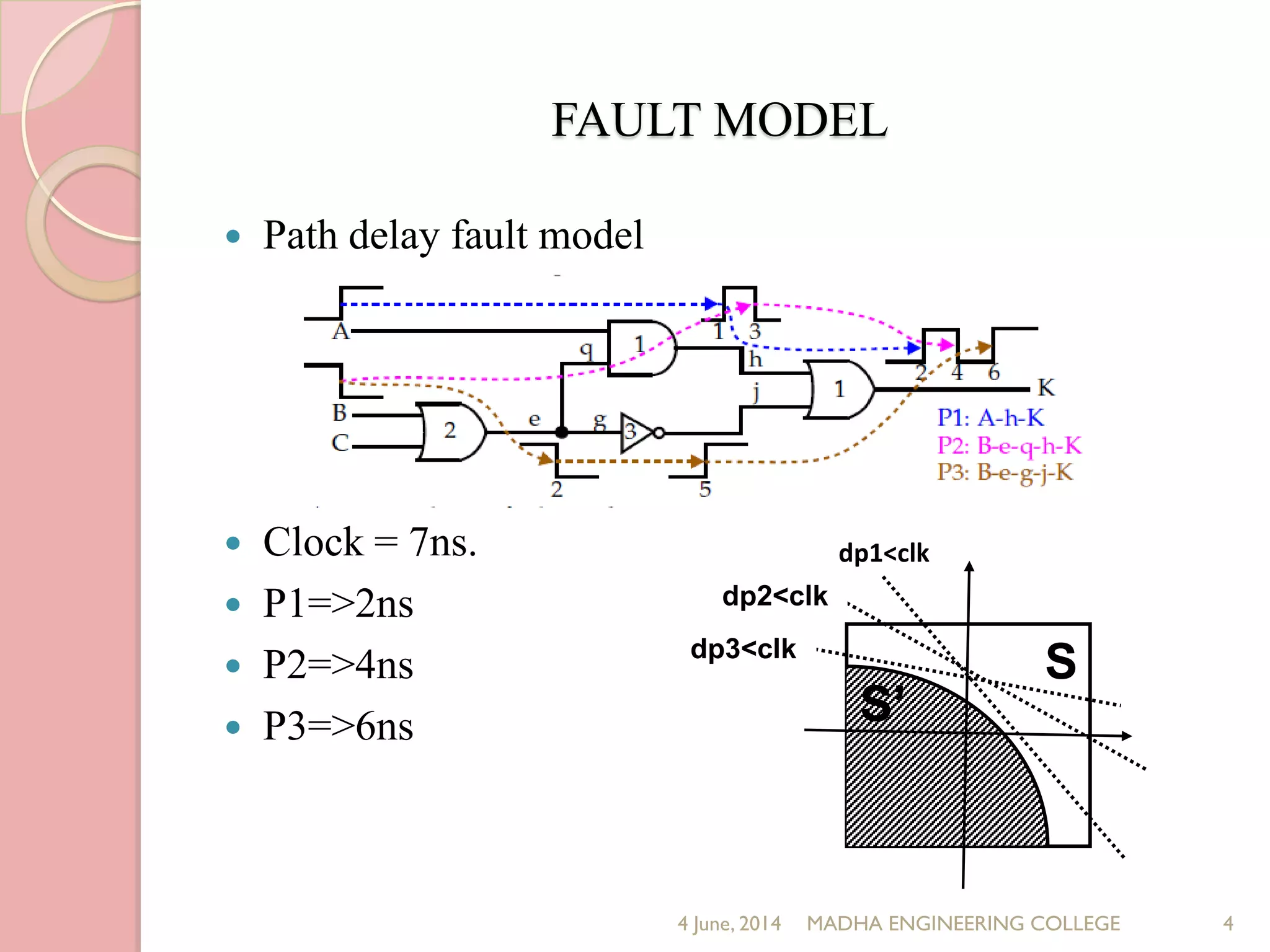
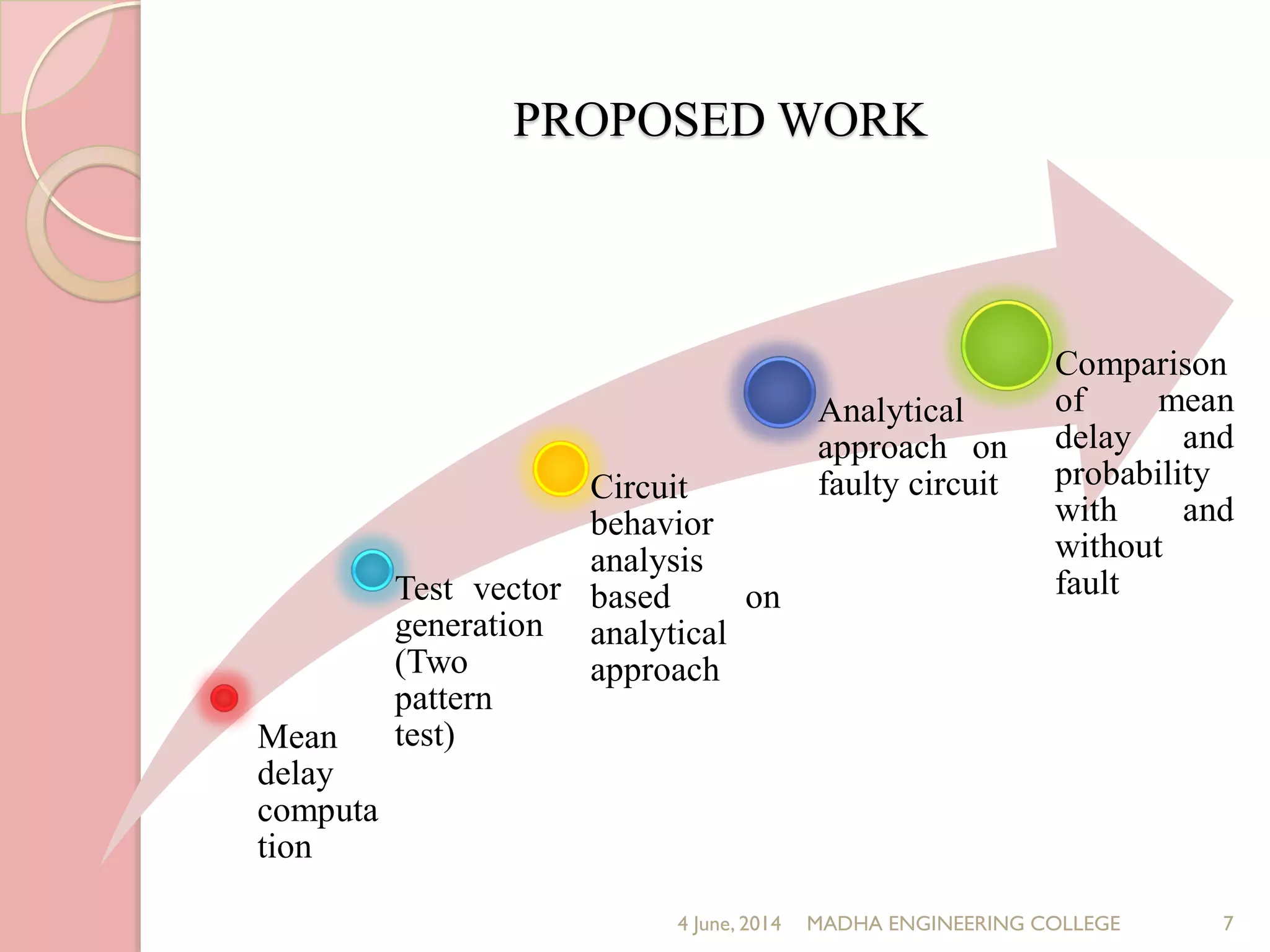
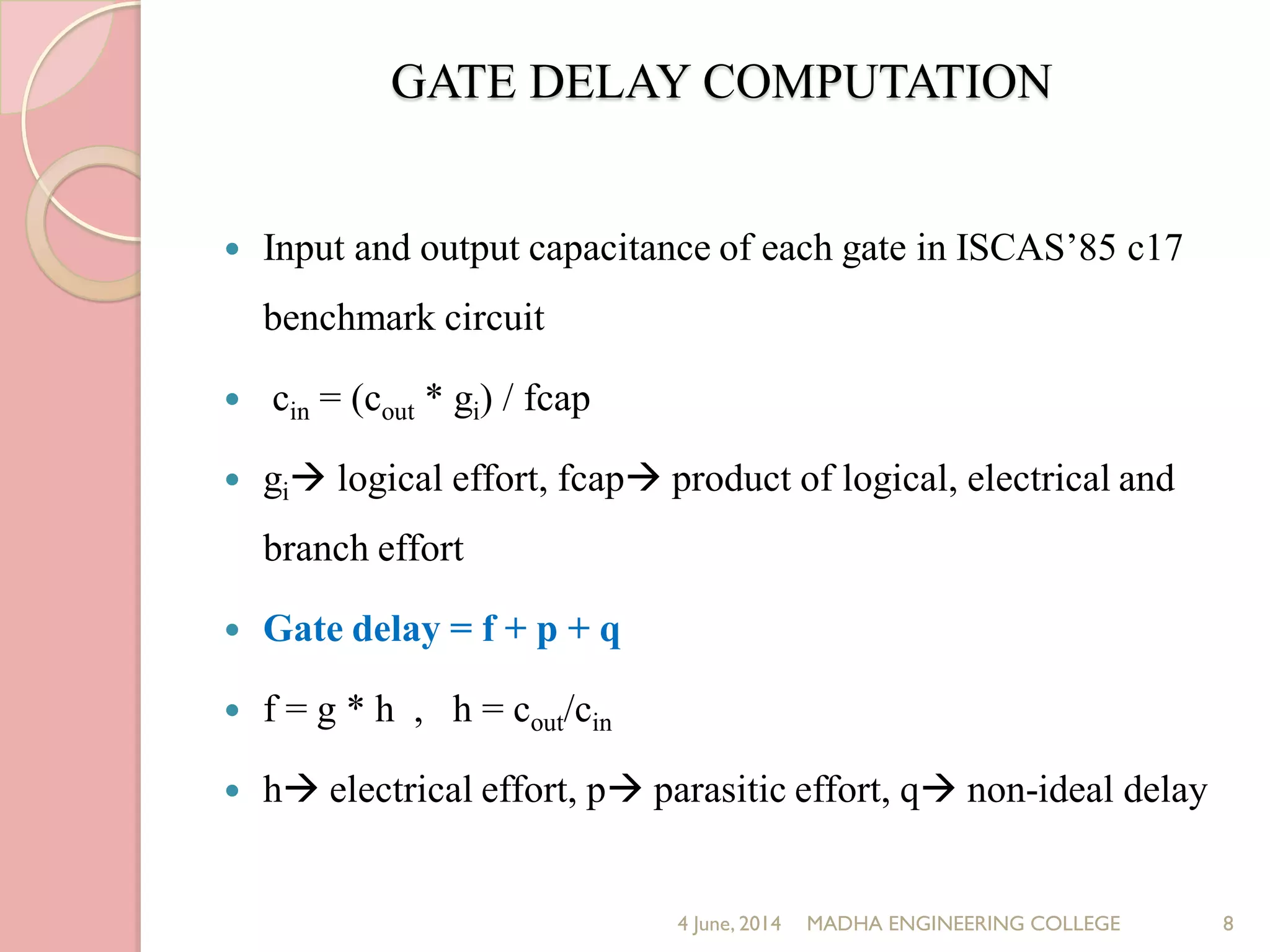
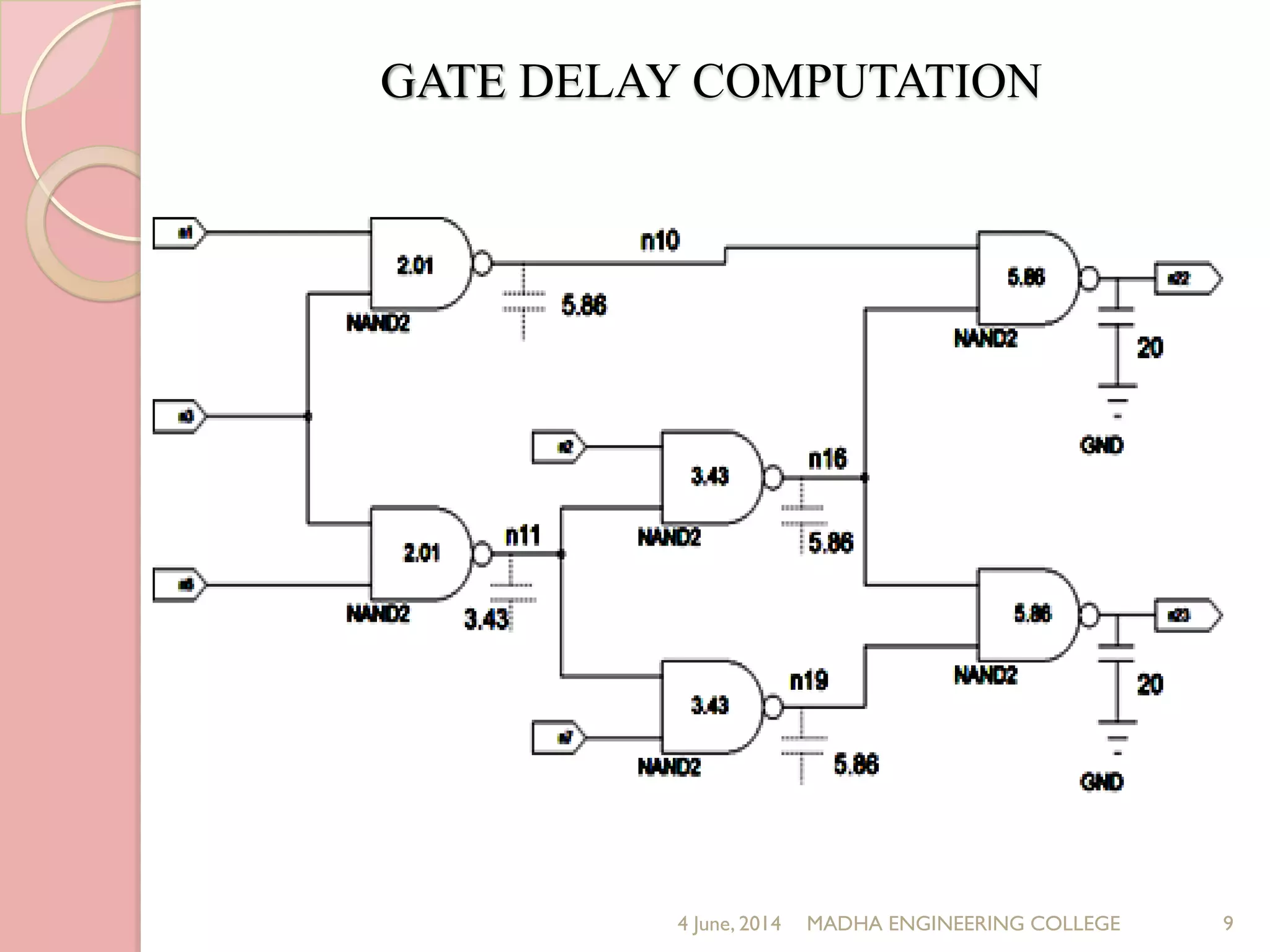
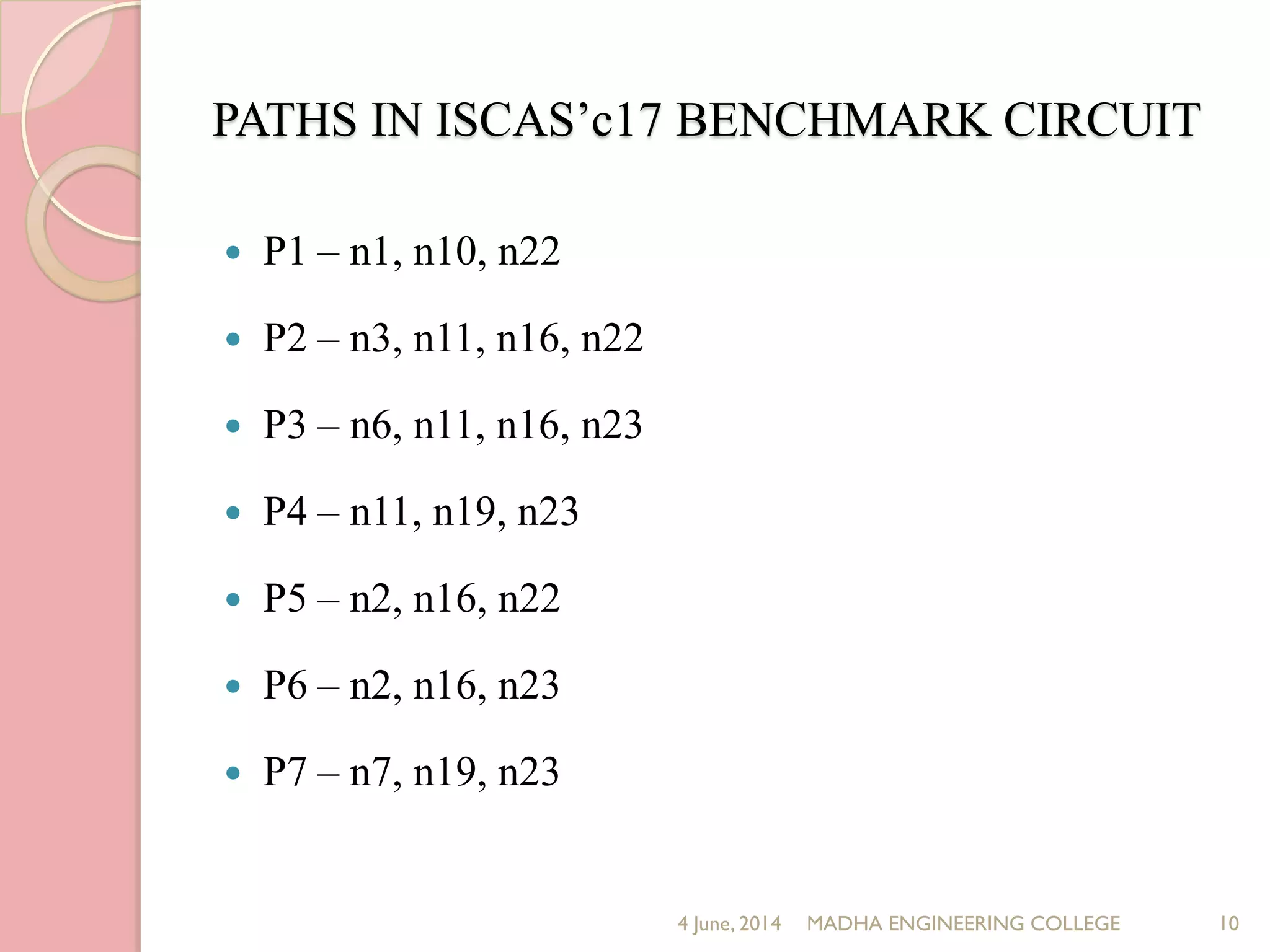
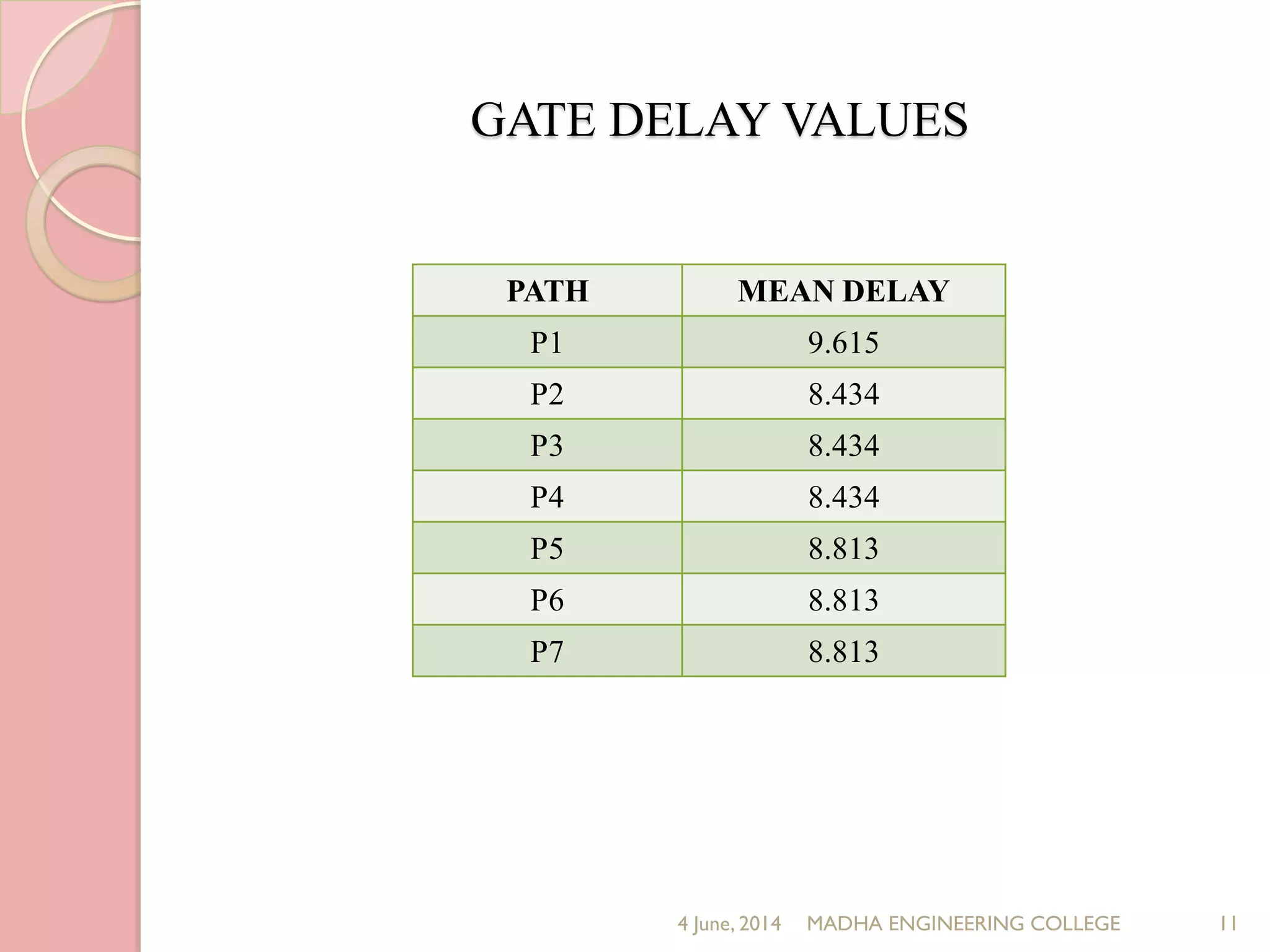
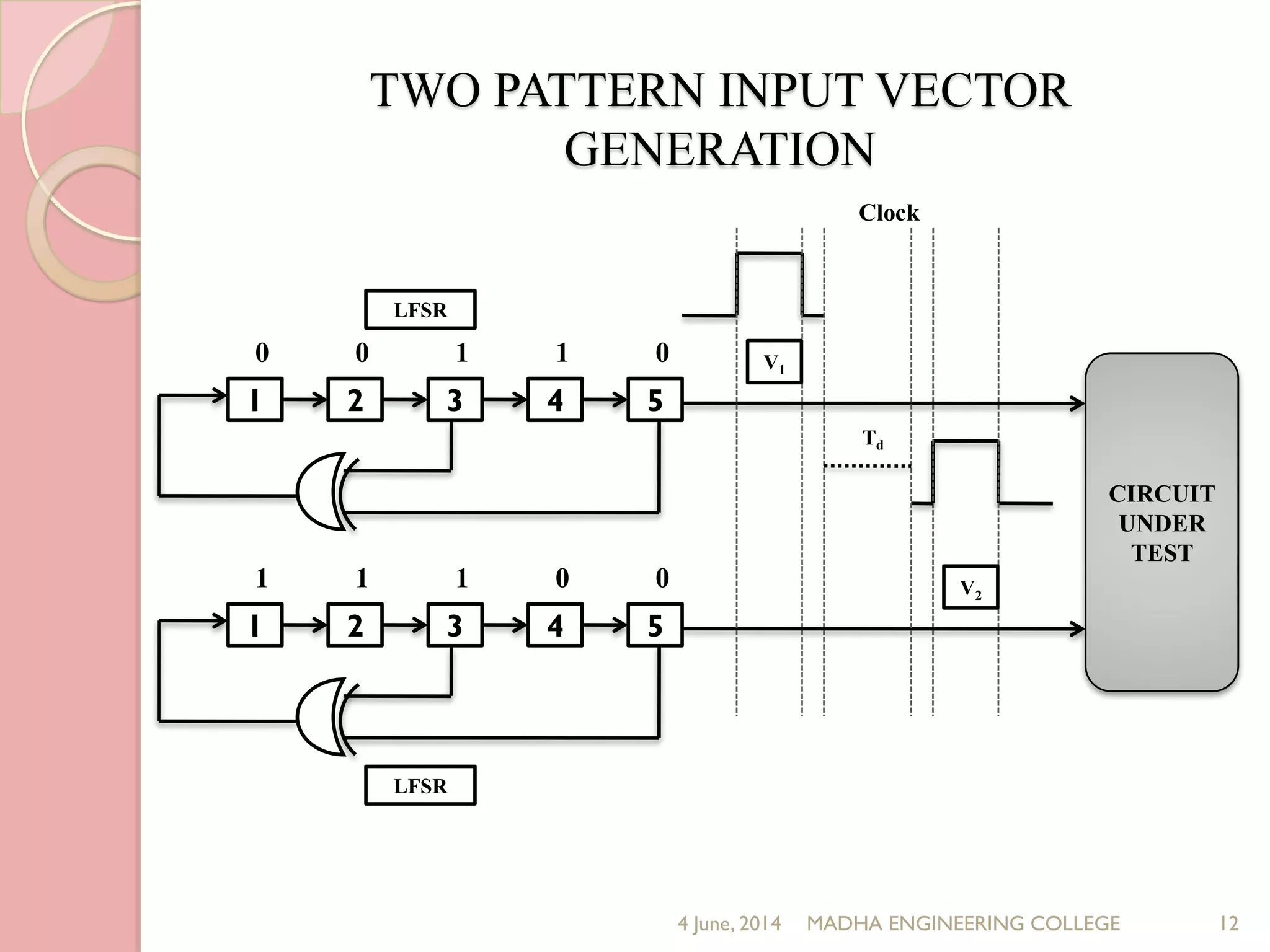
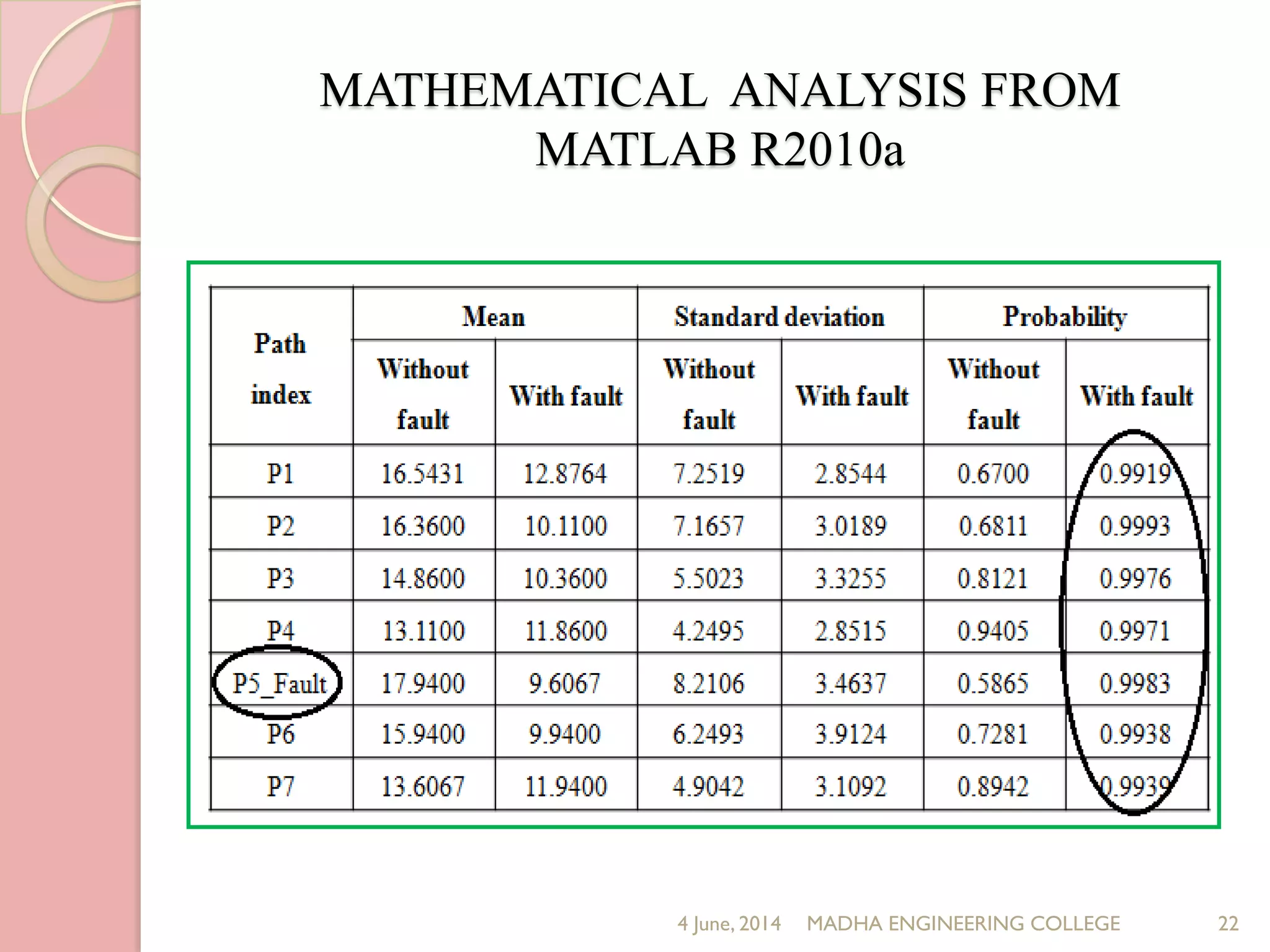
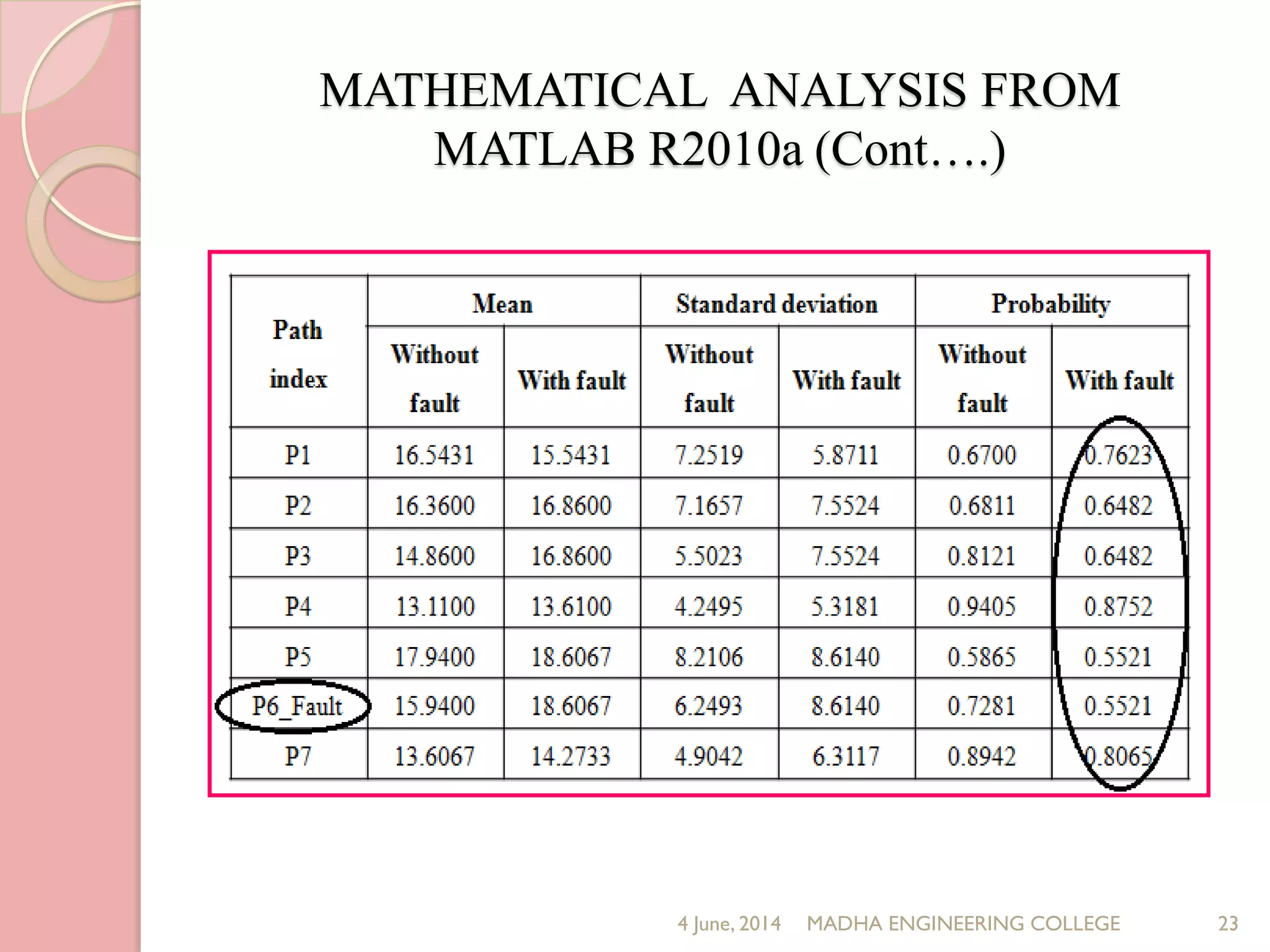
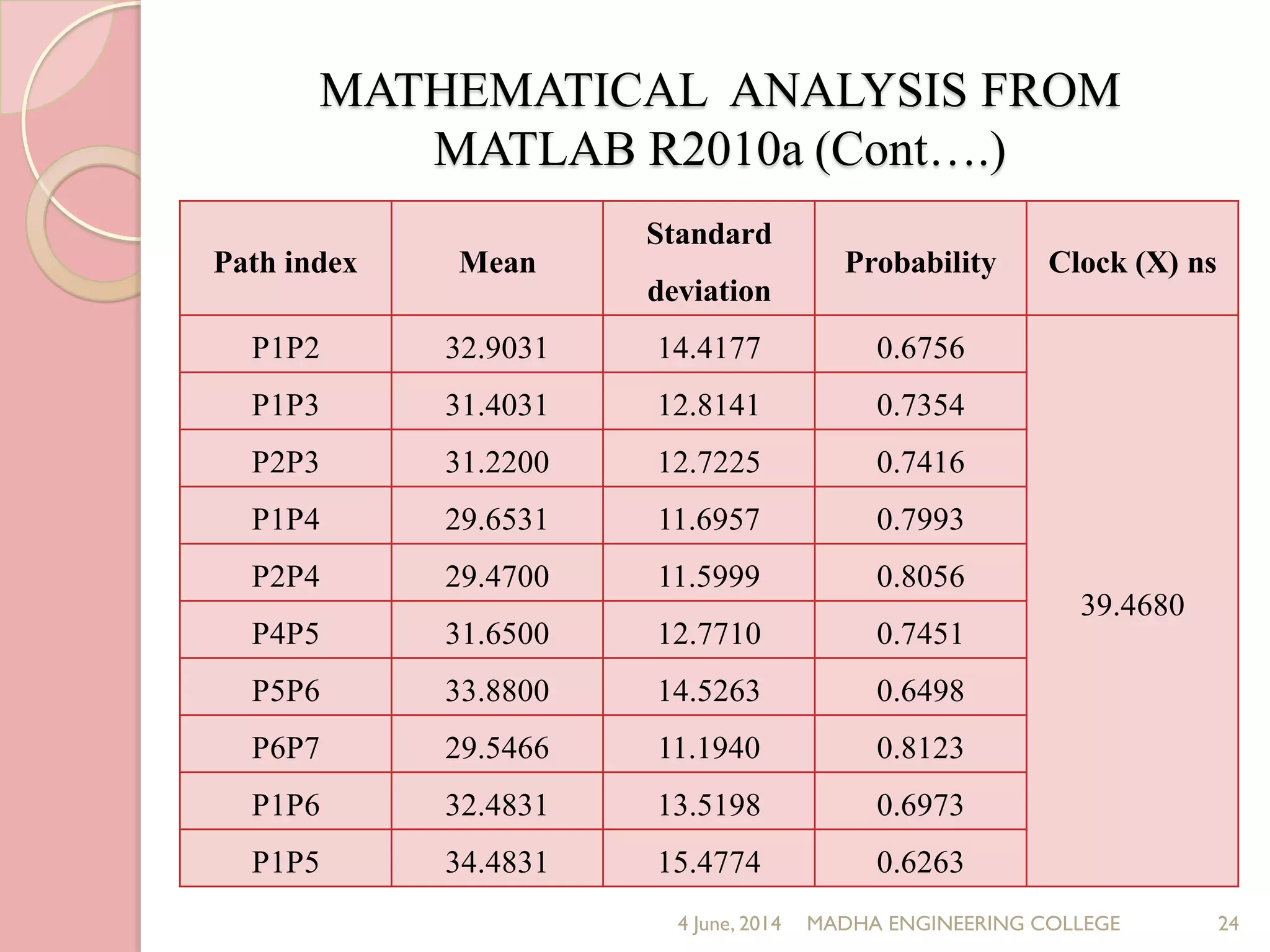
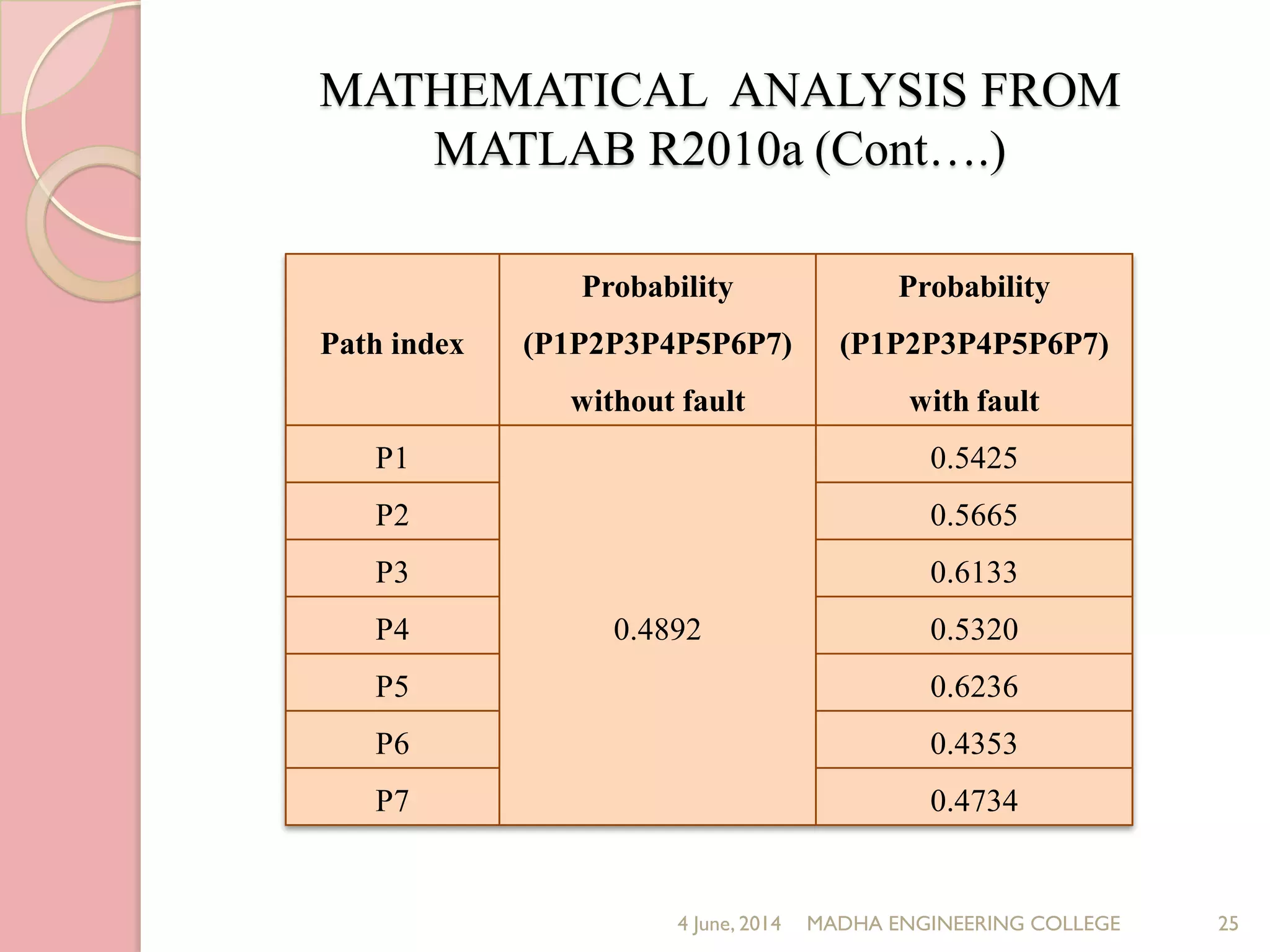
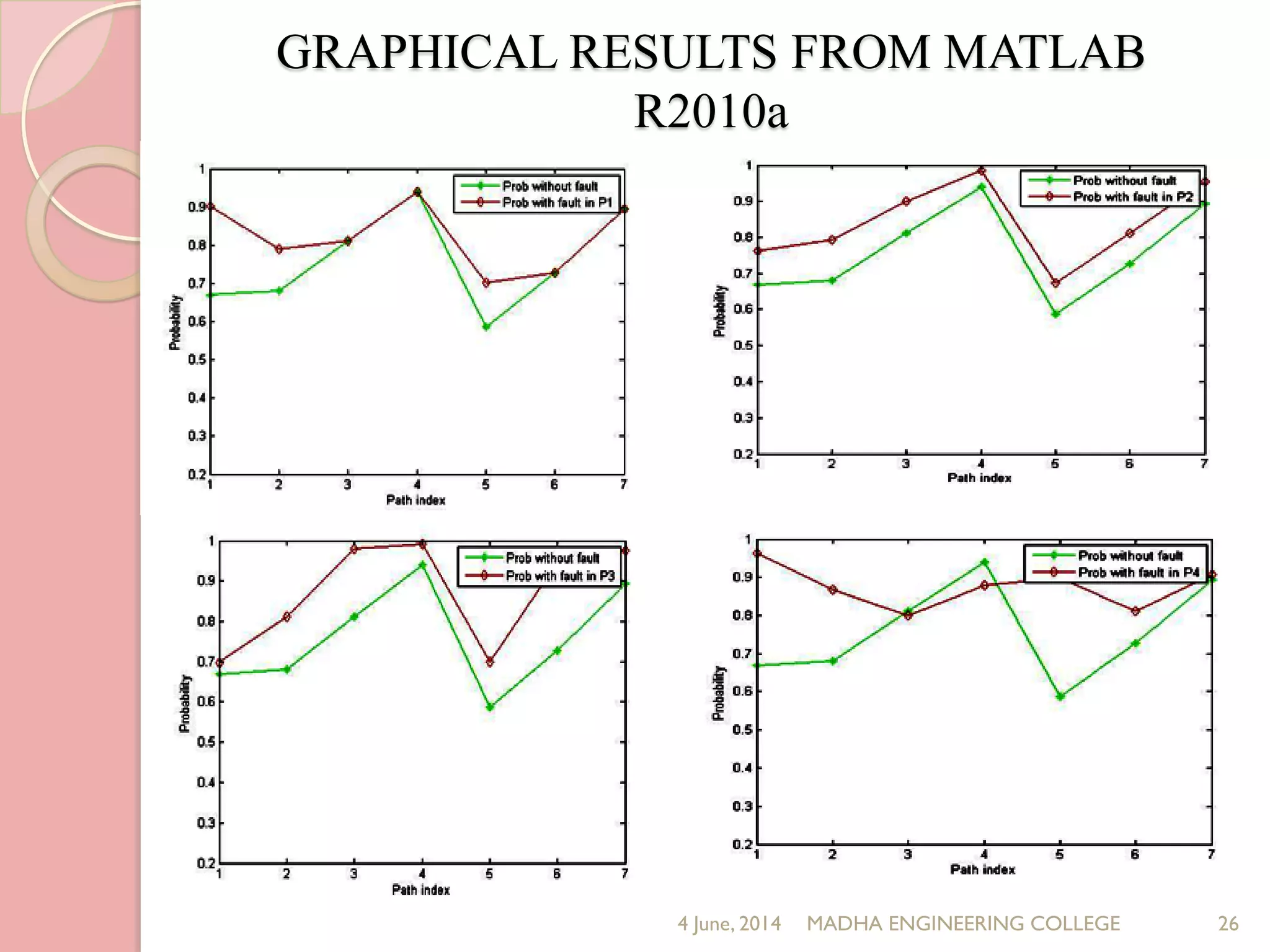
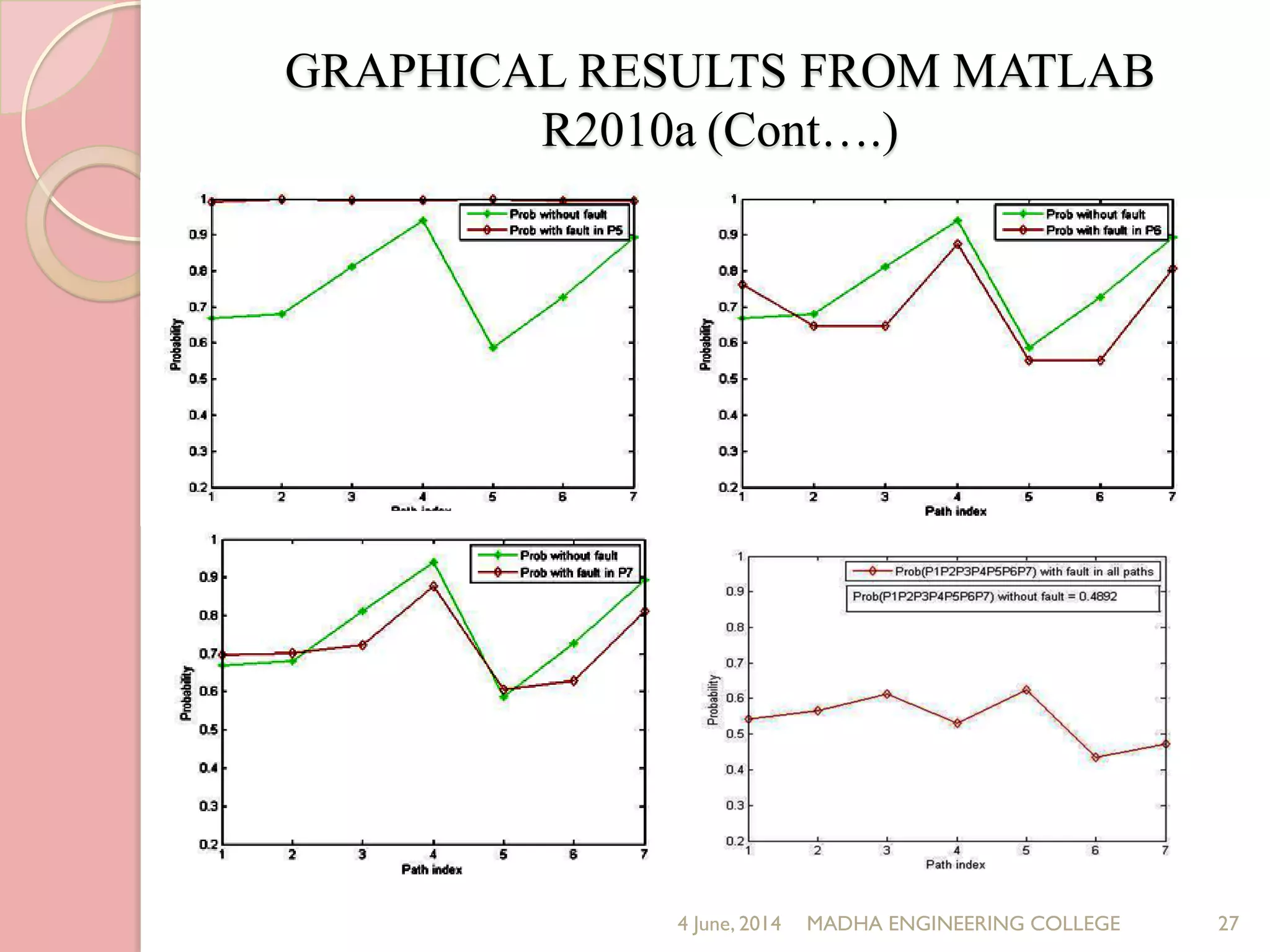
This document presents a novel approach for analyzing gate delay and path delay faults in VLSI circuits. It aims to compute the probability of circuit delay failures by estimating gate delays, switching activity, and correlating path delays. The proposed work involves computing mean delays for paths in an ISCAS'85 benchmark circuit using gate delays and switching activities. It then calculates path delay probabilities and compares the probabilities with and without faults using mathematical analysis in MATLAB. The results show the probability values are higher without faults compared to with faults, indicating the approach can detect delay faults.




![REFERENCES [1] Alok S. Doshi and Anand S(2008), “Test Pattern Generator for Built-in Self Test using Spectral Methods ” , Mudlapur Auburn University Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Auburn, AL, USA doshias. [2] Hongliang Chang and Sachin S. Sapatnekar(2003), “Statistical Timing Analysis Under Spatial Correlations,” Fellow, IEEE.”Computer Aided Design of integrated circuits and systems, IEEE Transactions on vol 24, no. 9. [3] lrith Pomeranz and Sudhakar M. Reddy(Jan.1996), “On the number of tests to delect all path delay faults in combinational logic circuits, “IEEE transactions on computers, vol. 45, No. 1. [4] Jing-Jia Liou, Angela Krstic, Li-C. Wang and Kwang-Ting Cheng(Jun 2002), “False-Path-Aware Statistical Timing Analysis and Efficient Path Selection for Delay Testing and Timing Validation,” Electrical and Computer Engineering Department,University of California, Santa Barbara., IEEE 39th proceedings. [5] Li-C. Wang, Jing-Jia Liou and Kwang-Ting Cheng(Nov 2004), “Critical Path Selection for Delay Fault Testing Based Upon a Statistical Timing Model,” IEEE transactions on computer-aided design of integrated circuits and systems, vol. 23, no. 11,. [6] Vladimir Zolotov, Jinjun Xiong, Hanif Fatemi,and Chandu Visweswariah(May 2010), “Statistical Path Selection for At- Speed Test,” IEEE transactions on computer-aided design of integrated circuits and systems, vol. 29, no. 5. [7] W.B.Jone, W.S.Yeh and S.R.Das(2000),”An Adaptive Path Selection Method for Delay Testing”, IEEE transactions on very large scale integration system, volume 50, issue 5. [8] Wing Ning Li, Sudhakar M. Reddy, Sartaj Sahni(Aug 2002), “On Path Selection In Combinational Logic Circuits,” IEEE transactions in computer aided design of integrated circuits and systems, vol 8, no. 1. [9] Wangqi Qiu D. M. H. Walker, “An Efficient Algorithm for Finding the K Longest Testable Paths Through Each Gate in a Combinational Circuit,” Department of Computer ScienceTexas A&M University, IEEE proceedings, volume 1. [10] Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker and Weiping Shi, “Longest Path Selection for Delay Test under Process Variation,” Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843, IEEE transactions on vol 24, no. 12. [11] Zijian He, Tao Lv, Huawei Li and Xiaowei Li(Jul 2013), “Test Path Selection for Capturing Delay Failures Under Statistical Timing Model”IEEE transactions on very large scale integration (VLSI) systems, vol. 21, No. 7. 4 June, 2014 MADHA ENGINEERING COLLEGE 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anovelapproachongatedelaytransitionbasedpathdelayfaultmodel-140604103409-phpapp01/75/A-novel-approach-on-gate-delay-transition-based-path-delay-fault-model-32-2048.jpg)
