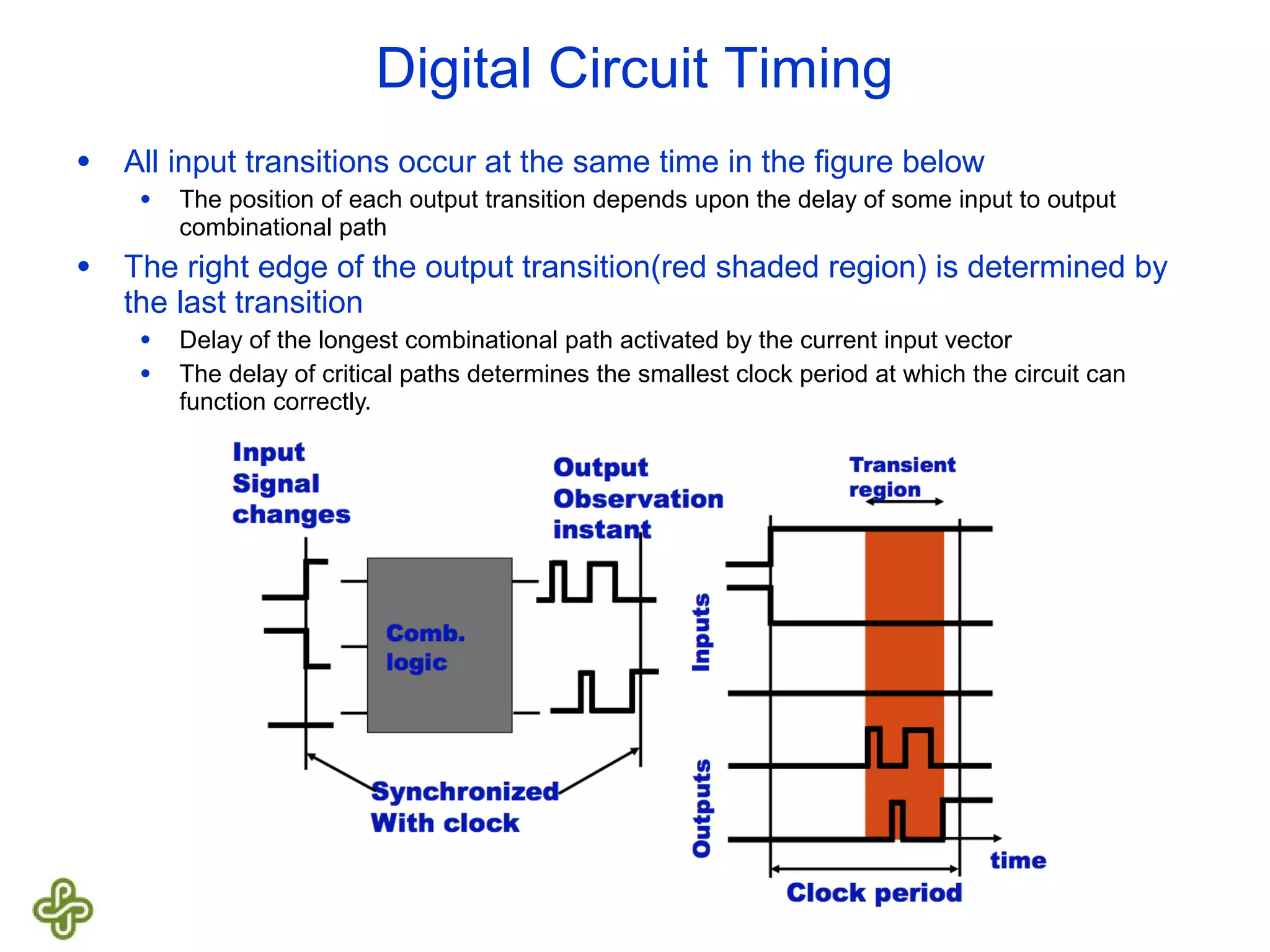
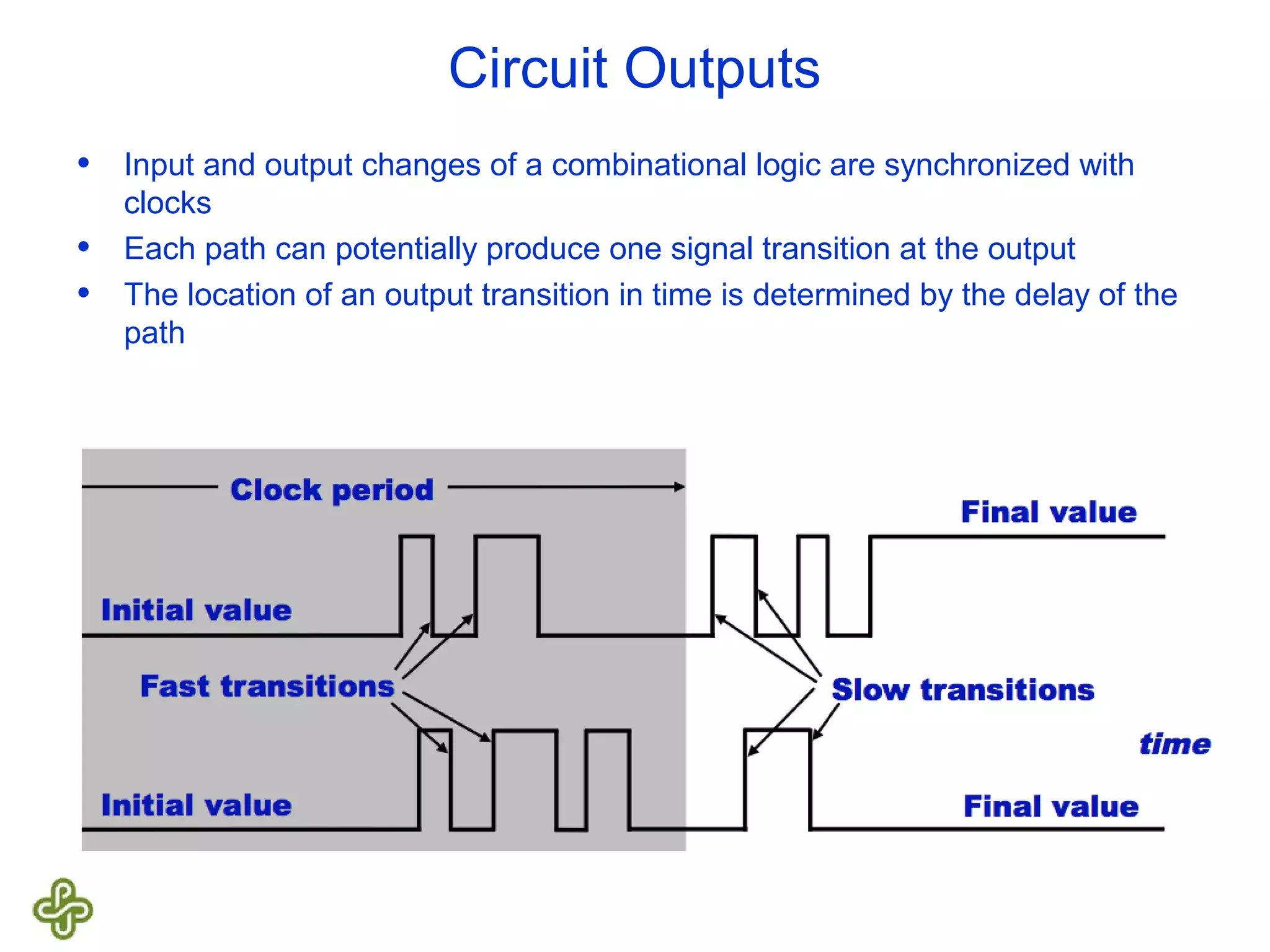
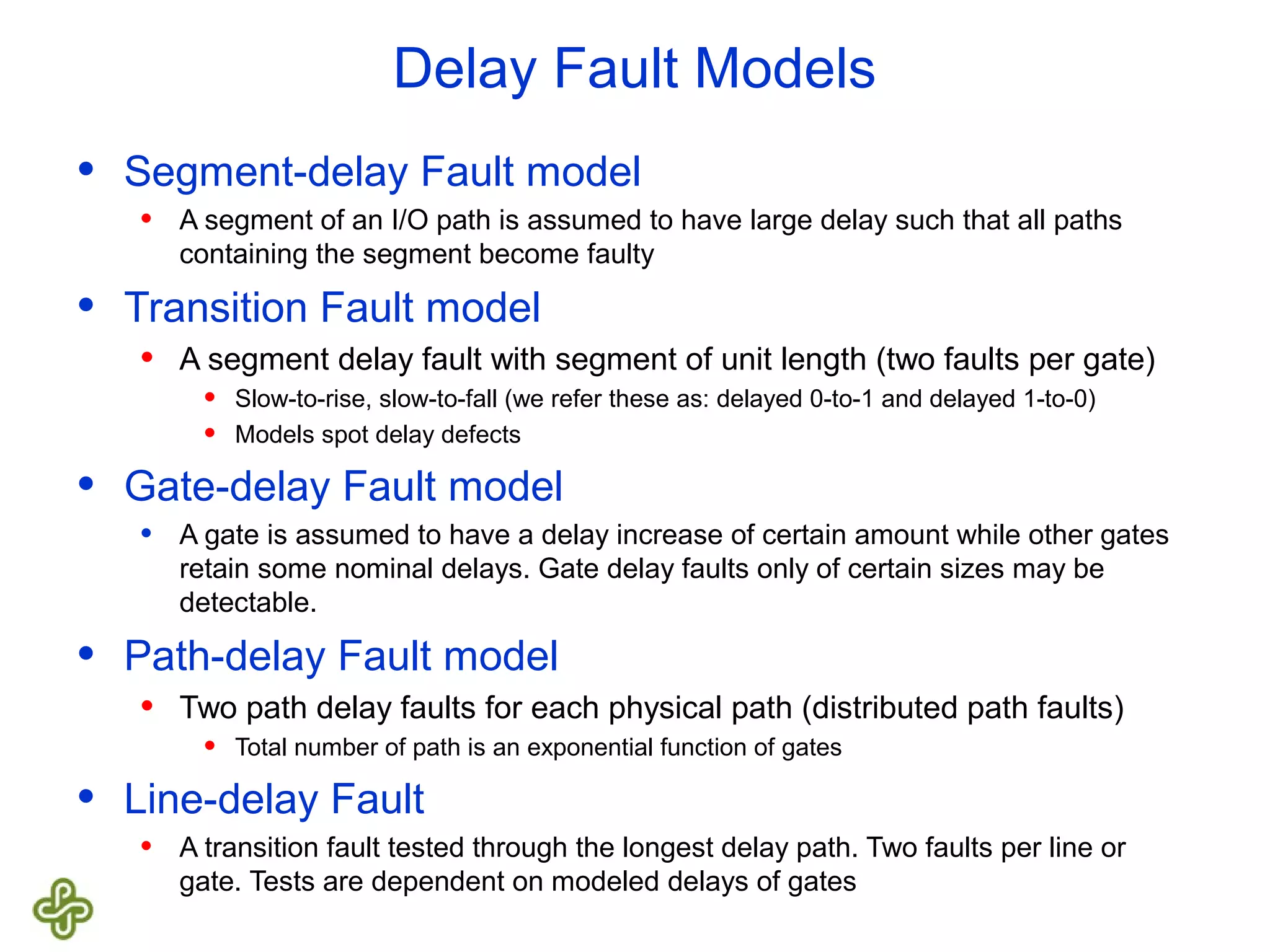
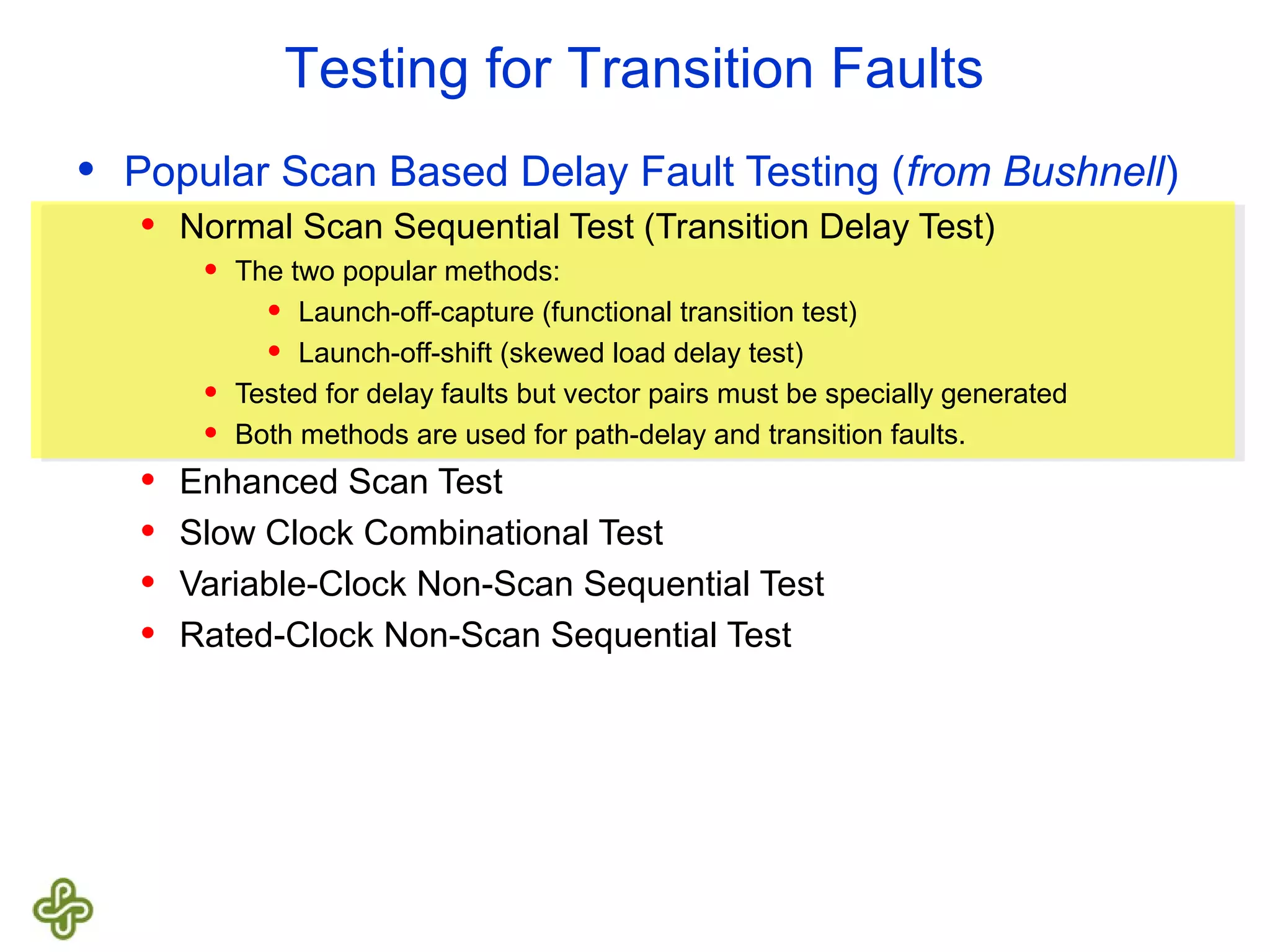
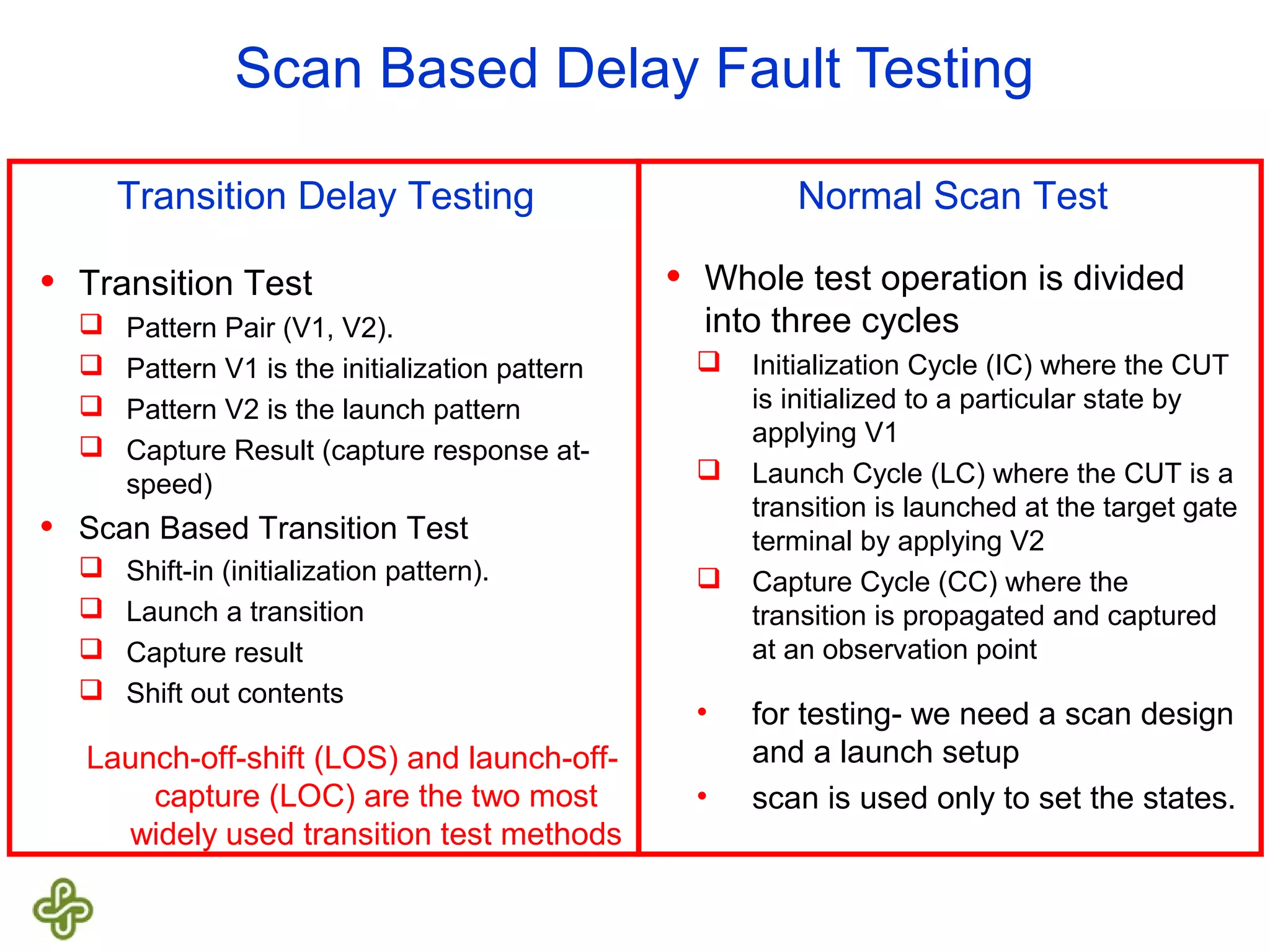
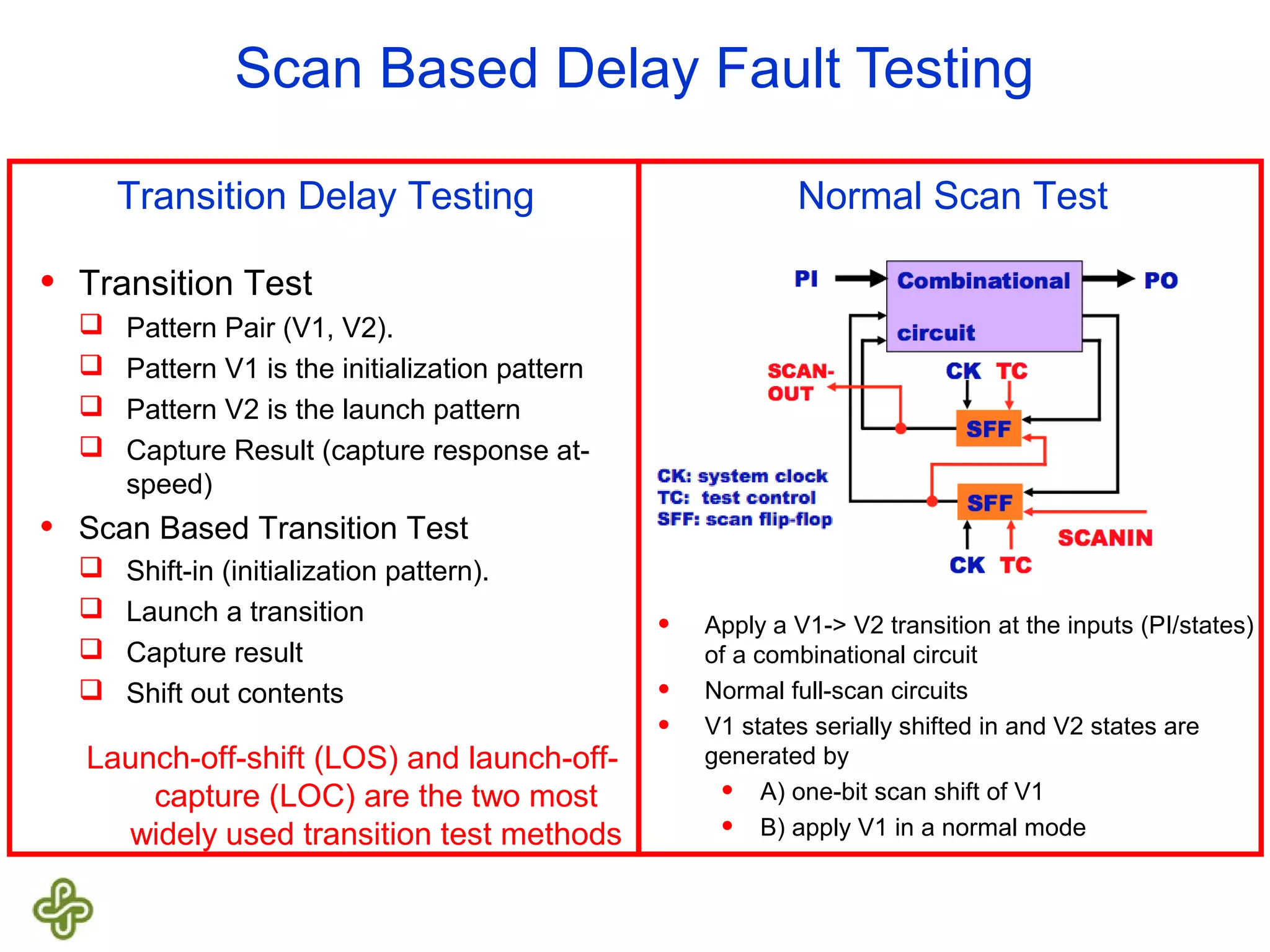
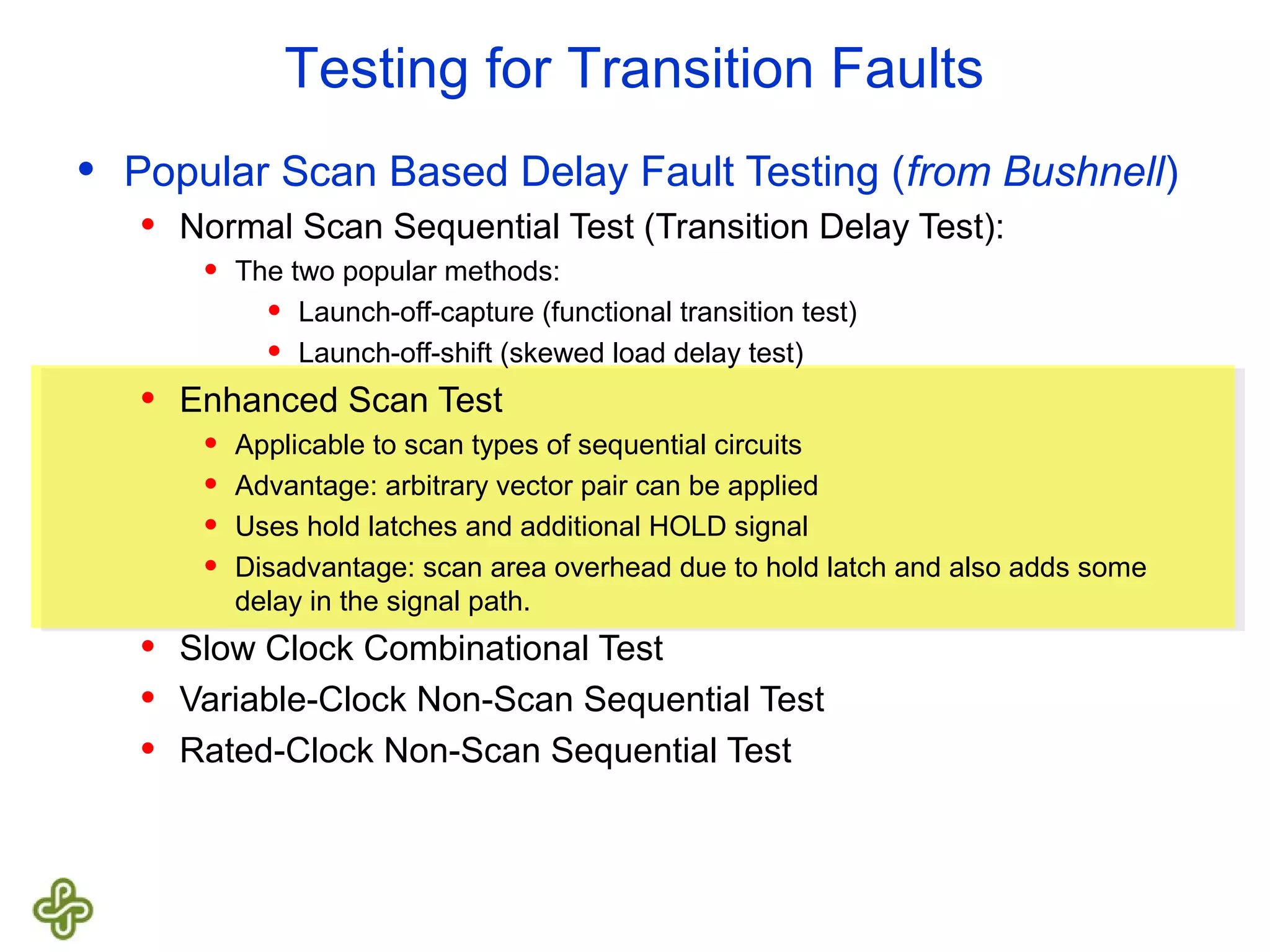
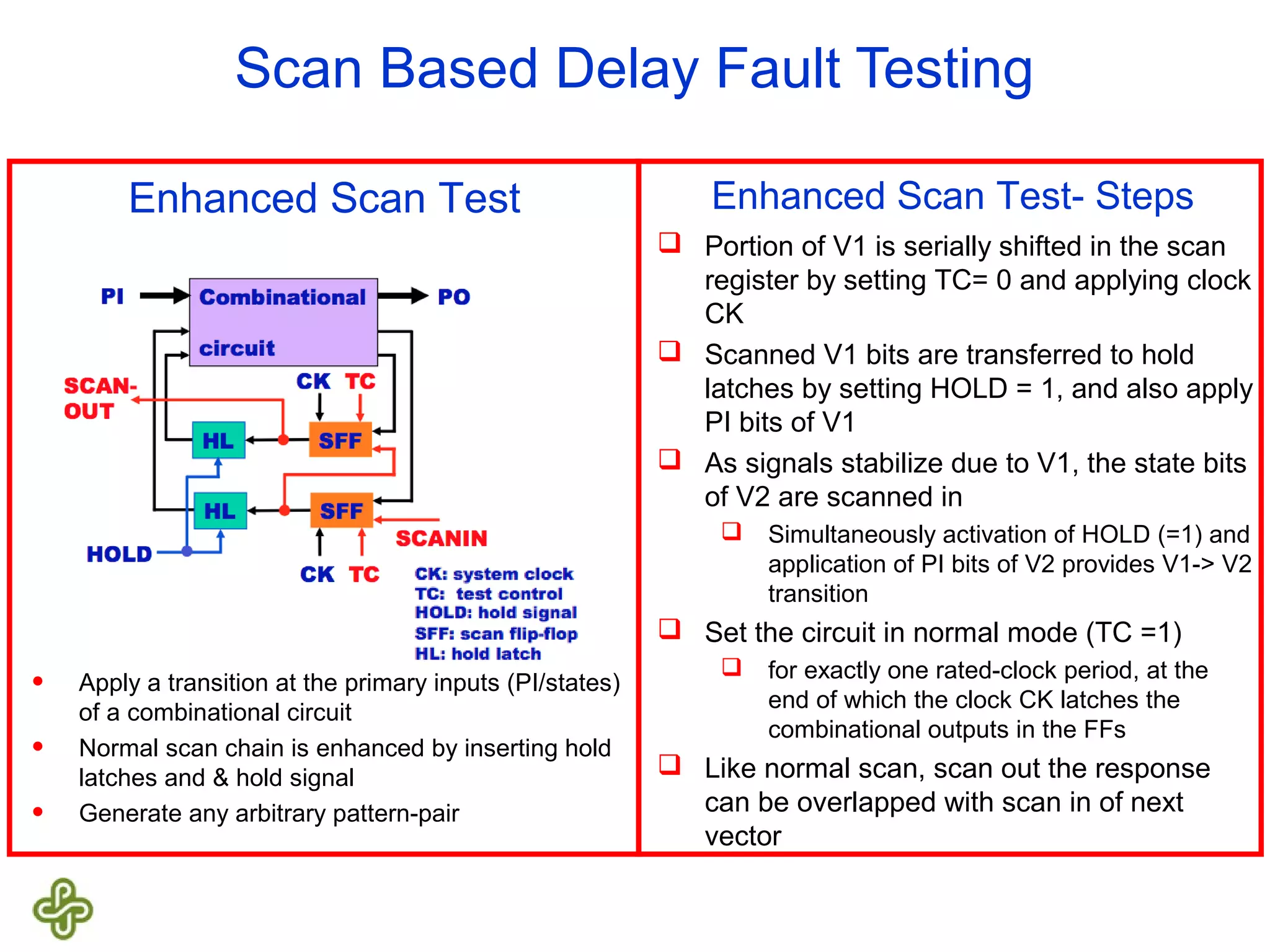
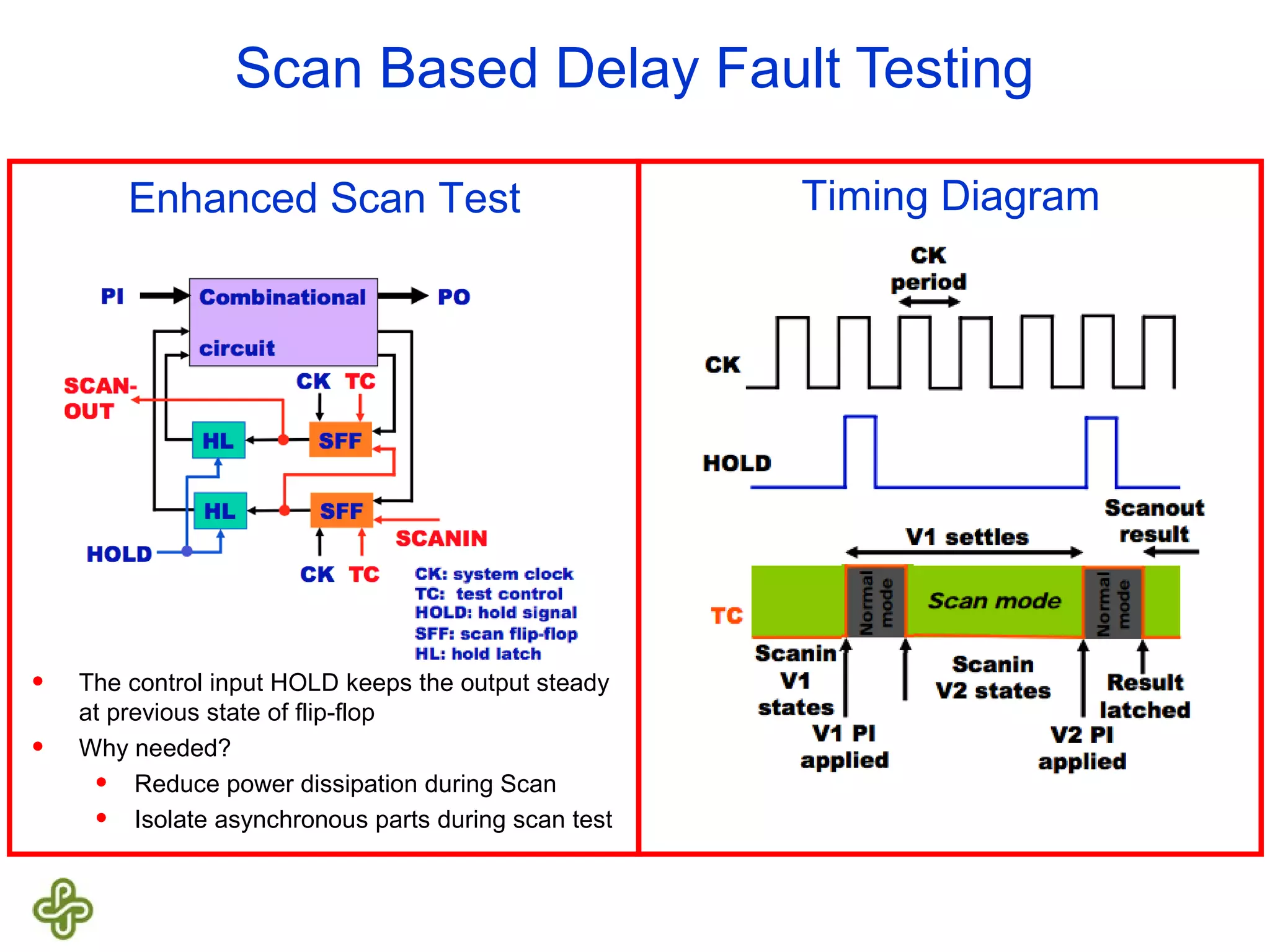
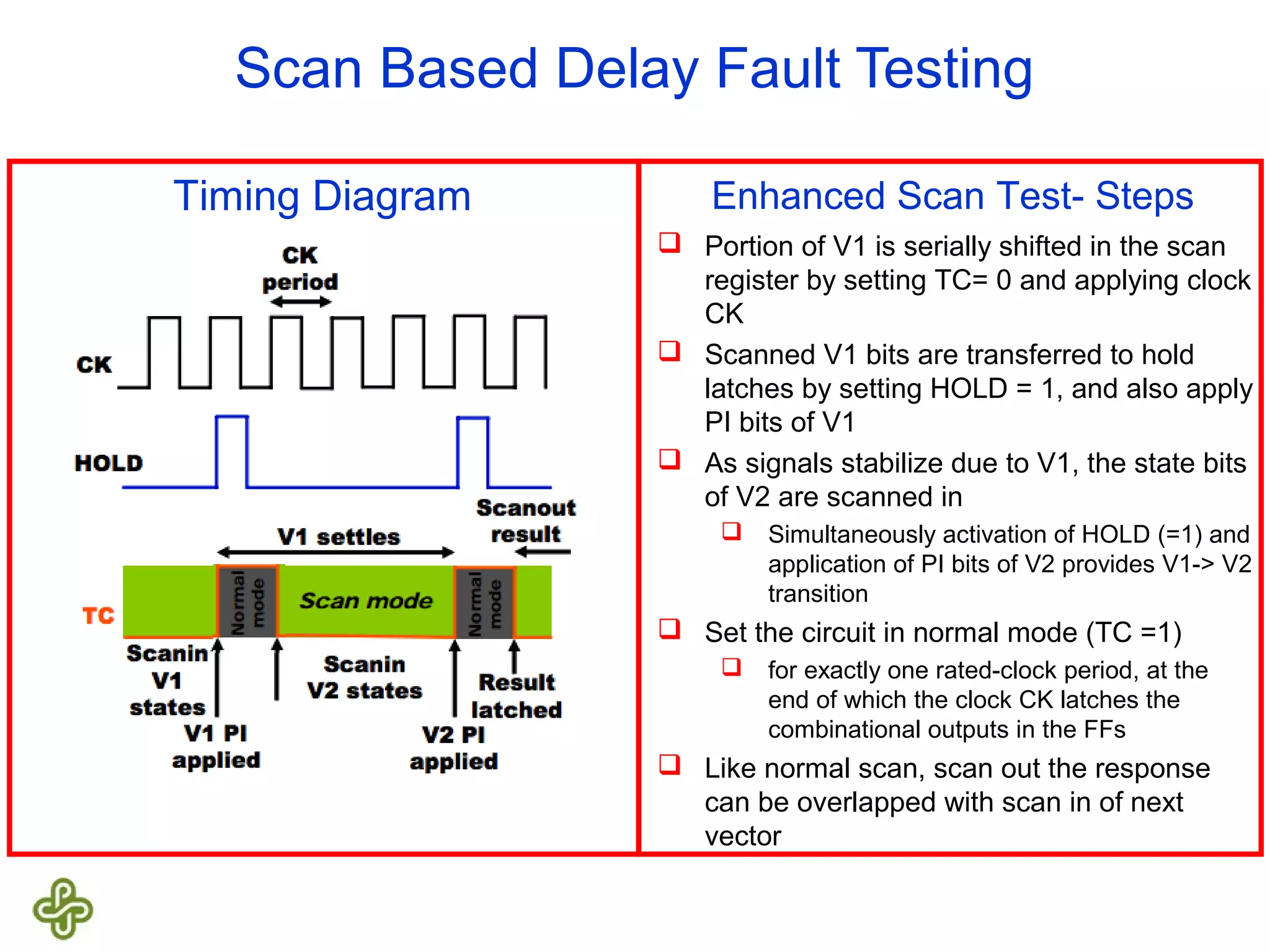
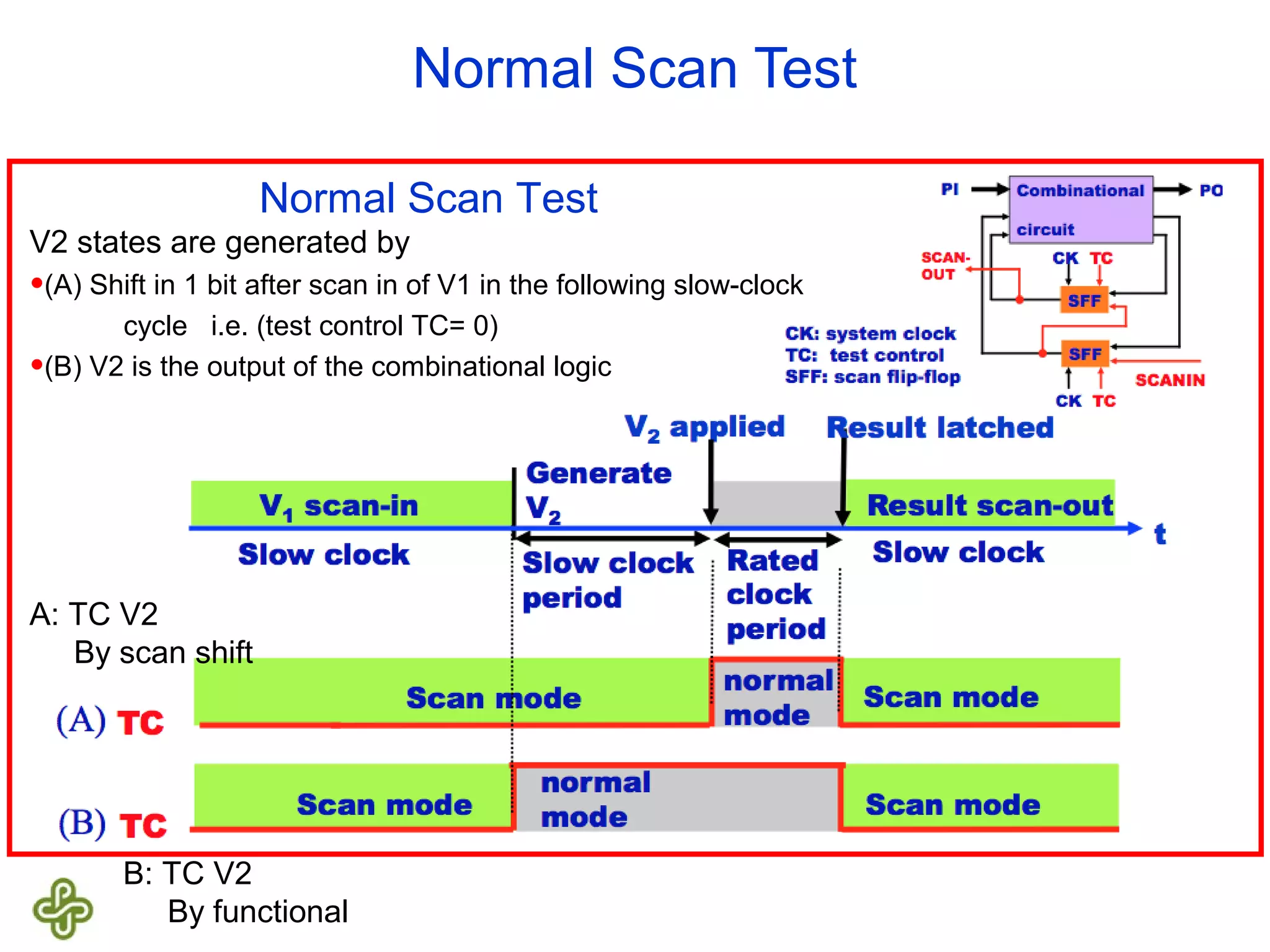
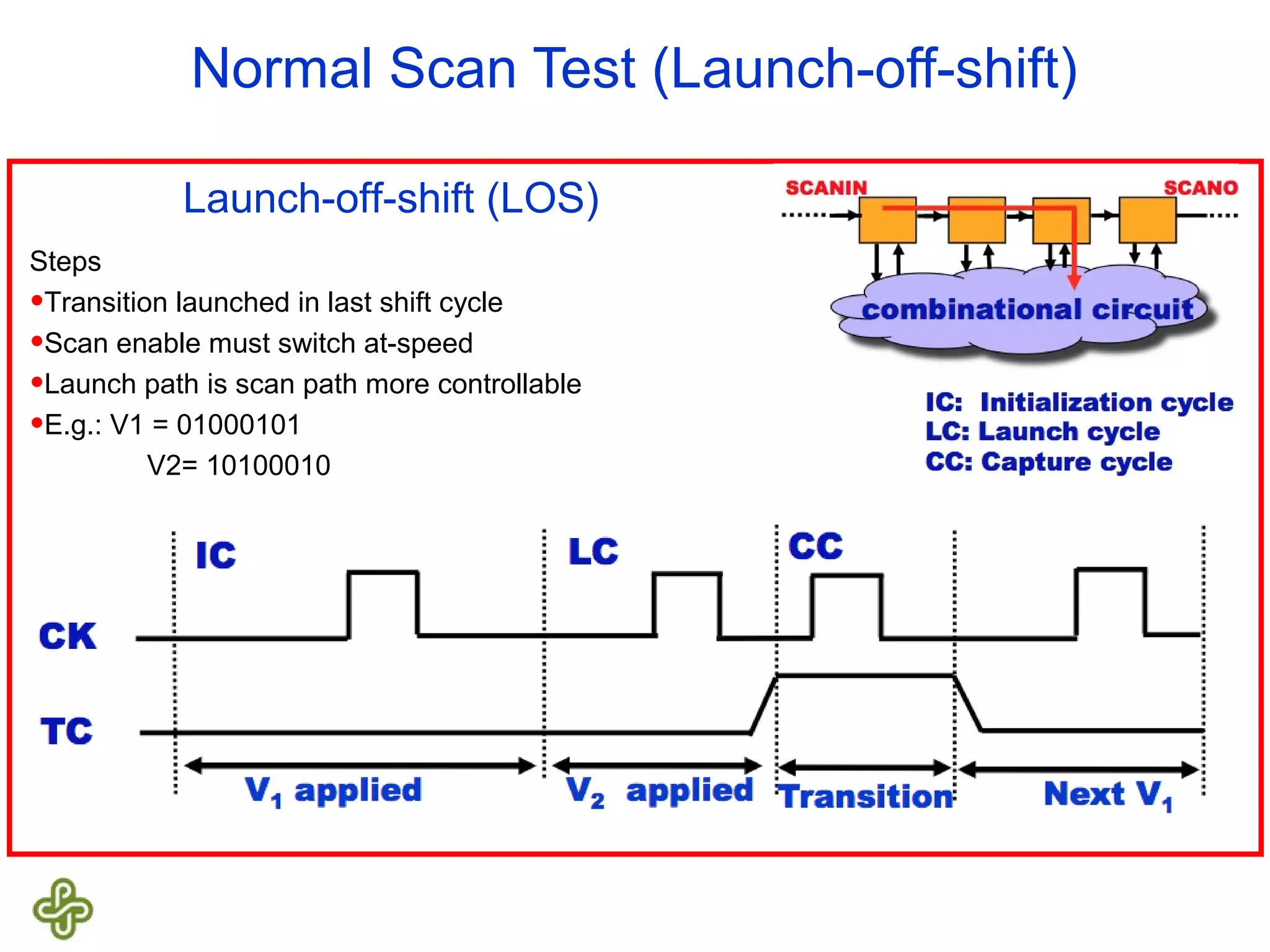
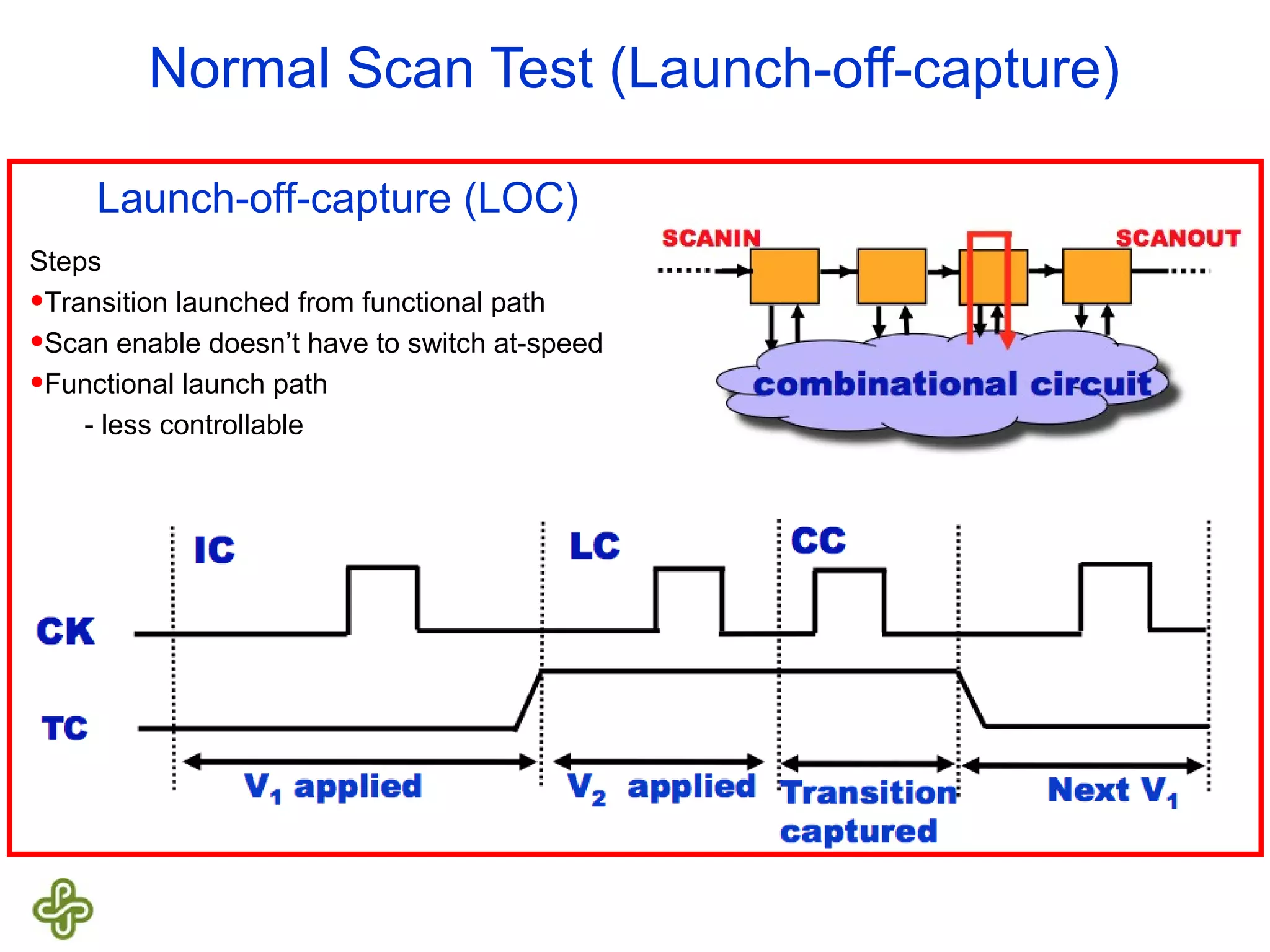
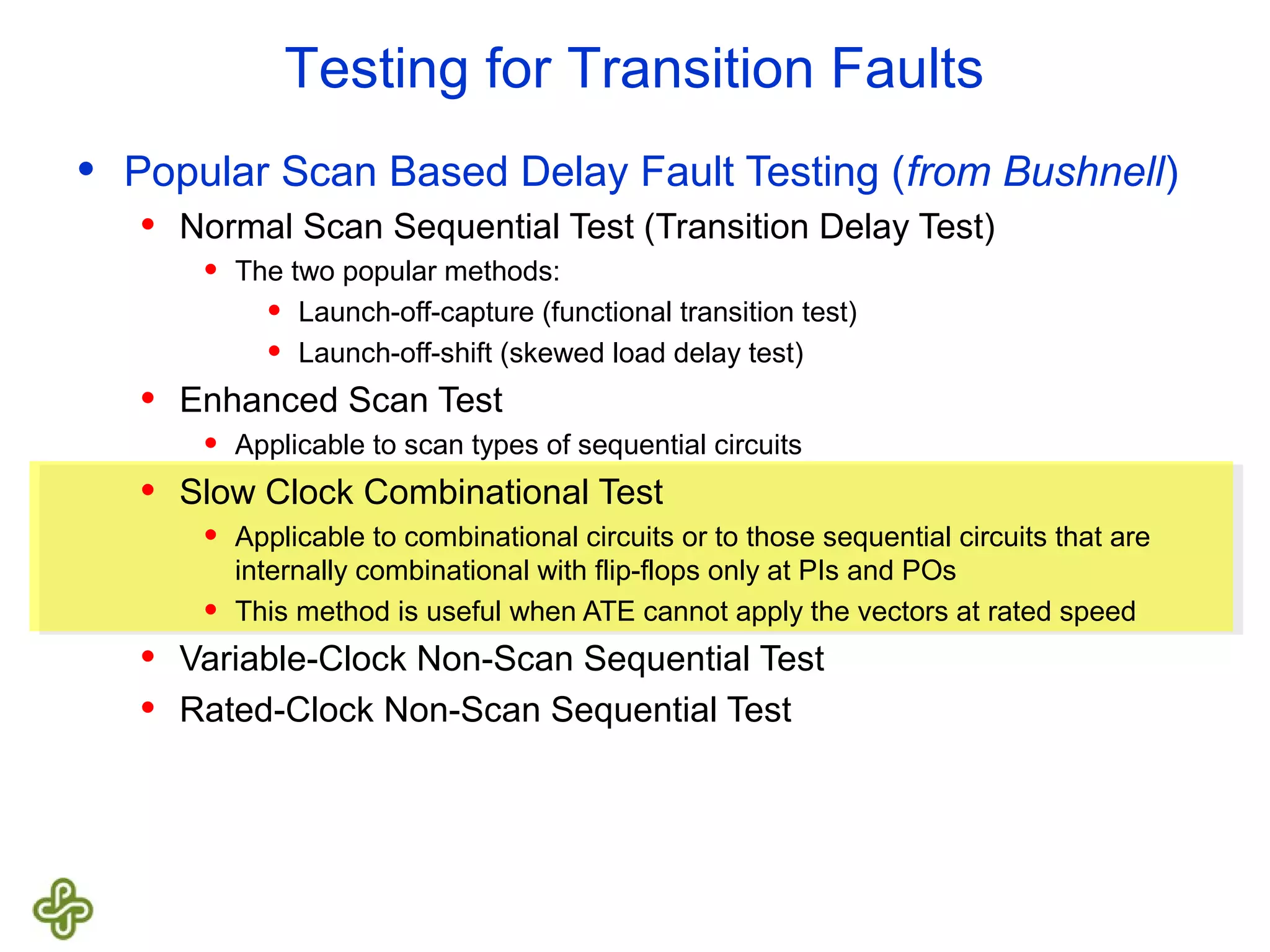
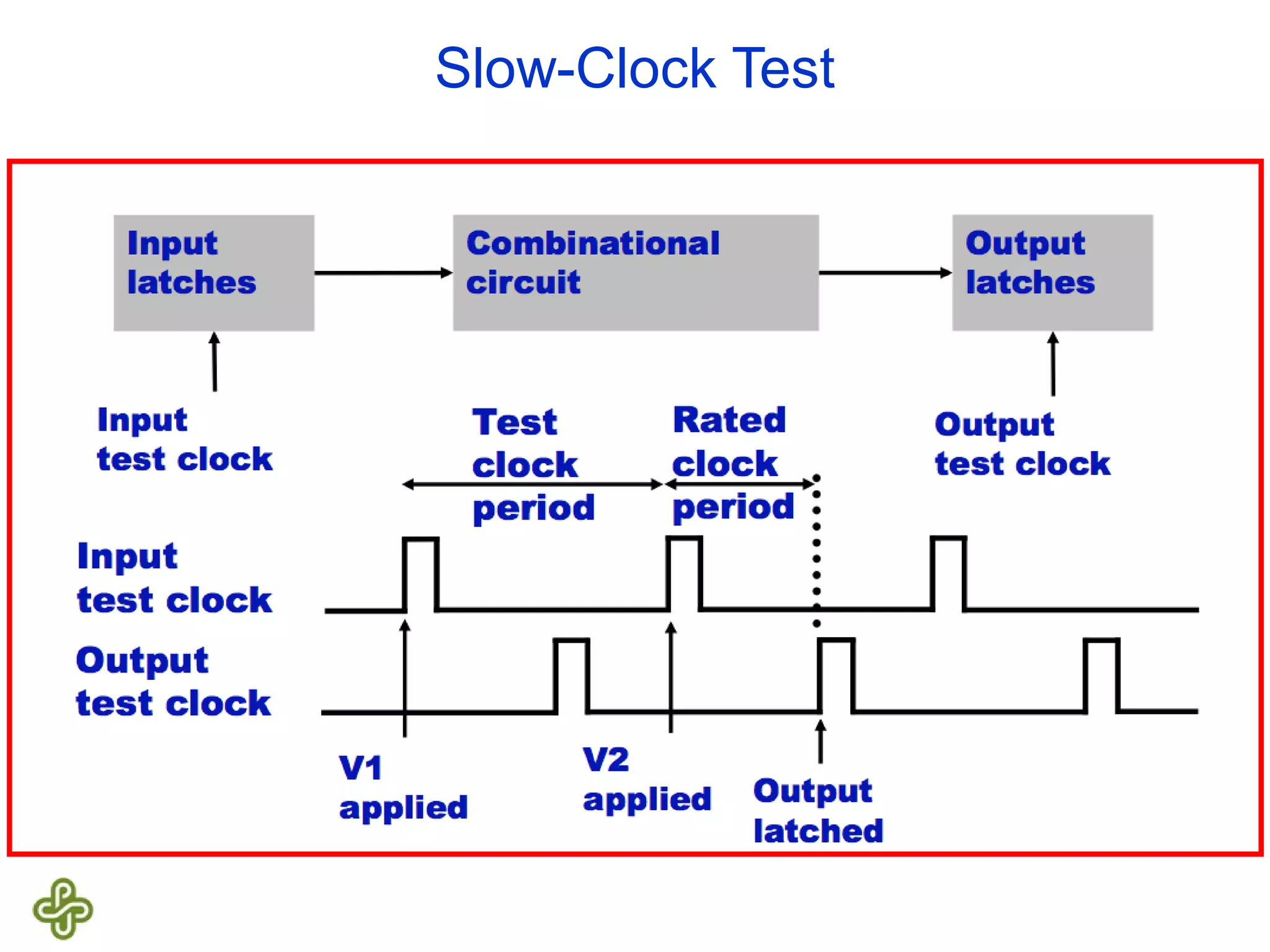
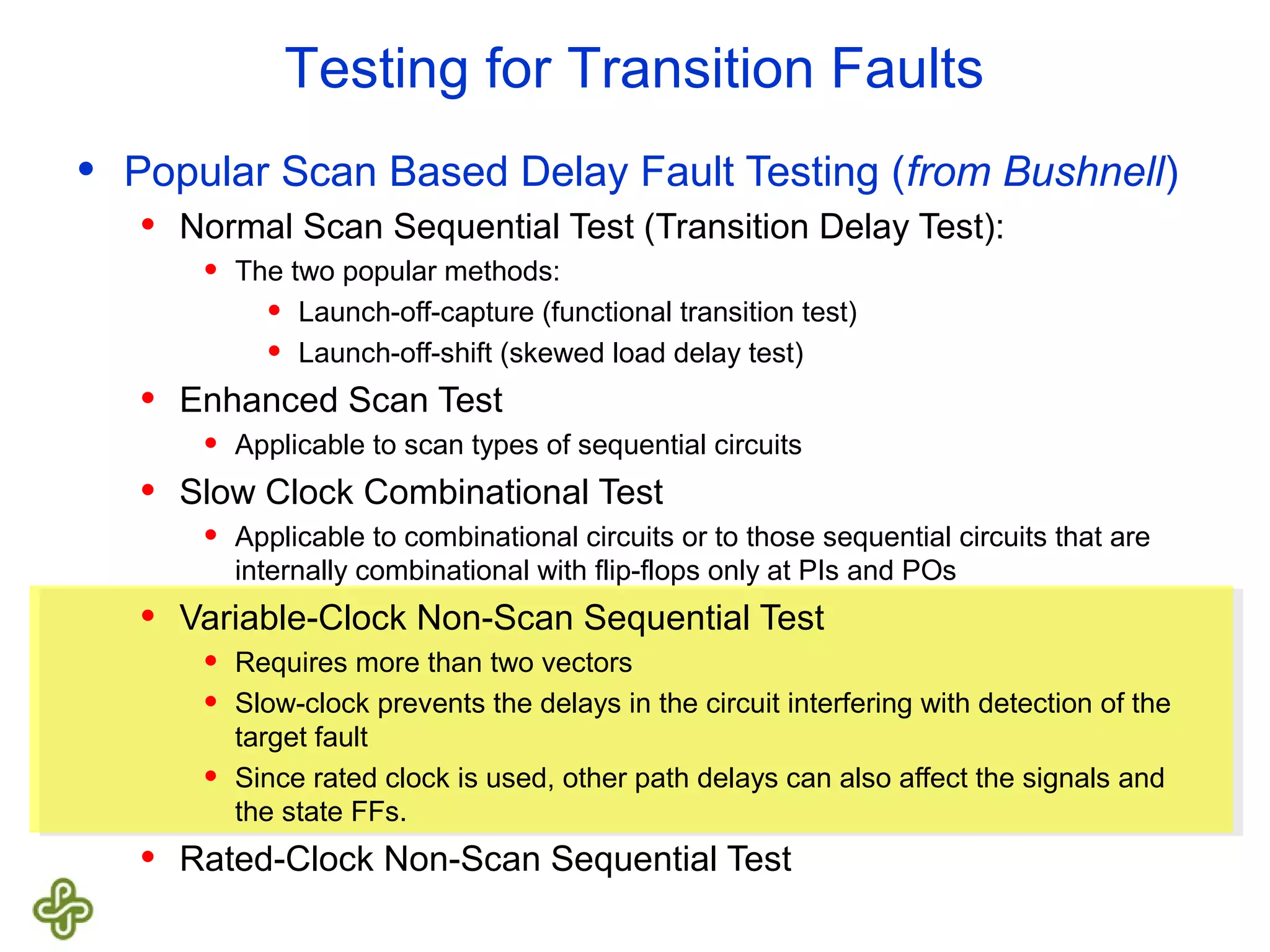
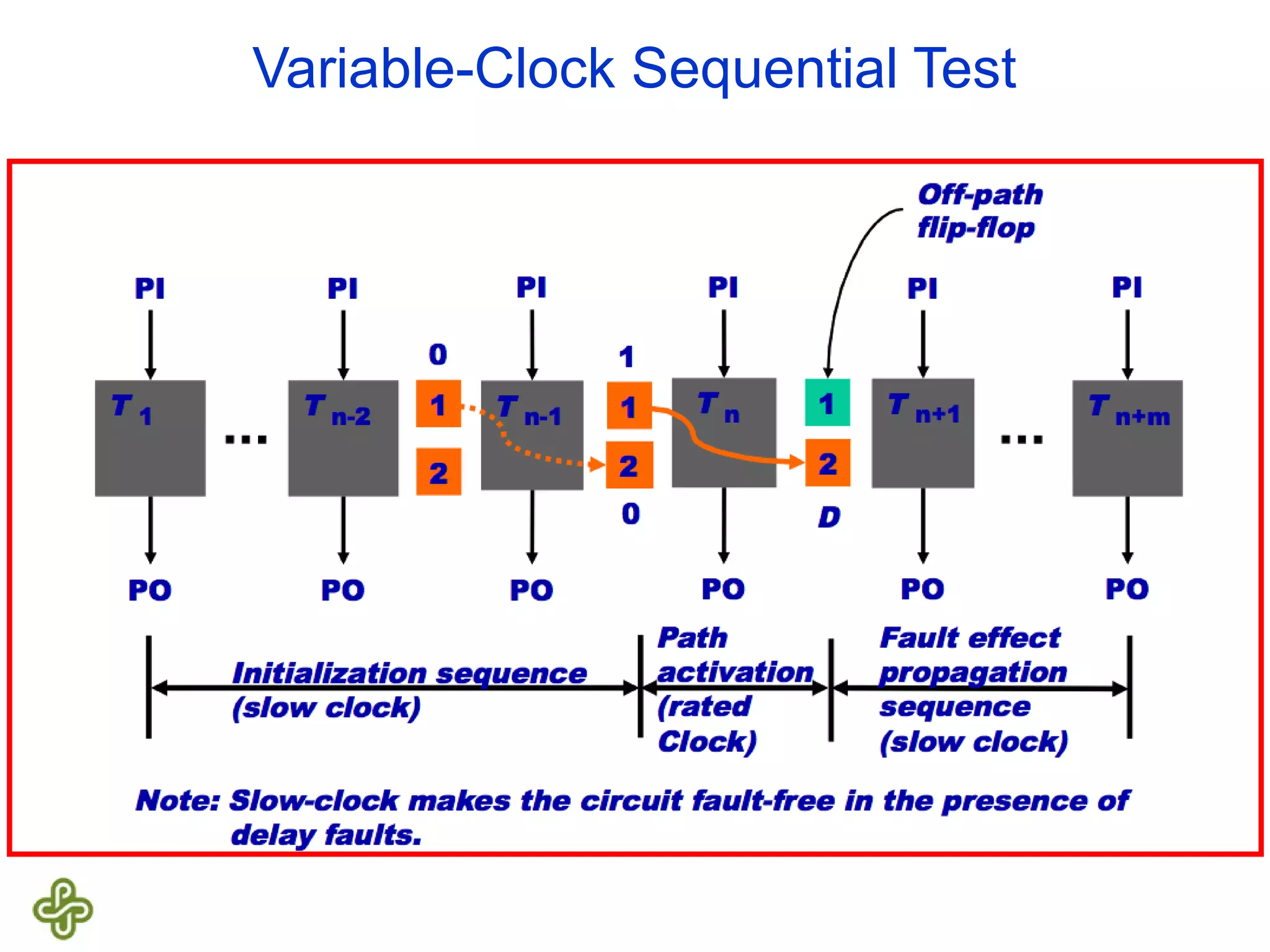
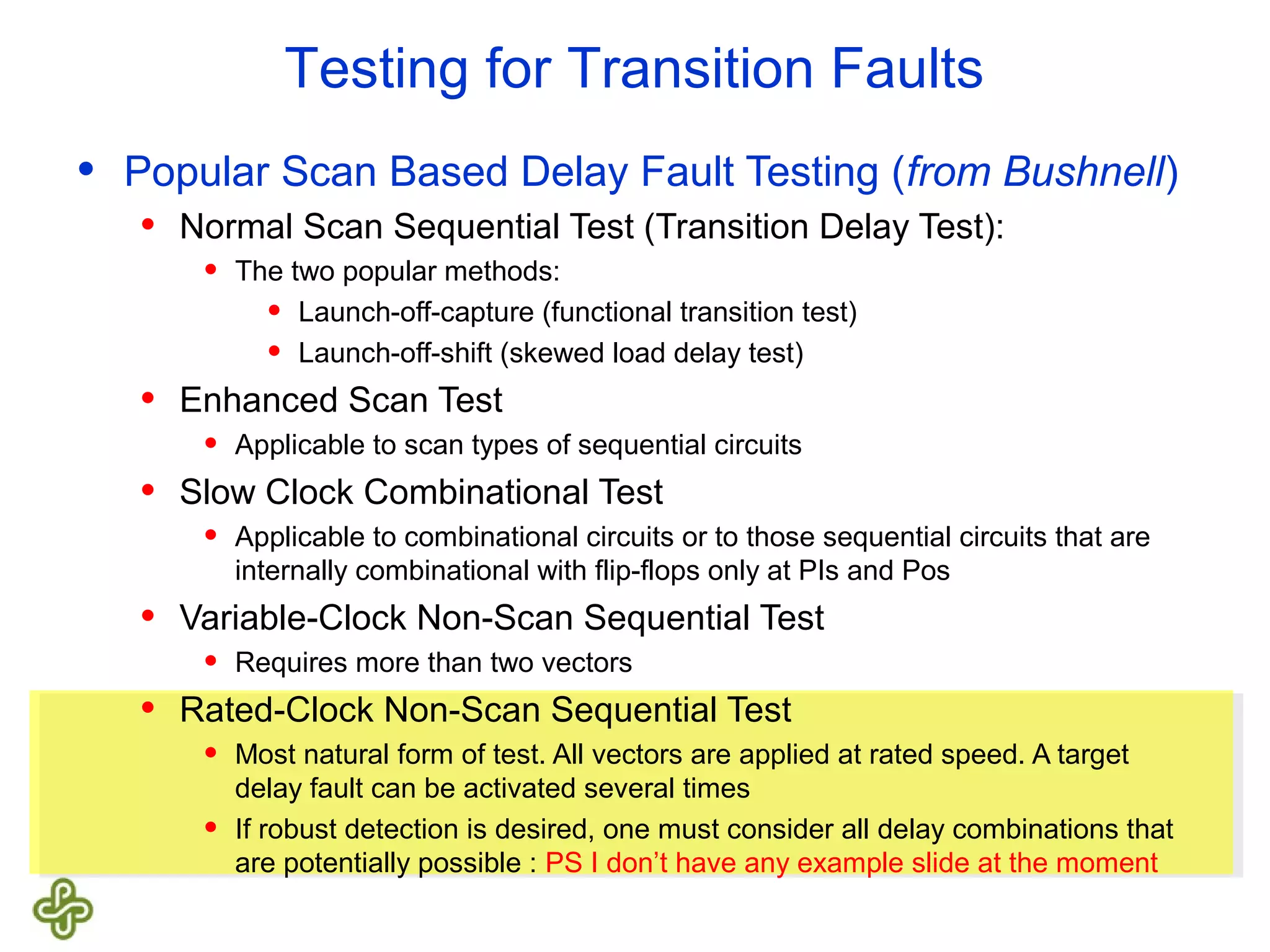
The document discusses transition fault testing and delay fault models in digital circuits, emphasizing the impact of manufacturing defects and design errors on circuit timing. It categorizes faults into logical and parametric, elaborating on delay faults, particularly gate and path delay faults, and their testing methodologies. Various testing techniques, including scan-based methods, are explored for effective detection of transition faults in digital systems.
![Book References [1] M. L. Bushnell and V. D. Agrawal “Chapter 12- Delay Test, Book -Essentials of Electronic Testing for Digital, Memory, and Mixed-Signal VLSI Circuits,” Springer, 2005. [2] M. Abramovici et al., “Digital Systems Testing and Testable Design,” IEEE 2009. [3] A. Krstic and K.T Cheng, “Delay Fault Testing for VLSI Circuits,” IEEE 1998. [4] S. K. Goel, “Testing for Small-Delay Defects in Nanoscale CMOS Integrated Circuits,” Taylor and Francis Group, 2013. [5] M. Tehranipoor et al., “Chapter 2: Delay Test, Book: Test and Diagnosis for Small-Delay Defects,” Springer, 2011.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01transitionfaultdetectionmethodsjune12015-170825234028/75/01-Transition-Fault-Detection-methods-by-Swetha-2-2048.jpg)

![Transition Delay Fault • Transition fault (or Gross Gate Delay fault) • Even though the circuit doesn’t have a logical defect, it may have some physical defect such as a process variation and that creates a large enough gate delay to cause problems • Transition Fault model • Assumes that the delay fault affects only one gate in the circuit • Assumes the logic function of circuit under test (CUT) is error-free • Types of faults: delayed 0-to-1 & delayed 1-to-0 Fault at any node means the effect of any transition from 0 to 1 for delayed high (or 1 to 0 for delayed low) will not reach primary output within the stipulated time extra delay (delay above the nominal delay) caused by the fault is assumed to be large enough to prevent the transition from reaching primary output at the time of observation • Advantages • the number of faults in the circuit increase linearly with the number of gates • Practically used: stuck-at fault CAD tools with minor modifications [Goel2013][Waicukauski1987]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01transitionfaultdetectionmethodsjune12015-170825234028/75/01-Transition-Fault-Detection-methods-by-Swetha-12-2048.jpg)

![Other References [1] N. Ahmed et al, “Enhanced Launch-off-capture Transition Fault Testing,” IEC, pp. 279–289, 2005. [2] M. Roncken, “Defect-Oriented Testability for Asynchronous ICs,” In Proc. IEEE, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 363–375, Feb.1999. [3] D. Vasudevan, “Automatic Test Pattern Generation for Asynchronous Circuits,” Dissertation, 2012. [4] S. Jayanthy et al, “Fuzzy Delay Model Based Fault Simulator for Crosstalk Delay Fault Test Generation in Asynchronous Sequential Circuits,” IAS, 2015. [5] M. Roncken et al, “Fsimac: A Fault Simulator for Asynchronous Sequential Circuits,” IEEE, 2000. [6] J. A. Waicukauski et al., “Transition Fault Simulation,” IEEE Design and Test, 1987.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01transitionfaultdetectionmethodsjune12015-170825234028/75/01-Transition-Fault-Detection-methods-by-Swetha-29-2048.jpg)