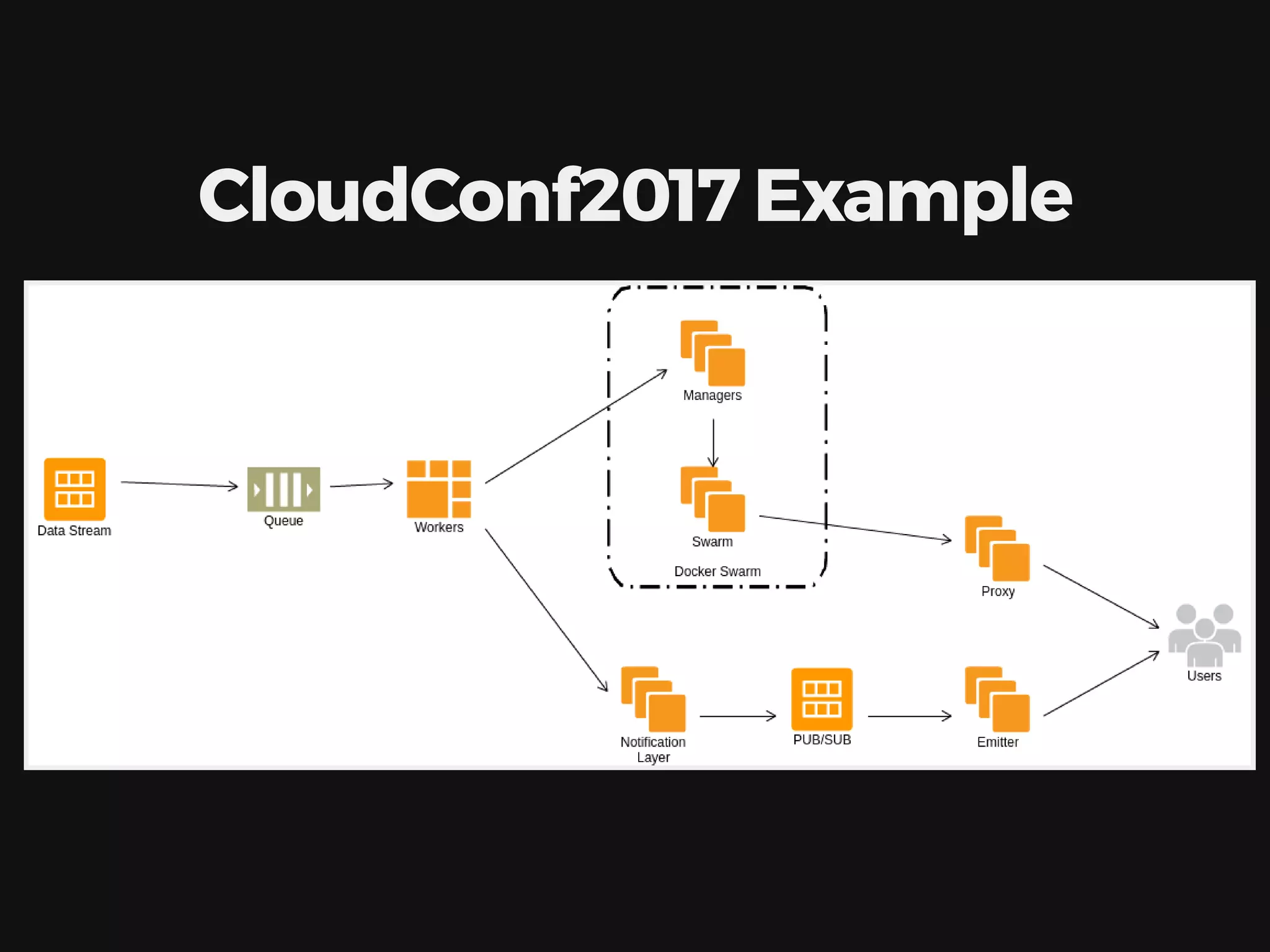
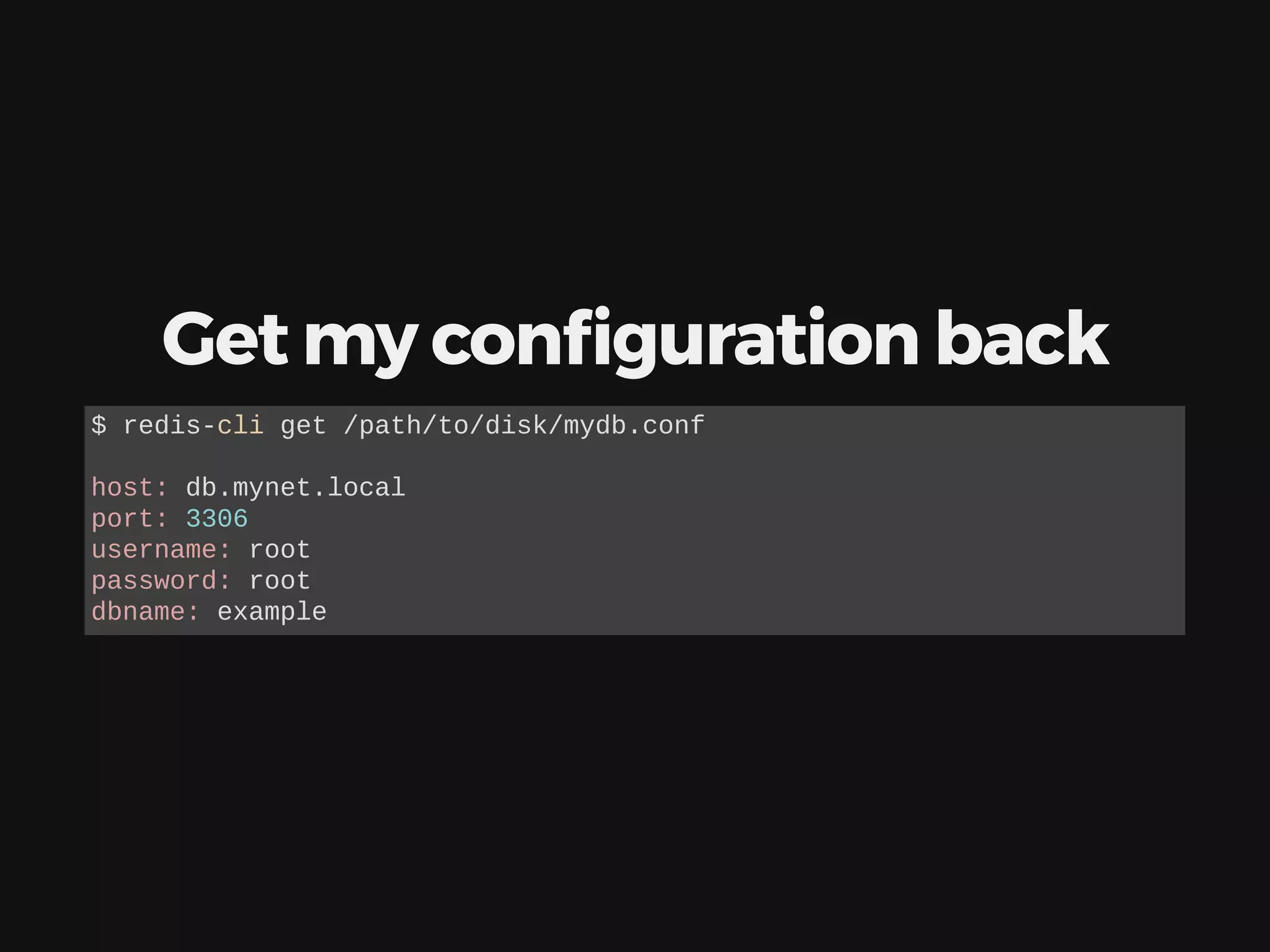
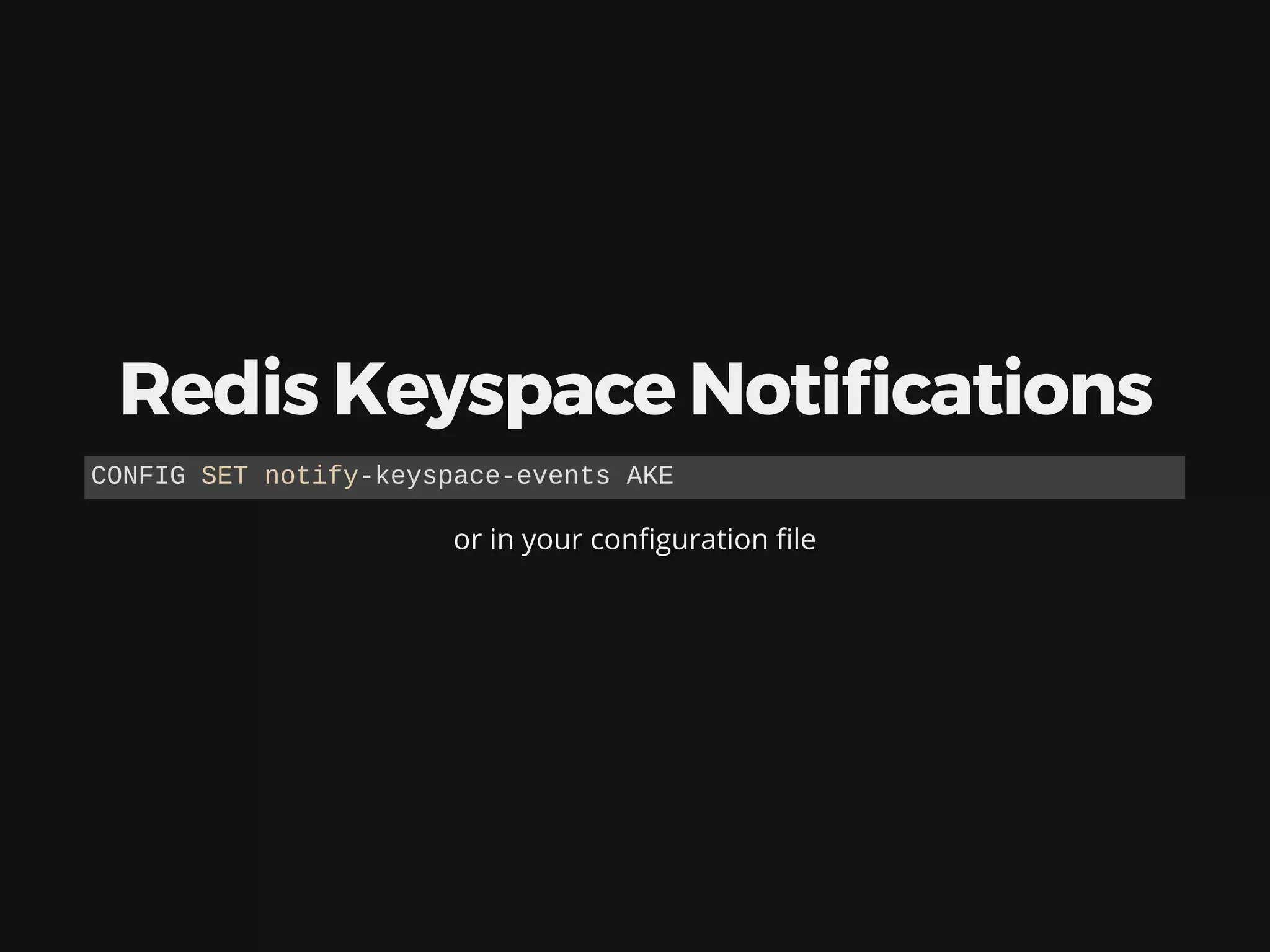
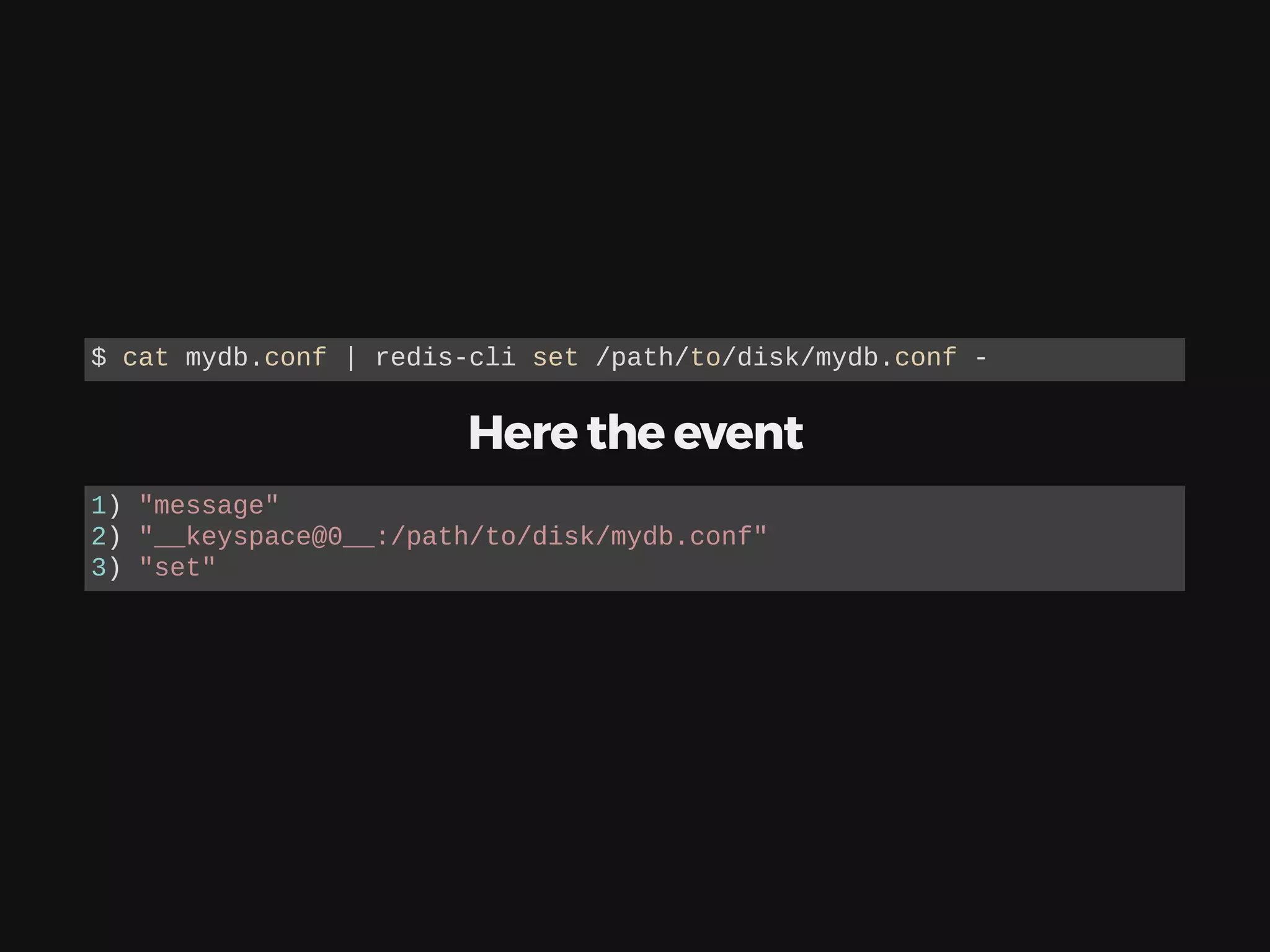
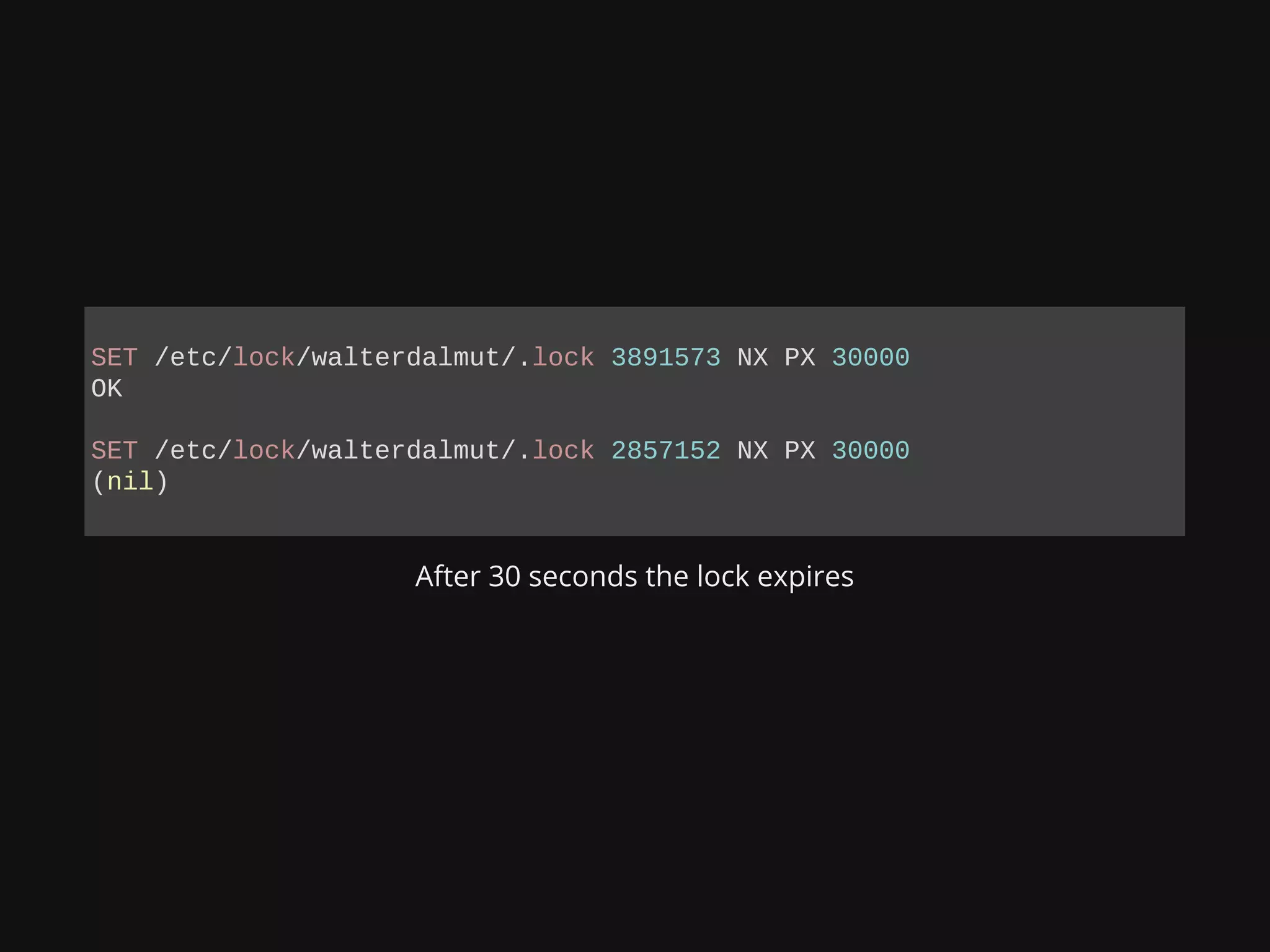
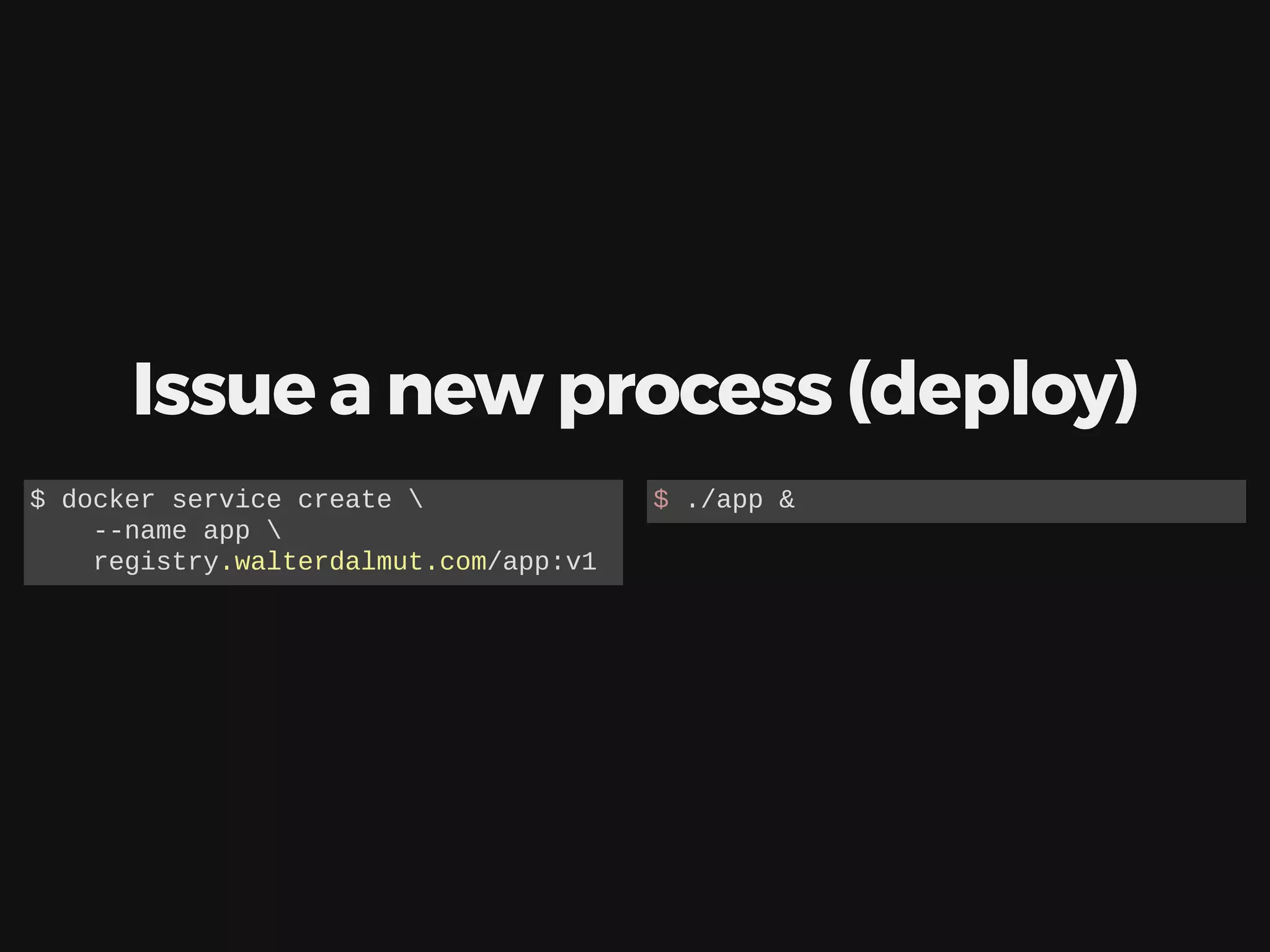
The document discusses deploying, scaling, and coordinating microservices using Docker and a distributed locking system. It outlines the use of DNS for service coordination, how to report application status through health checks, and the integration of various coordination systems like etcd and Redis. Additionally, the document explains how to manage service configurations and locks effectively in a distributed system.











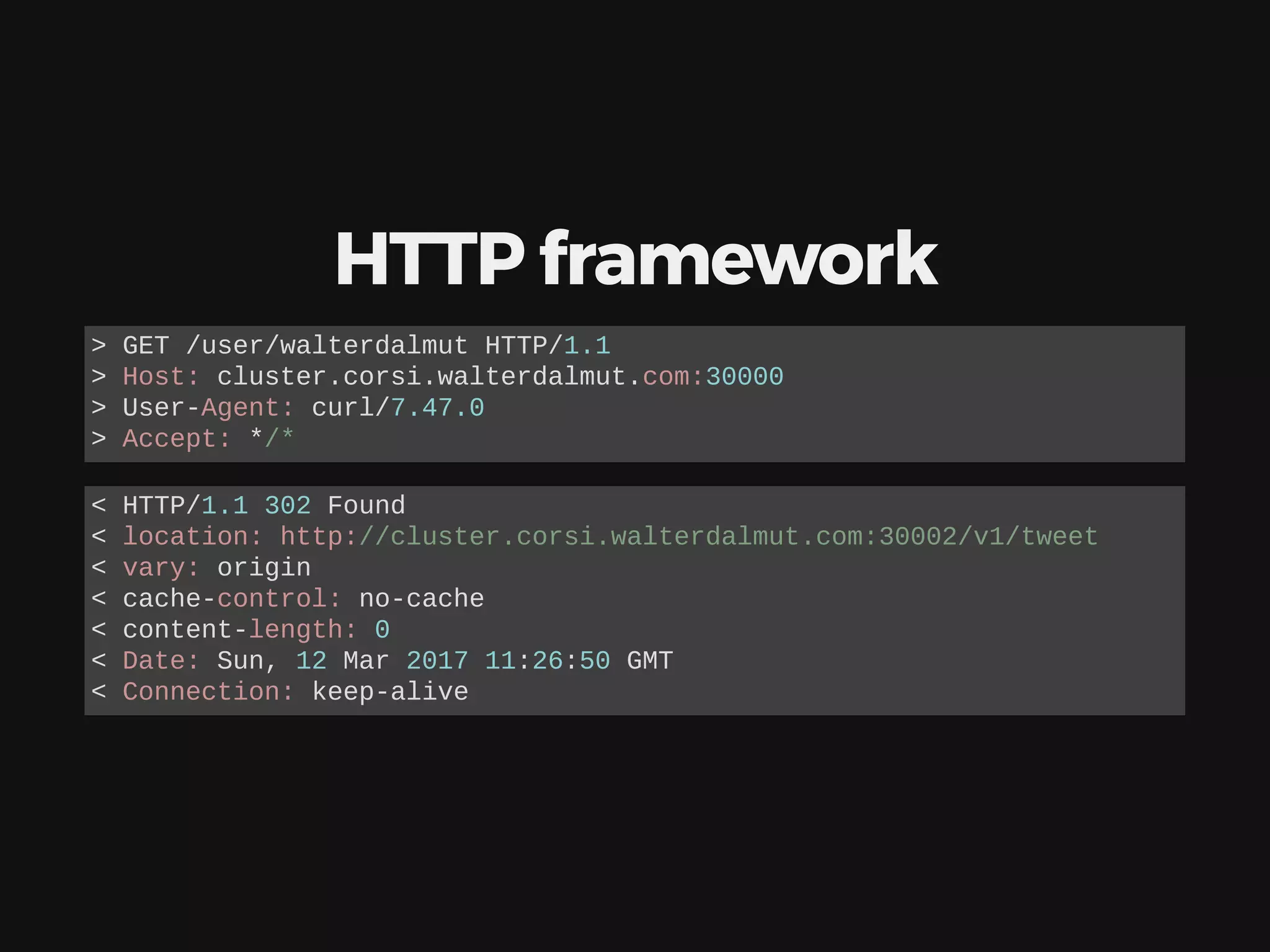
![users that tweet with this handle create a reserved API service [ JSON over HTTP ] GET /tweet - list my tweets POST /tweet - record a new tweet The database to store tweets is self-contained in the API service](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudconf2017-170324181904/75/CloudConf2017-Deploy-Scale-Coordinate-a-microservice-oriented-application-13-2048.jpg)