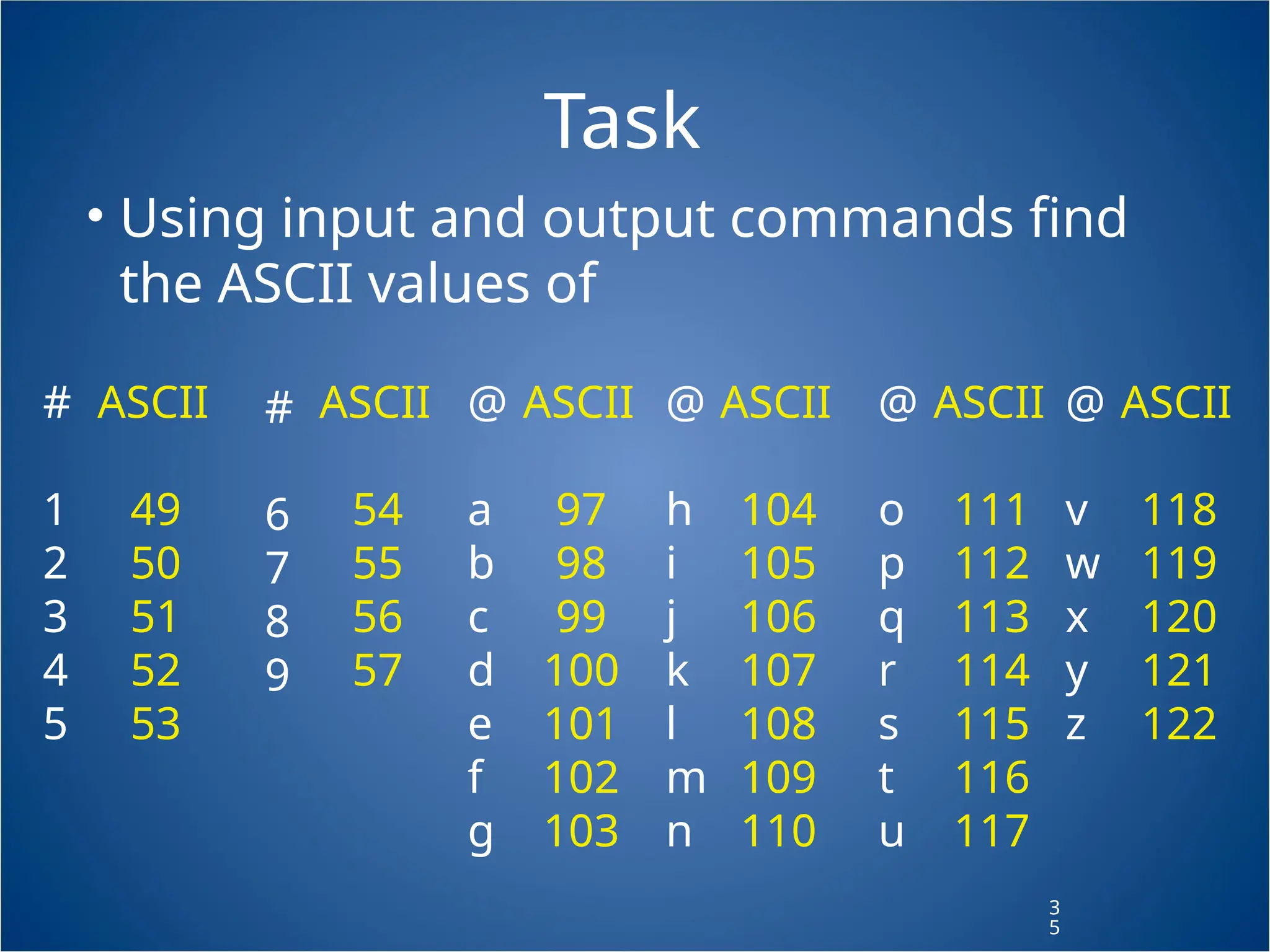
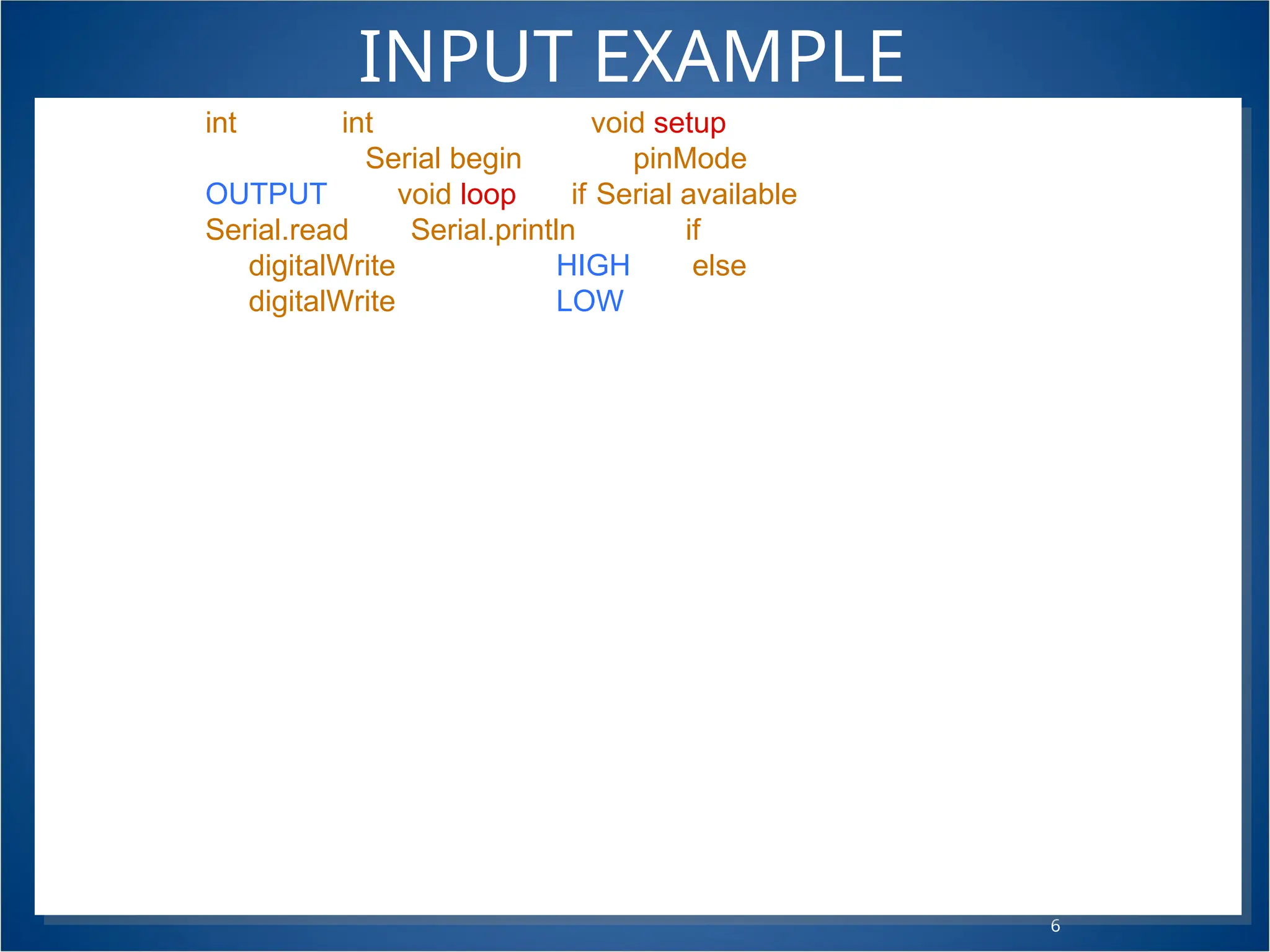
The document provides a comprehensive guide on Arduino programming, focused on creating an automated mini city with features like traffic lights and streetlights. It explains fundamental coding concepts, such as functions, variables, and input/output communications, through tasks and examples for building projects. Additionally, it covers advanced programming techniques using conditional statements and user input to enhance program functionality.




























![4 3 Christmas Light Assignment • Using at least 5 LEDs create a program that has at least 4 different modes • Must use if statements and user input to switch modes • Marks: – Creativity [4 Marks] – Working user input [2 Marks] – Four Working modes [2 Marks] – Instructions [1 Mark] 4 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arduino-21-250105085048-2a189b1d/75/Arduino-arduino-arduino-programming-hhhh-43-2048.jpg)