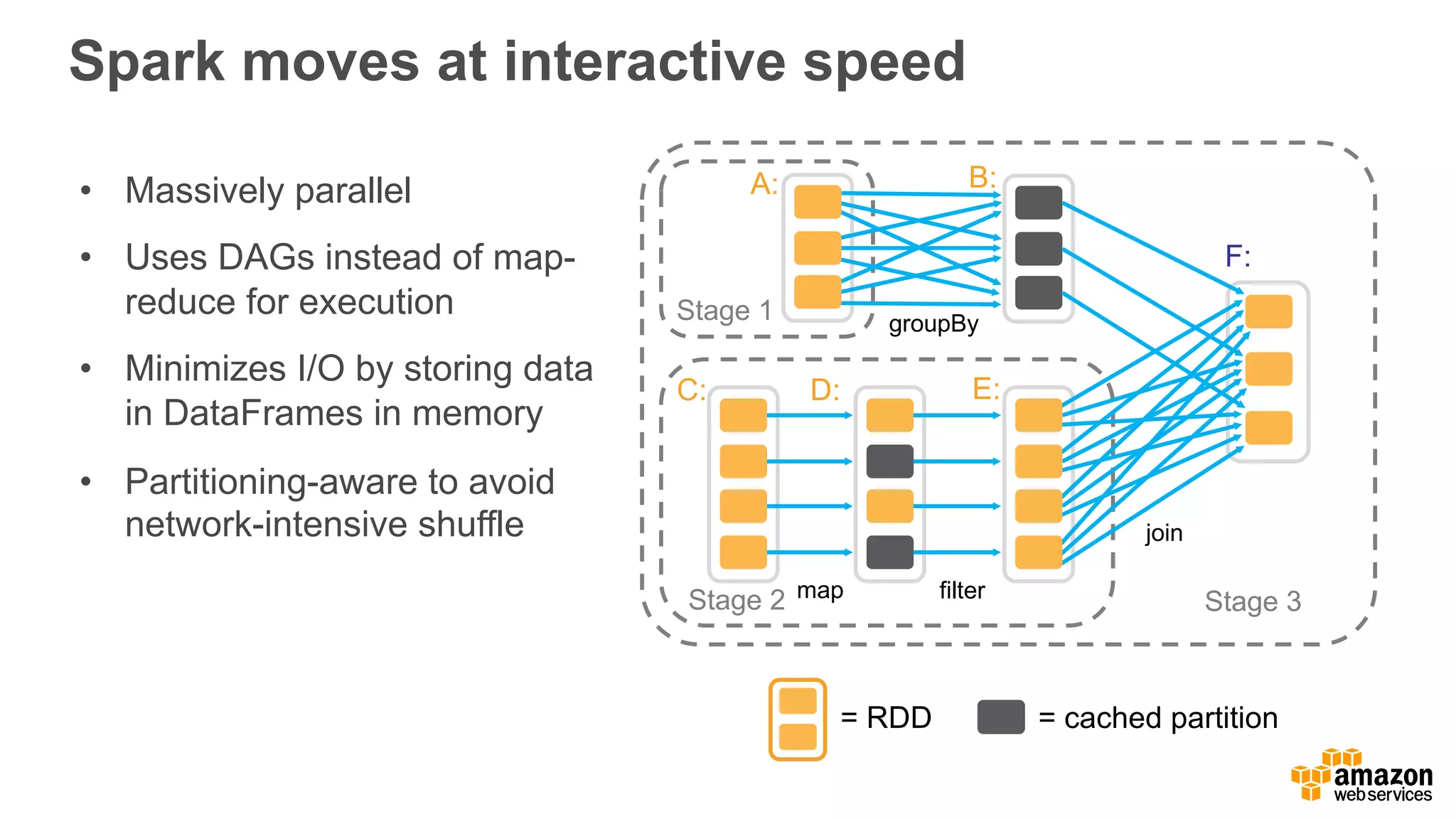
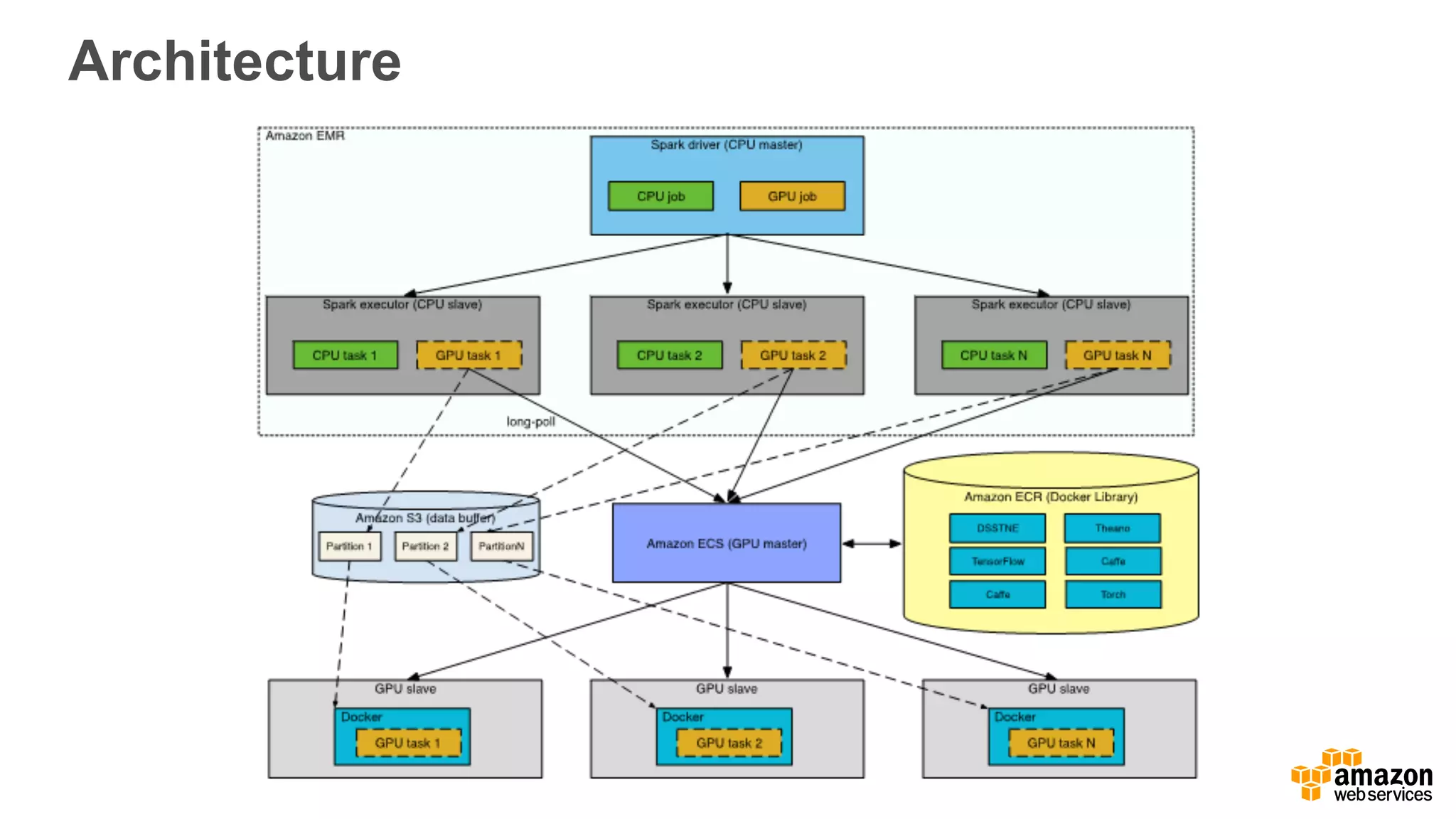
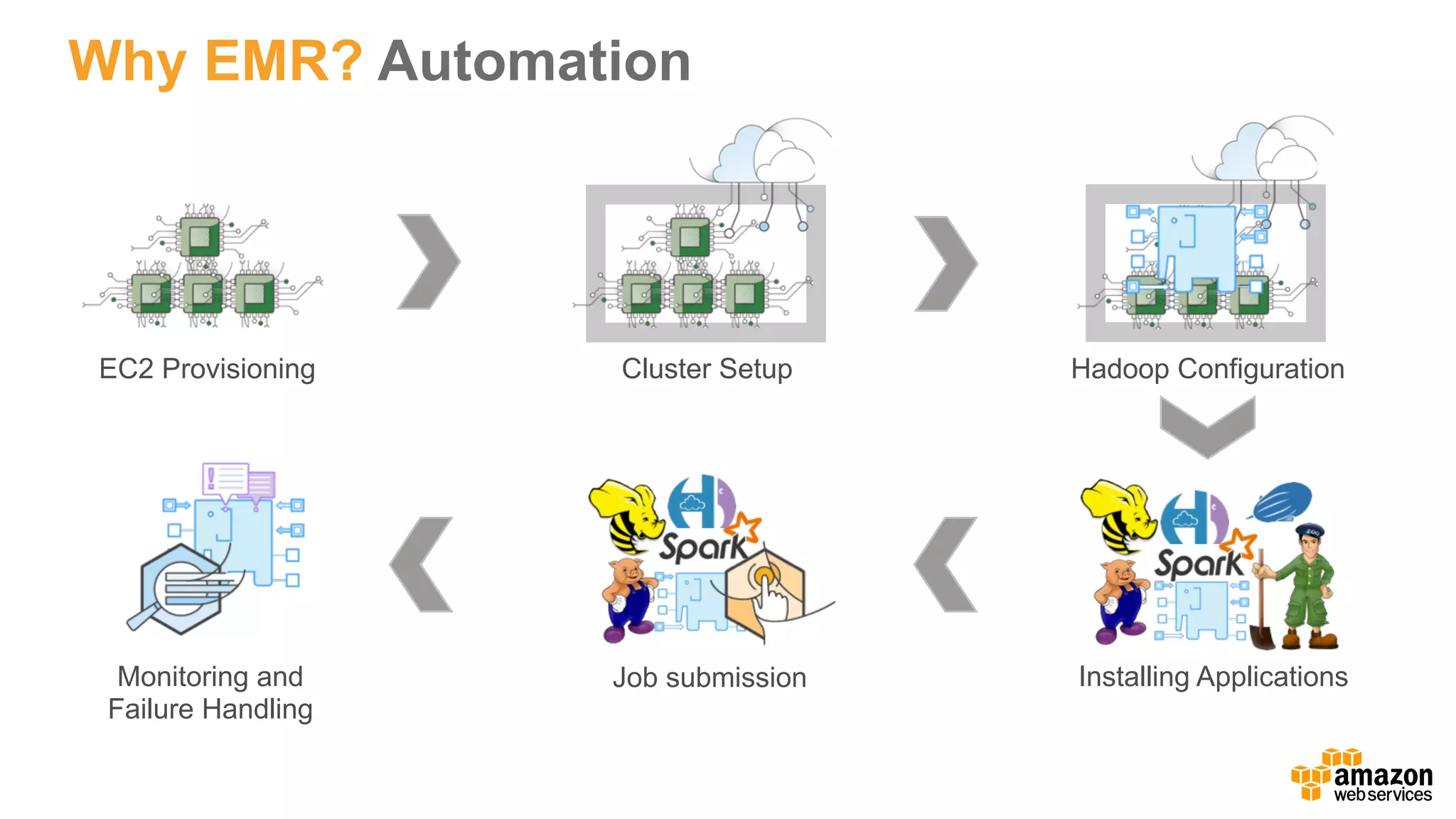
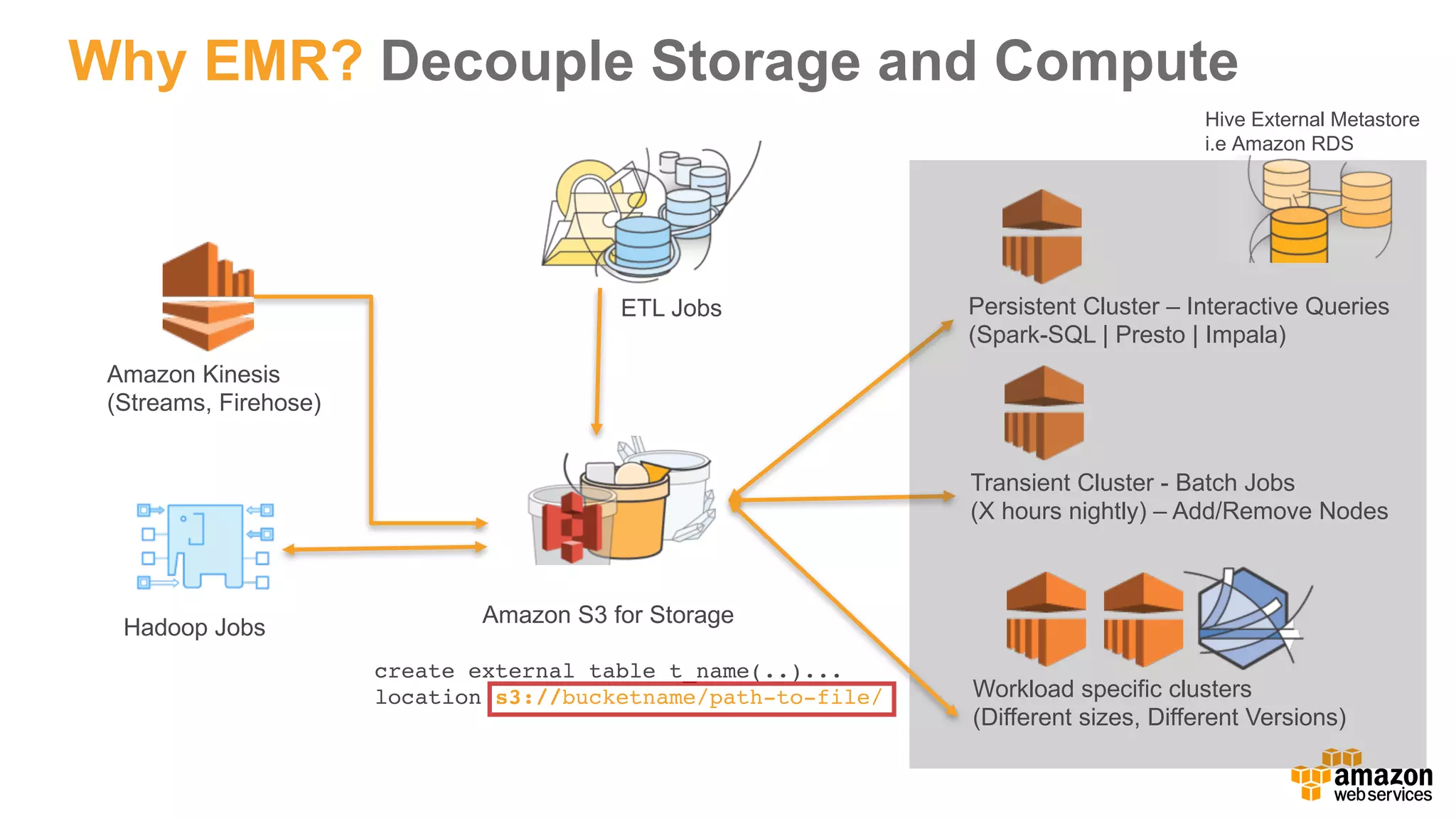
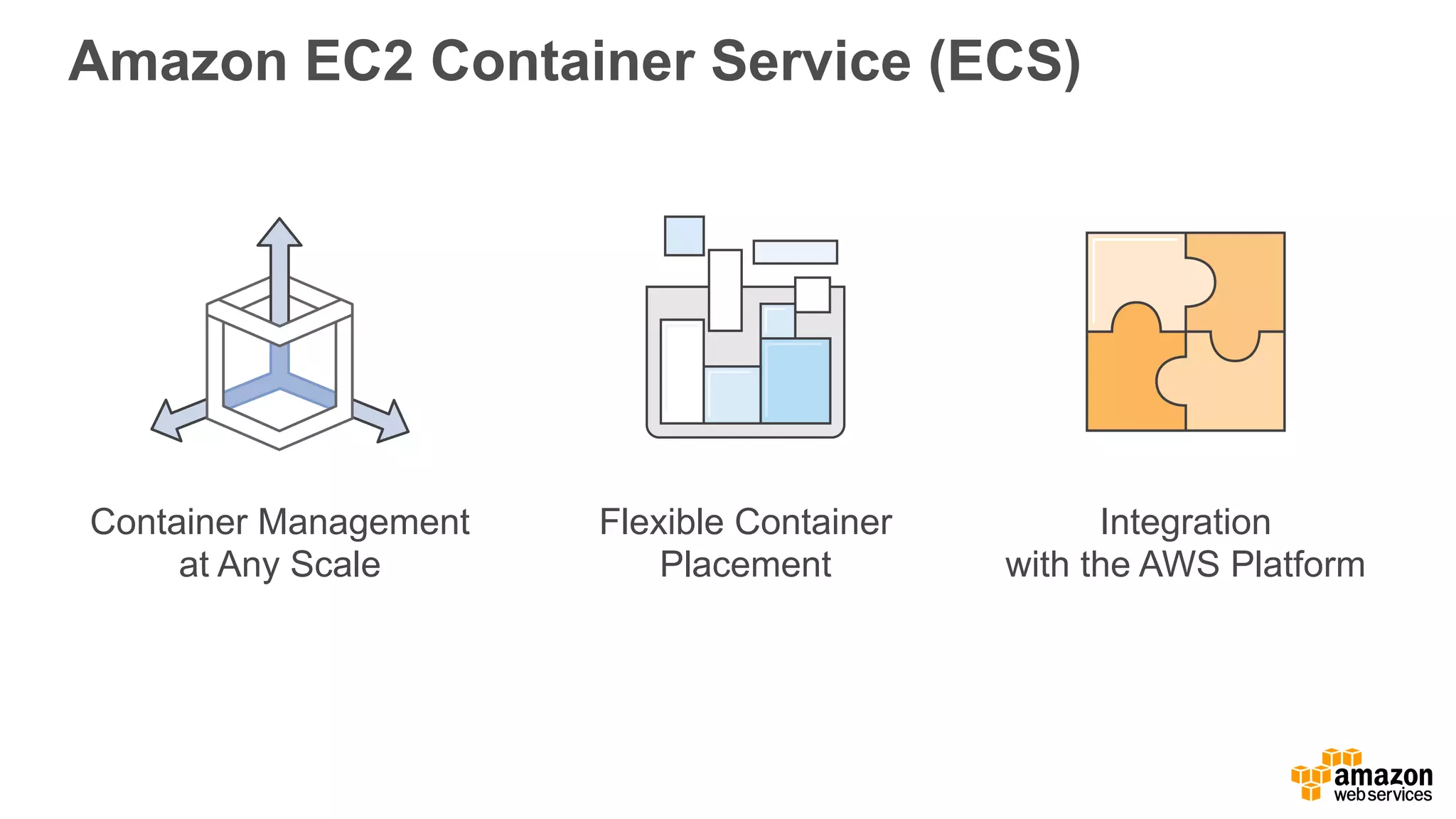
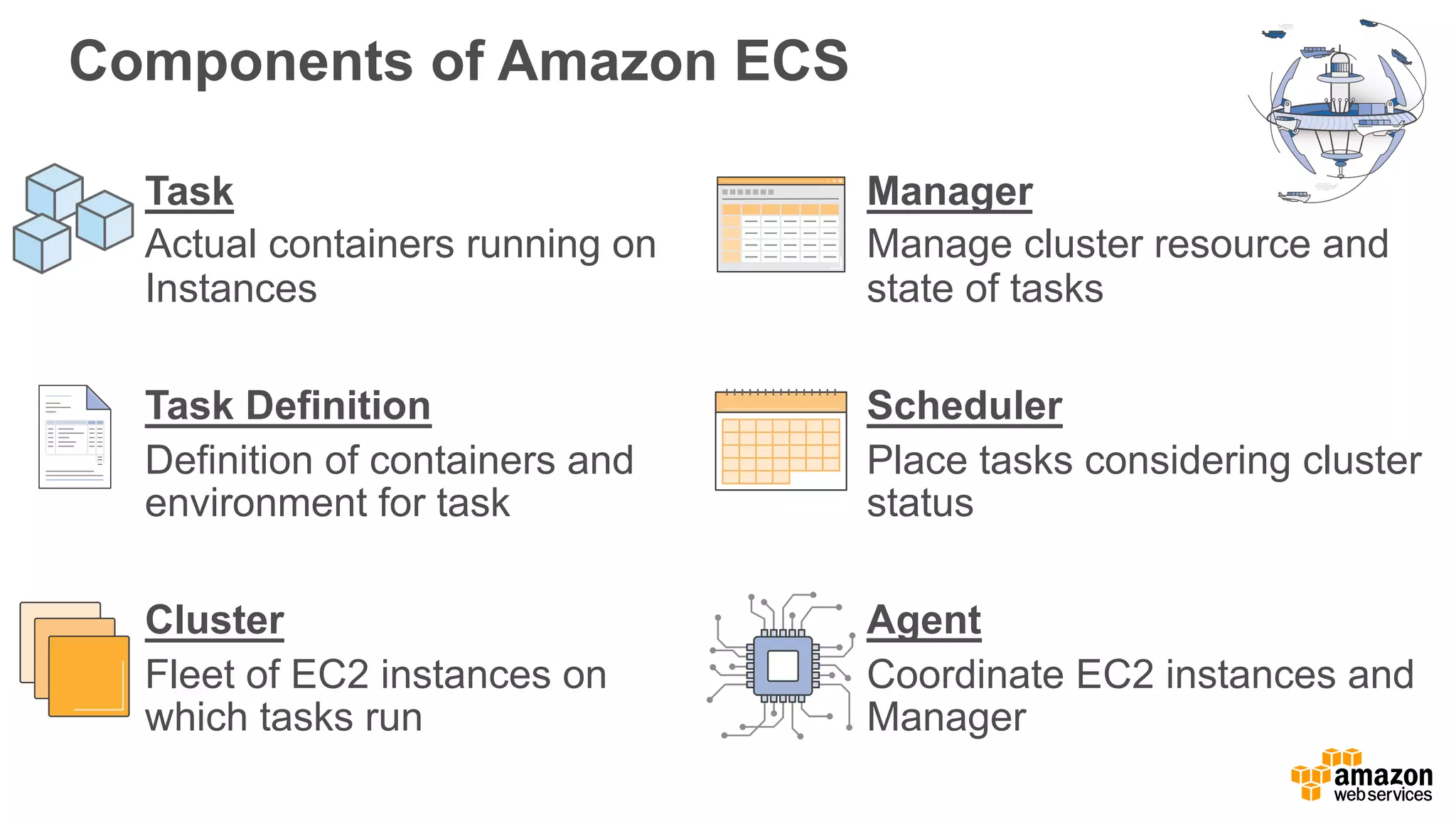
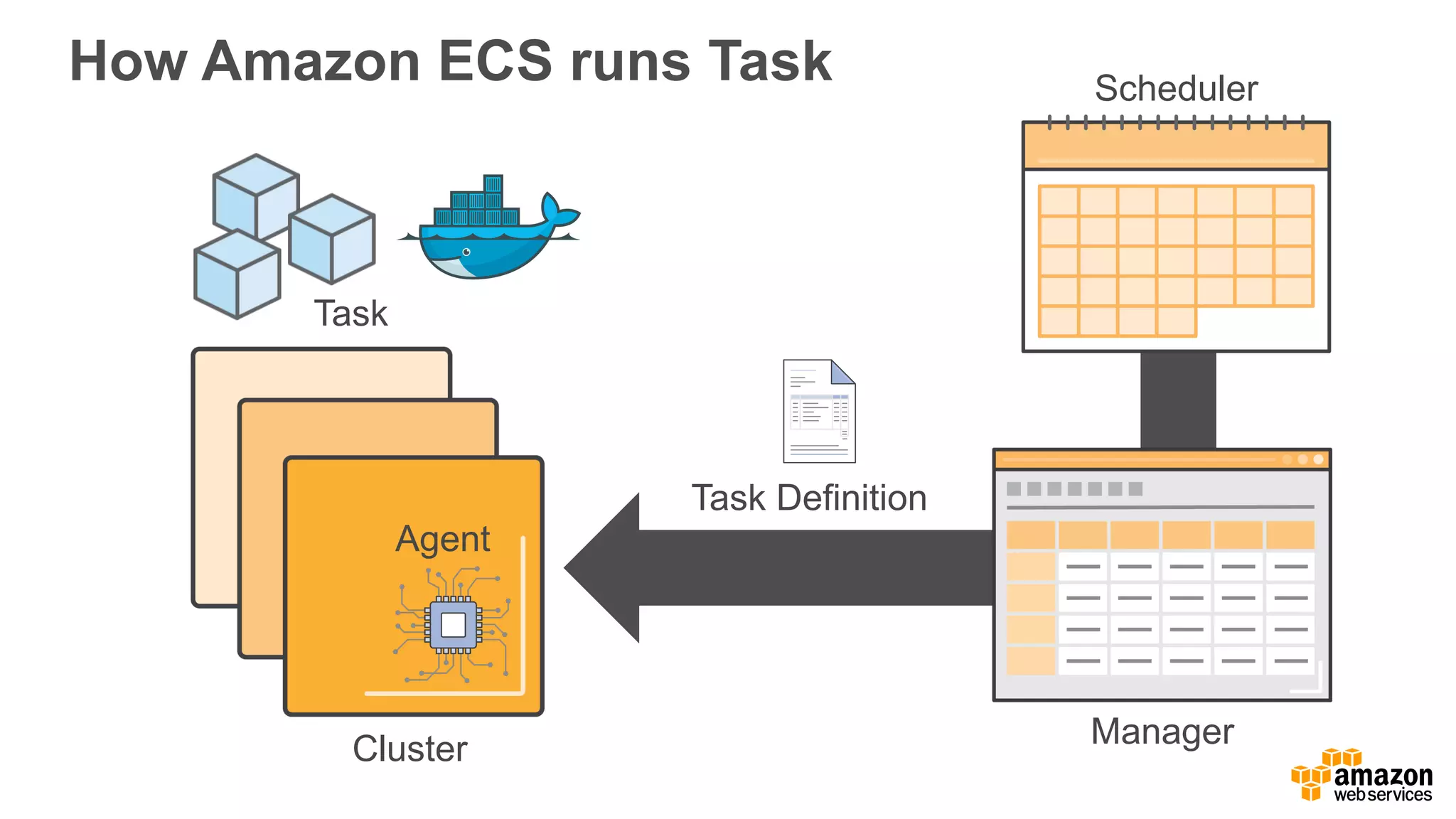
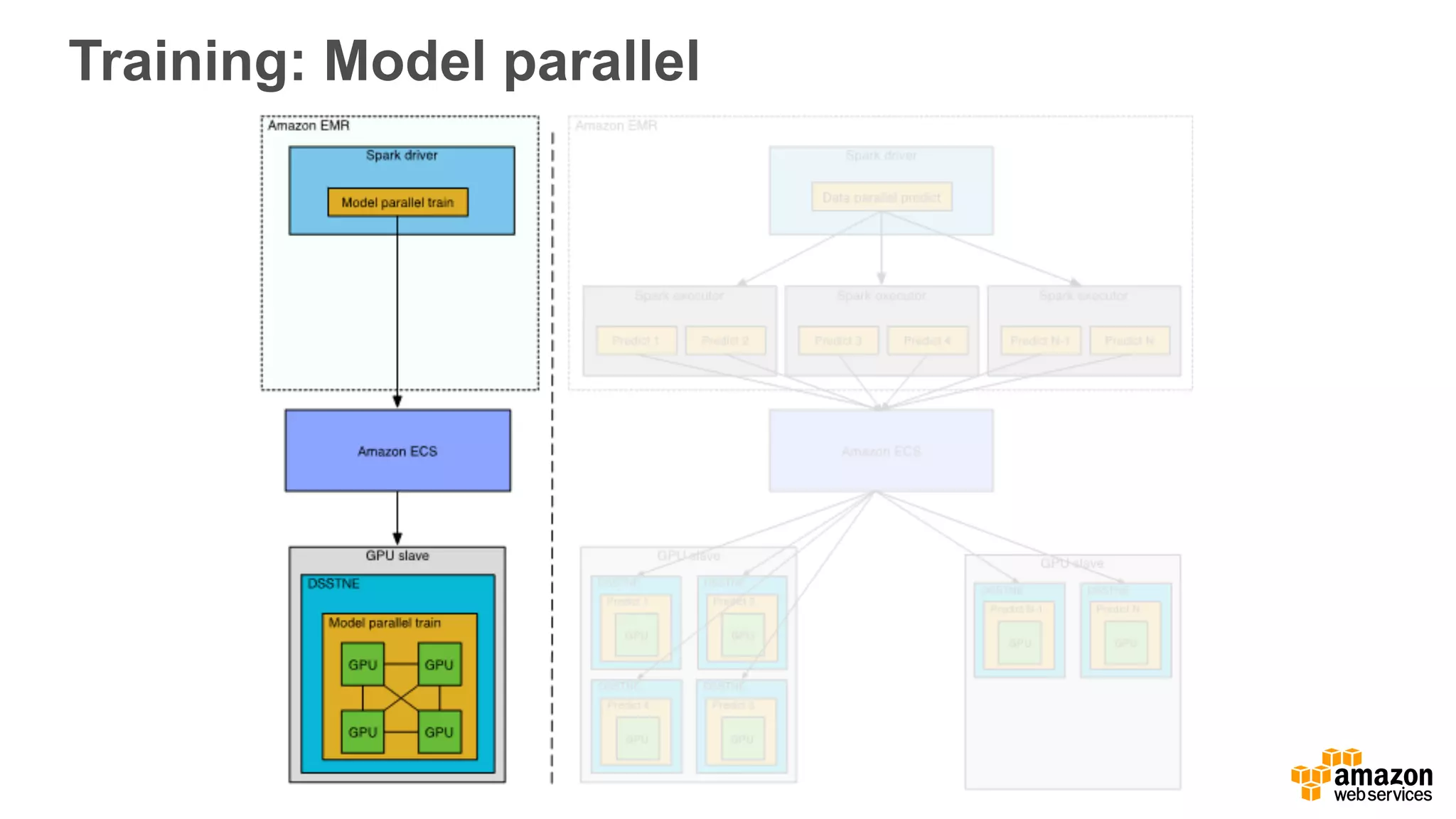
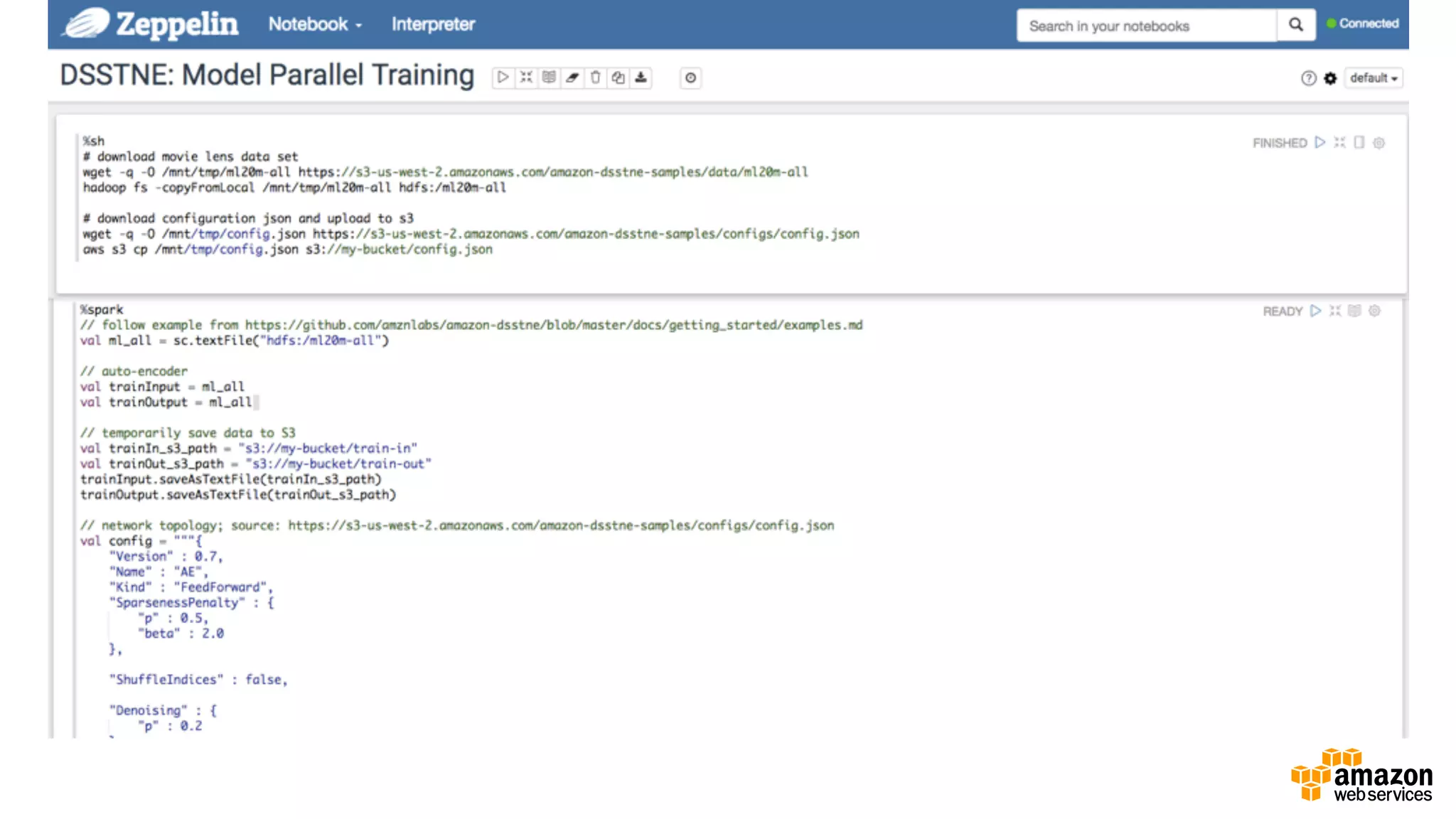
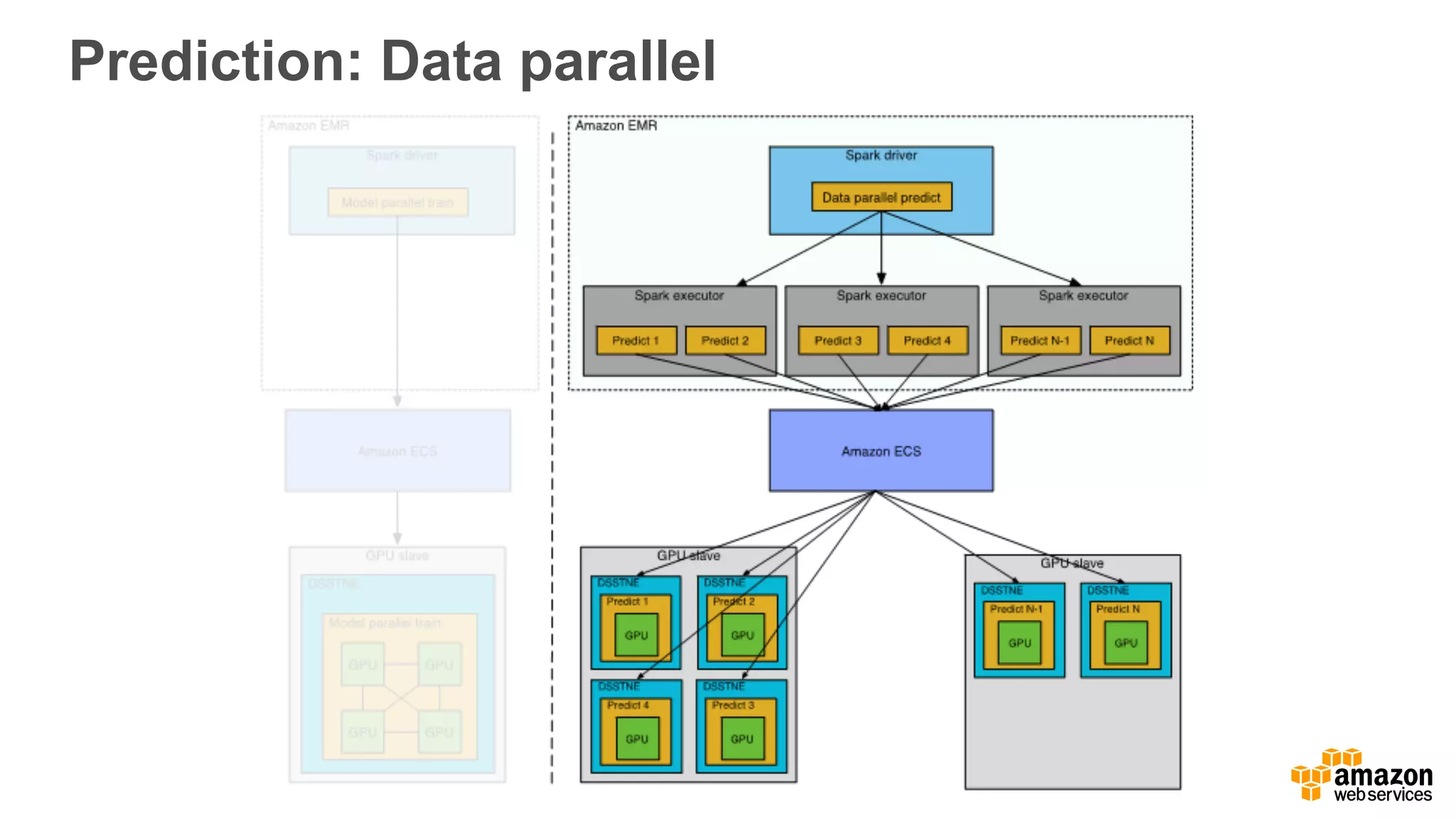
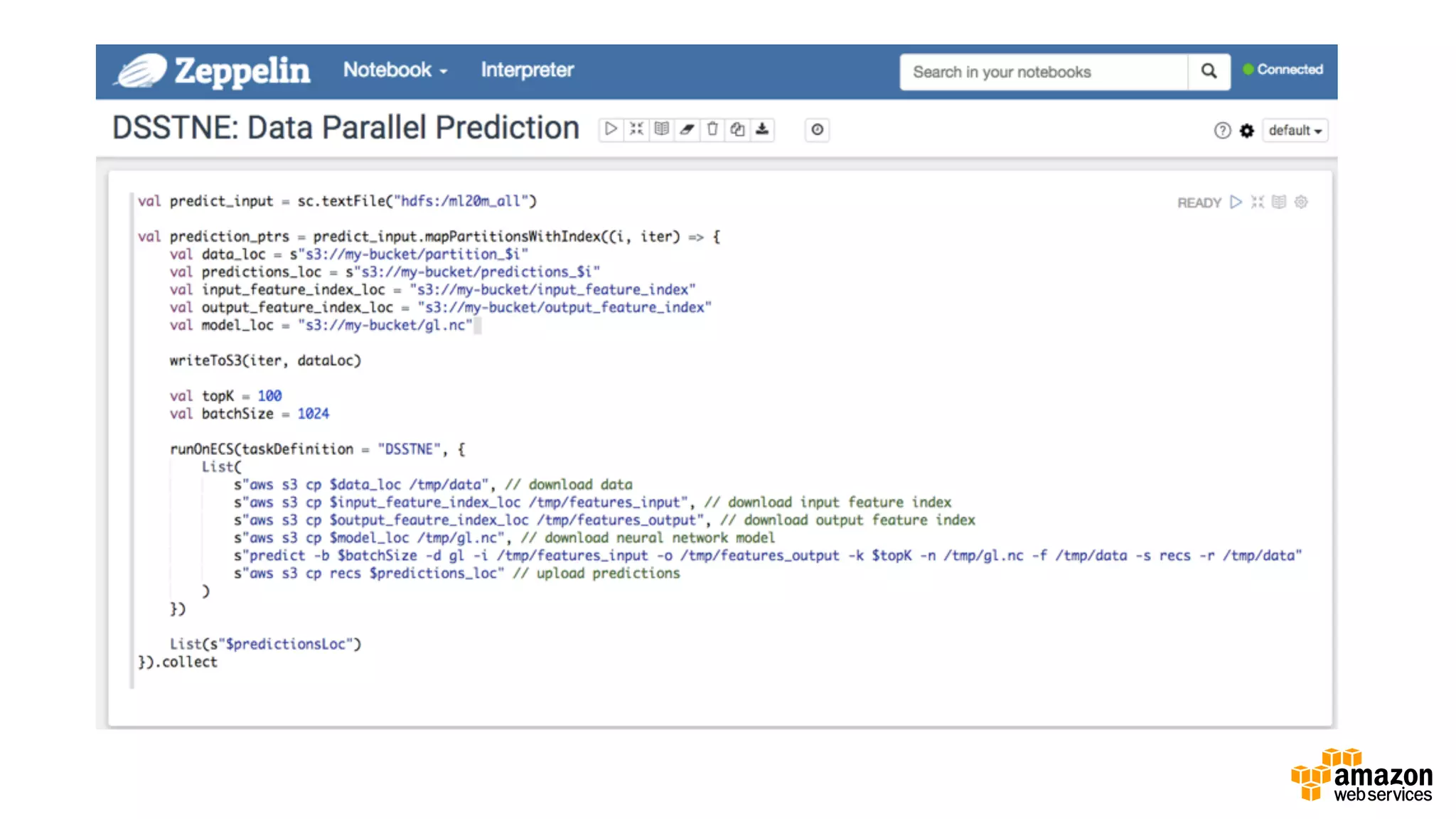
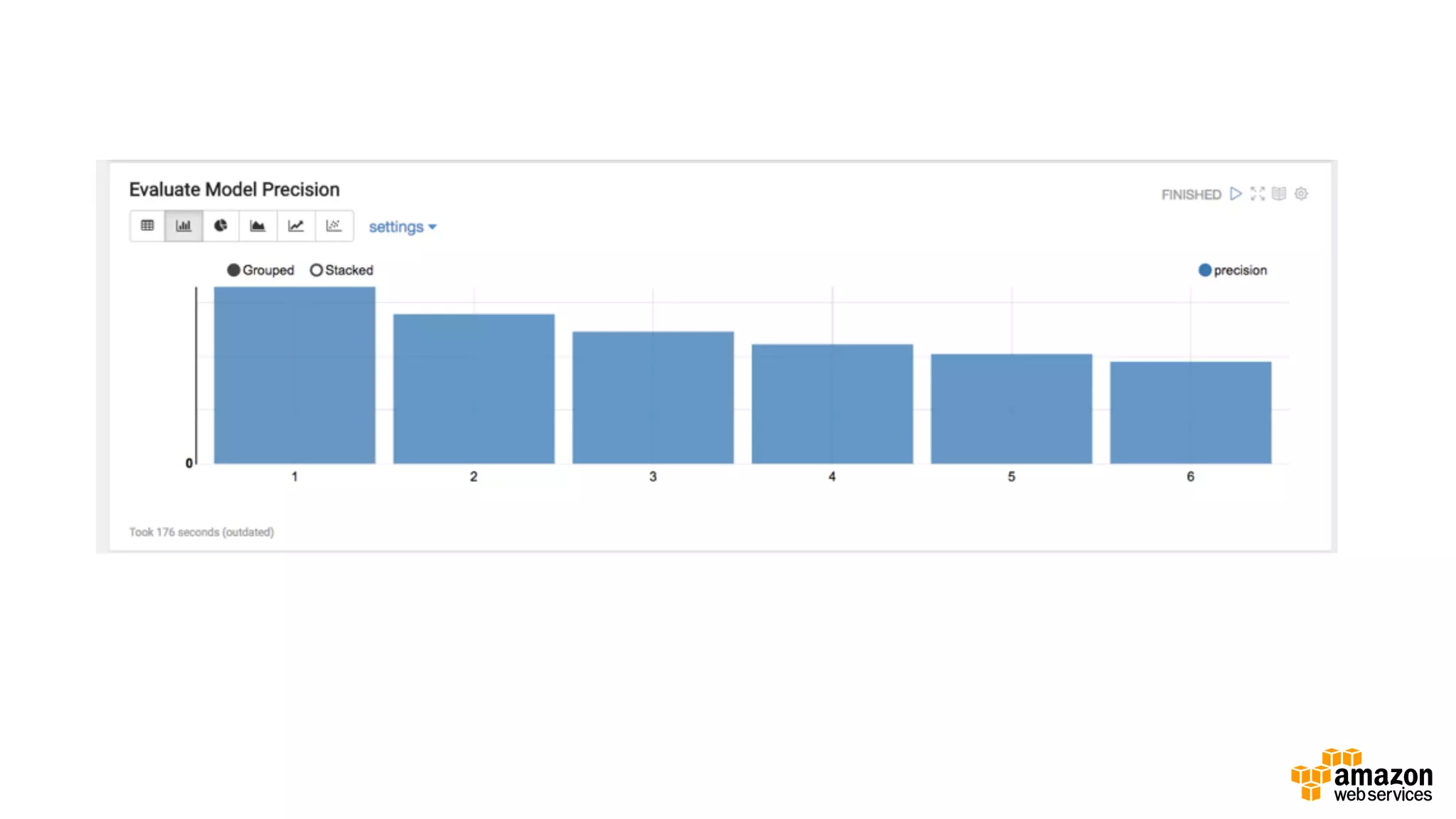
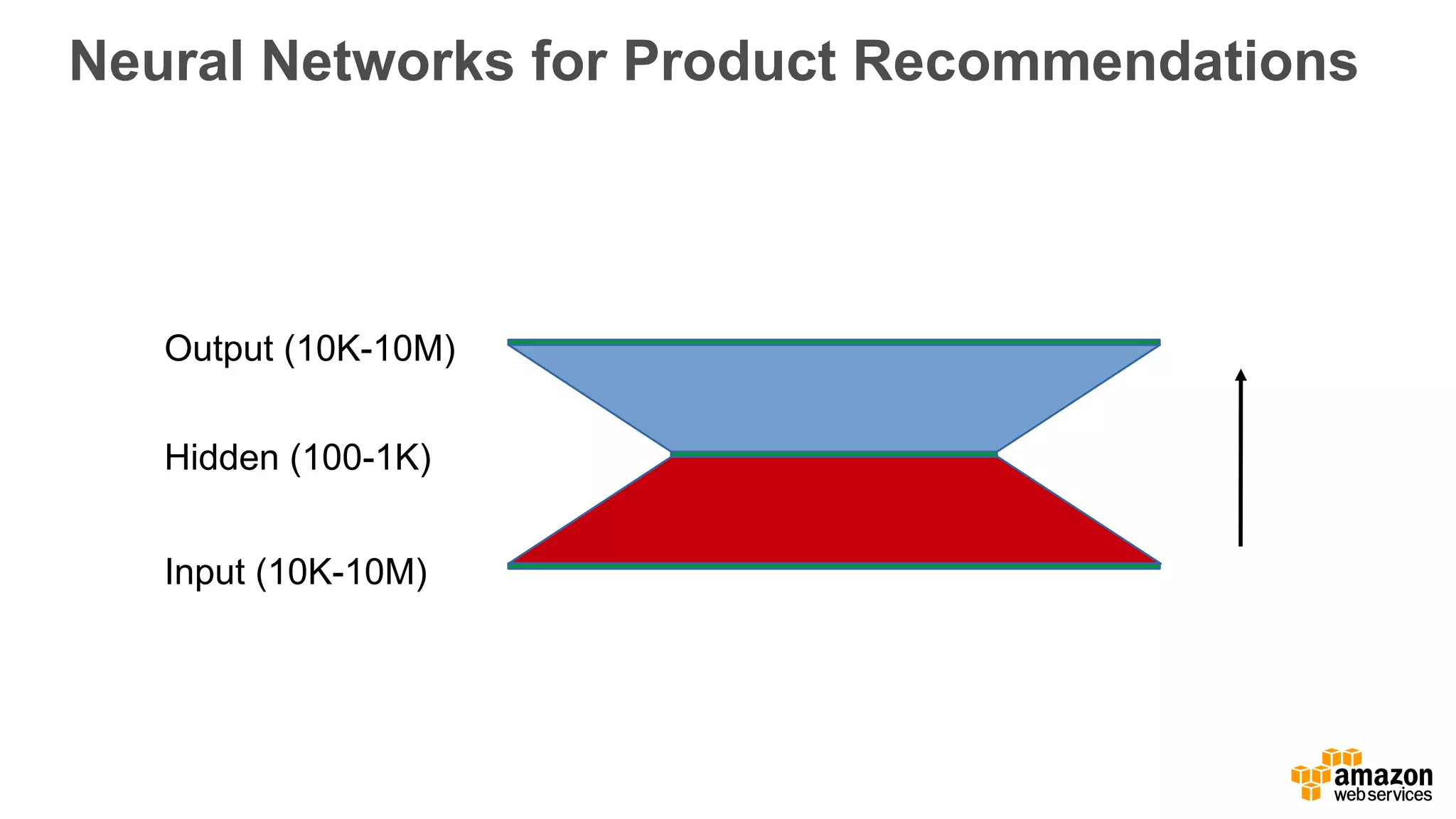
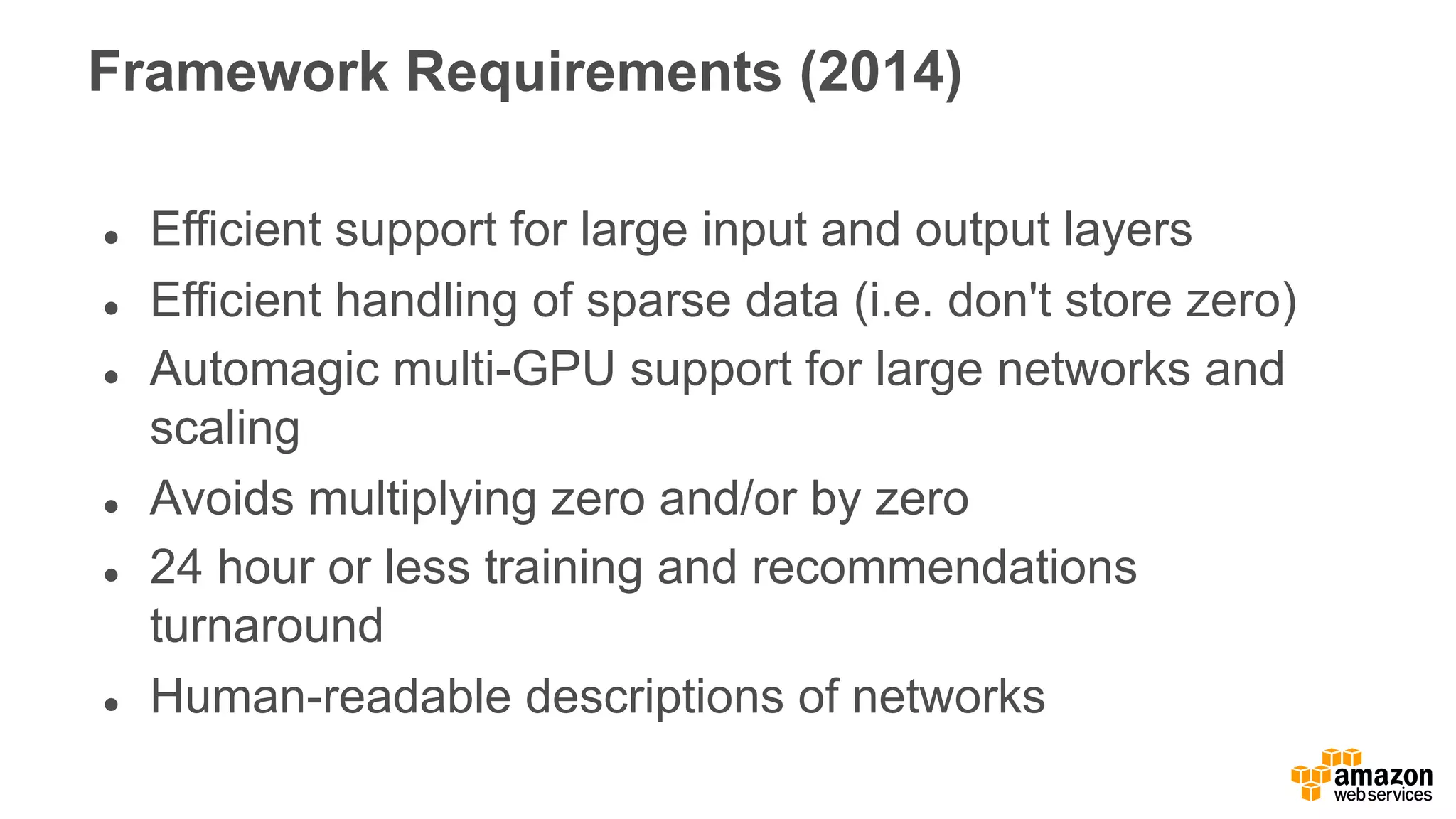
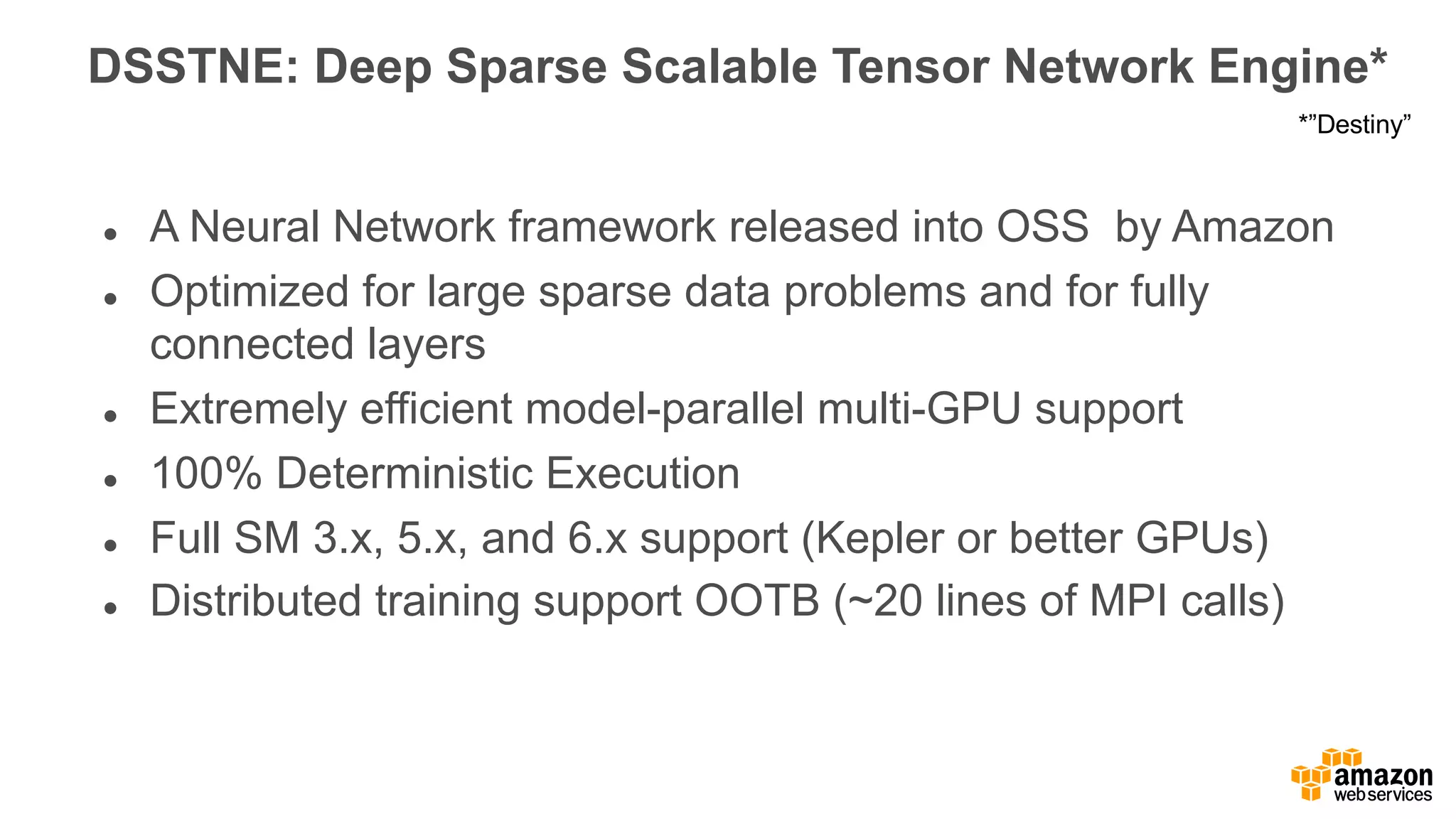
This document discusses using Apache Spark and Amazon DSSTNE to generate product recommendations at scale. It summarizes that Amazon uses Spark and Zeppelin notebooks to allow data scientists to develop queries in an agile manner. Deep learning jobs are run on GPUs using Amazon ECS, while CPU jobs run on Amazon EMR. DSSTNE is optimized for large sparse neural networks and allows defining networks in a human-readable JSON format to efficiently handle Amazon's large recommendation problems.







![Describes Neural Networks As JSON Objects{ "Version" : 0.7, "Name" : "AE", "Kind" : "FeedForward", "SparsenessPenalty" : { "p" : 0.5, "beta" : 2.0 }, "ShuffleIndices" : false, "Denoising" : { "p" : 0.2 }, "ScaledMarginalCrossEntropy" : { "oneTarget" : 1.0, "zeroTarget" : 0.0, "oneScale" : 1.0, "zeroScale" : 1.0 }, "Layers" : [ { "Name" : "Input", "Kind" : "Input", "N" : "auto", "DataSet" : "input", "Sparse" : true }, { "Name" : "Hidden", "Kind" : "Hidden", "Type" : "FullyConnected", "N" : 128, "Activation" : "Sigmoid", "Sparse" : true }, { "Name" : "Output", "Kind" : "Output", "Type" : "FullyConnected", "DataSet" : "output", "N" : "auto", "Activation" : "Sigmoid", "Sparse" : true } ], "ErrorFunction" : "ScaledMarginalCrossEntropy" }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1700ryosukeiwanagav1-161031190630/75/Generating-Recommendations-at-Amazon-Scale-with-Apache-Spark-and-Amazon-DSSTNE-11-2048.jpg)