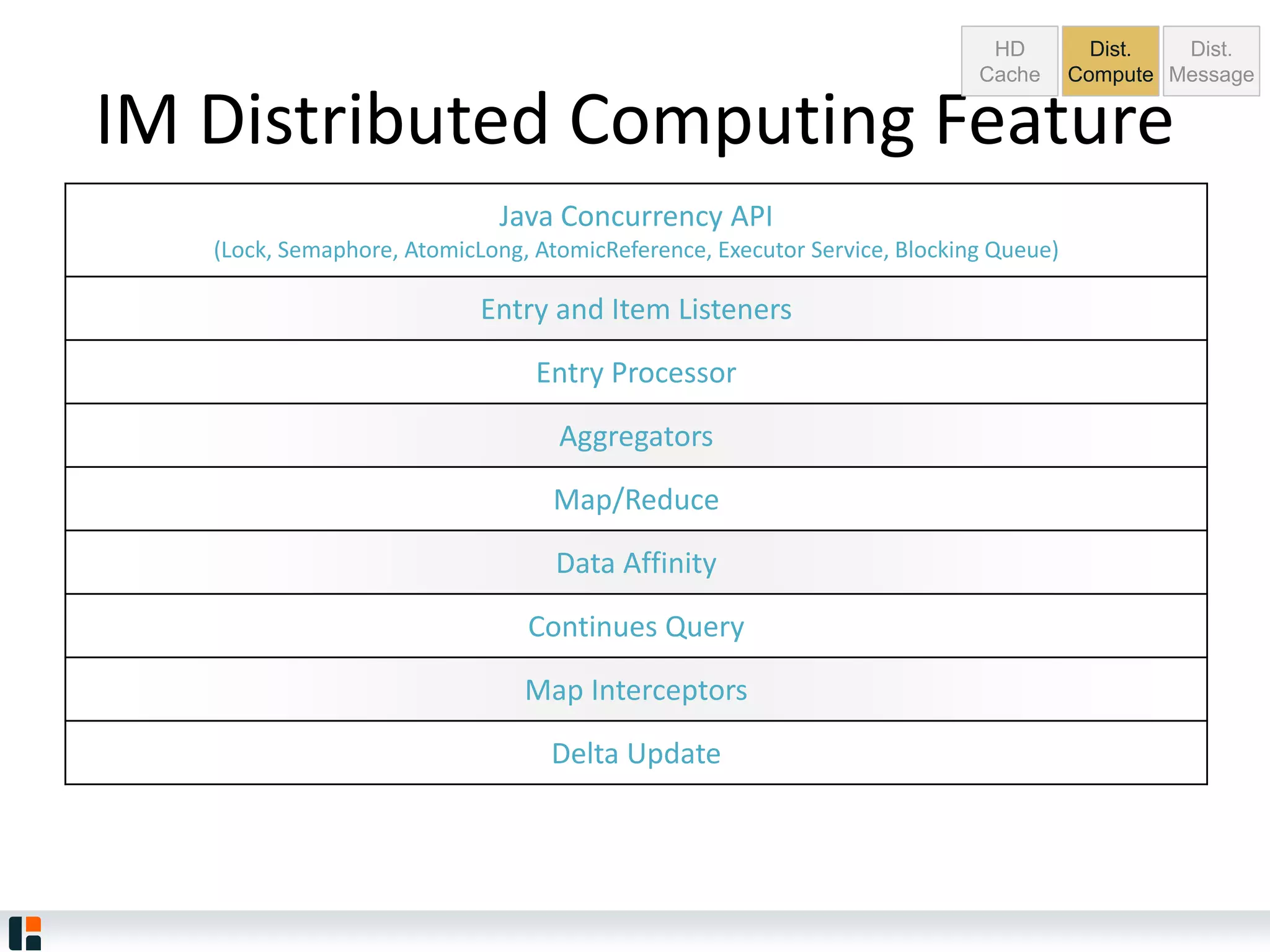
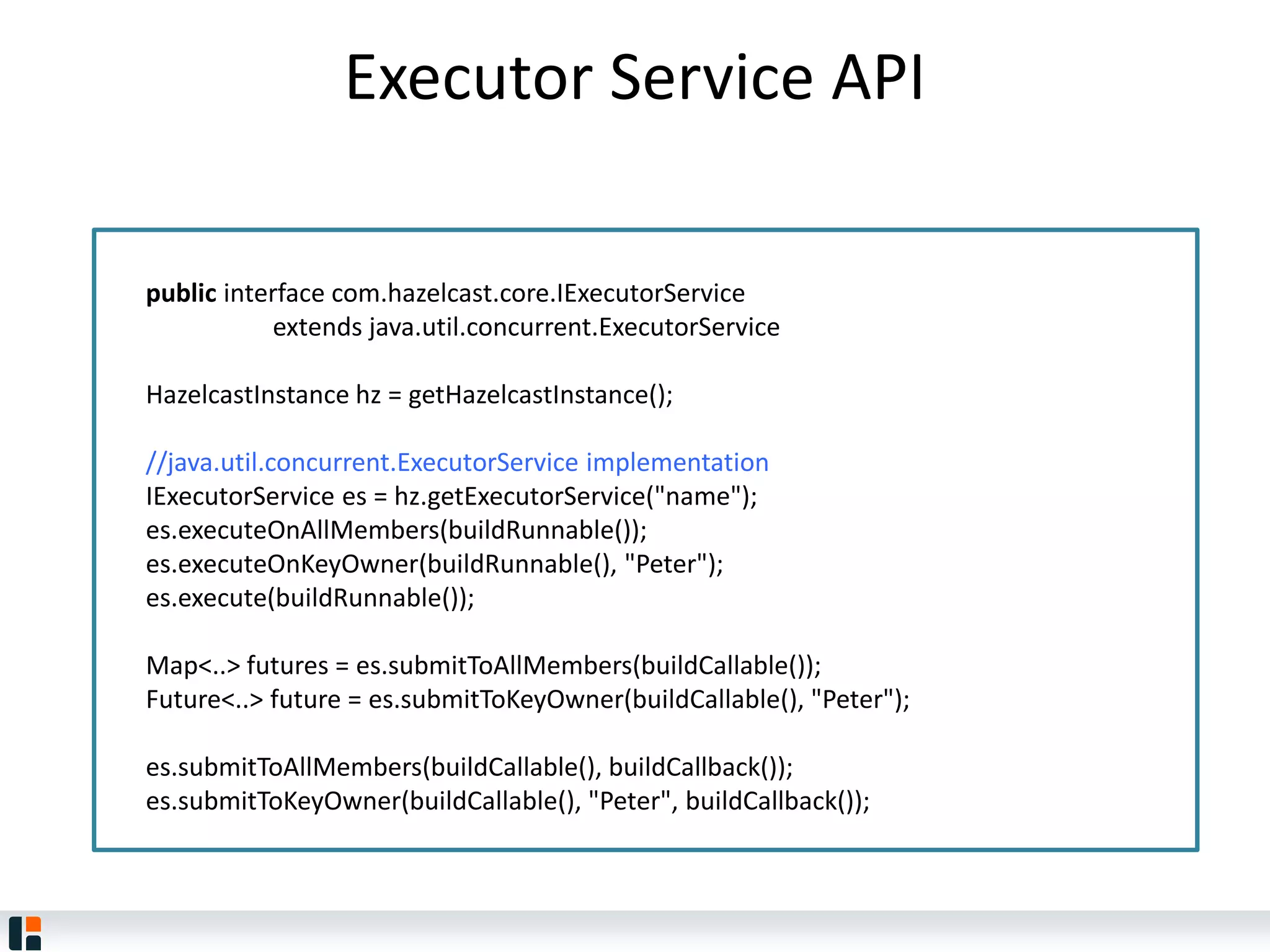
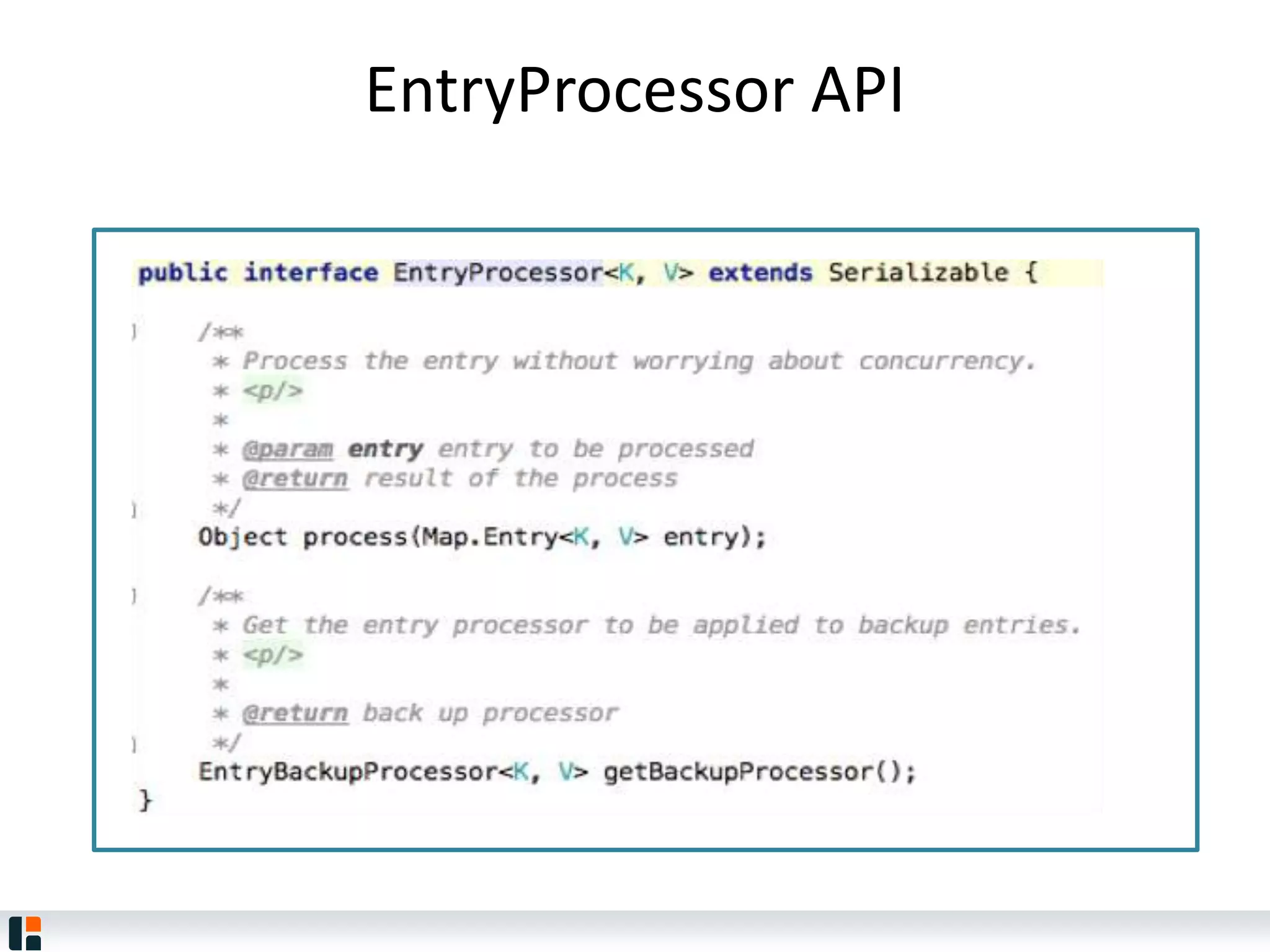
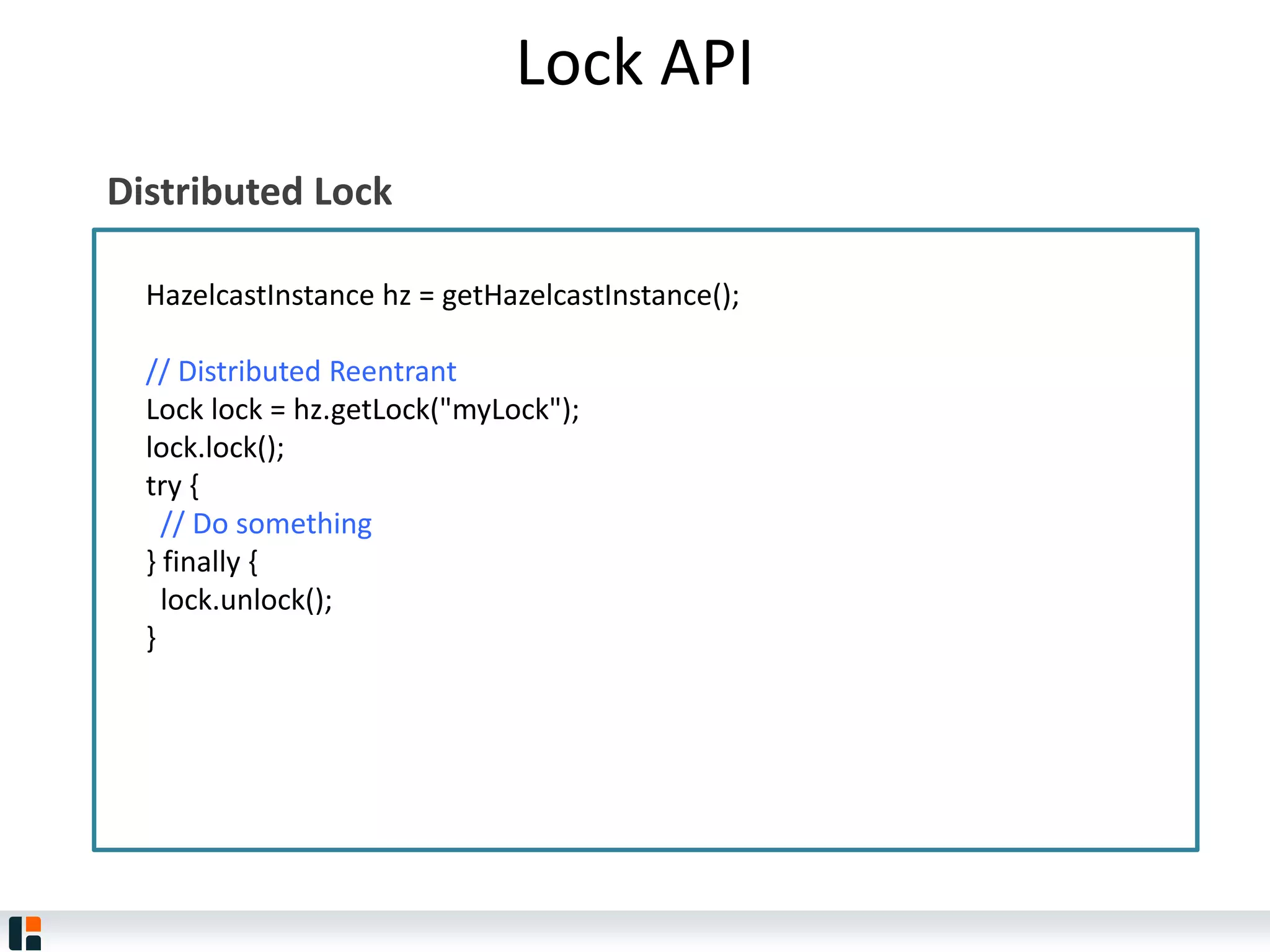
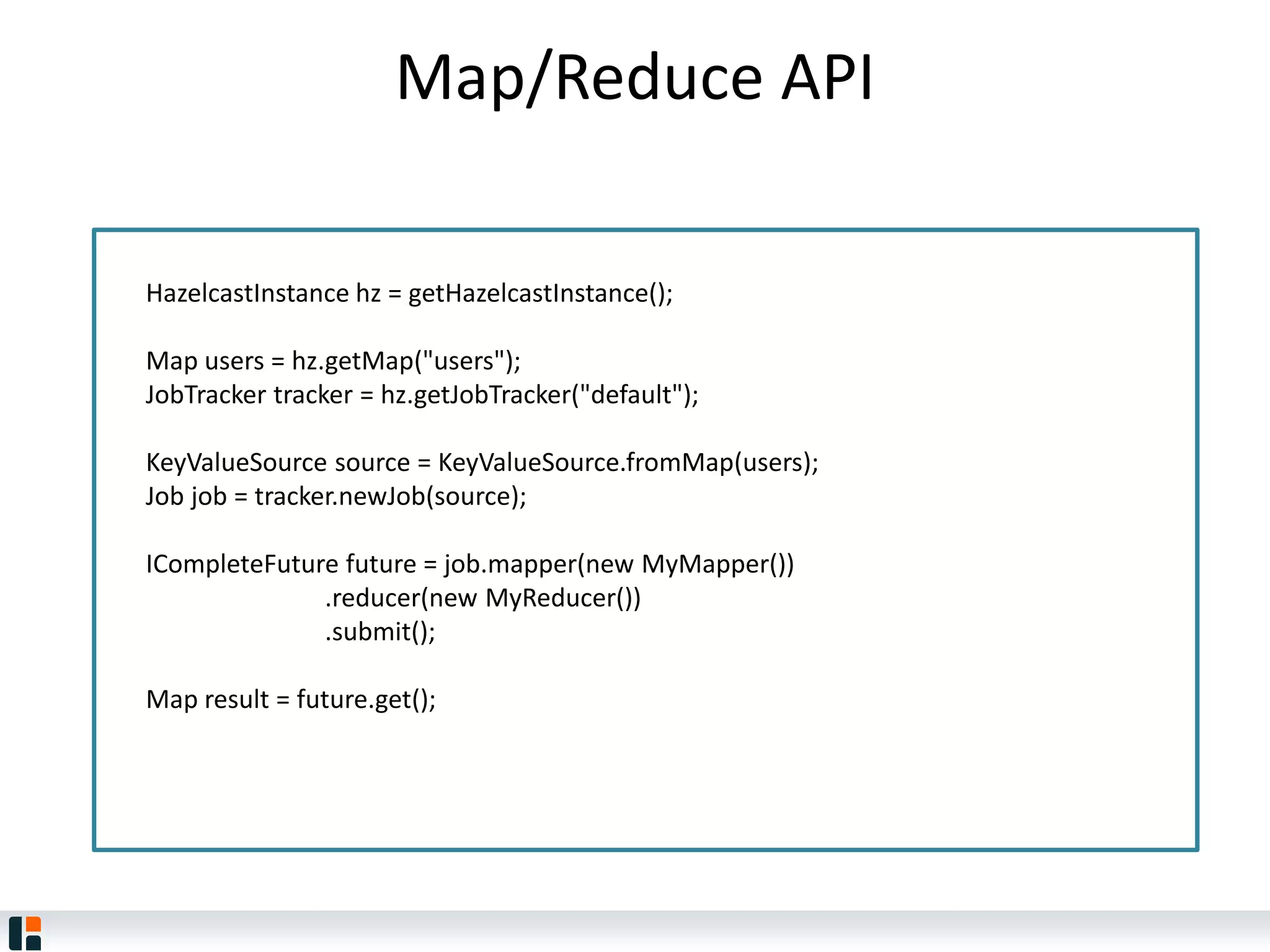
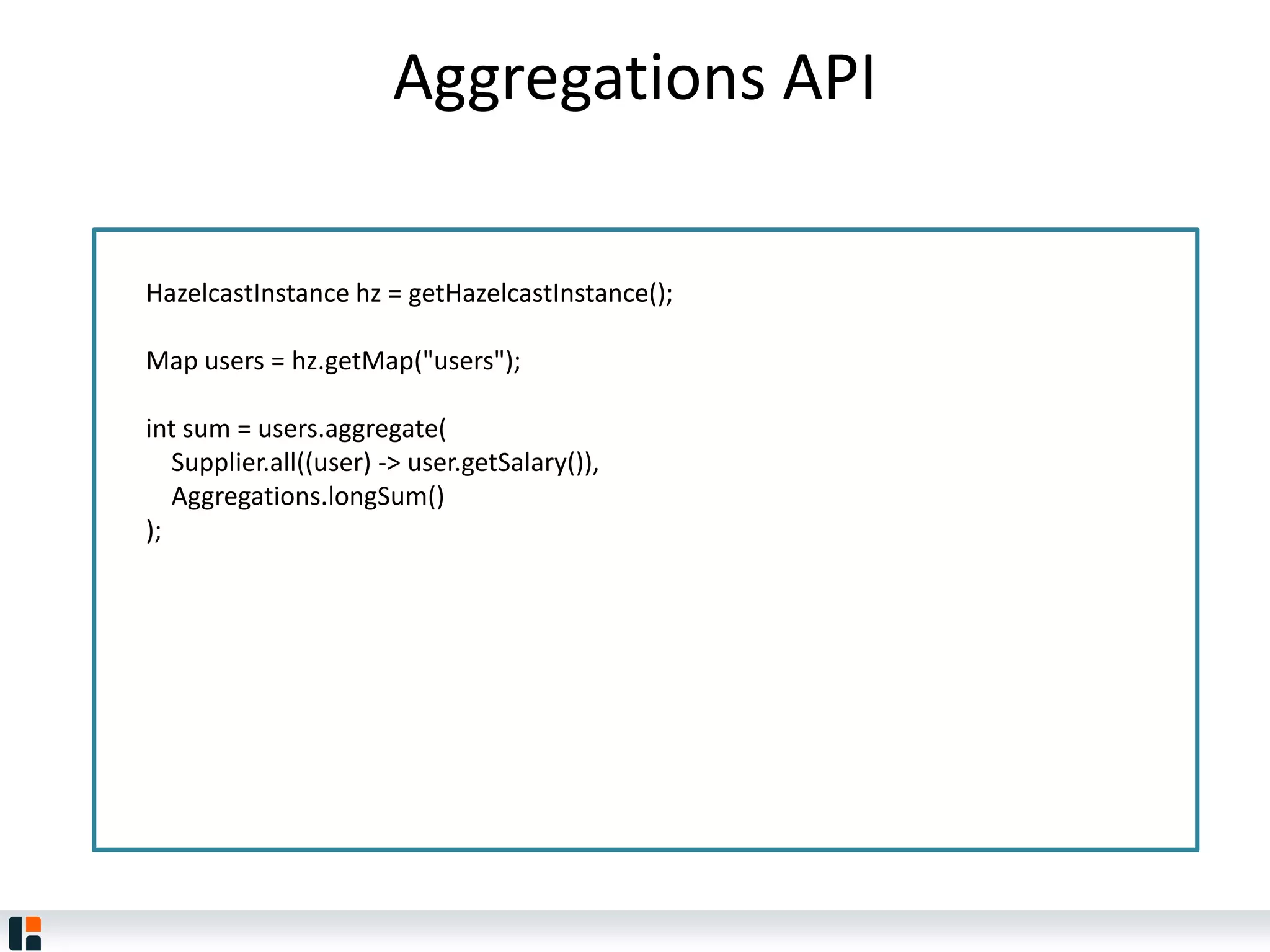
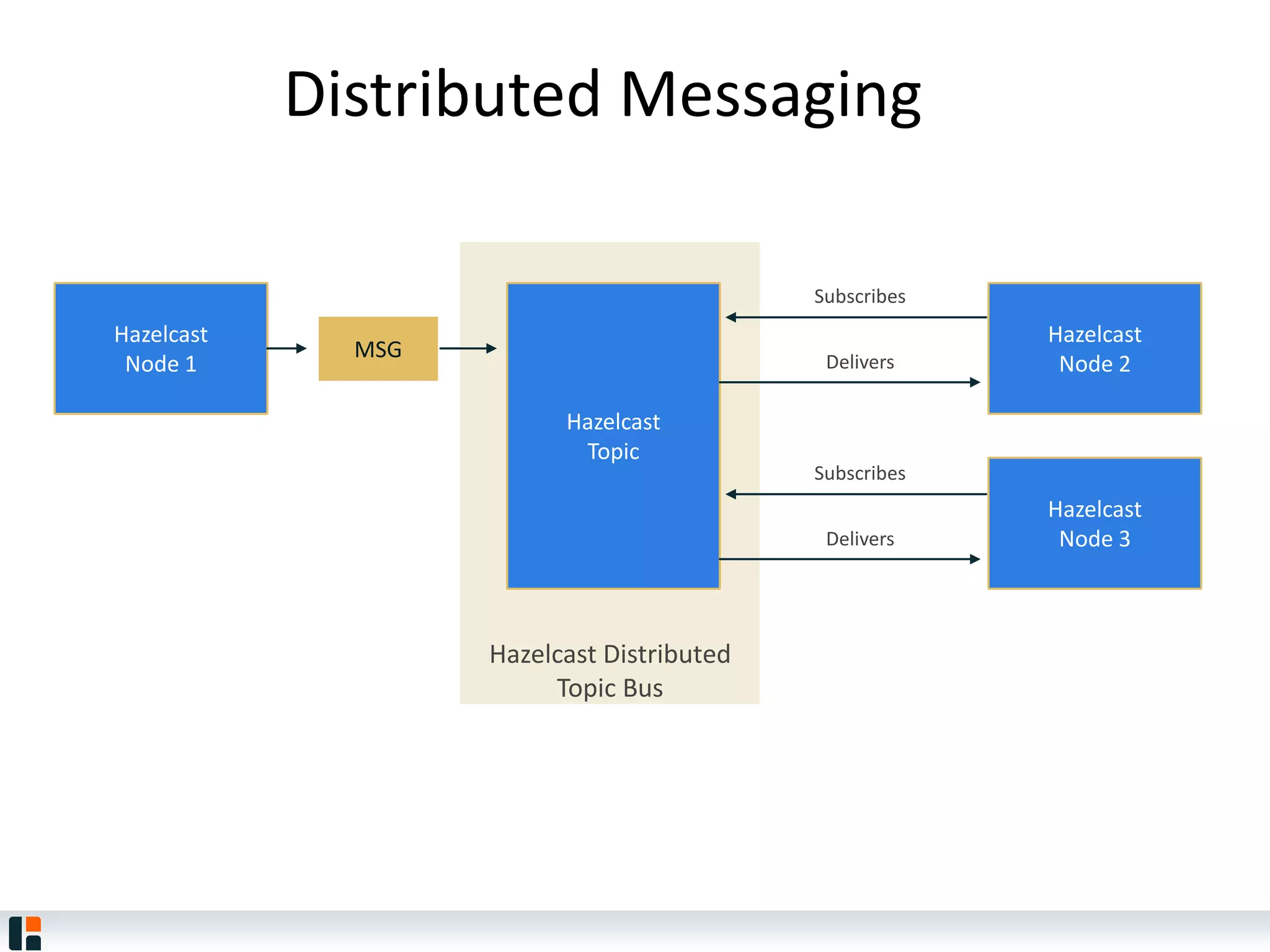
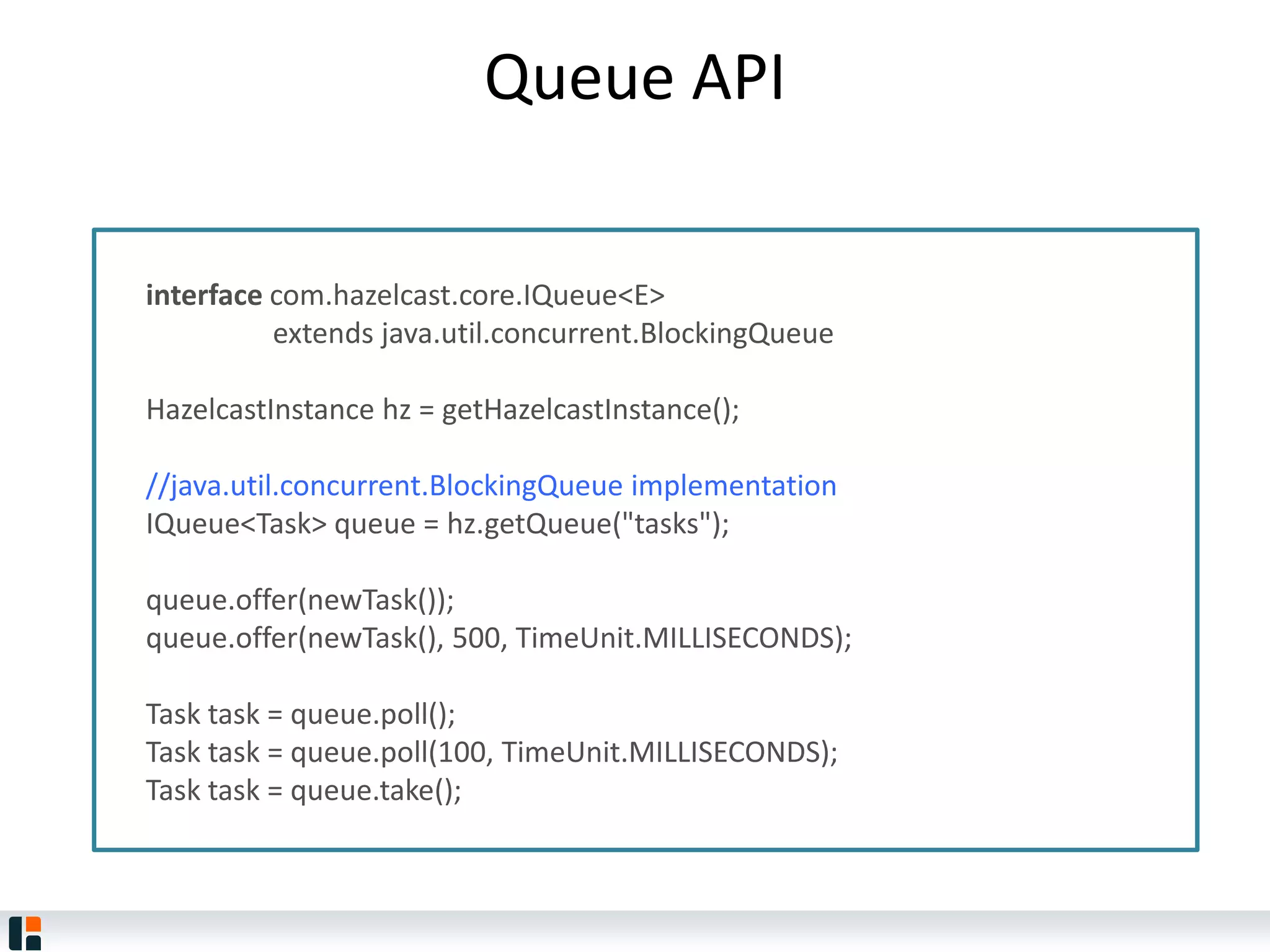
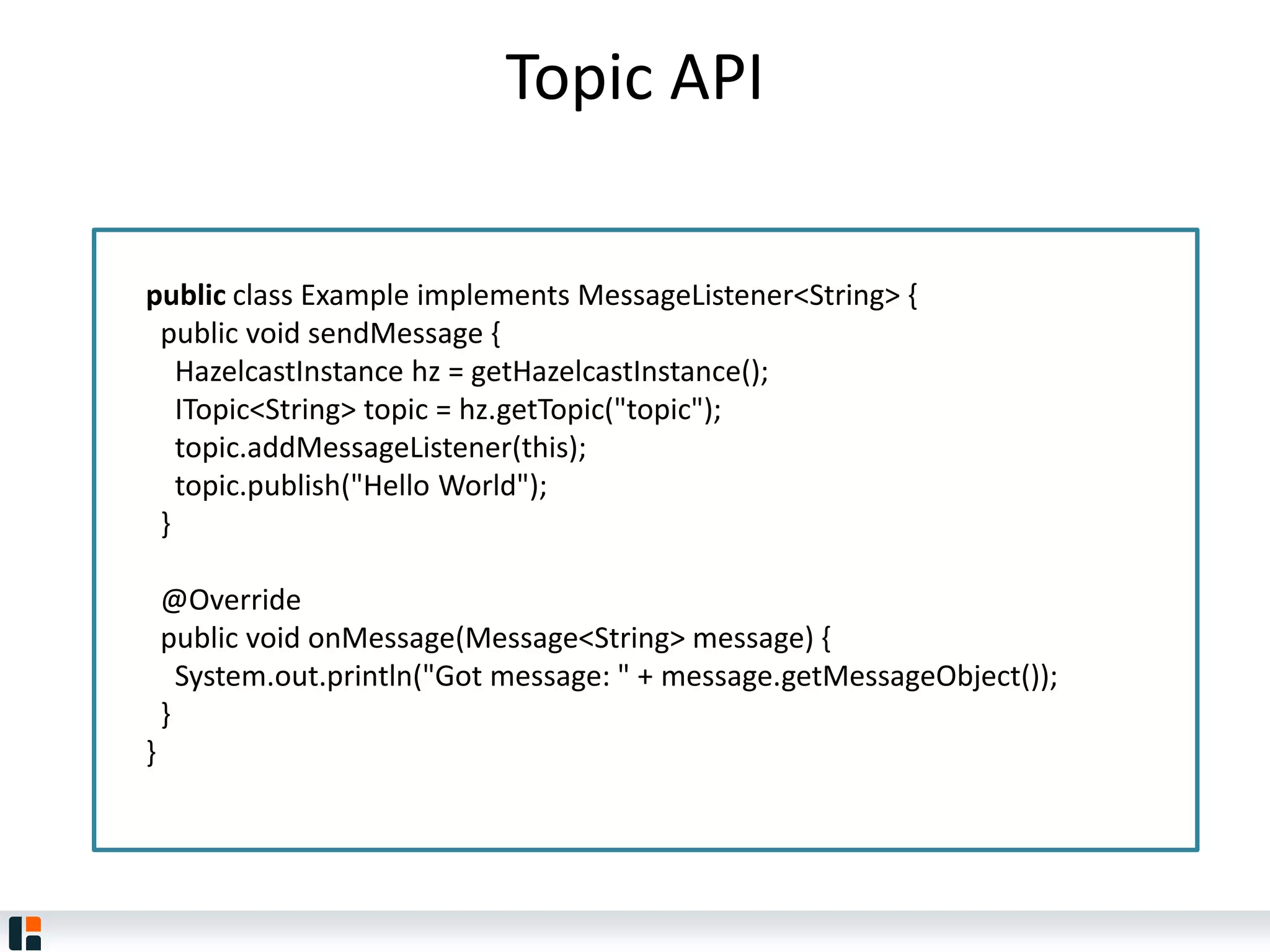
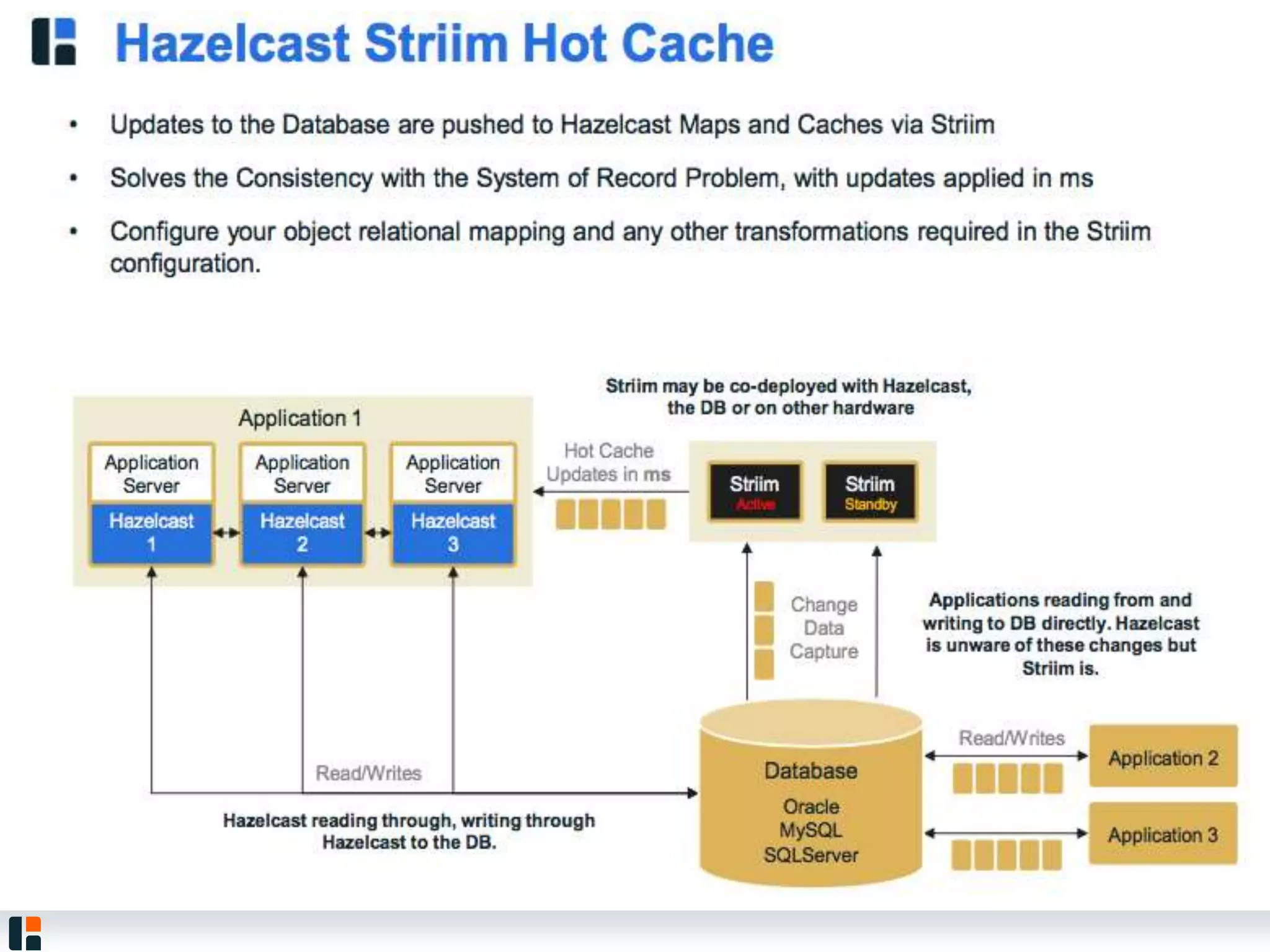
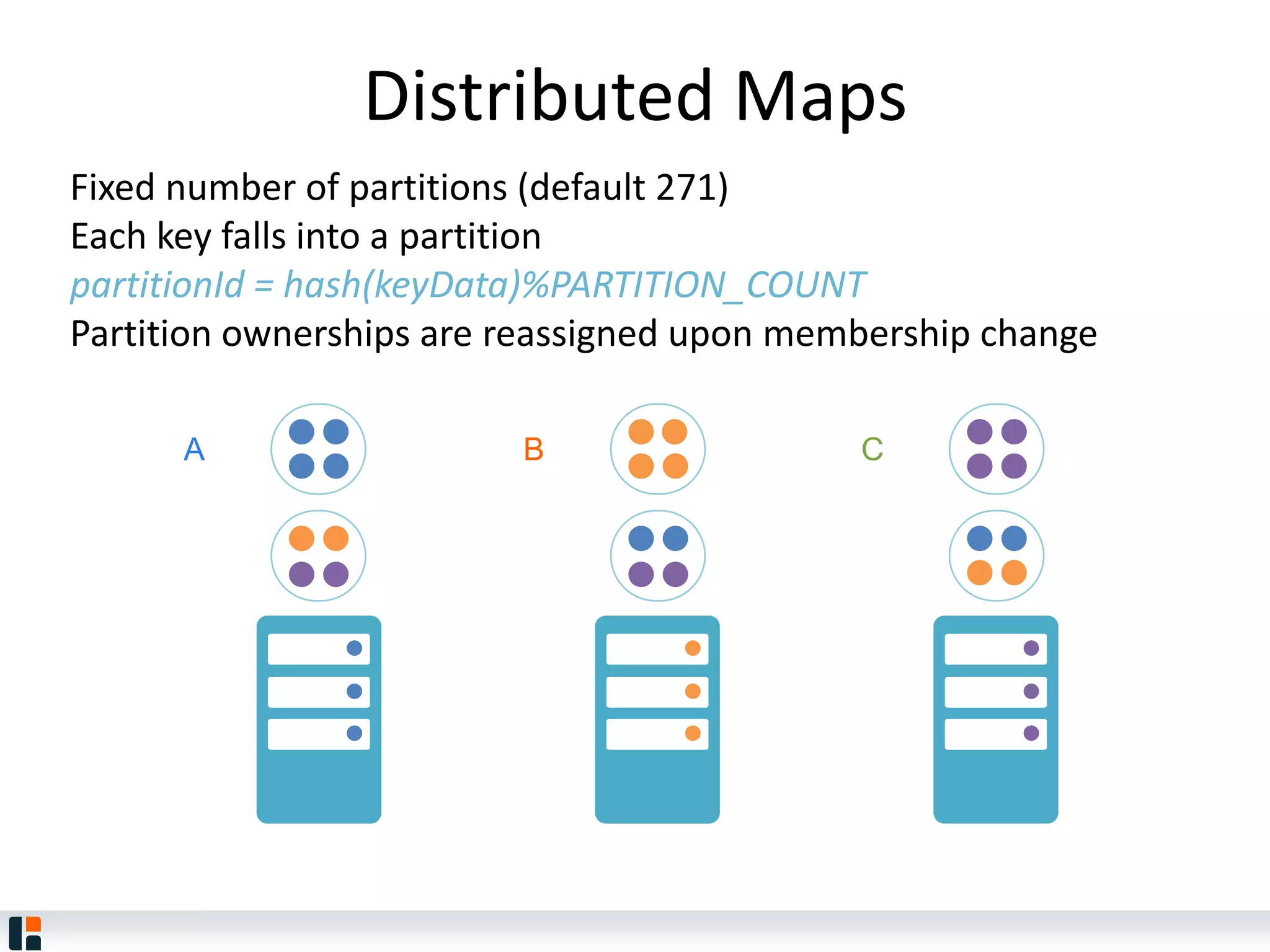
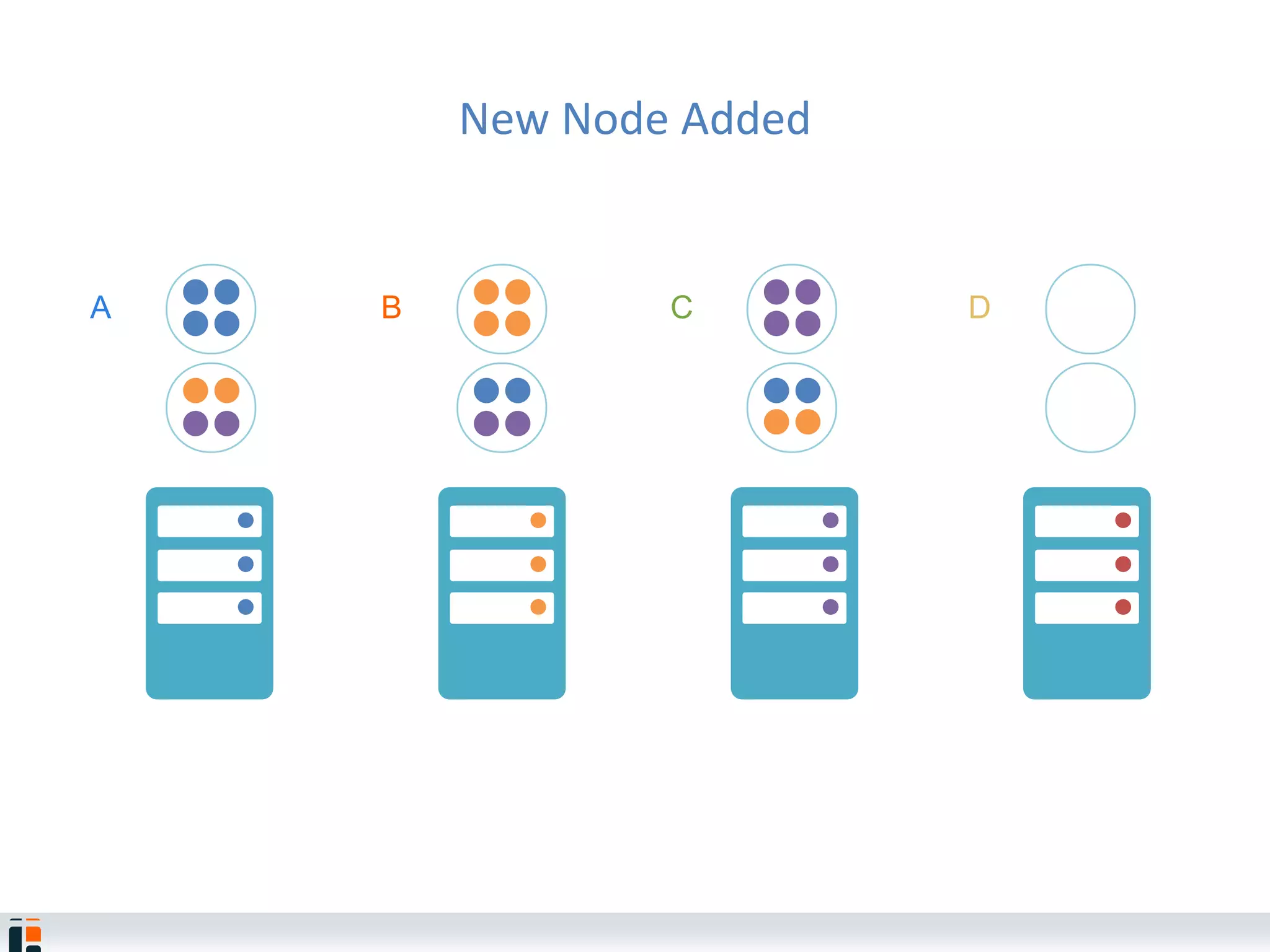
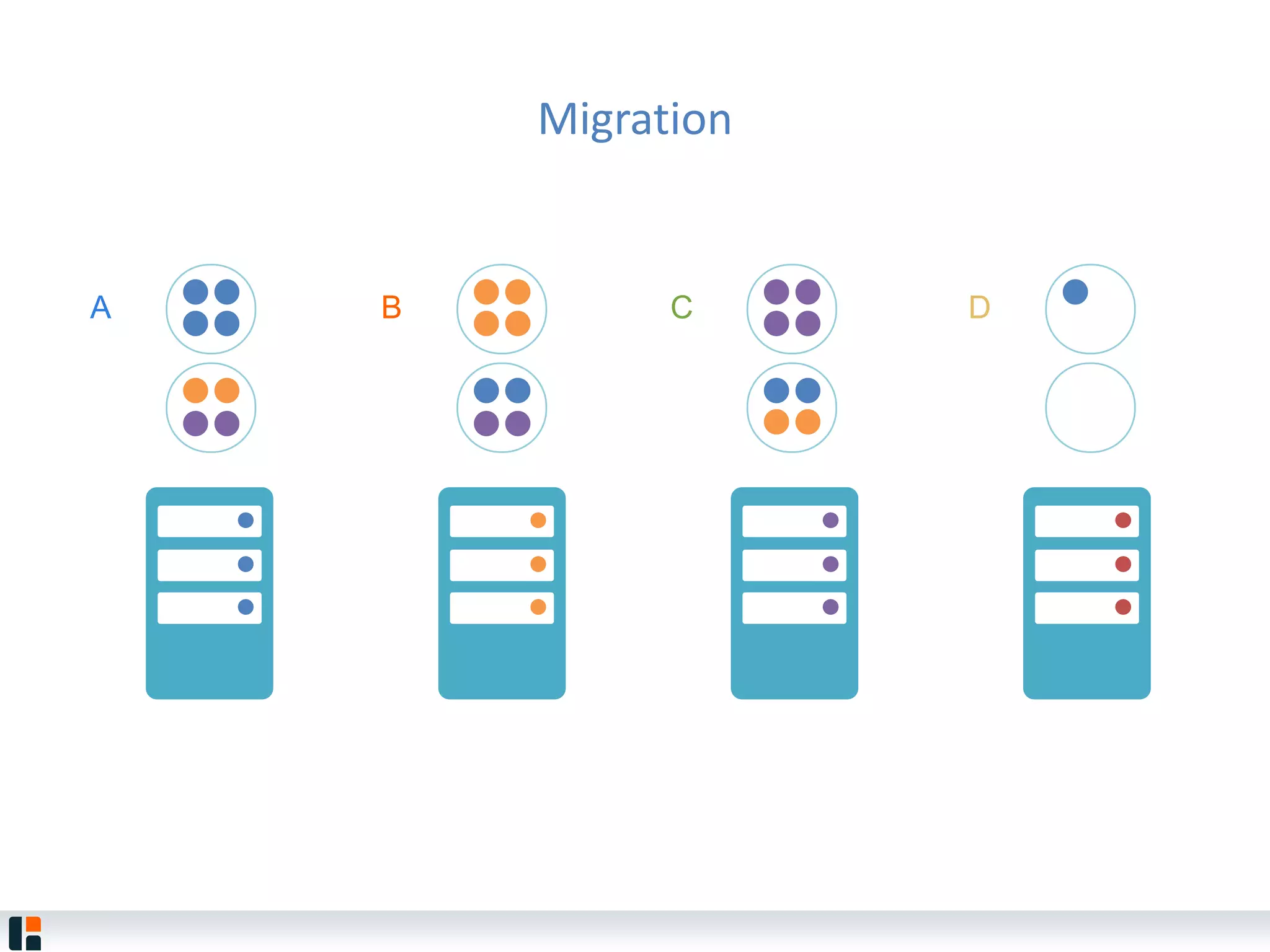
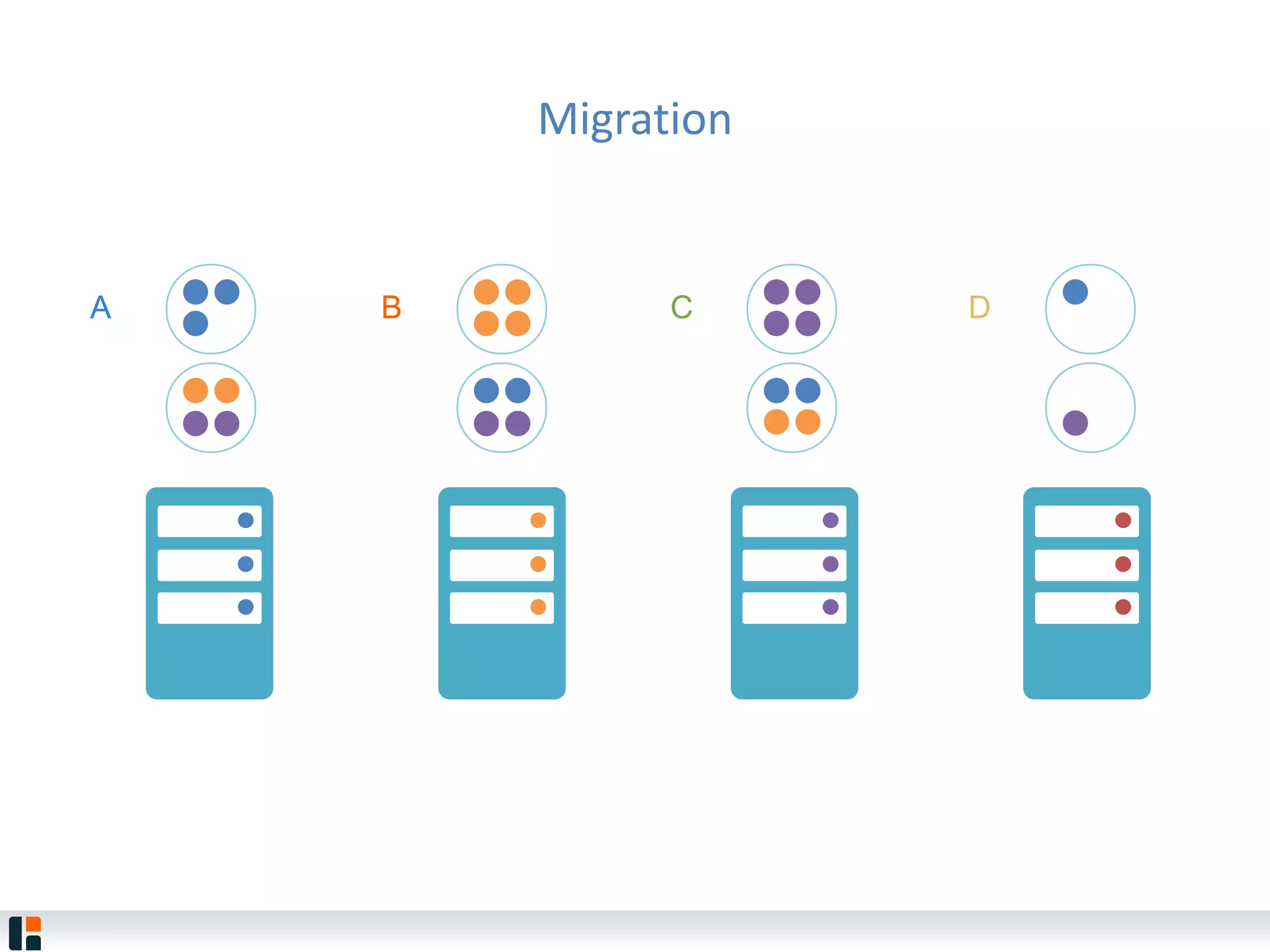
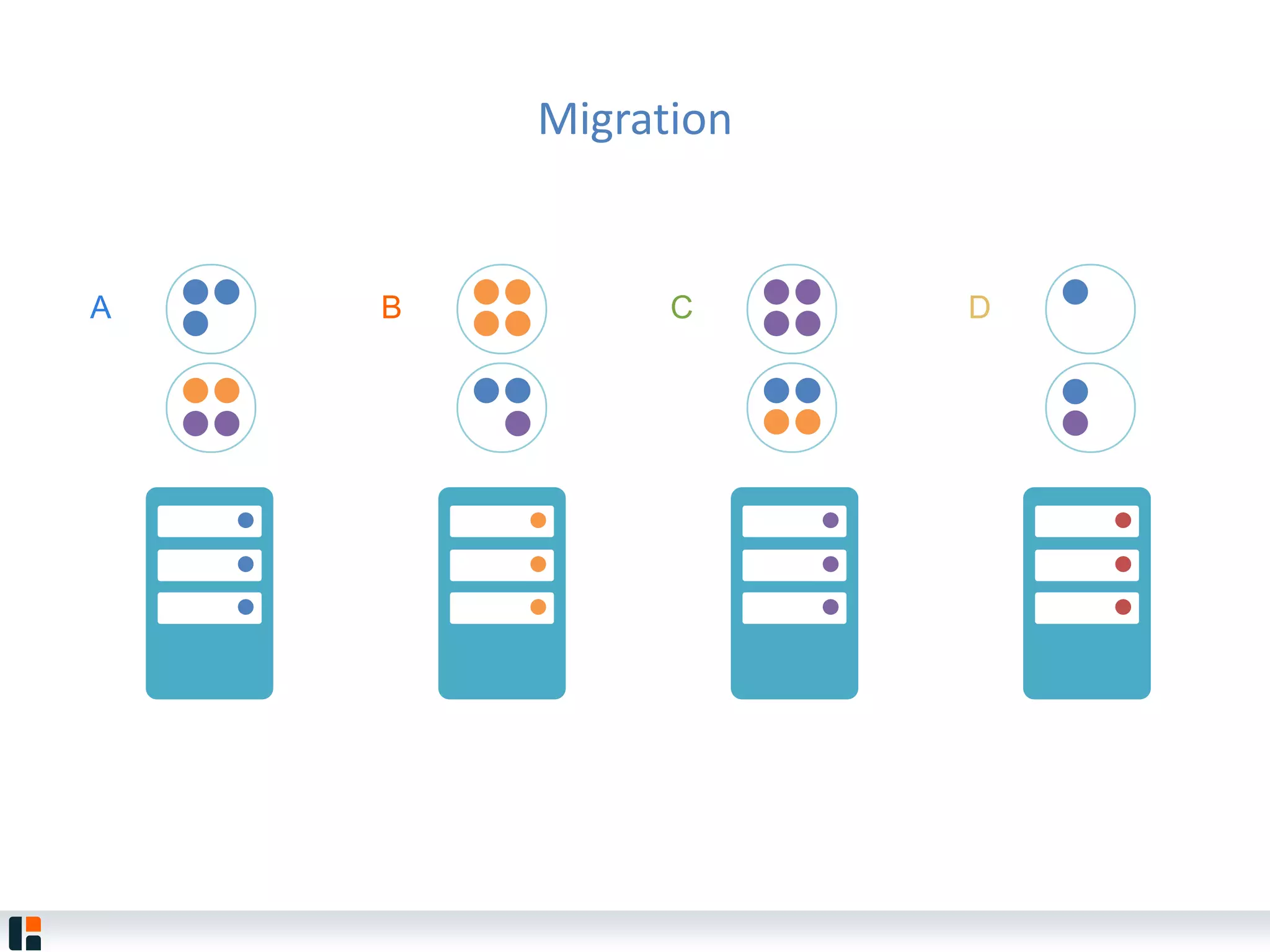
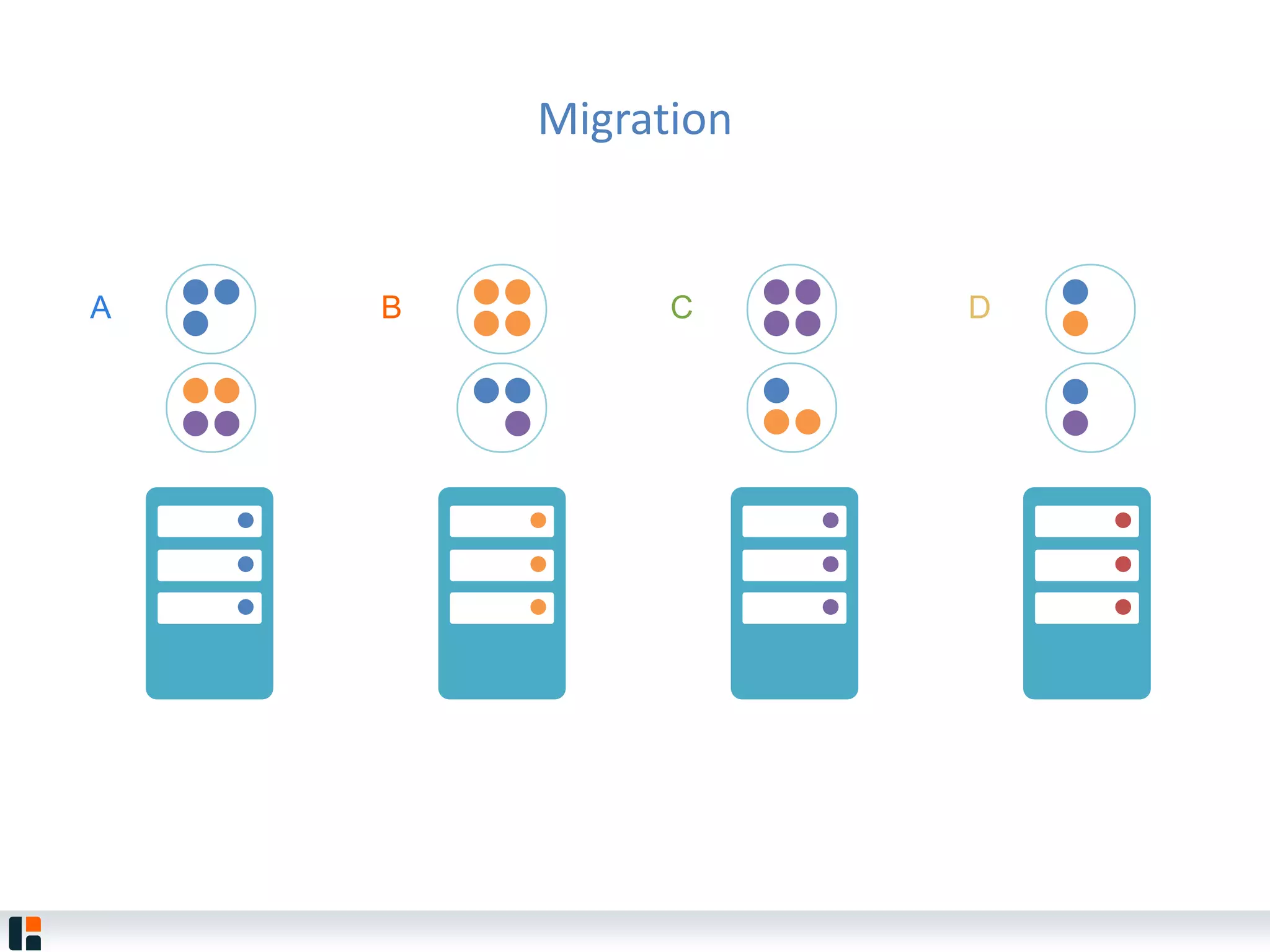
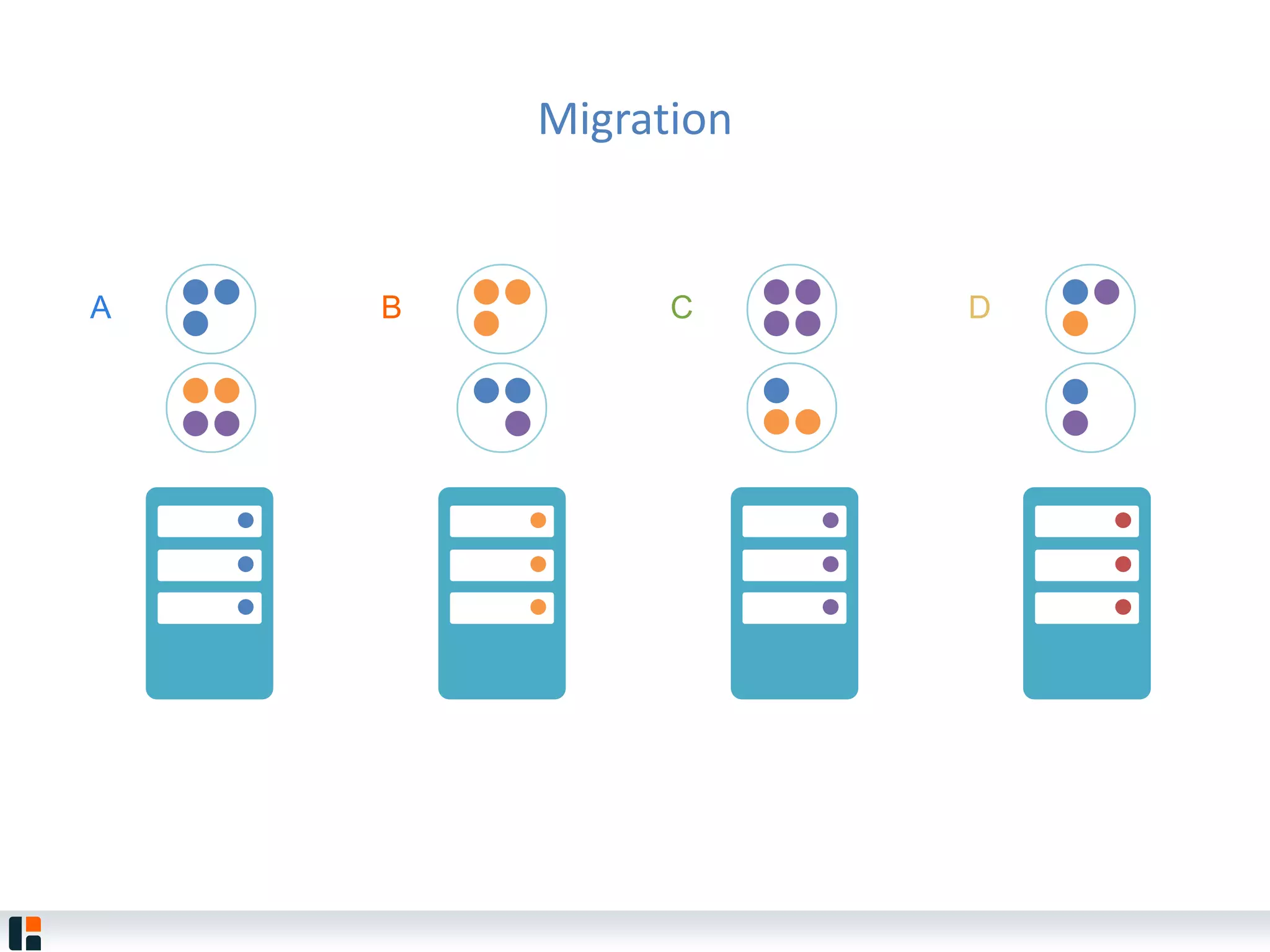
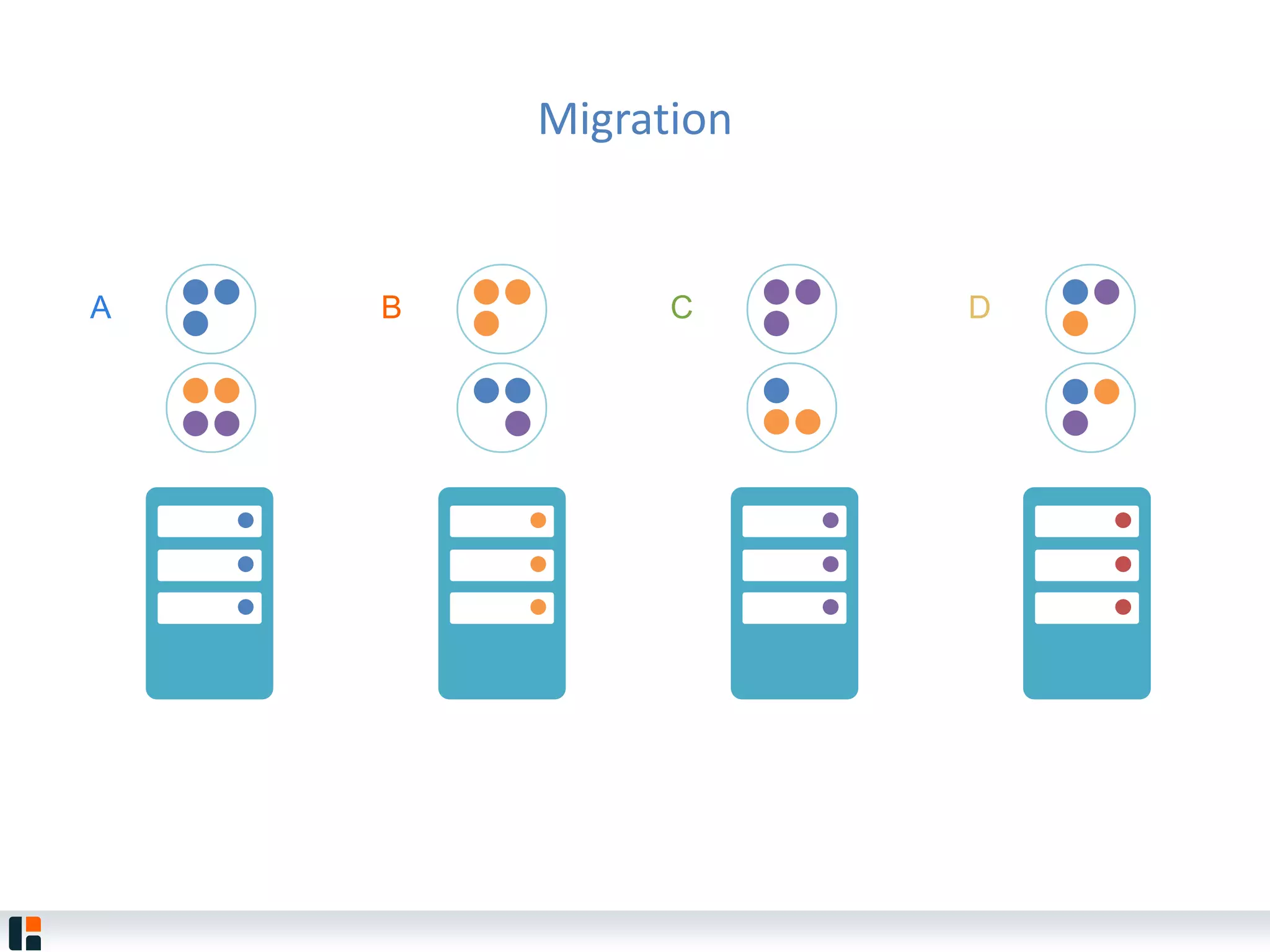
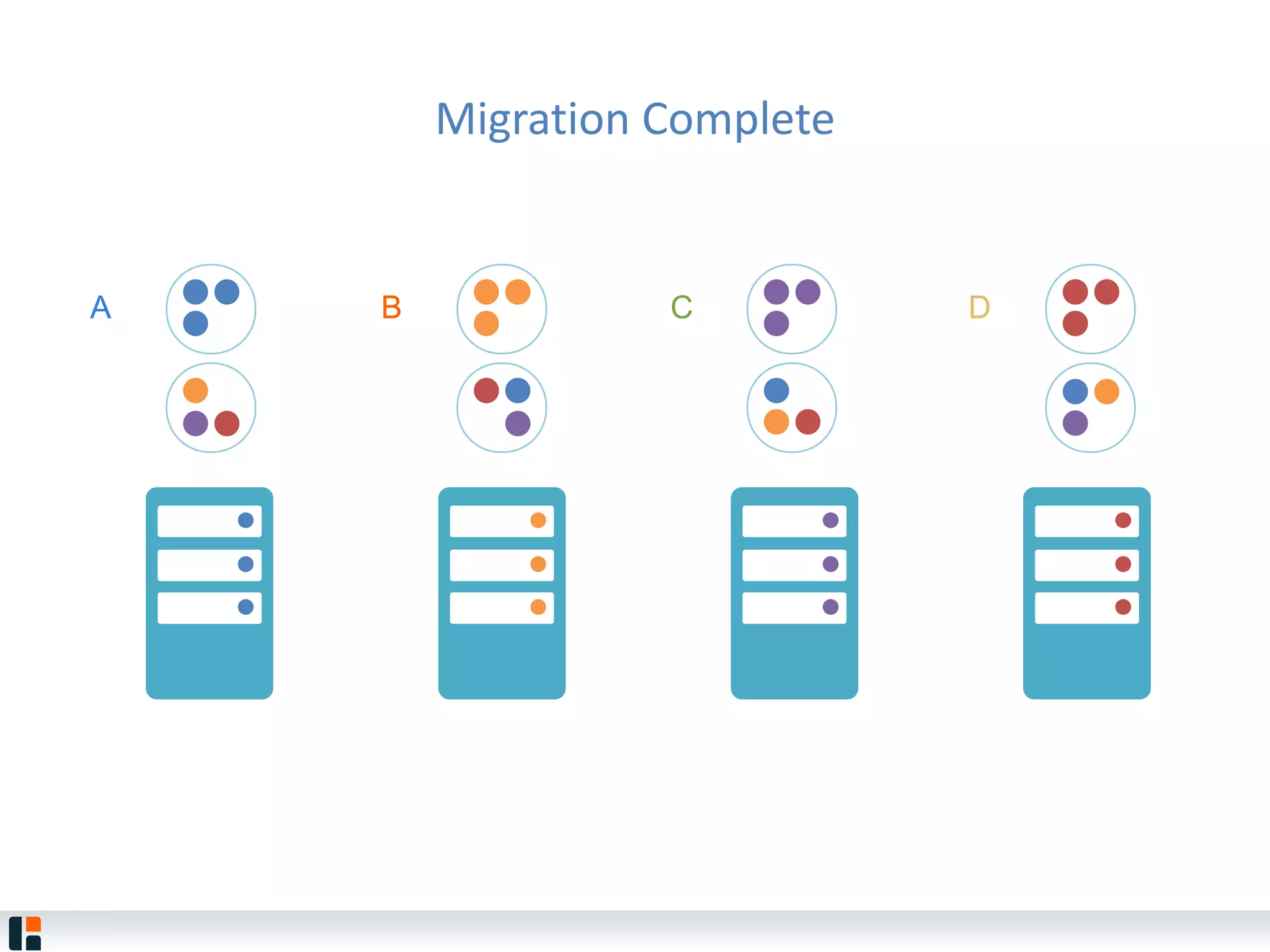
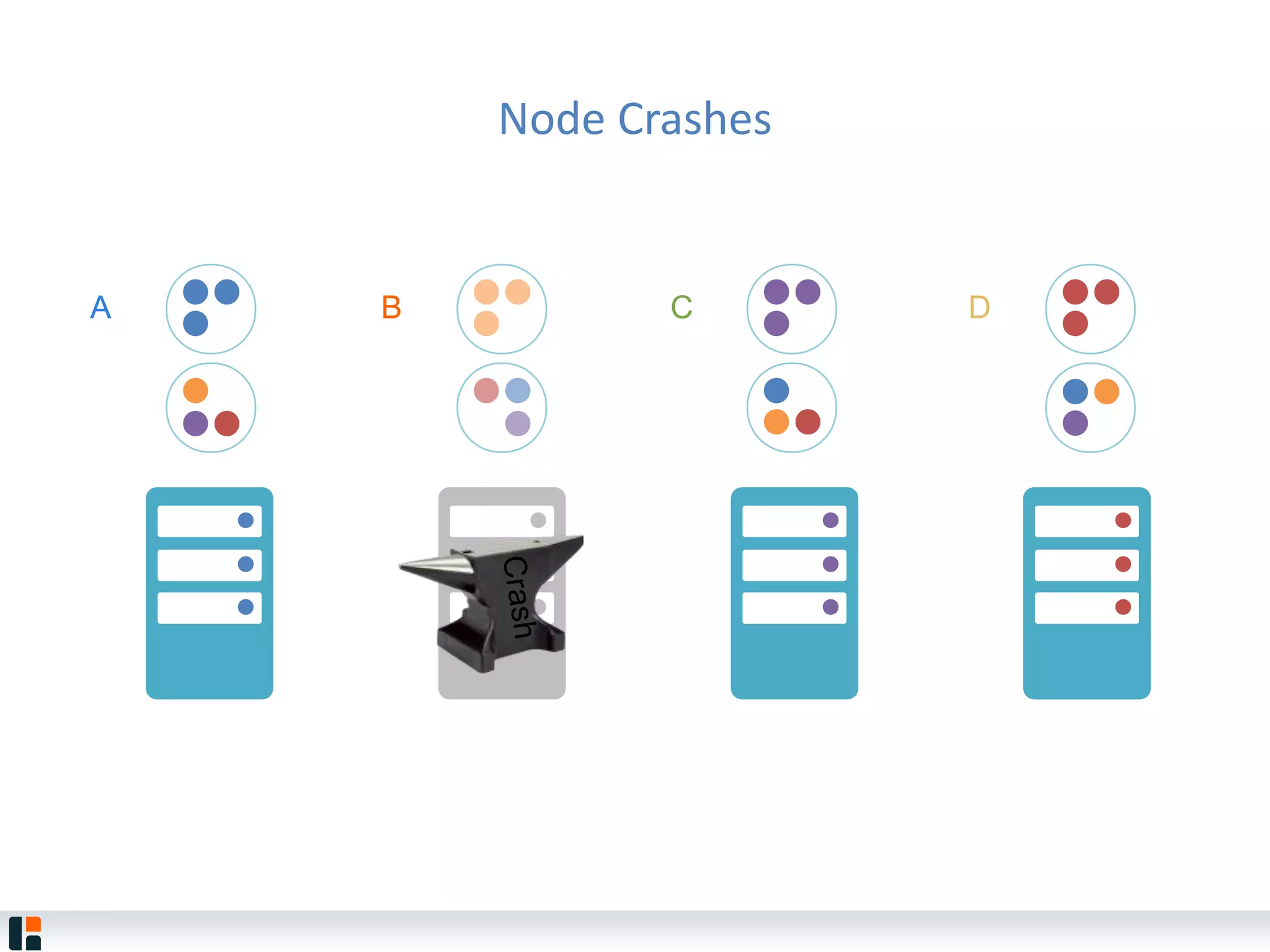
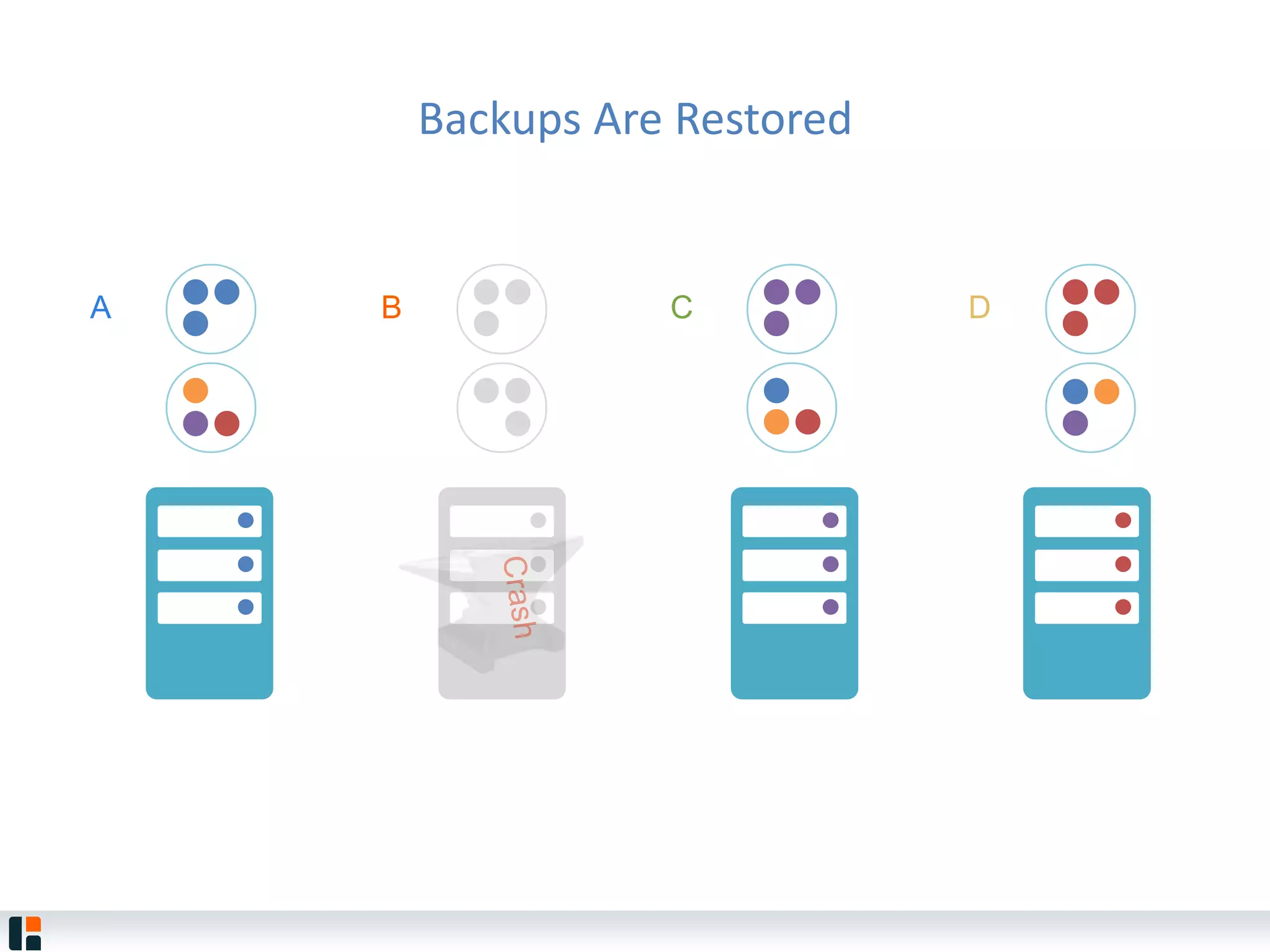
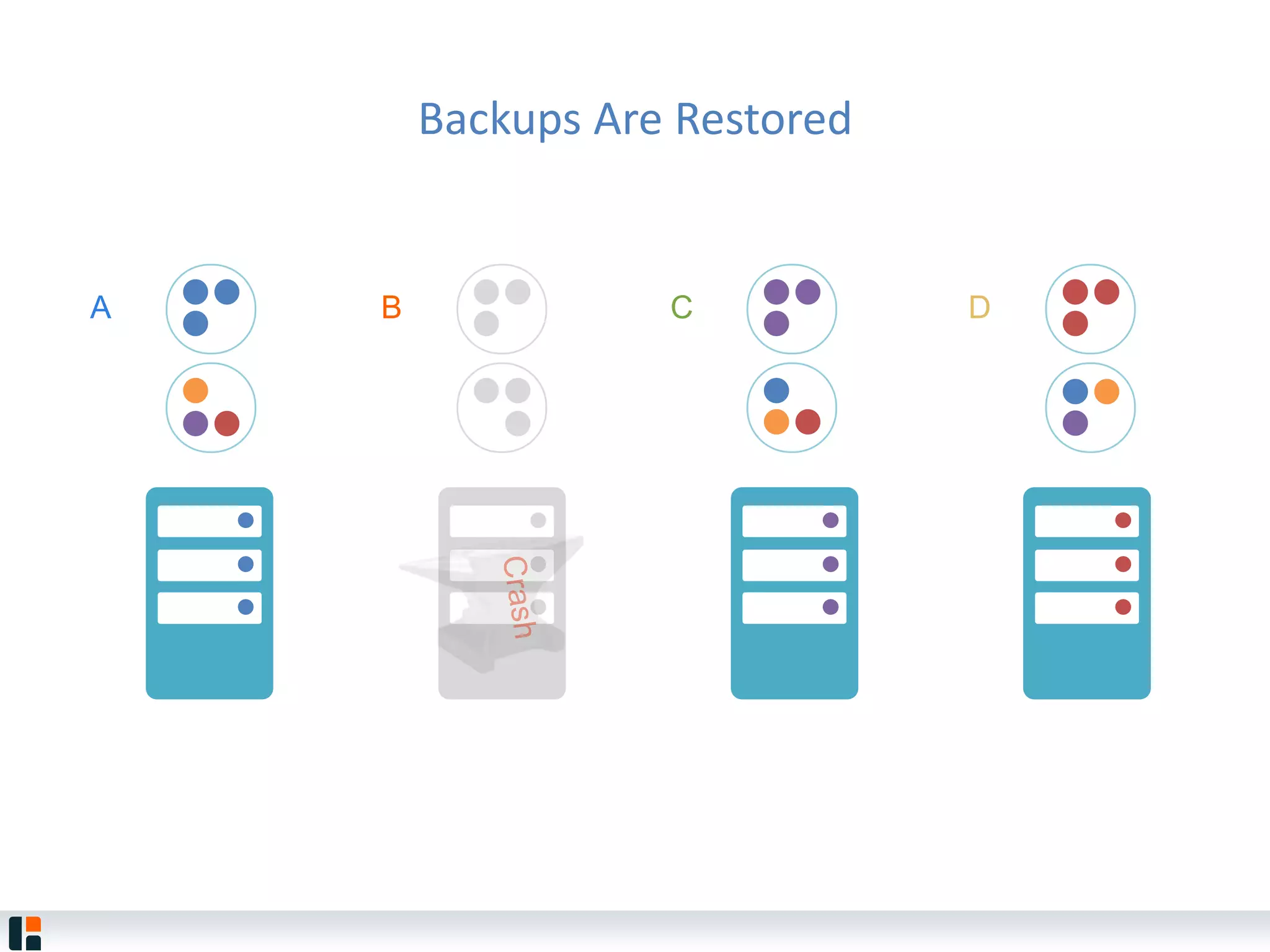
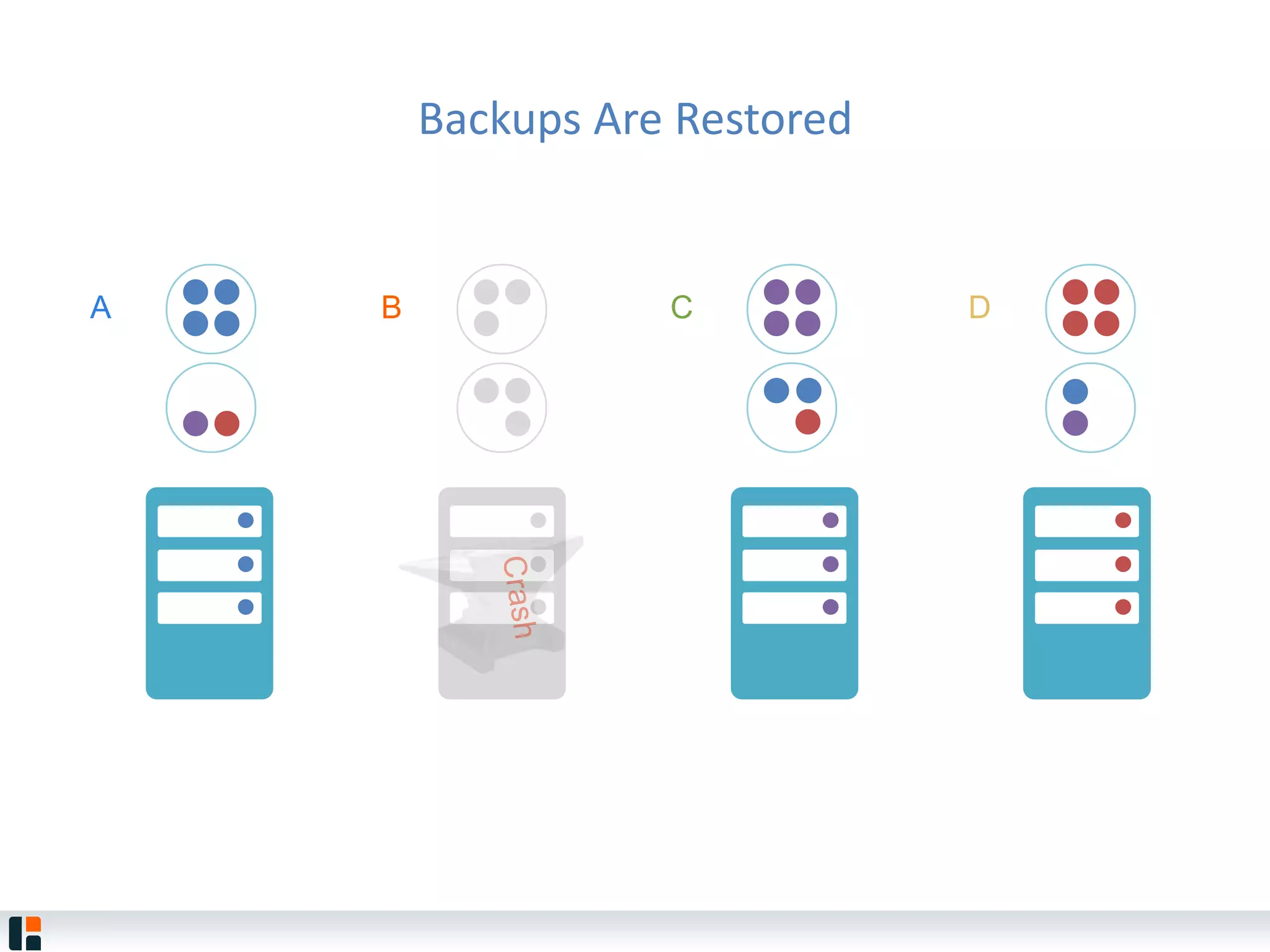
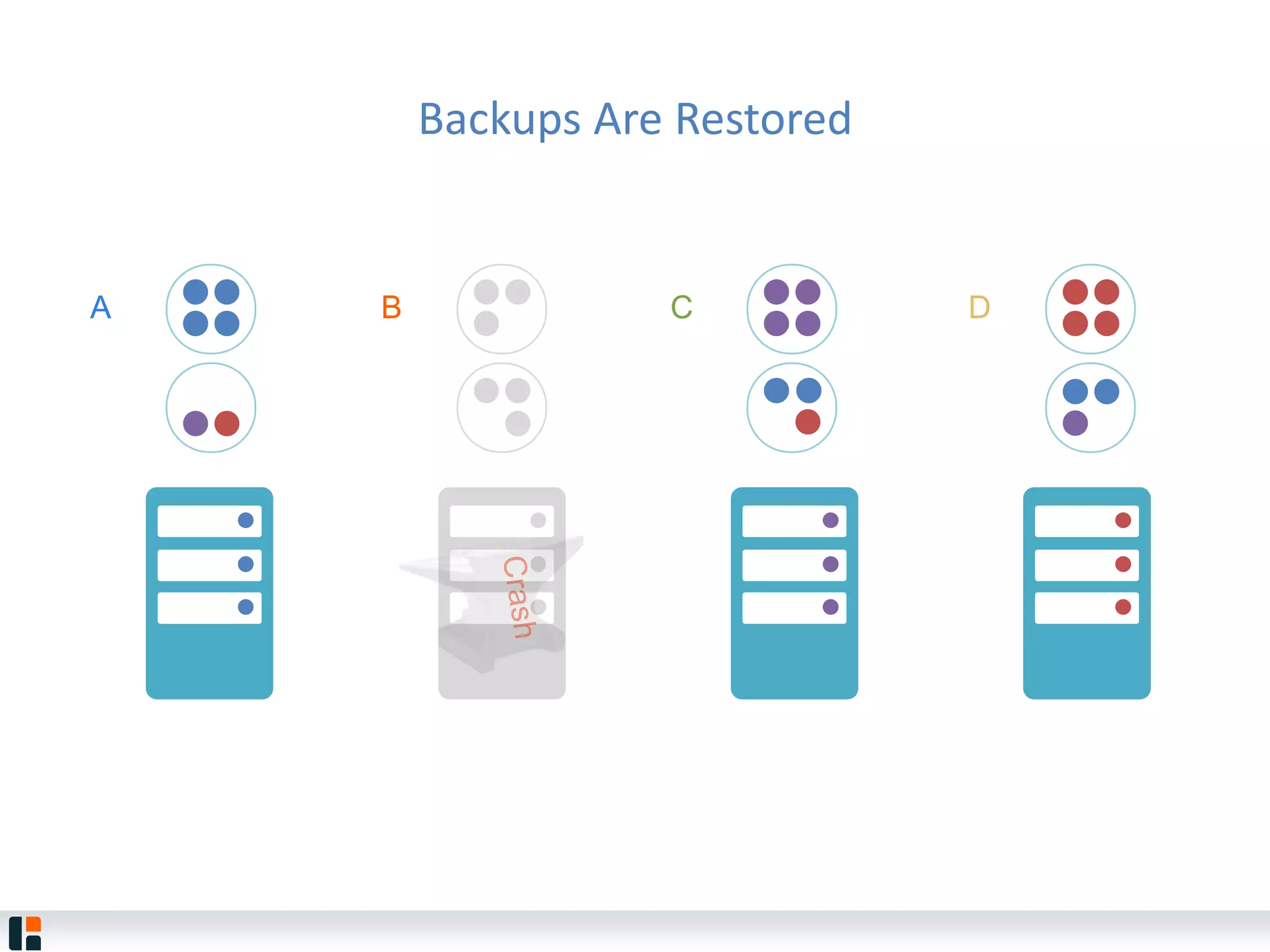
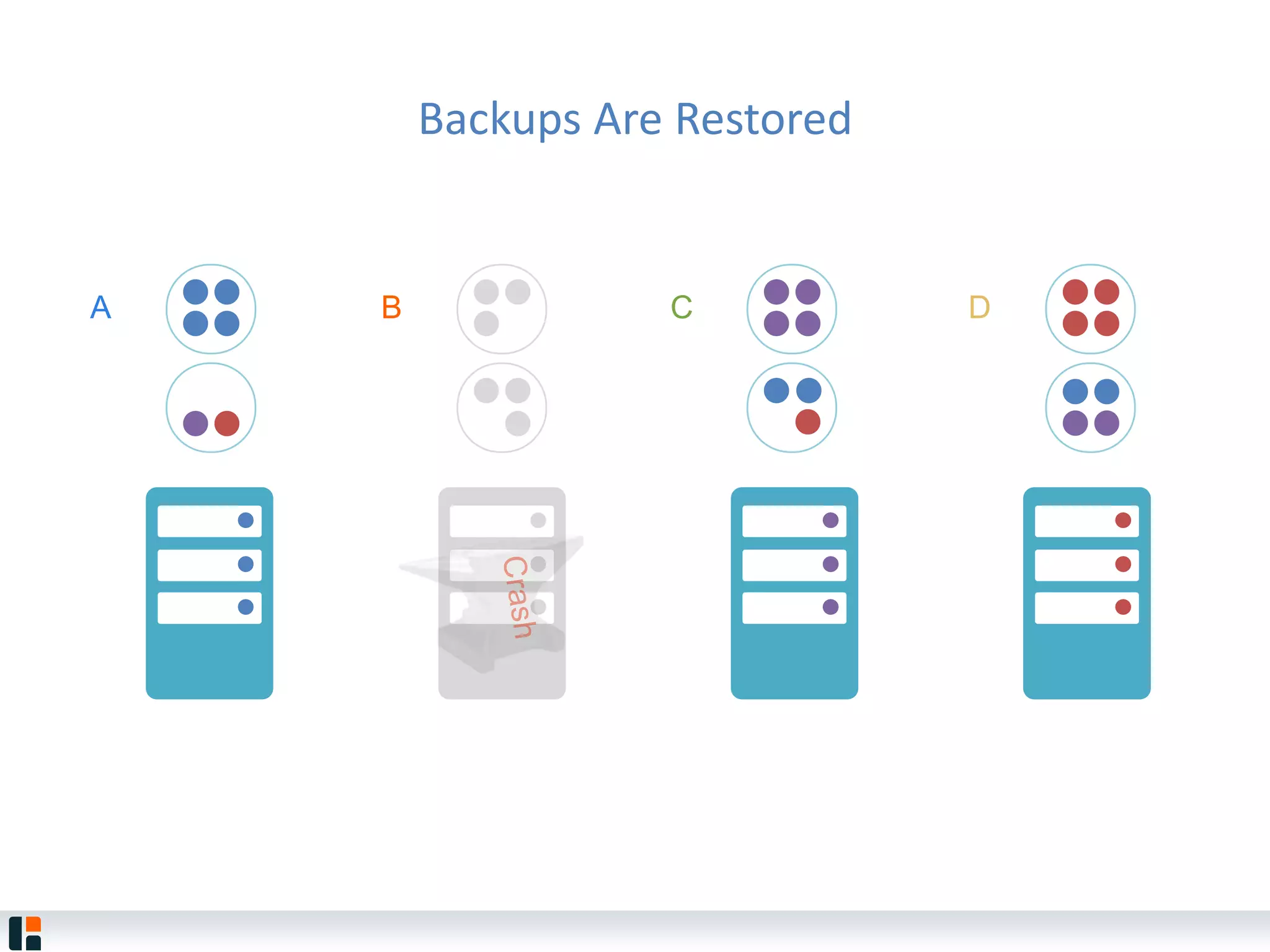
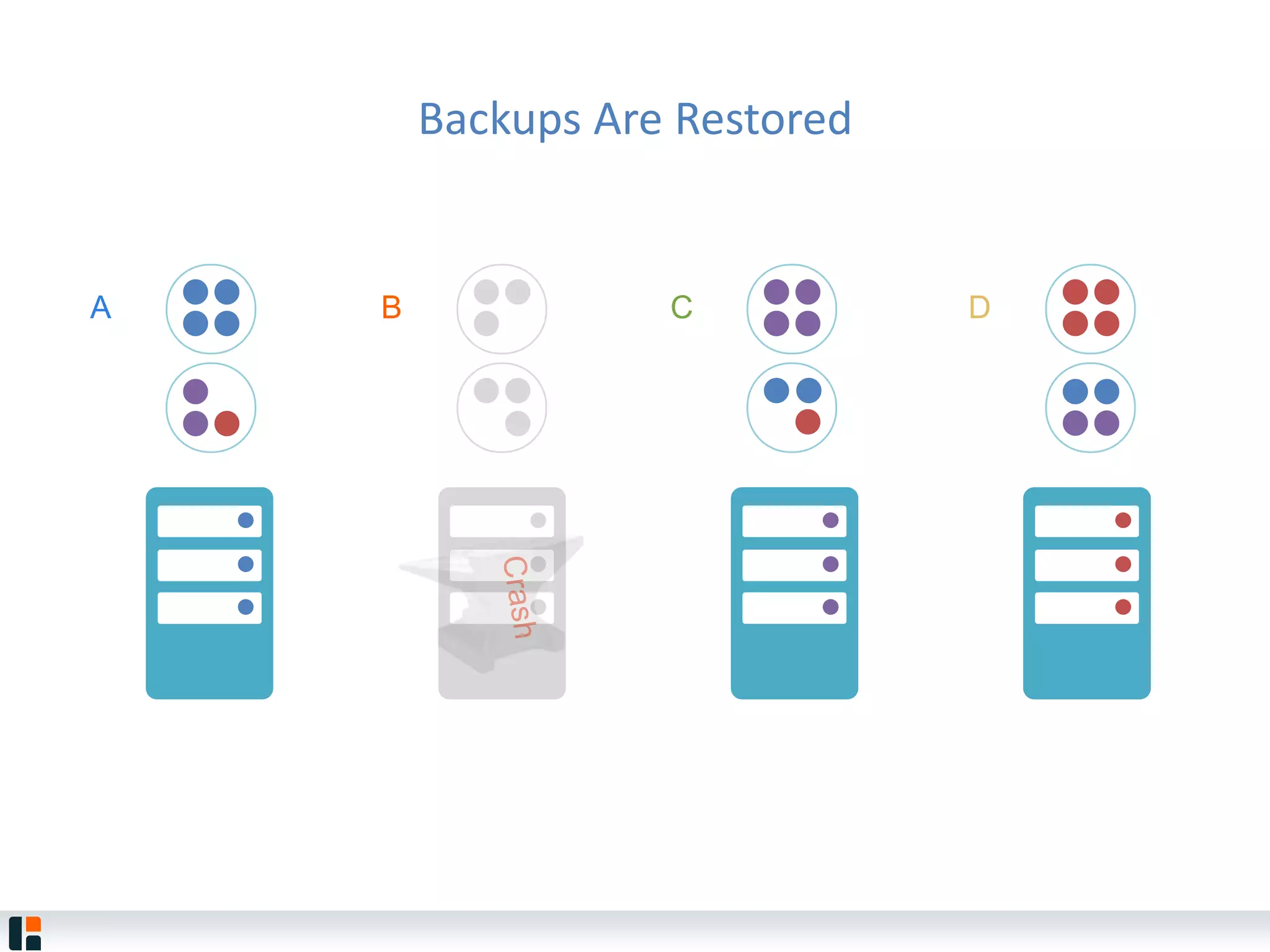
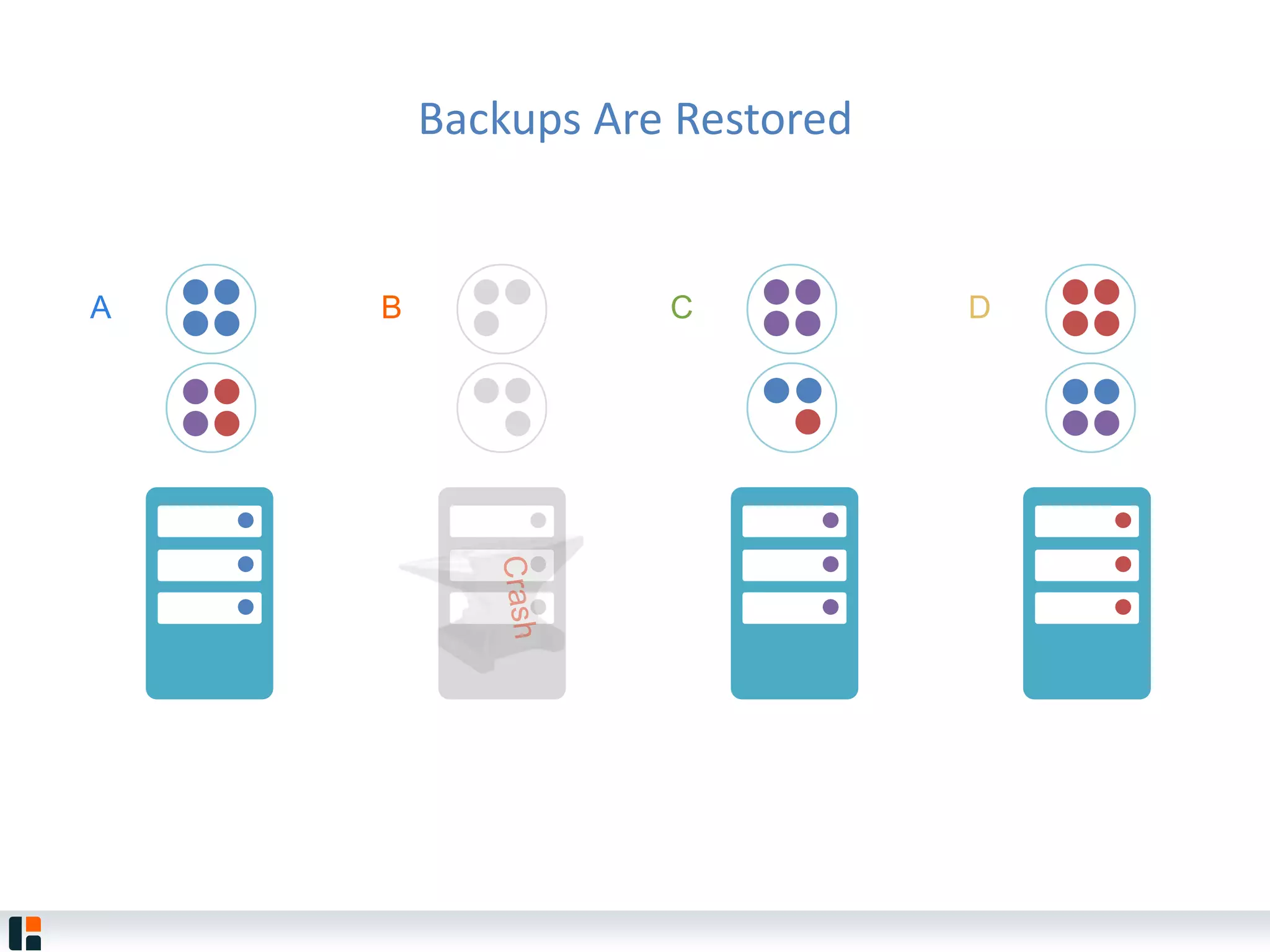
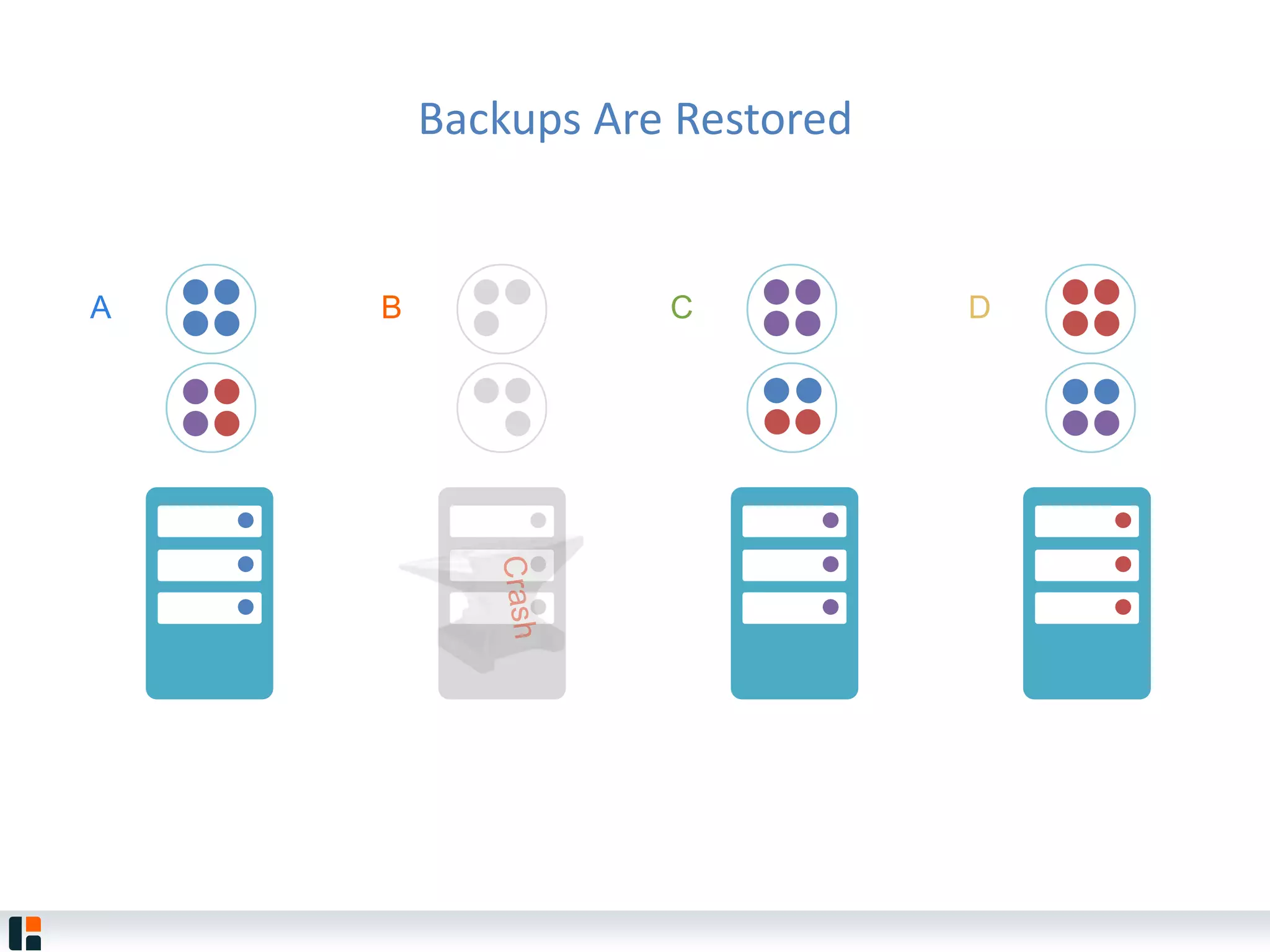
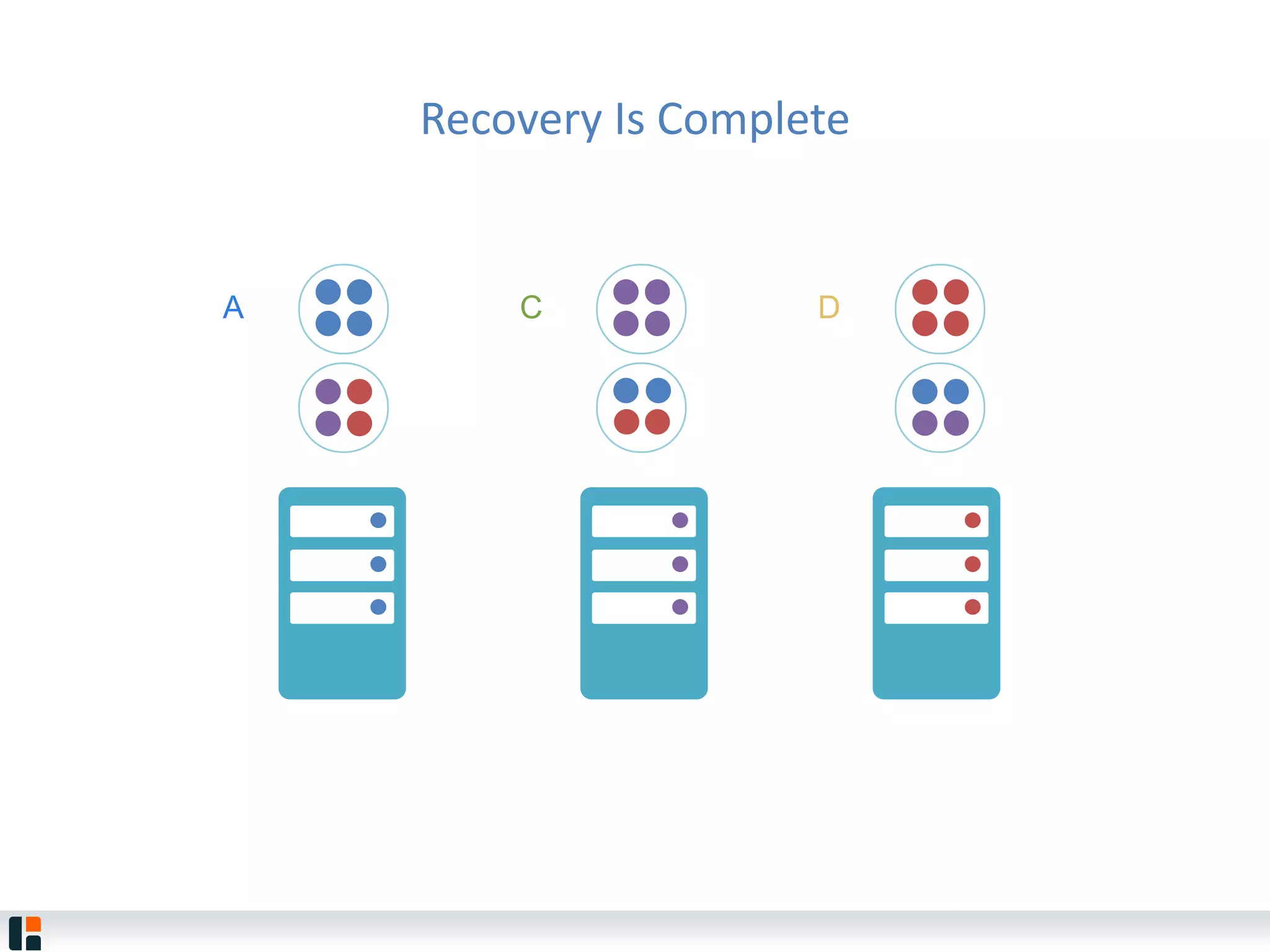
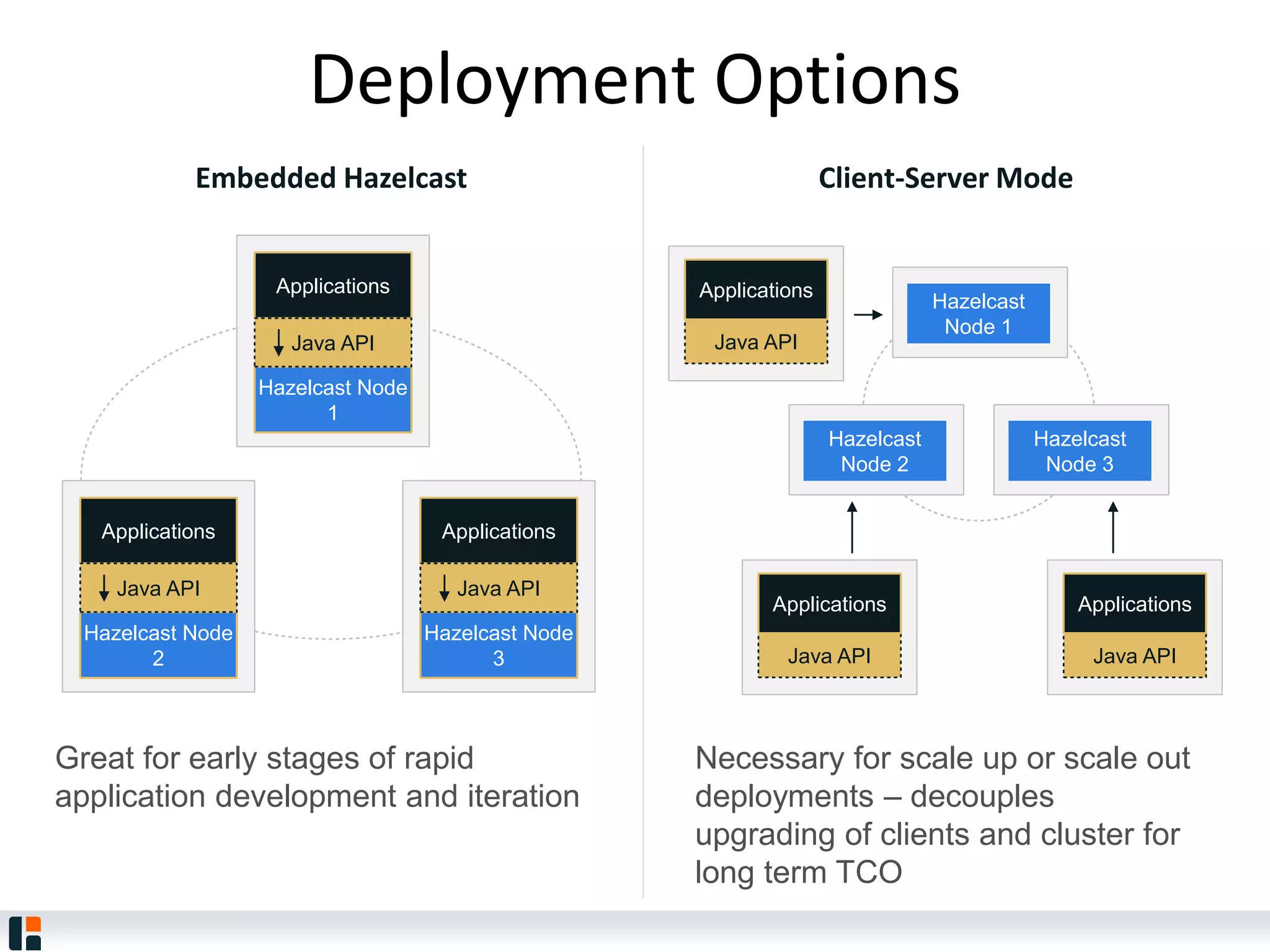
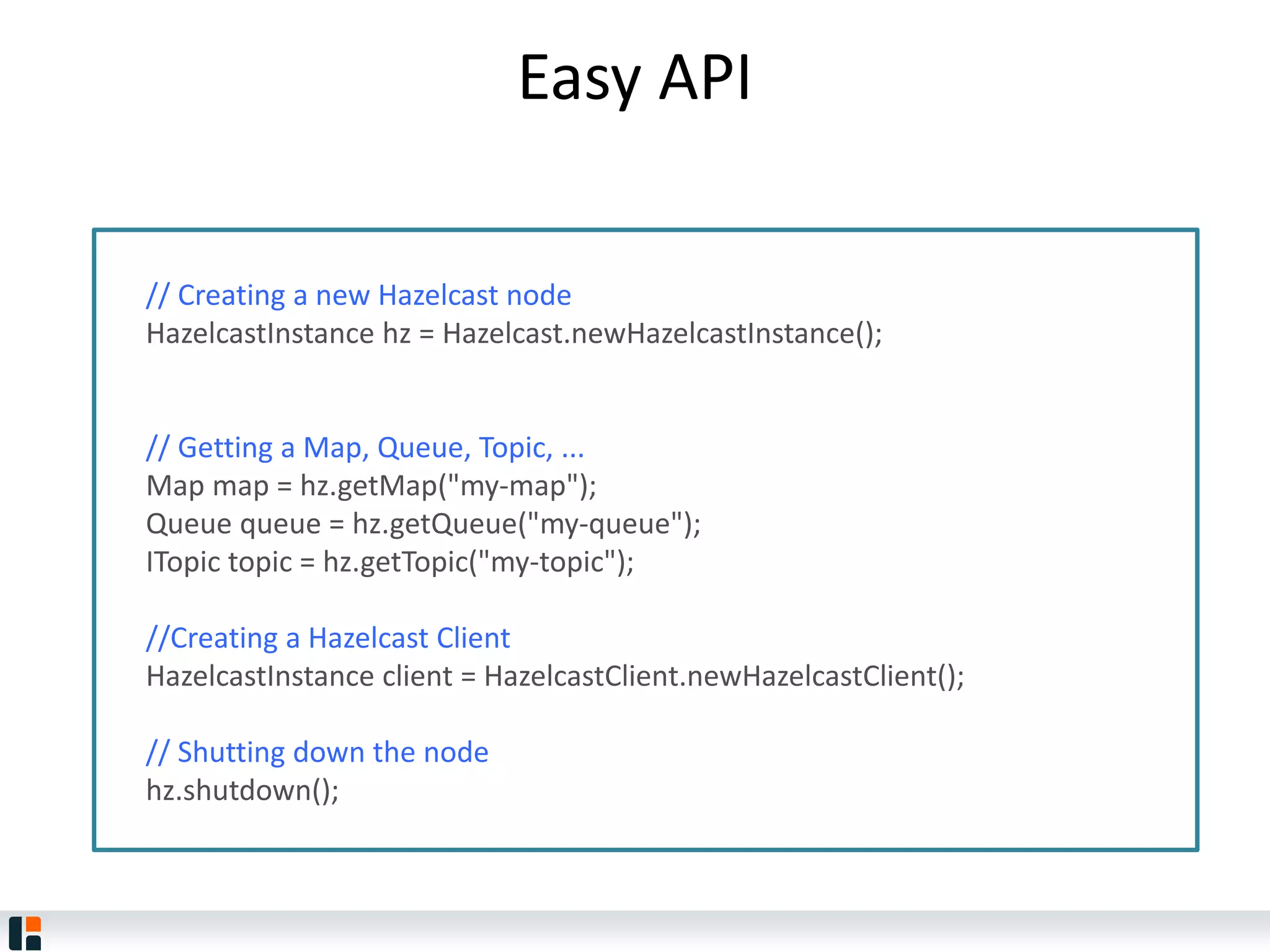
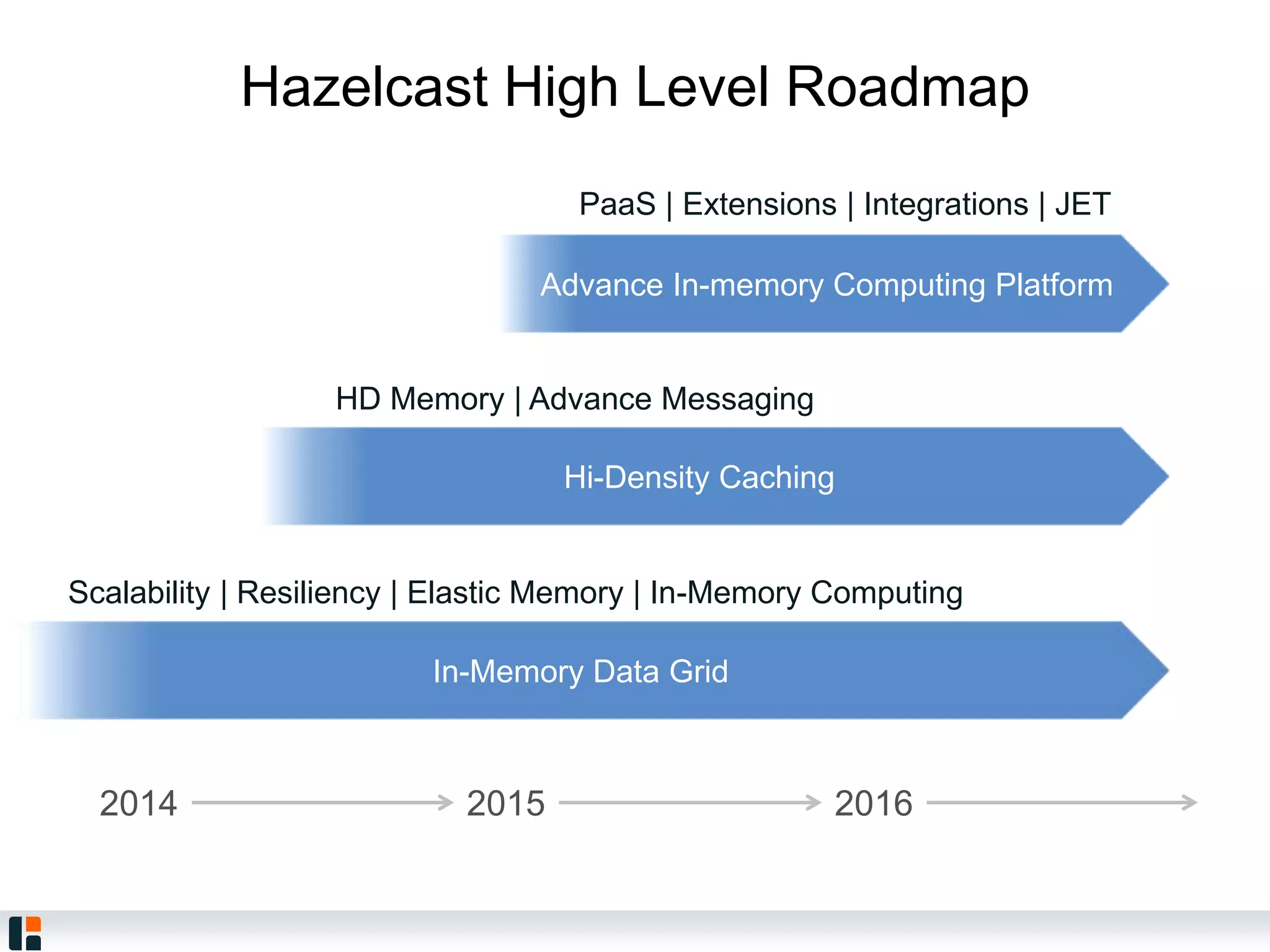
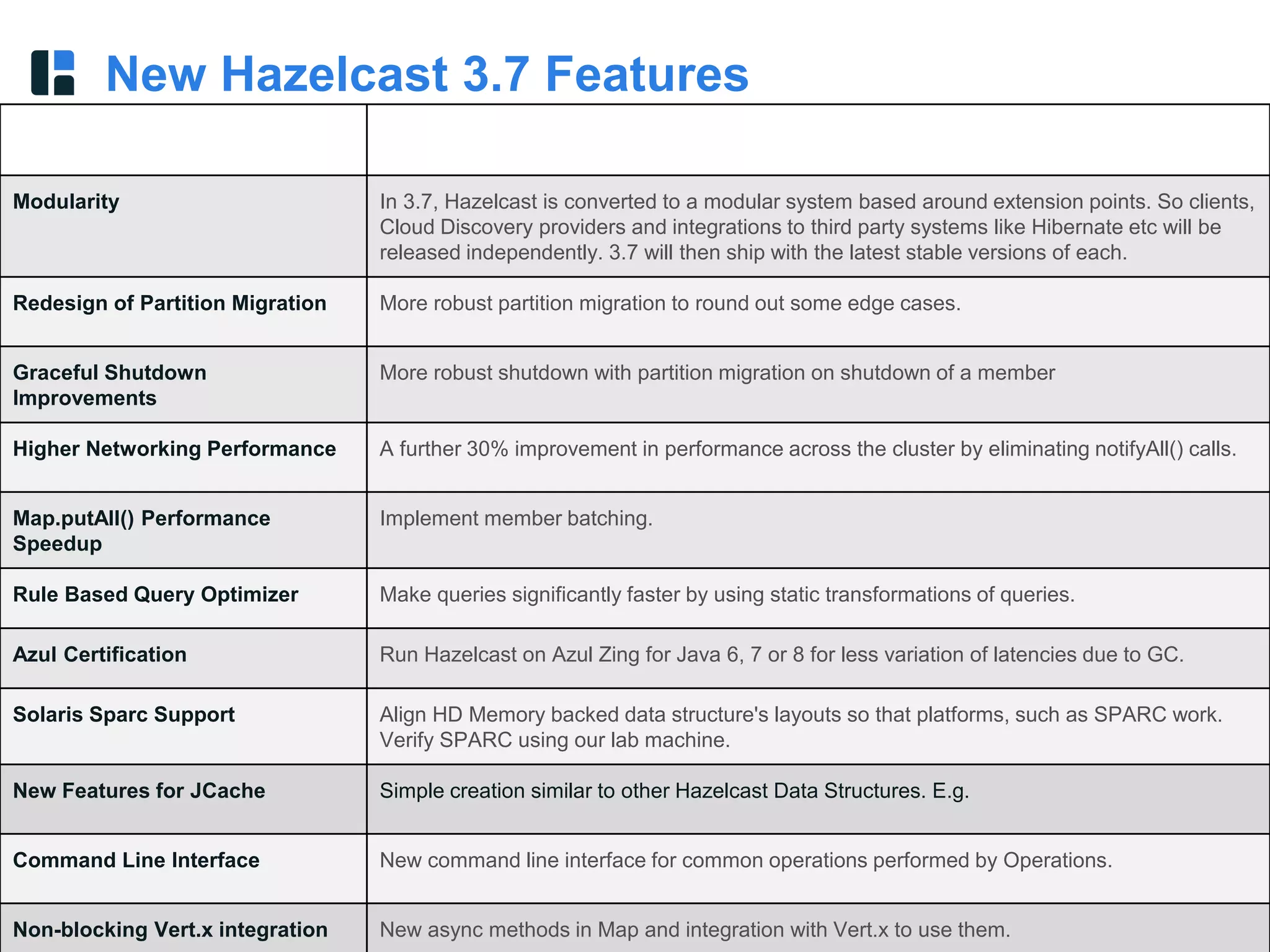
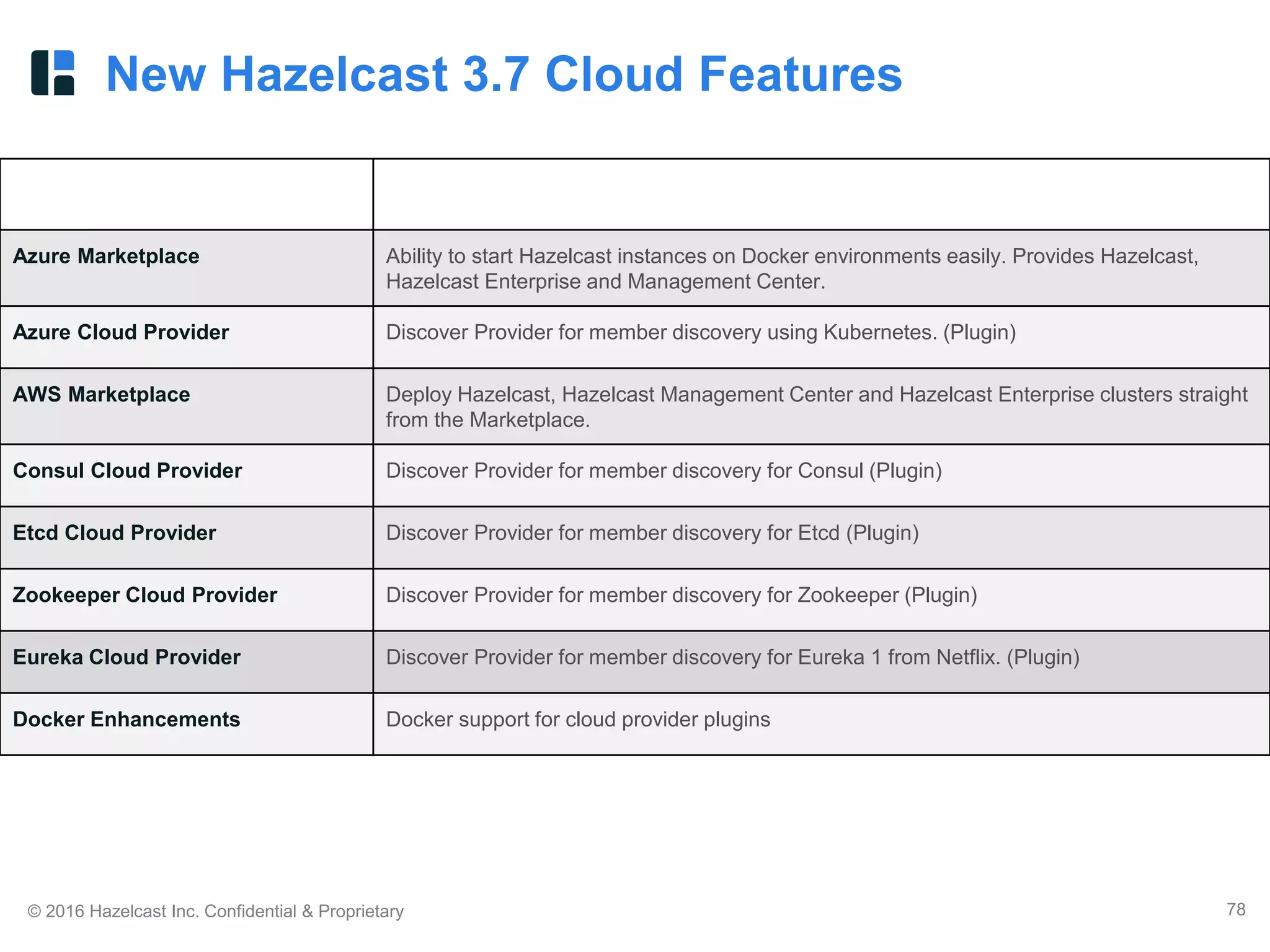
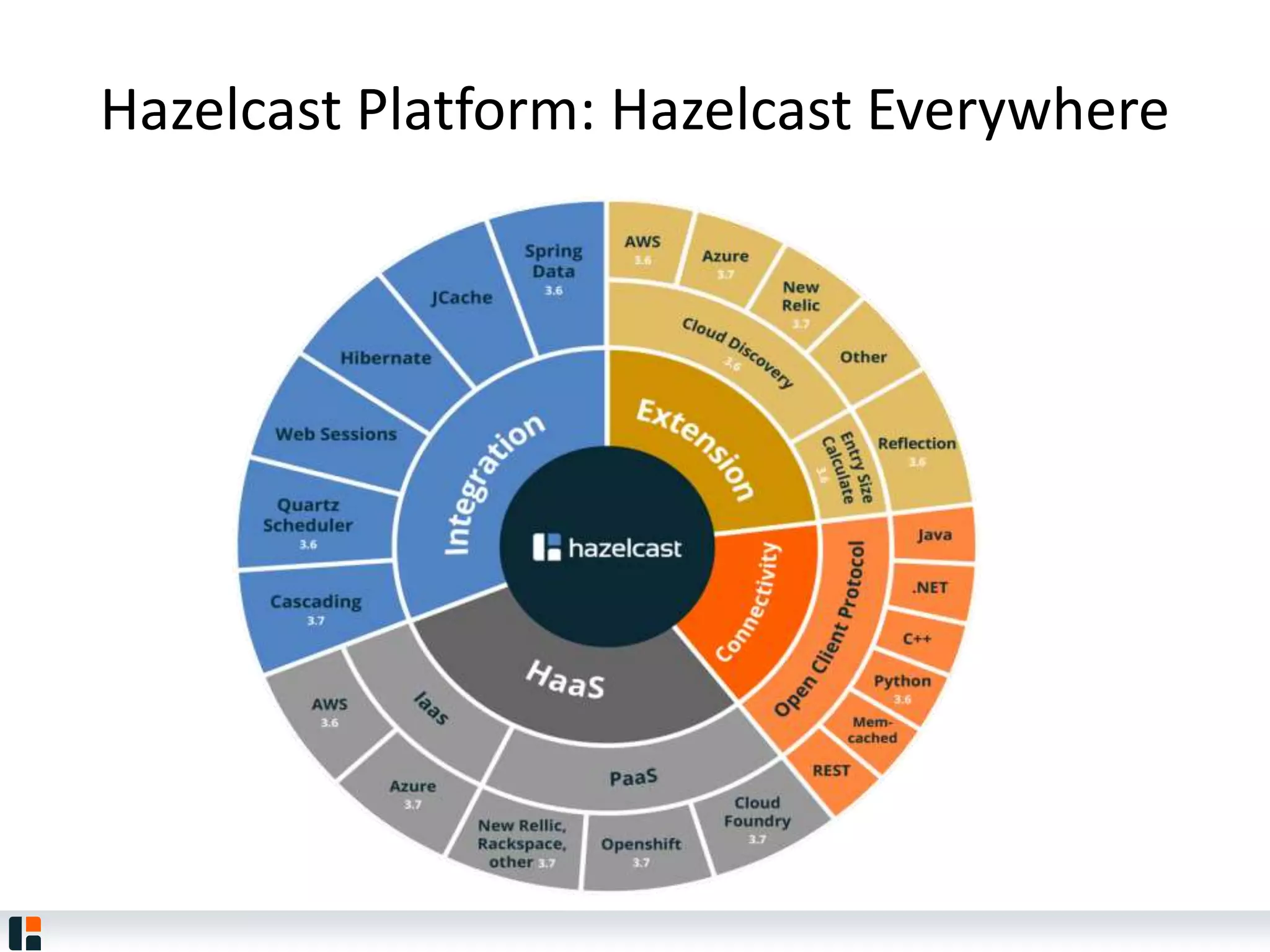
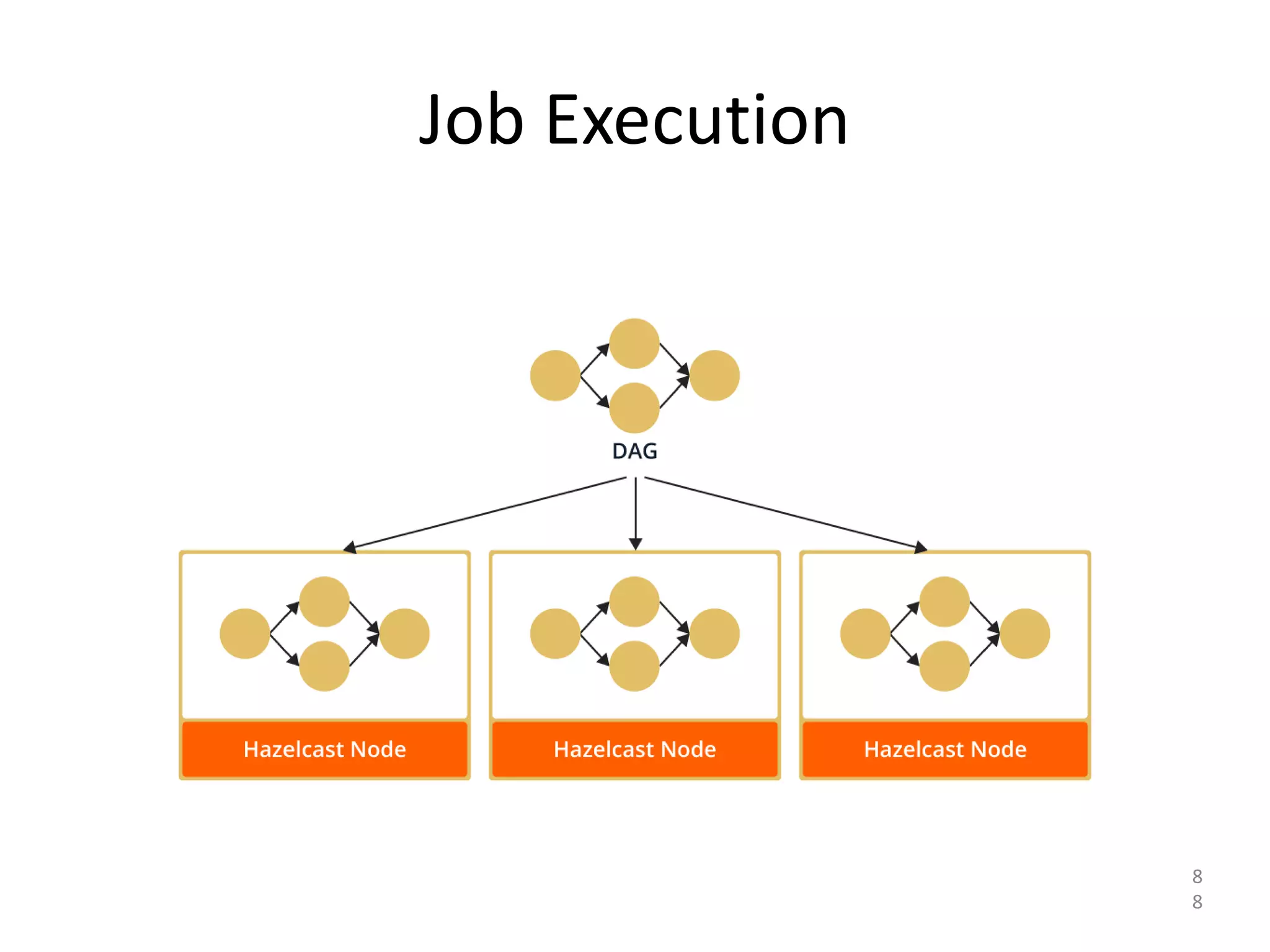
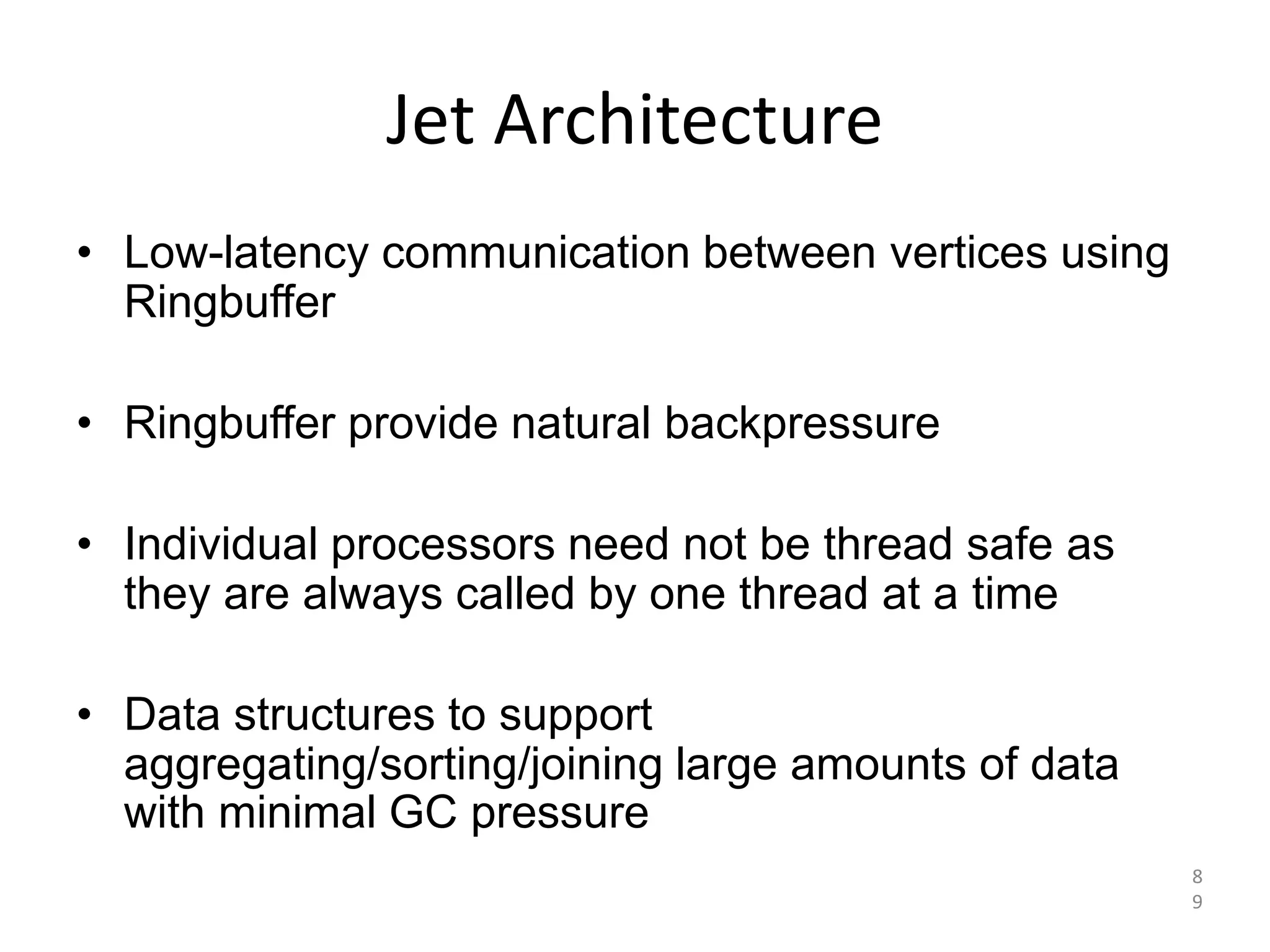
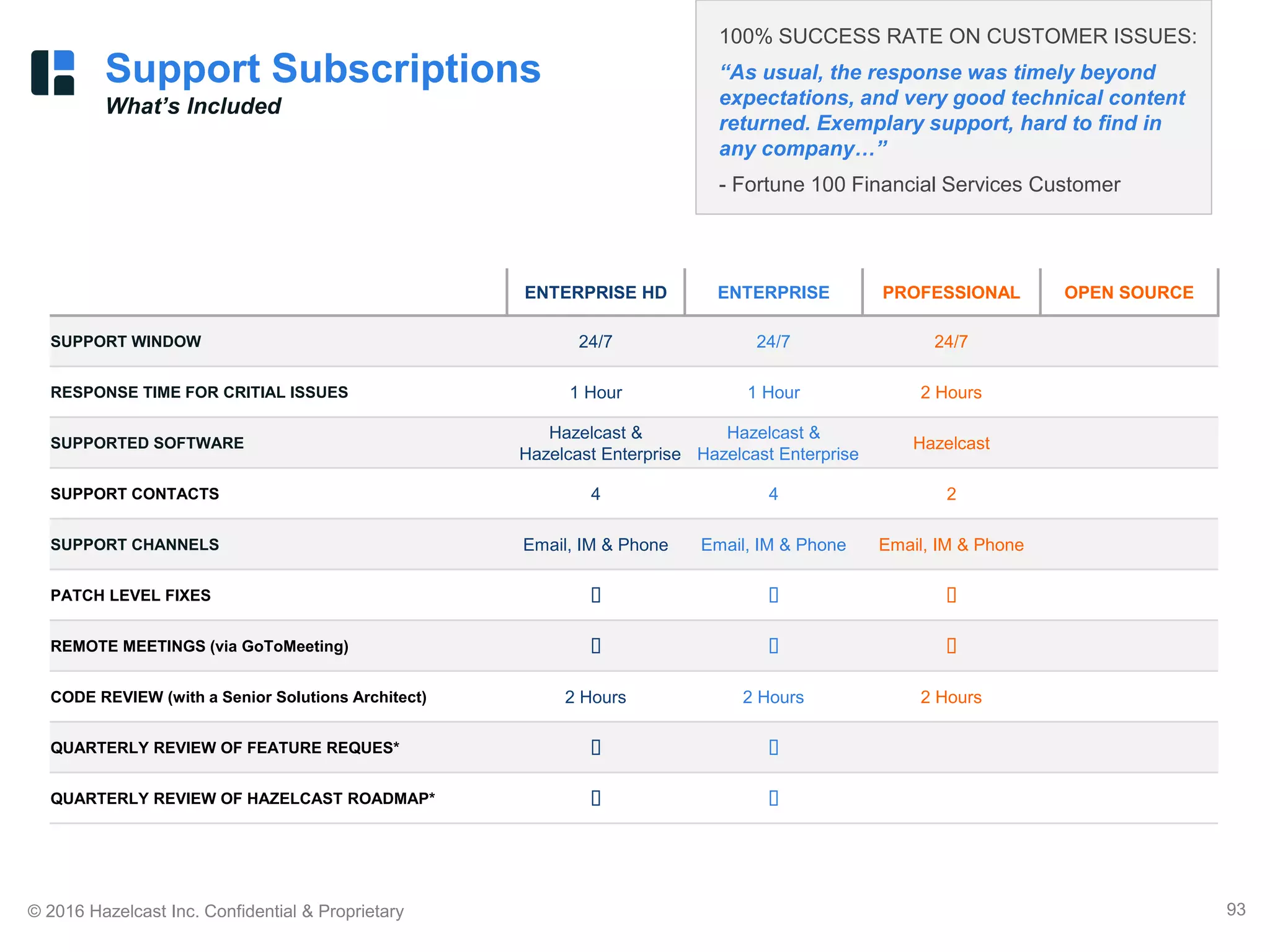
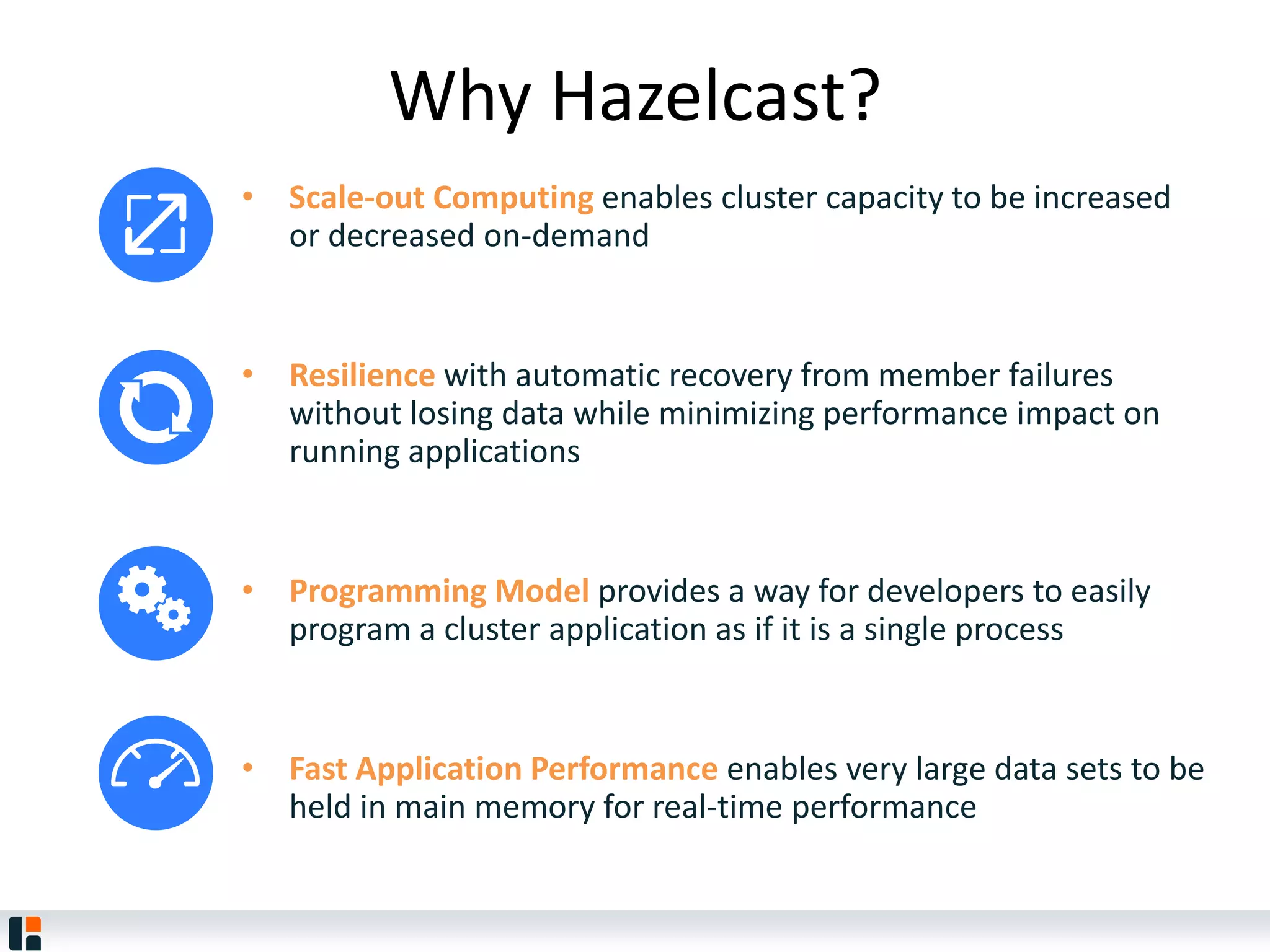
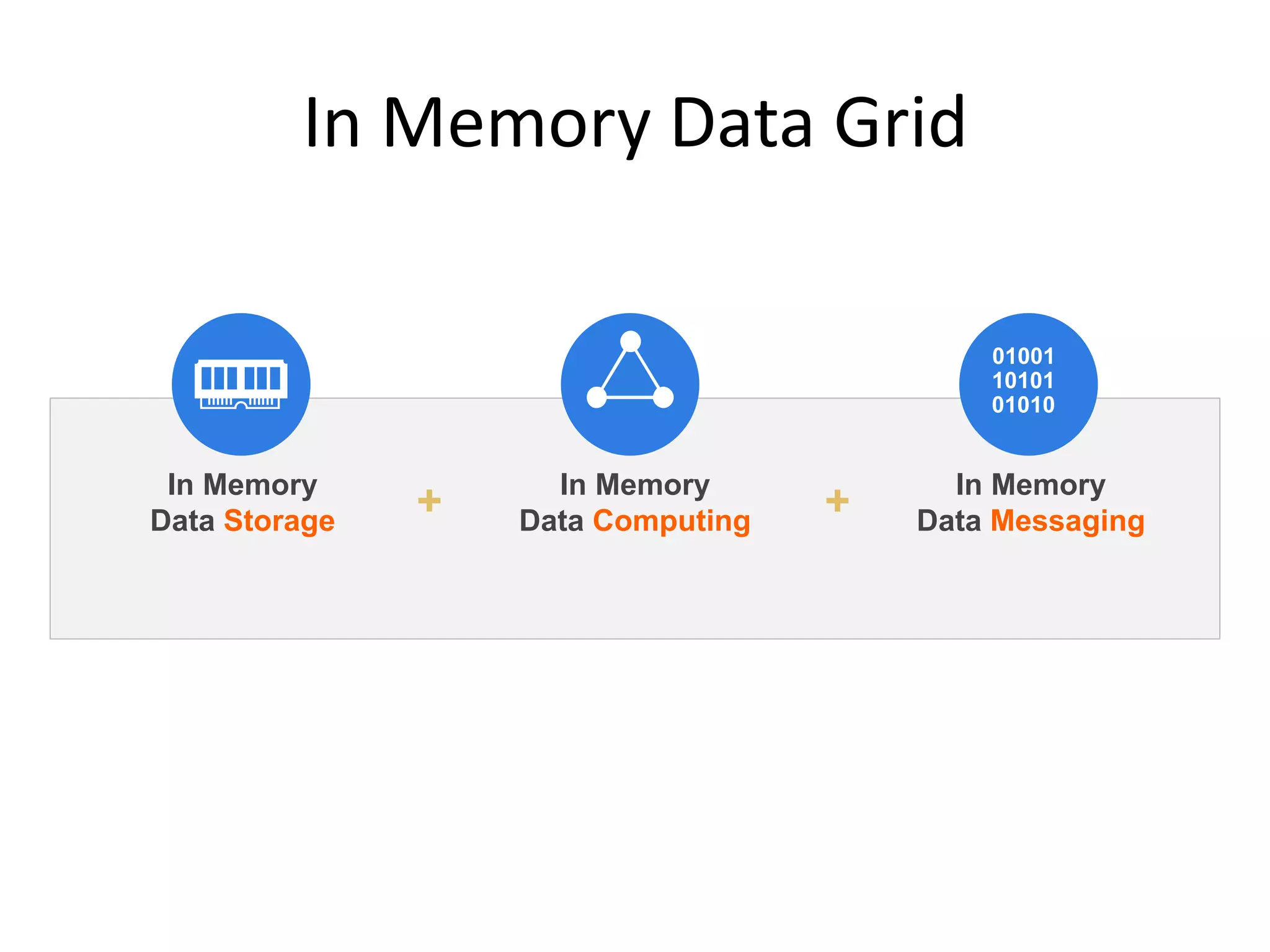
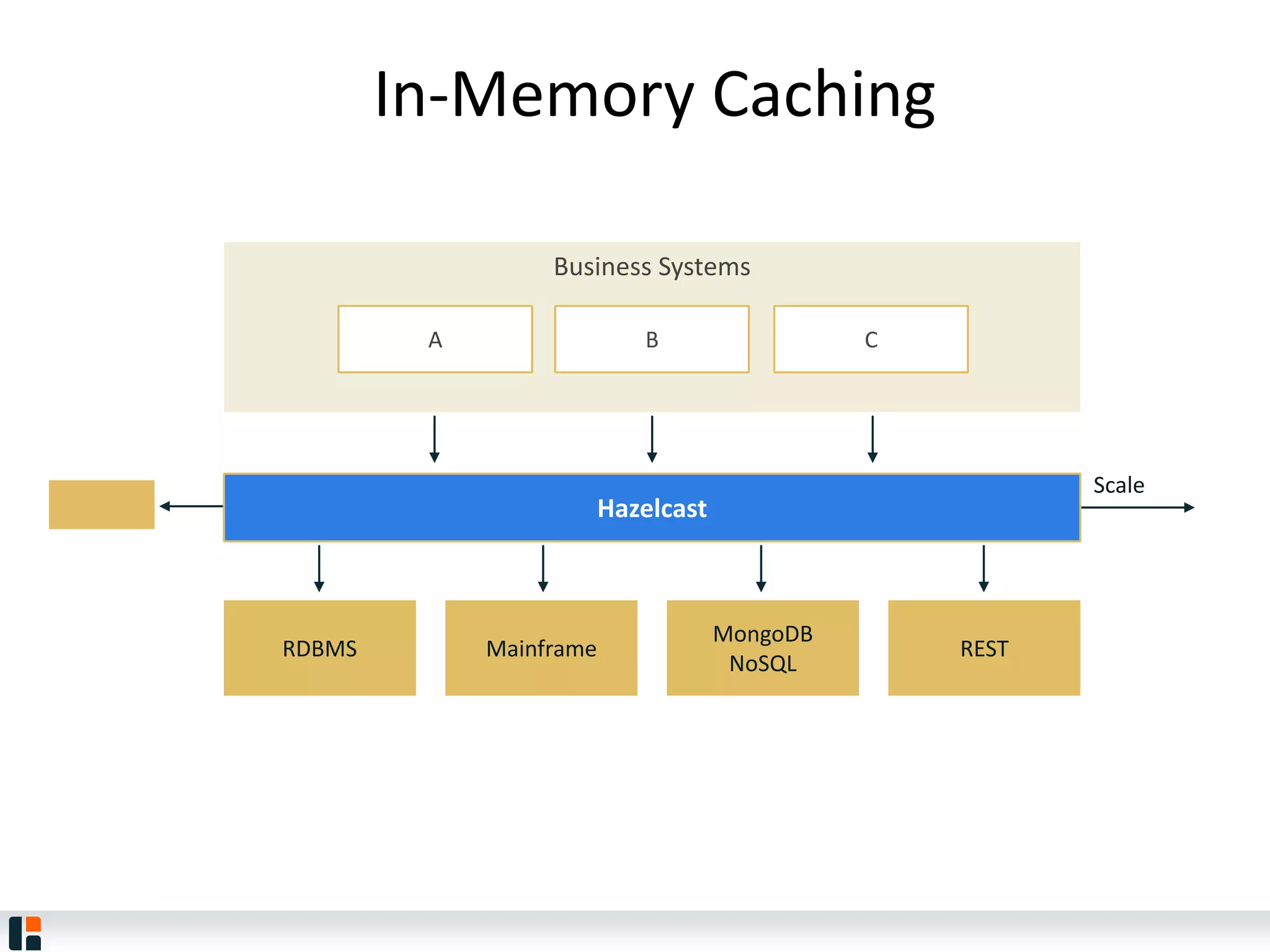
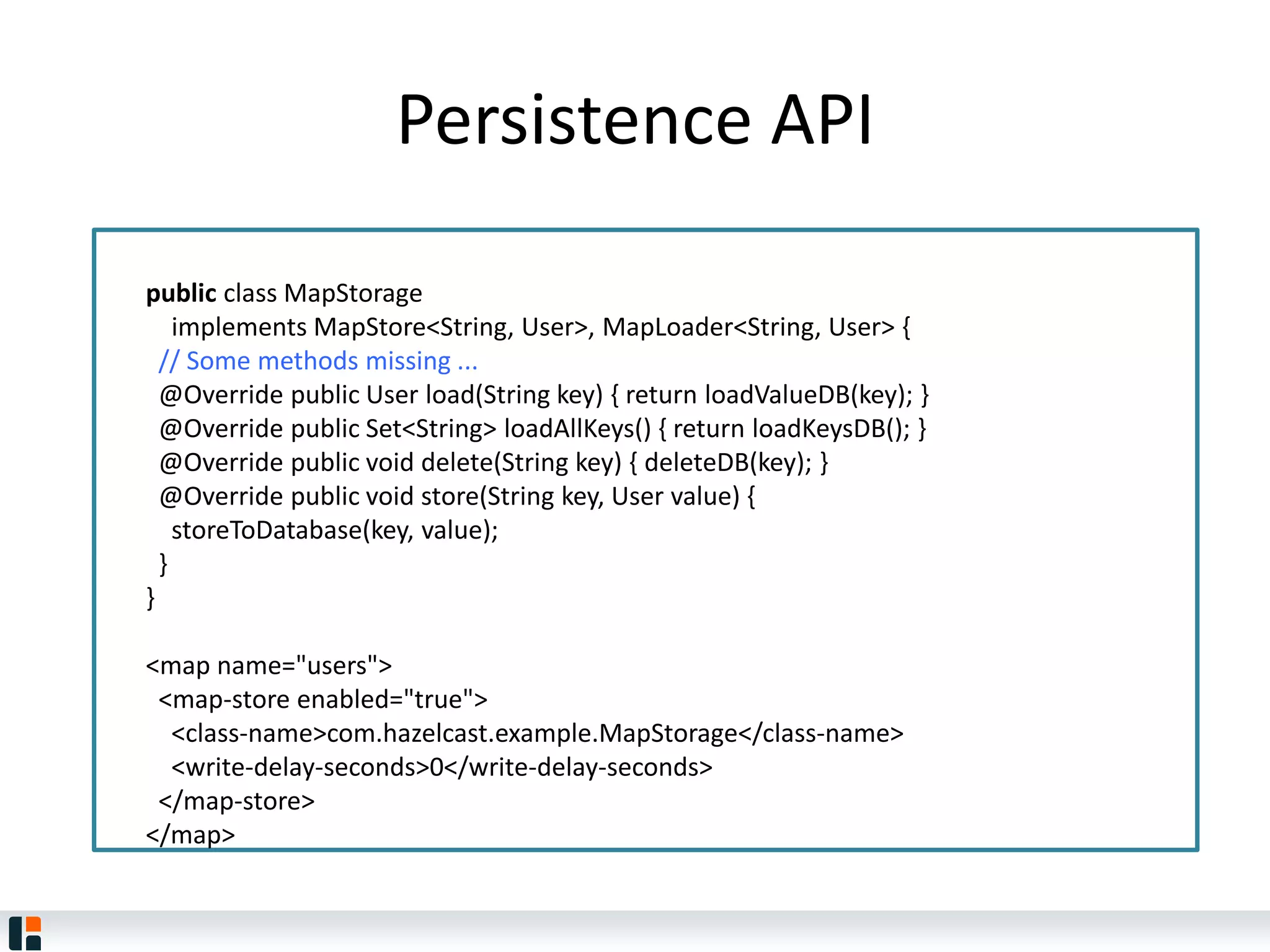
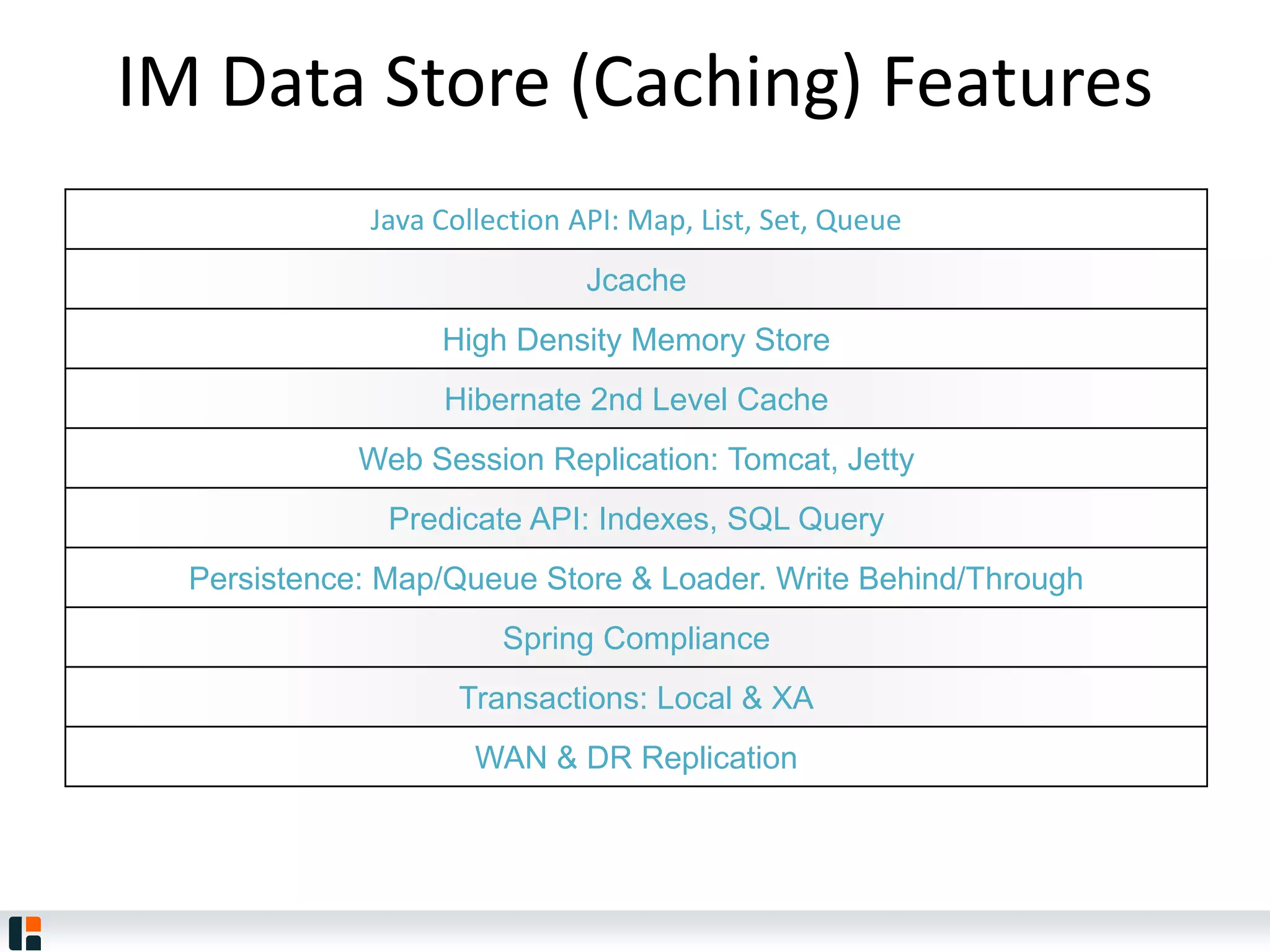
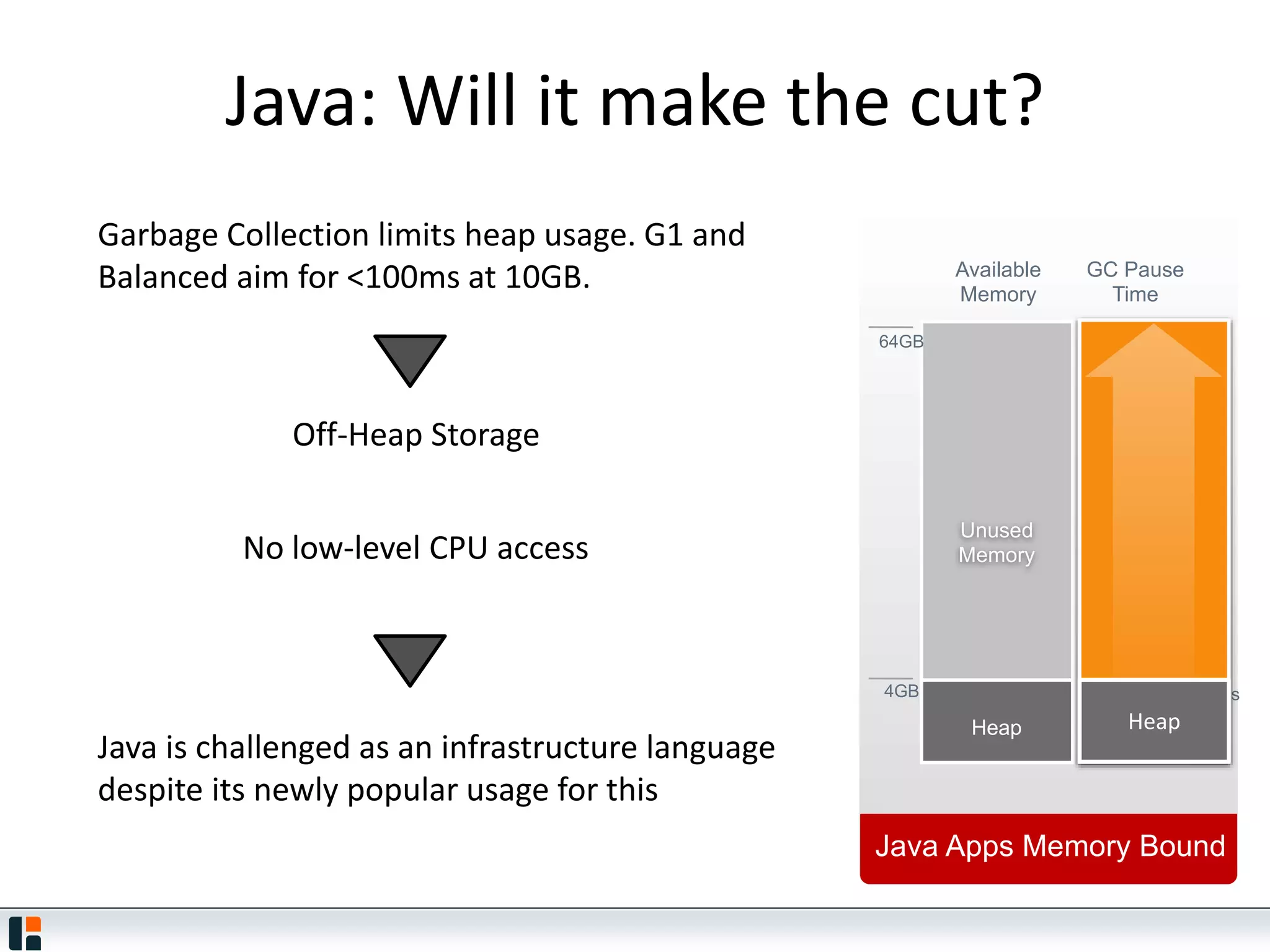
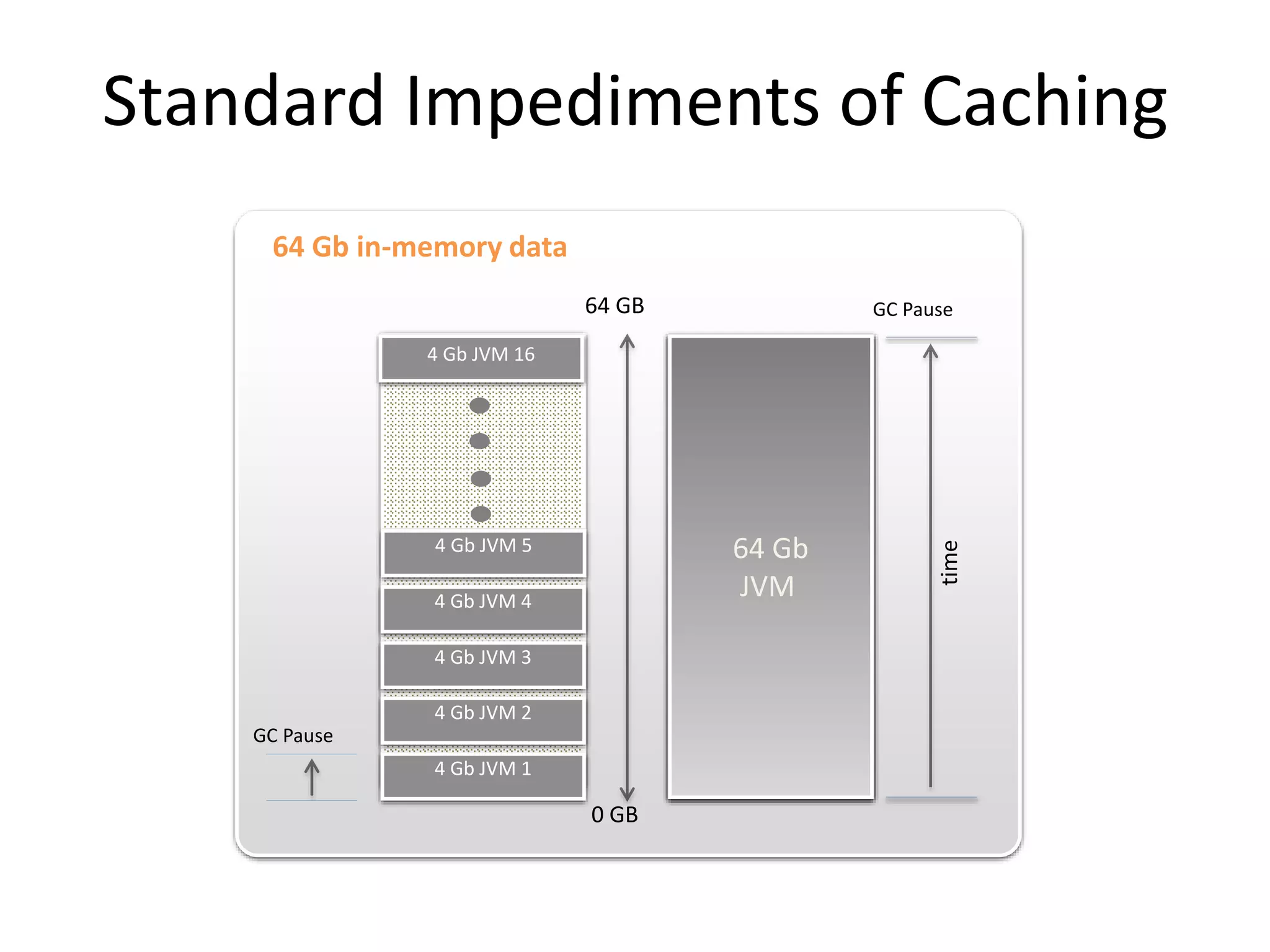
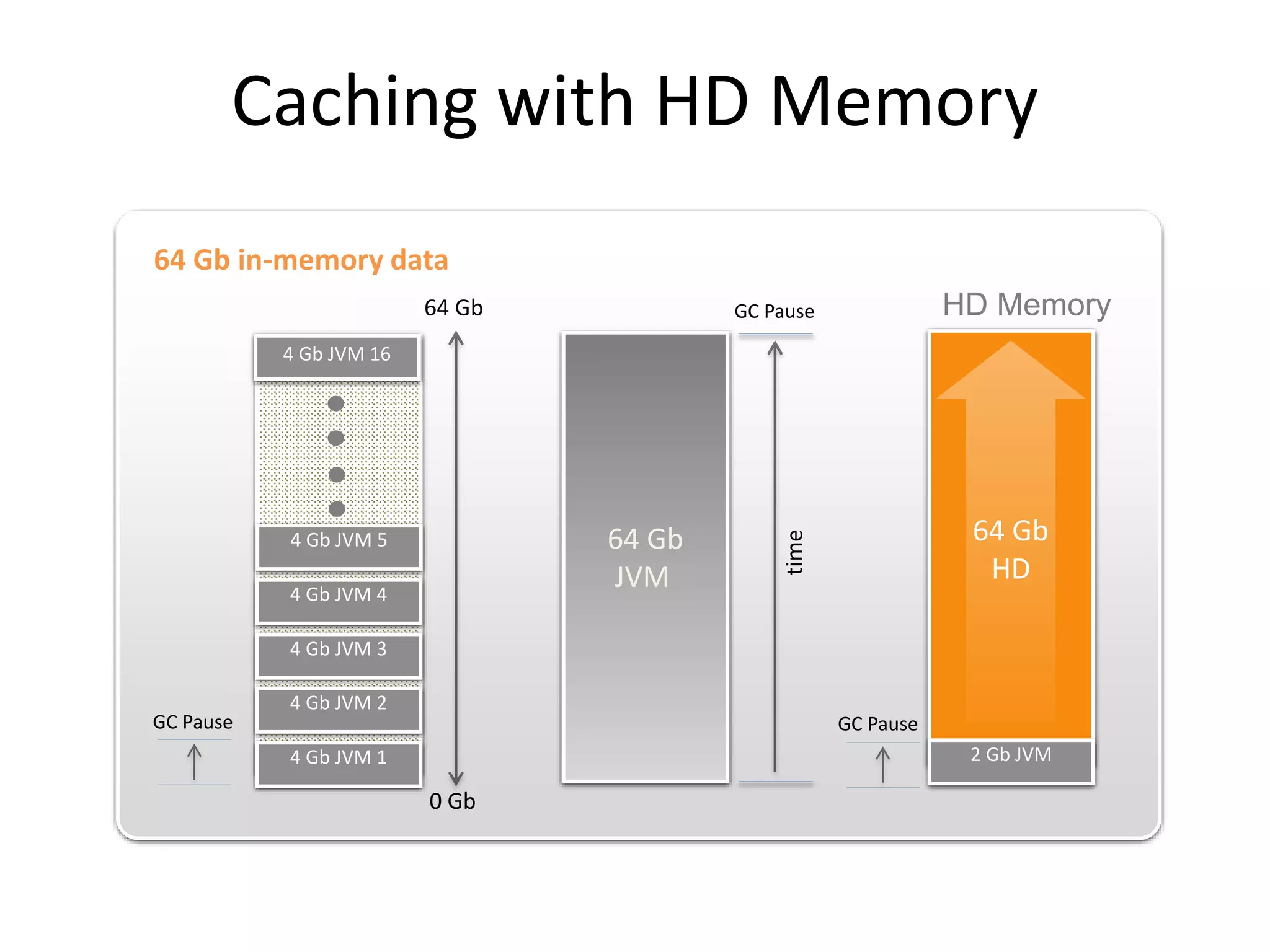
The document discusses Hazelcast, an in-memory data grid platform. Hazelcast provides features like scale-out computing, resilience, fast performance, and an easy programming model. It can be used for distributed caching, computing, messaging, and data storage. Hazelcast runs as a distributed system across multiple nodes and provides APIs for Java and other languages.




![java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap; public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); map.put(1, "Paris"); map.put(2, "London"); map.put(3, "San Francisco"); String oldValue = map.remove(2); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributed-caching-computing-170110043339/75/Distributed-caching-and-computing-v3-7-10-2048.jpg)
![Distributed Map import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap; import com.hazelcast.core.Hazelcast; import com.hazelcast.core.HazelcastInstance; public static void main(String[] args) { HazelcastInstance h = Hazelcast.newHazelcastInstance(); ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> map = h.getMap("myMap"); map.put(1, "Paris"); map.put(2, "London"); map.put(3, "San Francisco"); String oldValue = map.remove(2); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributed-caching-computing-170110043339/75/Distributed-caching-and-computing-v3-7-11-2048.jpg)

![Hazelcast Servers Hazelcast Server JVM [Memory] A B C Business Logic Data Data Data CE = Compute Engine Result Business / Processing Logic Result TCP / IP Client Client Distributed Computing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributed-caching-computing-170110043339/75/Distributed-caching-and-computing-v3-7-25-2048.jpg)