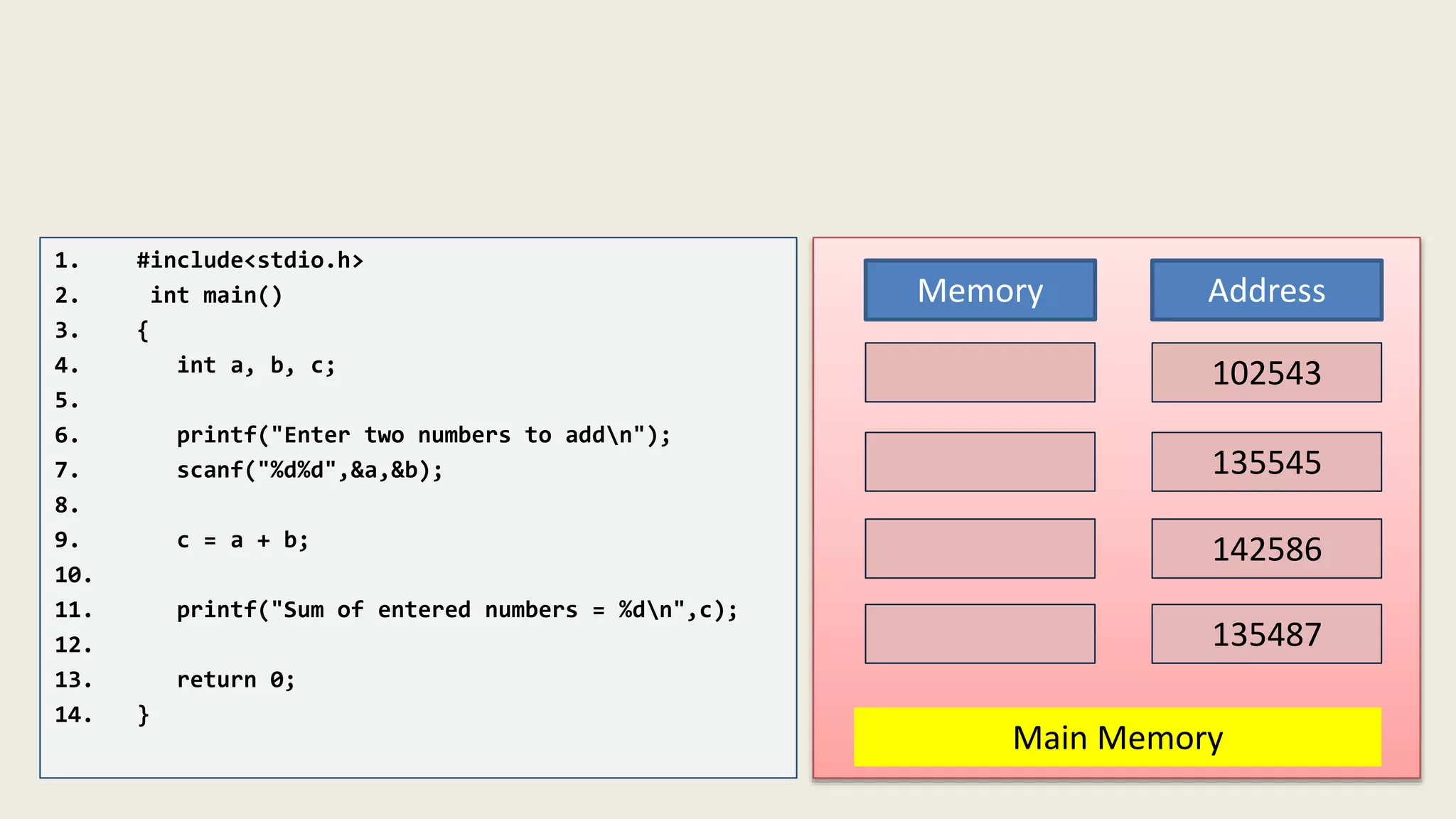
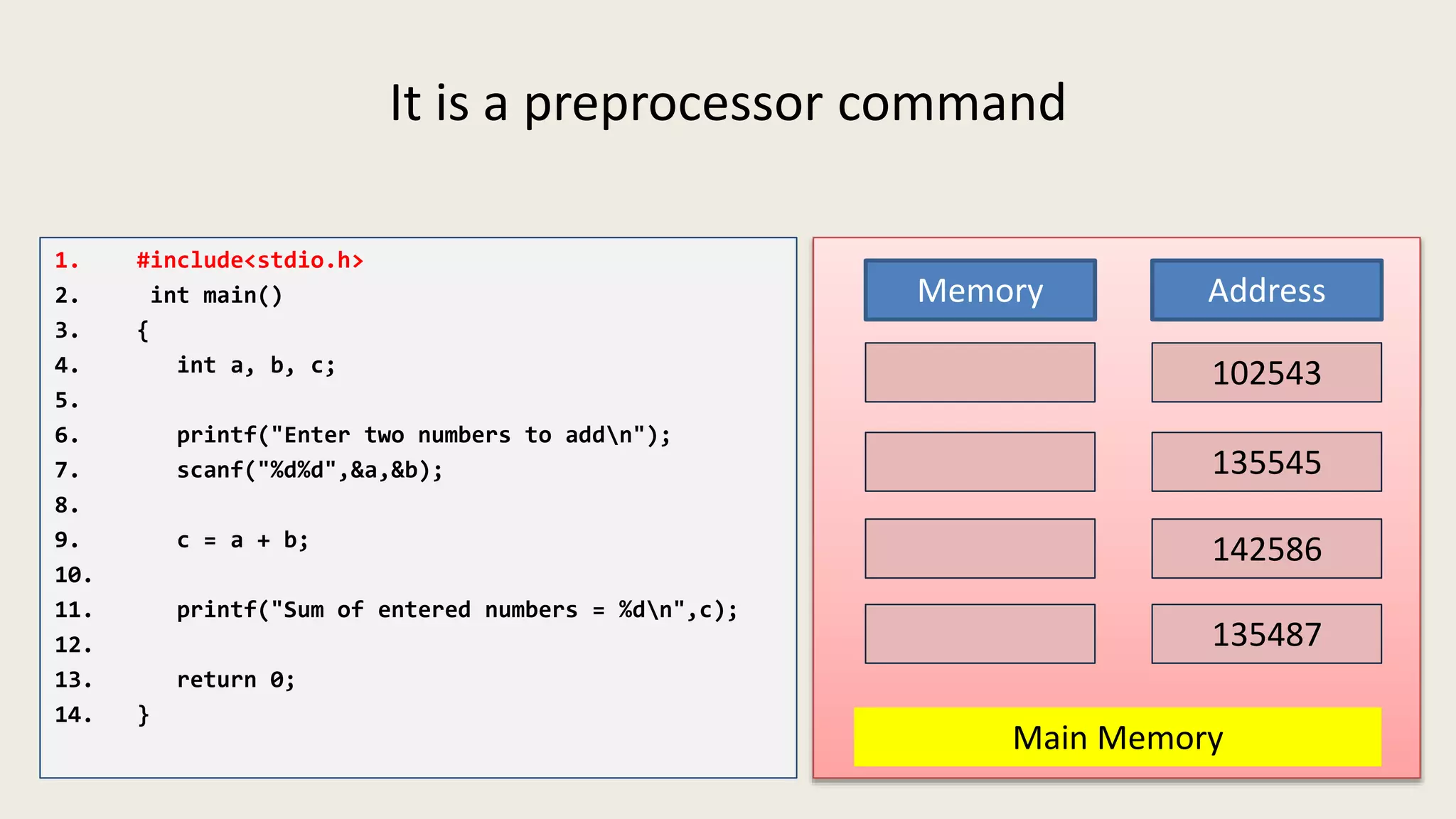
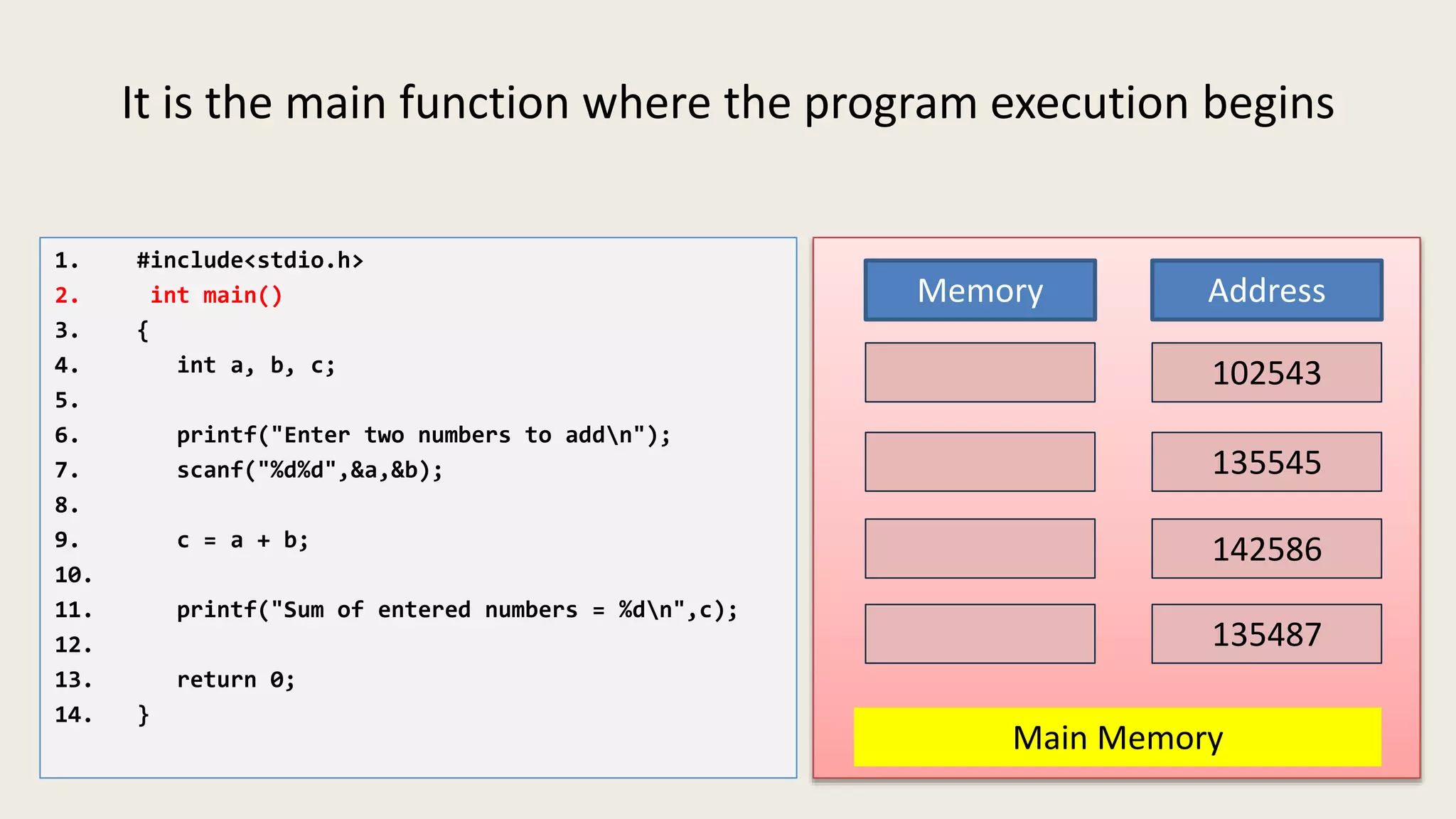
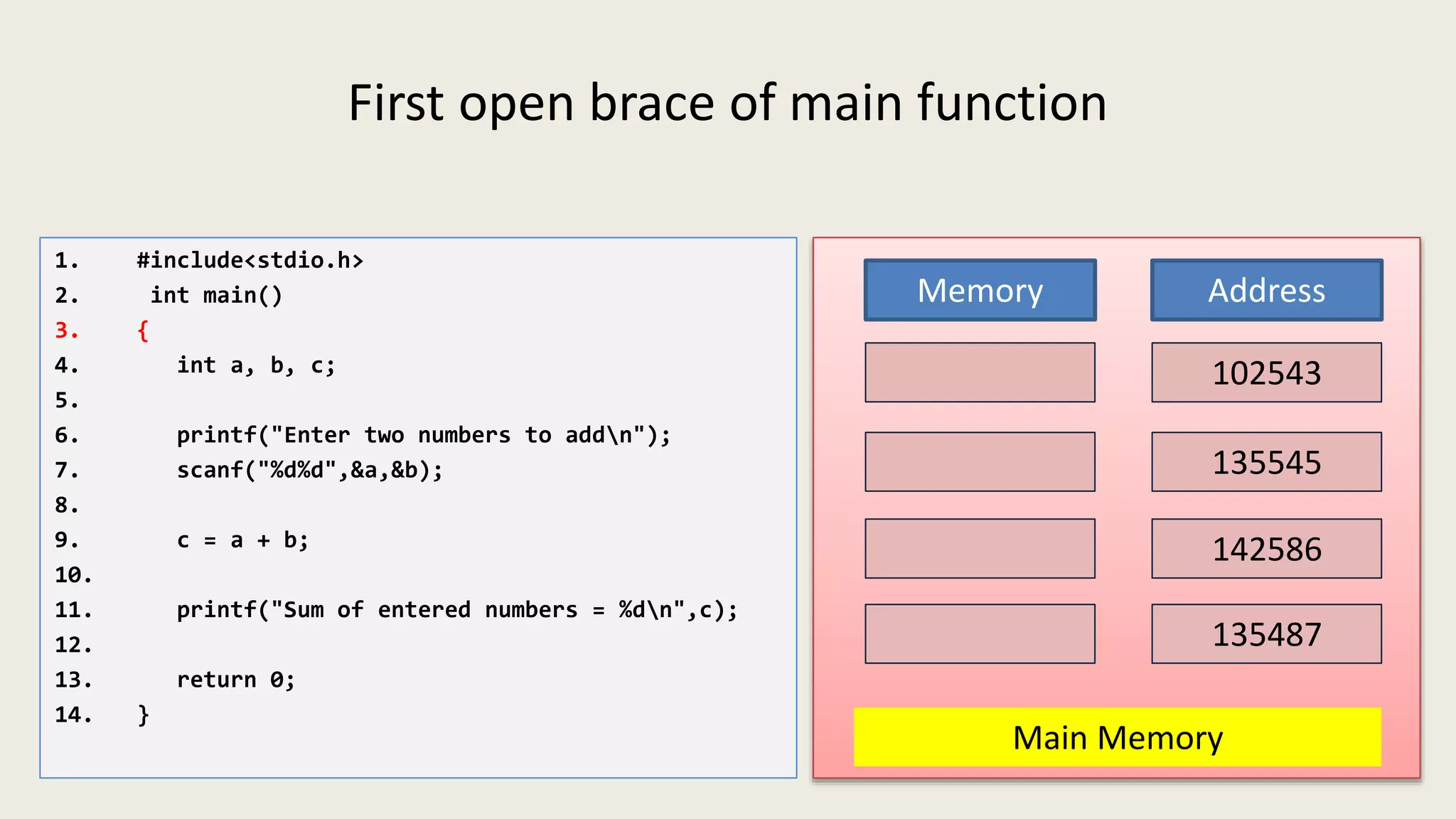
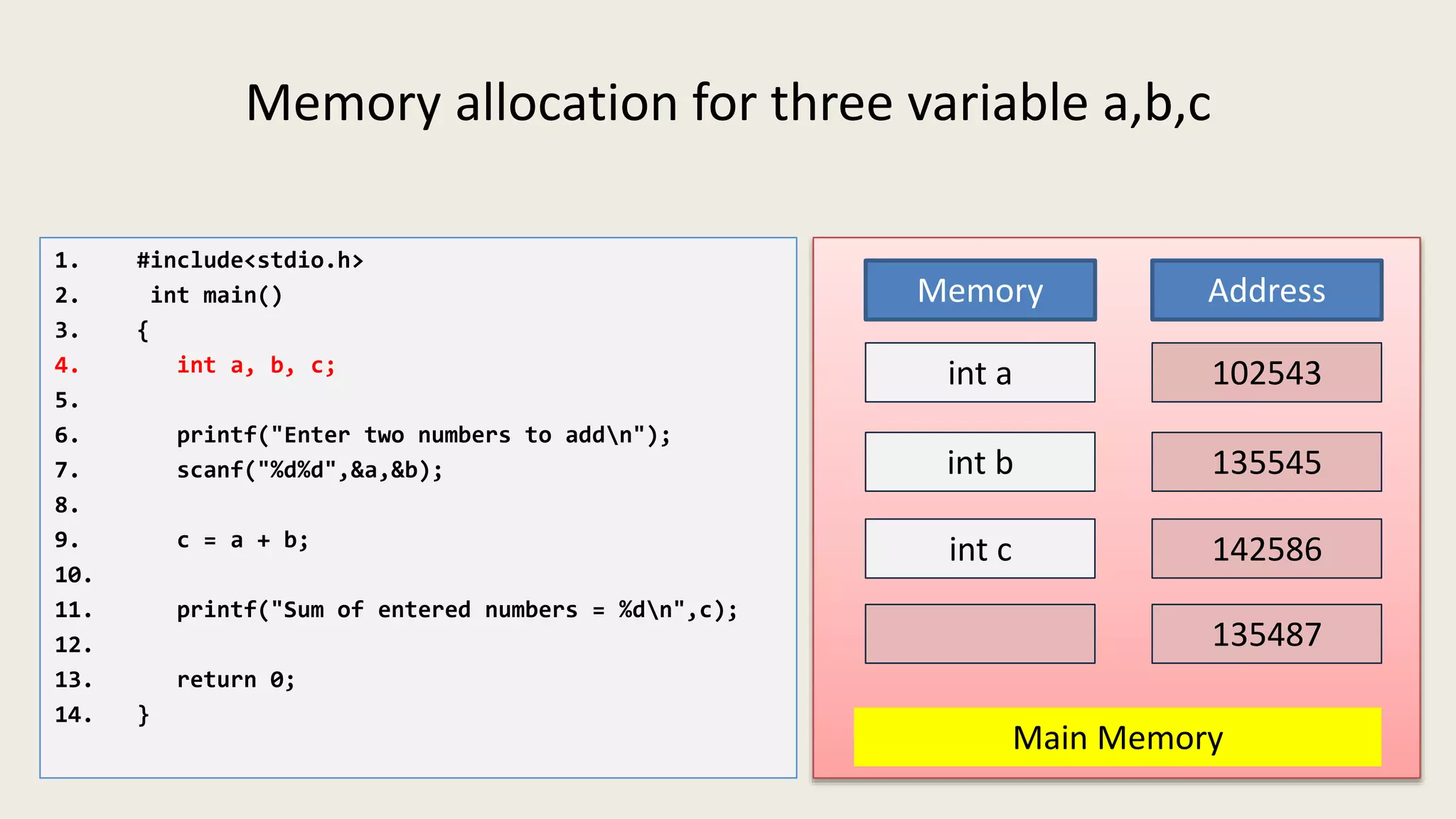
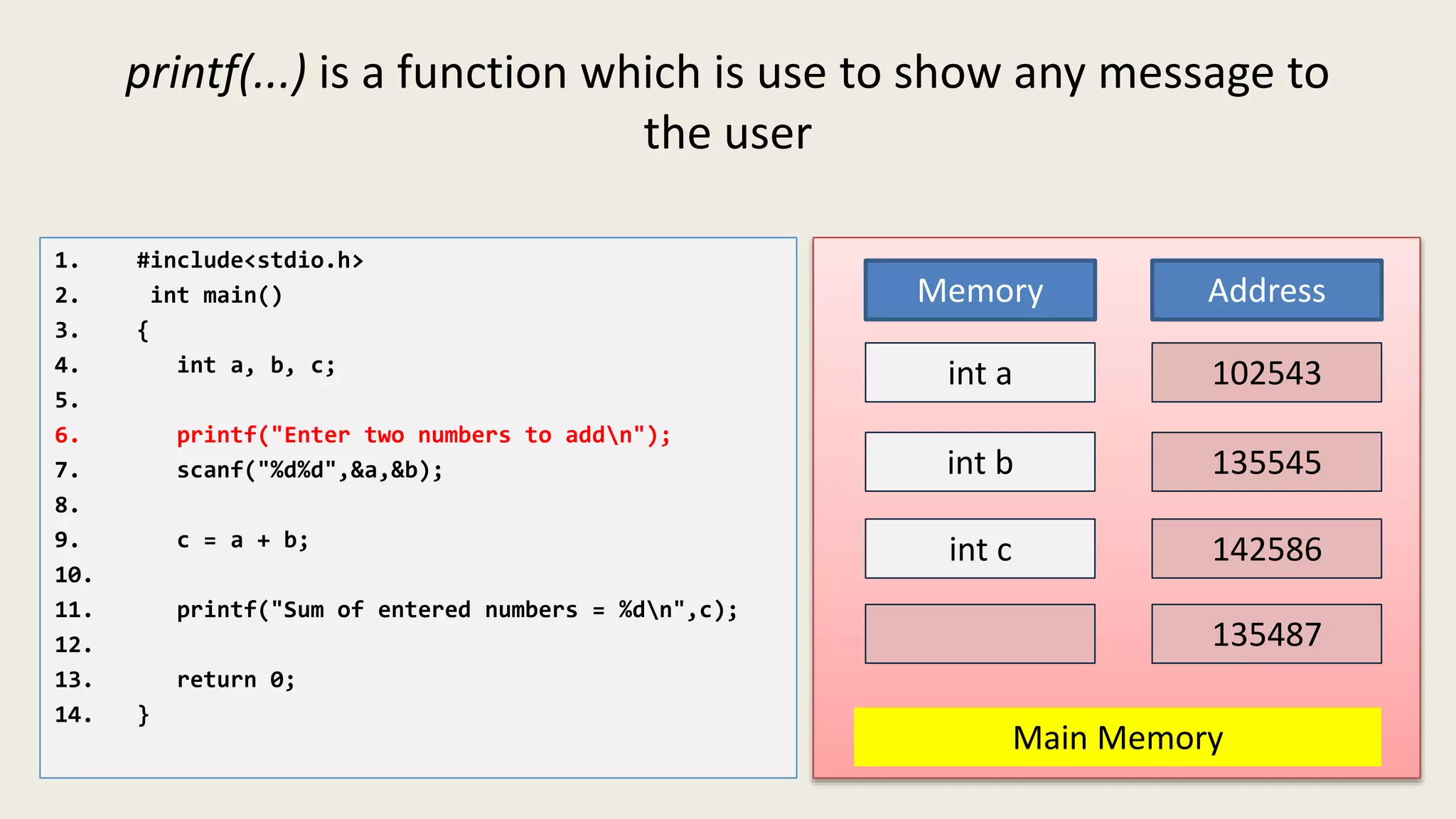
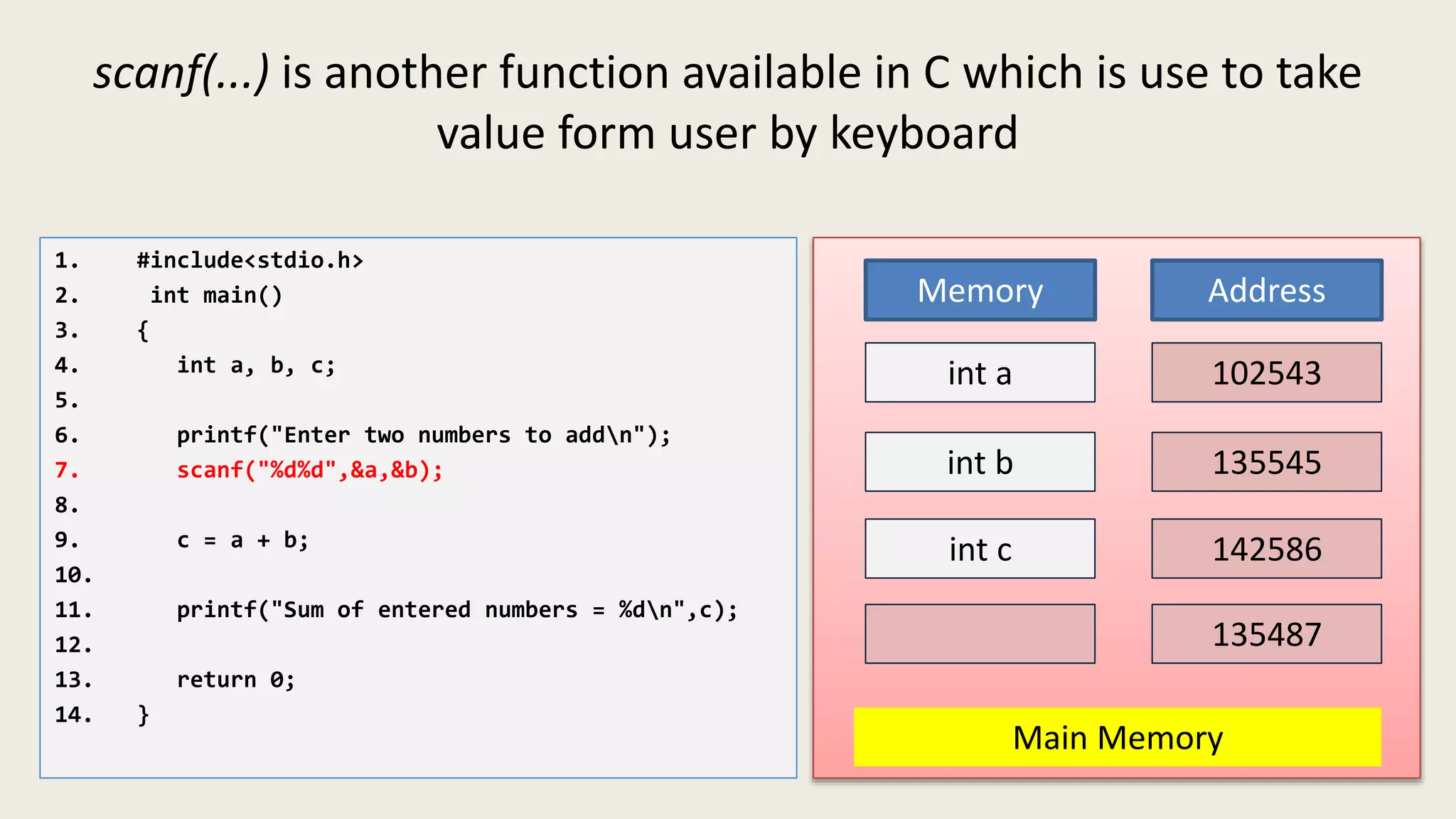
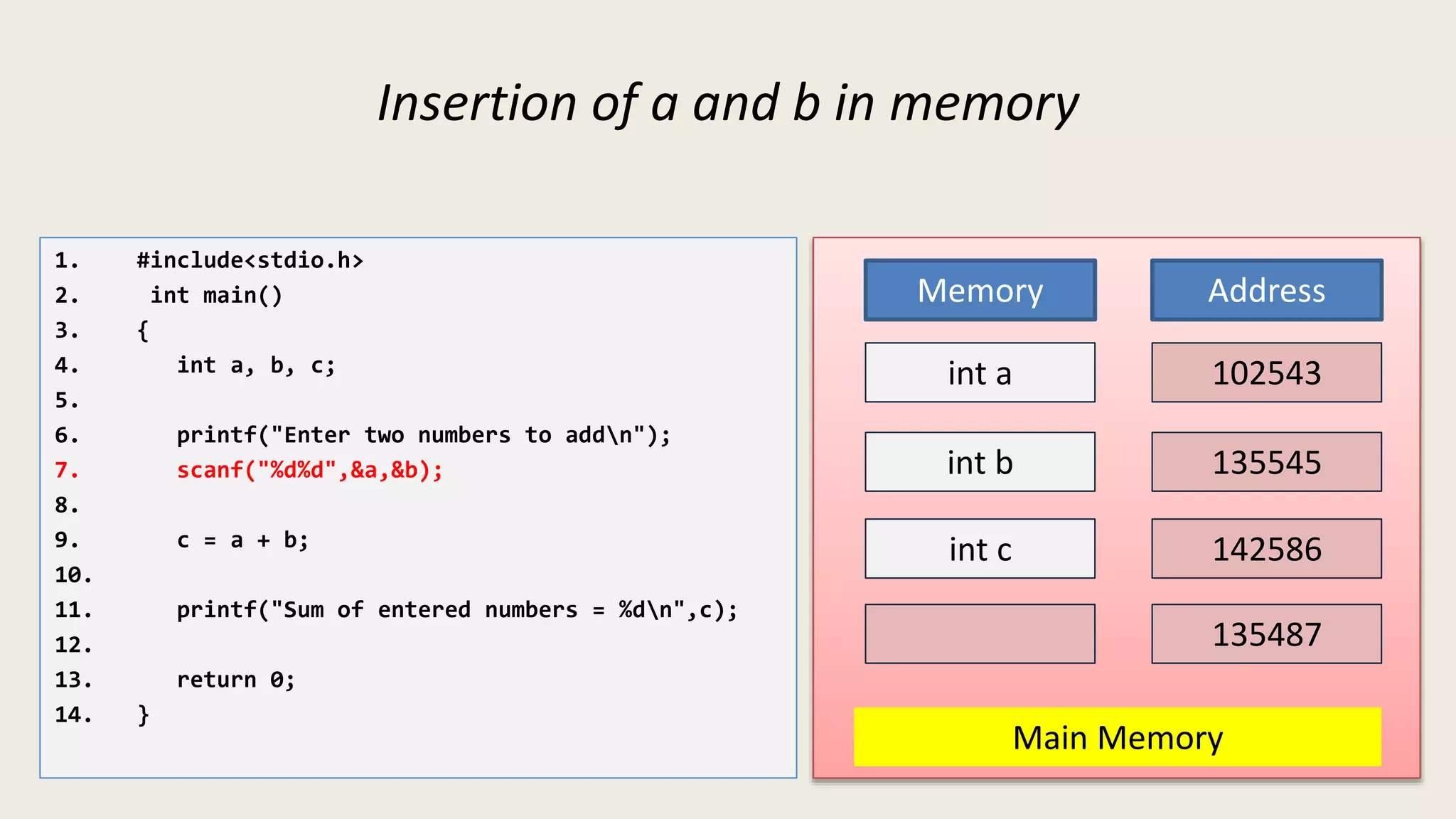
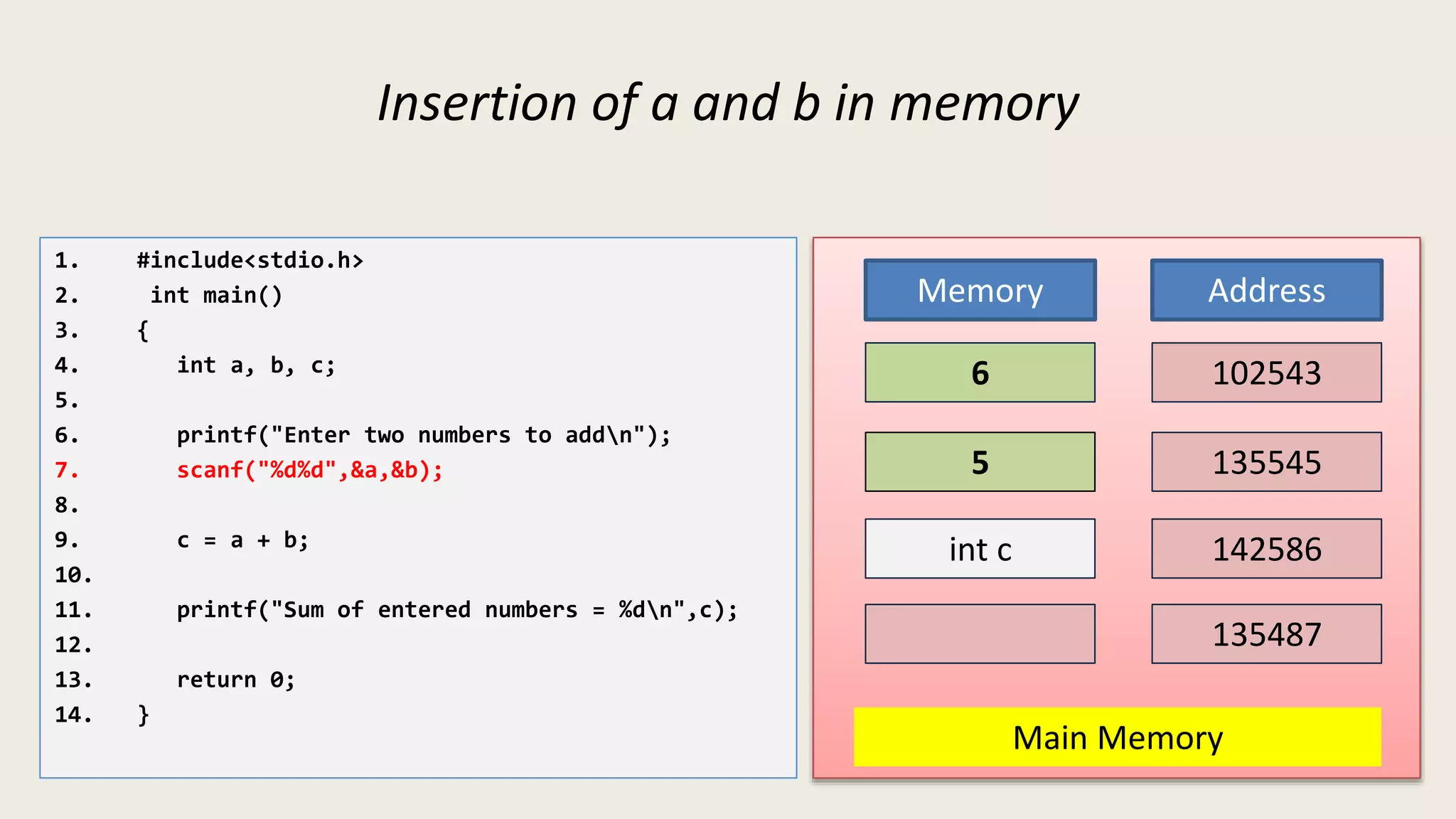
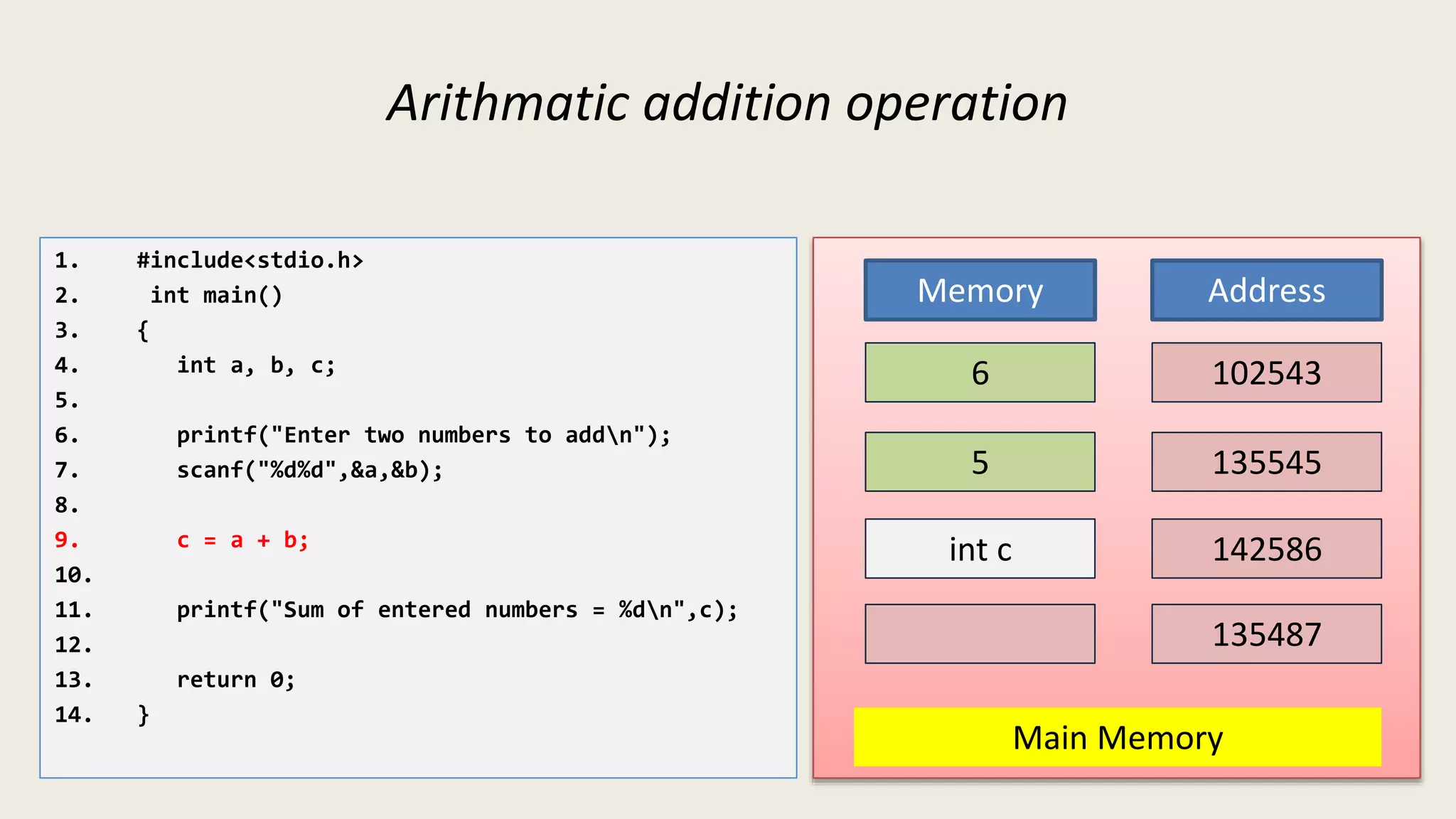
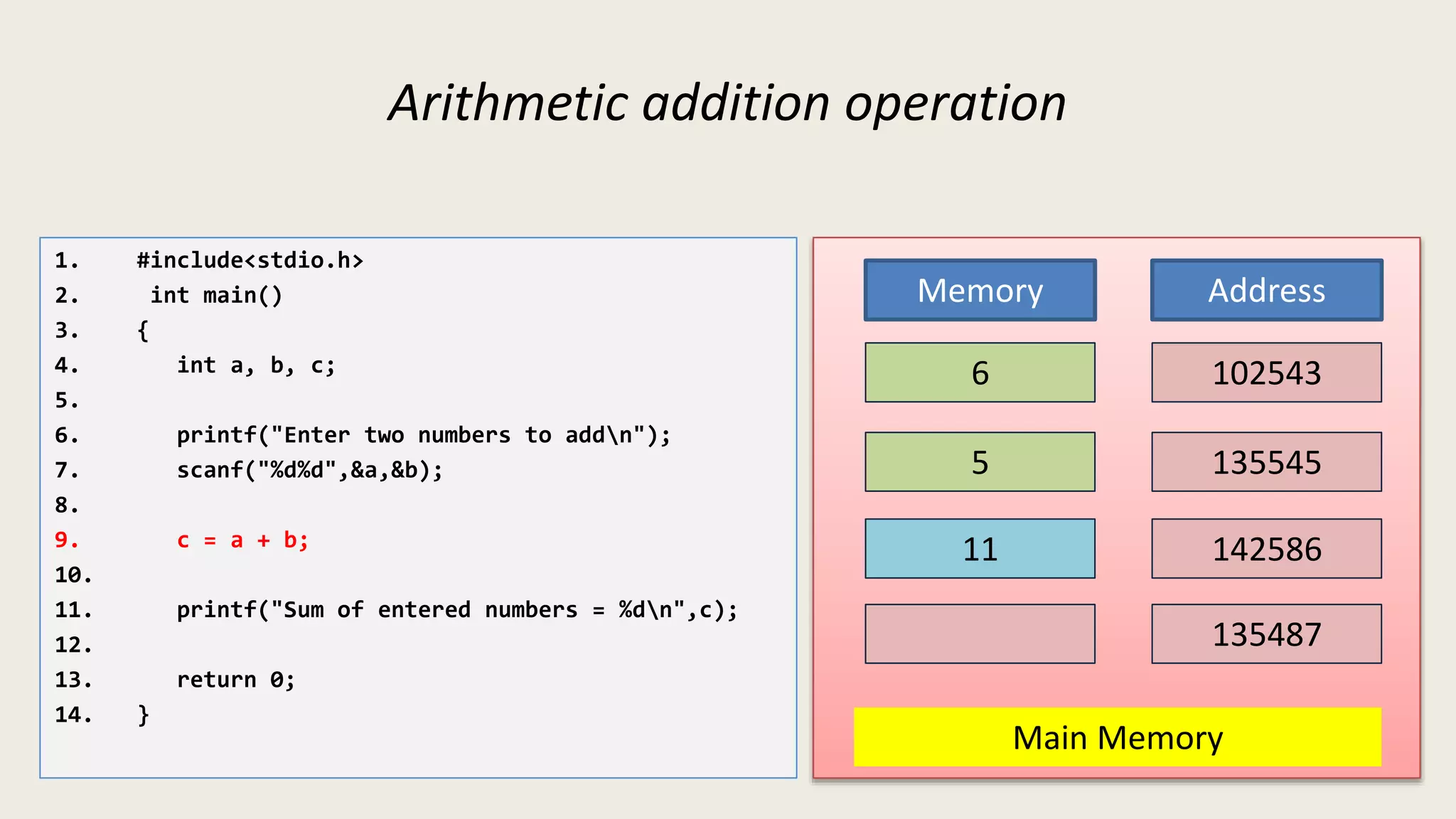
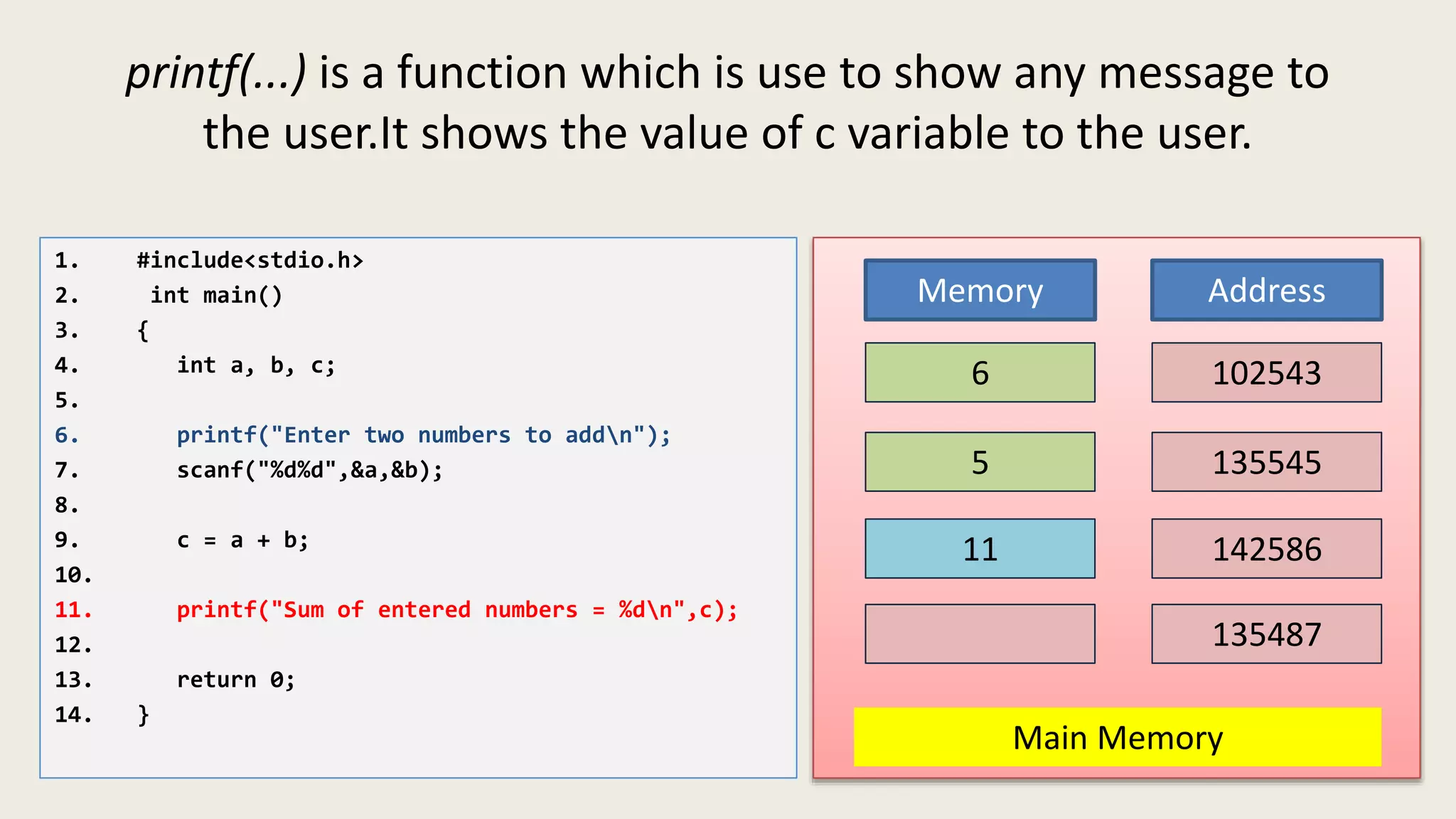
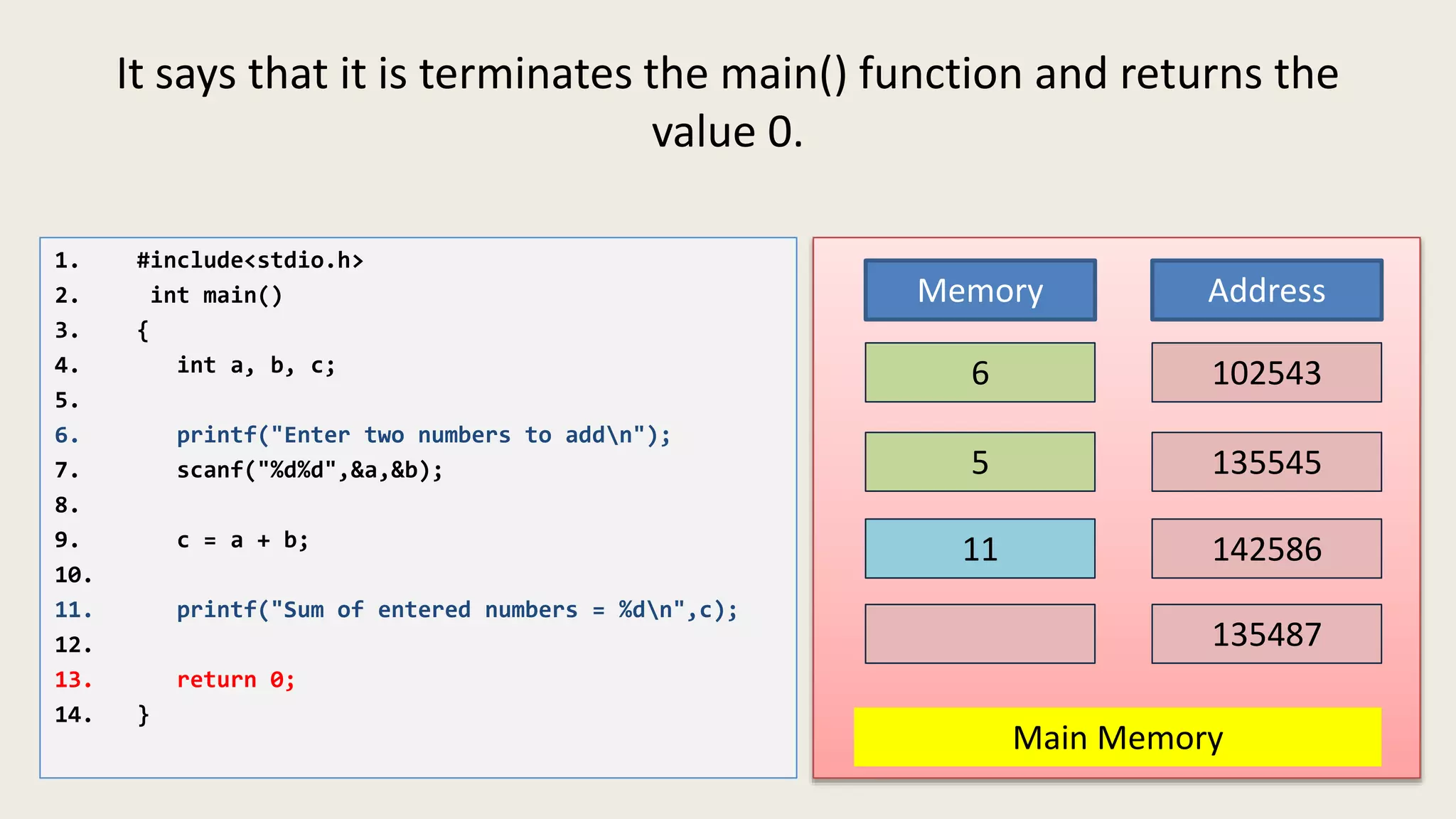
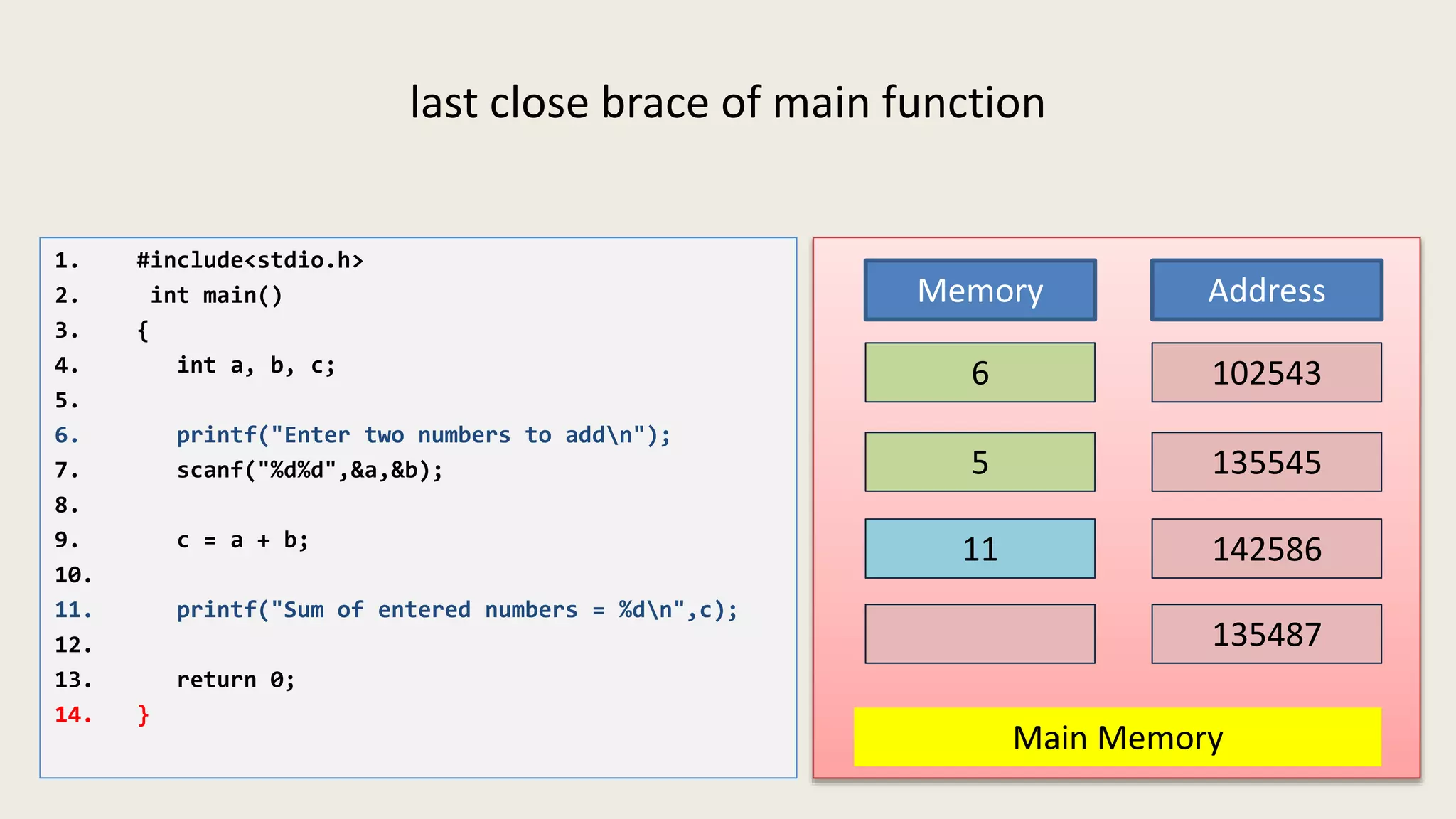
The C program executes as follows: 1. A text editor is used to write the C program code and save it as a file with a .c extension. 2. A compiler converts the C source code into machine-readable object code. 3. The object code is executed by the CPU, which follows the program's instructions step-by-step to carry out the desired operations and output.