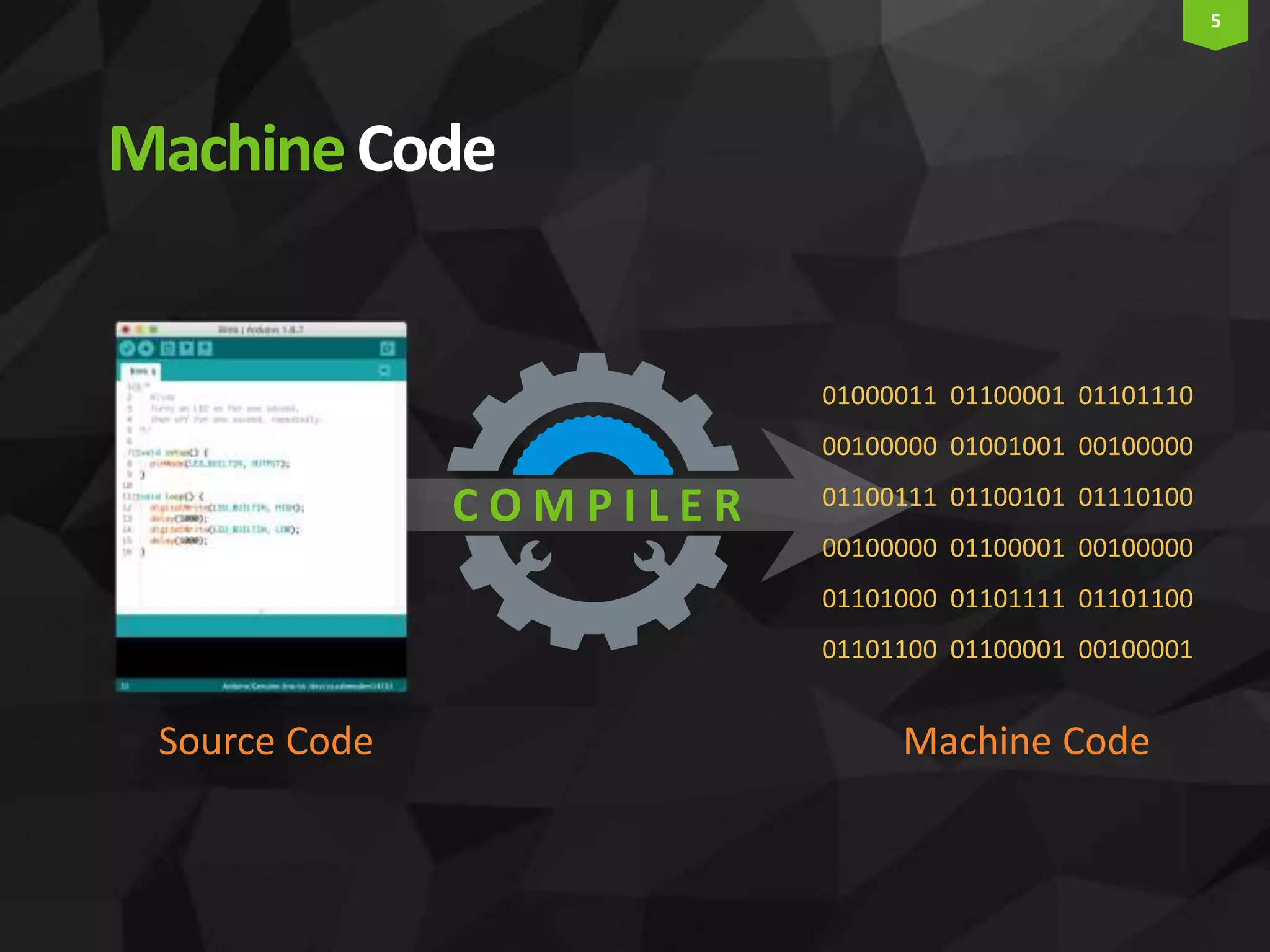
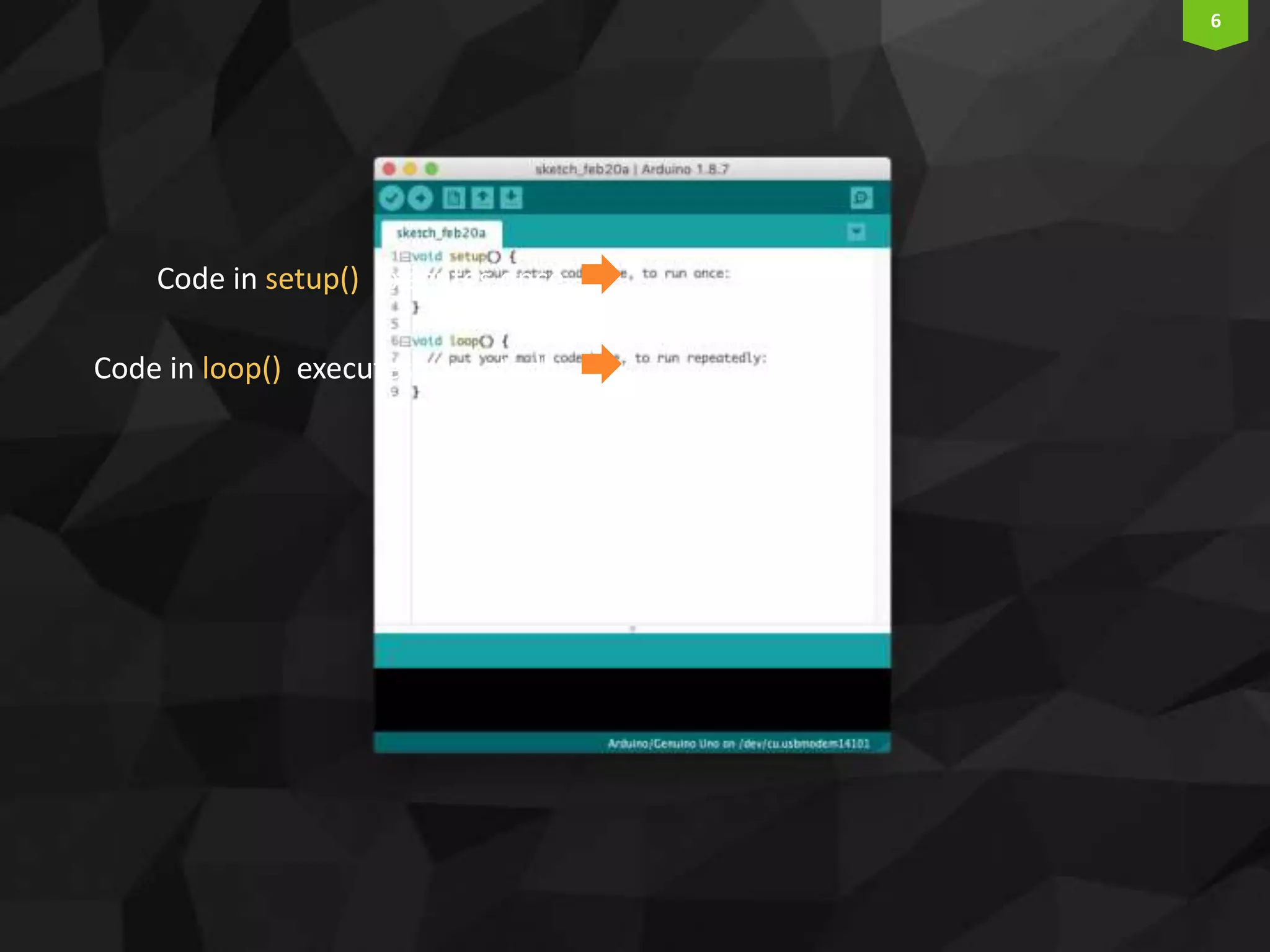
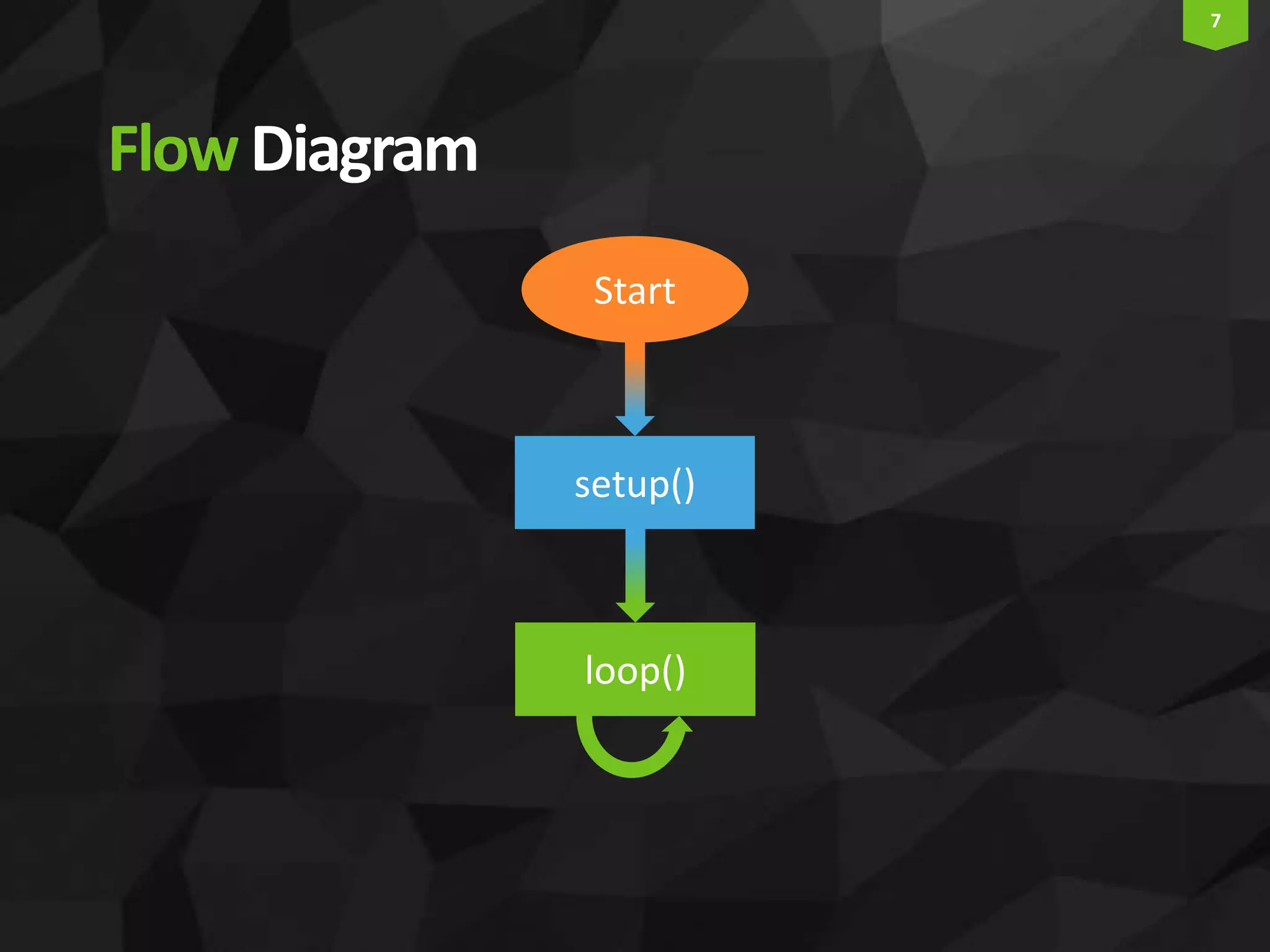
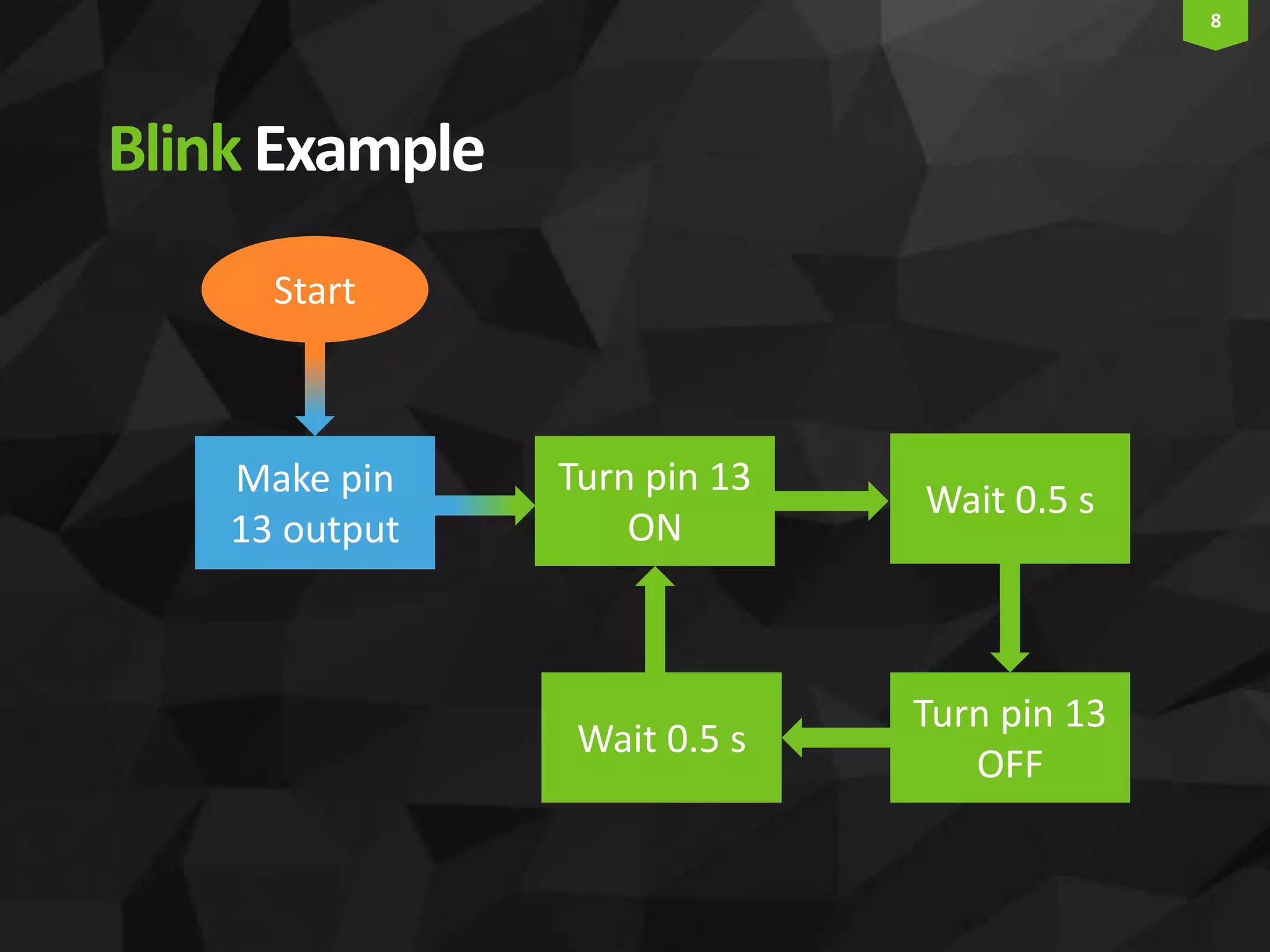
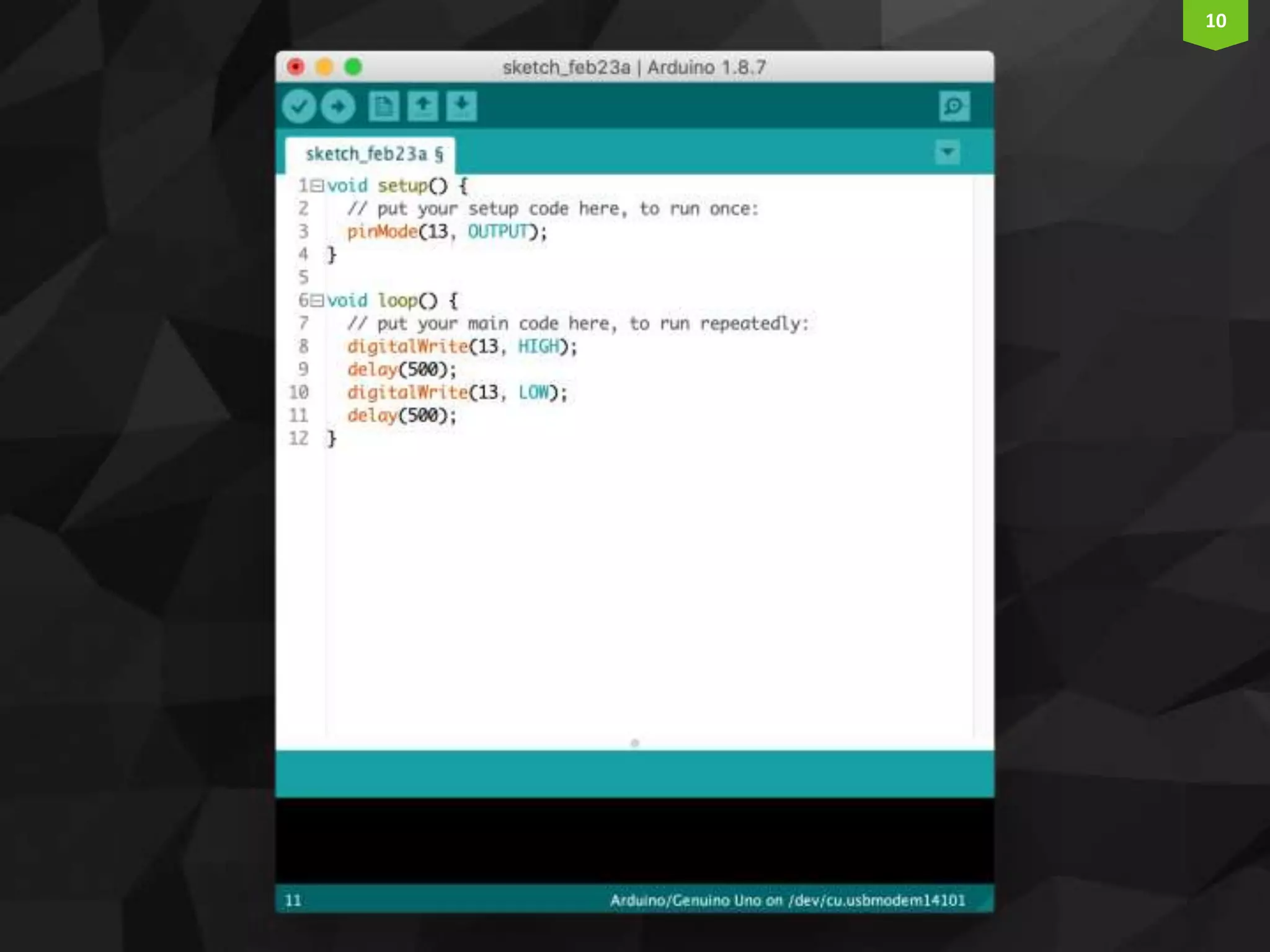
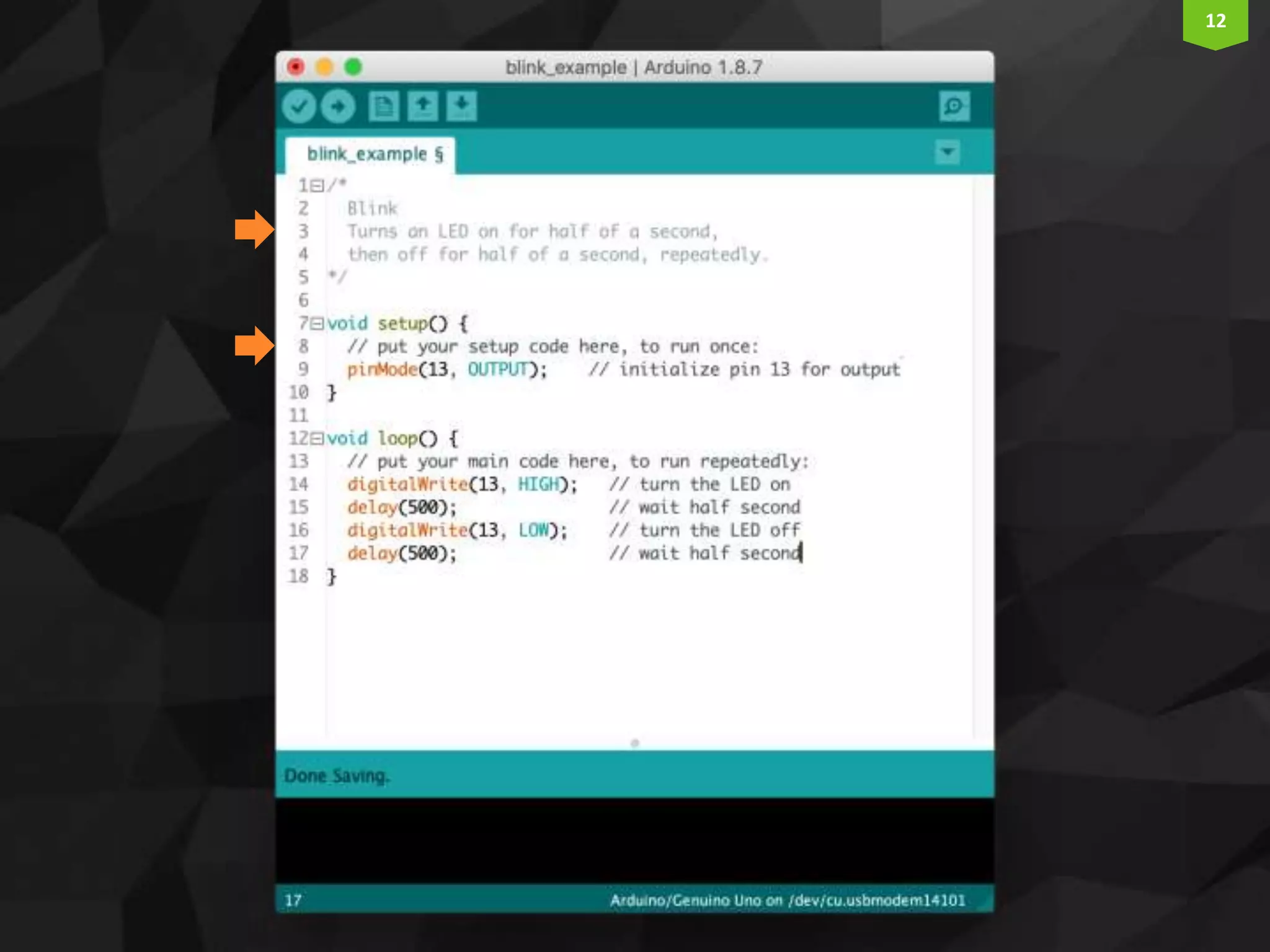
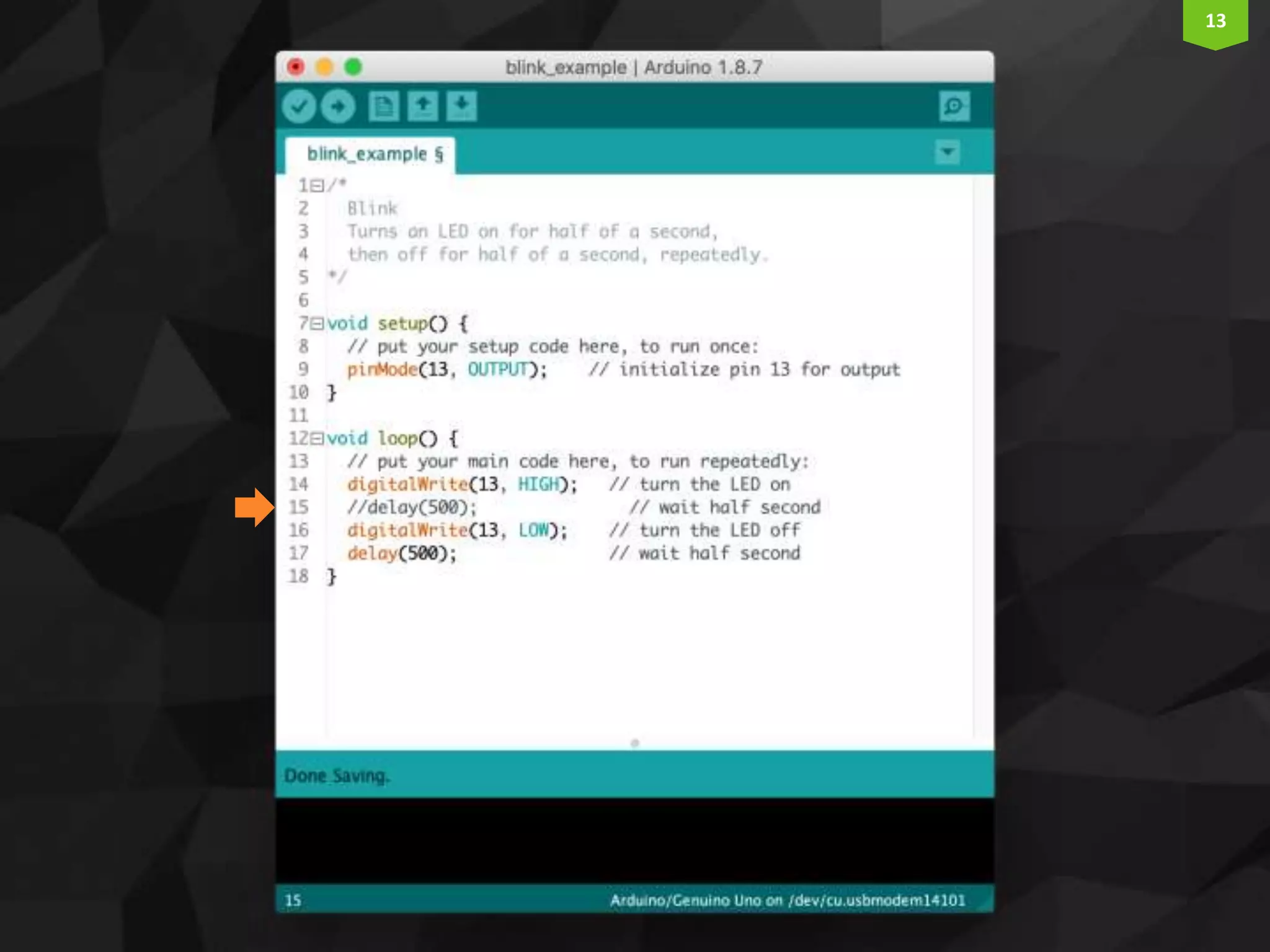
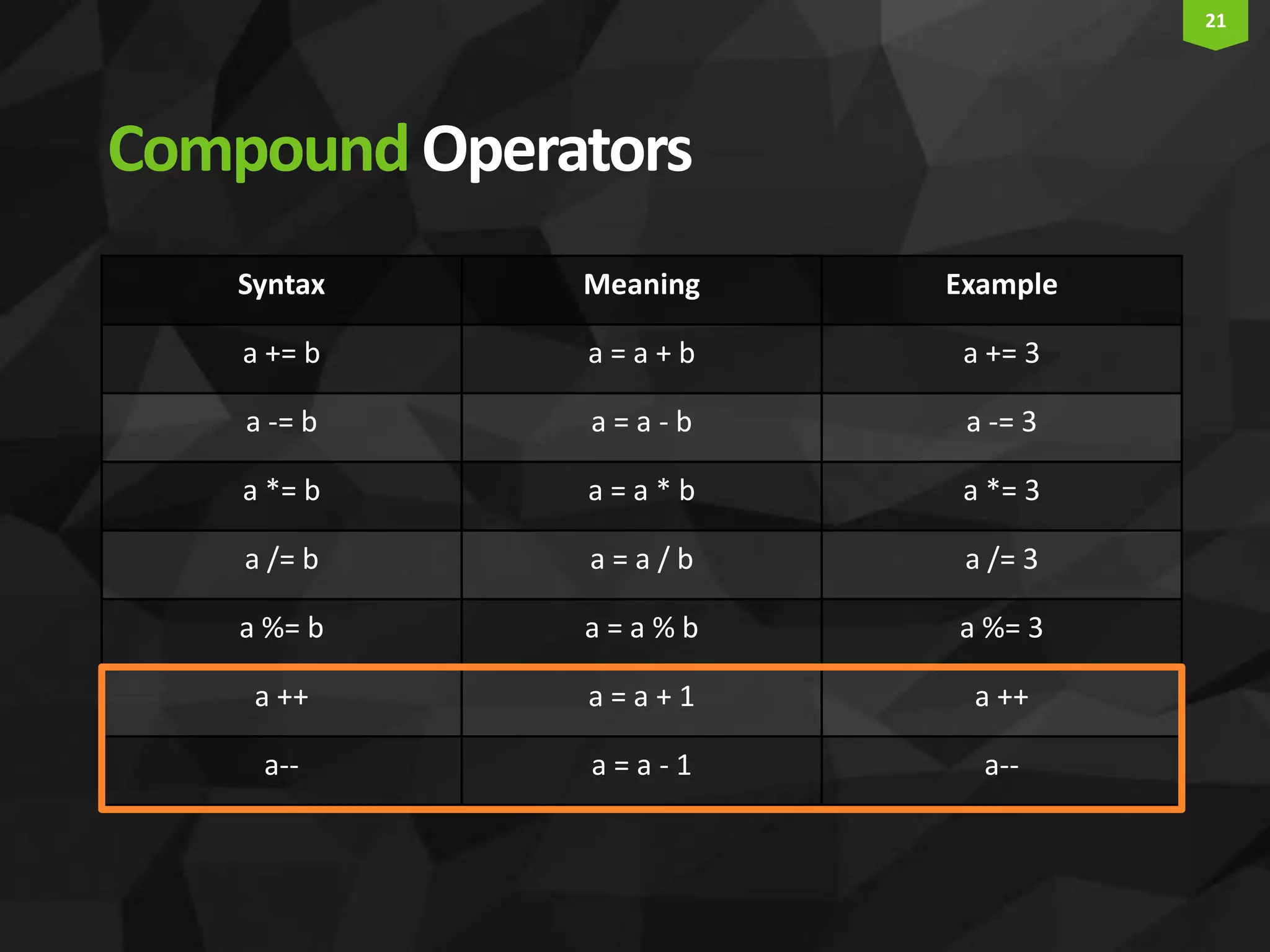
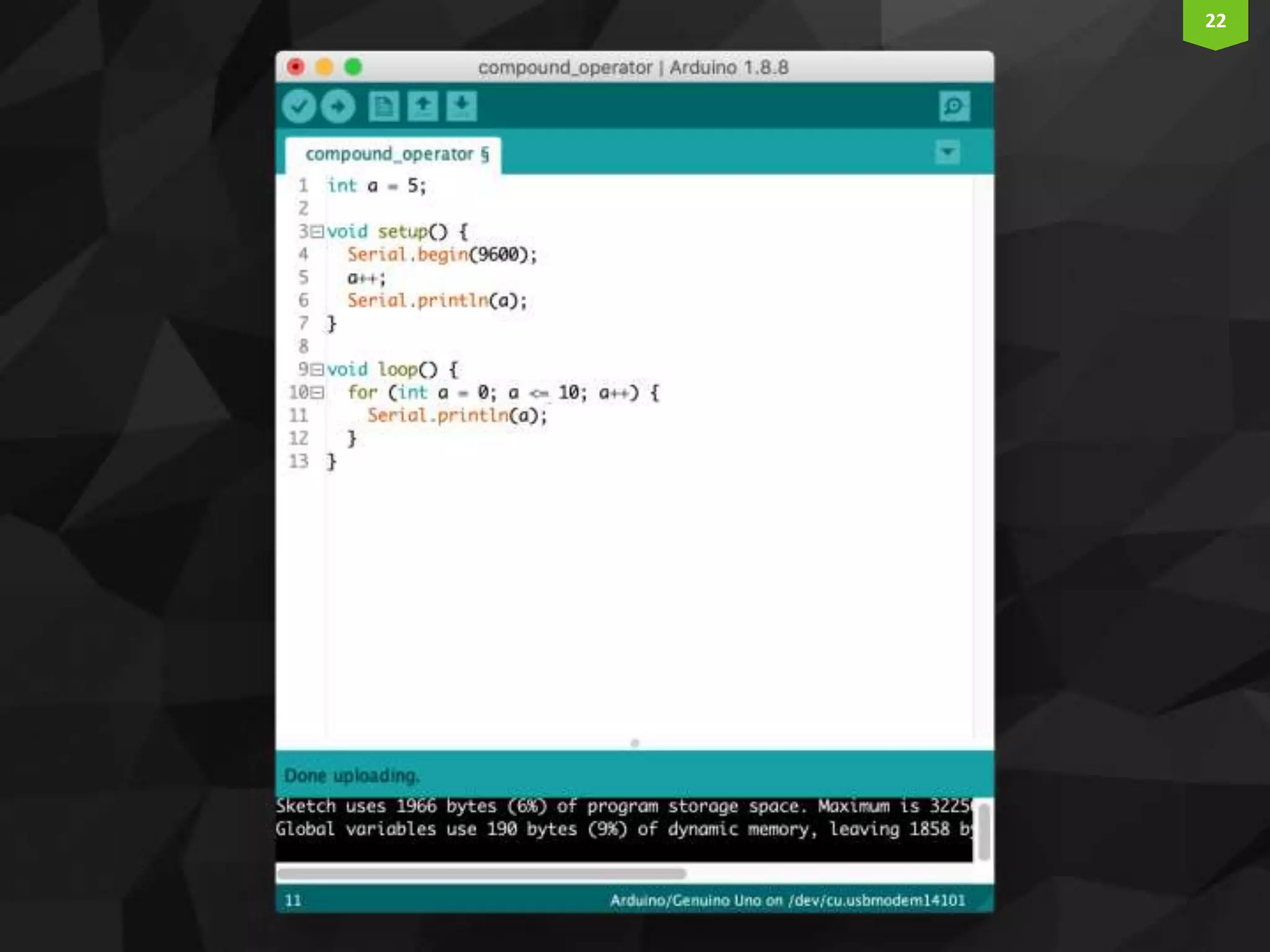
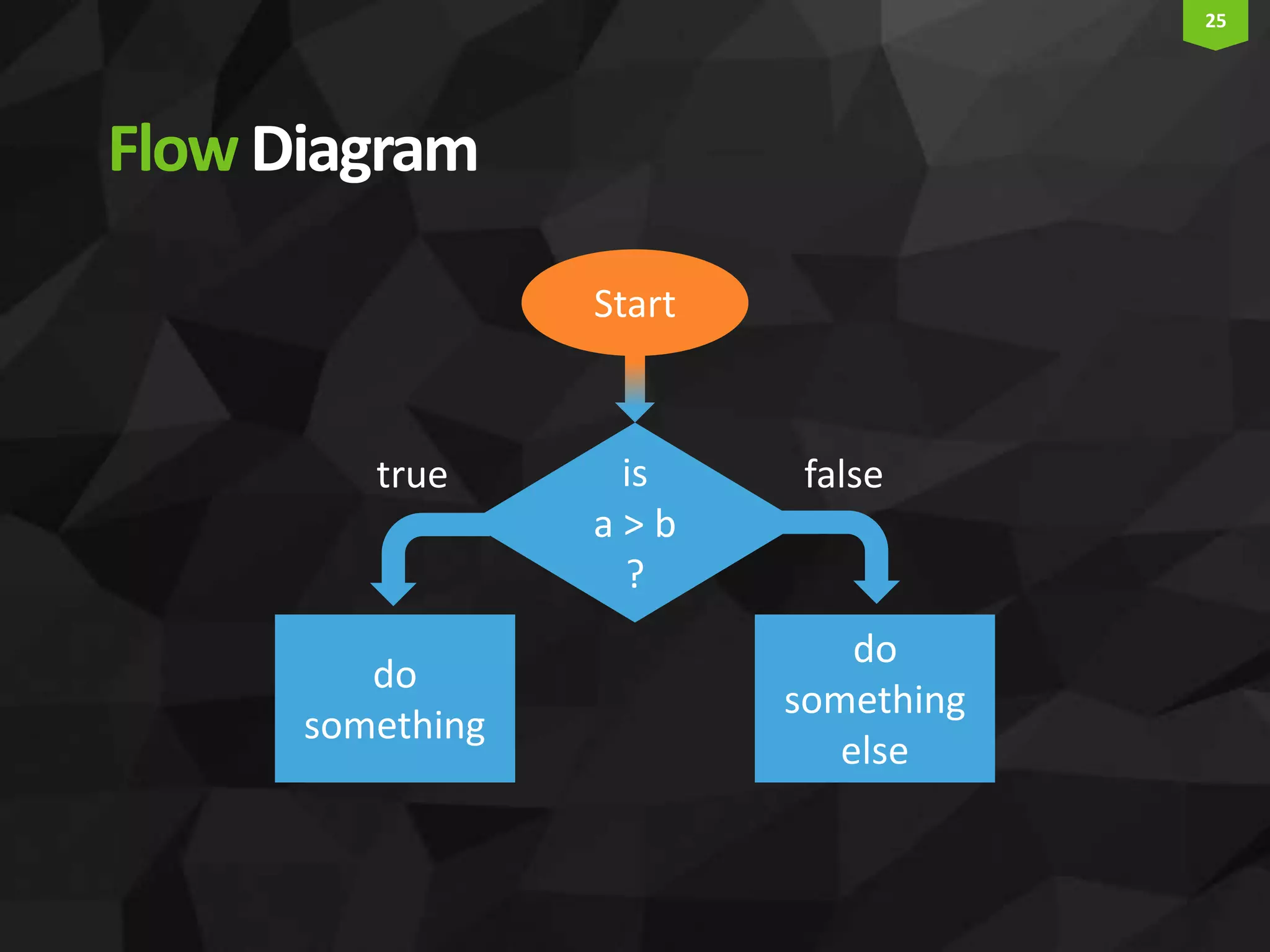
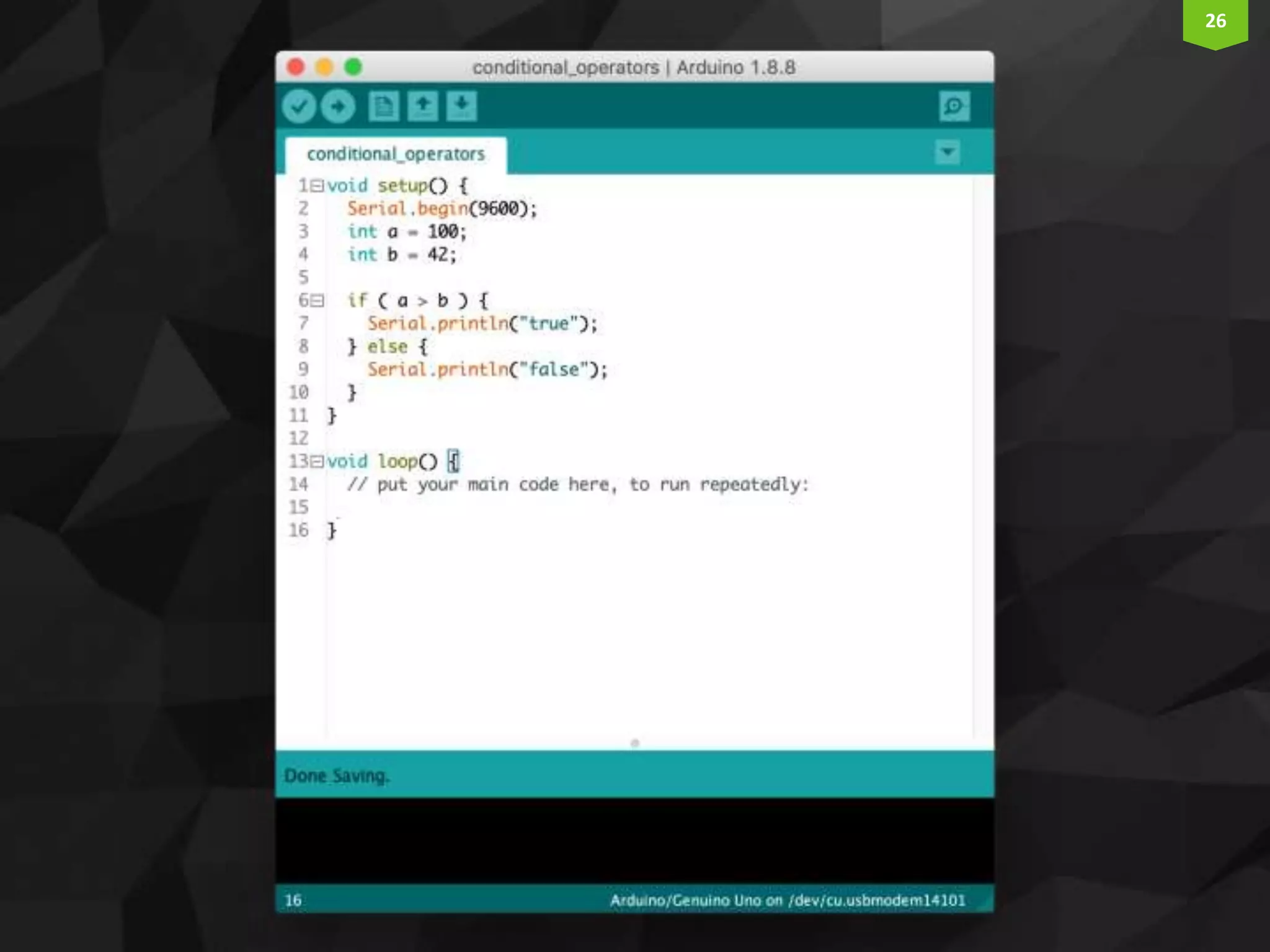
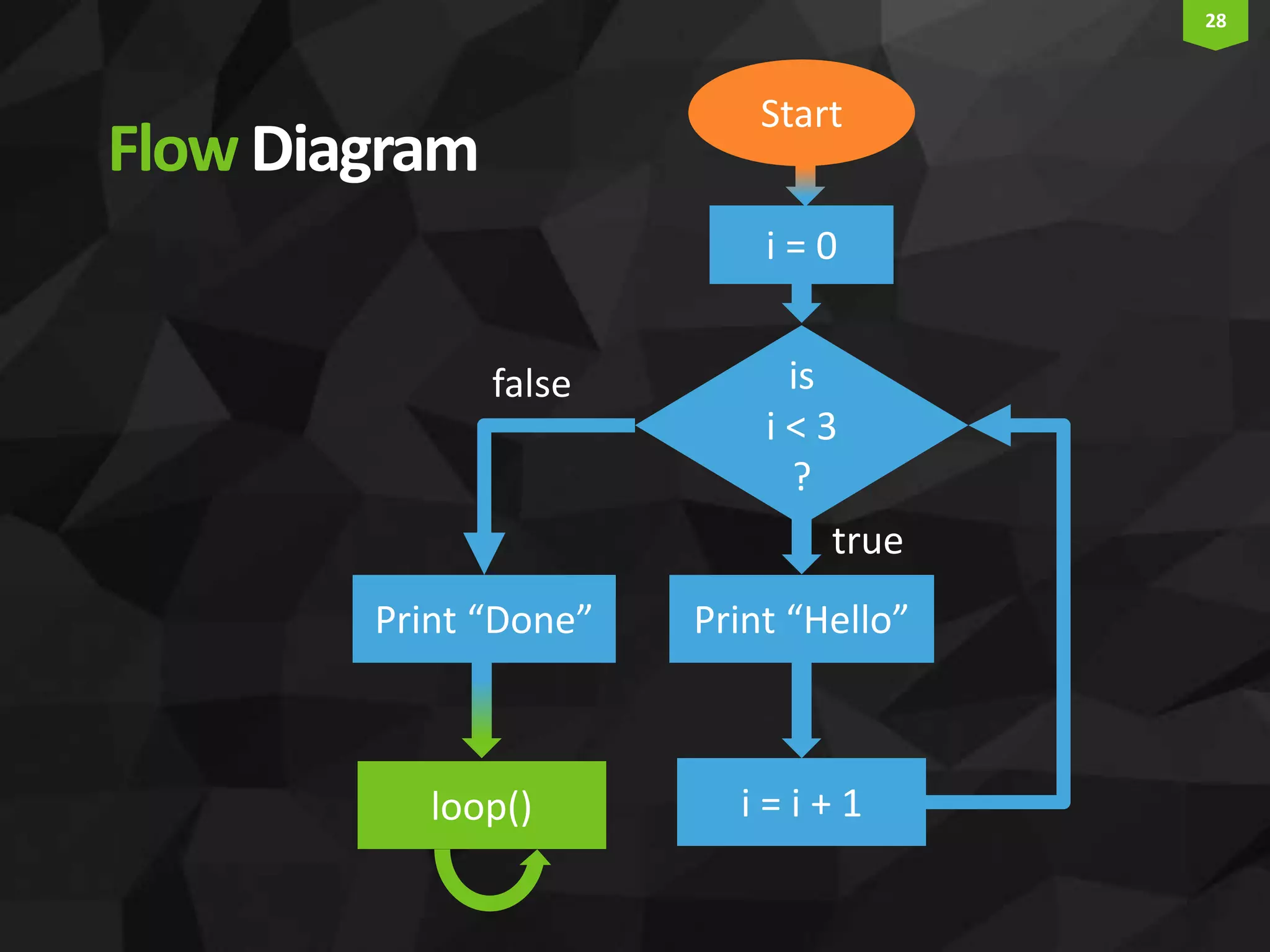
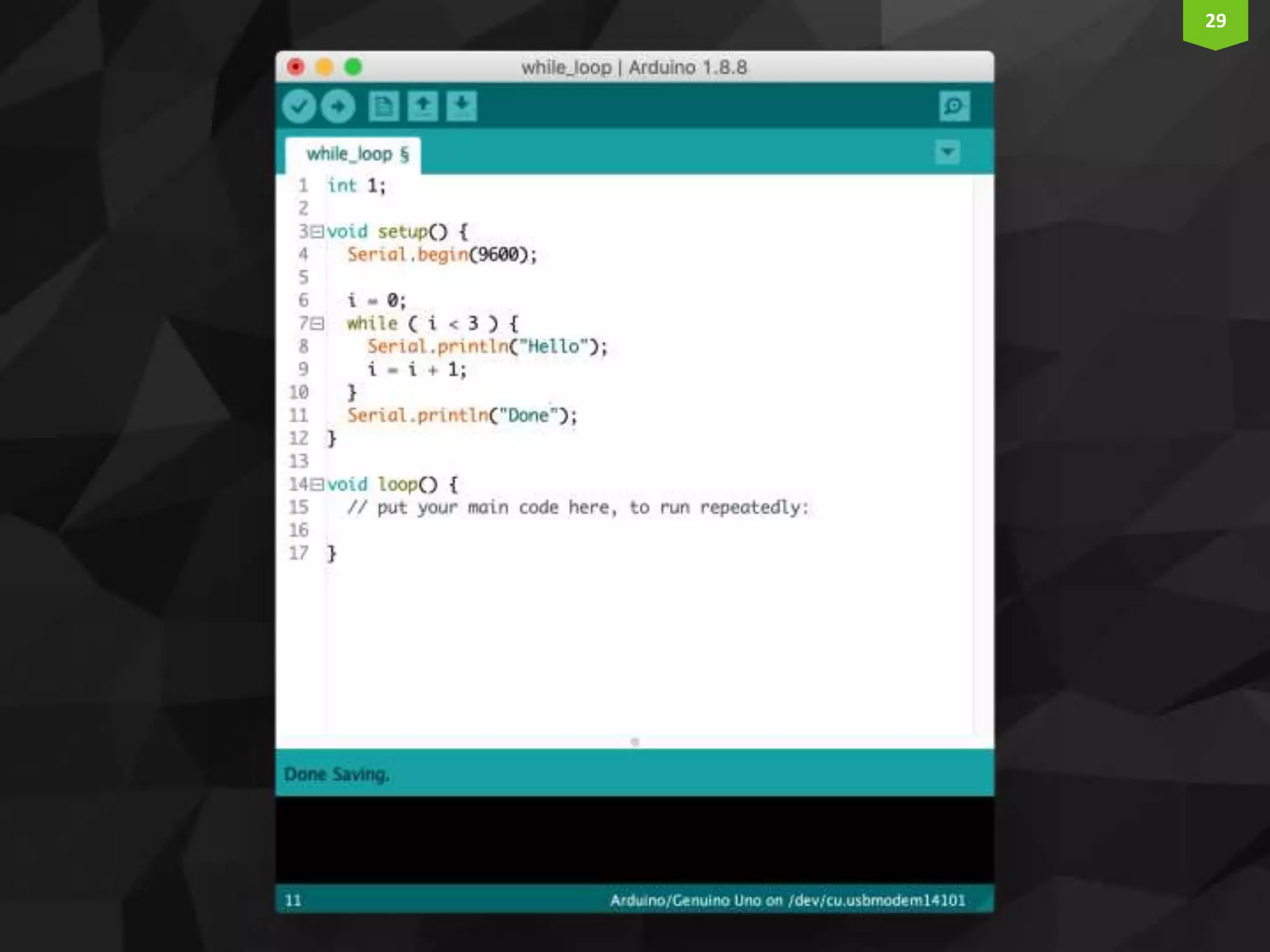
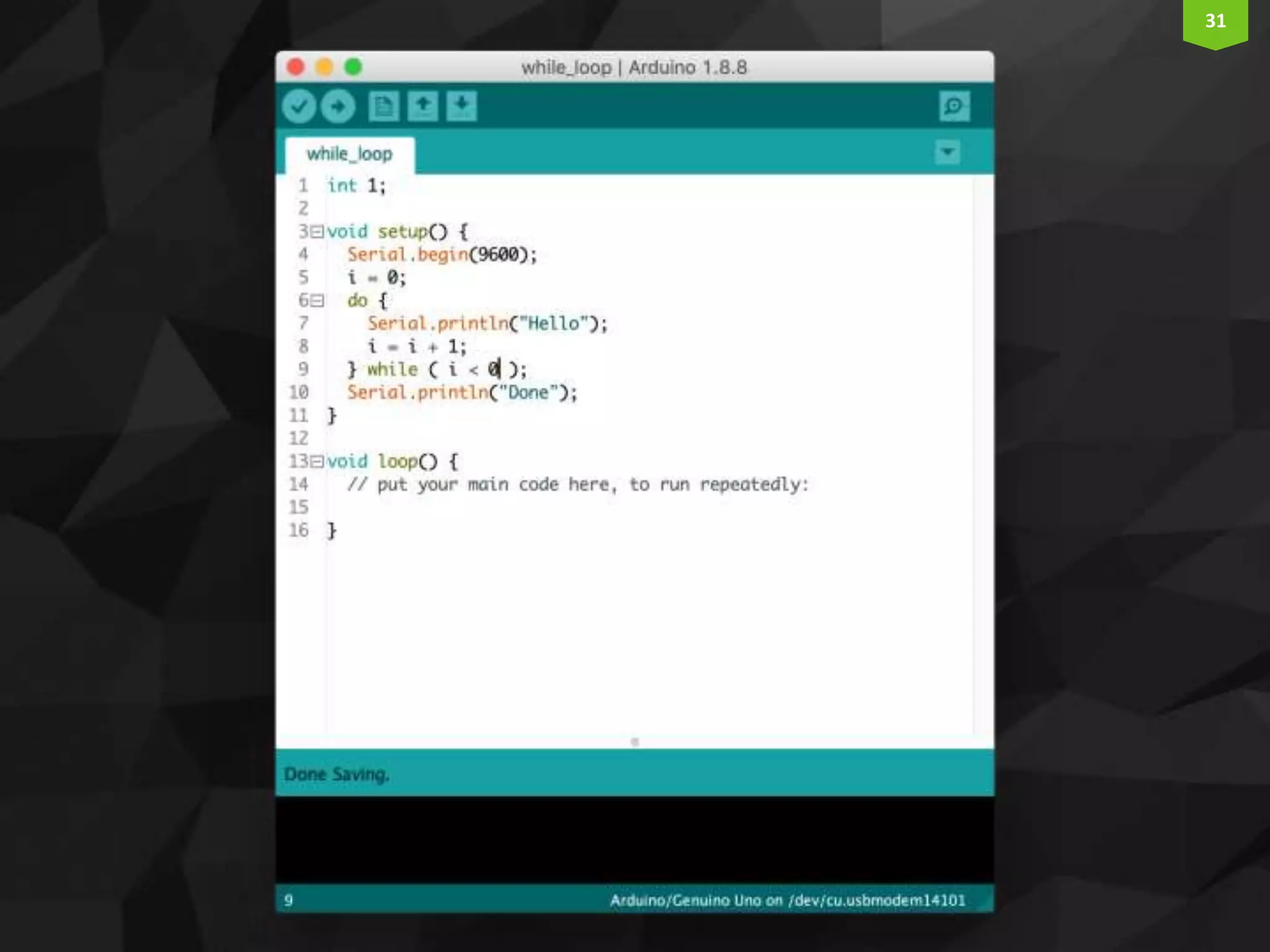
This document provides an introduction and overview of Arduino programming. It discusses the Arduino IDE software, how Arduino code is executed sequentially in single threads, how source code is compiled to machine code. It also covers basic concepts like the structure of an Arduino sketch with setup() and loop() functions, how to describe programs with pseudocode, common data types, arithmetic and comparison operators, control structures like if/else and loops, and switch statements.